Ischemic Neuroprotection by Insulin with Down-Regulation of Divalent Metal Transporter 1 (DMT1) Expression and Ferrous Iron-Dependent Cell Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
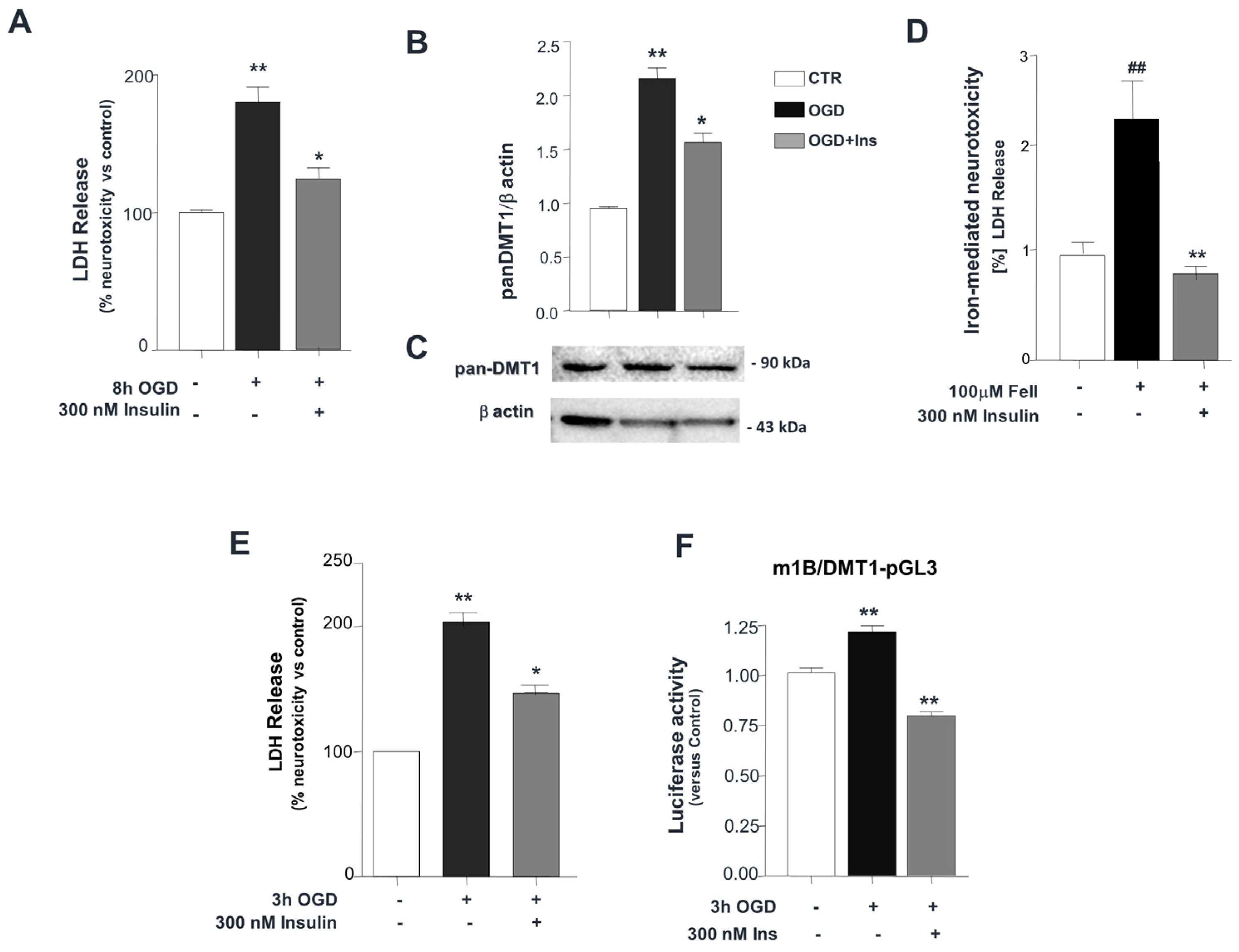
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunshin, H.; Mackenzie, B.; Berger, U.V.; Gunshin, Y.; Romero, M.F.; Boron, W.F.; Nussberger, S.; Gollan, J.L.; Hediger, M.A. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 1997, 388, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, M.D.; Trenor, C.C.; Su, M.A.; Foernzler, D.; Beier, D.R.; Dietrich, W.F.; Andrews, N.C. Microcytic anaemia mice have a mutation in Nramp2, a candidate iron transporter gene. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrick, M.D.; Dolan, K.G.; Horbinski, C.; Ghio, A.J.; Higgins, D.; Porubcin, M.; Moore, E.G.; Hainsworth, L.N.; Umbreit, J.N.; Conrad, M.E.; et al. DMT1: A mammalian transporter for multiple metals. Biometals 2003, 16, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T. Iron and infection. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 107, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, R.; Garavaglia, B.; Memo, M. DMT1 Expression and Iron Levels at the Crossroads Between Aging and Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradkar, P.N.; Roth, J.A. Nitric oxide transcriptionally down-regulates specific isoforms of divalent metal transporter (DMT1) via NF-kappaB. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, N.; Hentze, M.W. Previously uncharacterized isoforms of divalent metal transporter DMT1: Implications for regulation and cellular function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12345–12350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, J.; Mena, N.; Hunot, S.; Prigent, A.; Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Arredondo, M.; Duyckaerts, C.; Sazdovitch, V.; Zhao, L.; Garrick, L.M.; et al. Divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) contributes to neurodegeneration in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18578–18583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzillotta, A.; Sarnico, I.; Ingrassia, R.; Boroni, F.; Branca, C.; Benarese, M.; Faraco, G.; Blasi, F.; Chiarugi, A.; Spano, P.; et al. The acetylation of RelA in Lys310 dictates the NF-kB-dependent response in post-ischemic injury. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiguera, C.; Alghisi, M.; Pinna, A.; Bellucci, A.; De Luca, M.A.; Frau, L.; Morelli, M.; Ingrassia, R.; Benarese, M.; Porrini, V.; et al. Late-onset Parkinsonism in NF-kB/c-Rel-deficient mice. Brain 2012, 135 Pt 9, 2750–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, R.; Lanzillotta, A.; Sarnico, I.; Benarese, M.; Blasi, F.; Borgese, L.; Bilo, F.; Depero, L.; Chiarugi, A.; Spano, P.F.; et al. 1B/(−)IRE DMT1 expression during brain ischemia contributes to cell death mediated by NF-kB/RelA acetylation at Lys310. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.B.; Tonnesen, M.F.; Madsen, A.N.; Hagedorn, P.H.; Friberg, J.; Grunnet, L.G.; Heller, R.S.; Østergren, A.; Nielsen, A.; Størling, J.; et al. Divalent metal transporter 1 regulates iron-mediated ROS and pancreatic β cell fate in response to cytokines. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundh, M.; Christensen, D.P.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Mascagni, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Billestrup, N.; Grunnet, L.G.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Lysine deacetylases are produced in pancreatic beta cells and are differentially regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2569–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.Q.; He, W.; Xu, K.F.; Wang, Z.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, H. FTO Inhibits Insulin Secretion and Promotes NF-kB Activation through Positively Regulating ROS Production in Pancreatic β cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127705. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Ding, N.; Lu, M.; Jia, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z. Activation of NF-kB-Inducing Kinase in Islet β Cells Causes β Cell Failure and Diabetes. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 2430–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakic, T.; Jevdjovic, T.; Lakic, I.; Ruzicic, A.; Jasnic, N.; Djurasevic, S.; Djordjevic, J.; Vujovic, P. The Expression of Insulin in the Central Nervous System: What Have We Learned So Far? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milstein, J.L.; Heather, A.; Ferris, H.A. The brain as an insulin-sensitive metabolic organ. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.C.; Stouffer, M.A.; Mancini, M.; Nicholson, C.; Carr, K.D.; Rice, M.E. Interactions between insulin and diet on striatal dopamine uptake kinetics in rodent brain slices. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2019, 49, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorina, I.I.; Avrova, N.F.; Zakharova, I.O.; Shpakov, A.O. Biochemistry (Mosc). Prospects for the Use of Intranasally Administered Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Cerebral Ischemia. Biochemistry 2023, 88, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lioutas, V.A.; Alfaro-Martinez, F.; Bedoya, F.; Chung, C.C.; Pimentel, D.A.; Novak, V. Intranasal Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 as Neuroprotectants in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravanpour, F.; Dargahi, F.; Rezaei, M.; Haghani, M.; Heidari, R.; Valian, N.; Ahmadiani, A. Intranasal insulin improves mitochondrial function and attenuates motor deficits in a rat 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, A.; Humeres, C.; González, V.; Gómez, M.T.; Montt, N.; Sanchez, G.; Chiong, M.; García, L. Insulin/NFkB protects against ischemia-induced necrotic cardiomyocyte death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanh, D.V.; Choi, Y.H.; Moh, S.H.; Kinyua, A.W.; Kim, K.W. Leptin and insulin signaling in dopaminergic neurons: Relationship between energy balance and reward system. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, A.; Dossena, M.; Bertolotti, P.; Boroni, F.; Sarnico, I.; Faraco, G.; Chiarugi, A.; Frontini, A.; Giordano, A.; Liou, H.C.; et al. Leptin is induced in the ischemic cerebral cortex and exerts neuroprotection through NF-kappaB/c-Rel-dependent transcription. Stroke 2009, 40, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, R.; Memo, M.; Garavaglia, B. Ferrous Iron Up-regulation in Fibroblasts of Patients with Beta Propeller Protein-Associated Neurodegeneration (BPAN). Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.E.; Jin, O.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kuo, F.; Andrews, N.C. Transferrin receptor is necessary for development of erythrocytes and the nervous system. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucheux, B.A.; Hirsch, E.C.; Villares, J.; Selimi, F.; Mouatt-Prigent, A.; Javoy-Agid, F.; Hauw, J.J.; Agid, Y. Distribution of 125I-ferrotransferrin binding sites in the mesencephalon of control subjects and patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 2338–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzi, M.; Boroni, F.; Bianchetti, A.; Moraitis, C.; Sarnico, I.; Benarese, M.; Goffi, F.; Valerio, A.; Spano, P. Expression of functional NR1/NR2B-type NMDA receptors in neuronally differentiated SK-N-SH human cell line. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrick, M.D.; Kuo, H.C.; Vargas, F.; Singleton, S.; Zhao, L.; Smith, J.J.; Paradkar, P.; Roth, J.A.; Garrick, L.M. Comparison of mammalian cell lines expressing distinct isoforms of divalent metal transporter 1 in a tetracycline-regulated fashion. Biochem. J. 2006, 398, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inta, I.; Paxian, S.; Maegele, I.; Zhang, W.; Pizzi, M.; Spano, P.; Sarnico, I.; Muhammad, S.; Herrmann, O.; Inta, D.; et al. Bim and Noxa are candidates to mediate the deleterious effect of the NF-kappa B subunit RelA in cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12896–12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, M.D. Non-transferrin-bound iron transporters. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setoodeh, S.; Khorsand, M.; Takhshid, M.A. The effects of iron overload, insulin resistance and oxidative stress on metabolic disorders in patients with beta-thalassemia major. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Kim, J.; Veuthey, T.; Lee, C.H.; Wessling-Resnick, M. Glucose metabolism in the Belgrade rat, a model of iron-loading anemia. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G1095-102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Seufert, J.; Gallwitz, G. The extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: A focus on the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, W.G.; Remy, P.; Giordana, C.; Maltête, D.; Derkinderen, P.; Houéto, J.L.; Anheim, M.; Benatru, I.; Boraud, T.; Brefel-Courbon, C.; et al. Trial of Lixisenatide in Early Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpakov, A.O.; Zorina, I.I.; Derkach, K.V. Hot Spots for the Use of Intranasal Insulin: Cerebral Ischemia, Brain Injury, Diabetes Mellitus, Endocrine Disorders and Postoperative Delirium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, P.; Maldonado, D.A.A.P.; Novak, V. Safety and preliminary efficacy of intranasal insulin for cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy: A double-blinded placebo-controlled pilot study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fenaroli, F.; Valerio, A.; Ingrassia, R. Ischemic Neuroprotection by Insulin with Down-Regulation of Divalent Metal Transporter 1 (DMT1) Expression and Ferrous Iron-Dependent Cell Death. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070856
Fenaroli F, Valerio A, Ingrassia R. Ischemic Neuroprotection by Insulin with Down-Regulation of Divalent Metal Transporter 1 (DMT1) Expression and Ferrous Iron-Dependent Cell Death. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(7):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070856
Chicago/Turabian StyleFenaroli, Francesca, Alessandra Valerio, and Rosaria Ingrassia. 2024. "Ischemic Neuroprotection by Insulin with Down-Regulation of Divalent Metal Transporter 1 (DMT1) Expression and Ferrous Iron-Dependent Cell Death" Biomolecules 14, no. 7: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070856
APA StyleFenaroli, F., Valerio, A., & Ingrassia, R. (2024). Ischemic Neuroprotection by Insulin with Down-Regulation of Divalent Metal Transporter 1 (DMT1) Expression and Ferrous Iron-Dependent Cell Death. Biomolecules, 14(7), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14070856






