Charge Variants Characterization of Co-Formulated Antibodies by Three-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instrument
2.3. HIC Condition
2.4. IEC Condition
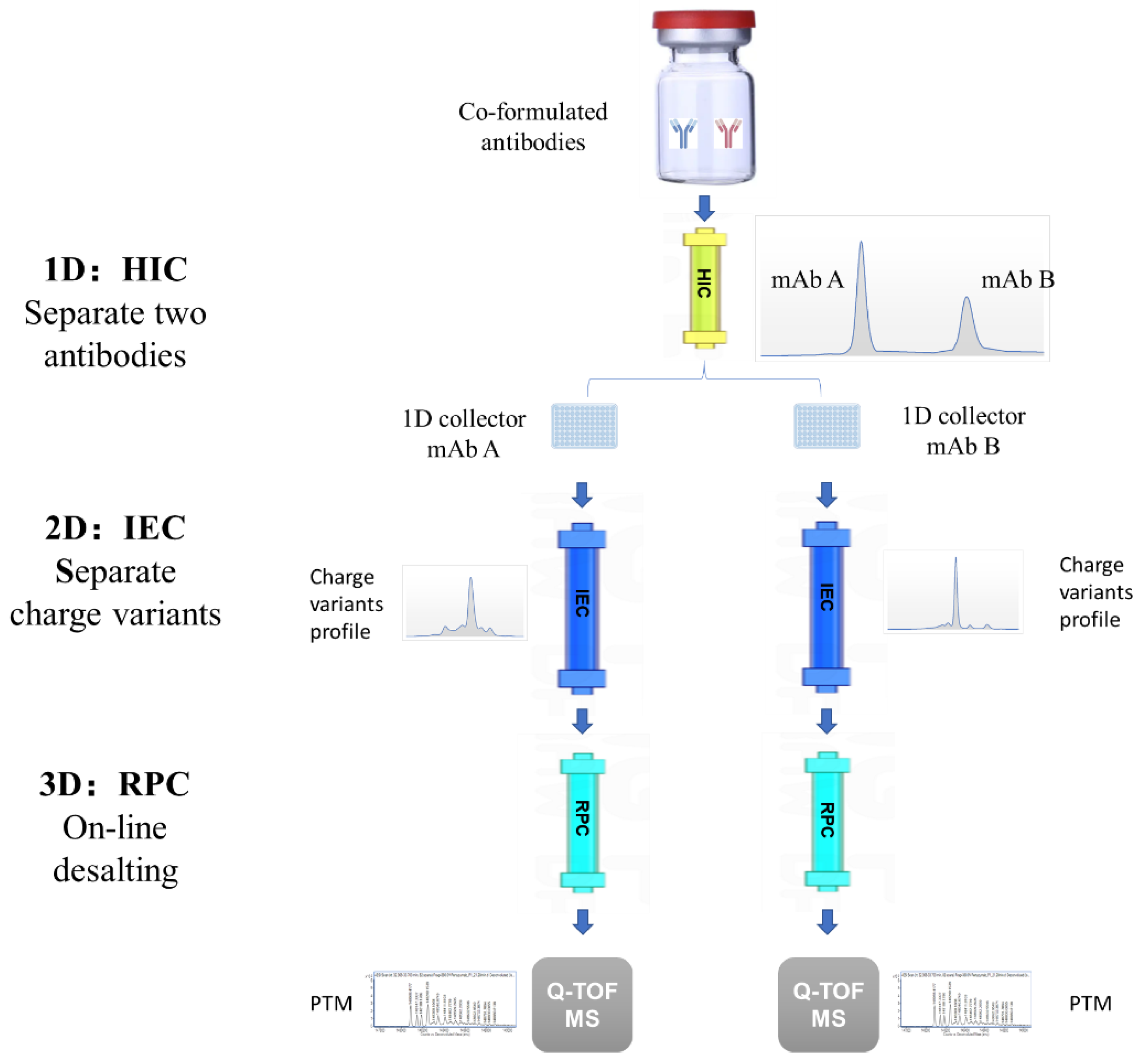
2.5. 3D-LC-MS Method
3. Results
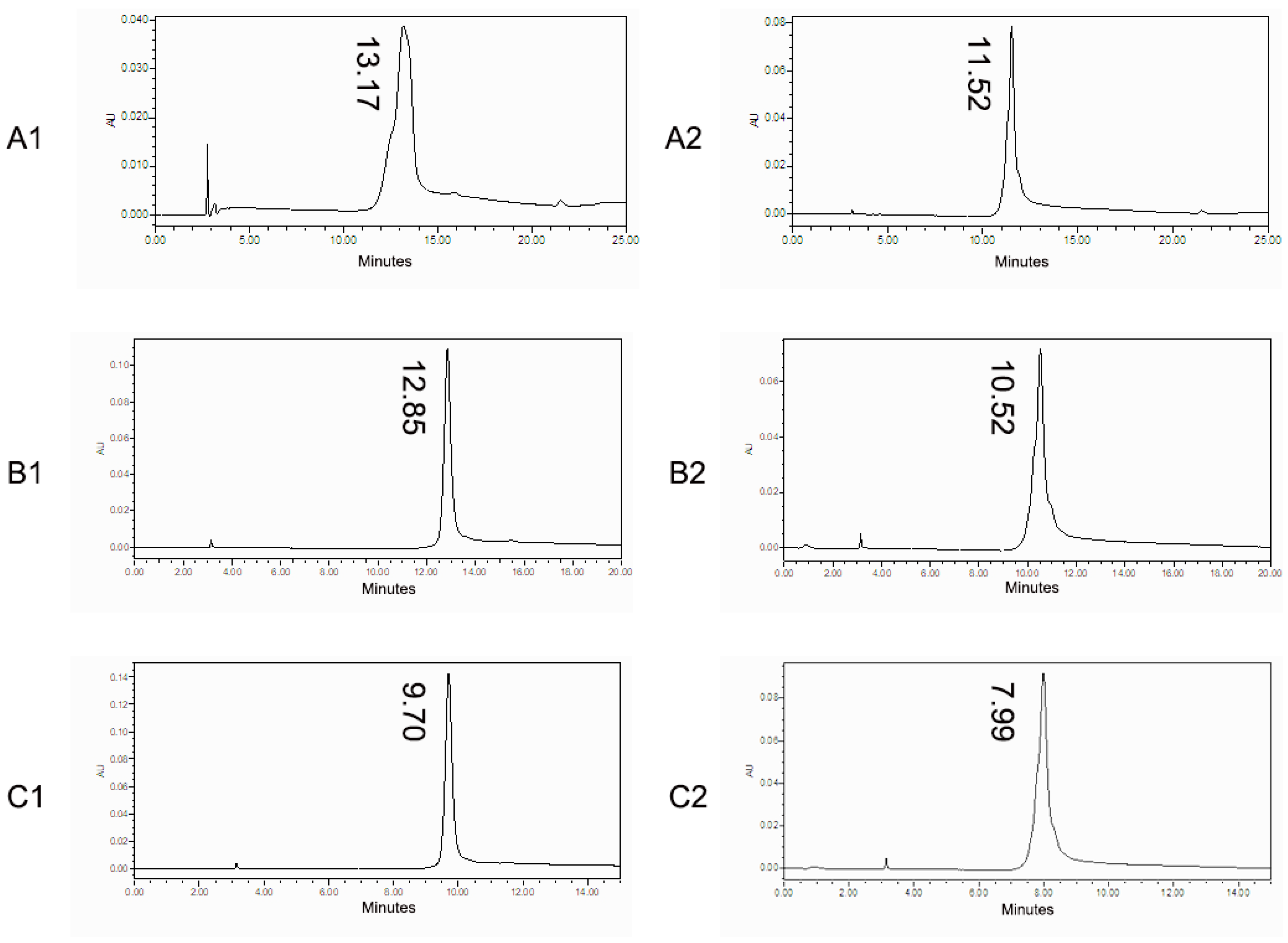
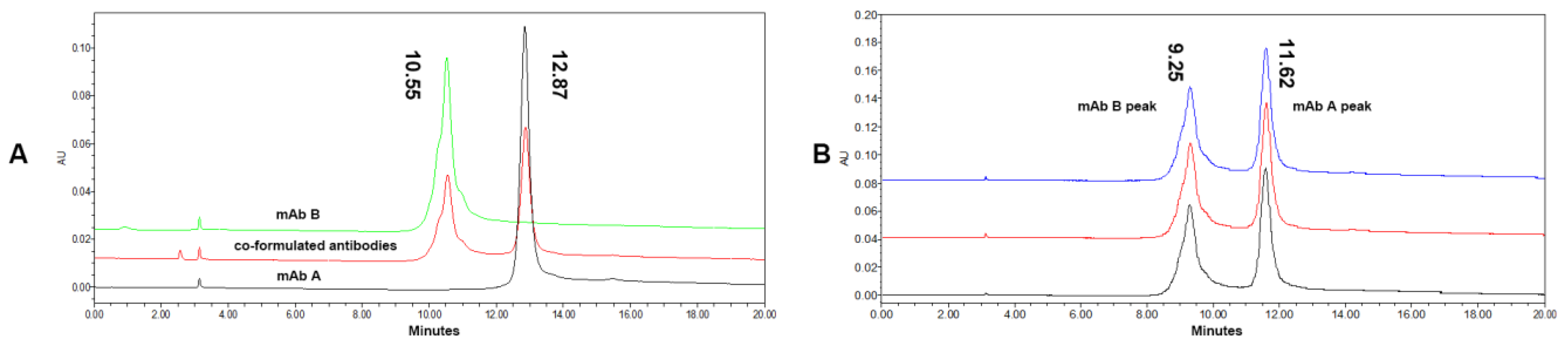
3.1. HIC Condition Optimization
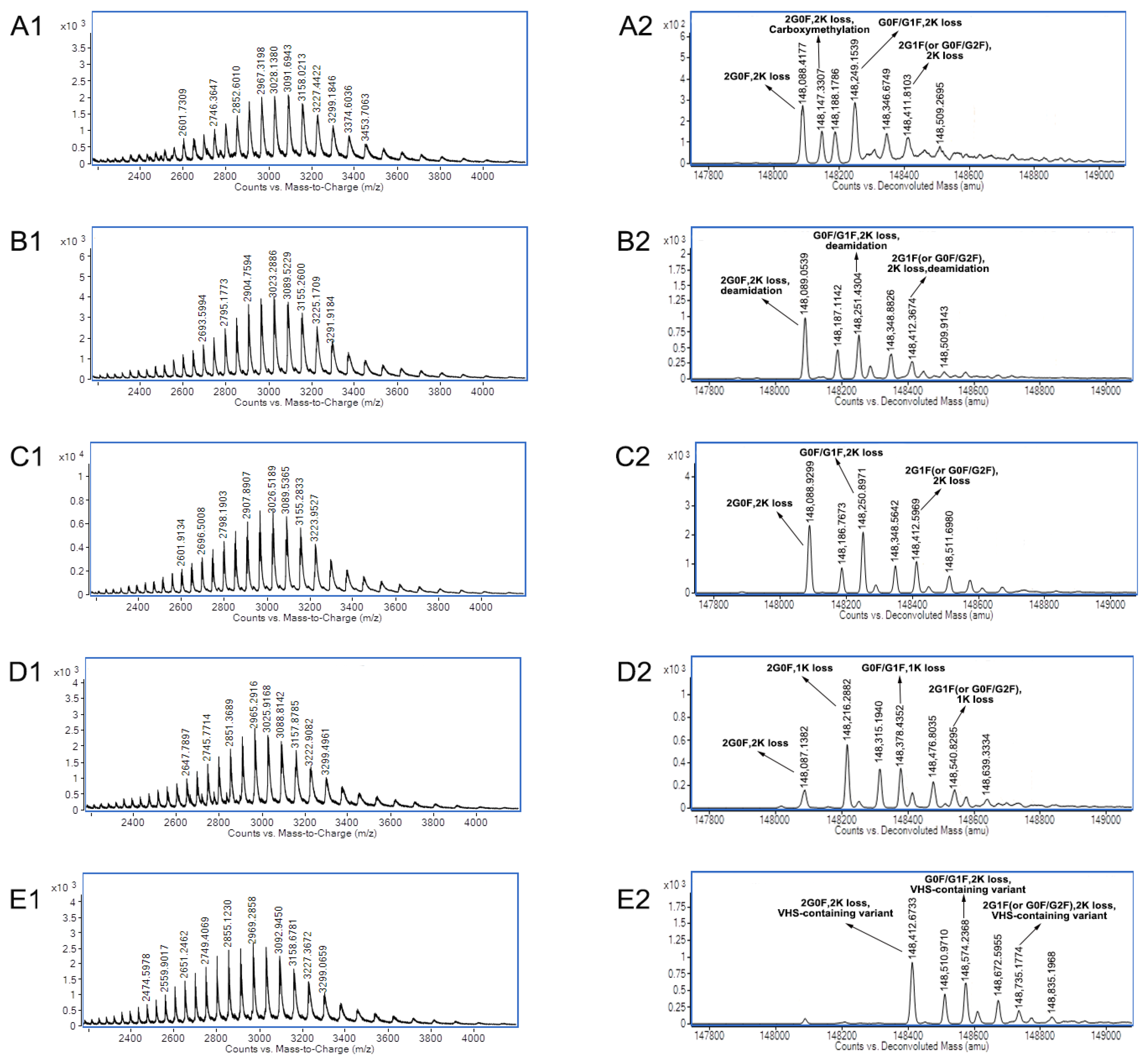
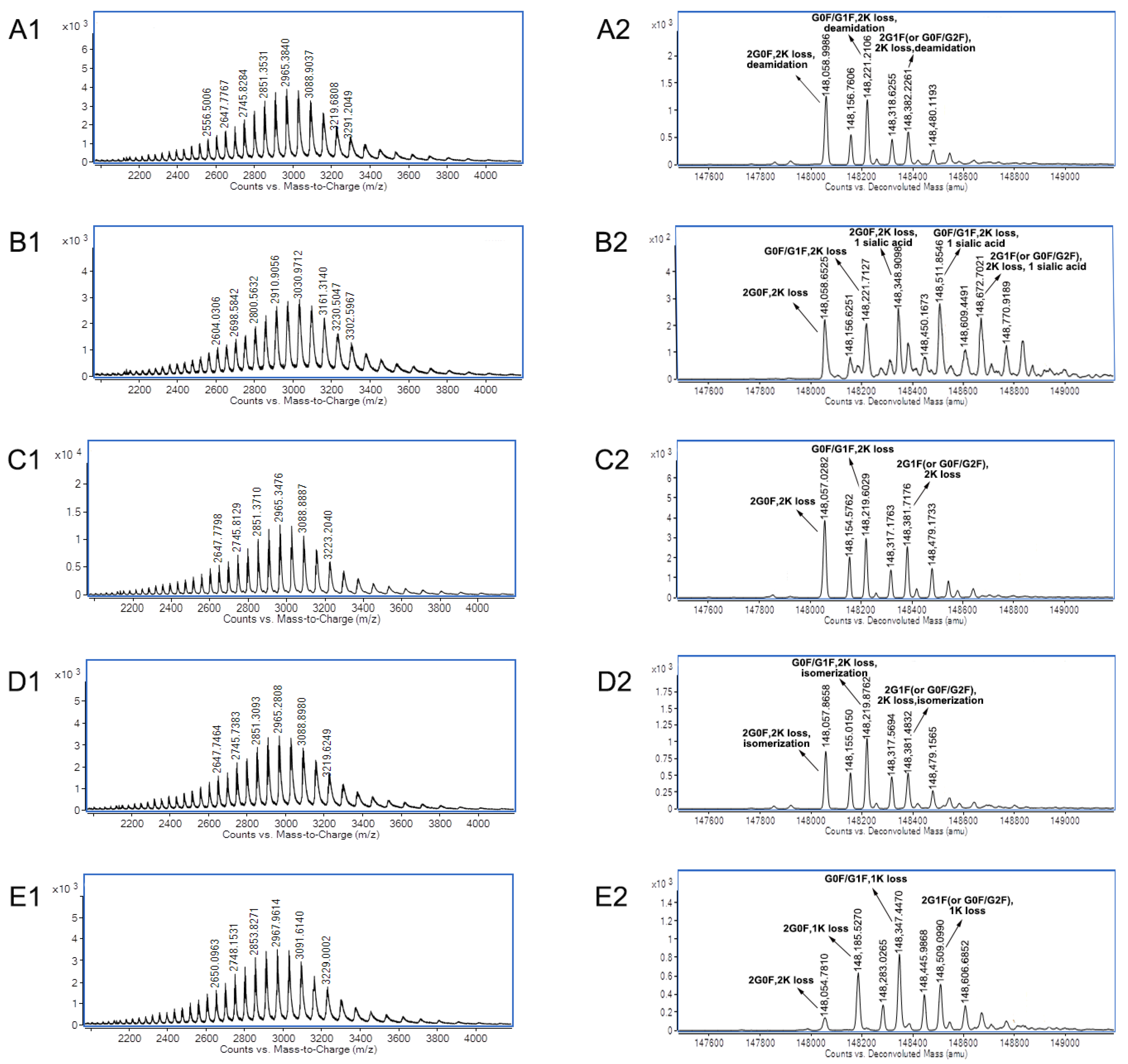
3.2. Charge Variants Characterization of Co-Formulated Antibodies by the 3D-LC-MS Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Posner, J.; Barrington, P.; Brier, T.; Datta-Mannan, A. Monoclonal Antibodies: Past, Present and Future. In Concepts and Principles of Pharmacology: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 260, pp. 81–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaozhi. Top10 Best-Selling Drugs in 2023. Available online: https://m.baidu.com/bh/m/detail/ar_9971613961676379877 (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Ning, L.; Abagna, H.B.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, S.; Huang, J. Development and application of therapeutic antibodies against COVID-19. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, V.M.; Zhang, H.; Dalby, P.A.; Aylott, J.W. Advancements in the co-formulation of biologic therapeutics. J. Control Release 2020, 327, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focosi, D. From Co-Administration to Co-Formulation: The Race for New Vaccines against COVID-19 and Other Respiratory Viruses. Vaccines 2023, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, D.R.; Li, J.; Nguyen, N.X.; Falkenberg, F.W.; Henning, L.; Krile, R.; Chou, Y.L.; Herron, J.N.; Hale, J.S.; Williamson, E.D. Co-formulation of the rF1V plague vaccine with depot-formulated cytokines enhances immunogenicity and efficacy to elicit protective responses against aerosol challenge in mice. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1277526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.J.; Osgood, C.L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Bloomquist, E.W.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, J.; Yu, J.; Song, P.; Rahman, N.A.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pertuzumab, Trastuzumab, and Hyaluronidase-zzxf Injection for Subcutaneous Use in Patients with HER2-positive Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2126–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.R.; Im, S.A.; Mattar, A.; Colomer, R.; Stroyakovskii, D.; Nowecki, Z.; De Laurentiis, M.; Pierga, J.Y.; Jung, K.H.; Schem, C.; et al. Fixed-dose combination of pertuzumab and trastuzumab for subcutaneous injection plus chemotherapy in HER2-positive early breast cancer (FeDeriCa): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, non-inferiority, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, J. Nivolumab Plus Relatlimab: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regeneron. FDA Expands Authorized Use of REGEN-COV™ (Casirivimab and Imdevimab). Available online: https://investor.regeneron.com/news-releases/news-release-details/fda-expands-authorized-use-regen-covtm-casirivimab-and-imdevimab (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Cao, M.; De Mel, N.; Albarghouthi, M.; Miller, K.; Bee, J.S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Analytical characterization of coformulated antibodies as combination therapy. mAbs 2020, 12, 1738691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo Reis Teixeira, A.; Erasmus, M.F.; D’Angelo, S.; Naranjo, L.; Ferrara, F.; Leal-Lopes, C.; Durrant, O.; Galmiche, C.; Morelli, A.; Scott-Tucker, A.; et al. Drug-like antibodies with high affinity, diversity and developability directly from next-generation antibody libraries. mAbs 2021, 13, 1980942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, M.; Park, S.-J.; Balakrishnan, G.; Zhou, K.; Pan, D.; Das, T.K. Bridging size and charge variants of a therapeutic monoclonal antibody by two-dimensional liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 183, 113178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieczkowski, C.A. The Evolution of Commercial Antibody Formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Misra, B.; McManus, K.T.; Avula, S.; Nellaiappan, K.; Caskey, M.; Horowitz, J.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Seaman, M.S.; Javeri, I.; et al. Characterization of Co-Formulated High-Concentration Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Subcutaneous Administration. Antibodies 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutanu, A.; Kiessig, S.; Bathke, A.; Ketterer, R.; Riner, S.; Olaf Stracke, J.; Wild, M.; Moritz, B. Application of affinity capillary electrophoresis for charge heterogeneity profiling of biopharmaceuticals. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 3014–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Jiang, B.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Shameem, M.; Liu, D. A hydrophobic interaction chromatography method suitable for quantitating individual monoclonal antibodies contained in co-formulated drug products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; De Mel, N.; Shannon, A.; Prophet, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Niu, B.; Kim, J.; Albarghouthi, M.; Liu, D.; et al. Charge variants characterization and release assay development for co-formulated antibodies as a combination therapy. mAbs 2019, 11, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.K.; Katta, V.; Beavis, R.C.; Chait, B.T. Origin and removal of adducts (molecular mass = 98 u) attached to peptide and protein ions in electrospray ionization mass spectra. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 1990, 1, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Joshi, S.; Guttman, A.; Rathore, A.S. N-Glycosylation of monoclonal antibody therapeutics: A comprehensive review on significance and characterization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1209, 339828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Pan, H.; Flynn, G.C. C-terminal lysine processing of human immunoglobulin G2 heavy chain in vivo. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournet, M.; Bonte, F.; Desmouliere, A. Glycation Damage: A Possible Hub for Major Pathophysiological Disorders and Aging. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 880–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanov, B.; Olaleye, O.; Mesurado, T.; Govorukhina, N.; Jungbauer, A.; van de Merbel, N.C.; Lingg, N.; Bischoff, R. Pertuzumab Charge Variant Analysis and Complementarity-Determining Region Stability Assessment to Deamidation. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 3951–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Yu, C.; Yadav, D.B.; Hu, Z.; Amurao, A.; Duenas, E.; Wong, M.; Iverson, M.; Zheng, K.; Lam, X.; et al. Evaluation of Heavy-Chain C-Terminal Deletion on Product Quality and Pharmacokinetics of Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Raoufi, F.; Bailly, M.A.; Fayadat-Dilman, L.; Tomazela, D. Hyphenation of strong cation exchange chromatography to native mass spectrometry for high throughput online characterization of charge heterogeneity of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. mAbs 2020, 12, 1763762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawli, L.A.; Goswami, S.; Hutchinson, R.; Kwong, Z.W.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Yao, Z.; Sreedhara, A.; Cano, T.; Tesar, D.; et al. Charge variants in IgG1: Isolation, characterization, in vitro binding properties and pharmacokinetics in rats. mAbs 2010, 2, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaschak, T.; Boyd, D.; Lu, F.; Derfus, G.; Kluck, B.; Nogal, B.; Emery, C.; Summers, C.; Zheng, K.; Bayer, R.; et al. Characterization of the basic charge variants of a human IgG1: Effect of copper concentration in cell culture media. mAbs 2011, 3, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyon, A.; Excoffier, M.; Janin-Bussat, M.C.; Bobaly, B.; Fekete, S.; Guillarme, D.; Beck, A. Determination of isoelectric points and relative charge variants of 23 therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1065–1066, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Nowak, C.; Meshulam, D.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, D.; Pacardo, D.B.; Nicholls, S.B.; Carven, G.J.; Gu, Z.; Fang, J.; et al. Risk-Based Control Strategies of Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody Charge Variants. Antibodies 2022, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camperi, J.; Grunert, I.; Heinrich, K.; Winter, M.; Ozipek, S.; Hoelterhoff, S.; Weindl, T.; Mayr, K.; Bulau, P.; Meier, M.; et al. Inter-laboratory study to evaluate the performance of automated online characterization of antibody charge variants by multi-dimensional LC-MS/MS. Talanta 2021, 234, 122628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverick, M.; Mengisen, S.; Shameem, M.; Ambrogelly, A. Separation of mAbs molecular variants by analytical hydrophobic interaction chromatography HPLC: Overview and applications. mAbs 2014, 6, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; He, B. Combination of On-Line and Off-Line Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Comprehensive Characterization of mAb Charge Variants and Precise Instructions for Rapid Process Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z. In-Depth Characterization of mAb Charge Variants by On-Line Multidimensional Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 7977–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieczkowski, C.; Zhang, X.; Lee, D.; Nguyen, K.; Lv, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Way, J.; Gries, J.M. Blueprint for antibody biologics developability. mAbs 2023, 15, 2185924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Tomioka, Y.; Kurosawa, Y.; Akuta, T. Elucidating the mechanisms of additive effects at high concentrations on hydrophobic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1702, 464091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Xing, T.; Wang, S.; Daly, T.J.; Li, N. Coupling Mixed-Mode Size Exclusion Chromatography with Native Mass Spectrometry for Sensitive Detection and Quantitation of Homodimer Impurities in Bispecific IgG. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11417–11424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Nguyen, J.B.; Rosconi, M.P.; Pyles, E.A.; Qiu, H.; Li, N. High-sensitivity and high-resolution therapeutic antibody charge variant and impurity characterization by microfluidic native capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 223, 115147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Desai, R.; Cui, W.; Harrahy, J.J.; Ivanov, A.R. Characterization of bispecific antigen-binding biotherapeutic fragmentation sites using microfluidic capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry (mCZE-MS). Analyst 2023, 148, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Charge Variants | 3D-LC-MS Method | Data of Individual mAb A or mAb B by IEC * | RSD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Average | RSD | ||||
| mAb A | Acidic peak 1 | 11.06% | 11.13% | 11.53% | 11.24% | 2.26% | 10.78% | 2.80% |
| Acidic peak 2 | 8.50% | 8.50% | 8.74% | 8.58% | 1.61% | 8.27% | 2.27% | |
| Main peak 3 | 69.22% | 69.15% | 68.96% | 69.11% | 0.19% | 70.00% | 0.66% | |
| Basic peak 4 | 4.80% | 4.86% | 4.70% | 4.79% | 1.59% | 5.04% | 2.88% | |
| Basic peak 5 | 6.42% | 6.36% | 6.06% | 6.28% | 3.11% | 5.92% | 3.88% | |
| mAb B | Acidic peak 1 | 14.77% | 14.04% | 13.79% | 14.20% | 3.59% | 14.12% | 2.95% |
| Acidic peak 2 | 12.79% | 11.96% | 11.71% | 12.15% | 4.66% | 12.19% | 3.81% | |
| Main peak 3 | 49.70% | 50.58% | 49.17% | 49.82% | 1.43% | 50.67% | 1.44% | |
| Basic peak 4 | 7.07% | 6.66% | 6.32% | 6.69% | 5.58% | 7.33% | 6.46% | |
| Basic peak 5 | 7.55% | 7.55% | 7.42% | 7.51% | 1.00% | 7.68% | 1.41% | |
| Name | Charge Variants | PTM Data |
|---|---|---|
| mAb A | Acidic peak 1 | Carboxymethylation |
| Acidic peak 2 | Deamidation | |
| Main peak 3 | C- terminal lysine loss of two heavy chains | |
| Basic peak 4 | One heavy chain with C-terminal lysine | |
| Basic peak 5 | VHS-containing variant | |
| mAb B | Acidic peak 1 | Deamidation |
| Acidic peak 2 | Glycans with one sialic acid | |
| Main peak 3 | C- terminal lysine loss of two heavy chains | |
| Basic peak 4 | Isomerization of aspartic acid | |
| Basic peak 5 | One heavy chain with C-terminal lysine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, X.; Chen, L.; Chu, J.; He, B. Charge Variants Characterization of Co-Formulated Antibodies by Three-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080999
Jin X, Chen L, Chu J, He B. Charge Variants Characterization of Co-Formulated Antibodies by Three-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(8):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080999
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Xiaoqing, Luna Chen, Jianlin Chu, and Bingfang He. 2024. "Charge Variants Characterization of Co-Formulated Antibodies by Three-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry" Biomolecules 14, no. 8: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080999
APA StyleJin, X., Chen, L., Chu, J., & He, B. (2024). Charge Variants Characterization of Co-Formulated Antibodies by Three-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Biomolecules, 14(8), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14080999





