Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissues
2.2. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Assessment
2.3. Interpretation of the Immunohistochemical Results
2.4. In Silico Data Analysis
2.5. LINC-ROR rs1942347 (A/T) Variant Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
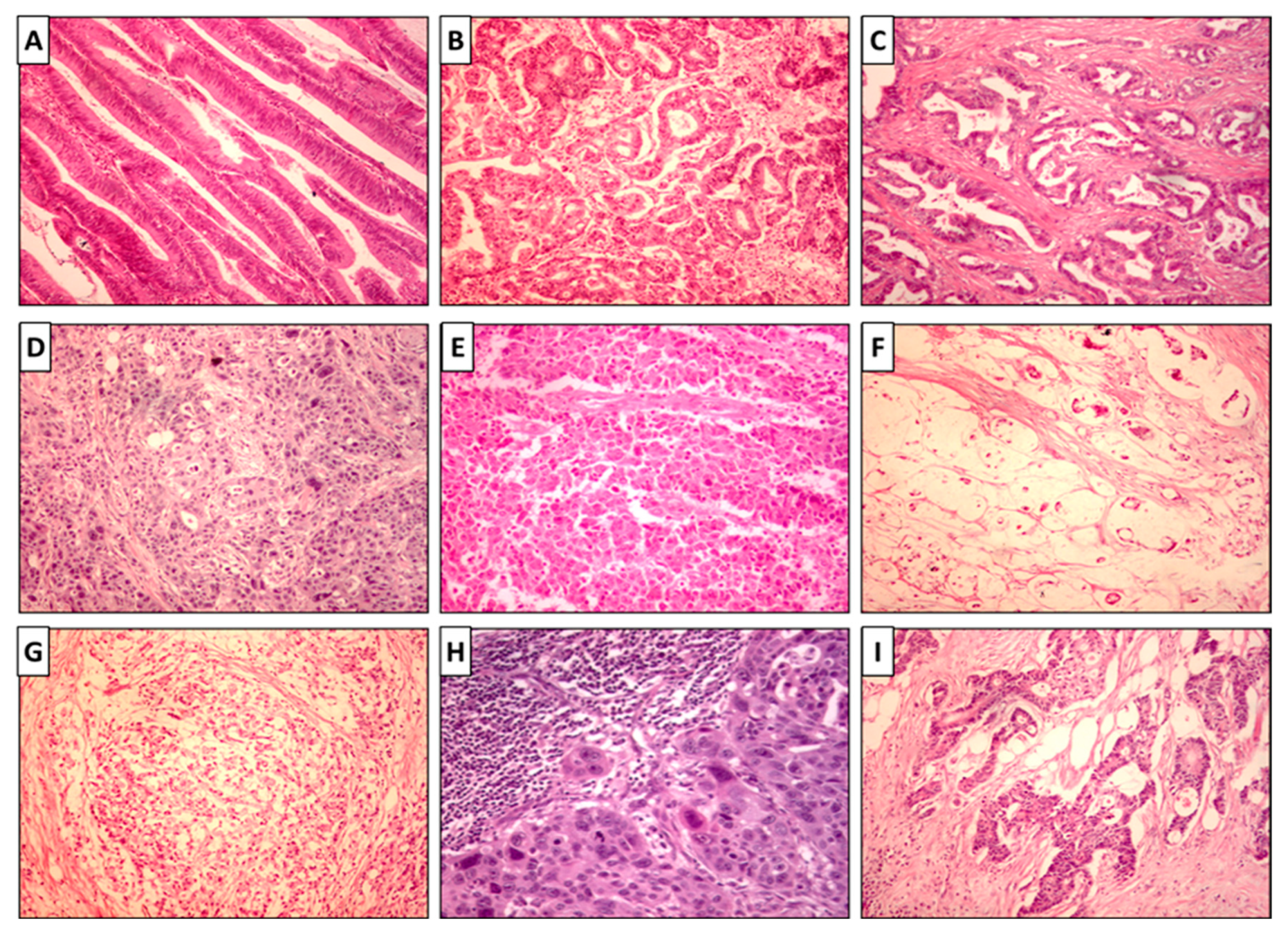
3.2. Histopathological Assessment and BRAF Mutation Analysis
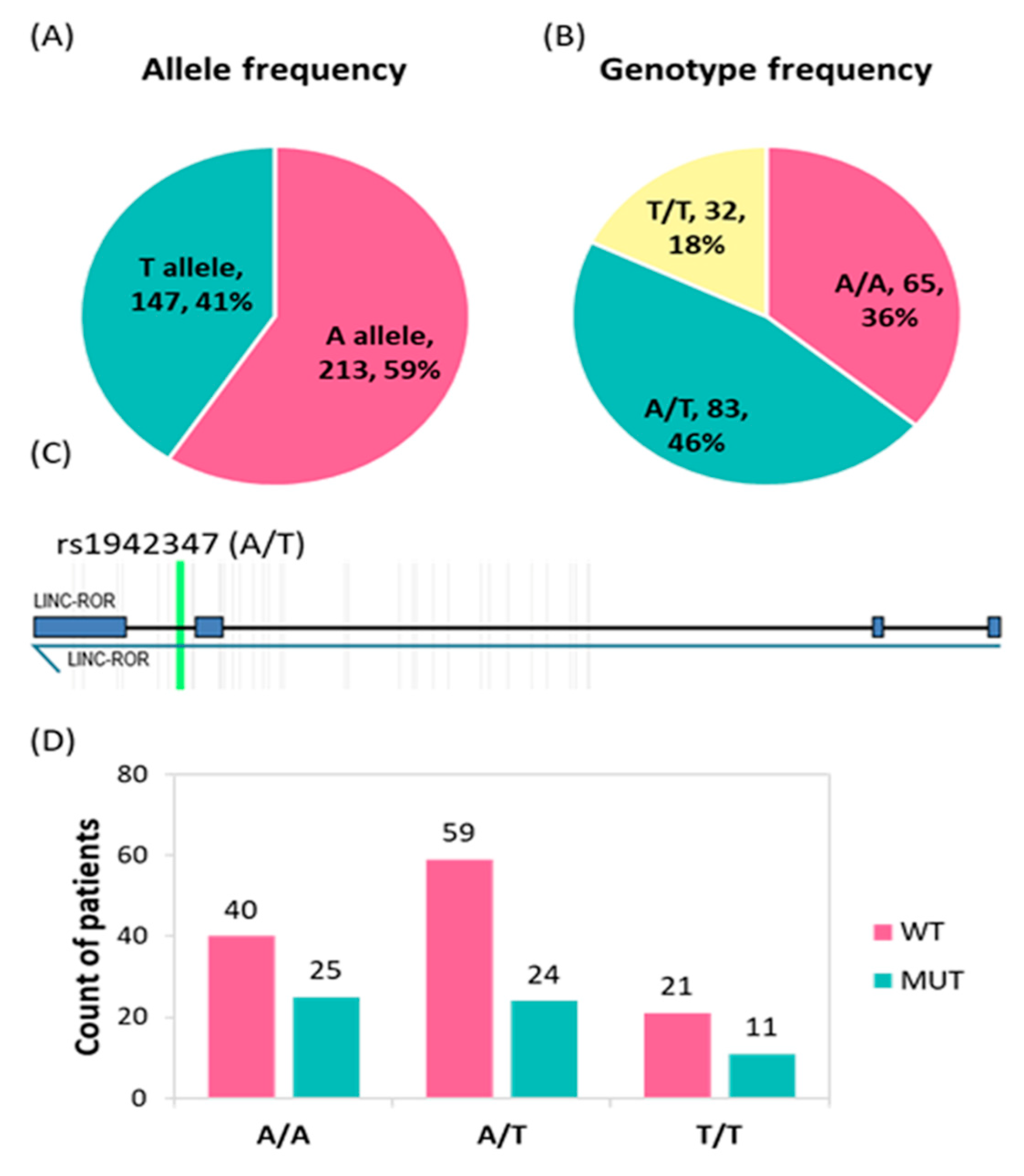
3.3. Genotype and Allele Frequencies of the LINC-ROR Variant in CRC Patients
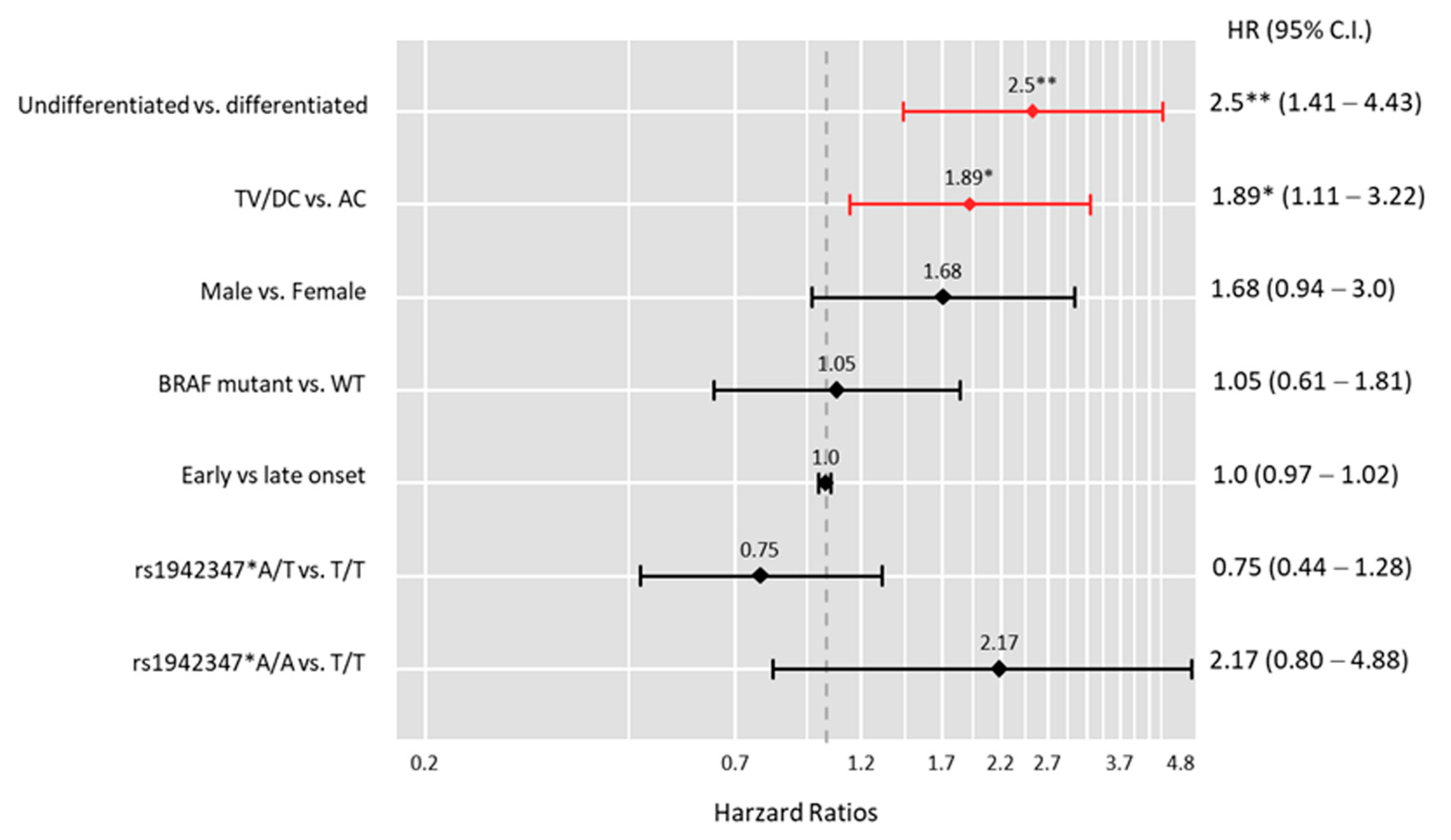
3.4. Prognostic Value of the LINC-ROR Genotypes in CRC
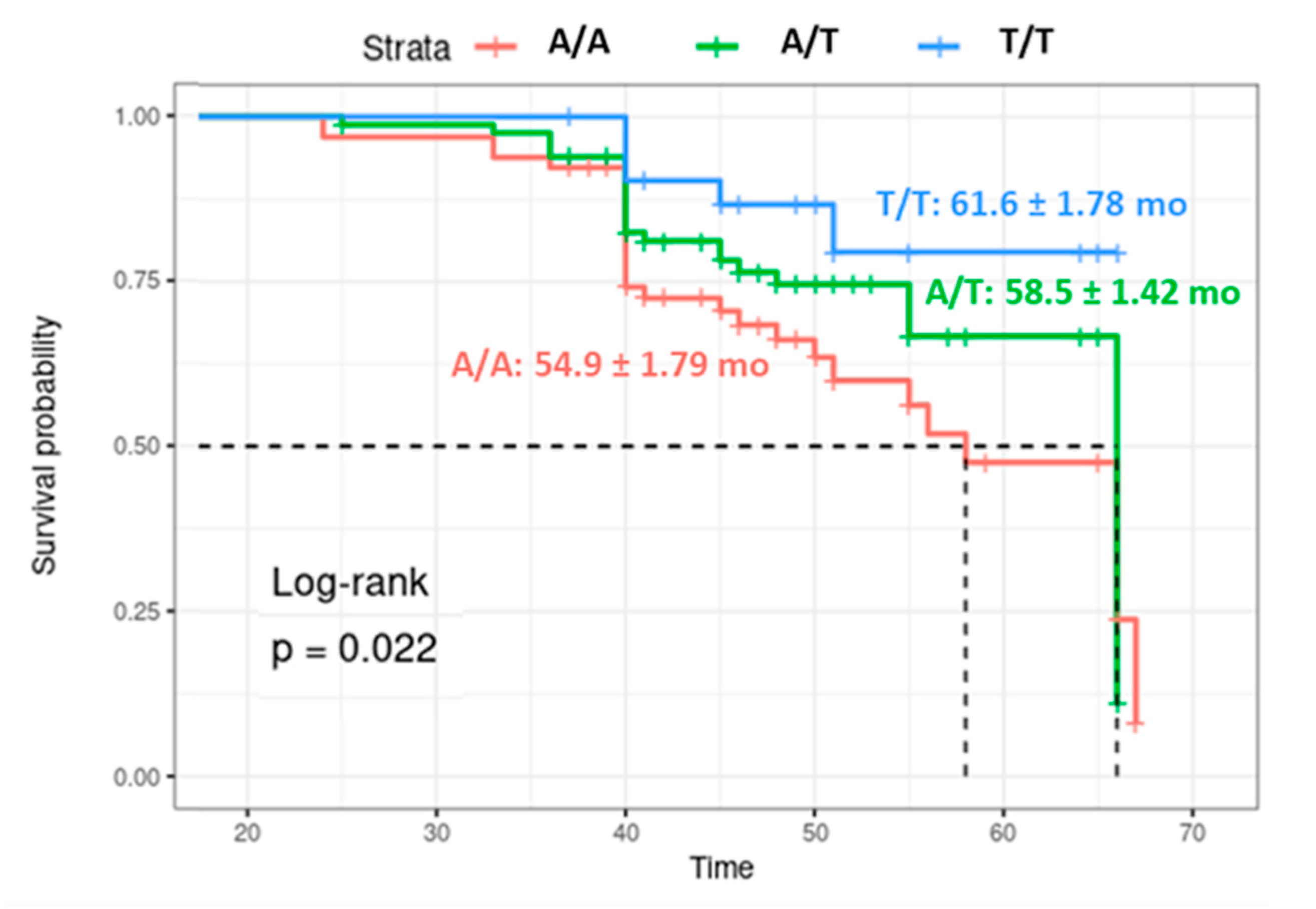
3.5. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormi, S.M.A.; Ardehkhani, S.; Kerachian, M.A. New insights into colorectal cancer screening and early detection tests. Colorectal. Cancer 2017, 6, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursheikhani, A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Kerachian, M.A. Mechanisms of long non-coding RNA function in colorectal cancer tumorigenesis. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diori Karidio, I.; Sanlier, S.H. Reviewing cancer’s biology: An eclectic approach. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 33, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahiem, A.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Abu AlSel, B.T.; Toraih, E.A. Prognostic value of BRAF/MIR-17 signature and B-Raf protein expression in patients with colorectal cancer: A pilot study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Du, L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Duan, W.; Yan, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Identification of long non-coding RNAs as potential novel diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Nie, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhou, J.; Ou, C. The Emerging Landscape of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 641343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.A.; Hosek, P.; Kralovcova, E.; Ostasov, P.; Liska, V.; Bruha, J.; Vycital, O.; Rosendorf, J.; Opattova, A.; Horak, J.; et al. lncRNAs in Non-Malignant Tissue Have Prognostic Value in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toraih, E.A.; El-Wazir, A.; Hussein, M.H.; Khashana, M.S.; Matter, A.; Fawzy, M.S.; Hosny, S. Expression of long intergenic non-coding RNA, regulator of reprogramming, and its prognostic value in patients with glioblastoma. Int. J. Biol. Mark. 2019, 34, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Fang, H.; Li, L.; Sun, J. Relevance Function of Linc-ROR in the Pathogenesis of Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; El-Wazir, A.; Ageeli, E.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Eltoukhy, M.M.; Killackey, M.T.; Kandil, E.; Fawzy, M.S. Unleash multifunctional role of long non-coding RNAs biomarker panel in breast cancer: A predictor classification model. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1215–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Jia, J.; You, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, R. The Long Non-Coding RNA-RoR Promotes the Tumorigenesis of Human Colorectal Cancer by Targeting miR-6833-3p Through SMC4. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fawzy, M.S.; Toraih, E.A.; El-Wazir, A.; Hosny, M.M.; Badran, D.I.; El Kelish, A. Long intergenic non-coding RNA, regulator of reprogramming (LINC-ROR) over-expression predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Guan, Y.J.; Gao, F.M. Long non-coding RNA ROR promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by inhibiting tumor suppressor gene NF2 through interacting with miR-223-3p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2401–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, Y.; An, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Jie, J.; Zhang, Q. The long non-coding RNA-ROR promotes the resistance of radiotherapy for human colorectal cancer cells by targeting the p53/miR-145 pathway. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between long non-coding RNA polymorphisms and cancer risk. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 771, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Cao, J.; Peng, R.; Guo, Q.; Ye, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Song, C. Functional Variants in Linc-ROR are Associated with mRNA Expression of Linc-ROR and Breast Cancer Susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmans, P.A.; Riley, B.; Pulver, A.E.; Owen, M.J.; Wildenauer, D.B.; Gejman, P.V.; Mowry, B.J.; Laurent, C.; Kendler, K.S.; Nestadt, G.; et al. Genomewide linkage scan of schizophrenia in a large multicenter pedigree sample using single nucleotide polymorphisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aust, D.E. WHO classification 2010 for the lower gastrointestinal tract: What is new? Pathologe 2011, 32 (Suppl. S2), 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkoca, A.N.; Yanık, S.; Ozdemir, Z.T.; Cihan, F.G.; Sayar, S.; Cincin, T.G.; Cam, A.; Ozer, C. TNM and Modified Dukes staging along with the demographic characteristics of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar]
- Choden, S.; Keelawat, S.; Jung, C.K.; Bychkov, A. VE1 Immunohistochemistry Improves the Limit of Genotyping for Detecting. Cancers 2020, 12, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashid, F.A.; Tabassum, S.; Khan, M.S.; Ansari, H.R.; Asif, M.; Sheikh, A.K.; Sameer Aga, S. VE1 immunohistochemistry is an adjunct tool for detection of BRAF. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, K.; Higgins, A.; Palting, J.; Cohen, M.; Brunhoeber, P. Immunohistochemistry with Anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody is a Sensitive Method for Detection of the BRAF V600E Mutation in Colon Cancer: Evaluation of 120 Cases with and without KRAS Mutation and Literature Review. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coordinators, N.R. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D7–D19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, H.M.F.; Abdelghany, A.A.; Al Ageeli, E.; Kattan, S.W.; Hassan, R.; Toraih, E.A.; Fawzy, M.S.; Mokhtar, N. Long Non-Coding RNAs Gene Variants as Molecular Markers for Diabetic Retinopathy Risk and Response to Anti-VEGF Therapy. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwazir, M.Y.; Hussein, M.H.; Toraih, E.A.; Al Ageeli, E.; Esmaeel, S.E.; Fawzy, M.S.; Faisal, S. Association of Angio-LncRNAs MIAT rs1061540/MALAT1 rs3200401 Molecular Variants with Gensini Score in Coronary Artery Disease Patients Undergoing Angiography. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, X.; Guinó, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MS, F.; MH, H.; EZ, A.; HA, Y.; HM, I.; EA, T. Association of MicroRNA-196a2 Variant with Response to Short-Acting β2-Agonist in COPD: An Egyptian Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0152834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, G.; Diermeier, S.D.; Spector, D.L. Therapeutic Targeting of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.L.; Huang, Z.; Wu, L.N.; Wu, R.; Ding, H.X.; Wang, B.G. lncRNA-PCAT1 rs2632159 polymorphism could be a biomarker for colorectal cancer susceptibility. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Meng, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhu, H.; Tang, W.; Li, X.; Aschner, M.; et al. MALAT1 rs664589 Polymorphism Inhibits Binding to miR-194-5p, Contributing to Colorectal Cancer Risk, Growth, and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5432–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, R. Association between polymorphism in the promoter region of lncRNA GAS5 and the risk of colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Hua, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, H.; Du, M.; Zhu, L.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Association of genetic variants in lncRNA H19 with risk of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25470–25477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Jing, F.; Ding, Y.; He, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, C. Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 polymorphisms are associated with the risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Genet. 2018, 222–223, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Tian, J.; Lou, J.; Ke, J.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A functional polymorphism in lnc-LAMC2-1:1 confers risk of colorectal cancer by affecting miRNA binding. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Z.; Xu, Q.; Sun, L.; Wen, J.; Fang, X.; Xing, C.; Yuan, Y. Four novel polymorphisms in long non-coding RNA HOTTIP are associated with the risk and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, SR20180573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheetham, S.W.; Gruhl, F.; Mattick, J.S.; Dinger, M.E. Long non-coding RNAs and the genetics of cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, H.; Vincent, K.; Pichler, M.; Fodde, R.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Slack, F.J.; Calin, G.A. Junk DNA and the long non-coding RNA twist in cancer genetics. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5003–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Jin, M.; Ye, D.; Li, Y.; Jing, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, K. Polymorphisms of a novel long non-coding RNA RP11-108K3.2 with colorectal cancer susceptibility and their effects on its expression. Int. J. Biol. Mark. 2020, 35, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg: A resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D930–D934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Y.; An, L.; Wu, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of lncRNA-p53 regulatory network genes are associated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy toxicities and efficacy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Wu, L.; Yao, J.; Meng, X.; Jiang, H.; Xiao, C.; Wu, F. Identification of Specific Long Non-Coding RNA Expression: Profile and Analysis of Association with Clinicopathologic Characteristics and BRAF Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Zhou, N.; Huang, J.; Liu, Q.; Fukuda, K.; Ma, D.; Lu, Z.; Bai, C.; Watabe, K.; Mo, Y.Y. The human long non-coding RNA-RoR is a p53 repressor in response to DNA damage. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Variable | Total (n = 180) | Survived (n = 118) | Died (n = 62) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | ≤60 | 92 (51.1) | 57 (48.3) | 35 (56.5) | 0.34 |
| >60 | 88 (48.9) | 61 (51.7) | 27 (43.5) | ||
| Sex | Male | 111 (61.7) | 68 (57.6) | 43 (69.4) | 0.14 |
| Female | 69 (38.3) | 50 (42.4) | 19 (30.6) | ||
| Location | Right | 97 (53.9) | 73 (61.9) | 24 (38.7) | 0.004 |
| Transverse/left | 83 (46.1) | 45 (38.1) | 38 (61.3) | ||
| Type | Adenocarcinoma | 128 (71.1) | 82 (69.5) | 46 (74.2) | 0.60 |
| Others | 52 (28.9) | 36 (30.5) | 16 (25.8) | ||
| Grade | G1 | 136 (75.6) | 97 (82.2) | 39 (62.9) | 0.006 |
| G2/G3 | 44 (24.4) | 21 (17.8) | 23 (37.1) | ||
| T stage | T1/2 | 132 (73.3) | 87 (73.7) | 45 (72.6) | 0.86 |
| T3/4 | 48 (26.7) | 31 (26.3) | 17 (27.4) | ||
| N stage | Negative | 72 (40) | 42 (35.6) | 30 (48.4) | 0.11 |
| Positive | 108 (60) | 76 (64.4) | 32 (51.6) | ||
| M stage | Negative | 144 (80) | 100 (84.7) | 44 (71) | 0.032 |
| Positive | 36 (20) | 18 (15.3) | 18 (29) | ||
| Duke’s stage | A/B | 111 (61.7) | 73 (61.9) | 38 (61.3) | 1.00 |
| C/D | 69 (38.3) | 45 (38.1) | 24 (38.7) | ||
| BRAF mutation | Wild type | 120 (66.7) | 80 (67.8) | 40 (64.5) | 0.74 |
| Mutant | 60 (33.3) | 38 (32.2) | 22 (35.5) | ||
| Relapse | No | 127 (70.6) | 89 (75.4) | 38 (61.3) | 0.06 |
| Yes | 53 (29.4) | 29 (24.6) | 24 (38.7) | ||
| Variable | Number | T/T (N = 32) | A/T (N = 83) | A/A (N = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | ≤60 | 92 | 11 (34.4) | 41 (49.4) | 40 (61.5) | 0.039 |
| >60 | 88 | 21 (65.6) | 42 (50.6) | 25 (38.5) | ||
| Sex | Female | 111 | 17 (53.1) | 57 (68.7) | 37 (56.9) | 0.18 |
| Male | 69 | 15 (46.9) | 26 (31.3) | 28 (43.1) | ||
| Location | Right | 97 | 19 (59.4) | 41 (49.4) | 37 (56.9) | 0.52 |
| Transverse/left | 83 | 13 (40.6) | 42 (50.6) | 28 (43.1) | ||
| Type | Adenocarcinoma | 128 | 25 (78.1) | 57 (68.7) | 46 (70.8) | 0.60 |
| Others | 52 | 7 (21.9) | 26 (31.3) | 19 (29.2) | ||
| Grade | G1 | 136 | 31 (96.9) | 60 (72.3) | 45 (69.2) | 0.008 |
| G2/3 | 44 | 1 (3.1) | 23 (27.7) | 20 (30.8) | ||
| T stage | T1/2 | 132 | 29 (90.6) | 62 (74.7) | 41 (63.1) | 0.014 |
| T3/4 | 48 | 3 (9.4) | 21 (25.3) | 24 (36.9) | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | Negative | 72 | 12 (37.5) | 34 (41) | 26 (40) | 0.94 |
| Positive | 108 | 20 (62.5) | 49 (59) | 39 (60) | ||
| Distant metastasis | Negative | 144 | 30 (93.8) | 68 (81.9) | 46 (70.8) | 0.024 |
| Positive | 36 | 2 (6.3) | 15 (18.1) | 19 (29.2) | ||
| Duke’s stage | A/B | 111 | 25 (78.1) | 51 (61.4) | 35 (53.8) | 0.06 |
| C/D | 69 | 7 (21.9) | 32 (38.6) | 30 (46.2) | ||
| BRAF mutation | Wild type | 120 | 21 (65.6) | 59 (71.1) | 40 (61.5) | 0.46 |
| Mutant | 60 | 11 (34.4) | 24 (28.9) | 25 (38.5) | ||
| Relapse | Negative | 127 | 22 (68.8) | 62 (74.7) | 43 (66.2) | 0.51 |
| Positive | 53 | 10 (31.3) | 21 (25.3) | 22 (33.8) | ||
| Mortality | Negative | 118 | 27 (84.4) | 57 (68.7) | 34 (52.3) | 0.005 |
| Positive | 62 | 5 (15.6) | 26 (31.3) | 31 (47.7) | ||
| DFS (months) | Prolonged (≥48) | 61 | 15 (46.9) | 28 (33.7) | 18 (27.7) | 0.17 |
| Short (<48) | 119 | 17 (53.1) | 55 (66.3) | 47 (72.3) | ||
| OS (months) | Prolonged (≥48) | 87 | 19 (59.4) | 40 (48.2) | 28 (43.1) | 0.31 |
| Short (<48) | 93 | 13 (40.6) | 43 (51.8) | 37 (56.9) | ||
| Frequency | Genotype | Late Onset | Early Onset | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codominant | T/T | 21 (23.9%) | 11 (12%) | Reference | 0.034 | 252.1 |
| A/T | 42 (47.7%) | 41 (44.6%) | 1.64 (0.84–3.23) | |||
| A/A | 25 (28.4%) | 40 (43.5%) | 3.13 (1.28–7.69) | |||
| Dominant | T/T | 21 (23.9%) | 11 (12%) | Reference | 0.031 | 252.2 |
| A/A-A/T | 67 (76.1%) | 81 (88%) | 2.38 (1.06–5.26) | |||
| Recessive | A/T-T/T | 63 (71.6%) | 52 (56.5%) | Reference | 0.033 | 252.3 |
| A/A | 25 (28.4%) | 40 (43.5%) | 1.96 (1.05–3.7) |
| Frequency | Genotype | Survived | Died | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codominant | T/T | 27 (22.9%) | 5 (8.1%) | Reference | 0.0037 | 230.0 |
| A/T | 57 (48.3%) | 26 (41.9%) | 2.13 (1.08–4.35) | |||
| A/A | 34 (28.8%) | 31 (50%) | 5.0 (1.69–14.29) | |||
| Dominant | T/T | 27 (22.9%) | 5 (8.1%) | Reference | 0.011 | 232.7 |
| A/A-A/T | 91 (77.1%) | 57 (91.9%) | 3.33 (1.2–9.09) | |||
| Recessive | A/T-T/T | 84 (71.2%) | 31 (50%) | Reference | 0.0035 | 230.6 |
| A/A | 34 (28.8%) | 31 (50%) | 2.63 (1.37–5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaalan, A.A.M.; Mokhtar, S.H.; Ahmedah, H.T.; Almars, A.I.; Toraih, E.A.; Ibrahiem, A.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Salem, M.A. Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040569
Shaalan AAM, Mokhtar SH, Ahmedah HT, Almars AI, Toraih EA, Ibrahiem AT, Fawzy MS, Salem MA. Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040569
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaalan, Aly A. M., Sara H. Mokhtar, Hanadi Talal Ahmedah, Amany I. Almars, Eman A. Toraih, Afaf T. Ibrahiem, Manal S. Fawzy, and Mai A. Salem. 2022. "Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040569
APA StyleShaalan, A. A. M., Mokhtar, S. H., Ahmedah, H. T., Almars, A. I., Toraih, E. A., Ibrahiem, A. T., Fawzy, M. S., & Salem, M. A. (2022). Prognostic Value of LINC-ROR (rs1942347) Variant in Patients with Colon Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Biomolecules, 12(4), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040569








