MyD88 and Its Inhibitors in Cancer: Prospects and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
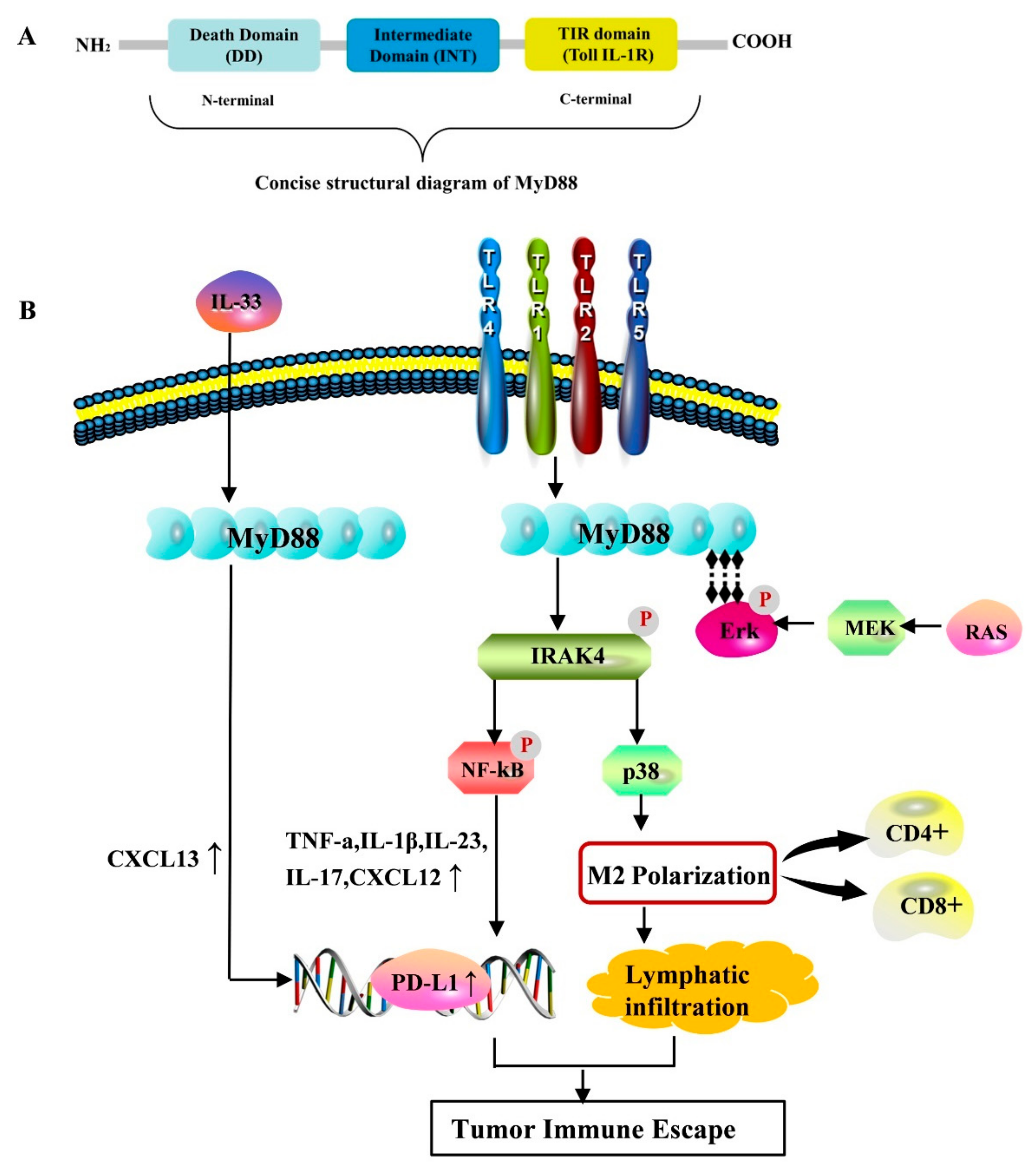
2. Biological Structure and Function of MyD88
3. MyD88 Is Associated with Immune Inflammatory Response
4. MyD88 Is Associated with Tumor Progression
4.1. Abnormal MyD88 Signaling Is a Carcinogen
4.2. MyD88 Is Associated with Tumor Cell Proliferation and Metastasis
4.3. MyD88 Is Associated with Tumor Prognosis
4.4. MyD88 Could Be Considered as a Novel Tumor Marker
5. MyD88-Mediated Tumorigenic Pathway
6. MyD88 Is Involved in Tumor Immune Escape
7. Drug Therapy Targeting MyD88
| Inhibitor | Structure | Machine | Effect | Year of Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGN1703 | 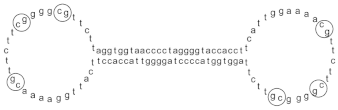 | Acts on TLR9/MyD88 signaling pathway | Benefits the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer [88], enhancing anti-viral immune response to chronic HIV-1 infection [89] | 2015 |
| Tomisetron | 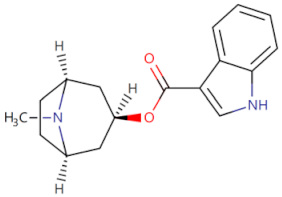 | Inhibits TLR4/MyD88 signaling | Inhibits the development of colorectal cancer [84] | 2016 |
| Curcumin | 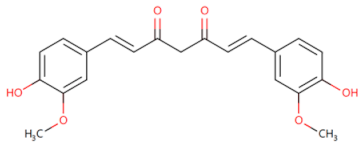 | Inhibits the expression of TLR4/MyD88 and EGFR in a dose- and time-dependent manner | Inhibits the proliferation and migration of NSCLC [83] | 2019 |
| Mesalazine | 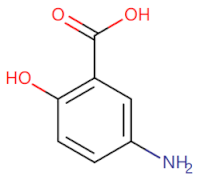 | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88-dependent pathway | Resists ulcerative colitis in mice model [76] | 2019 |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | Compound of traditional Chinese Medicine | Inhibits MD2/TLR4-MyD88 complex formation and signaling | Reduces cardiac dysfunction and inflammatory response in heart failure rats [67] | 2020 |
| Radix gentianae | Compound of traditional Chinese Medicine | Inhibits the galectin-3/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway | Prevents acute myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol in rats [68] | 2020 |
| Oxyberberine | Compound of traditional Chinese Medicine | Inhibits the TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway and the translocation of NF-κB p65 from cytoplasm to nucleus | Anti-colitis effect [90] | 2020 |
| Dexmedetomidine | 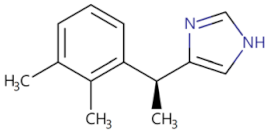 | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway | Resists Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury [73] | 2021 |
| Rifampicin | 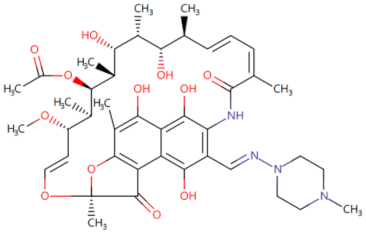 | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway | Ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive and motor impairments in mice [77] | 2021 |
| Astragaloside IV | 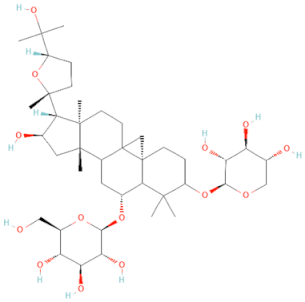 | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway | Prevents acute myocardial infarction [70] | 2021 |
| Icariin |  | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibits the progression of cervical cancer [82] | 2021 |
| Sevoflurane |  | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 signaling pathway | Sevoflurane postconditioning ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats [78] | 2022 |
| Polyene Phosphatidylcholine | — | Acts on TLR2, reduction of the activation of MyD88 IKKs complex | Inhibits the synovial inflammation induced by LPS [81] | 2022 |
| Emodin |  | Inhibits the MyD88/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway | Inhibits the activation of microglia and inflammatory response [79] | 2022 |
| Biogenic AgNPs | — | Targets the TLR4/MyD88 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways | Inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation [71] | 2023 |
| Fluoxetine |  | Attenuates the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway activation | Alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice [72] | 2023 |
| Salvianolic acid A |  | Inhibits TLR2/TLR4-mediated MyD88 activation and its downstream molecules TRAF6 and IRAK4 | Attenuates cardiac inflammation and cardiac disfunction in heart failure mice [80] | 2023 |
| Atorvastatin |  | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway | Reduces contrast media-induced proptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells [74] | 2023 |
| Pioglitazone |  | Attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway | Ameliorates cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity [75] | 2023 |
| Xianglian Pill | Compound of traditional Chinese Medicine | Inhibits the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway | Attenuates ulcerative colitis [69] | 2023 |
| Combined treatment with ZA and Tα1 |  Structure of ZA | Blocks MyD88/NF-κB signaling in PCa cells and activates the MyD88/NF-κB signaling in macrophages and T cells, leading to increased cytotoxic T cell infiltration and enhanced tumor inflammation | Alleviates the non-immunoreactive patients with advanced or metastatic prostate cancer [85] | 2023 |
| Si jun zi tang | Compound of traditional Chinese Medicine | Regulates the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and reduces PD-L1 expression | Inhibits the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells and reduces the expression of PD-L1 protein in A549 cells [86] | 2024 |
| Inhibitor | Structure | Machine | Effect | Year of Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| linear RDVLPGT | — | Inhibits MyD88 dimerization | Inhibits the NF-κB signal pathway [91] | 2008 |
| AS-1 |  | Inhibited the interaction between IL-1R and MyD88 and weakened the binding activity of NF-κB | Protects the myocardium from ischaemia/reperfusion injury [92] | 2009 |
| 4210 |  | Inhibits MyD88 dimerization | Inhibits the pro-inflammatory immune signaling induced by bacterial toxins [107] | 2015 |
| Inhibits the interaction between MyD88 and IRF3/IRF7 and upregulated IFN-α | Anti-viral effect [111] | 2020 | ||
| T6167923 |  | Disrupts the formation of MyD88 homodimer | Protects mice from toxic shock induced by SEB [105] | 2015 |
| Inhibits MyD88 expression | Down-regulates the expression of Col I, Col III, and α-SMA [112] | 2023 | ||
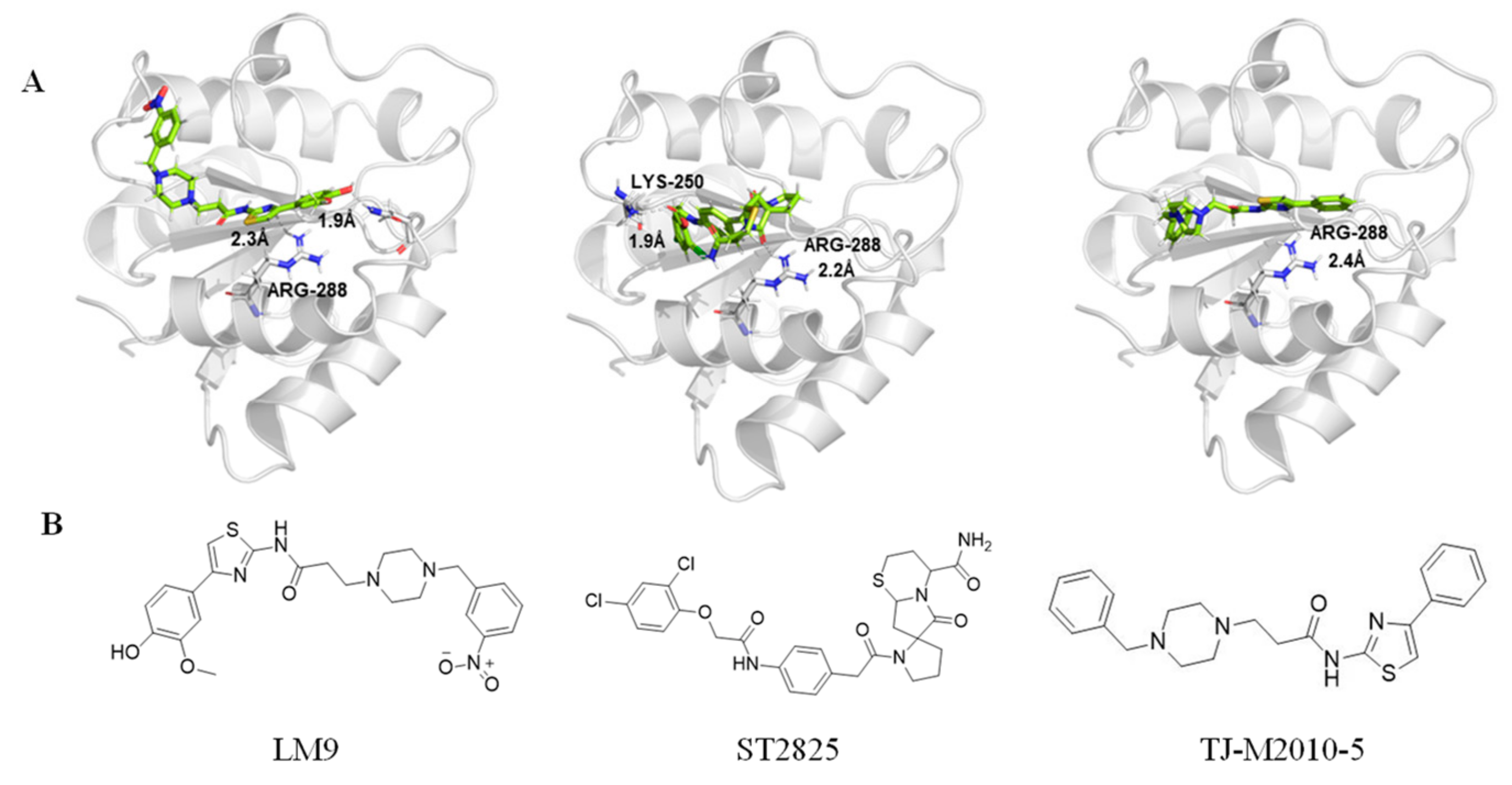
| TJ-M2010-5 | 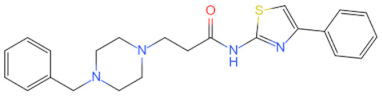 | Inhibits MyD88 homologous dimerization | Prevents colorectal cancer related to colitis [99], increases the tolerance of allogeneic transplantation in mice [102], prevents DSS-induced acute liver injury in mice [113] and reduces transplant rejection in mice [101] | 2015–2019 |
| Inhibits the MyD88 signaling pathway | Anti-hepatocellular carcinoma [100] | 2019 | ||
| Inhibits the TLR7/MyD88/NF-κB and TLR7/MyD88/MAPK signaling pathways | Relieves B cell lupus-like immune disease [103] | 2020 | ||
| Inhibits MyD88 homologous dimerization | Reverses myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury [114] | 2020 | ||
| Inhibits the MyD88/NF-κB and Erk pathways Inhibits myeloid cell infiltration and microglia activation | Relieves acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [115] | 2022 | ||
| Inhibits MyD88 homologous dimerization | Alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury during heart transplantation [98] | 2022 | ||
| Blocks the activation of MyD88/NF-κB | Alleviates liver fibrosis [97] | 2022 | ||
| Overcomes the inhibitory function of myeloid suppressor cells | Prevents colorectal cancer development associated with colitis [53] | 2022 | ||
| Inhibits cell proptosis | Prevents liver ischemia-reperfusion injury [116] | 2023 | ||
| Blocks MyD88 signal transduction | Prevents the development of CAC as well as downregulating GPNMB mRNA [117] | 2023 | ||
| ST2825 | 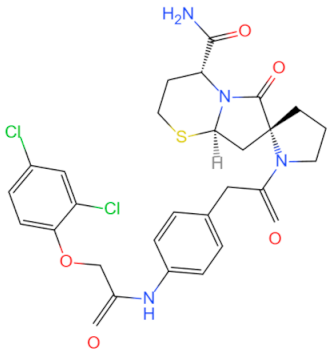 | Prevents MyD88 from dimerizing | Provides neuroprotection after experimental traumatic brain injury in mice [118], inhibits HCC cell proliferation [94] and relieves lymphoma and leukemia [96] | 2016, 2017 |
| Inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway Inhibits the production of IL-10 and IFN-β | Relieves B-cell neoplasms driven by activated MyD88 signaling [119] | 2019 | ||
| Prevents MyD88 from dimerizing | Prevents synovitis and joint degeneration [120] | 2021 | ||
| Inhibits NF-κB activation and the ROS/NLRP3 signaling pathway | Attenuates LPS-stimulated neuroinflammation [121] | 2022 | ||
| Prevents MyD88 from dimerizing | Inhibits pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [95] and alleviates synovial lesions [122] | 2023 | ||
| TJ-M2010-6 | 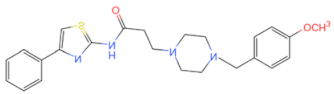 | Inhibits MyD88 homologous dimerization | Prevents and cures type 1 diabetes in NOD mice [104] | 2016 |
| TJ-M2010-2 | 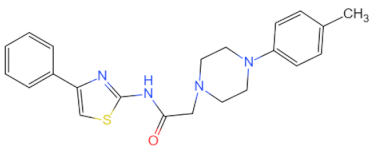 | Inhibits MyD88 homologous dimerization | Offsetting renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal injury [123] and alleviates renal interstitial fibrosis [124] | 2016, 2018 |
| Regulates the MyD88/GSK-3β and MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathways | Inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion in breast cancer cells [32] | 2020 | ||
| Cyclic c (MyD 4-4) | — | Prevents MyD88 from dimerizing | Alleviates immune encephalomyelitis in mice [93] | 2018 |
| LM9 | 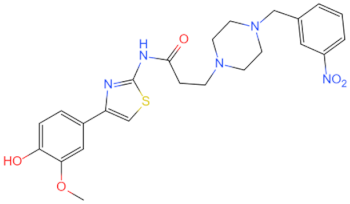 | Inhibits the MyD88 and inflammatory pathways in macrophages | Prevents atherosclerosis [125] | 2019 |
| Inhibits the formation of TLR4/MyD88 complexes | Reduces inflammatory response and cardiac fibrosis [106] | 2020 | ||
| LM8 | 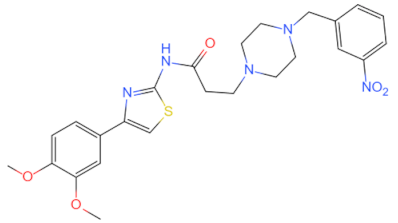 | Inhibits the MyD88 Erk/NF-κB-dependent inflammatory pathway | Relieves heart damage [108] | 2020 |
| Inhibits TLR4-MyD88 interaction and NF-κB activation | Protects the kidney from inflammatory damage of diabetes [126], relieves heart inflammation in diabetes mice [127] and relieves hypertensive nephropathy-induced by angiotensin II [128] | 2021, 2022 | ||
| M20 | 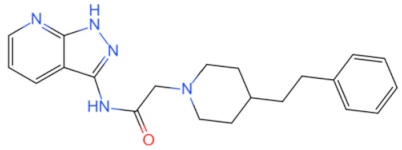 | Prevents MyD88 from dimerizing | Reduces sepsis-mediated acute lung injury [109] | 2021 |
| Low temperature oxygenation perfusion combined with TJ-M2010-5 | 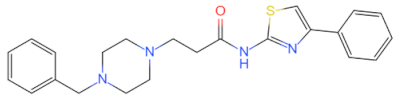 | Inhibits the TLR/MyD88 signaling pathway | Relieves liver ischemia-reperfusion injury [129] | 2022 |
| C17 | 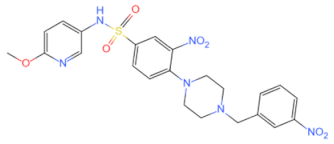 | Inhibits the interaction between TLR4-MyD88 and NF-κB signaling pathway | Alleviates acute lung injury [110] | 2023 |
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CacyBP/SIP | calcycin-binding protein and Siah-1 interaction protein |
| CI | confidence interval |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase 2 |
| CX3CL1 | C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| DD | death domain |
| DLBCL | diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| EVs | extracellular vehicles |
| HGSOC | high-grade serous ovarian cancer |
| HMGB1 | High mobility group box-1 protein |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| IDO | Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase |
| IFNs | type I interferons |
| IFN-γ | interferon-gamma |
| IKK | IκB kinase |
| IL-10 | interleukin-10 |
| IL-18R | interleukin-18 receptor |
| IL-1R | interleukin-1 receptor |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| INT | intermediate domain |
| IRAK | IL-1R-associated kinase |
| IRF-7 | interferon regulatory factor 7 |
| LGSOC | low-grade serous ovarian cancer |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MDSCs | myeloid suppressor cells |
| MT1-MMP | membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinases |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation factor 88 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| PAUF | pancreatic adenocarcinoma up-regulated factor |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| PD-1 | programmed death 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed death ligand 1 |
| Ras/ERK | rat sarcoma virus/extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| TAMs | tumor-associated macrophages |
| TIR | toll interleukin-1 receptor |
| TLRs | toll-like receptors |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| WM | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia |
| WT | wild-type |
References
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. TLR signaling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klekotka, P.A.; Yang, L.; Yokoyama, W.M. Contrasting roles of the IL-1 and IL-18 receptors in MyD88-dependent contact hypersensitivity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, C.D.; Canto, F.B.; Gomes, A.; Brandao, L.M.; Lima, J.R.; Melo, G.A.; Granato, A.; Neves, E.G.A.; Dutra, W.O.; Oliveira, A.C.; et al. Cytotoxic CD4(+) T cells driven by T-cell intrinsic IL-18R/MyD88 signaling predominantly infiltrate Trypanosoma cruzi-infected hearts. eLife 2022, 11, e74636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguine, J.; Barton, G.M. MyD88: A central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.F. Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 3270–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Precopio, M.; Lan, T.; Yu, D.; Tang, J.X.; Kandimalla, E.R.; Agrawal, S. Antitumor activity and immune response induction of a dual agonist of Toll-like receptors 7 and 8. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, A.; Virard, F.; Renno, T.; Coste, I. Dual function of MyD88 in inflammation and oncogenesis: Implications for therapeutic intervention. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coste, I.; Le Corf, K.; Kfoury, A.; Hmitou, I.; Druillennec, S.; Hainaut, P.; Eychene, A.; Lebecque, S.; Renno, T. Dual function of MyD88 in RAS signaling and inflammation, leading to mouse and human cell transformation. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3663–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S. Dual functional roles of the MyD88 signaling in colorectal cancer development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartey, S.; Neale, G.; Vogel, P.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. A MyD88/IL1R Axis Regulates PD-1 Expression on Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Sustains Their Immunosuppressive Function in Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2358–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of spontaneous intestinal tumorigenesis through the adaptor protein MyD88. Science 2007, 317, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Worschech, A.; Cardone, M.; Jones, Y.; Gyulai, Z.; Dai, R.M.; Wang, E.; Ma, W.; Haines, D.; O’HUigin, C.; et al. MyD88-mediated signaling prevents development of adenocarcinomas of the colon: Role of interleukin 18. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sugiyama, M.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiarro, M.; Gallo, G.; Fantò, N.; De Santis, R.; Carminati, P.; Ruggiero, V.; Sette, C. Identification of critical residues of the MyD88 death domain involved in the recruitment of downstream kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28093–28103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, H.; Olerenshaw, D.; Sankar, A.; Federwisch, M.; McDonald, N.Q.; Driscoll, P.C. The three-dimensional solution structure and dynamic properties of the human FADD death domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, N.J.; Gangloff, M.; O’Neill, L.A. What the Myddosome structure tells us about the initiation of innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, L.; Chen, P.; Liang, G. Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Protein 88 (MyD88): The Central Hub of TLR/IL-1R Signaling. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13316–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, M.; Ni, J.; Feng, P.; Dixit, V.M. IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 1997, 278, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.; Gazzinelli, R.T. Regulation of innate immune signaling by IRAK proteins. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1133354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; He, Z.; Chen, J.; Ma, M.; Deng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, T. Protection of toll-like receptor 9 against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress of pulmonary epithelial cells via MyD88-mediated pathways. Physiol. Res. 2022, 71, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, K.S.; Peroulis, M.; Schizas, D.; Kapelouzou, A. MYD88 and Proinflammatory Chemokines in Aortic Atheromatosis: Exploring Novel Statin Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.L.; Alcaide, P. MyD88: At the heart of inflammatory signaling and cardiovascular disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2021, 161, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Su, L.; Deng, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, G. Incomplete Knockdown of MyD88 Inhibits LPS-Induced Lung Injury and Lung Fibrosis in a Mouse Model. Inflammation 2023, 46, 2276–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Kim, M.; Gordon, R.A.; Leibler, C.; Cosgrove, H.A.; Bastacky, S.; Nickerson, K.M.; Shlomchik, M.J. B cell-intrinsic Myd88 regulates disease progression in murine lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20230263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echizen, K.; Hirose, O.; Maeda, Y.; Oshima, M. Inflammation in gastric cancer: Interplay of the COX-2/prostaglandin E2 and Toll-like receptor/MyD88 pathways. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, F.; Scheltema, R.A.; Mollenkopf, H.J.; Mann, M. Direct proteomic quantification of the secretome of activated immune cells. Science 2013, 340, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yang, S.; Lin, C.; Ye, J. MyD88 mediates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via NF-κB/AP-1 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, B.; Bossuyt, V.; Li, X.; Wali, V.B.; Patwardhan, G.A.; Frederick, C.; Silber, A.; Park, T.; Harigopal, M.; Pelekanou, V.; et al. Immunological differences between primary and metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2232–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, W.; Deng, Q.; Li, L.; Hsi, E.D.; Young, K.H.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. MYD88 L265P Mutation in Lymphoid Malignancies. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2457–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.S.; Vierkant, R.A.; Rambau, P.F.; Winham, S.J.; Wagner, P.; Traficante, N.; Tołoczko, A.; Tiezzi, D.G.; Taran, F.A.; Sinn, P.; et al. MyD88 and TLR4 Expression in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.; Viailly, P.J.; Bohers, E.; Bertrand, P.; Ruminy, P.; Marchand, V.; Maingonnat, C.; Mareschal, S.; Picquenot, J.M.; Penther, D.; et al. Biological and Clinical Relevance of Associated Genomic Alterations in MYD88 L265P and non-L265P-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Analysis of 361 Cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2232–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.Y.; Zou, Z.M.; Gao, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, X.W.; Sun, Z.H.; Zheng, W.J.; Zhou, P.; et al. The MyD88 inhibitor TJ-M2010-2 suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by regulating MyD88/GSK-3β and MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Chen, B.; Meng, Y.; Lu, J.; Shi, X.; Hu, A.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D. Role of the CXCR3-mediated TLRs/MyD88 signaling pathway in promoting the development of hepatitis B into cirrhosis and liver cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.P. IL33 activates CD8+T and NK cells through MyD88 pathway to suppress the lung cancer cell growth in mice. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, F.; Arribas, A.J.; Sartori, G.; Spriano, F.; Barnabei, L.; Tarantelli, C.; Von Roemeling, R.; Martinez, E.; Zucca, E.; Bertoni, F. Targeting IRAK4 with Emavusertib in Lymphoma Models with Secondary Resistance to PI3K and BTK Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinnakota, K.; Hu, F.; Ku, M.C.; Georgieva, P.B.; Szulzewsky, F.; Pohlmann, A.; Waiczies, S.; Waiczies, H.; Niendorf, T.; Lehnardt, S.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 mediates microglia/brain macrophage MT1-MMP expression and glioma expansion. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, M.; Jiang, Z. Involvement of TLR2/4-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of intracranial aneurysm. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, F.; Ni, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, R.; Kang, X. Increased expression of MyD88 and association with paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 6017–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.E.; Jiang, F.; Won, H.Y.; Hong, D.E.; Kang, T.H.; Park, Y.Y.; Koh, S.S. PAUF Induces Migration of Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells Exclusively via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, J.M.; Zhang, G.N.; Li, J.M.; Huang, J. Expression of lnc-MyD88 and its relationship with the prognosis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2022, 57, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, F.; Yu, L.; Chen, X. TLR4/MyD88 signaling determines the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, K.; Tan, G. Significance of TLR4/MyD88 expression in breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7034–7039. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.L.; Qian, Z.R.; Nakasono, M.; Tanahashi, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Bando, Y.; Kudo, E.; Shimada, M.; Sano, T. High expression of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signals correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupi, L.A.; Cucielo, M.S.; Silveira, H.S.; Gaiotte, L.B.; Cesário, R.C.; Seiva, F.R.F.; de Almeida Chuffa, L.G. The role of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway in ovarian, cervical, and endometrial cancers. Life Sci. 2020, 247, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, N.; Kondo, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Mochizuki, K.; Tanioka, F.; Oyama, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Iizuka, J.; Tanabe, K.; Shibata, N.; et al. High prevalence of the MYD88 mutation in testicular lymphoma: Immunohistochemical and genetic analyses. Pathol. Int. 2015, 65, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohs, A.; Kuttkat, N.; Otto, T.; Youssef, S.A.; De Bruin, A.; Trautwein, C. MyD88-dependent signaling in non-parenchymal cells promotes liver carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Cheng, Z.; Lin, C.; Hoffman, R.M.; Huang, Y.; Singh, S.R.; Zheng, W.; Yang, S.; Ye, J. MyD88 Regulates LPS-induced NF-ĸB/MAPK Cytokines and Promotes Inflammation and Malignancy in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, J. MYD88 Is a Potential Prognostic Gene and Immune Signature of Tumor Microenvironment for Gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 654388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilanczyk, E.; Filipek, S.; Filipek, A. ERK1/2 is dephosphorylated by a novel phosphatase—CacyBP/SIP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Cai, M.; Xiao, L.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lian, Y. Blockage of CacyBP inhibits macrophage recruitment and improves anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shacter, E.; Weitzman, S.A. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology 2002, 16, 217–226, 229; discussion 230–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kfoury, A.; Le Corf, K.; El Sabeh, R.; Journeaux, A.; Badran, B.; Hussein, N.; Lebecque, S.; Manié, S.; Renno, T.; Coste, I. MyD88 in DNA repair and cancer cell resistance to genotoxic drugs. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, D.; Xie, B.; Xie, L. Blockade of Myd88 signaling by a novel MyD88 inhibitor prevents colitis-associated colorectal cancer development by impairing myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Du, Y.; Hao, J.; Wu, R.; Du, L. UTMD inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis by inducing macrophage polarization and vessel normalization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Gu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Tian, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. MyD88 in myofibroblasts enhances colitis-associated tumorigenesis via promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.S.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, L.L.; Chua, K.V.; Hung, H.C.; Hsu, J.T.; Huang, T.S. Extracellular HSP90α Induces MyD88-IRAK Complex-Associated IKKα/β-NF-κB/IRF3 and JAK2/TYK2-STAT-3 Signaling in Macrophages for Tumor-Promoting M2-Polarization. Cells 2022, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Yan, H.; Han, X.; Weng, L.; Wei, Q.; Sun, X.; Lu, W.; Wei, Q.; Ye, J.; Cai, X.; et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zou, J.; Zhong, X.; Li, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. HMGB1 in the interplay between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2024, 581, 216494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Tesniere, A.; Obeid, M.; Ortiz, C.; Criollo, A.; Mignot, G.; Maiuri, M.C.; Ullrich, E.; Saulnier, P.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Jia, K.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; He, Y.; Zhou, C. Alterations of DNA damage response pathway: Biomarker and therapeutic strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, E.J.; Johnson, J.R.; Saada, J.I.; Humen, M.; House, J.; Dann, S.; Qiu, S.; Brasier, A.R.; Powell, D.W.; Reyes, V.E.; et al. TLR4 activation enhances the PD-L1-mediated tolerogenic capacity of colonic CD90+ stromal cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2218–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Pu, N.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; Wang, D.; Kuang, T.; Jin, D.; Lou, W.; et al. Gut-derived lipopolysaccharide remodels tumoral microenvironment and synergizes with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade via TLR4/MyD88/AKT/NF-κB pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.F.; Liu, H.; Gao, R.; Zhou, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Huang, F.; et al. Tumor cell-released autophagosomes (TRAPs) promote immunosuppression through induction of M2-like macrophages with increased expression of PD-L1. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, F.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, R.; Chu, Y. The IFN-γ/PD-L1 axis between T cells and tumor microenvironment: Hints for glioma anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, Y.; Zhu, N.; Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Ding, L. IL-33/ST2 signaling promotes constitutive and inductive PD-L1 expression and immune escape in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, Y. Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) restricts MD2/TLR4-MyD88 complex formation and signalling in acute myocardial infarction-induced heart failure. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10677–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Yang, H.X.; Yao, T.T.; Li, Y.; Ruan, L.; Xu, G.R.; Zhang, C.; Guo, G.X.; Li, A.Y. Gentianella acuta prevents acute myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol in rats via inhibition of galectin-3/TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB inflammatory signalling. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, P.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, T.; Hu, Y.; Ding, K.; Zhao, M. Xianglian Pill attenuates ulcerative colitis through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 300, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, P.; Gao, G.; Liu, P.P.; Wang, S.S.; Song, R.; Zou, Y.Y.; Yin, G.; Wang, L. Astragaloside IV prevents acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sanjay; Jaiswal, V.; Park, M.; Lee, H.J. Biogenic silver NPs alleviate LPS-induced neuroinflammation in a human fetal brain-derived cell line: Molecular switch to the M2 phenotype, modulation of TLR4/MyD88 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways, and molecular docking analysis. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 148, 213363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lin, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, X. Fluoxetine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by attenuating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway activation in aged mice. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jia, J.; Xi, W.; Deng, H.; Tu, W. Dexmedetomidine Resists Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 260, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, R.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Su, B.H.; Li, C.J.; Zeng, R. Atorvastatin reduces contrast media-induced pyroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, S.; Kamel, G.A.M. Pioglitazone ameliorates cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 80, 127287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tang, J.H.; Wen, J.J.; Zhu, J.Q. Regulatory mechanism of mesalazine on TLR4/MyD88-dependent pathway in mouse ulcerative colitis model. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 6637–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Cheng, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, R.; Luo, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L. Rifampicin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive and motor impairments via inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in mice. Neurol. Res. 2021, 43, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Chi, F.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Q. Sevoflurane postconditioning ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 signaling pathway. Aging 2022, 14, 10153–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Lv, B.; Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Z. Protecting effect of emodin in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice by inhibiting microglia activation and inflammation via Myd88/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signalling pathway. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 9322–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawuti, A.; Sun, S.; Wang, R.; Gong, D.; Liu, R.; Kong, D.; Yuan, T.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Salvianolic acid A alleviates heart failure with preserved ejection fraction via regulating TLR/Myd88/TRAF/NF-κB and p38MAPK/CREB signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hao, W.; Xu, D.; He, Y.; Yan, Z.; Sun, F.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Tang, R.; et al. Polyene Phosphatidylcholine Interacting with TLR-2 Prevents the Synovial Inflammation via Inactivation of MAPK and NF-κB Pathways. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, S.; Ma, H.; Ruan, M.; Fang, L.; Cheng, J. Influence of icariin on inflammation, apoptosis, invasion, and tumor immunity in cervical cancer by reducing the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tao, X.; Fu, Q.; Ge, C.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, M.; et al. Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation and migration in NSCLC through a synergistic effect on the TLR4/MyD88 and EGFR pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini-Khoei, H.; Momeny, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Dehpour, A.R.; Amiri, S.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Tavangar, S.M.; Ghaffari, S.H.; Rahimian, R.; Mehr, S.E. Tropisetron suppresses colitis-associated cancer in a mouse model in the remission stage. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 36, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, M.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Ye, G.; Pan, J.; Ye, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, D. Zoledronic acid and thymosin α1 elicit antitumor immunity against prostate cancer by enhancing tumor inflammation and cytotoxic T cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Qi, D.; Zhang, Z. Si Jun Zi decoction inhibits the growth of lung cancer by reducing the expression of PD-L1 through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, B.; Schmidt, M.; Scheithauer, W.; Schmoll, H.J. MGN1703, an immunomodulator and toll-like receptor 9 (TLR-9) agonist: From bench to bedside. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 94, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmoll, H.J.; Wittig, B.; Arnold, D.; Riera-Knorrenschild, J.; Nitsche, D.; Kroening, H.; Mayer, F.; Andel, J.; Ziebermayr, R.; Scheithauer, W. Maintenance treatment with the immunomodulator MGN1703, a Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonist, in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma and disease control after chemotherapy: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vibholm, L.K.; Konrad, C.V.; Schleimann, M.H.; Frattari, G.; Winckelmann, A.; Klastrup, V.; Jensen, N.M.; Jensen, S.S.; Schmidt, M.; Wittig, B.; et al. Effects of 24-week Toll-like receptor 9 agonist treatment in HIV type 1+ individuals. Aids 2019, 33, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ai, G.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Luo, C.; Tan, L.; Lin, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H.; et al. Oxyberberine, a novel gut microbiota-mediated metabolite of berberine, possesses superior anti-colitis effect: Impact on intestinal epithelial barrier, gut microbiota profile and TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantò, N.; Gallo, G.; Ciacci, A.; Semproni, M.; Vignola, D.; Quaglia, M.; Bombardi, V.; Mastroianni, D.; Zibella, M.P.; Basile, G.; et al. Design, synthesis, and in vitro activity of peptidomimetic inhibitors of myeloid differentiation factor 88. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Ha, T.; Kelley, J.; Deng, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Li, Y. The TIR/BB-loop mimetic AS-1 protects the myocardium from ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dishon, S.; Schumacher, A.; Fanous, J.; Talhami, A.; Kassis, I.; Karussis, D.; Gilon, C.; Hoffman, A.; Nussbaum, G. Development of a Novel Backbone Cyclic Peptide Inhibitor of the Innate Immune TLR/IL1R Signaling Protein MyD88. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.D. Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 15016826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; He, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, S. The MyD88 inhibitor, ST2825, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by suppressing the activation of the NF-κB/AKT1/p21 pathway in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 50, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiratori, E.; Itoh, M.; Tohda, S. MYD88 Inhibitor ST2825 Suppresses the Growth of Lymphoma and Leukaemia Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6203–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Du, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Shang, R.; Zhou, P. TJ-M2010-5, A self-developed MyD88 inhibitor, attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 354, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, P.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; et al. TJ-M2010-5 Attenuates Severe Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Heart Transplantation by Inhibiting MyD88 Homodimerization In Vivo. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2022, 15, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, F.C.; Zhang, L.M.; He, W.T.; Liu, J.H.; Li, M.Q.; Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P. Targeting of MyD88 Homodimerization by Novel Synthetic Inhibitor TJ-M2010-5 in Preventing Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, L.; Jiang, F.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Implication of myeloid differentiation factor 88 inhibitor TJ-M2010-5 for therapeutic intervention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Miao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.K.; Jiang, F.; Chang, S.; Zhou, P. A novel MyD88 inhibitor attenuates allograft rejection after heterotopic tracheal transplantation in mice. Transpl. Immunol. 2019, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.Q.; Xing, S.; Yang, T.; Xie, L.; Jiang, F.C.; et al. Short-term Pharmacological Inhibition of MyD88 Homodimerization by a Novel Inhibitor Promotes Robust Allograft Tolerance in Mouse Cardiac and Skin Transplantation. Transplantation 2017, 101, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Du, D.; Miao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, F. TJ-M2010-5, a novel MyD88 inhibitor, corrects R848-induced lupus-like immune disorders of B cells in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xing, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; He, W.; Liu, J.; Chang, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, P. Beyond knockout: A novel homodimerization-targeting MyD88 inhibitor prevents and cures type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.A.; Lee, M.S.; Kissner, T.L.; Alam, S.; Waugh, D.S.; Saikh, K.U. Discovery of small molecule inhibitors of MyD88-dependent signaling pathways using a computational screen. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Sun, C.C.; Liu, Q.; Lu, X.Y.; Fu, L.L.; Liang, G.; Zhang, X.H.; Chen, G.Z. Compound LM9, a novel MyD88 inhibitor, efficiently mitigates inflammatory responses and fibrosis in obesity-induced cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Javor, S.; Degardin, M.; Ajami, D.; Rebek, M.; Kissner, T.L.; Waag, D.M.; Rebek, J., Jr.; Saikh, K.U. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of a Small Molecule that Exhibits Anti-inflammatory Activity by Inhibition of MyD88-mediated Signaling to Bacterial Toxin Exposure. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jia, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Yan, J.; Ding, W.; Cao, H.; Liang, G.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Inhibition of MyD88 by LM8 Attenuates Obesity-Induced Cardiac Injury. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, Q.; Lu, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Cai, Y. Discovery of a Novel MyD88 Inhibitor M20 and Its Protection Against Sepsis-Mediated Acute Lung Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 775117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zou, Y.; Li, X.; Liao, J.; Dai, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Bioevaluation of Novel MyD88 Inhibitor c17 against Acute Lung Injury Derived from the Virtual Screen. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 6938–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikh, K.U.; Morazzani, E.M.; Piper, A.E.; Bakken, R.R.; Glass, P.J. A small molecule inhibitor of MyD88 exhibits broad spectrum antiviral activity by up regulation of type I interferon. Antivir. Res. 2020, 181, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Jing, W.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Lipopolysaccharide induces skin scarring through the TLR4/Myd88 inflammatory signaling pathway in dermal fibroblasts. Burns 2023, 49, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Du, D.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Miao, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Short-term use of MyD88 inhibitor TJ-M2010-5 prevents d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Inhibition of MyD88 by a novel inhibitor reverses two-thirds of the infarct area in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 5151–5169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Shang, R.; Zhang, L.; et al. TJ-M2010-5, a novel CNS drug candidate, attenuates acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the MyD88/NF-κB and ERK pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1080438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Shang, R.; Zhou, L.; Du, D.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Novel MyD88 Inhibitor TJ-M2010-5 Protects Against Hepatic Ischemia-reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Pyroptosis in Mice. Transplantation 2023, 107, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Shang, R.; Xie, L. MDSC suppresses T cell antitumor immunity in CAC via GPNMB in a MyD88-dependent manner. Cancer Med. 2023, 13, e6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.S.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.D.; Yan, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhou, C.H.; Ye, Z.N.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, T.W.; Liu, J.P.; et al. Inhibition of myeloid differentiation factor 88(MyD88) by ST2825 provides neuroprotection after experimental traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1643, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, N.; Gao, M.; Zhou, F.; Hu, J.; Feng, W. Disrupting myddosome assembly in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells using the MYD88 dimerization inhibitor ST2825. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Perez, S.; Oregon-Romero, E.; Reyes-Perez, I.V.; Bhattaram, P. Targeting MyD88 Downregulates Inflammatory Mediators and Pathogenic Processes in PBMC From DMARDs-Naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 800220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Liu, M.; Liu, D.N.; Shang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Du, G.H. ST2825, a Small Molecule Inhibitor of MyD88, Suppresses NF-κB Activation and the ROS/NLRP3/Cleaved Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway to Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Neuroinflammation. Molecules 2022, 27, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Perez, S.; Vekariya, R.; Gautam, S.; Reyes-Perez, I.V.; Drissi, H.; Bhattaram, P. MyD88 dimerization inhibitor ST2825 targets the aggressiveness of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.M.; Liu, J.H.; Xue, C.B.; Li, M.Q.; Xing, S.; Zhang, X.; He, W.T.; Jiang, F.C.; Lu, X.; Zhou, P. Pharmacological inhibition of MyD88 homodimerization counteracts renal ischemia reperfusion-induced progressive renal injury in vivo and in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.H.; He, L.; Zou, Z.M.; Ding, Z.C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, P.; Xie, L.; Xing, S.; Yi, C.Z. A Novel Inhibitor of Homodimerization Targeting MyD88 Ameliorates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis by Counteracting TGF-β1-Induced EMT in Vivo and in Vitro. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Luo, W.; Wu, G.; Wu, L.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, W.; Liang, G. A novel MyD88 inhibitor LM9 prevents atherosclerosis by regulating inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in macrophages. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 370, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Xu, S.J.; Qian, J.C.; Yang, L.B.; Chen, P.Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Luo, W.; Liang, G. Pharmacological inhibition of MyD88 suppresses inflammation in tubular epithelial cells and prevents diabetic nephropathy in experimental mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Wu, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chattipakorn, N.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G. Blockage of MyD88 in cardiomyocytes alleviates cardiac inflammation and cardiomyopathy in experimental diabetic mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Luo, W.; Yang, N.; Su, L.; Zhou, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Khan, Z.A.; Huang, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Inhibition of MyD88 attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertensive kidney disease via regulating renal inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Peng, S.; Du, P.; Zhou, P.; Xue, C.; Ye, Q. Hypothermic oxygenated perfusion combined with TJ-M2010-5 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in donation after circulatory death. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Wolynes, P.G.; Zheng, S. DynamicBind: Predicting ligand-specific protein-ligand complex structure with a deep equivariant generative model. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clabbers, M.T.B.; Holmes, S.; Muusse, T.W.; Vajjhala, P.R.; Thygesen, S.J.; Malde, A.K.; Hunter, D.J.B.; Croll, T.I.; Flueckiger, L.; Nanson, J.D.; et al. MyD88 TIR domain higher-order assembly interactions revealed by microcrystal electron diffraction and serial femtosecond crystallography. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Hu, Y.; Fang, L. MyD88 and Its Inhibitors in Cancer: Prospects and Challenges. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050562
Song J, Li Y, Wu K, Hu Y, Fang L. MyD88 and Its Inhibitors in Cancer: Prospects and Challenges. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(5):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050562
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jiali, Yuying Li, Ke Wu, Yan Hu, and Luo Fang. 2024. "MyD88 and Its Inhibitors in Cancer: Prospects and Challenges" Biomolecules 14, no. 5: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050562
APA StyleSong, J., Li, Y., Wu, K., Hu, Y., & Fang, L. (2024). MyD88 and Its Inhibitors in Cancer: Prospects and Challenges. Biomolecules, 14(5), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14050562





