A Novel Tandem-Tag Purification Strategy for Challenging Disordered Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of pSUMO Plasmid
2.2. Generation of pSUMO Expression Constructs
2.2.1. Generating pSUMO Constructs by HiFi Cloning (pSUMO-AF1, pSUMO-Tau-441)
2.2.2. Generating pSUMO Constructs by Site-Directed Mutagenesis (pSUMO-Tau-NTMT, pSUMO-Tau-MTBR and pSUMO-AF1 (Only N-tag))
2.3. Expression and Purification of pSUMO Constructs
2.3.1. Expression and Purification of pSUMO-AF1(Only N-tag)
2.3.2. Expression and Purification of pSUMO-AF1
2.3.3. Expression and Purification of pSUMO-Tau-441
2.3.4. Expression and Purification of pSUMO-Tau-NTMT
2.3.5. Expression and Purification of pSUMO-Tau-MTBR
2.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3. Results
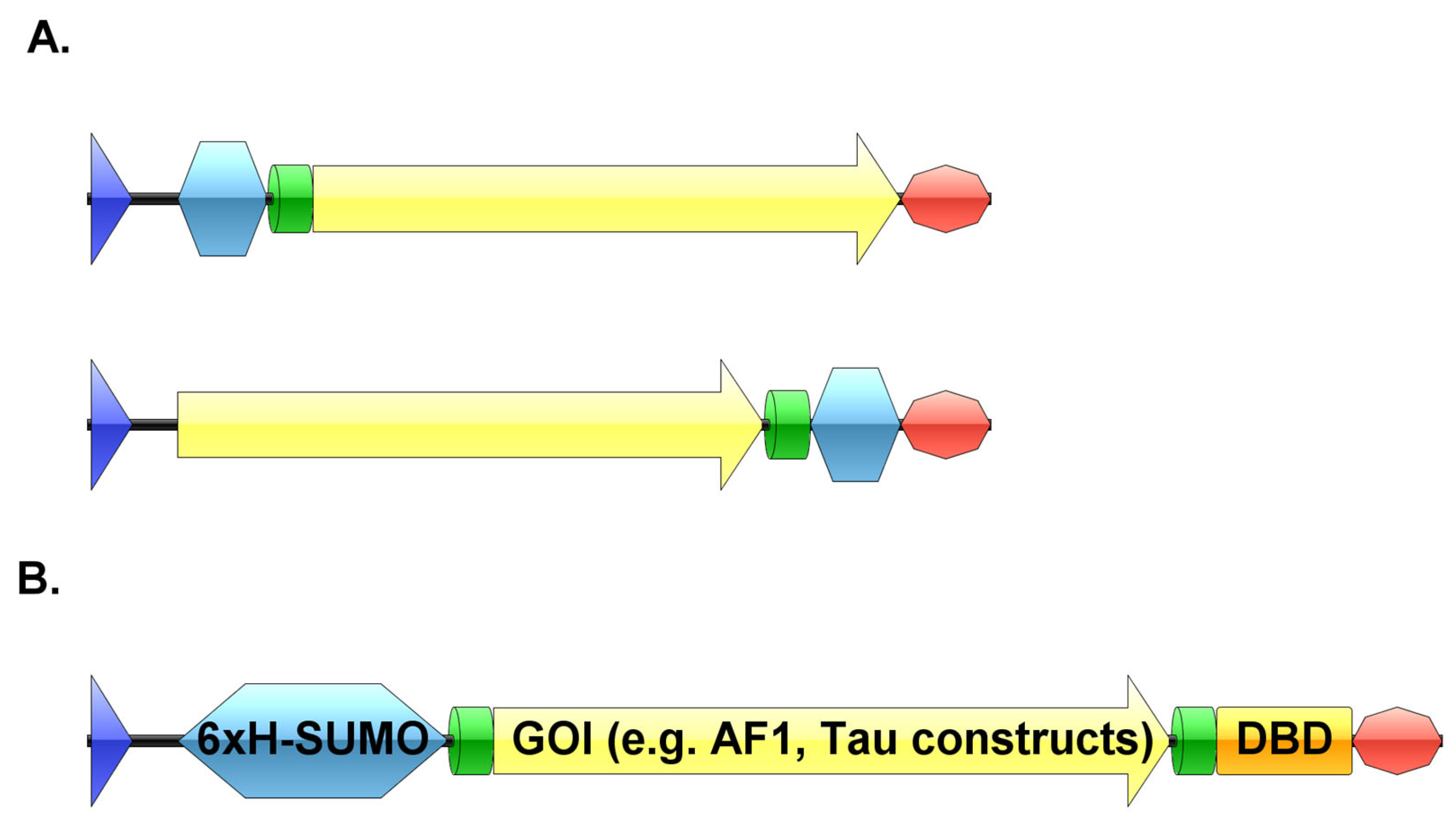
3.1. Generation of pSUMO Plasmid with Tandem-Tags
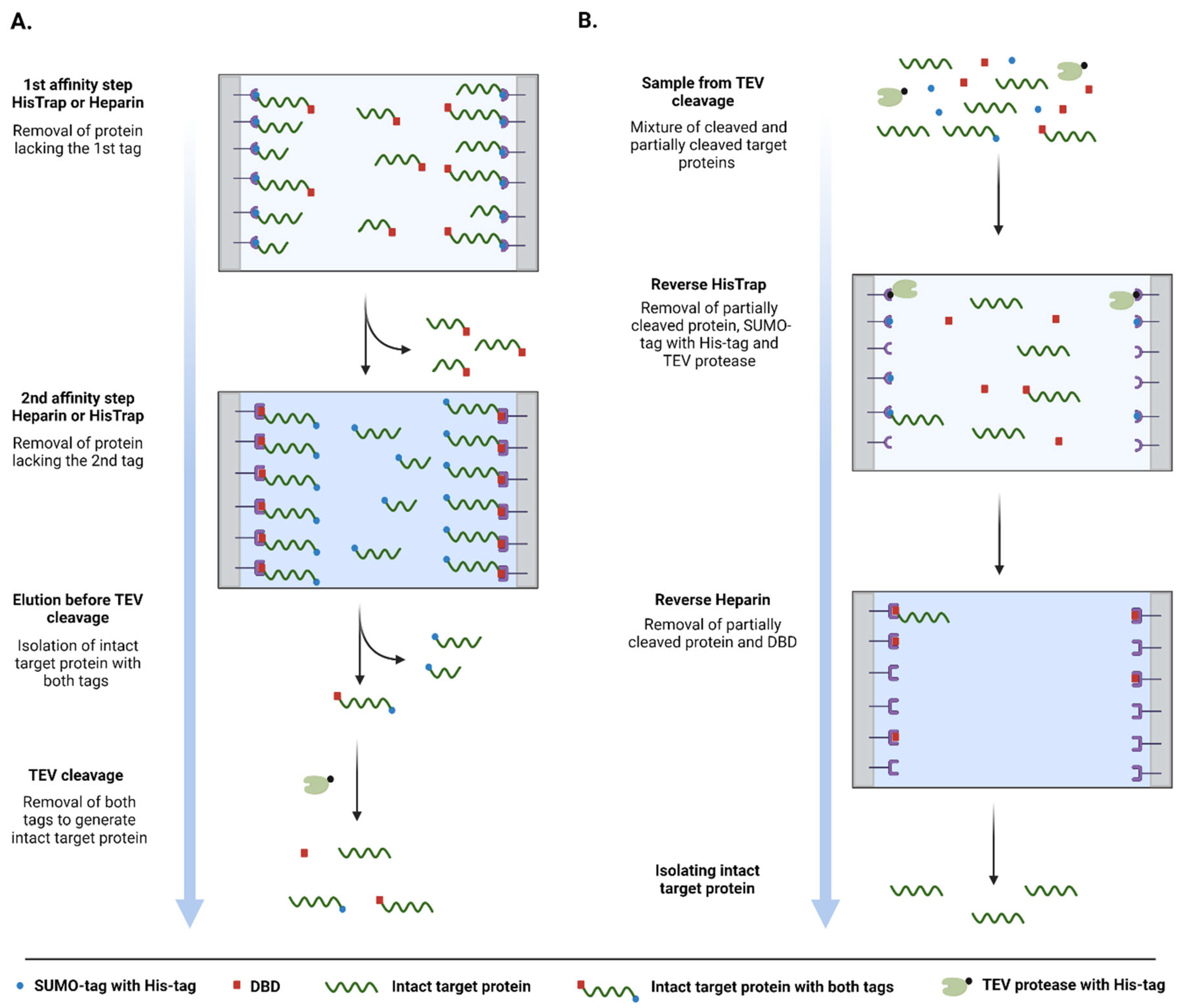
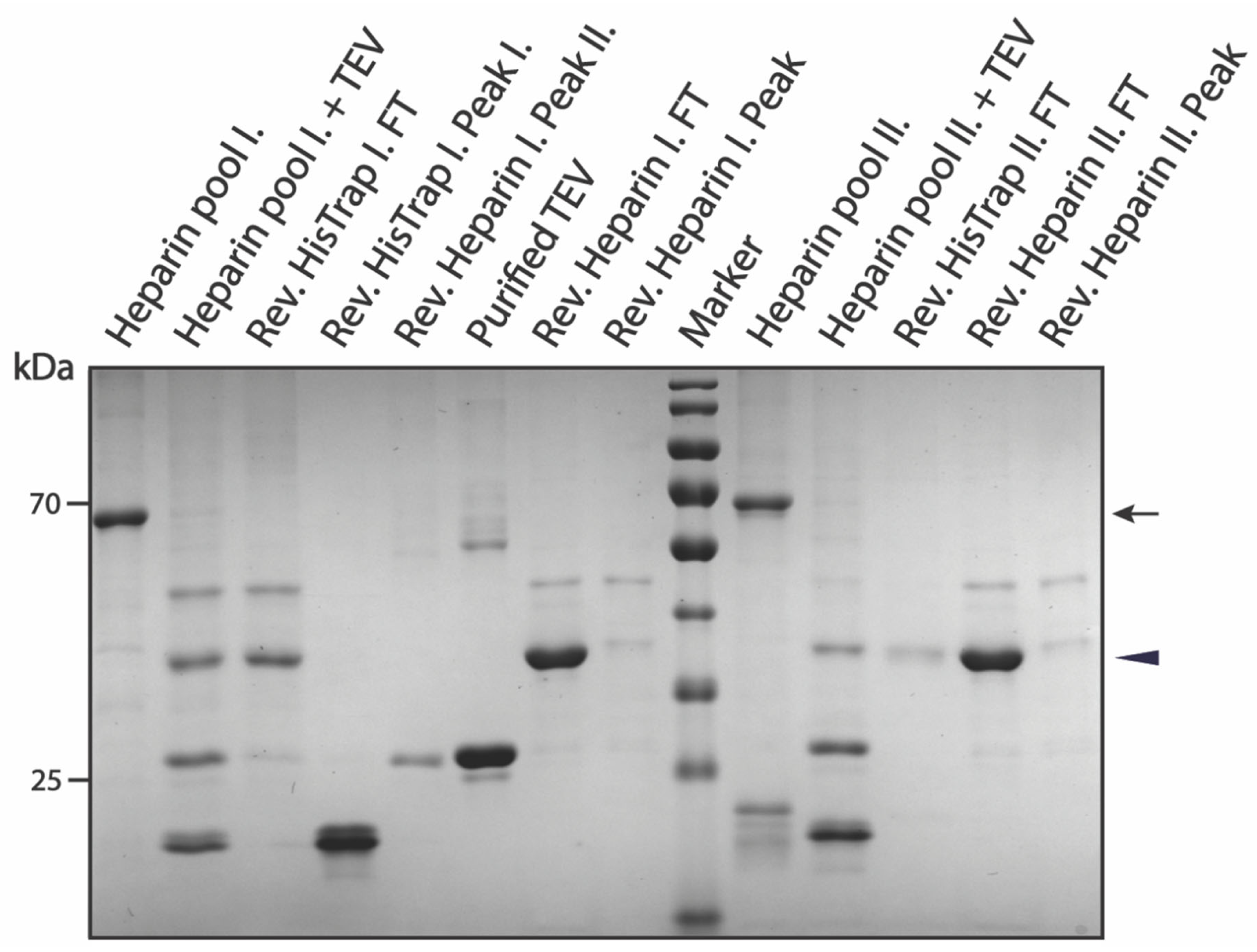
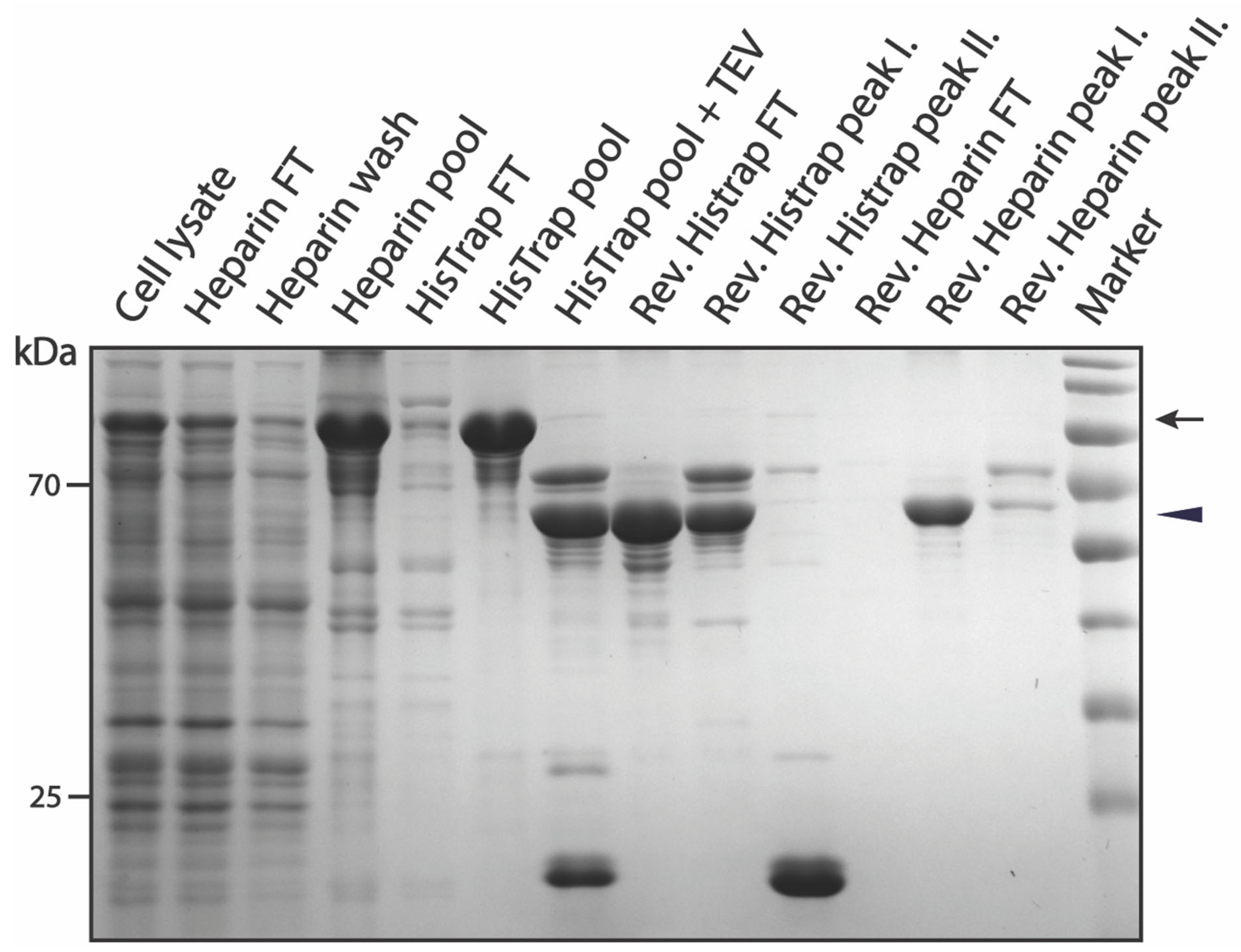
3.2. Purification of pSUMO-AF1 and pSUMO-AF1(Only N-tag): Comparison of the Two Methods
3.3. Purification of pSUMO-Tau Constructs
3.3.1. Purification of pSUMO-Tau-441
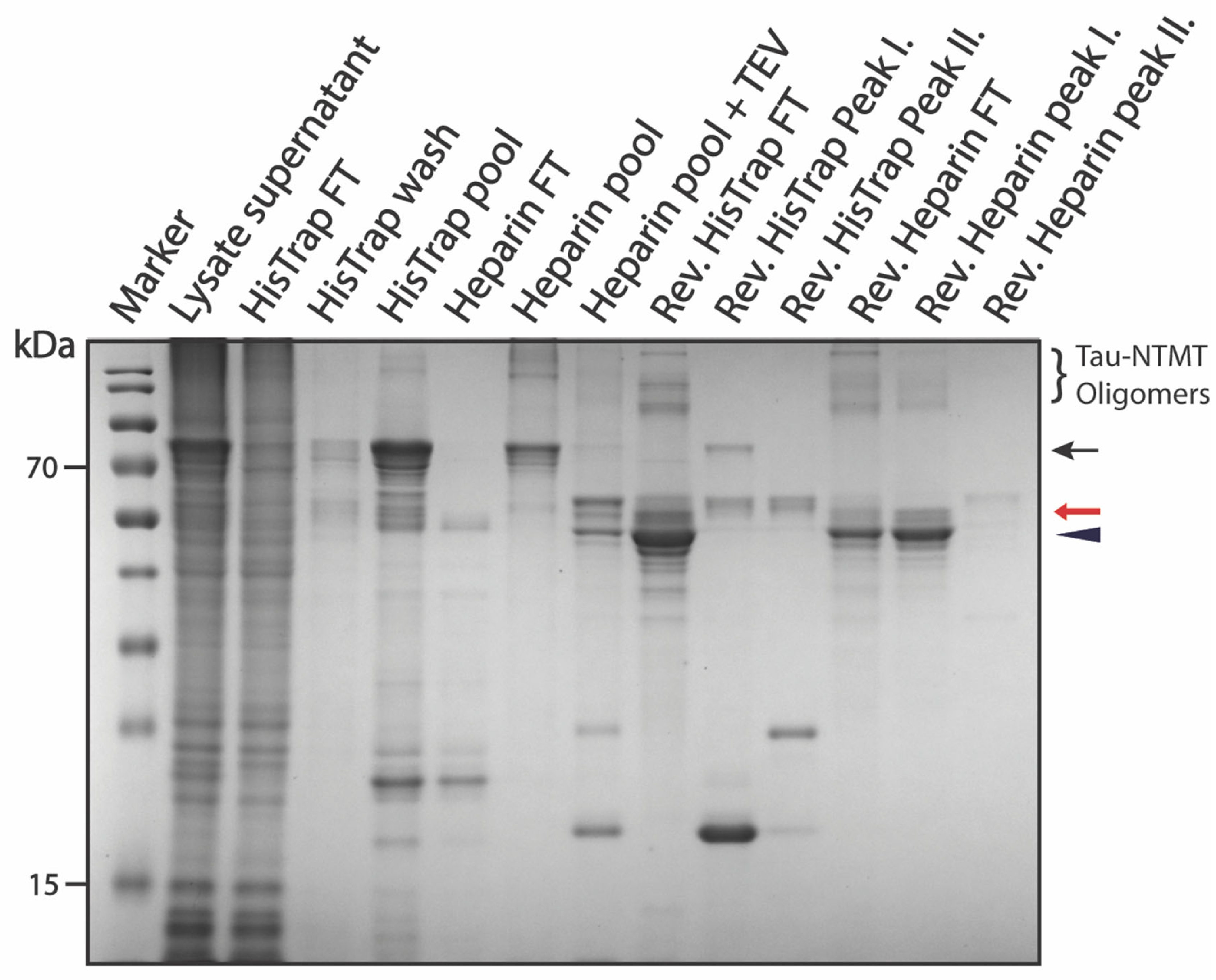
3.3.2. Purification of pSUMO-Tau-NTMT
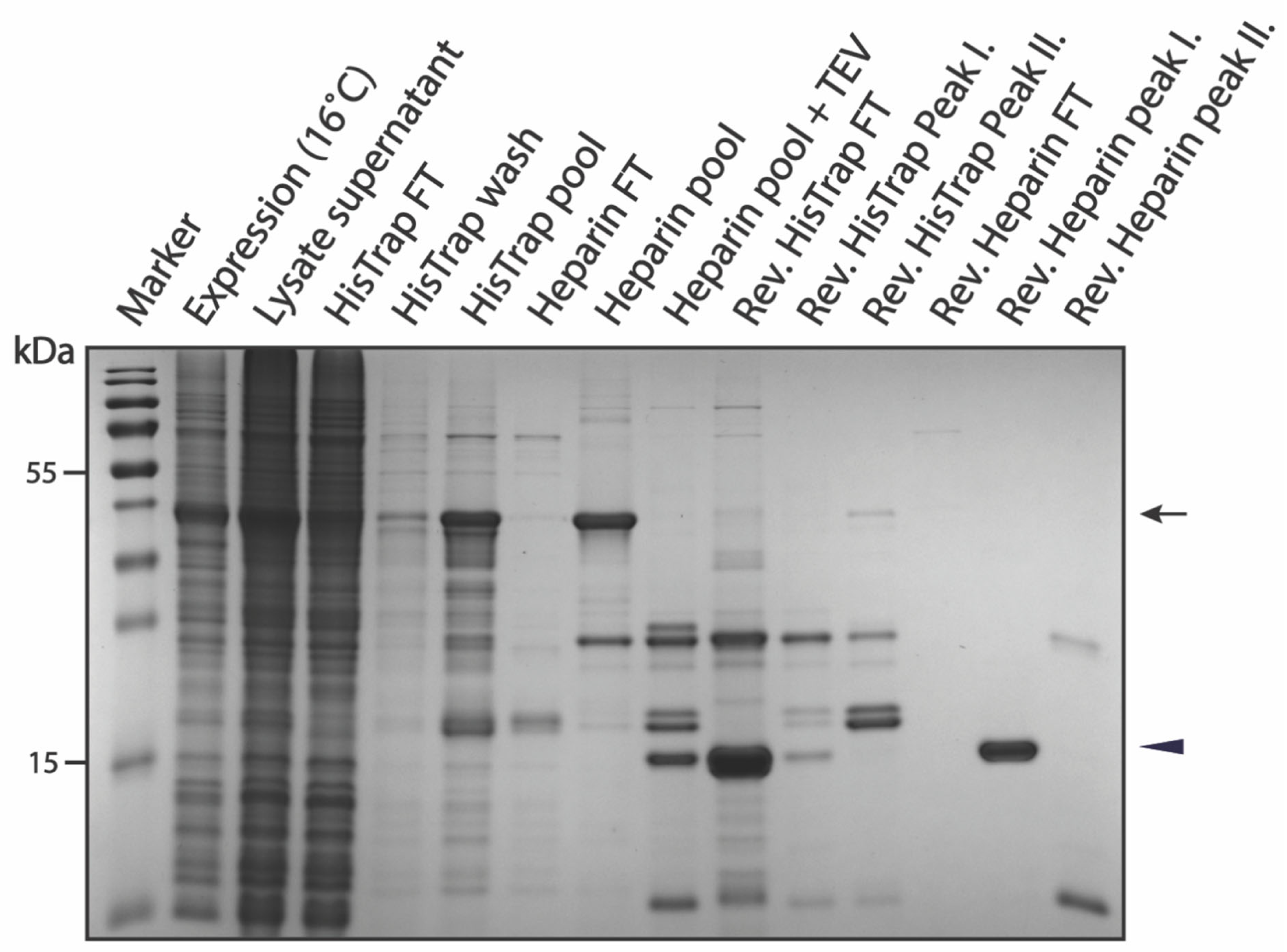
3.3.3. Purification of pSUMO-Tau-MTBR
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wingfield, P.T. Overview of the Purification of Recombinant Proteins. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2015, 80, 6.1.1–6.1.35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, G. Biopharmaceutical Benchmarks 2018. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Bigelow, L.; Borovilos, M.; Dementieva, I.; Duggan, E.; Eschenfeldt, W.; Hatzos, C.; Joachimiak, G.; Li, H.; Maltseva, N.; et al. Chapter 3. High-Throughput Protein Purification for X-Ray Crystallography and NMR. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2008, 75, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.M.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Christendat, D.; Dharamsi, A.; Friesen, J.D.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Vedadi, M. Protein Production: Feeding the Crystallographers and NMR Spectroscopists. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hura, G.L.; Menon, A.L.; Hammel, M.; Rambo, R.P.; Poole, F.L., 2nd; Tsutakawa, S.E.; Jenney, F.E., Jr.; Classen, S.; Frankel, K.A.; Hopkins, R.C.; et al. Robust, High-Throughput Solution Structural Analyses by Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS). Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, H.; Chari, A. Sample Preparation of Biological Macromolecular Assemblies for the Determination of High-Resolution Structures by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Microscopy 2016, 65, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Commonly Used Tag Combinations for Tandem Affinity Purification. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2010, 55, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.G.M.; Skerra, A. The Strep-Tag System for One-Step Purification and High-Affinity Detection or Capturing of Proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronqvist, N.; Sarr, M.; Lindqvist, A.; Nordling, K.; Otikovs, M.; Venturi, L.; Pioselli, B.; Purhonen, P.; Landreh, M.; Biverstål, H.; et al. Efficient Protein Production Inspired by How Spiders Make Silk. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.K.; Shrivastava, A. Recent Developments in Bioprocessing of Recombinant Proteins: Expression Hosts and Process Development. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Vaishnav, P. Production of Recombinant Proteins by Microbes and Higher Organisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrio, J.-L.; Demain, A.L. Recombinant Organisms for Production of Industrial Products. Bioeng. Bugs 2010, 1, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, P. Advanced Technologies for Improved Expression of Recombinant Proteins in Bacteria: Perspectives and Applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Domingo-Espín, J.; Corchero, J.L.; Vázquez, E.; Villaverde, A. Microbial Factories for Recombinant Pharmaceuticals. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, U.; Wilke, K.; Bramhill, D.; Schromm, A.B.; Lindner, B.; Kohl, T.A.; Corchero, J.L.; Villaverde, A.; Schaffer, L.; Head, S.R.; et al. Detoxifying Escherichia coli for Endotoxin-Free Production of Recombinant Proteins. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrió, M.M.; Villaverde, A. Protein Aggregation as Bacterial Inclusion Bodies Is Reversible. FEBS Lett. 2001, 489, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrió, M.M.; Villaverde, A. Construction and Deconstruction of Bacterial Inclusion Bodies. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 96, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, B.; Gerszberg, A.; Hnatuszko-Konka, K. A Brief Reminder of Systems of Production and Chromatography-Based Recovery of Recombinant Protein Biopharmaceuticals. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4216060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E.; Krivoruchko, A.; Nielsen, J. Industrial Systems Biology and Its Impact on Synthetic Biology of Yeast Cell Factories. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, E.A.; Abbott, W.M. Expression of Recombinant Proteins in Insect and Mammalian Cells. Methods 2018, 147, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puetz, J.; Wurm, F.M. Recombinant Proteins for Industrial versus Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Review of Process and Pricing. Processes 2019, 7, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, F.; Tozawa, Y. Cell-Free Expression--Making a Mark. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, A.D.; Karim, A.S.; Jewett, M.C. Cell-Free Gene Expression: An Expanded Repertoire of Applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant Protein Expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezonov, G.; Joseleau-Petit, D.; D’Ari, R. Escherichia coli Physiology in Luria-Bertani Broth. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8746–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahdev, S.; Khattar, S.K.; Saini, K.S. Production of Active Eukaryotic Proteins through Bacterial Expression Systems: A Review of the Existing Biotechnology Strategies. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 307, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, G.J.; Kumar, A. Strategies for the Production of Recombinant Protein in Escherichia coli. Protein J. 2013, 32, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Morales, E.S.; Ceccarelli, E.A. New Tools for Recombinant Protein Production in Escherichia coli: A 5-Year Update. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, F.; Yang, Z.; Gao, D.; Zhang, C.; Ma, L.; Yu, X. Soluble Expression of Single-Chain Variable Fragment (scFv) in Escherichia coli Using Superfolder Green Fluorescent Protein as Fusion Partner. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6071–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, V.; Falcone, F.H. Polyionic Tags as Enhancers of Protein Solubility in Recombinant Protein Expression. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A. Protocol for Preparing Proteins with Improved Solubility by Co-Expressing with Molecular Chaperones in Escherichia coli. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2632–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.H. An Intrinsically Disordered Peptide Tag That Confers an Unusual Solubility to Aggregation-Prone Proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0009722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Dangi, A.K.; Smita, M.; Dwivedi, S.; Shukla, P. Effectual Bioprocess Development for Protein Production. In Applied Microbiology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 203–227. ISBN 9780128154076. [Google Scholar]
- Wacker, M.; Linton, D.; Hitchen, P.G.; Nita-Lazar, M.; Haslam, S.M.; North, S.J.; Panico, M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Wren, B.W.; et al. N-Linked Glycosylation in Campylobacter Jejuni and Its Functional Transfer into E. coli. Science 2002, 298, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama-Rincon, J.D.; Fisher, A.C.; Merritt, J.H.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Reading, C.A.; Chhiba, K.; Heiss, C.; Azadi, P.; Aebi, M.; DeLisa, M.P. An Engineered Eukaryotic Protein Glycosylation Pathway in Escherichia coli. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, P. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: A 10-Year Recap. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Introduction to Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs). Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6557–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskiewicz, M.J.; Sussman, J.L.; Silman, I.; Shaul, Y. Context-Dependent Resistance to Proteolysis of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarberg, B.; Nygren, P.A.; Holmgren, E.; Elmblad, A.; Tally, M.; Hellman, U.; Moks, T.; Uhlén, M. Dual Affinity Fusion Approach and Its Use to Express Recombinant Human Insulin-like Growth Factor II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4367–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, J.; Zhou, L.; Verstreken, A.P. Purification of Soluble Recombinant Human Tau Protein from Bacteria Using Double-Tag Affinity Purification. Bio. Protoc. 2018, 8, e3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, C.; Prieto, D.; Abreu, C.; Oppezzo, P.; Correa, A. Multi-Compartment and Multi-Host Vector Suite for Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekesi, A.; Abdellaoui, S.; Holroyd, N.; Van Delm, W.; Pardon, E.; Pauwels, J.; Gevaert, K.; Steyaert, J.; Derveaux, S.; Borysik, A.; et al. Challenges in the Structural-Functional Characterization of Multidomain, Partially Disordered Proteins CBP and p300: Preparing Native Proteins and Developing Nanobody Tools. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 611, 607–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Qu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Huang, C. Sandwiched-Fusion Strategy Facilitates Recombinant Production of Small Labile Proteins. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhauer, A.; Jungbauer, A. The FLAG Peptide, a Versatile Fusion Tag for the Purification of Recombinant Proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, F.; Ciragan, A.; Iwaï, H. Tandem SUMO Fusion Vectors for Improving Soluble Protein Expression and Purification. Protein Expr. Purif. 2015, 116, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.L.; Britton, Z.T.; Robinson, A.S. Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification: A Comprehensive Review of Affinity Tags and Microbial Applications. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri, A.; Balza, E.; Carnemolla, B.; Castellani, P.; Borsi, L.; Zardi, L. DNA-Binding Domains of Human Plasma Fibronectin. pH and Calcium Ion Modulation of Fibronectin Binding to DNA and Heparin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 154, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolten, S.N.; Rinas, U.; Scheper, T. Heparin: Role in Protein Purification and Substitution with Animal-Component Free Material. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8647–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staby, A.; Sand, M.-B.; Hansen, R.G.; Jacobsen, J.H.; Andersen, L.A.; Gerstenberg, M.; Bruus, U.K.; Jensen, I.H. Comparison of Chromatographic Ion-Exchange Resins IV. Strong and Weak Cation-Exchange Resins and Heparin Resins. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1069, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An Illustrator for the Presentation and Visualization of Biological Sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, R.A.; Grossmann, M. Androgen Receptor Structure, Function and Biology: From Bench to Bedside. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan, A.E.; McEwan, I.J. A Sting in the Tail: The N-Terminal Domain of the Androgen Receptor as a Drug Target. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 687–694. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, J.; Kelly, S.M.; Watt, K.; Price, N.C.; McEwan, I.J. Conformational Analysis of the Androgen Receptor Amino-Terminal Domain Involved in Transactivation. Influence of Structure-Stabilizing Solutes and Protein-Protein Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20079–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.-X. Tau and Neurodegenerative Disease: The Story so Far. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukrasch, M.D.; Bibow, S.; Korukottu, J.; Jeganathan, S.; Biernat, J.; Griesinger, C.; Mandelkow, E.; Zweckstetter, M. Structural Polymorphism of 441-Residue Tau at Single Residue Resolution. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, N.M.; Hamel, C.; Grabinski, T.; Combs, B. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Induces Pathogenic Tau Conformations in vitro. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, S.; Eftekharzadeh, B.; Tepper, K.; Zoltowska, K.M.; Bennett, R.E.; Dujardin, S.; Laskowski, P.R.; MacKenzie, D.; Kamath, T.; Commins, C.; et al. Tau Protein Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Can Initiate Tau Aggregation. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e98049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, J.; Exner, C.; Franck, M.; Dominguez-Baquero, A.; Diez, L.; Brognaro, H.; Kraushar, M.L.; Mielke, T.; Radbruch, H.; Kaniyappan, S.; et al. Molecular Crowding and RNA Synergize to Promote Phase Separation, Microtubule Interaction, and Seeding of Tau Condensates. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeda, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Almeida, O.F.X.; Sumioka, A.; Maeda, S.; Osada, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Saito, A.; Miyasaka, T.; Kimura, T.; et al. Toxic Tau Oligomer Formation Blocked by Capping of Cysteine Residues with 1,2-Dihydroxybenzene Groups. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.L.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Aloe, S.; Bechberger, K.; König, S.; Morfini, G.; Brady, S.T. Defined Tau Phosphospecies Differentially Inhibit Fast Axonal Transport Through Activation of Two Independent Signaling Pathways. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 610037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramani, A.; Panda, D. Regulation of Neuronal Microtubule Dynamics by Tau: Implications for Tauopathies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, P.; Zejneli, O.; Martinho, M.; Lasorsa, A.; Belle, V.; Smet-Nocca, C.; Tsvetkov, P.O.; Devred, F.; Landrieu, I. Role of Tau as a Microtubule-Associated Protein: Structural and Functional Aspects. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadavath, H.; Hofele, R.V.; Biernat, J.; Kumar, S.; Tepper, K.; Urlaub, H.; Mandelkow, E.; Zweckstetter, M. Tau Stabilizes Microtubules by Binding at the Interface between Tubulin Heterodimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7501–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frappier, T.F.; Georgieff, I.S.; Brown, K.; Shelanski, M.L. Tau Regulation of Microtubule-Microtubule Spacing and Bundling. J. Neurochem. 1994, 63, 2288–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulisano, W.; Maugeri, D.; Baltrons, M.A.; Fà, M.; Amato, A.; Palmeri, A.; D’Adamio, L.; Grassi, C.; Devanand, D.P.; Honig, L.S.; et al. Role of Amyloid-β and Tau Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease: Confuting the Amyloid Cascade. J. Alzheimers’s Dis. 2018, 64, S611–S631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bergen, M.; Barghorn, S.; Li, L.; Marx, A.; Biernat, J.; Mandelkow, E.M.; Mandelkow, E. Mutations of Tau Protein in Frontotemporal Dementia Promote Aggregation of Paired Helical Filaments by Enhancing Local Beta-Structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48165–48174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-C.; Nana, A.L.; Hepker, M.; Hwang, J.-H.L.; Gaus, S.E.; Spina, S.; Cosme, C.G.; Gan, L.; Grinberg, L.T.; Geschwind, D.H.; et al. Preferential Tau Aggregation in von Economo Neurons and Fork Cells in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration with Specific MAPT Variants. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, F.; Tira, R.; Barracchia, C.G.; Munari, F.; Capaldi, S.; D’Onofrio, M.; Assfalg, M. Ubiquitination of Alzheimer’s-Related Tau Protein Affects Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in a Site- and Cofactor-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Rüdiger, S.G.D. Recombinant Production and Purification of the Human Protein Tau. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2018, 31, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghorn, S.; Biernat, J.; Mandelkow, E. Purification of Recombinant Tau Protein and Preparation of Alzheimer-Paired Helical Filaments in Vitro. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 299, 35–51. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mészáros, A.; Muwonge, K.; Janvier, S.; Ahmed, J.; Tompa, P. A Novel Tandem-Tag Purification Strategy for Challenging Disordered Proteins. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111566
Mészáros A, Muwonge K, Janvier S, Ahmed J, Tompa P. A Novel Tandem-Tag Purification Strategy for Challenging Disordered Proteins. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111566
Chicago/Turabian StyleMészáros, Attila, Kevin Muwonge, Steven Janvier, Junaid Ahmed, and Peter Tompa. 2022. "A Novel Tandem-Tag Purification Strategy for Challenging Disordered Proteins" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111566
APA StyleMészáros, A., Muwonge, K., Janvier, S., Ahmed, J., & Tompa, P. (2022). A Novel Tandem-Tag Purification Strategy for Challenging Disordered Proteins. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111566









