Folding and Binding Mechanisms of the SH2 Domain from Crkl
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification
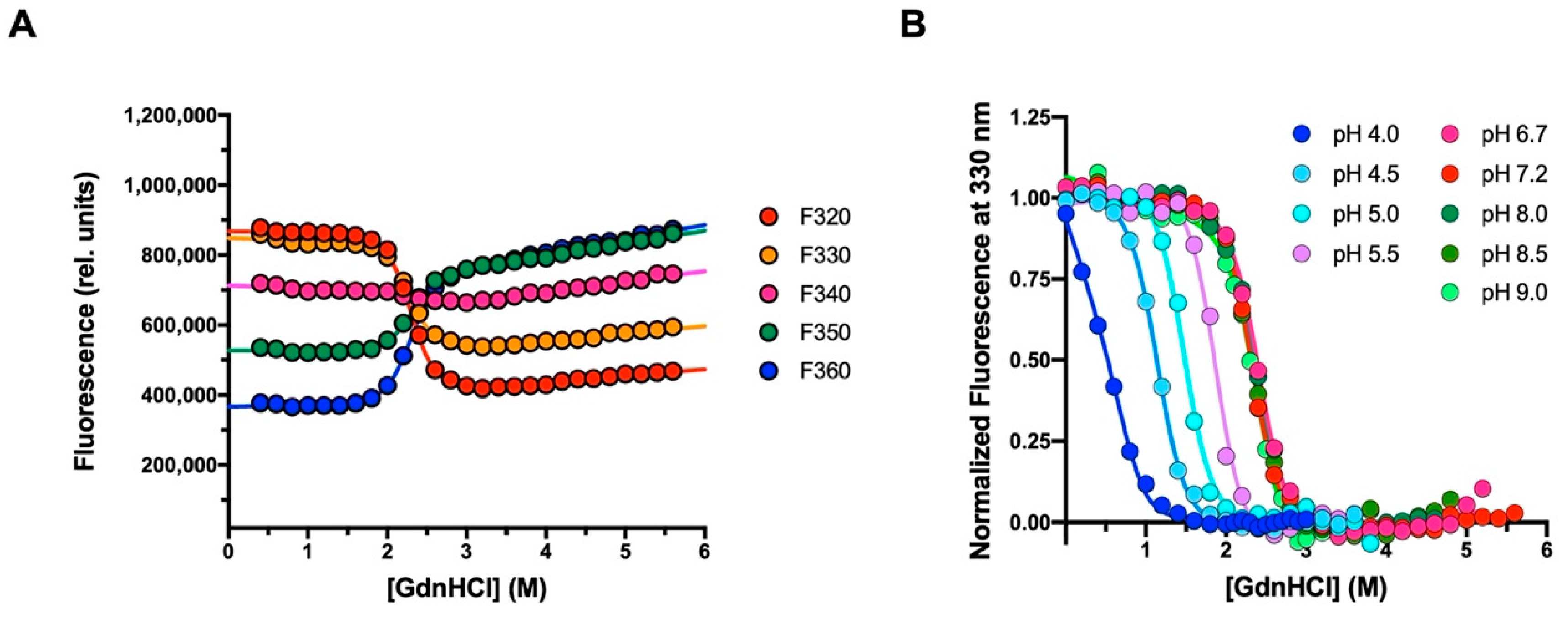
2.2. Equilibrium Unfolding Experiments
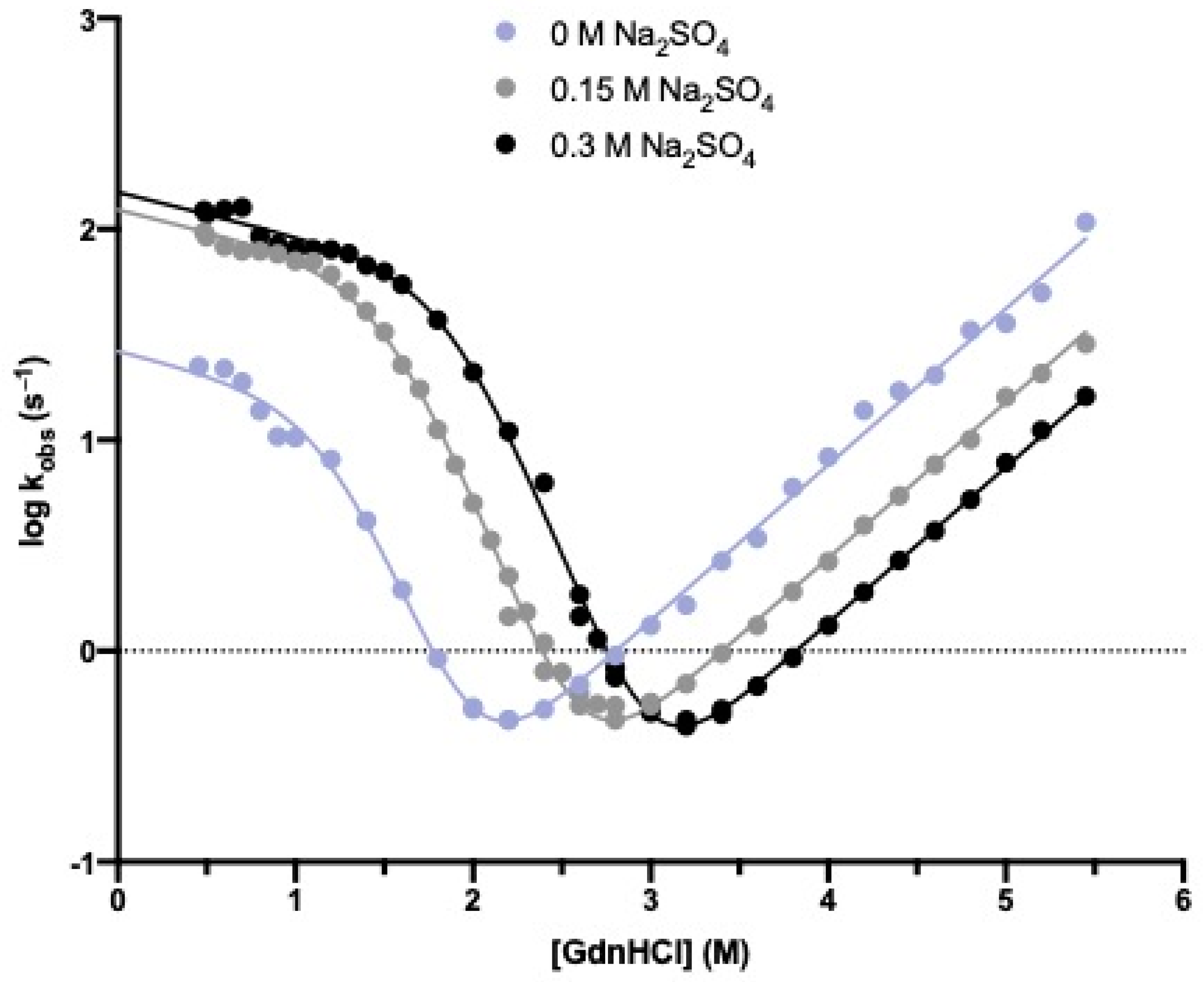
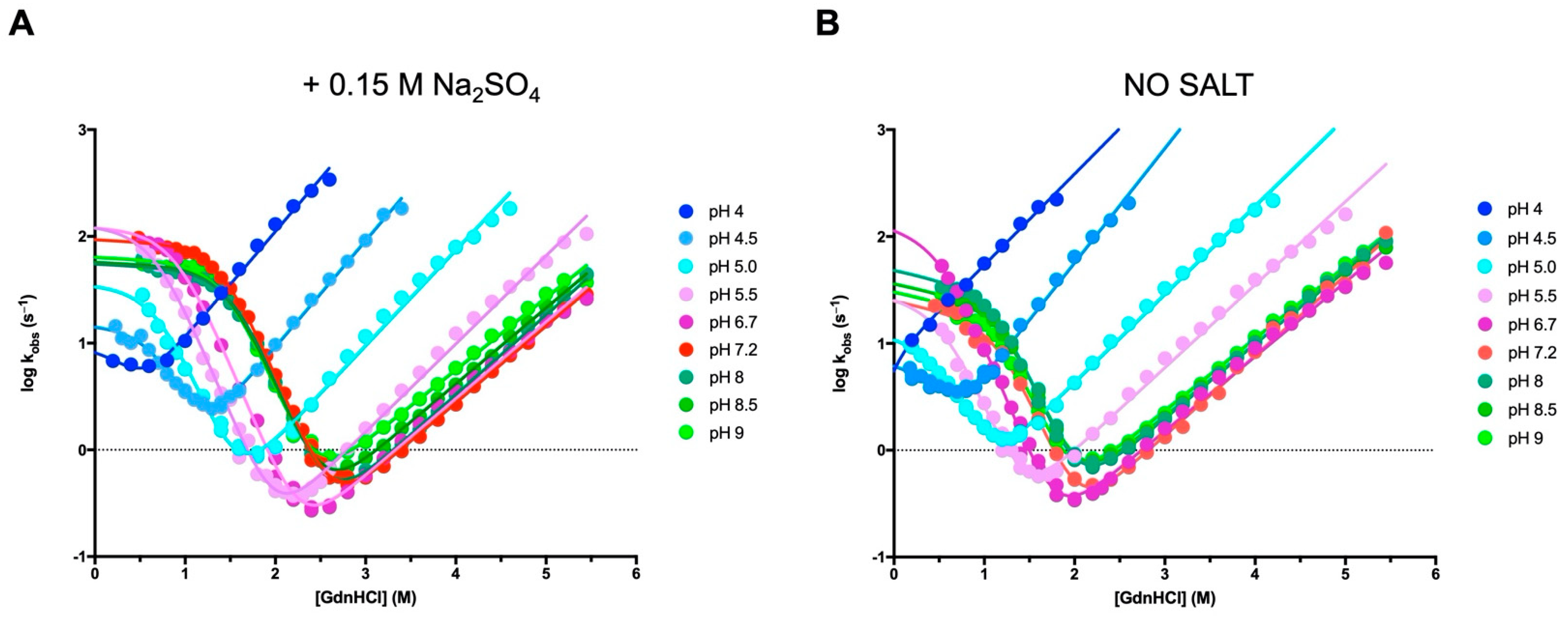
2.3. Stopped-Flow (Un)Folding Experiments
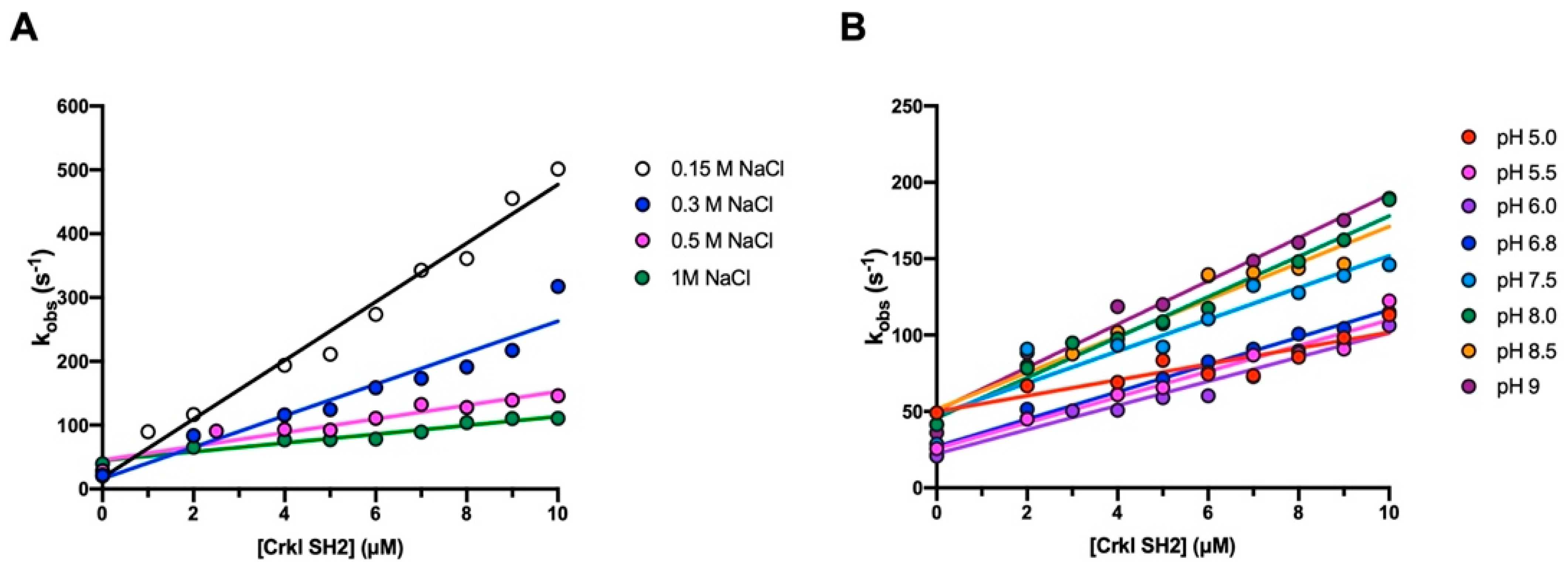
2.4. Stopped-Flow Binding Experiments
2.5. Stopped-Flow Displacement Experiments
3. Results
3.1. The Folding Pathway of Crkl SH2 Domain
3.2. The Binding Reaction between the SH2 Domain of Crkl and Paxillin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, B.J. Protein-protein interactions in signaling cascades. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 332, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.A.; Engelmann, B.W.; Nash, P.D. The language of SH2 domain interactions defines phosphotyrosine-mediated signal transduction. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marasco, M.; Carlomagno, T. Specificity and regulation of phosphotyrosine signaling through SH2 domains. J. Struct. Biol. X. 2020, 4, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappalainen, I.; Thusberg, J.; Shen, B.; Vihinen, M. Genome wide analysis of pathogenic SH2 domain mutations. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 2008, 72, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, E.D.; Orlova, A.; Neubauer, H.A.; Bajusz, D.; Seo, H.S.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Keserű, G.M.; Moriggl, R.; Gunning, P.T. Structural implications of stat3 and stat5 sh2 domain mutations. Cancers 2019, 11, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Müller, S.; Knapp, S. SH2 domains: Modulators of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase activity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidal, M.; Gigoux, V.; Garbay, C. SH2 and SH3 domains as targets for anti-proliferative agents. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2001, 40, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlacchi, P.; Robertson, F.M.; Klostergaard, J.; McMurray, J.S. Targeting SH2 domains in breast cancer. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1909–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobone, S.; Pannone, L.; Biondi, B.; Solman, M.; Flex, E.; Canale, V.C.; Calligari, P.; de Faveri, C.; Gandini, T.; Quercioli, A.; et al. Targeting Oncogenic Src Homology 2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase 2 (SHP2) by Inhibiting Its Protein-Protein Interactions. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 15973–15990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T. Crk and CrkL as therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. Cells 2021, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.Y.; Hahn, W.C. Oncogenic Signaling Adaptor Proteins. J. Genet. Genom. 2015, 42, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feller, S.M. Crk family adaptors-signalling complex formation and biological roles. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6348–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sattler, M.; Salgia, R. Role of the adapter protein CRKL in signal transduction of normal hematopoietic and BCR/ABL-transformed cells. Leukemia 1998, 12, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birge, R.B.; Kalodimos, C.; Inagaki, F.; Tanaka, S. Crk and CrkL adaptor proteins: Networks for physiological and pathological signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.A.; Jablonowski, K.; Raina, M.; Arcé, M.; Pawson, T.; Nash, P.D. The Human and Mouse Complement of SH2 Domain Proteins-Establishing the Boundaries of Phosphotyrosine Signaling. Mol. Cell. 2006, 22, 851–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, R.T.; Eck, M.J.; Schlessinger, J.; Shoelson, S.E.; Harrison, S.C. Crystal structure of the PI 3-kinase p85 amino-terminal SH2 domain and its phosphopeptide complexes. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, P.; Pluskey, S.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Eck, M.J.; Shoelson, S.E. Crystal Structure of the Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-2. Cell 1998, 92, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, A.; Kolibaba, K.; Oda, T.; Ohno-Jones, S.; Heaney, C.; Druker, B.J. Interactions of CBL with BCR-ABL and CRKL in BCR-ABL-transformed Myeloid Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16170–16175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arai, A.; Kanda, E.; Nosaka, Y.; Miyasaka, N.; Miura, O. CrkL is Recruited through Its SH2 Domain to the Erythropoietin Receptor and Plays a Role in Lyn-mediated Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33282–33290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgia, R.; Uemura, N.; Okuda, K.; Li, J.-L.; Pisick, E.; Sattler, M.; de Jong, R.; Druker, B.; Heisterkamp, N.; Chen, L.B.; et al. CRKL Links p210 BCR/ABL with Paxillin in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29145–29150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaller, M.D. Paxillin: A focal adhesion-associated adaptor protein. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6459–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singer, A.U.; Forman-Kay, J.D. pH titration studies of an SH2 domain-phosphopeptide complex: Unusual histidine and phosphate pKa values. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.K.; Pace, C.N.; Scholtz, J.M.; Scholtz, M. Denaturant m values and heat capacity changes: Relation to changes in accessible surface areas of protein unfolding. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2138–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, M.J.; Spencer, J.; Clarke, A.R. An Integrated Kinetic Analysis of Intermediates and Transition States in Protein Folding Reactions. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 253, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, S.; Calosci, N.; Aelen, J.M.A.; Vuister, G.W.; Brunori, M.; Travaglini-Allocatelli, C. Kinetic folding mechanism of PDZ2 from PTP-BL. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2005, 18, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonetti, D.; Troilo, F.; Toto, A.; Travaglini-Allocatelli, C.; Brunori, M.; Gianni, S. Mechanism of Folding and Binding of the N-Terminal SH2 Domain from SHP2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 11108–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardella, C.; Malagrinò, F.; Pagano, L.; Rinaldo, S.; Gianni, S.; Toto, A. Determining folding and binding properties of the C-terminal SH2 domain of SHP2. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildes, D.; Anderson, L.M.; Sabogal, A.; Marqusee, S. Native state energetics of the Src SH2 domain: Evidence for a partially structured state in the denatured ensemble. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visconti, L.; Malagrinò, F.; Toto, A.; Gianni, S. The kinetics of folding of the NSH2 domain from p85. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, N.; Capaldi, A.P.; James, R.; Kleanthous, C.; Radford, S.E. Rapid Folding with and without Populated Intermediates in the Homologous Four-helix Proteins Im7 and Im9. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 286, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
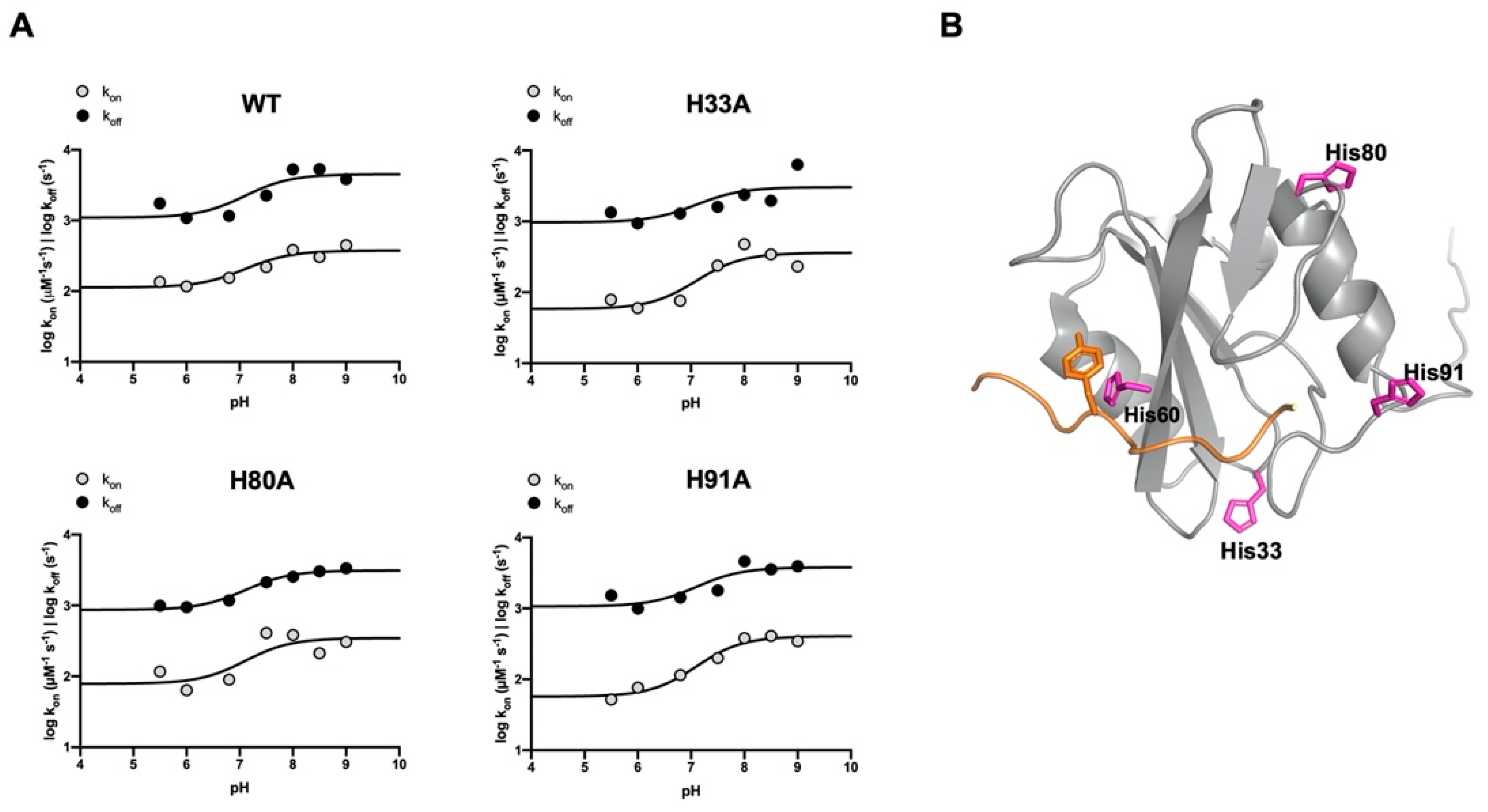
| WT | H33A | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | kon (μM−1 s−1) | koff (s−1) | KD (μM) | pH | kon (μM−1 s−1) | koff (s−1) | KD (μM) |
| 5.0 | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 49.1 ± 1.7 | 9.5 ± 1.7 | 5.0 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 33.2 ± 1.4 | 7.6 ± 0.7 |
| 5.5 | 8.4 ± 0.7 | 25.6 ± 0.4 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 5.5 | 6.7 ± 0.4 | 22.8 ± 2.2 | 3.4 ± 0.4 |
| 6.0 | 7.9 ± 0.6 | 20.8 ± 0.3 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | 6.0 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 19.5 ± 0.4 | 3.3 ± 0.2 |
| 6.8 | 8.9 ± 0.4 | 21.4 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 6.8 | 6.6 ± 0.4 | 22.4 ± 0.5 | 3.4 ± 0.2 |
| 7.5 | 10.4 ± 1.4 | 28.6 ± 0.5 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 7.5 | 10.8 ± 1.9 | 24.6 ± 3.2 | 2.3 ± 0.5 |
| 8.0 | 13.2 ± 0.7 | 41.4 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 8.0 | 14.6 ± 1.1 | 29.3 ± 3.4 | 2.0 ± 0.3 |
| 8.5 | 12.0 ± 1.1 | 41.6 ± 0.9 | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 8.5 | 12.6 ± 1.4 | 26.9 ± 2.8 | 2.1 ± 0.3 |
| 9.0 | 14.1 ± 0.9 | 36.1 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 9.0 | 10.6 ± 1.0 | 44.7 ± 4.0 | 4.2 ± 0.5 |
| H80A | H91A | ||||||
| pH | kon (μM−1 s−1) | koff (s−1) | KD (μM) | pH | kon (μM−1 s−1) | koff (s−1) | KD (μM) |
| 5.0 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 52.7 ± 3.2 | 11.5 ± 1.2 | 5.0 | * | * | * |
| 5.5 | 7.9 ± 0.9 | 20.0 ± 3.7 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 5.5 | 5.6 ± 0.3 | 24.1 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.2 |
| 6.0 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 19.6 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 6.0 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 20.0 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.1 |
| 6.8 | 7.1 ± 0.4 | 21.6 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 6.8 | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 23.4 ± 0.4 | 3.0 ± 0.1 |
| 7.5 | 13.6 ± 1.1 | 27.8 ± 2.3 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 7.5 | 10.0 ± 0.5 | 25.9 ± 0.3 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| 8.0 | 13.2 ± 0.7 | 30.1 ± 3.3 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 8.0 | 13.2 ± 0.5 | 39.0 ± 0.7 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| 8.5 | 10.2 ± 1.2 | 32.5 ± 2.7 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 8.5 | 13.6 ± 0.6 | 34.9 ± 0.5 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| 9.0 | 12.0 ± 0.9 | 34.0 ± 2.3 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 9.0 | 12.7 ± 0.5 | 36.4 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nardella, C.; Toto, A.; Santorelli, D.; Pagano, L.; Diop, A.; Pennacchietti, V.; Pietrangeli, P.; Marcocci, L.; Malagrinò, F.; Gianni, S. Folding and Binding Mechanisms of the SH2 Domain from Crkl. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12081014
Nardella C, Toto A, Santorelli D, Pagano L, Diop A, Pennacchietti V, Pietrangeli P, Marcocci L, Malagrinò F, Gianni S. Folding and Binding Mechanisms of the SH2 Domain from Crkl. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(8):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12081014
Chicago/Turabian StyleNardella, Caterina, Angelo Toto, Daniele Santorelli, Livia Pagano, Awa Diop, Valeria Pennacchietti, Paola Pietrangeli, Lucia Marcocci, Francesca Malagrinò, and Stefano Gianni. 2022. "Folding and Binding Mechanisms of the SH2 Domain from Crkl" Biomolecules 12, no. 8: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12081014
APA StyleNardella, C., Toto, A., Santorelli, D., Pagano, L., Diop, A., Pennacchietti, V., Pietrangeli, P., Marcocci, L., Malagrinò, F., & Gianni, S. (2022). Folding and Binding Mechanisms of the SH2 Domain from Crkl. Biomolecules, 12(8), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12081014








