Association of IL-9 Cytokines with Hepatic Injury in Echinococcus granulosus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Mice
2.3. Cells
2.4. Preparation of E. granulosus and EgP
2.5. Mouse Model of E. granulosus Infection and In Vivo Blockade
2.6. Preparation of PBMCs
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISAs) and Liver Enzyme Assays
2.10. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)
2.11. Immunohistochemical Staining (IHC)
2.12. Fluorescence-Based Multiplex Immunohistochemistry (mIHC) Staining
2.13. Data Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
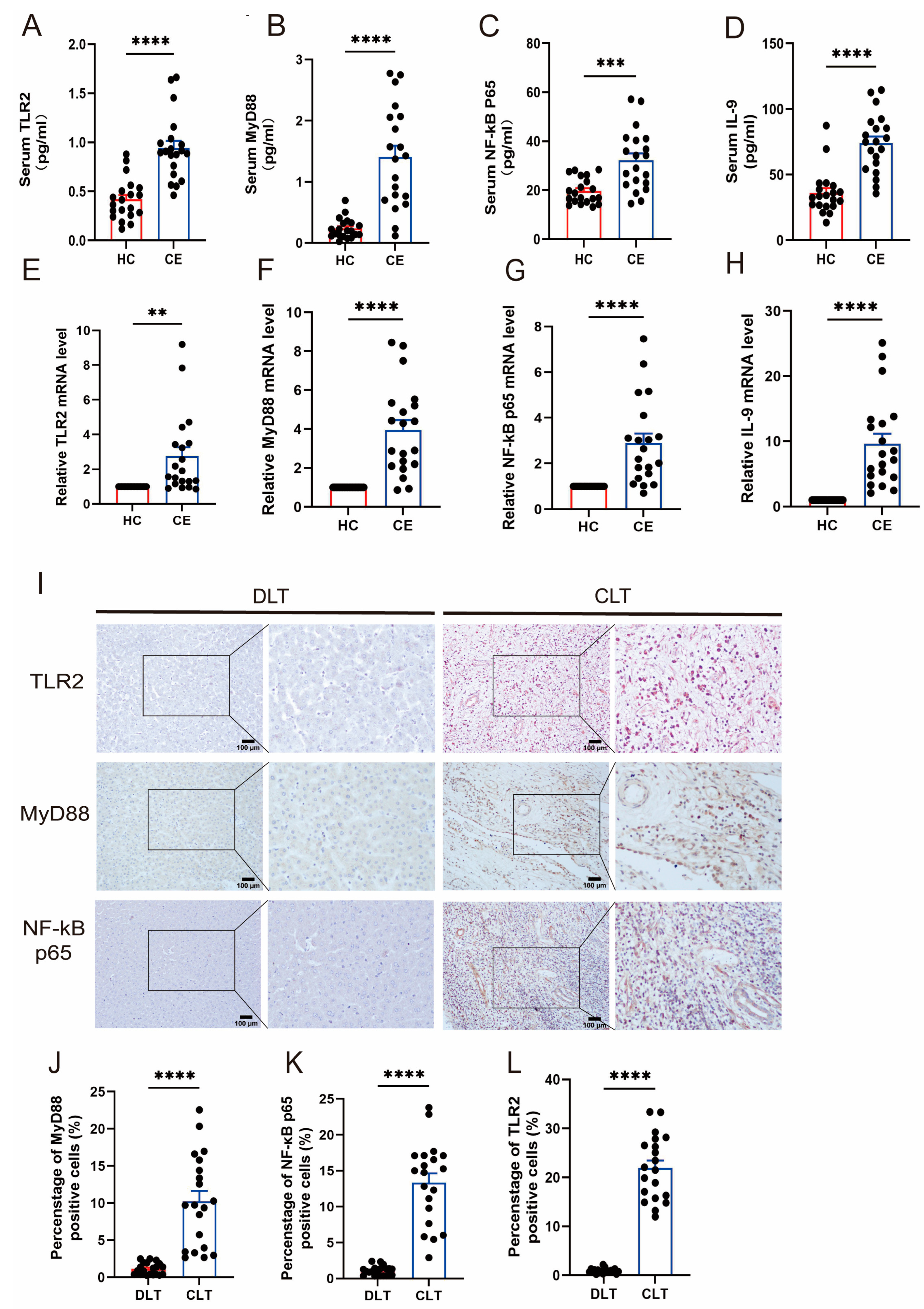
3.1. The Expression of TLR2 and IL-9 Increased in CE
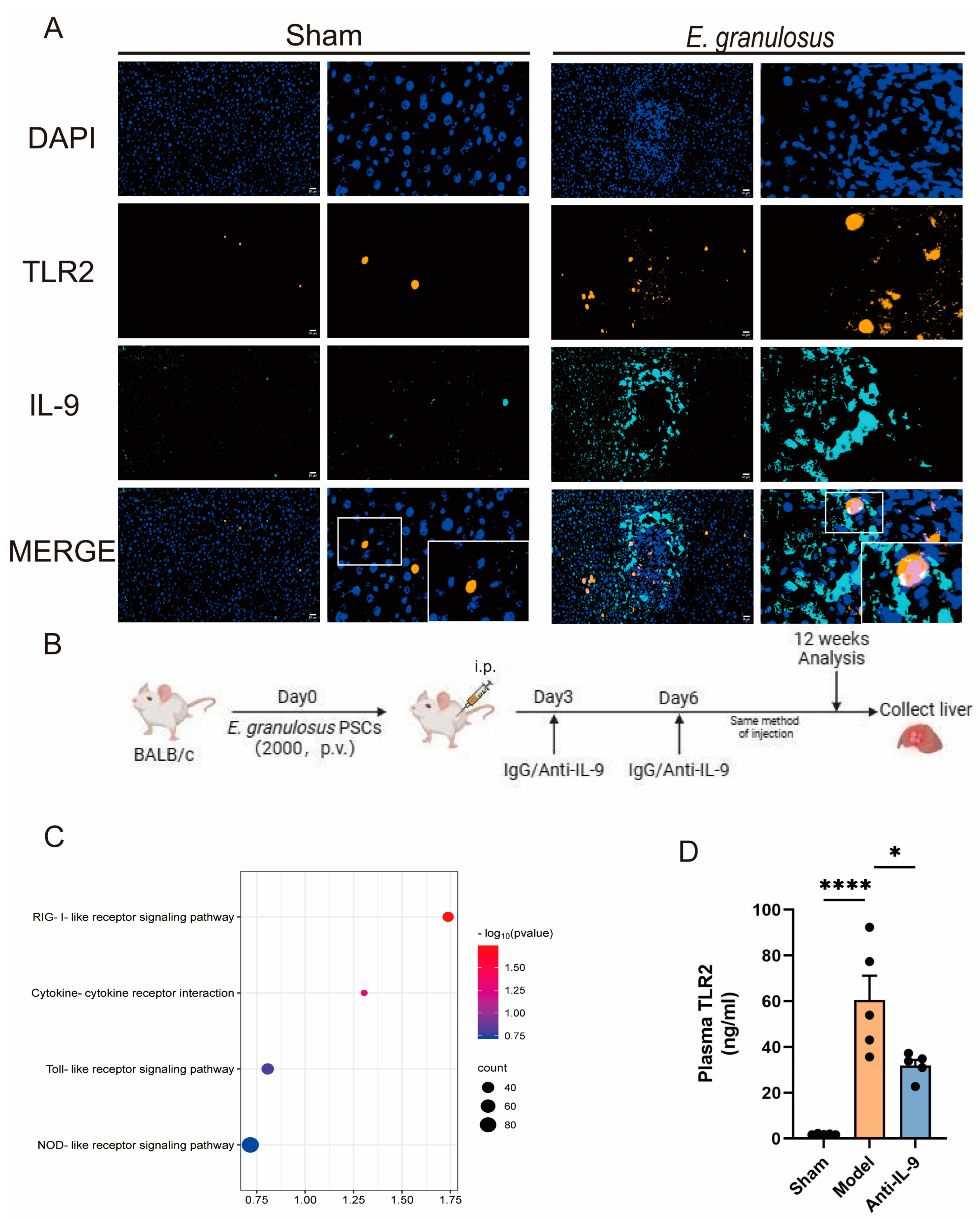
3.2. The Expression of TLR2 Increased with the Time of Infection
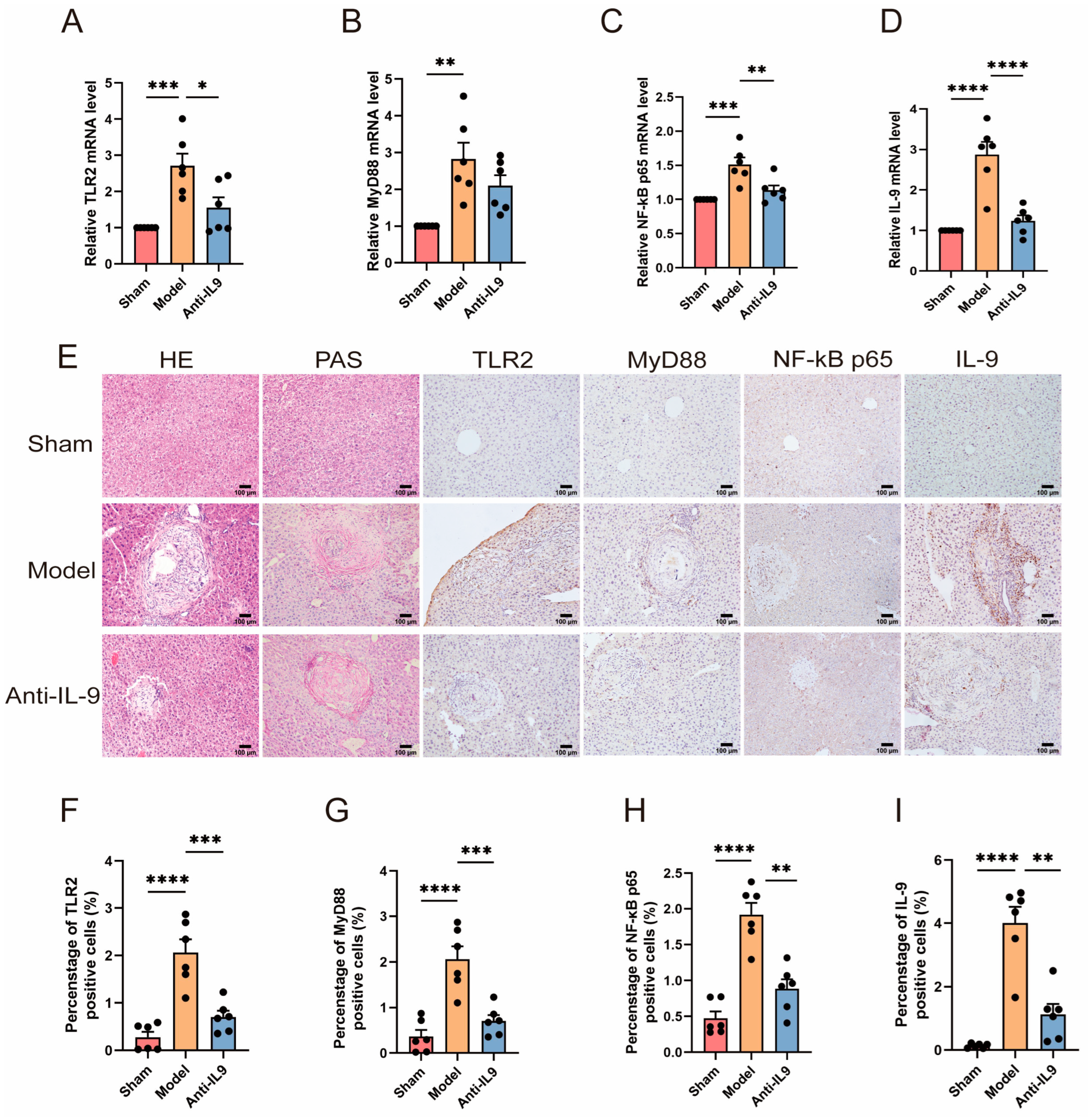
3.3. Injection of Anti-IL-9 Reduced TLR2 in E. granulosus-Infected Mice
3.4. The Effects of Immunity and Fibrosis Play an Important Role in RAW264.7 and HSCs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00075-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Tamarozzi, F. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Siracusa, M.C. First Responders: Innate Immunity to Helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Cell-Mediated Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Jana, M.; Majumder, M.; Mondal, S.; Roy, A.; Pahan, K. Selective targeting of the TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB pathway reduces α-synuclein spreading in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, D.S. Toll-like receptor signaling in parasitic infections. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuxun, T.; Ma, H.Z.; Apaer, S.; Zhang, H.; Aierken, A.; Li, Y.P.; Lin, R.Y.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Wen, H. Expression of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and Related Cytokines in Patients with Hepatic Cystic and Alveolar Echinococcosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 632760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanger, A.P.; Pallandre, J.R.; Gbaguidi-Haore, H.; Knapp, J.; Malézieux, N.; Lignon, T.; Borg, C.; Millon, L. Investigating the impact of Echinococcus multilocularis vesicular fluid on human cells from healthy blood donors. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 417, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghib, M.; Kariminik, A.; Kazemi Arababadi, M. TLR2, as a Pathogen Recognition Receptor, Plays Critical Roles in Hepatitis B Outcome. Viral Immunol. 2022, 35, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, J.D.; Davies, Z. In vitro culture of the strobilar state of Echinococcus granulosus (sheep strain): A review of basic problems and results. Int. J. Parasitol. 1974, 4, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, A.; Riganò, R.; Ortona, E.; Profumo, E.; Margutti, P.; Buttari, B.; Delunardo, F.; Teggi, A. Immunomodulatory mechanisms during Echinococcus granulosus infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.Y.; Ji, W.Z.; Li, H.T.; Tuxun, T.; Lin, R.Y.; Wen, H. TLR2 and TLR4 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic cystic echinococcosis and its relationship with IL-10. Parasite Immunol. 2011, 33, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkasekwinai, P.; Dong, C. IL-9-producing T cells: Potential players in allergy and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Zuleta, W.G.; Sanchez, E. IL-9: Function, Sources, and Detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1585, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Sopel, N.; Finotto, S. Th9 and other IL-9-producing cells in allergic asthma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimbara, A.; Christodoulopoulos, P.; Soussi-Gounni, A.; Olivenstein, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Levitt, R.C.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Holroyd, K.J.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Lafitte, J.J.; et al. IL-9 and its receptor in allergic and nonallergic lung disease: Increased expression in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temann, U.A.; Geba, G.P.; Rankin, J.A.; Flavell, R.A. Expression of interleukin 9 in the lungs of transgenic mice causes airway inflammation, mast cell hyperplasia, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, N.C.; Holroyd, K.J.; Ewart, S.L.; Eleff, S.M.; Kiser, M.B.; Dragwa, C.R.; Sullivan, C.D.; Grasso, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Messler, C.J.; et al. Interleukin 9: A candidate gene for asthma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13175–13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, H.; Humphreys, N.; Renauld, J.C.; Van Snick, J.; Grencis, R. Interleukin-9 is involved in host protective immunity to intestinal nematode infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2536–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, J.M.; Wahid, F.N.; Grencis, R.K.; Else, K.J.; Ben-Smith, A.W.; Goyal, P.K. Immunological relationships during primary infection with Heligmosomoides polygyrus (Nematospiroides dubius): Downregulation of specific cytokine secretion (IL-9 and IL-10) correlates with poor mastocytosis and chronic survival of adult worms. Parasite Immunol. 1993, 15, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grencis, R.K.; Hültner, L.; Else, K.J. Host protective immunity to Trichinella spiralis in mice: Activation of Th cell subsets and lymphokine secretion in mice expressing different response phenotypes. Immunology 1991, 74, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pang, N.; Zhang, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, H.; Ding, J. Th9/IL-9 profile in human echinococcosis: Their involvement in immune response during infection by Echinococcus granulosus. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 781649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, N.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; An, M.; Wang, H.; Mamuti, W.; Ding, J.; Fan, H. TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway positively up-regulates the differentiation of Interleukin-9-producing CD4(+) T cells in human Echinococcus granulosus infection. J. Infect. 2018, 76, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.F.; Reba, S.M.; Li, Q.; Boom, W.H.; Rojas, R.E. Toll like Receptor 2 engagement on CD4(+) T cells promotes TH9 differentiation and function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Informal Working Group. International classification of ultrasound images in cystic echinococcosis for application in clinical and field epidemiological settings. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei, R.; Mohajerzadeh, M.S.; Masomi, H.F.A.; Tavakoli, M.; Turki, H.; Firouzeh, N. Discordance Therapeutic Protocol of Cystic Echinococcosis With WHO Guideline: A Descriptive Study Based on Liver Ultra-Sonographic Data in North Khorasan Province, Northeastern of Iran. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2024, 43, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, R.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Bi, X.; Wang, H.; Aini, A.; Zhang, N.; Abulizi, A.; Sun, C.; et al. Immune Exhaustion of T Cells in Alveolar Echinococcosis Patients and Its Reversal by Blocking Checkpoint Receptor TIGIT in a Murine Model. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1297–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Duan, L.; Zhang, W. In vitro and in vivo efficacies of novel carbazole aminoalcohols in the treatment of cystic echinococcosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Qi, W.; Zheng, X.; Duan, L.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Han, X.; et al. Transcriptome analysis uncovers the key pathways and candidate genes related to the treatment of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces with the repurposed drug pyronaridine. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shao, Y.; Yang, S.; Bi, X.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, N.; Li, Z.; Sun, C.; Li, L.; et al. T-cell tolerance and exhaustion in the clearance of Echinococcus multilocularis: Role of inoculum size in a quantitative hepatic experimental model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Hou, X.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Involvement of TIGIT in Natural Killer Cell Exhaustion and Immune Escape in Patients and Mouse Model With Liver Echinococcus multilocularis Infection. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3376–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, T.; Sultanpuram, N.; Sendi, H. The role of liver microenvironment in hepatic metastasis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Shi, Y.; Kang, X.; Rousu, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, M.; Ainiwaer, A.; Zheng, X.; Wang, M.; Jiensihan, B.; et al. Echinococcus granulosus: The establishment of the metacestode in the liver is associated with control of the CD4(+) T-cell-mediated immune response in patients with cystic echinococcosis and a mouse model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 983119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolsey, I.D.; Miller, A.L. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato and Echinococcus multilocularis: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuxun, T.; Apaer, S.; Ma, H.Z.; Zhang, H.; Aierken, A.; Lin, R.Y.; Wen, H. The Potential Role of Th9 Cell Related Cytokine and Transcription Factors in Patients with Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 895416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijo, M.; Anesetti, G.; Martínez, L.; Sim, R.B.; Ferreira, A.M. Echinococcus granulosus: The establishment of the metacestode is associated with control of complement-mediated early inflammation. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 118, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Q.; Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, M.; Kang, X.; Hou, X.; Li, D.; Rousu, Z.; Jiang, T.; et al. Hepatic macrophages play critical roles in the establishment and growth of hydatid cysts in the liver during Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto infection. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, A.; Yi, H.; Gu, R.; Yi, Q.; et al. Interleukin-33 Contributes to the Induction of Th9 Cells and Antitumor Efficacy by Dectin-1-Activated Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.P.; Srivastava, R.N.; Goswami, R. Calcitriol attenuates TLR2/IL-33 signaling pathway to repress Th9 cell differentiation and potentially limits the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, B.; Van Snick, J.; Brombacher, F. IL-9 is a susceptibility factor in Leishmania major infection by promoting detrimental Th2/type 2 responses. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Grencis, R.K.; Humphreys, N.E.; Renauld, J.C.; Van Snick, J. Anti-IL-9 vaccination prevents worm expulsion and blood eosinophilia in Trichuris muris-infected mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure-Dupuy, S.; Durantel, D.; Lucifora, J. Liver macrophages: Friend or foe during hepatitis B infection? Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, A.; Bohnacker, S.; Esser-von Bieren, J. Macrophage regulation & function in helminth infection. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 53, 101526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, H.; Pang, N.; Ma, X.; Wen, H.; Fan, H.; et al. Upregulation of PD-1 on CD4⁺CD25⁺ T cells is associated with immunosuppression in liver of mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, C.M.; Jung, E.; Pearce, E.J. Schistosoma mansoni egg antigen-mediated modulation of Toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced activation occurs independently of TLR2, TLR4, and MyD88. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5754–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.; Wang, S.; Friedman, S.L. The Power of Plasticity-Metabolic Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Ali, T.; Li, L.; Bi, X.; Wang, J.; Lü, G.; Shao, Y.; Vuitton, D.A.; Wen, H.; et al. Hydatid cyst fluid promotes peri-cystic fibrosis in cystic echinococcosis by suppressing miR-19 expression. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | HC | CE | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case | 20 | 20 | |
| Sex (male/female) | 9:11 | 7:13 | |
| Age (years) | 37.65 ± 10.38 | 38.55 ± 18.22 | |
| BMI | 26.75 ± 3.55 | 22.85 ± 4.65 | |
| Location (right/left) | 0 | 5:15 | |
| AST (U/L) | 20.48 ± 4.51 | 29.52 ± 10.31 | *** |
| ALT (U/L) | 20.75 ± 10.88 | 29.74 ± 16.18 | * |
| Primers Name | Primers Sequences (5′ to 3′) | Length (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mus-TLR2 | Forward | ATGCTTCGTTGTTCCCTGTGTTG | 23 |
| Reverse | AGTGGTTGTCGCCTGCTTCC | 20 | |
| Mus-MyD88 | Forward | GCAGAACCAGGAGTCCGAGAAG | 22 |
| Reverse | GATGCCTCCCAGTTCCTTTGTTTG | 24 | |
| Mus-NF-κB p65 | Forward | ATGGGAAACCGTATGAGCCTGTG | 23 |
| Reverse | AGTTGTAGCCTCGTGTCTTCTGTC | 24 | |
| Mus-IL-9 | Forward | GATGCGGCTGATTGTTT | 17 |
| Reverse | CTCGTGCTCACTGTGGAGT | 19 | |
| Mus-α-SMA | Forward | TTCGTGACTACTGCCGAGC | 19 |
| Reverse | GTCAGGCAGTTCGTAGCTCT | 20 | |
| Mus-Collagen I | Forward | CCCTGGTCCCTCTGGAAATG | 20 |
| Reverse | GGACCTTTGCCCCCTTCTTT | 20 | |
| Mus-GAPDH | Forward | GGTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA | 20 |
| Reverse | TGGTCCAGGGTTTCTTACTCC | 21 | |
| Homo-TLR2 | Forward | CTCCCAGCAGGAACATCTGCTA | 21 |
| Reverse | CCAGGAATGAAGTCCCGCTTA | 21 | |
| Homo-MyD88 | Forward | CGCCGCCTGTCTCTGTTCTTG | 21 |
| Reverse | GGTCCGCTTGTGTCTCCAGTTG | 22 | |
| Homo-NF-κB p65 | Forward | GCAGTTTGATGATGAAGACC | 20 |
| Reverse | CTGTCACTAGGCGAGT | 16 | |
| Homo-IL-9 | Forward | GATCCAGCTTCCAAGTGCCACTG | 23 |
| Reverse | AAGCATGGTCTGGTGCAGTTGTC | 23 | |
| Homo-GAPDH | Forward | CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT | 20 |
| Reverse | GAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTT | 18 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Xu, X.; Zhu, J.; Aizezi, M.; Aierken, A.; Meng, M.; He, R.; Aimulajiang, K.; Wen, H. Association of IL-9 Cytokines with Hepatic Injury in Echinococcus granulosus Infection. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14081007
Zhou T, Xu X, Zhu J, Aizezi M, Aierken A, Meng M, He R, Aimulajiang K, Wen H. Association of IL-9 Cytokines with Hepatic Injury in Echinococcus granulosus Infection. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(8):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14081007
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tanfang, Xinlu Xu, Jiang Zhu, Mayire Aizezi, Aili Aierken, Menggen Meng, Rongdong He, Kalibixiati Aimulajiang, and Hao Wen. 2024. "Association of IL-9 Cytokines with Hepatic Injury in Echinococcus granulosus Infection" Biomolecules 14, no. 8: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14081007
APA StyleZhou, T., Xu, X., Zhu, J., Aizezi, M., Aierken, A., Meng, M., He, R., Aimulajiang, K., & Wen, H. (2024). Association of IL-9 Cytokines with Hepatic Injury in Echinococcus granulosus Infection. Biomolecules, 14(8), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14081007






