Molecular Detection of Venous Thrombosis in Mouse Models Using SPECT/CT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptide Synthesis and Radiolabelling
2.2. In Vitro Probe Validation
2.3. Animals
2.4. Ferric Chloride Thrombosis Model
2.5. Ivc Stenosis Thrombosis Model
2.6. Computed Tomography (CT)
2.7. Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
2.8. Biodistribution
2.9. Histology
3. Results
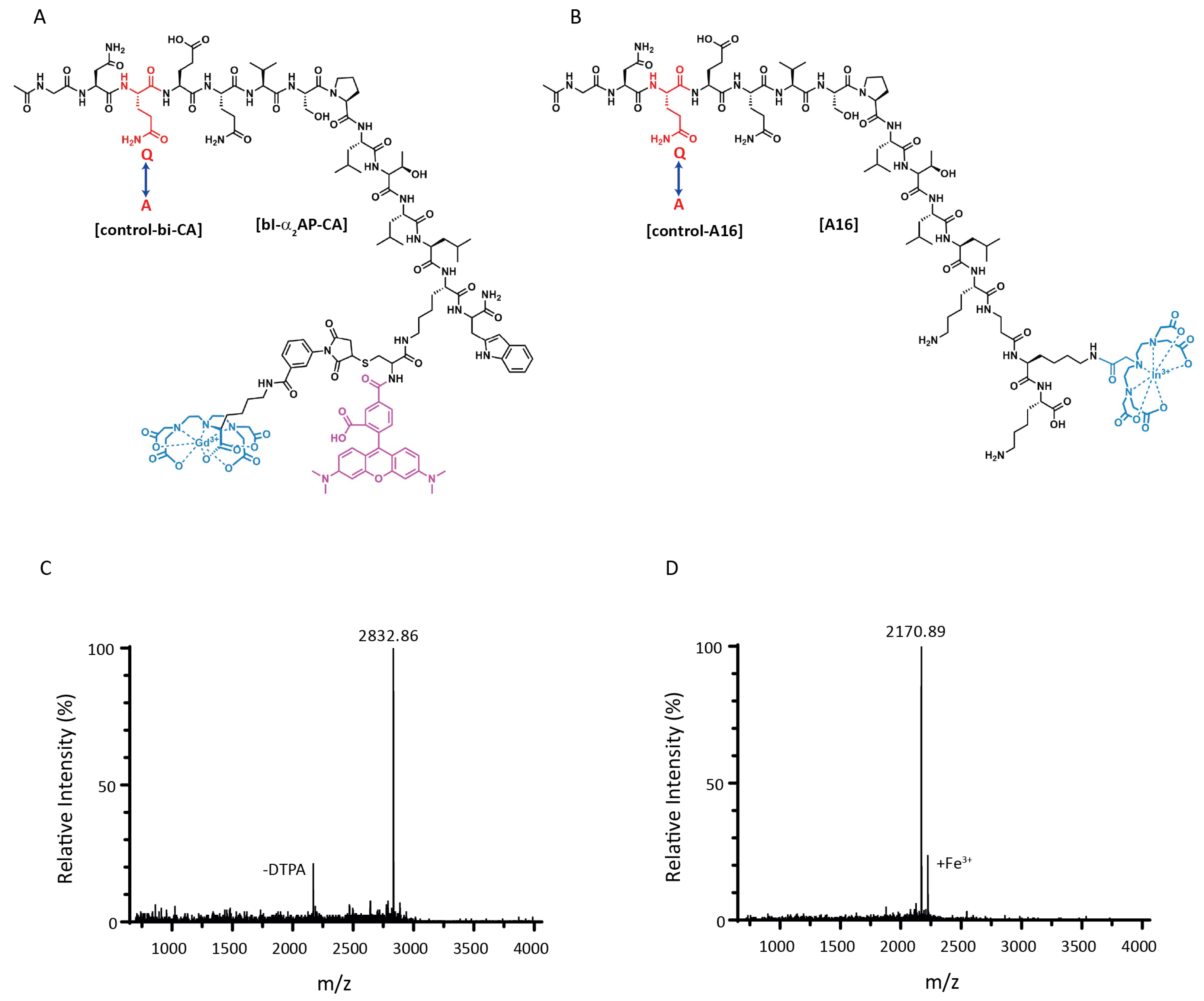
3.1. Peptide Synthesis
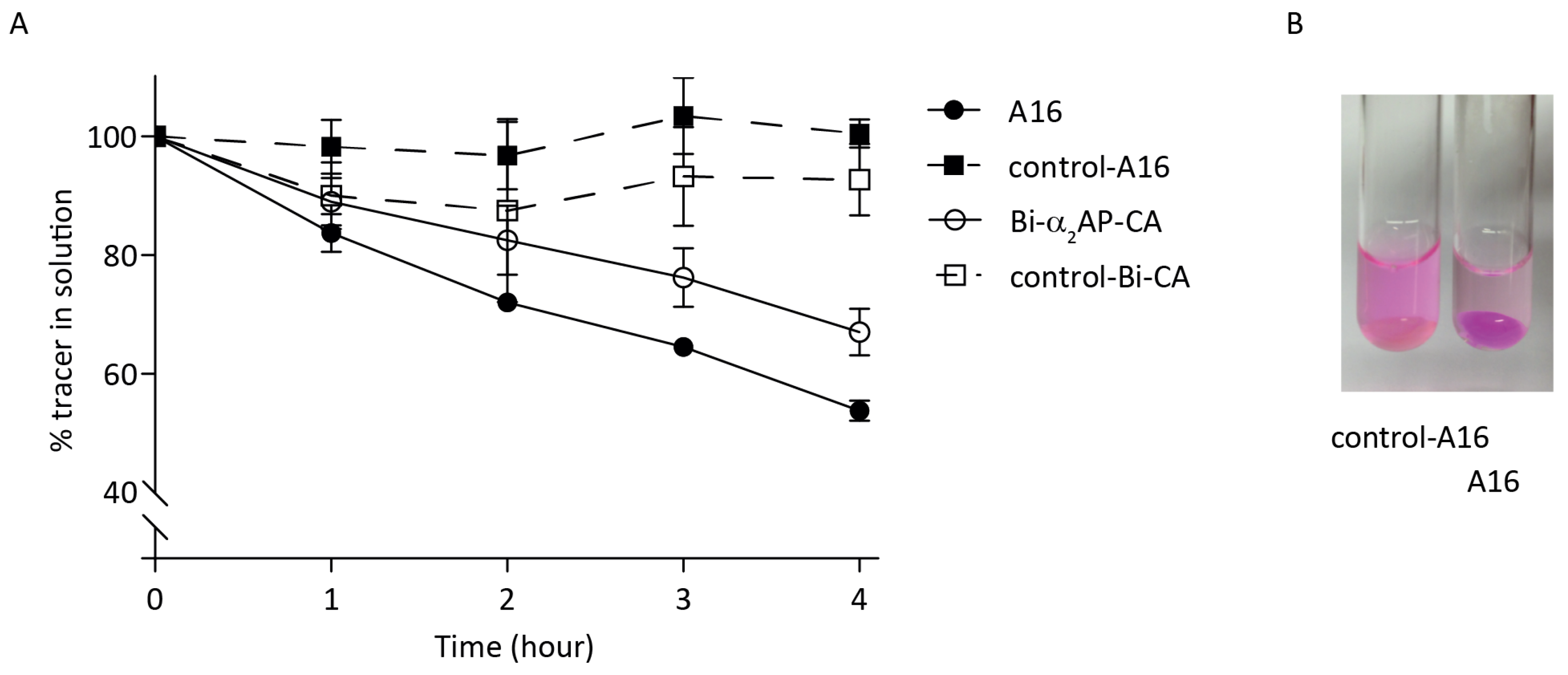
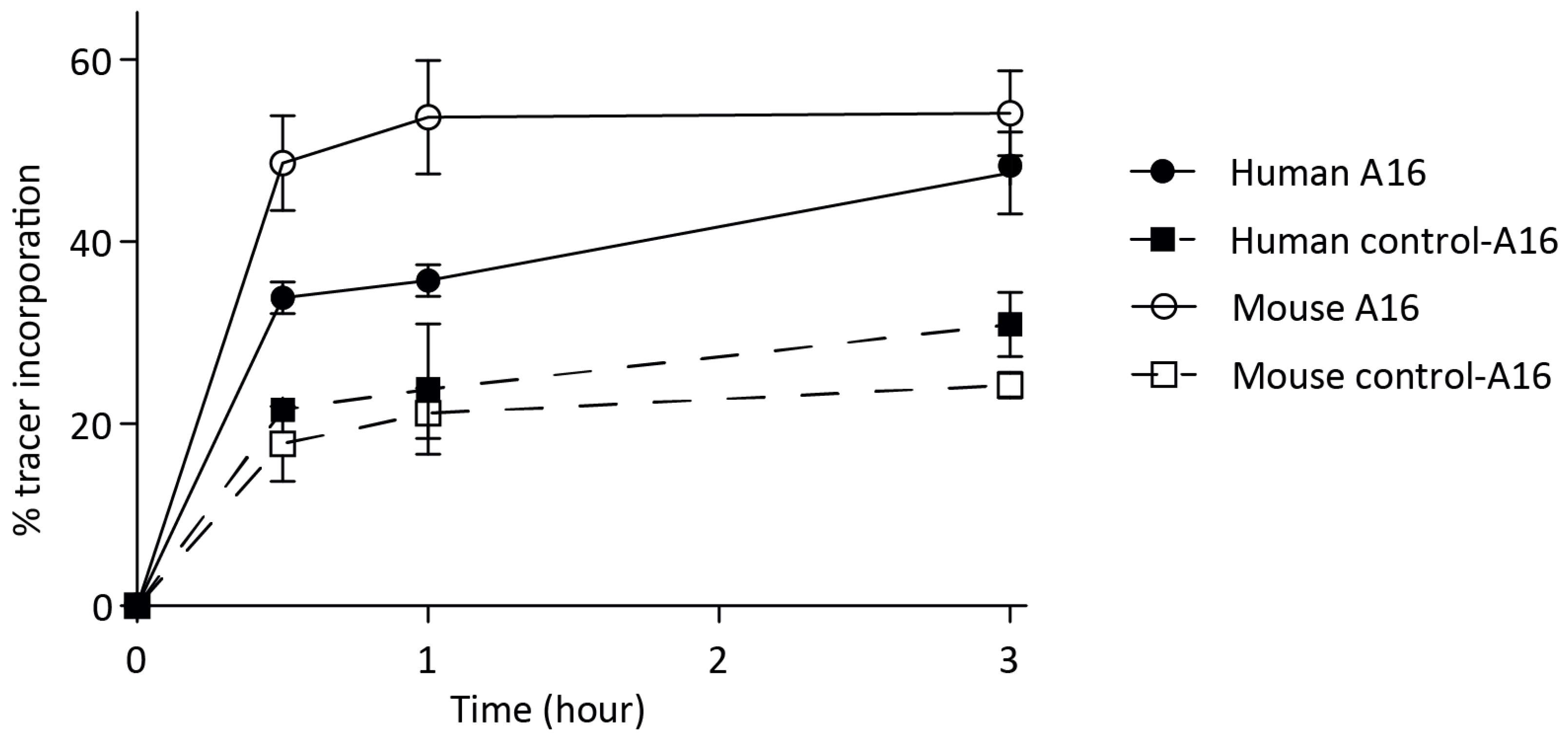
3.2. In Vitro Probe Incorporation
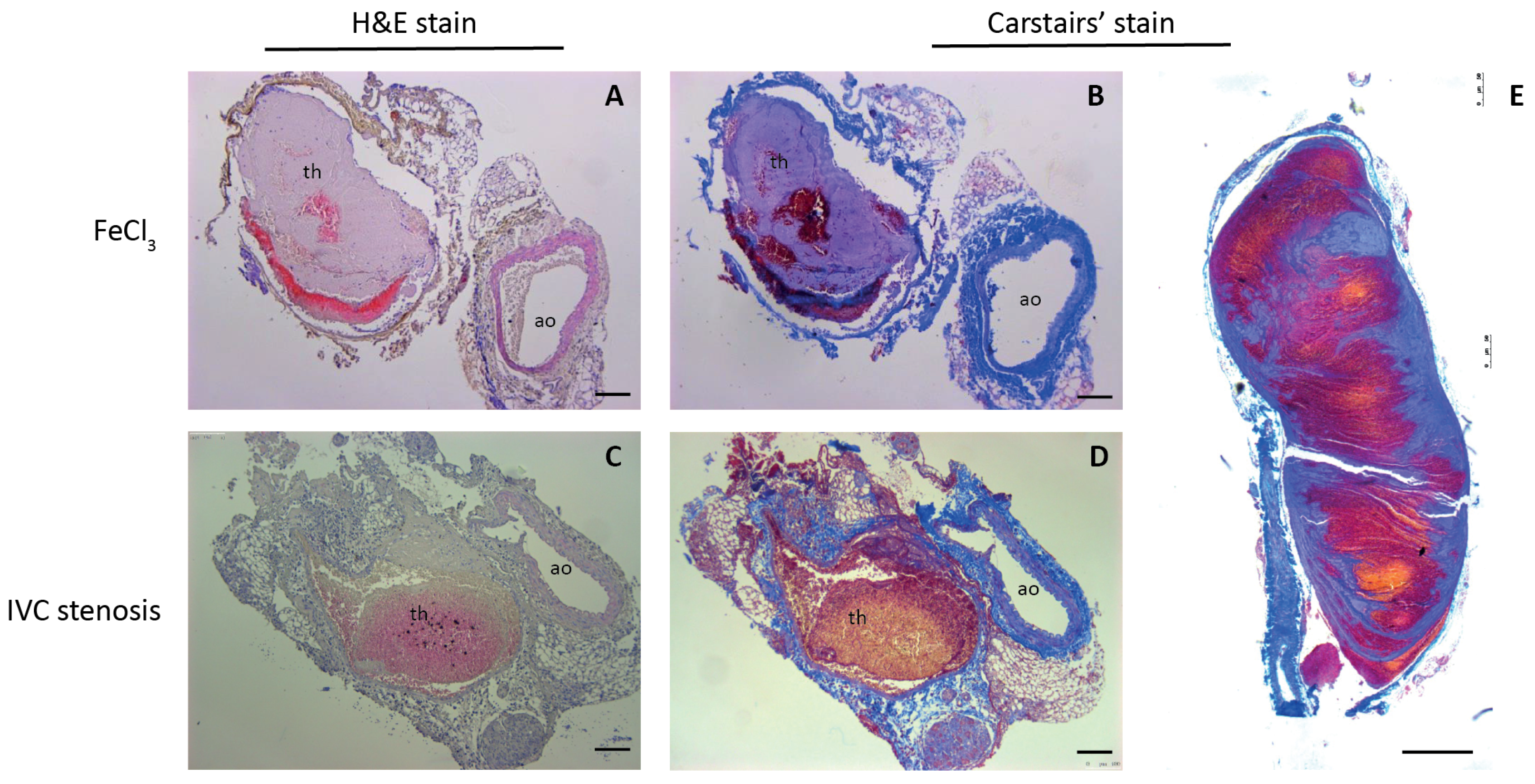
3.3. Validation of Mouse DVT Models
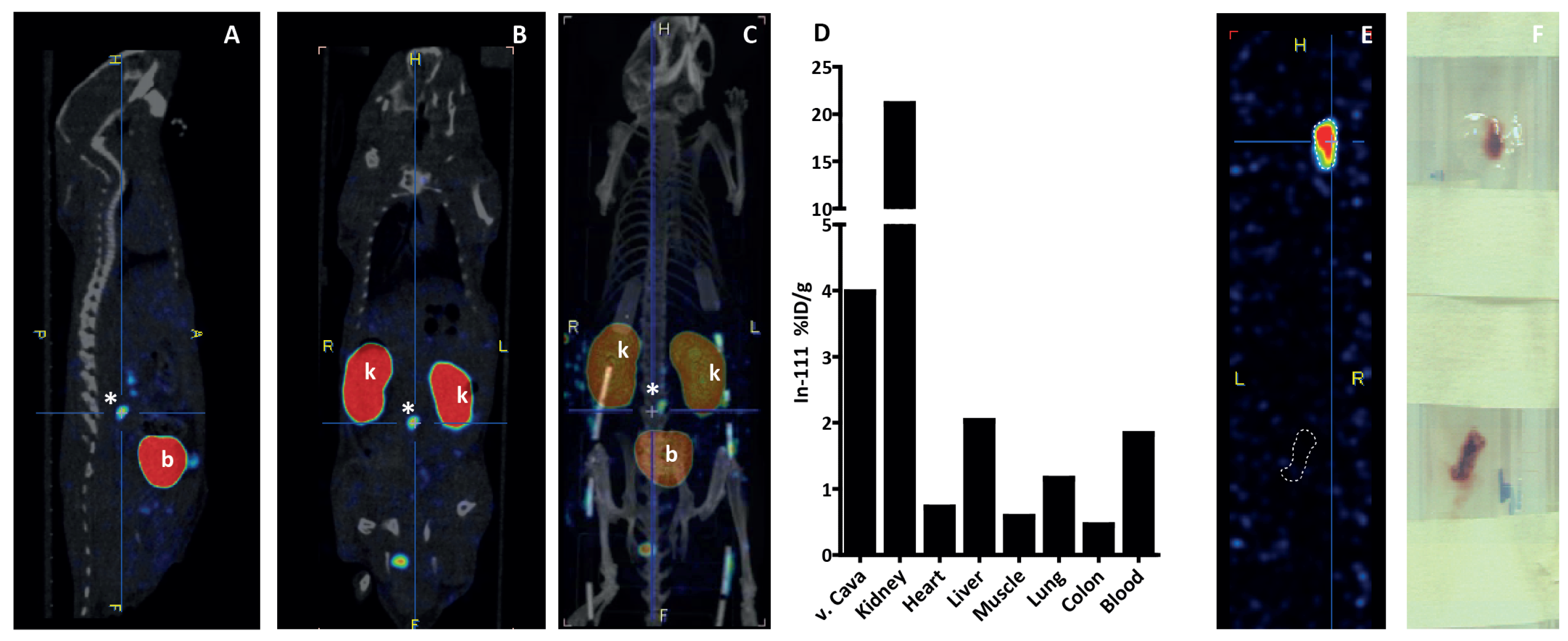
3.4. In Vivo Thrombus Imaging in Vena Cava
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, G.A.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fibrinolytic Therapy Trialists’ Collaborative, G. Indications for fibrinolytic therapy in suspected acute myocardial infarction: Collaborative overview of early mortality and major morbidity results from all randomised trials of more than 1000 patients. Lancet 1994, 343, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, G.W.; Rossi, J.E.; Cannon, C.P. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2017, 389, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.J.; Weitz, J.I.; Kim, P.Y. Fibrinolysis: Strategies to enhance the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, W.; Le Gal, G.; Bates, S.M.; Righini, M.; Haramati, L.B.; Lang, E.; Kline, J.A.; Chasteen, S.; Snyder, M.; Patel, P.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Diagnosis of venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3226–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, B.L.; Caravan, P. Peptide-based fibrin-targeting probes for thrombus imaging. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 14488–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, F.; Oliveira, B.L.; Rietz, T.A.; Rotile, N.J.; Naha, P.C.; Cormode, D.P.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Catana, C.; Caravan, P. Multisite Thrombus Imaging and Fibrin Content Estimation With a Single Whole-Body PET Scan in Rats. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 2114–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, K.; Zheng, X.; Kessinger, C.W.; Mauskapf, A.; Li, W.; Kawamura, Y.; Orii, M.; Hilderbrand, S.A.; Jaffer, F.A.; McCarthy, J.R. In Vivo Platelet Detection Using a Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Probe. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bruhl, M.L.; Stark, K.; Steinhart, A.; Chandraratne, S.; Konrad, I.; Lorenz, M.; Khandoga, A.; Tirniceriu, A.; Coletti, R.; Kollnberger, M.; et al. Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, J.R.; Wolberg, A.S. Newly-Recognized Roles of Factor XIII in Thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vymazal, J.; Spuentrup, E.; Cardenas-Molina, G.; Wiethoff, A.J.; Hartmann, M.G.; Caravan, P.; Parsons, E.C., Jr. Thrombus imaging with fibrin-specific gadolinium-based MR contrast agent EP-2104R: Results of a phase II clinical study of feasibility. Investig. Radiol. 2009, 44, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botnar, R.M.; Buecker, A.; Wiethoff, A.J.; Parsons, E.C., Jr.; Katoh, M.; Katsimaglis, G.; Weisskoff, R.M.; Lauffer, R.B.; Graham, P.B.; Gunther, R.W.; et al. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of coronary thrombosis using a fibrin-binding molecular magnetic resonance contrast agent. Circulation 2004, 110, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flacke, S.; Fischer, S.; Scott, M.J.; Fuhrhop, R.J.; Allen, J.S.; McLean, M.; Winter, P.; Sicard, G.A.; Gaffney, P.J.; Wickline, S.A.; et al. Novel MRI contrast agent for molecular imaging of fibrin: Implications for detecting vulnerable plaques. Circulation 2001, 104, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirol, M.; Fuster, V.; Badimon, J.J.; Fallon, J.T.; Moreno, P.R.; Toussaint, J.F.; Fayad, Z.A. Chronic thrombus detection with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and a fibrin-targeted contrast agent. Circulation 2005, 112, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stracke, C.P.; Katoh, M.; Wiethoff, A.J.; Parsons, E.C.; Spangenberg, P.; Spüntrup, E. Molecular MRI of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis using a new fibrin-specific MR contrast agent. Stroke 2007, 38, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaeianpour, S.; Mosayebnia, M.; Moghimi, A.; Amidi, S.; Geramifar, P.; Kobarfard, F.; Shahhosseini, S. [18F]FDG-Labeled CGPRPPC Peptide Serving as a Small Thrombotic Lesions Probe, Including a Comparison with [(99m)Tc]-Labeled Form. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2018, 33, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesienski, K.L.; Yang, Y.; Ay, I.; Chonde, D.B.; Loving, G.S.; Rietz, T.A.; Catana, C.; Caravan, P. Fibrin-targeted PET probes for the detection of thrombi. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starmans, L.W.; Van Duijnhoven, S.M.; Rossin, R.; Berben, M.; Aime, S.; Daemen, M.J.; Nicolay, K.; Grüll, H. Evaluation of 111In-labeled EPep and FibPep as tracers for fibrin SPECT imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4309–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, M.J.; Abran, M.; Maafi, F.; Busseuil, D.; Merlet, N.; Mihalache-Avram, T.; Geoffroy, P.; Tardif, P.L.; Abulrob, A.; Arbabi-Ghahroudi, M.; et al. In Vivo Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging of Atherosclerosis Using Local Delivery of Novel Targeted Molecular Probes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Bhayana, B.; Thompson, B.; Kessinger, C.W.; Khatri, A.; McCarthy, J.R.; Weissleder, R.; Lin, C.P.; Tearney, G.J.; Jaffer, F.A. Molecular imaging of fibrin deposition in deep vein thrombosis using a new fibrin-targeted near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) imaging strategy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Chakraborty, S.; Liu, S. Radiolabeled Cyclic RGD Peptides as Radiotracers for Imaging Tumors and Thrombosis by SPECT. Theranostics 2011, 1, 58–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tung, C.H.; Ho, N.H.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Jaffer, F.A.; Reed, G.L.; Weissleder, R. Novel factor XIII probes for blood coagulation imaging. Chembiochem 2003, 4, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miserus, R.J.; Herias, M.V.; Prinzen, L.; Lobbes, M.B.; Van Suylen, R.J.; Dirksen, A.; Hackeng, T.M.; Heemskerk, J.W.; van Engelshoven, J.M.; Daemen, M.J.; et al. Molecular MRI of early thrombus formation using a bimodal alpha2-antiplasmin-based contrast agent. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muszbek, L.; Yee, V.C.; Hevessy, Z. Blood coagulation factor XIII: Structure and function. Thromb. Res. 1999, 94, 271–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.N.; Lee, C.S.; Tae, W.C.; Jackson, K.W.; Christiansen, V.J.; McKee, P.A. Crosslinking of alpha 2-antiplasmin to fibrin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 936, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.R.; Houng, A.K.; Reed, G.L. Catalytic life of activated factor XIII in thrombi. Implications for fibrinolytic resistance and thrombus aging. Circulation 2000, 102, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okano, M.; Hara, T.; Nishimori, M.; Irino, Y.; Satomi-Kobayashi, S.; Shinohara, M.; Toh, R.; Jaffer, F.A.; Ishida, T.; Hirata, K.I. In Vivo Imaging of Venous Thrombus and Pulmonary Embolism Using Novel Murine Venous Thromboembolism Model. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnölzer, M.; Alewood, P.; Jones, A.; Alewood, D.; Kent, S.B.H. In Situ Neutralization in Boc-chemistry Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2007, 13, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, F.; Bernhagen, D.; García-Arévalo, C.; de Torre, I.G.; Timmerman, P.; Rodríguez-Cabello, J.C. Bicyclic RGD peptides with high integrin αvβ3 and α5β1 affinity promote cell adhesion on elastin-like recombinamers. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnatowich, D.J. Label stability in serum of four radionuclides on DTPA-coupled antibodies–an evaluation. Int. J. Rad. Appl. Instrum. B 1986, 13, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Smith, P.L.; Hsu, M.Y.; Gailani, D.; Schumacher, W.A.; Ogletree, M.L.; Seiffert, D.A. Effects of factor XI deficiency on ferric chloride-induced vena cava thrombosis in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.A.; Obi, A.T.; Myers, D.D.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Henke, P.K.; Mackman, N.; Wakefield, T.W. Critical Review of Mouse Models of Venous Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Houng, A.K.; Reed, G.L. Venous stasis-induced fibrinolysis prevents thrombosis in mice: Role of alpha2-antiplasmin. Blood 2019, 134, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchaikovski, S.N.; van Vlijmen, B.J.M.; Rosing, J.; Tans, G. Development of a calibrated automated thrombography based thrombin generation test in mouse plasma. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brill, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Chauhan, A.K.; Yang, J.J.; De Meyer, S.F.; Kollnberger, M.; Wakefield, T.W.; Lammle, B.; Massberg, S.; Wagner, D.D. Von Willebrand factor-mediated platelet adhesion is critical for deep vein thrombosis in mouse models. Blood 2011, 117, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diaz, J.A.; Saha, P.; Cooley, B.; Palmer, O.R.; Grover, S.P.; Mackman, N.; Wakefield, T.W.; Henke, P.K.; Smith, A.; Lal, B.K. Choosing a mouse model of venous thrombosis: A consensus assessment of utility and application. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchenko, O.; van der Have, F.; Goorden, M.C.; Ramakers, R.M.; Beekman, F.J. Ultra-high-sensitivity submillimeter mouse SPECT. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deleye, S.; Van Holen, R.; Verhaeghe, J.; Vandenberghe, S.; Stroobants, S.; Staelens, S. Performance evaluation of small-animal multipinhole μSPECT scanners for mouse imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Have, F.; Vastenhouw, B.; Ramakers, R.M.; Branderhorst, W.; Krah, J.O.; Ji, C.; Staelens, S.G.; Beekman, F.J. U-SPECT-II: An Ultra-High-Resolution Device for Molecular Small-Animal Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, M.M.; Tremoleda, J.L.; Bayomy, T.B.; Gsell, W. Molecular SPECT Imaging: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Imaging 2011, 2011, 796025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yap, M.L.; McFadyen, J.D.; Wang, X.; Zia, N.A.; Hohmann, J.D.; Ziegler, M.; Yao, Y.; Pham, A.; Harris, M.; Donnelly, P.S.; et al. Targeting Activated Platelets: A Unique and Potentially Universal Approach for Cancer Imaging. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dickhout, A.; Van de Vijver, P.; Bitsch, N.; van Hoof, S.J.; Thomassen, S.L.G.D.; Massberg, S.; Timmerman, P.; Verhaegen, F.; Koenen, R.R.; Dijkgraaf, I.; et al. Molecular Detection of Venous Thrombosis in Mouse Models Using SPECT/CT. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12060829
Dickhout A, Van de Vijver P, Bitsch N, van Hoof SJ, Thomassen SLGD, Massberg S, Timmerman P, Verhaegen F, Koenen RR, Dijkgraaf I, et al. Molecular Detection of Venous Thrombosis in Mouse Models Using SPECT/CT. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(6):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12060829
Chicago/Turabian StyleDickhout, Annemiek, Pieter Van de Vijver, Nicole Bitsch, Stefan J. van Hoof, Stella L. G. D. Thomassen, Steffen Massberg, Peter Timmerman, Frank Verhaegen, Rory R. Koenen, Ingrid Dijkgraaf, and et al. 2022. "Molecular Detection of Venous Thrombosis in Mouse Models Using SPECT/CT" Biomolecules 12, no. 6: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12060829
APA StyleDickhout, A., Van de Vijver, P., Bitsch, N., van Hoof, S. J., Thomassen, S. L. G. D., Massberg, S., Timmerman, P., Verhaegen, F., Koenen, R. R., Dijkgraaf, I., & Hackeng, T. M. (2022). Molecular Detection of Venous Thrombosis in Mouse Models Using SPECT/CT. Biomolecules, 12(6), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12060829






