SLC26A9 as a Potential Modifier and Therapeutic Target in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
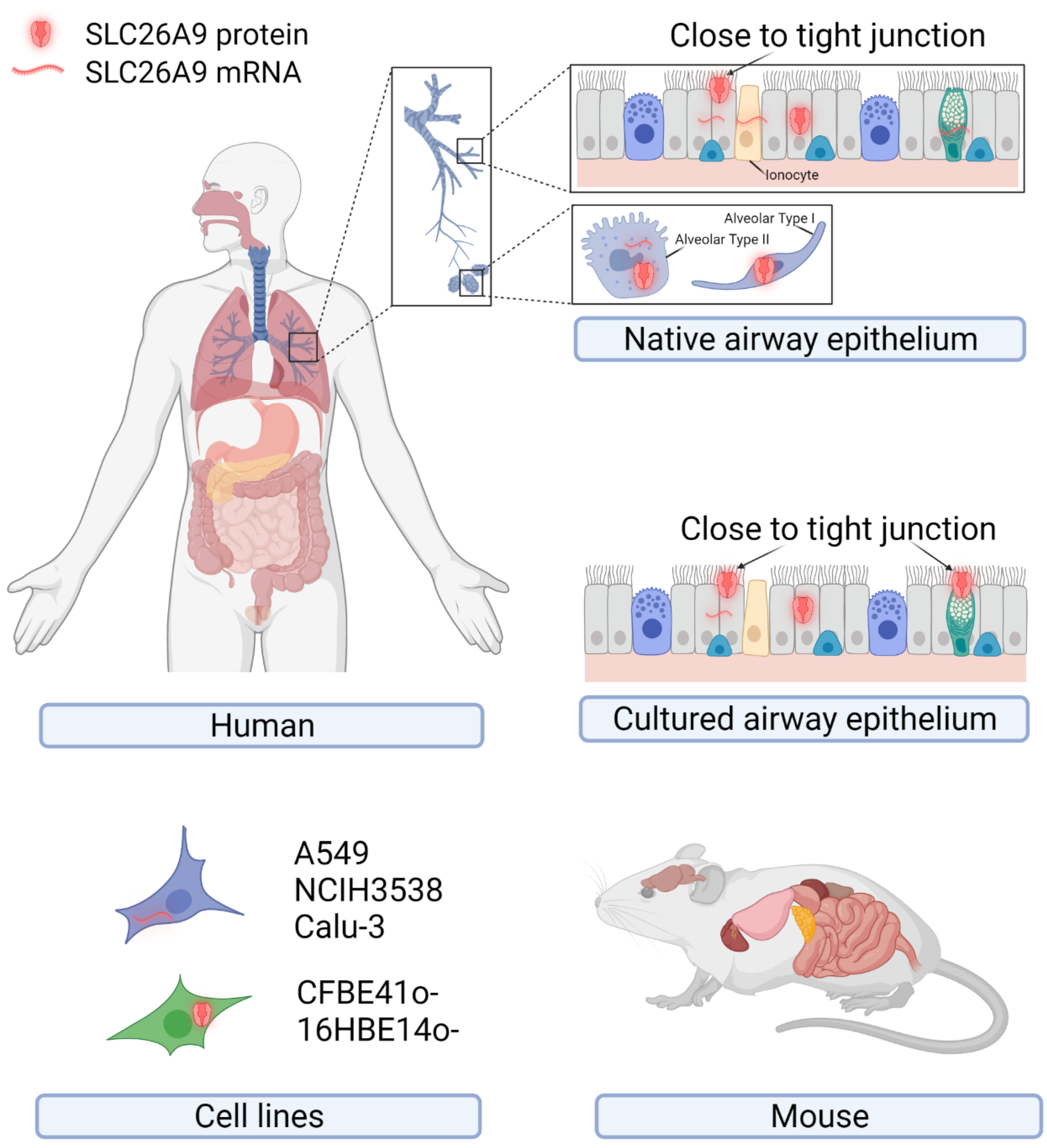
2. SLC26A9 Tissue, Cellular, and Subcellular Localization
2.1. SLC26A9 Expression in Human
2.2. SLC26A9 Expression in Mouse
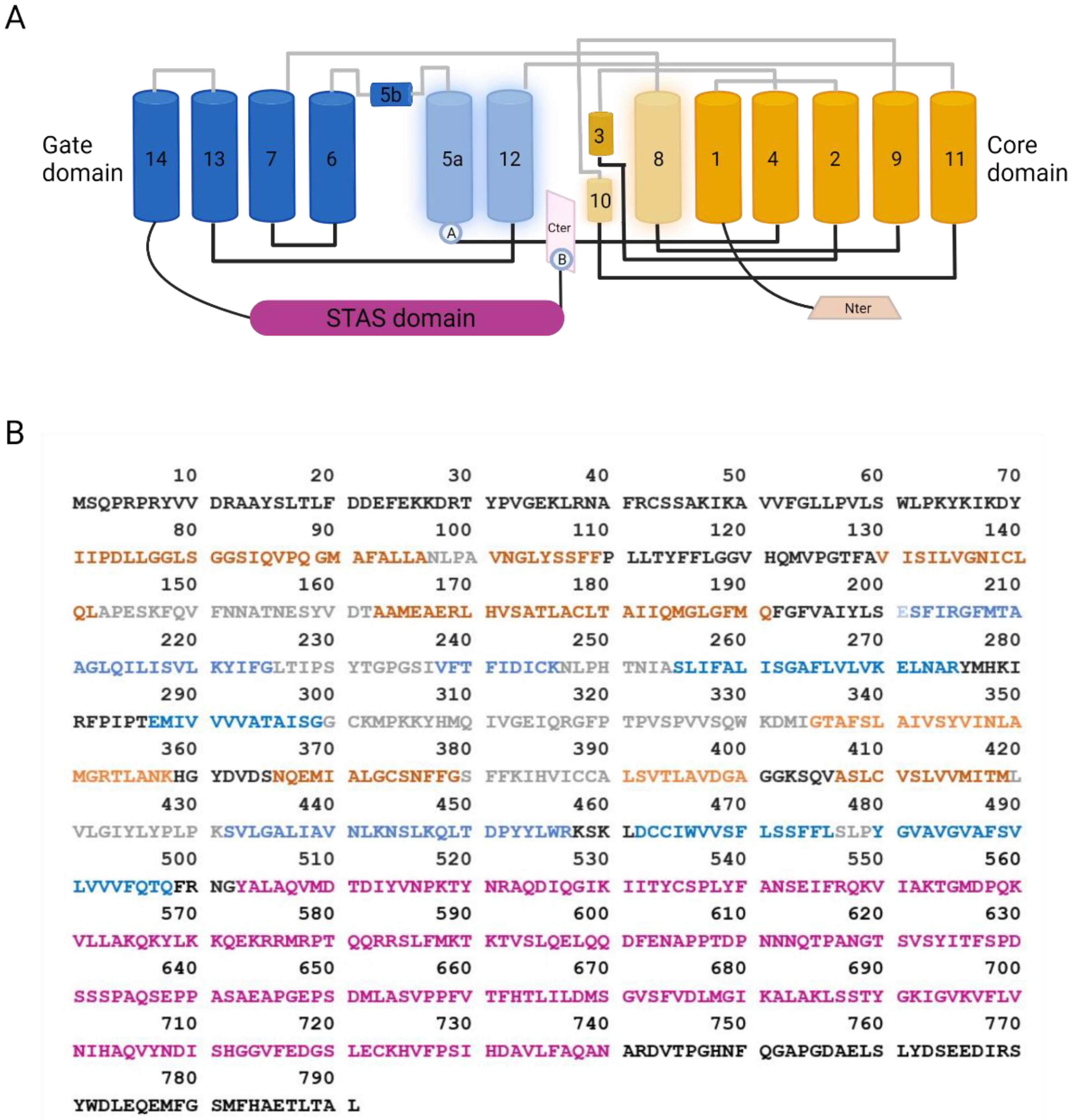
3. SLC26A9 Protein Structure and Function
3.1. SLC26A9 Structure
3.2. SLC26A9 Transport Properties
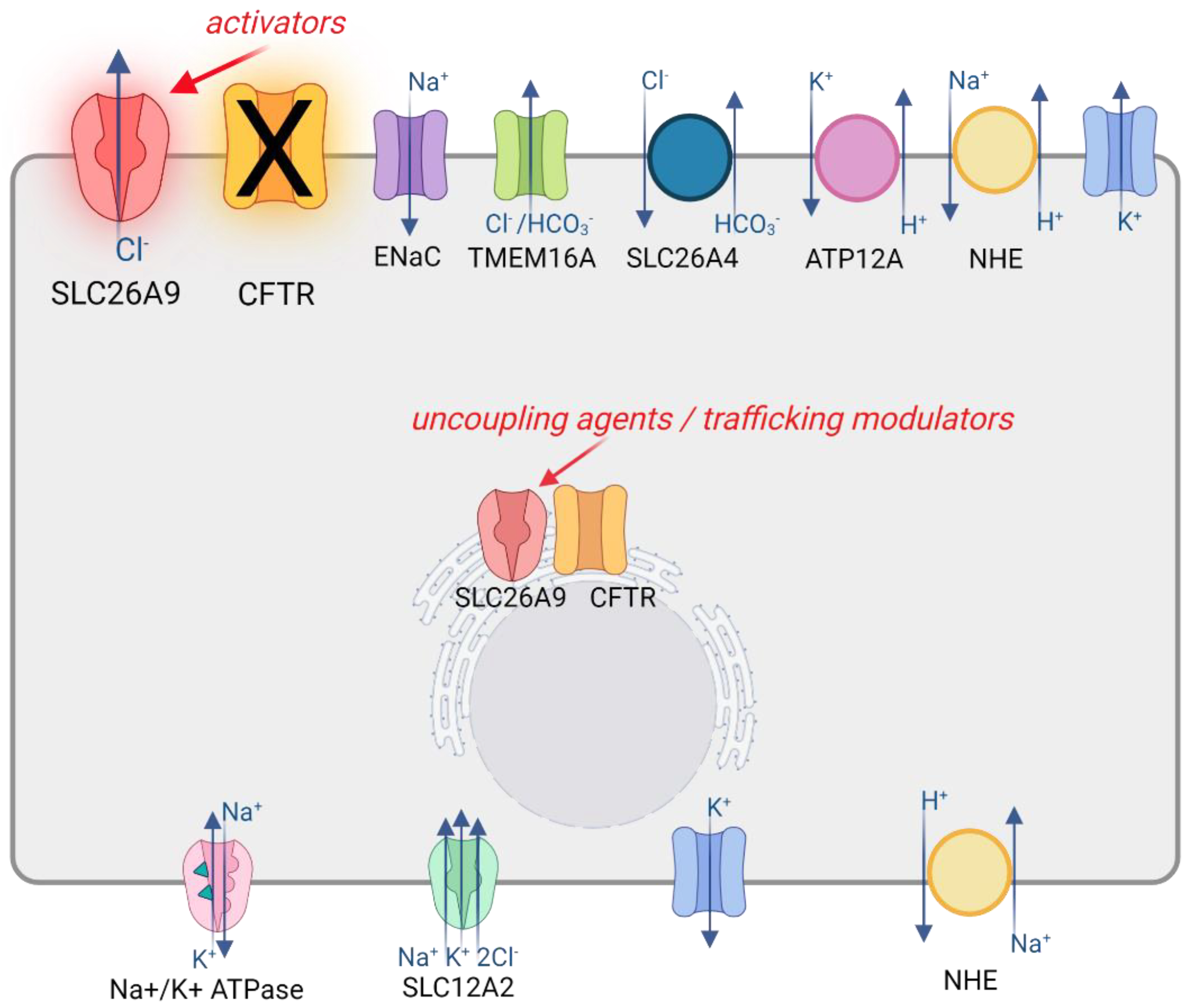
3.3. SLC26A9 Interaction with CFTR
3.4. SLC26A9 Contribution to Epithelial Ion Transport
4. SLC26A9 as a Modifier of CF Phenotype and Treatment
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alper, S.L.; Sharma, A.K. The SLC26 Gene Family of Anion Transporters and Channels. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 494–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geertsma, E.R.; Chang, Y.-N.; Shaik, F.R.; Neldner, Y.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Dutzler, R. Structure of a Prokaryotic Fumarate Transporter Reveals the Architecture of the SLC26 Family. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, D.B.; Romero, M.F. The SLC26 Gene Family of Multifunctional Anion Exchangers. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2004, 447, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedenoja, S.; Pekansaari, E.; Höglund, P.; Mäkelä, S.; Holmberg, C.; Kere, J. Update on SLC26A3 Mutations in Congenital Chloride Diarrhea. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everett, L.A.; Glaser, B.; Beck, J.C.; Idol, J.R.; Buchs, A.; Heyman, M.; Adawi, F.; Hazani, E.; Nassir, E.; Baxevanis, A.D.; et al. Pendred syndrome is caused by mutations in a putative sulphate transporter gene (PDS). Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.S.; Park, H.-J.; Yoo, S.-Y.; Namkung, W.; Jo, M.J.; Koo, S.K.; Park, H.-Y.; Lee, W.-S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.G. Heterogeneity in the Processing Defect of SLC26A4 Mutants. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Stewart, A.K.; Chebib, F.; Hsu, A.; Rozenfeld, J.; Huang, D.; Kang, D.; Lip, V.; Fang, H.; Shao, H.; et al. Distinct and Novel SLC26A4/Pendrin Mutations in Chinese and U.S. Patients with Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss. Physiol. Genom. 2009, 38, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shteinberg, M.; Haq, I.J.; Polineni, D.; Davies, J.C. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2021, 397, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randell, S.H.; Boucher, R.C. Effective Mucus Clearance Is Essential for Respiratory Health. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Button, B.; Cai, L.-H.; Ehre, C.; Kesimer, M.; Hill, D.B.; Sheehan, J.K.; Boucher, R.C.; Rubinstein, M. Periciliary Brush Promotes the Lung Health by Separating the Mucus Layer from Airway Epithelia. Science 2012, 337, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birket, S.E.; Chu, K.K.; Liu, L.; Houser, G.H.; Diephuis, B.J.; Wilsterman, E.J.; Dierksen, G.; Mazur, M.; Shastry, S.; Li, Y.; et al. A Functional Anatomic Defect of the Cystic Fibrosis Airway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Ambort, D.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Nilsson, H.E.; Thorell, K.; Hebert, H.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. Bicarbonate and Functional CFTR Channel Are Required for Proper Mucin Secretion and Link Cystic Fibrosis with Its Mucus Phenotype. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pezzulo, A.A.; Tang, X.X.; Hoegger, M.J.; Abou Alaiwa, M.H.; Ramachandran, S.; Moninger, T.O.; Karp, P.H.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.L.; Haagsman, H.P.; van Eijk, M.; et al. Reduced Airway Surface PH Impairs Bacterial Killing in the Porcine Cystic Fibrosis Lung. Nature 2012, 487, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, K.; Jia, Y.X.; Hirai, H.; Shinkawa, M.; Yamaya, M.; Sekizawa, K.; Sasaki, H. Acid Stimulation Reduces Bactericidal Activity of Surface Liquid in Cultured Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 26, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Alaiwa, M.H.; Beer, A.M.; Pezzulo, A.A.; Launspach, J.L.; Horan, R.A.; Stoltz, D.A.; Starner, T.D.; Welsh, M.J.; Zabner, J. Neonates with Cystic Fibrosis Have a Reduced Nasal Liquid pH.; A Small Pilot Study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keating, D.; Marigowda, G.; Burr, L.; Daines, C.; Mall, M.A.; McKone, E.F.; Ramsey, B.W.; Rowe, S.M.; Sass, L.A.; Tullis, E.; et al. VX-445–Tezacaftor–Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and One or Two Phe508del Alleles. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Burton, B.; Huang, C.-J.; Worley, J.; Cao, D.; Johnson, J.P.; Urrutia, A.; Joubran, J.; Seepersaud, S.; Sussky, K.; et al. Ivacaftor potentiation of multiple CFTR channels with gating mutations. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lohi, H.; Kujala, M.; Makela, S.; Lehtonen, E.; Kestila, M.; Saarialho-Kere, U.; Markovich, D.; Kere, J. Functional characterization of three novel tissue-specific anion exchangers SLC26A7, -A8, and -A9. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14246–14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anagnostopoulou, P.; Riederer, B.; Duerr, J.; Michel, S.; Binia, A.; Agrawal, R.; Liu, X.; Kalitzki, K.; Xiao, F.; Chen, M.; et al. SLC26A9-Mediated Chloride Secretion Prevents Mucus Obstruction in Airway Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3629–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strug, L.J.; Gonska, T.; He, G.; Keenan, K.; Ip, W.; Boëlle, P.-Y.; Lin, F.; Panjwani, N.; Gong, J.; Li, W.; et al. Cystic Fibrosis Gene Modifier SLC26A9 Modulates Airway Response to CFTR-Directed Therapeutics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 4590–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.-P.; Chang, M.-H.; Romero, M.F. Functional Analysis of Non-Synonymous Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Human SLC26A9. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, S.V.N.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Bertuzzo, C.S.; Marson, F.A.L. Interaction among Variants in the SLC Gene Family (SLC6A14, SLC26A9, SLC11A1, and SLC9A3) and CFTR Mutations with Clinical Markers of Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmit, A.; Marson, F.A.L.; Pereira, S.V.-N.; Vinagre, A.M.; Leite, G.S.; Servidoni, M.F.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Bertuzzo, C.S.; Amaral, M.D. Extent of Rescue of F508del-CFTR Function by VX-809 and VX-770 in Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Correlates with SNP Rs7512462 in SLC26A9 Gene in F508del/F508del Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.C.; Quaresma, M.C.; Silva, I.A.L.; Railean, V.; Ramalho, S.S.; Amaral, M.D. Synergy in Cystic Fibrosis Therapies: Targeting SLC26A9. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, T.; Riederer, B.; Lenzen, H.; Ludolph, L.; Yeruva, S.; Tuo, B.; Soleimani, M.; Seidler, U. Loss of Slc26a9 Anion Transporter Alters Intestinal Electrolyte and HCO3− Transport and Reduces Survival in CFTR-Deficient Mice. Pflug. Arch. 2015, 467, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, A.-T.N.; Aksit, M.A.; Vecchio-Pagan, B.; Shelton, C.A.; Osorio, D.L.; Anzmann, A.F.; Goff, L.A.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Blackman, S.M.; Cutting, G.R. Increased Expression of Anion Transporter SLC26A9 Delays Diabetes Onset in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Single Cell Type—SLC26A9—The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000174502-SLC26A9/single+cell+type (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- Bertrand, C.A.; Zhang, R.; Pilewski, J.M.; Frizzell, R.A. SLC26A9 Is a Constitutively Active, CFTR-Regulated Anion Conductance in Human Bronchial Epithelia. J. Gen. Physiol. 2009, 133, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Huang, J.; Billet, A.; Abu-Arish, A.; Goepp, J.; Matthes, E.; Tewfik, M.A.; Frenkiel, S.; Hanrahan, J.W. Pendrin Mediates Bicarbonate Secretion and Enhances Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Function in Airway Surface Epithelia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.B.; Choi, J.J.; Wang, X.; Myerburg, M.M.; Frizzell, R.A.; Bertrand, C.A. Separating the Contributions of SLC26A9 and CFTR to Anion Secretion in Primary Human.n Bronchial Epithelia. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L1147–L1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Thomas, D.Y.; Hanrahan, J.W. The Anion Transporter SLC26A9 Localizes to Tight Junctions and Is Degraded by the Proteasome When Co-Expressed with F508del–CFTR. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18269–18284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.D.; Sawicka, M.; Dutzler, R. Cryo-EM Structures and Functional Characterization of Murine Slc26a9 Reveal Mechanism of Uncoupled Chloride Transport. eLife 2019, 8, e46986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Tu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Structural Insights into the Gating Mechanism of Human SLC26A9 Mediated by Its C-Terminal Sequence. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, J.J.; Spahn, S.; Wang, X.; Füllekrug, J.; Bertrand, C.A.; Mall, M.A. Generation and Functional Characterization of Epithelial Cells with Stable Expression of SLC26A9 Cl− Channels. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 310, L593–L602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, C.A.; Mitra, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Pilewski, J.M.; Madden, D.R.; Frizzell, R.A. The CFTR Trafficking Mutation F508del Inhibits the Constitutive Activity of SLC26A9. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L912–L925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avella, M.; Loriol, C.; Boulukos, K.; Borgese, F.; Ehrenfeld, J. SLC26A9 Stimulates CFTR Expression and Function in Human Bronchial Cell Lines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorwart, M.R.; Shcheynikov, N.; Wang, Y.; Stippec, S.; Muallem, S. SLC26A9 Is a Cl− Channel Regulated by the WNK Kinases. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Henriksnäs, J.; Barone, S.; Witte, D.; Shull, G.E.; Forte, J.G.; Holm, L.; Soleimani, M. SLC26A9 Is Expressed in Gastric Surface Epithelial Cells, Mediates Cl−/HCO3− Exchange, and Is Inhibited by NH4+. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, C493–C505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-H.; Plata, C.; Zandi-Nejad, K.; Sinđić, A.; Sussman, C.R.; Mercado, A.; Broumand, V.; Raghuram, V.; Mount, D.B.; Romero, M.F. Slc26A9—Anion Exchanger, Channel and Na+ Transporter. J. Membr. Biol. 2009, 228, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amlal, H.; Xu, J.; Barone, S.; Zahedi, K.; Soleimani, M. The Chloride Channel/Transporter Slc26a9 Regulates the Systemic Arterial Pressure and Renal Chloride Excretion. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 91, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-H.; Plata, C.; Sindic, A.; Ranatunga, W.K.; Chen, A.-P.; Zandi-Nejad, K.; Chan, K.W.; Thompson, J.; Mount, D.B.; Romero, M.F. Slc26a9 Is Inhibited by the R-Region of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator via the STAS Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28306–28318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ousingsawat, J.; Schreiber, R.; Kunzelmann, K. Differential Contribution of SLC26A9 to Cl− Conductance in Polarized and Non-Polarized Epithelial Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Song, P.; Miller, M.L.; Borgese, F.; Barone, S.; Riederer, B.; Wang, Z.; Alper, S.L.; Forte, J.G.; Shull, G.E.; et al. Deletion of the Chloride Transporter Slc26a9 Causes Loss of Tubulovesicles in Parietal Cells and Impairs Acid Secretion in the Stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17955–17960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Rommens, J.M.; Corvol, H.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Chiang, T.; Lin, F.; Dorfman, R.; Busson, P.-F.; Parekh, R.V.; et al. Multiple Apical Plasma Membrane Constituents Are Associated with Susceptibility to Meconium Ileus in Individuals with Cystic Fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Soave, D.; Miller, M.R.; Keenan, K.; Lin, F.; Gong, J.; Chiang, T.; Stephenson, A.L.; Durie, P.; Rommens, J.; et al. Unraveling the Complex Genetic Model for Cystic Fibrosis: Pleiotropic Effects of Modifier Genes on Early Cystic Fibrosis-Related Morbidities. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.M.; Commander, C.W.; Watson, C.; Arcara, K.M.; Strug, L.J.; Stonebraker, J.R.; Wright, F.A.; Rommens, J.M.; Sun, L.; Pace, R.G.; et al. Genetic Modifiers of Cystic Fibrosis–Related Diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3627–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, S.V.-N.; Ribeiro, J.D.; Bertuzzo, C.S.; Marson, F.A.L. Association of Clinical Severity of Cystic Fibrosis with Variants in the SLC Gene Family (SLC6A14, SLC26A9, SLC11A1 and SLC9A3). Gene 2017, 629, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvol, H.; Mésinèle, J.; Douksieh, I.-H.; Strug, L.J.; Boëlle, P.-Y.; Guillot, L. SLC26A9 Gene Is Associated with Lung Function Response to Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, A.C.; Pace, R.G.; Dang, H.; Aksit, M.A.; Vecchio-Pagán, B.; Lam, A.-T.N.; O’Neal, W.K.; Blackman, S.M.; Knowles, M.R.; Cutting, G.R. SLC26A9 SNP Rs7512462 Is Not Associated with Lung Disease Severity or Lung Function Response to Ivacaftor in Cystic Fibrosis Patients with G551D-CFTR. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, D.T.; Haber, A.L.; Biton, M.; Vinarsky, V.; Lin, B.; Birket, S.; Yuan, F.; Chen, S.; Leung, H.M.; Villoria, J.; et al. A Revised Airway Epithelial Hierarchy Includes CFTR-Expressing Ionocytes. Nature 2018, 560, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasschaert, L.W.; Žilionis, R.; Choo-Wing, R.; Savova, V.; Knehr, J.; Roma, G.; Klein, A.M.; Jaffe, A.B. A Single Cell Atlas of the Tracheal Epithelium Reveals the CFTR-Rich.h.h Pulmonary Ionocyte. Nature 2018, 560, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrieri, G.; Scudieri, P.; Caci, E.; Schiavon, M.; Tomati, V.; Sirci, F.; Napolitano, F.; Carrella, D.; Gianotti, A.; Musante, I.; et al. Goblet Cell Hyperplasia Requires High Bicarbonate Transport to Support Mucin Release. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Tissues | Primary Cells | Cell lines | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA | Protein | mRNA | Protein | mRNA | Protein | |
| RT-PCR, Northern blot: lung, pancreas, prostate | IHC: lung bronchial and alveolar cells | - | - | RT-PCR: NCIH3538, A549 | - | [18] |
| - | - | RT-PCR: CF and non-CF bronchial epithelial cells | - | - | - | [28] |
| real-time PCR: GI tract (mostly stomach) | - | - | - | - | - | [25] |
| - | - | qRT-PCR: non-CF nasal cells, CF, and non-CF bronchial epithelial cells | - | qRT-PCR: Calu-3 | - | [29] |
| - | - | TaqMan®SNP Genotyping system: nasal cells | - | - | - | [23] |
| - | - | - | IF: non-CF bronchial epithelial cells (goblet and ciliated cells) | - | - | [31] |
| scRNA-Seq: pancreas (ductal and ductar/acinar cells) | - | - | - | - | - | [26] |
| - | - | sqRT-PCR: CF and non-CF bronchial epithelial cells | - | - | - | [30] |
| IF: CF and non-CF lung tissues | - | - | Western blot: nasal epithelial cells | Western blot: Immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells–16HBE14o-, CFBE41o- | - | [24] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorrieri, G.; Zara, F.; Scudieri, P. SLC26A9 as a Potential Modifier and Therapeutic Target in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020202
Gorrieri G, Zara F, Scudieri P. SLC26A9 as a Potential Modifier and Therapeutic Target in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(2):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020202
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorrieri, Giulia, Federico Zara, and Paolo Scudieri. 2022. "SLC26A9 as a Potential Modifier and Therapeutic Target in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease" Biomolecules 12, no. 2: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020202
APA StyleGorrieri, G., Zara, F., & Scudieri, P. (2022). SLC26A9 as a Potential Modifier and Therapeutic Target in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Biomolecules, 12(2), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020202







