The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
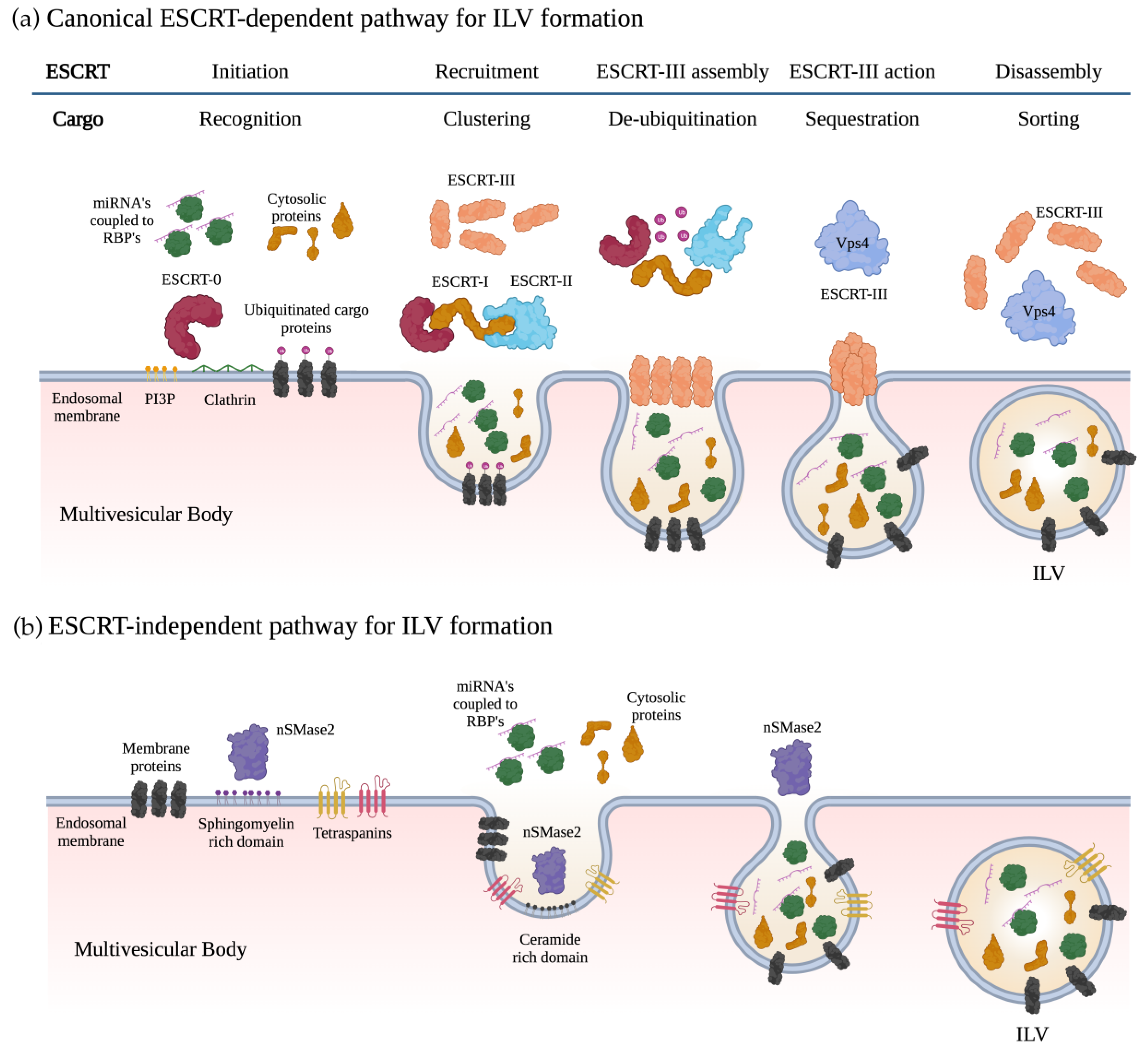
2. Exosome Biogenesis and miRNA Sorting
2.1. Biogenesis of Exosomes
2.2. Loading of miRNAs into Exosomes
2.3. Exosome Incorporation and Cargo Processing in the Recipient Cells
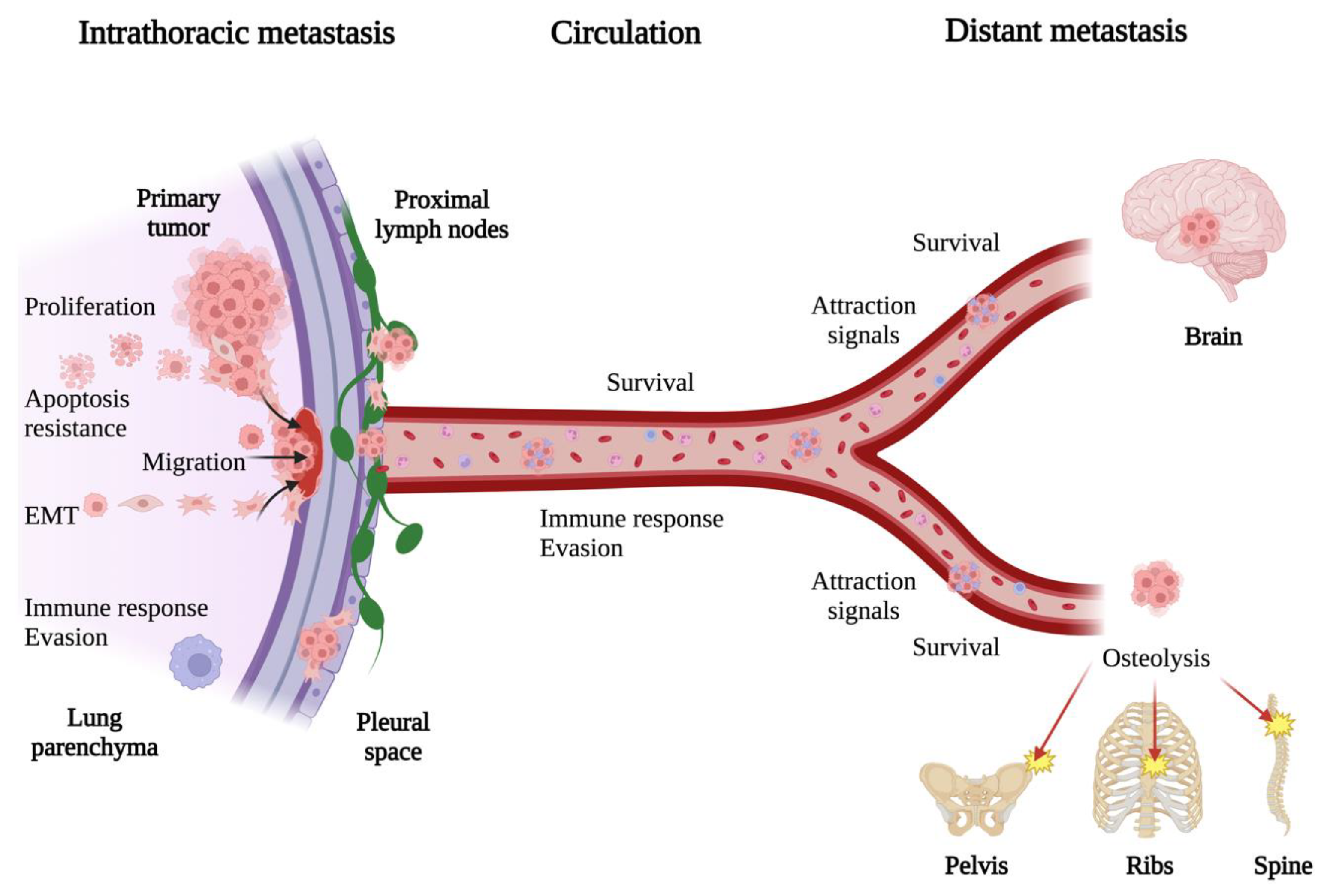
3. General Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Metastasis
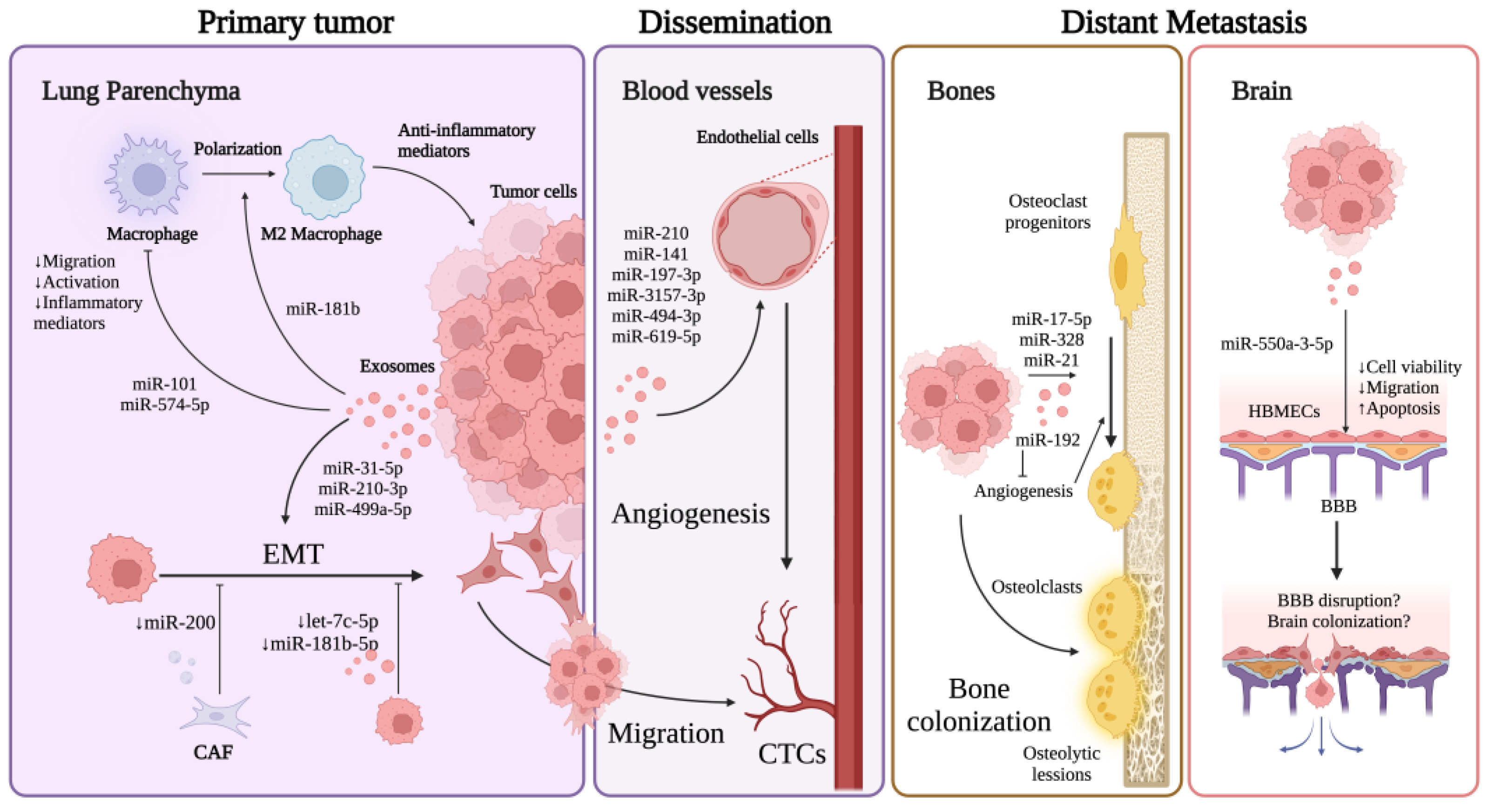
4. Exosomal miRNAs in Lung Cancer EMT
5. Exosomal miRNAs in Lung Cancer Angiogenesis
6. Exosomal miRNAs in Other Mechanisms Affecting Lung Cancer Metastasis
6.1. Regulation of Immune Response
6.2. Regulation of Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Apoptosis
7. Exosomal miRNAs in Bone and Brain Metastasis
7.1. Bone Metastasis
7.2. Brain Metastasis
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Today. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Islami, F.; Goding Sauer, A.; Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Patel, A.V.; Ma, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; et al. Proportion and Number of Cancer Cases and Deaths Attributable to Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors in the United States. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.L. Lung Cancer: Epidemiology and Screening. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 102, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung Cancer Survival Rates|5-Year Survival Rates for Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Xavier, C.P.R.; Caires, H.R.; Barbosa, M.A.G.; Bergantim, R.; Guimarães, J.E.; Vasconcelos, M.H. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Hallmarks of Cancer and Drug Resistance. Cells 2020, 9, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, R.; Hu, Z.; Tao, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Exosomal Cargos-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming in Tumor Microenvironment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamana, K.; Inoue, J.; Yoshida, R.; Sakata, J.; Nakashima, H.; Arita, H.; Kawaguchi, S.; Gohara, S.; Nagao, Y.; Takeshita, H.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Radioresistant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Contribute to the Acquisition of Radioresistance via the miR-503-3p-BAK Axis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Pancreatic Cancer-Derived Exosomes Promote the Proliferation, Invasion, and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer by the miR-3960/TFAP2A Axis. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3590326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour Exosome Integrins Determine Organotropic Metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Ahmadi, M.; Ravanbakhsh, R.; Mojarad, B.; Mahbubfam, S.; Shaban, S.A.; Shadi, K.; Berenjabad, N.J.; Etemadi, T. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: The Metastatic Organotropism Drivers. Life Sci. 2022, 289, 120216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, S.M.; Zhang, F.; Ding, C.; Montoya-Durango, D.E.; Hu, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Fox, M.; Zhang, H.; et al. Tumor-Derived Exosomes Drive Immunosuppressive Macrophages in a Pre-Metastatic Niche through Glycolytic Dominant Metabolic Reprogramming. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2040–2058.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, R.; Zappulli, V.; Sammarco, A.; Murillo, O.D.; Cheah, P.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tai, E.; Ting, D.T.; Wei, Z.; Roth, M.E.; et al. Glioma-Derived miRNA-Containing Extracellular Vesicles Induce Angiogenesis by Reprogramming Brain Endothelial Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2065–2074.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasov, V.V.; Svistunov, A.A.; Chubarev, V.N.; Dostdar, S.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Brzecka, A.; Sukocheva, O.; Neganova, M.E.; Klochkov, S.G.; Somasundaram, S.G.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Nanomedicine. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 69, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Lin, F.; Sun, W.; Zhu, W.; Fang, D.; Luo, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L. Exosome-Transmitted miRNA-335-5p Promotes Colorectal Cancer Invasion and Metastasis by Facilitating EMT via Targeting RASA1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sai, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J. Hypoxic BMSC-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Promote Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cells via STAT3-Induced EMT. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, T.-K.; Pack, C.-G.; Choi, C.-M.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K. Exosomal miR-1260b Derived from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Promotes Tumor Metastasis through the Inhibition of HIPK2. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Distribution of miRNA Expression across Human Tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Qiu, M. MicroRNAs and Glial Cell Development. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, E.; Sang Yong, K.; Carmell, M.A.; Murchison, E.P.; Alcorn, H.; Li, M.Z.; Mills, A.A.; Elledge, S.J.; Anderson, K.V.; Hannon, G.J. Dicer Is Essential for Mouse Development. Nat. Genet. 2003, 35, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez, A.J.; Cinalli, R.M.; Glasner, M.E.; Enright, A.J.; Thomson, J.M.; Baskerville, S.; Hammond, S.M.; Bartel, D.P.; Schier, A.F. MicroRNAs Regulate Brain Morphogenesis in Zebrafish. Science 2005, 308, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Yin, W.; Tang, C.; Lu, Y.; He, Y. Molecular Mechanism of microRNAs Regulating Apoptosis in Osteosarcoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 6945–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. Elegans Heterochronic Gene Lin-4 Encodes Small RNAs with Antisense Complementarity to Lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.G.; Tang, L. Conservation of the Heterochronic Regulator Lin-28, Its Developmental Expression and microRNA Complementary Sites. Dev. Biol. 2003, 258, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rocca, G.; Badin, M.; Shi, B.; Xu, S.-Q.; DeAngelis, T.; Sepp-Lorenzinoi, L.; Baserga, R. Mechanism of Growth Inhibition by MicroRNA 145: The Role of the IGF-I Receptor Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 220, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs Is a Novel Mechanism of Genetic Exchange between Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Li, F.; Li, F.; Cheng, Y.; Mei, H.; Meng, H.; et al. Use of Lung-Specific Exosomes for miRNA-126 Delivery in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Cheng, Z.; Qin, W.; Jiang, L. Exosomes as a Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 116, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.-B.; Hou, L.-K.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.-M.; Sun, F.; Lu, H.-M.; Deng, J.; et al. Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer: Significance in Diagnostics, Prediction, and Treatment Monitoring. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Quintero, B. Extracellular MicroRNAs as Intercellular Mediators and Noninvasive Biomarkers of Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, R.C.; Katzmann, D.J. Biogenesis and Function of Multivesicular Bodies. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, P.I.; Cashikar, A. Multivesicular Body Morphogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pols, M.S.; Klumperman, J. Trafficking and Function of the Tetraspanin CD63. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.L.; Urbé, S. The Emerging Shape of the ESCRT Machinery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, Biologic Function and Clinical Potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseervatham, J. Dynamic Role of Exosome microRNAs in Cancer Cell Signaling and Their Emerging Role as Noninvasive Biomarkers. Biology 2023, 12, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current Knowledge on Exosome Biogenesis and Release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, D.; Kirkbride, K.C.; Costello, K.; Clark, E.S.; Sinha, S.; Grega-Larson, N.; Tyska, M.J.; Weaver, A.M. Exosome Secretion Is Enhanced by Invadopodia and Drives Invasive Behavior. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreux, M.; Garaigorta, U.; Boyd, B.; Décembre, E.; Chung, J.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Wieland, S.; Chisari, F.V. Short-Range Exosomal Transfer of Viral RNA from Infected Cells to Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Triggers Innate Immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brügger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide Triggers Budding of Exosome Vesicles into Multivesicular Endosomes. Science 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.R.; Eden, E.R.; Futter, C.E. Hrs- and CD63-Dependent Competing Mechanisms Make Different Sized Endosomal Intraluminal Vesicles. Traffic 2014, 15, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbiano, F.; Corsi, J.; Gurrieri, E.; Trevisan, C.; Notarangelo, M.; D’Agostino, V.G. RNA Packaging into Extracellular Vesicles: An Orchestra of RNA-Binding Proteins? J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 10, e12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and Exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, Sorting, and Function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory Mechanisms and Intercellular Transfer of microRNAs in Living Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-Dependent Exosomal Transfer of Angiogenic microRNAs Regulate Cancer Cell Metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10849–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 Controls the Sorting of miRNAs into Exosomes through Binding to Specific Motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, L.; Giurato, G.; Cicchini, C.; Montaldo, C.; Mancone, C.; Tarallo, R.; Battistelli, C.; Alonzi, T.; Weisz, A.; Tripodi, M. The RNA-Binding Protein SYNCRIP Is a Component of the Hepatocyte Exosomal Machinery Controlling MicroRNA Sorting. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobor, F.; Dallmann, A.; Ball, N.J.; Cicchini, C.; Battistelli, C.; Ogrodowicz, R.W.; Christodoulou, E.; Martin, S.R.; Castello, A.; Tripodi, M.; et al. A Cryptic RNA-Binding Domain Mediates Syncrip Recognition and Exosomal Partitioning of miRNA Targets. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zeng, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Ke, X.; Hu, X. YBX-1 Mediated Sorting of miR-133 into Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced EPC-Derived Exosomes to Increase Fibroblast Angiogenesis and MEndoT. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-Box Protein 1 Is Required to Sort microRNAs into Exosomes in Cells and in a Cell-Free Reaction. eLife 2016, 5, e19276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Singh, R.N.; Bishop, C.E.; Chen, X.; Lu, B. MEX3C Interacts with Adaptor-Related Protein Complex 2 and Involves in miR-451a Exosomal Sorting. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Hu, X.; Mu, J.; Samykutty, A.; Zhuang, X.; Deng, Z.; Kumar, A.; Zhang, L.; Merchant, M.L.; et al. MVP-Mediated Exosomal Sorting of miR-193a Promotes Colon Cancer Progression. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Shurtleff, M.J.; Nottingham, R.M.; Yao, J.; Fadadu, R.P.; Lambowitz, A.M.; Schekman, R. Distinct Mechanisms of microRNA Sorting into Cancer Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes. eLife 2019, 8, e47544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A.J.; Hoshino, D.; Hong, N.H.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Coffey, R.J.; Patton, J.G.; Weaver, A.M. KRAS-MEK Signaling Controls Ago2 Sorting into Exosomes. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Yue, S.; Stadel, D.; Zöller, M. Toward Tailored Exosomes: The Exosomal Tetraspanin Web Contributes to Target Cell Selection. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.F. Routes and Mechanisms of Extracellular Vesicle Uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrès, C.; Blanc, L.; Bette-Bobillo, P.; André, S.; Mamoun, R.; Gabius, H.-J.; Vidal, M. Galectin-5 Is Bound onto the Surface of Rat Reticulocyte Exosomes and Modulates Vesicle Uptake by Macrophages. Blood 2010, 115, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, S.; Minamisawa, T.; Suga, K.; Kishita, H.; Akagi, T.; Ichiki, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Shiba, K. Subtypes of Tumour Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Having Differently Externalized Phosphatidylserine. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1579541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laulagnier, K.; Javalet, C.; Hemming, F.J.; Chivet, M.; Lachenal, G.; Blot, B.; Chatellard, C.; Sadoul, R. Amyloid Precursor Protein Products Concentrate in a Subset of Exosomes Specifically Endocytosed by Neurons. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Zhou, Y.-Y.; Liang, G.-F.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Hu, F.-H.; Xiao, Z.-D. Exosome Uptake through Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis and Macropinocytosis and Mediating miR-21 Delivery. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22258–22267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhao, W.-L.; Ye, Y.-Y.; Bai, X.-C.; Liu, R.-Q.; Chang, L.-F.; Zhou, Q.; Sui, S.-F. Cellular Internalization of Exosomes Occurs through Phagocytosis. Traffic 2010, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, Z. Visualizing of the Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Exosomes by Live-Cell Microscopy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massagué, J.; Obenauf, A.C. Metastatic Colonization by Circulating Tumour Cells. Nature 2016, 529, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.H. Progression and Metastasis of Lung Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Smit, E.F.; Vosse, B.A.H.; Mellema, W.W.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Bootsma, G.P.; Westenend, M.; Pitz, C.; de Vries, G.J.; Houben, R.; et al. EGFR Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: More Prone to Development of Bone and Brain Metastases? Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Pan, J.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.-J.; Wang, S.-H.; Huang, D.-Y.; Chen, X.-F. Patterns of Extrathoracic Metastases in Different Histological Types of Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihimäki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Fallah, M.; Thomsen, H.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. Metastatic Sites and Survival in Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Yu, J. The Prognostic Analysis of Different Metastatic Patterns in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Large Population-Based Study. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct Signaling between Platelets and Cancer Cells Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal-like Transition and Promotes Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengler, V.L.; Galbraith, M.; Espinosa, J.M. Transcriptional Regulation by Hypoxia Inducible Factors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Donaldson, M.C.; Wittner, B.S.; Spencer, J.A.; Yu, M.; Pely, A.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters Are Oligoclonal Precursors of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cell 2014, 158, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.J.; Ewald, A.J. A Collective Route to Metastasis: Seeding by Tumor Cell Clusters. Science 2016, 352, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bado, I.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Rosen, J.M.; Zhang, X.H.-F. Metastasis Organotropism: Redefining the Congenial Soil. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-Metastatic Niches: Organ-Specific Homes for Metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Exosomes Initiate Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation in the Liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gibbons, D.L.; Goswami, S.; Cortez, M.A.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Byers, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Yi, X.; Dwyer, D.; Lin, W.; et al. Metastasis Is Regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 Axis Control of Tumour Cell PD-L1 Expression and Intratumoral Immunosuppression. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 Family and miR-205 Regulate Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition by Targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y. Oncogenic microRNA-411 Promotes Lung Carcinogenesis by Directly Targeting Suppressor Genes SPRY4 and TXNIP. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaña, O.H.; Córcoles, R.; Fabra, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Acloque, H.; Vega, S.; Barrallo-Gimeno, A.; Cano, A.; Nieto, M.A. Metastatic Colonization Requires the Repression of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.H.; Donaher, J.L.; Murphy, D.A.; Chau, S.; Yang, J. Spatiotemporal Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Is Essential for Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liang, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, B.; Chen, C. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-31-5p Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastasis by Negatively Regulating SATB2-Reversed EMT and Activating MEK/ERK Signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, J.; Hu, H.; Tu, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, F. Lung CSC-Derived Exosomal miR-210-3p Contributes to a pro-Metastatic Phenotype in Lung Cancer by Targeting FGFRL1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6324–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisakane, K.; Seike, M.; Sugano, T.; Yoshikawa, A.; Matsuda, K.; Takano, N.; Takahashi, S.; Noro, R.; Gemma, A. Exosome-Derived miR-210 Involved in Resistance to Osimertinib and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Ji, W.; Xia, W.; Lu, S. Exosomal miR-499a-5p Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and EMT via mTOR Signaling Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 379, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 Family Determines the Epithelial Phenotype of Cancer Cells by Targeting the E-Cadherin Repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashige, J.; Kamohara, H.; Watanabe, M.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Iwatsuki, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kinoshita, K.; Saito, S.; Baba, Y.; Baba, H. MicroRNA-200b Regulates Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration by Directly Targeting ZEB2 in Gastric Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19 (Suppl. S3), S656–S664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; Xu, W.; Cai, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W.; Song, D.; Liu, T.; Zhou, W.; et al. Wnt Signaling through Snail1 and Zeb1 Regulates Bone Metastasis in Lung Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 748–755. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bracken, C.P.; Smith, E.; Bert, A.G.; Wright, J.A.; Roslan, S.; Morris, M.; Wyatt, L.; Farshid, G.; Lim, Y.-Y.; et al. An Autocrine TGF-Beta/ZEB/miR-200 Signaling Network Regulates Establishment and Maintenance of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, P.; Pan, P.; Hu, C.; Yang, H. Pirfenidone Promotes the Levels of Exosomal miR-200 to down-Regulate ZEB1 and Represses the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Su, C.-Y.; Yan, Y.-Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.-J.; Fu, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, J.-Y. Exosomes of A549 Cells Induced Migration, Invasion, and EMT of BEAS-2B Cells Related to Let-7c-5p and miR-181b-5p. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 926769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-J.; Temko, D.; Maliga, Z.; Moreira, A.L.; Sei, E.; Minussi, D.C.; Dean, J.; Lee, C.; Xu, Q.; Hochart, G.; et al. Spatial Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity Is Associated with Survival of Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; McGranahan, N.; Birkbak, N.J.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Veeriah, S.; Shafi, S.; Johnson, D.H.; Mitter, R.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Tracking the Evolution of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Bi, G.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, J.; Lu, T.; Jiang, W.; et al. Landscape and Dynamics of Single Tumor and Immune Cells in Early and Advanced-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eales, K.L.; Hollinshead, K.E.R.; Tennant, D.A. Hypoxia and Metabolic Adaptation of Cancer Cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Tameemi, W.; Dale, T.P.; Al-Jumaily, R.M.K.; Forsyth, N.R. Hypoxia-Modified Cancer Cell Metabolism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor Angiogenesis: Causes, Consequences, Challenges and Opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Vascular Permeability Factor/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor: A Critical Cytokine in Tumor Angiogenesis and a Potential Target for Diagnosis and Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor Vascular Permeability and the EPR Effect in Macromolecular Therapeutics: A Review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Xu, G.; Chang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yao, J. miR-210 Transferred by Lung Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomes May Act as Proangiogenic Factor in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts by Modulating JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Y.T.M.; Fujisawa, M.; Nguyen, T.B.; Suehara, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsuoka, R.; Abe, Y.; Fukumoto, K.; Hattori, K.; Noguchi, M.; et al. Tet2 Deficiency in Immune Cells Exacerbates Tumor Progression by Increasing Angiogenesis in a Lung Cancer Model. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4931–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S. Tet2 at the Interface between Cancer and Immunity. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Exosomal miR-141 Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis via KLF12 in Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzechowska-Licari, E.J.; LaComb, J.F.; Mojumdar, A.; Bialkowska, A.B. SP and KLF Transcription Factors in Cancer Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, X.; Xin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, Y.; Lv, L.; Ren, P.; Wu, H. KLF12 Promotes the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells by Reducing the Transcription of P21 in a P53-Dependent and P53-Independent Manner. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Ding, Y.; Kong, X.; Wu, J.; Fu, J.; Yan, G.; Zhou, H. Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 12 in the Development of Endometrial Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 152, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hong, G.; Wang, S.; Gao, W.; Wang, P. Tumor-Derived Exosomal miRNA-141 Promote Angiogenesis and Malignant Progression of Lung Cancer by Targeting Growth Arrest-Specific Homeobox Gene (GAX). Bioengineered 2021, 12, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Leal, A.D.; Gorski, D.H. The Homeobox Gene Gax Inhibits Angiogenesis through Inhibition of Nuclear Factor-κB–Dependent Endothelial Cell Gene Expression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.-M.; Fu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Gao, Y. Cancer-Derived Exosomal miR-197-3p Confers Angiogenesis via Targeting TIMP2/3 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wei, K.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z.; Pan, C.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-3157-3p Promotes Angiogenesis, Vascular Permeability and Metastasis by Targeting TIMP/KLF2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Huang, Y.; Fu, B.; Pan, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Targeting C-Jun in A549 Cancer Cells Exhibits Antiangiogenic Activity In Vitro and In Vivo through Exosome/miRNA-494-3p/PTEN Signal Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 663183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Sung, K.J.; Sung, Y.H.; Choi, C.-M.; Yun, M.; Yi, Y.-S.; et al. Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-619-5p Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis and Metastasis through the Inhibition of RCAN1.4. Cancer Lett. 2020, 475, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala-Kulawik, J.; Osinska, I.; Hoser, G. Mechanisms of Immune Response Regulation in Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, K.; Miyamoto, M.; Cho, Y.; Suzuoki, M.; Oshikiri, T.; Nakakubo, Y.; Itoh, T.; Ohbuchi, T.; Kondo, S.; Katoh, H. Concurrent Infiltration by CD8+ T Cells and CD4+ T Cells Is a Favourable Prognostic Factor in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnema-Luiting, J.; Vroman, H.; Aerts, J.; Cornelissen, R. Heterogeneity in Immune Cell Content in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qi, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, D.; Wu, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, S. The Role of CCL20/CCR6 Axis in Recruiting Treg Cells to Tumor Sites of NSCLC Patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 69, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Schäfer, M.; Hartmann, E.; Pries, R.; Parcina, M.; Schneider, P.; Giese, T.; Endres, S.; Wollenberg, B.; Hartmann, G. Tumour-Derived Prostaglandin E2 and Transforming Growth Factor-β Synergize to Inhibit Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell-Derived Interferon-α. Immunology 2009, 128, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, P.; Wu, D.; Guan, M.; Weng, X.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, R. Hypoxic Stress Suppresses Lung Tumor-Secreted Exosomal miR101 to Activate Macrophages and Induce Inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donzelli, J.; Proestler, E.; Riedel, A.; Nevermann, S.; Hertel, B.; Guenther, A.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Savai, R.; Larsson, K.; Saul, M.J. Small Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miR-574-5p Regulates PGE2-Biosynthesis via TLR7/8 in Lung Cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Gong, M.; Song, Y. The Role of Exosomal miR-181b in the Crosstalk between NSCLC Cells and Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Genes Genom. 2022, 44, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, R.; Wang, J.; Luan, X.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Hou, Q.; Mao, G.; Li, X. Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-770 Inhibits M2 Macrophage Polarization via Targeting MAP3K1 to Inhibit the Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 679658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, Z.; Wang, W.; Luo, X. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer-Derived Exosomes Promote Proliferation, Phagocytosis, and Secretion of Microglia via Exosomal microRNA in the Metastatic Microenvironment. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 27, 101594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell Cycle Proteins as Promising Targets in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolfathi, H.; Arabi, M.; Sheikhpour, M. A Literature Review of microRNA and Gene Signaling Pathways Involved in the Apoptosis Pathway of Lung Cancer. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-L.; Tsai, Y.-M.; Lien, C.-T.; Kuo, P.-L.; Hung, J.-Y. The Roles of MicroRNA in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhou, J.; Mei, S.; Wu, D.; Mu, Z.; Chen, B.; Xie, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, J. Circulating Exosomal microRNA-96 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Drug Resistance by Targeting LMO7. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Ding, Q.; Deng, Z. Exosomal miR-106b Serves as a Novel Marker for Lung Cancer and Promotes Cancer Metastasis via Targeting PTEN. Life Sci. 2020, 244, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Zheng, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Huang, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Exosomal miR-375-3p Breaks Vascular Barrier and Promotes Small Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Claudin-1. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Chen, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, T. M2 Macrophages-Derived Exosomal microRNA-501-3p Promotes the Progression of Lung Cancer via Targeting WD Repeat Domain 82. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.-Q.; Huang, J.-F.; Lin, J.-L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T.-T.; Chen, D.; Lin, D.-D.; Shen, J.-F.; Wu, A.-M. Incidence, Prognostic Factors, and a Nomogram of Lung Cancer with Bone Metastasis at Initial Diagnosis: A Population-Based Study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suva, L.J.; Washam, C.; Nicholas, R.W.; Griffin, R.J. Bone Metastasis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guise, T.A.; Mohammad, K.S.; Clines, G.; Stebbins, E.G.; Wong, D.H.; Higgins, L.S.; Vessella, R.; Corey, E.; Padalecki, S.; Suva, L.; et al. Basic Mechanisms Responsible for Osteolytic and Osteoblastic Bone Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6213s–6216s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.B.D.R.; Mello, F.C.d.Q.; Paschoal, M.E.M. The Relationship between Lung Cancer Histology and the Clinicopathological Characteristics of Bone Metastases. Lung Cancer 2016, 96, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuya, A.; Kurata, T.; Tamura, K.; Fukuoka, M. Skeletal Metastases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Study. Lung Cancer 2007, 57, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, H.; Yamada, K.; Sugiura, T.; Hida, T.; Mitsudomi, T. Predictors of Survival in Patients with Bone Metastasis of Lung Cancer. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onken, J.S.; Fekonja, L.S.; Wehowsky, R.; Hubertus, V.; Vajkoczy, P. Metastatic Dissemination Patterns of Different Primary Tumors to the Spine and Other Bones. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2019, 36, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujoomdar, A.; Austin, J.H.M.; Malhotra, R.; Powell, C.A.; Pearson, G.D.N.; Shiau, M.C.; Raftopoulos, H. Clinical Predictors of Metastatic Disease to the Brain from Non–Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Primary Tumor Size, Cell Type, and Lymph Node Metastases. Radiology 2007, 242, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, J.B.; Hansen, H.H.; Hansen, M.; Dombernowsky, P. Brain Metastases in Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: Frequency, Risk Groups, and Prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 1988, 6, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochstenbag, M.; Twijnstra, A.; Wilmink, J.; Wouters, E.; ten Velde, G. Asymptomatic Brain Metastases (BM) in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): MR-Imaging Is Useful at Initial Diagnosis. J. Neurooncol. 2000, 48, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delattre, J.Y.; Krol, G.; Thaler, H.T.; Posner, J.B. Distribution of Brain Metastases. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Homey, B.; Soto, H.; Ge, N.; Catron, D.; Buchanan, M.E.; McClanahan, T.; Murphy, E.; Yuan, W.; Wagner, S.N.; et al. Involvement of Chemokine Receptors in Breast Cancer Metastasis. Nature 2001, 410, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.J.; Burdick, M.D.; Lutz, M.; Belperio, J.A.; Keane, M.P.; Strieter, R.M. The Stromal Derived Factor-1/CXCL12-CXC Chemokine Receptor 4 Biological Axis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Metastases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, K.; Ormazábal, C.; Zandueta, C.; Luis-Ravelo, D.; Antón, I.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Montuenga, L.M.; Martínez-Canarias, S.; Leitinger, B.; et al. Inhibition of Collagen Receptor Discoidin Domain Receptor-1 (DDR1) Reduces Cell Survival, Homing, and Colonization in Lung Cancer Bone Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilvaer, T.K.; Rakaee, M.; Hellevik, T.; Vik, J.; Petris, L.D.; Donnem, T.; Strell, C.; Ostman, A.; Busund, L.-T.R.; Martinez-Zubiaurre, I. Differential Prognostic Impact of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Expression in NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, R.; Luis-Ravelo, D.; Antón, I.; Zandueta, C.; Salazar-Colocho, P.; Larzábal, L.; Calvo, A.; Lecanda, F. PDGFR Signaling Blockade in Marrow Stroma Impairs Lung Cancer Bone Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeley, B.T.; Liu, N.Q.; Conduah, A.H.; Krenek, L.; Roth, K.; Dougall, W.C.; Huard, J.; Dubinett, S.; Lieberman, J.R. Mixed Metastatic Lung Cancer Lesions in Bone Are Inhibited by Noggin Overexpression and Rank:Fc Administration. J. Bone Min. Res. 2006, 21, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chao, C.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Liu, P.-I.; Yang, Y.-C.; Su, C.-M.; Huang, W.-C.; Tang, C.-H. Thrombospondin Enhances RANKL-Dependent Osteoclastogenesis and Facilitates Lung Cancer Bone Metastasis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 166, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, S.Y. Current Understanding of RANK Signaling in Osteoclast Differentiation and Maturation. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roodman, G.D.; Dougall, W.C. RANK Ligand as a Therapeutic Target for Bone Metastases and Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Yano, S.; Hanibuchi, M.; Sone, S. Bone Metastasis Model with Multiorgan Dissemination of Human Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SBC-5) Cells in Natural Killer Cell-Depleted SCID Mice. Oncol. Res. 2000, 12, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, G.R. Metastasis to Bone: Causes, Consequences and Therapeutic Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qin, J.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, J.; Su, W.; Deng, H.; Wang, Z. Exosomal miR-328 Originated from Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma Cells Enhances Osteoclastogenesis via Downregulating Nrp-2 Expression. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlinden, L.; Kriebitzsch, C.; Beullens, I.; Tan, B.K.; Carmeliet, G.; Verstuyf, A. Nrp2 Deficiency Leads to Trabecular Bone Loss and Is Accompanied by Enhanced Osteoclast and Reduced Osteoblast Numbers. Bone 2013, 55, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, M.; Guo, Q.; Lou, J.; Wang, L. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-17-5p Promotes Osteoclast Differentiation by Targeting PTEN. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 408, 112834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Li, J.; Dong, C. Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-21 Facilitates Osteoclastogenesis. Gene 2018, 666, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, K.; Luis-Ravelo, D.; Bovy, N.; Antón, I.; Martínez-Canarias, S.; Zandueta, C.; Ormazábal, C.; Struman, I.; Tabruyn, S.; Rebmann, V.; et al. miRNA Cargo within Exosome-like Vesicle Transfer Influences Metastatic Bone Colonization. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanleenuwat, P.; Iwanowski, P. Metastases to the Central Nervous System: Molecular Basis and Clinical Considerations. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 412, 116755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-Endothelial Interactions at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, J.K.; Toborek, M. Blood–Brain Barrier Remodeling during Brain Metastasis Formation. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, I.J. The Role of the Organ Microenvironment in Brain Metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achrol, A.S.; Rennert, R.C.; Anders, C.; Soffietti, R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Nayak, L.; Peters, S.; Arvold, N.D.; Harsh, G.R.; Steeg, P.S.; et al. Brain Metastases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Jin, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.H.-F.; Lee, D.J.; Chaft, J.E.; Kris, M.G.; Huse, J.T.; Brogi, E.; et al. Serpins Promote Cancer Cell Survival and Vascular Co-Option in Brain Metastasis. Cell 2014, 156, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, H.-J.; He, J.; Wu, Q.; Langley, R.R.; Fidler, I.J.; Kim, S.-J. Role of the Endothelin Axis in Astrocyte- and Endothelial Cell-Mediated Chemoprotection of Cancer Cells. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Ranade, A.R.; Tran, N.L.; Nasser, S.; Sridhar, S.; Korn, R.L.; Ross, J.T.D.; Dhruv, H.; Foss, K.M.; Sibenaller, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-328 Is Associated with (Non-Small) Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Brain Metastasis and Mediates NSCLC Migration. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2621–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Garg, N.; Venugopal, C.; Hallett, R.; Tokar, T.; McFarlane, N.; Mahendram, S.; Bakhshinyan, D.; Manoranjan, B.; Vora, P.; et al. STAT3 Pathway Regulates Lung-Derived Brain Metastasis Initiating Cell Capacity through miR-21 Activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27461–27477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ning, J.; Wang, S. MicroRNA-378 Is Associated with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis by Promoting Cell Migration, Invasion and Tumor Angiogenesis. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remon, J.; Alvarez-Berdugo, D.; Majem, M.; Moran, T.; Reguart, N.; Lianes, P. miRNA-197 and miRNA-184 Are Associated with Brain Metastasis in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 18, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.J.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, H.R.; Song, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.; Shin, C.H.; Joung, J.-G.; Kim, D.-H.; Joo, K.M.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA-95-3p Suppresses Brain Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma through Downregulation of Cyclin D1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20434–20448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, A.; Alsidawi, S.; Jagannathan, S.; Sumita, K.; Sasaki, A.T.; Aronow, B.; Warnick, R.E.; Lawler, S.; Driscoll, J.J. The Brain Microenvironment Negatively Regulates miRNA-768-3p to Promote K-Ras Expression and Lung Cancer Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, C.; Li, Q. MicroRNA-550a-3-5p Controls the Brain Metastasis of Lung Cancer by Directly Targeting YAP1. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulzewsky, F.; Holland, E.C.; Vasioukhin, V. YAP1 and Its Fusion Proteins in Cancer Initiation, Progression and Therapeutic Resistance. Dev. Biol. 2021, 475, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, N.; Kosaka, N.; Ono, M.; Katsuda, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tamura, K.; Lötvall, J.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Brain Metastatic Cancer Cells Release microRNA-181c-Containing Extracellular Vesicles Capable of Destructing Blood–Brain Barrier. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Exosomal miRNA | Cellular Source | Recipient Cells | Molecular Targets | Possible Mechanism | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMT promoting | ||||||
| miR-31-5p | A549 H1299 | A549 H1299 | SATB2 | MEK/ERK signaling activation | ↑ Migration, invasion, EMT, and tumor progression | [87] |
| miR-210-3p | A549 | A549 NCI-H1703 | FGFRL1 | Unknown | ↑ Migration, invasion, EMT, and MMP-9/MMP-1 expression. | [88] |
| miR-210-3p | HCC827-OR | HCC827 (parental cells) | Unknown | Unknown | ↑ EMT and resistance to Osimertinib | [89] |
| miR-499a-5p | SPC-A-1BM | SPC-A-1 (parental cells) | S6K1, BP1 | mTOR pathway activation | ↑ EMT, proliferation, and migration. Larger tumor nodules | [90] |
| EMT inhibiting | ||||||
| miR-200 | CAF | A549 NCI-H460 | ZEB1 | Unknown | Inhibition of migration, invasion, and EMT | [95] |
| let-7c-5p and miR-181b-5p | A549 | BEAS-2B | Unknown | MAPK signaling pathway? | Inhibition of migration, invasion, and EMT | [96] |
| Exosomal miRNA | Cellular Source | Recipient Cells | Molecular Targets | Possible Mechanism | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-210 | A549 H460 | NIH/3T3 | TET2 | STAT3/JAK2 signaling activation | Promotion of CAF phenotype. ↑ Secretion of pro-angiogenic factors VEGF-A, FGF2, and MMP9 by CAF. ↑ Proliferation, migration, and tube formation of endothelial cells. ↑ In vivo microvessel density. | [105] |
| miR-141 | H466 H1048 | HUVEC | KLF12 | Unknown | ↑ In vivo microvessel density. | [108] |
| miR-141 | A549 | HUVEC | GAX | Unknown | ↑ Formation of tubes of endothelial cells. | [112] |
| miR-197-3p | A549 H1299 | HUVEC | TIMP2, TIMP3 | Unknown | ↑ In vivo tumor growth | [114] |
| miR-3157-3p | A549 H1299 | HUVEC | TIMP2, KLF2 | Unknown | ↑ Expression of VEFG, MMP2, and MMP9. ↑ Vascular permeability. | [115] |
| miR-494-3p | A549 | HUVEC | PTEN? | cJun/PTEN pathways | ↑ Formation of tube formation | [116] |
| miR-619-5p | A549 | HUVEC | RCAN1.4 | Unknown | ↑ In vitro invasiveness of A549 cells ↑ In vitro tumor expression of CD31 | [117] |
| Exosomal miRNA | Cellular Source | Recipient Cells | Molecular Targets | Possible Mechanism | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-17-5p | SPC-A-1BM | RAWR264.7 cells | PTEN | Inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway | Unknown | [161] |
| miR-328 | A549 | RAWR264.7 cells | Nrp-2 | Unknown | Unknown | [159] |
| miR-192 | A549 | HMS | Unknown | Unknown | ↓ In situ angiogenesis | [163] |
| miR-21 | A549 | BMM | Pdcd4 | c-Fos inhibition | Unknown | [162] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinez-Espinosa, I.; Serrato, J.A.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111574
Martinez-Espinosa I, Serrato JA, Ortiz-Quintero B. The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(11):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111574
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinez-Espinosa, Israel, José Antonio Serrato, and Blanca Ortiz-Quintero. 2023. "The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression" Biomolecules 13, no. 11: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111574
APA StyleMartinez-Espinosa, I., Serrato, J. A., & Ortiz-Quintero, B. (2023). The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression. Biomolecules, 13(11), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111574






