Comprehensive Transcriptomic Profiling of m6A Modification in Age-Related Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
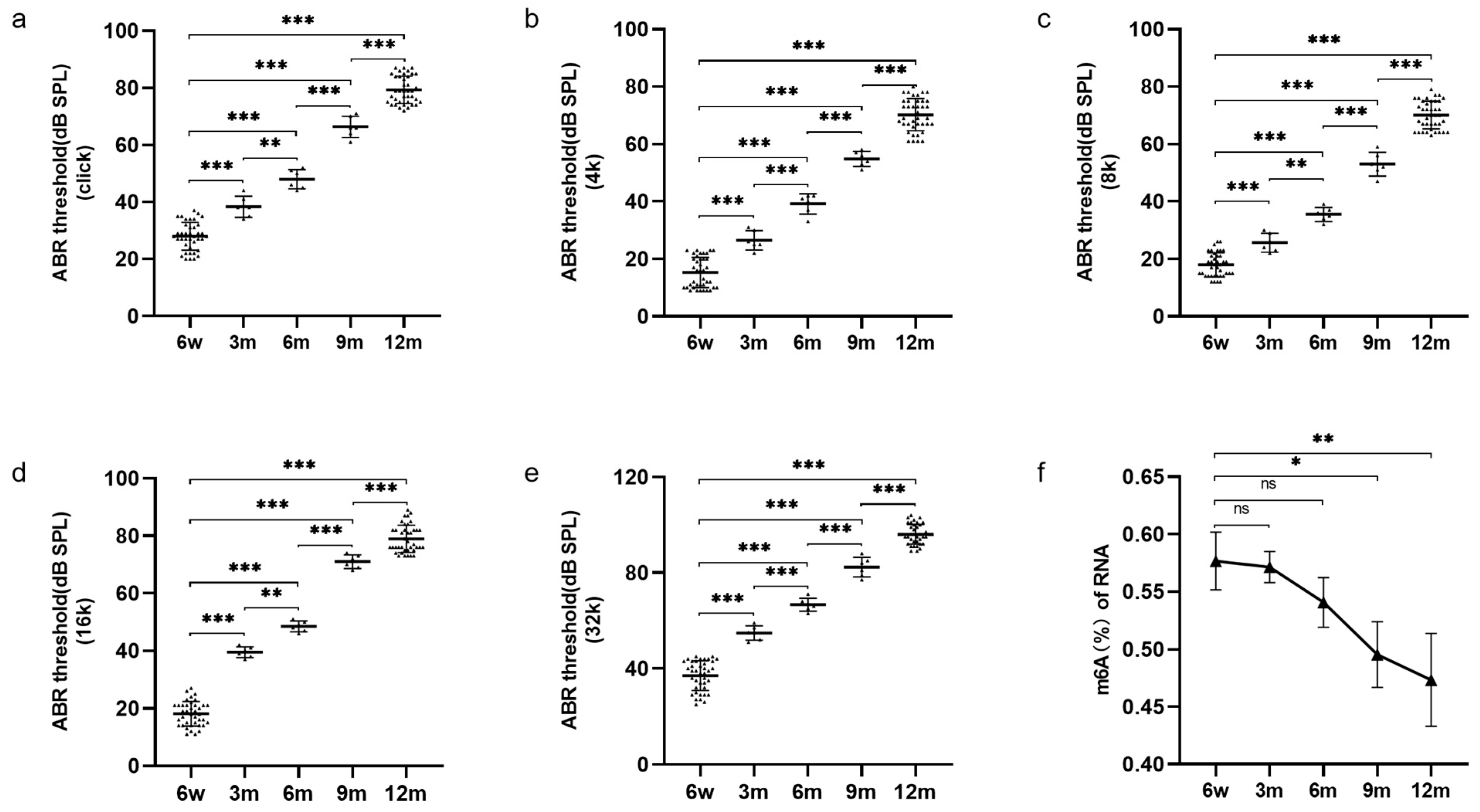
2.2. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Analysis
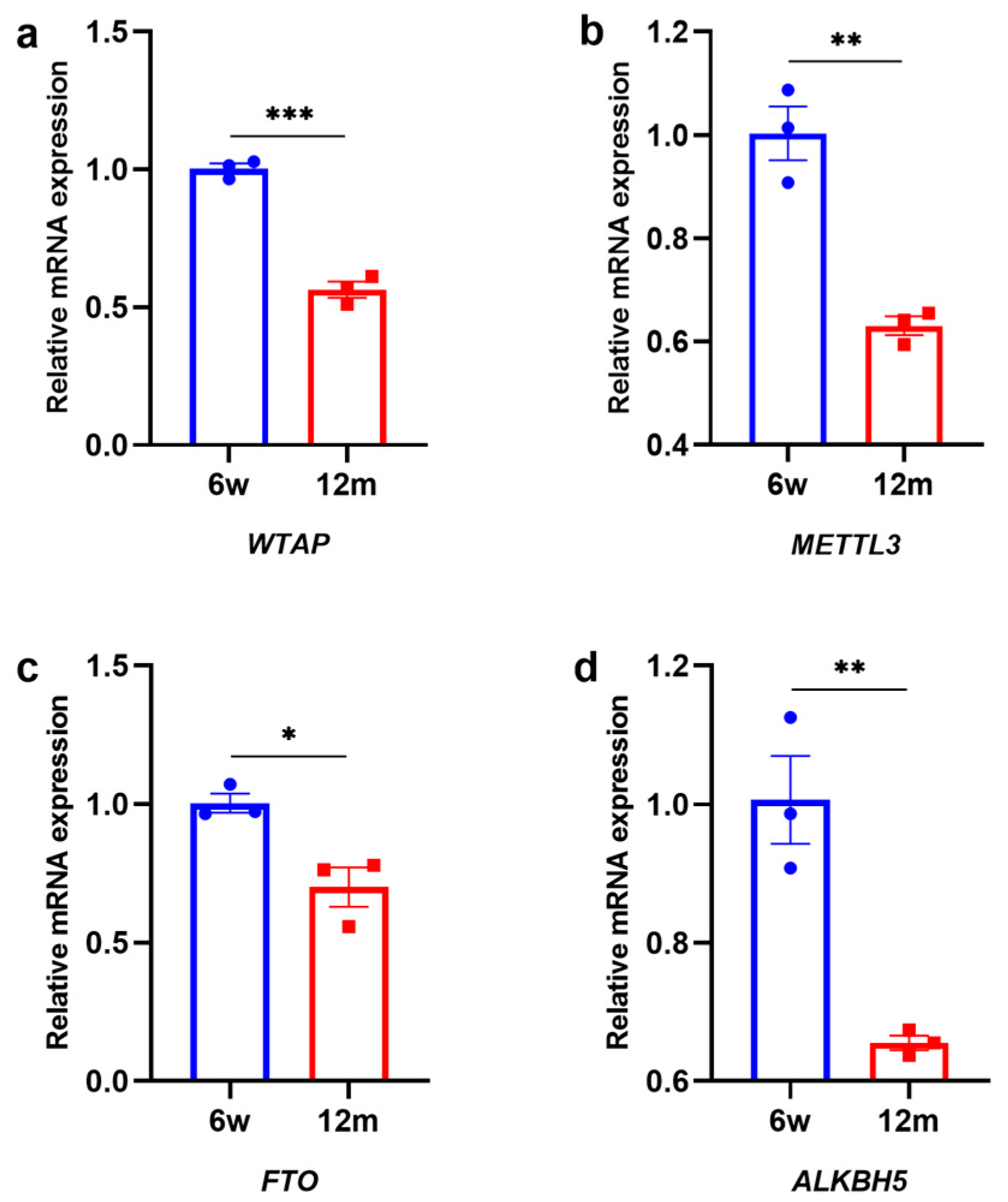
2.3. RNA Extraction and qRT–PCR
2.4. m6A Quantification
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
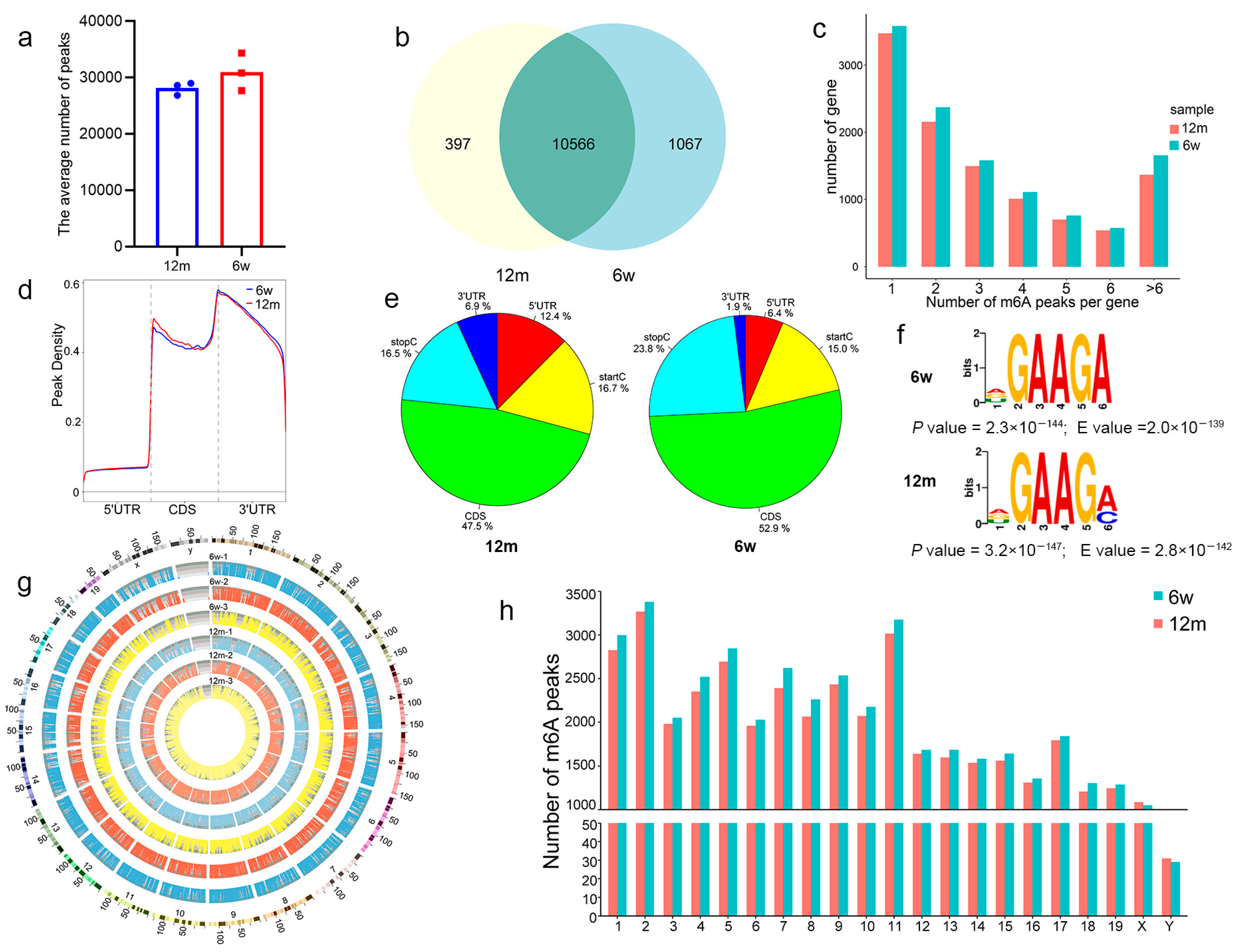
2.6. MeRIP-Seq and Data Analysis
2.7. RNA-Seq and Data Analysis
2.8. MeRIP-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Increased Hearing Thresholds and Decreased Cochlear m6A Modification in Ageing Mice
3.2. Changes in m6A-Related Modification Enzymes in the Cochleae of 6 w and 12 m Mice
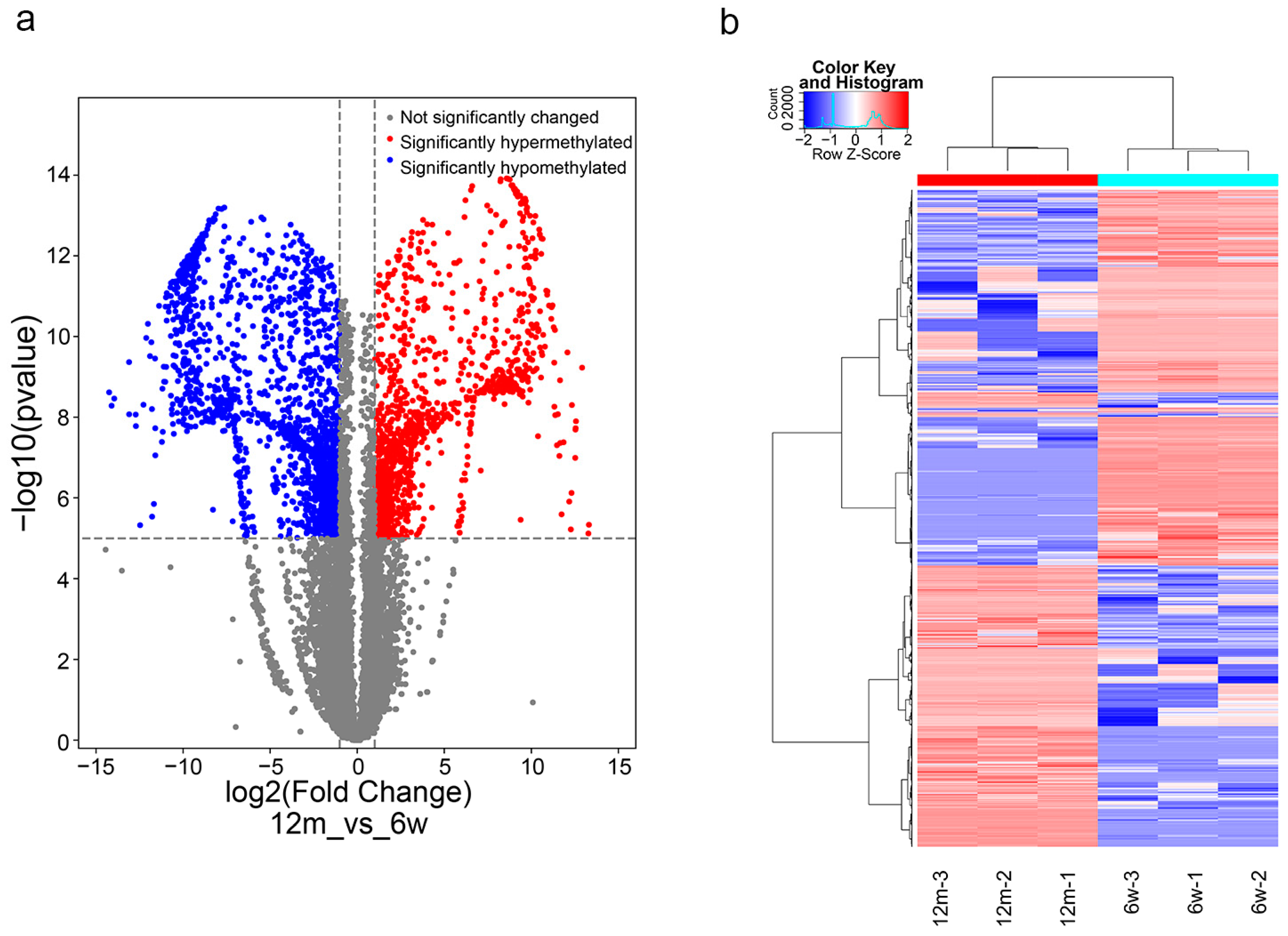
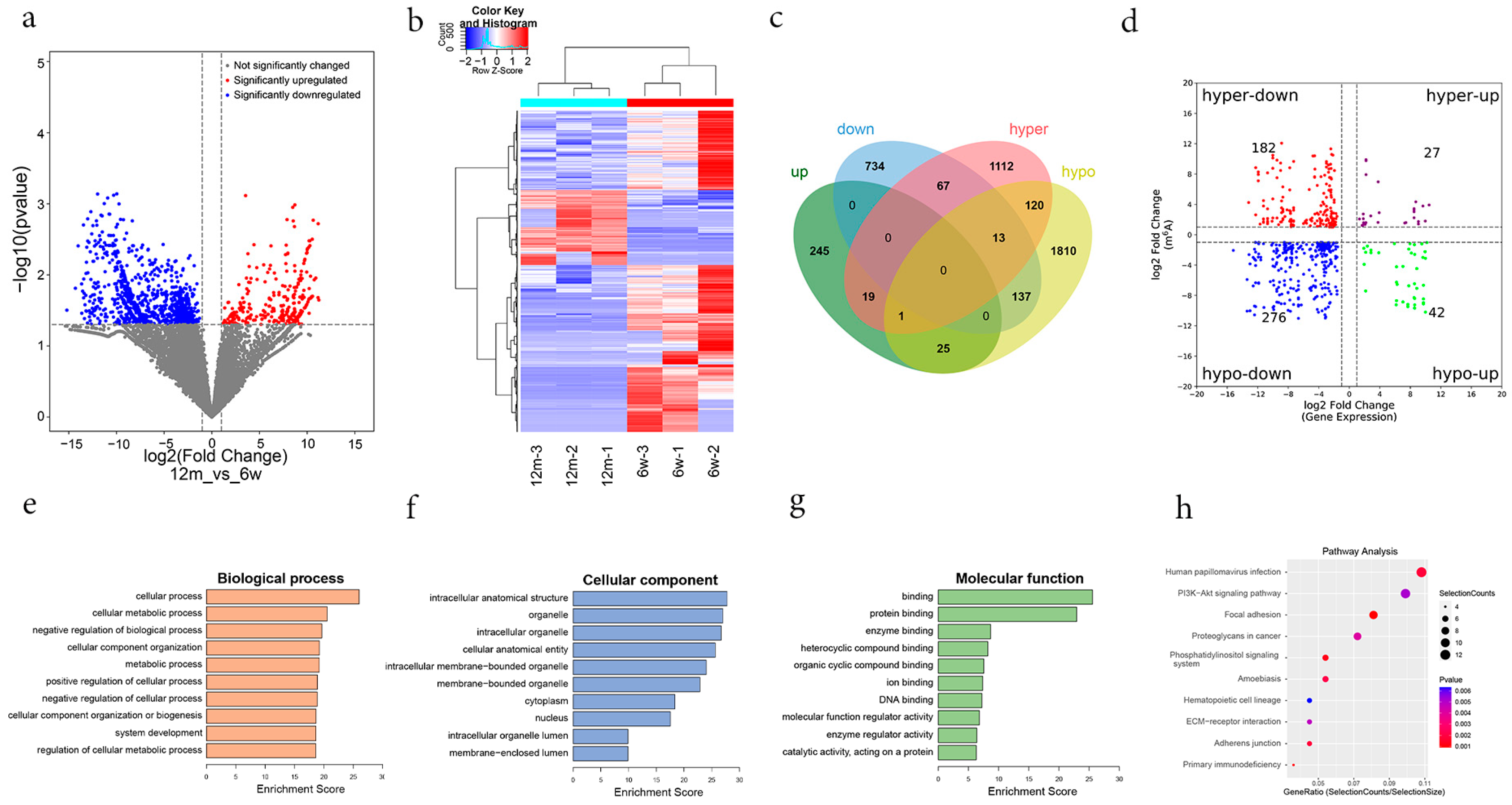
3.3. General Characteristics of m6A Methylation Modification in ARHL
3.4. Functional Enrichment and Pathway Analysis of Differentially m6A-Methylated Genes
3.5. Combined Analysis of MeRIP-Seq and RNA-Seq Data
3.6. Validation of Differentially m6A-Modified Genes by MeRIP-qPCR and qRT–PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
| Gene | Forward and Reverse Primer |
|---|---|
| WTAP | F: 5′ GAAGGAGACACGACAGCAGTTGG 3′ |
| R: 5′ GCTTGTGACCTCTGCCTGATCTAC 3′ | |
| METTL3 | F: 5′ CGCTGCCTCCGATGTTGATCTG 3′ |
| R: 5′ CTGACTGACCTTCTTGCTCTGCTG 3′ | |
| FTO | F: 5′ ATGAAGACGCTGTGCCACTGTG 3′ |
| R: 5′ CACGTTGTAGGCTGCTCTGCTC 3′ | |
| ALKBH5 | F: 5′ GCAAGGTGAAGAGCGGCATCC 3′ |
| R: 5′GTCCACCGTGTGCTCGTTGTAC 3′ | |
| RAPGEF6 | F: 5′ AGCTGTCAGGACCAAAGTCG 3′ |
| R: 5′ CGCTCAGGTGTTGCCTTGAT 3′ | |
| BIRC6 | F: 5′ TGCAGAGGCTCAAAGTAGCC 3′ |
| R: 5′ GGAACAGAATGCCCATTGGA 3′ | |
| RPS6KA3 | F: 5′ GACAGCGCGGAGAATGGACA 3′ |
| R: 5′ CCGAACACGGTCTCGAACTT 3′ | |
| SH2D1B1 | F: 5′ TGTGCCTCTGTGTCTCGTTTA 3′ |
| R: 5′ TTGTCCAATGTCCTTGTCTTCA 3′ | |
| β-ACTIN | F: 5′ AGTGTGACGTTGACATCCGT 3′ |
| R: 5′ TGCTAGGAGCCAGAGCAGTA 3′ |
| Gene | Forward and Reverse Primer |
|---|---|
| RAPGEF6 | F: 5′ CAGGGGATATGGAGCAGGC 3′ |
| R: 5′ CAGGCCTCCGTCACTAAATAG 3′ | |
| BIRC6 | F: 5′ GCCTCCTCTCTCTTCCTTGG 3′ |
| R: 5′ AATCAGCACCCCAGTAGTCA 3′ | |
| RPS6KA3 | F: 5′ GGCGTCCTCCTTTATACAATGC 3′ |
| R: 5′ GTCCTTTGCTGTGTCTGAAAC 3′ | |
| SH2D1B1 | F: 5′ TGACCAAGCGAGAGTGTGAA 3′ |
| R: 5′ GAGACACAGAGGCACAGGG 3′ |
| ID | Gene | M6a Fold Change | m6A p Value | Gene Log FC | Gene p Value | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSMUSG00000029661 | COL1A2 | 231.2 | 1.38075 × 10−10 | −1.6059902 | 0.04229598 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000055737 | GHR | 11.7 | 4.29725 × 10−11 | −3.0214016 | 0.03698555 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000003882 | IL7R | 5.1 | 8.2386 × 10−8 | −8.2804095 | 0.03681321 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000027111 | ITGA6 | 2.9 | 1.19754 × 10−7 | −5.6042221 | 0.00835887 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000038668 | LPAR1 | 4.4 | 4.55964 × 10−7 | −2.5137438 | 0.0377013 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000021702 | THBS4 | 1044.7 | 2.7696 × 10−12 | −3.5606082 | 0.02895484 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000005871 | APC | 7.7 | 1.8278 × 10−8 | −9.4020705 | 0.01765319 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000020538 | SREBF1 | 2.3 | 2.8006 × 10−10 | 1.68543898 | 0.04796545 | Hyper-up |
| ENSMUSG00000020122 | EGFR | 6.3 | 2.51291 × 10−6 | −3.4024714 | 0.04096643 | Hyper-down |
References
- De Iorio, M.L.; Rapport, L.J.; Wong, C.G.; Stach, B.A. Characteristics of Adults with Unrecognized Hearing Loss. Am. J. Audiol. 2019, 28, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makary, C.A.; Shin, J.; Kujawa, S.G.; Liberman, M.C.; Merchant, S.N. Age-Related Primary Cochlear Neuronal Degeneration in Human Temporal Bones. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2011, 12, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavant, M.; Kapoula, Z. Presbycusis and the Aging of Eye Movement: Common Attention Mechanisms. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, K.; McKinnon, B.J.; Eibling, D.; Gates, G.A. Challenges and Opportunities in Presbycusis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 144, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.C.; Friedman, R.A. Age-Related Hearing Loss: Unraveling the Pieces. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locher, H.; Frijns, J.H.; van Iperen, L.; de Groot, J.C.; Huisman, M.A.; de Sousa Lopes, S.M.C. Neurosensory Development and Cell Fate Determination in the Human Cochlea. Neural Dev. 2013, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Ahn, J.; Moon, I.J. Associations Between Age-Related Hearing Loss and Dietaryassessment Using Data From Korean National Health Andnutrition Examination Survey. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keithley, E.M. Pathology and Mechanisms of Cochlear Aging. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The Role of M6a Modification in the Biological Functions and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cong, S.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wang, H.-Q.; Zhang, J.-B.; Zhang, W.-D.; Guo, H.-X. Comprehensive Analysis of Differences in N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylomes in the Rat Adenohypophysis after Gnrh Treatment. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22204. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Novel Insights Into the Roles of N(6)-Methyladenosine (M(6)a) Modification and Autophagy in Human Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Ye, M.; Liu, B.; Wei, M.; Ma, D.; Dong, K. M6a Modification: A Double-Edged Sword in Tumor Development. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Yu, J.; Shan, G.; Su, L.; Yu, N.; Yang, S. N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes Angiogenesis and Atherosclerosis by Upregulating the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Via M6a Reader IGF2BP1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 731810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Guo, M.; Zheng, X.; Ali, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Qie, S.; et al. Down-Regulation of M6a mRNA Methylation is Involved in Dopaminergic Neuronal Death. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafik, A.M.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.; Dai, Q.; Pajdzik, K.; Li, Y.; Kang, Y.; Yao, B.; Wu, H.; He, C.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Dynamics in Neurodevelopment and Aging, and its Potential Role in Alzheimer’s Disease. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Cao, J.; Yao, J.; Fan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, M.; Duan, Q.; Han, B.; Duan, S. KDM1A-Mediated Upregulation of METTL3 Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease Via Enhancing Autophagic Clearance of P-Tau through M6a-Dependent Regulation of STUB1. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 195, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Ming, R.; Wei, J.; Du, P.; Li, X.; Zong, S.; Xiao, H. METTL3 Reduces Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Presbycusis by Regulating the N6-Methyladenosine Level of SIRT1 mRNA. Neuroscience 2023, 521, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, M.; Liebmann, L.; Hübner, C.A.; Bolz, J. Homeostatic Plasticity and Synaptic Scaling in the Adult Mouse Auditory Cortex. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemsiri, P.; Yimtae, K.; Thanawirattananit, P.; Israsena, P.; Noymai, A.; Laohasiriwong, S.; Vatanasapt, P.; Siripaopradith, P.; Kingkaew, P. Effectiveness of a Programable Body-Worn Digital Hearing Aid for Older Adults in a Developing Country: A Randomized Controlled Trial with a Cross-Over Design. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Puel, J.-L. Presbycusis: An Update On Cochlear Mechanisms and Therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H. Long Noncoding RNA GM44593 Attenuates Oxidative Stress From Age-Related Hearing Loss by Regulating Mir-29B/WNK1. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Shen, W.; Ma, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Tang, J.; Yan, J.; Wu, Z.; Zou, Z.; et al. Elevated SLC26A4 Gene Promoter Methylation is Associated with the Risk of Presbycusis in Men. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bouzid, A.; Smeti, I.; Dhouib, L.; Roche, M.; Achour, I.; Khalfallah, A.; Gibriel, A.A.; Charfeddine, I.; Ayadi, H.; Lachuer, J.; et al. Masmoudi. Down-Expression of P2RX2, KCNQ5, ERBB3 and SOCS3 through DNA Hypermethylation in Elderly Women with Presbycusis. Biomarkers 2018, 23, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.H.R.; Wijesinghe, P.; Nunez, D.A. Micrornas in Acquired Sensorineural Hearing Loss. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2019, 133, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Xiang, Q.; Bian, T.; Liu, Q. N6-Methyladenosine-Modified Circsav1 Triggers Ferroptosis in Copd through Recruiting YTHDF1 to Facilitate the Translation of IREB2. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, J.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, T.; Wan, X.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; et al. METTL3-Mediated M6a Modification of HMGA2 mRNA Promotes Subretinal Fibrosis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, R.; Li, X.; Tian, S.; Li, B.; Qin, G. N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA Modification Regulates Strawberry Fruit Ripening in an ABA-Dependent Manner. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ran, X.; Wang, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Yu, B.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. METTL14 Mediates the Inflammatory Response of Macrophages in Atherosclerosis through the NF-KAPPAB/Il-6 Signaling Pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Qiao, X.; Zhong, M. Landscape of N(6)-Methyladenosine Modification Patterns in Human Ameloblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 556497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ma, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F. Comprehensive Analysis of the Transcriptome-Wide M6a Methylation Modification Difference in Liver Fibrosis Mice by High-Throughput M6a Sequencing. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 767051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, W.V.; Bell, T.A.; Schaening, C. Messenger RNA Modifications: Form, Distribution, and Function. Science 2016, 352, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coling, D.E.; Yu, K.C.; Somand, D.; Satar, B.; Bai, U.; Huang, T.-T.; Seidman, M.D.; Epstein, C.J.; Mhatre, A.N.; Lalwani, A.K. Effect of SOD1 Overexpression on Age- and Noise-Related Hearing Loss. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, Y.; Raimundo, N.; Li, G.-L.; Shang, W.; Wu, H.; Song, L. Down-Regulation of AMPK Signaling Pathway Rescues Hearing Loss in TFB1 Transgenic Mice and Delays Age-Related Hearing Loss. Aging 2020, 12, 5590–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghbeli, M. Molecular Interactions of Mir-338 During Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Lai, D. Decreased Expression of IDH1 by Chronic Unpredictable Stress Suppresses Proliferation and Accelerates Senescence of Granulosa Cells through Ros Activated MAPK Signaling Pathways. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 169, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Rong, K.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, H.; et al. Eupatilin Attenuates the Senescence of Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Mitigates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Via Inhibition of the MAPK/NF-KAPPB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 940475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Li, W.; Tang, D.; Zhao, L.; He, Y.; Li, H. Inhibition of KDM5A Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss Via Regulation of the MAPK/AKT Pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Dai, X.; Xia, Z.-F.; Xiao, H.; He, X.-L.; Yang, R.; Li, J. SOD2 Alleviates Hearing Loss Induced by Noise and Kanamycin in Mitochondrial DNA4834-Deficient Rats by Regulating PI3K/MAPK Signaling. Curr. Med Sci. 2021, 41, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher, M.P. Degradation of RNA in Bacteria: Comparison of mRNA and Stable RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, H.; Kim, G.-W.; Mir, S.A.; Khan, M.; Siddiqui, A. Interferon-Stimulated Gene 20 (ISG20) Selectively Degrades N6-Methyladenosine Modified Hepatitis B Virus Transcripts. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, B.; Liu, D.; Weng, S.; Guo, R. Konjac Glucomannan Defends Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Rabbits by Promoting the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, B. PIN1 Protects Hair Cells and Auditory Hei-Oc1 Cells Against Senescence by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9980444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois-Cox, S.; Williams, S.M.G.; Reczek, E.E.; Johnson, B.W.; McGillicuddy, L.T.; Johannessen, C.M.; Hollstein, P.E.; MacCollin, M.; Cichowski, K. A Negative Feedback Signaling Network Underlies Oncogene-Induced Senescence. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, D.-J.; Chen, F.-Q.; Fan, B.; Lu, F.; Du, W.-J.; Chen, J.; An, X.-G.; Wang, R.-F.; Li, W.; Song, Y.-L. PTEN Inhibitor Bisperoxovanadium Protects Against Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Nie, G.; Li, H. Inhibiting DNA Methylation Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss by Decreasing Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis Via the LRP1-PI3K/AKT Pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fang, X.; Zhong, P.; Song, Z.; Hu, X. N6-Methyladenosine Modifications: Interactions with Novel RNA-Binding Proteins and Roles in Signal Transduction. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Guo, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. METTL3 Promotes Tumour Development by Decreasing APC Expression Mediated by APC mRNA N(6)-Methyladenosine-Dependent YTHDF Binding. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, C.; Yan, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Aberrant Elevation of FTO Levels Promotes Liver Steatosis by Decreasing the M6a Methylation and Increasing the Stability of SREBF1 and CHREBP mRNAs. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 14, mjac061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, B.; Migliaccio, I.; Gutierrez, M.C.; Wu, M.-F.; Chamness, G.C.; Wong, H.; Narasanna, A.; Chakrabarty, A.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Huang, J.; et al. Loss of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog or Phosphoinositol-3 Kinase Activation and Response to Trastuzumab or Lapatinib in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Overexpressing Locally Advanced Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.M.; Stone, J.S.; Groves, A.K.; Segil, N. EGFR Signaling is Required for Regenerative Proliferation in the Cochlea: Conservation in Birds and Mammals. Dev. Biol. 2012, 363, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Choi, S.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, C.K.; Moon, J.S. Impaired Glycolysis Promotes Alcoholexposure-Induced Apoptosis in Hei-Oc1 Cells Via Inhibition of EGFR Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-J.; Liu, H.-Y.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.-J.; Han, F.-Y.; Chen, G.-J.; Xu, X.-M.; Zhu, J.-H.; et al. IGF2BP3 Promotes the Progression of Colorectal Cancer and Mediates Cetuximab Resistance by Stabilizing EGFR mRNA in an M(6)a-Dependent Manner. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Liao, D.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Ma, H.; Kang, T. YTHDF2 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Growth Via Destabilizing the EGFR mRNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 442, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Xie, Y.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Lan, D. Use of RNA - Sequencing to Detect Abnormal Transcription of the Collagen Alpha-2 (Vi) Chain Gene that Can Lead to Bethlem Myopathy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

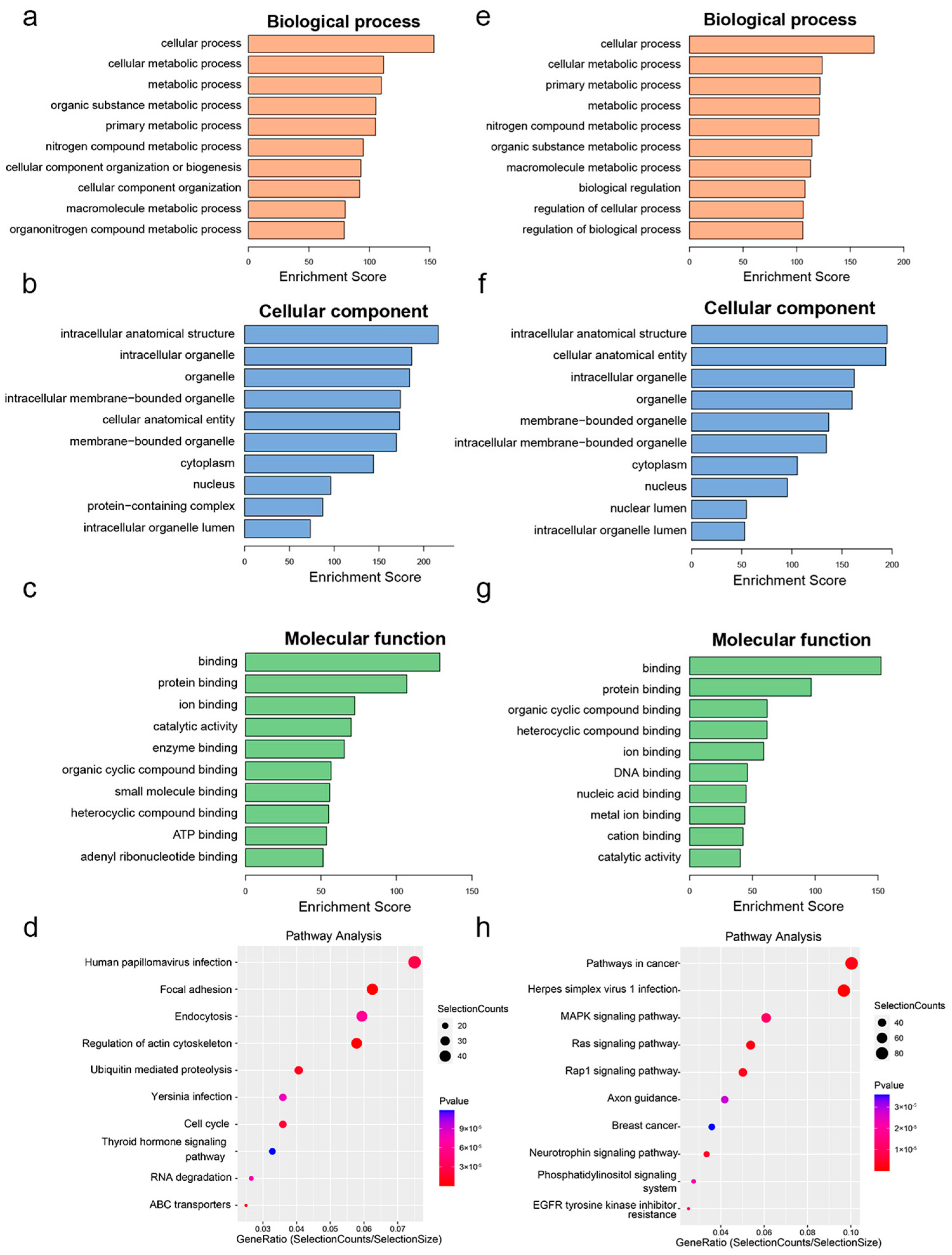

| ID | Gene | m6A Fold Change | m6A p-Value | Gene Log FC | Gene p-Value | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSMUSG00000037533 | RAPGEF6 | 433.2 | 1.2812 × 10−14 | −10.025374 | 0.00213148 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000024073 | BIRC6 | 800.7 | 5.0835 × 10−14 | −2.9943806 | 0.02636128 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000058997 | VWA8 | 201.1 | 7.6235 × 10−14 | −3.7058447 | 0.01945395 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000068036 | MLLT4 | 353.6 | 1.4383 × 10−13 | −1.9414922 | 0.04990249 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000022607 | PTK2 | 19.9 | 1.6866 × 10−13 | −3.4652058 | 0.01968117 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000032410 | XRN1 | 1434.8 | 2.9063 × 10−13 | −10.023874 | 0.00555607 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000003847 | NFAT5 | 8.6 | 3.6304 × 10−13 | −2.3516677 | 0.03805174 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000032555 | TOPBP1 | 11.8 | 8.4203 × 10−13 | −7.2946474 | 0.01763448 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000024672 | MS4A7 | 6.7 | 2.8421 × 10−12 | 1.83305783 | 0.04776993 | Hyper- up |
| ENSMUSG00000029186 | PI4K2B | 3.5 | 2.8892 × 10−12 | −10.125856 | 0.02227473 | Hyper-down |
| ENSMUSG00000067149 | IGJ | 312.9 | 1.4276 × 10−13 | 8.49015602 | 0.00112192 | Hypo-up |
| ENSMUSG00000031309 | RPS6KA3 | 24.95 | 1.8979 × 10−13 | −5.2427937 | 0.00759645 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000096334 | SH2D1B1 | 412.2 | 3.1109 × 10−13 | 6.18769686 | 0.02234852 | Hypo-up |
| ENSMUSG00000030231 | PLEKHA5 | 167.2 | 3.5733 × 10−13 | −6.9262512 | 0.00946439 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000024900 | CPT1A | 524.4 | 3.6441 × 10−13 | −2.580643 | 0.01844615 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000025278 | FLNB | 93.24 | 3.6648 × 10−13 | −3.7084202 | 0.03199615 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000030811 | FBXL19 | 470.7 | 3.9417 × 10−13 | −9.4987969 | 0.03882934 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000024749 | TMC1 | 543.7 | 5.0403 × 10−13 | −8.4734806 | 0.03470489 | Hypo-down |
| ENSMUSG00000061080 | LSAMP | 554.1 | 5.7905 × 10−13 | 9.7209504 | 0.00629816 | Hypo-up |
| ENSMUSG00000022297 | FZD6 | 698.6 | 6.9979 × 10−13 | −9.89231 | 0.0045972 | Hypo-down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, M.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, W. Comprehensive Transcriptomic Profiling of m6A Modification in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101537
Feng M, Zhou X, Hu Y, Zhang J, Yang T, Chen Z, Yuan W. Comprehensive Transcriptomic Profiling of m6A Modification in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(10):1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101537
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Menglong, Xiaoqing Zhou, Yaqin Hu, Juhong Zhang, Ting Yang, Zhiji Chen, and Wei Yuan. 2023. "Comprehensive Transcriptomic Profiling of m6A Modification in Age-Related Hearing Loss" Biomolecules 13, no. 10: 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101537
APA StyleFeng, M., Zhou, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, J., Yang, T., Chen, Z., & Yuan, W. (2023). Comprehensive Transcriptomic Profiling of m6A Modification in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Biomolecules, 13(10), 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101537





