Bisphenol a Exposure and Kidney Diseases: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and NHANES 03–16 Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
- Original data (excluding bibliographic reviews) accepted and published.
- Studies in human populations (adults or children).
- Quantification of BPA in urine or serum and its correlation with any predisposition or susceptibility marker of kidney damage or disease.
- Studies published in English.
2.3. Data Collection and Quality Assessment
2.4. Analytical Method
2.4.1. BPA in Blood
2.4.2. BPA in Urine
2.5. Study of the NHANES 03-16 Cohort
3. Results
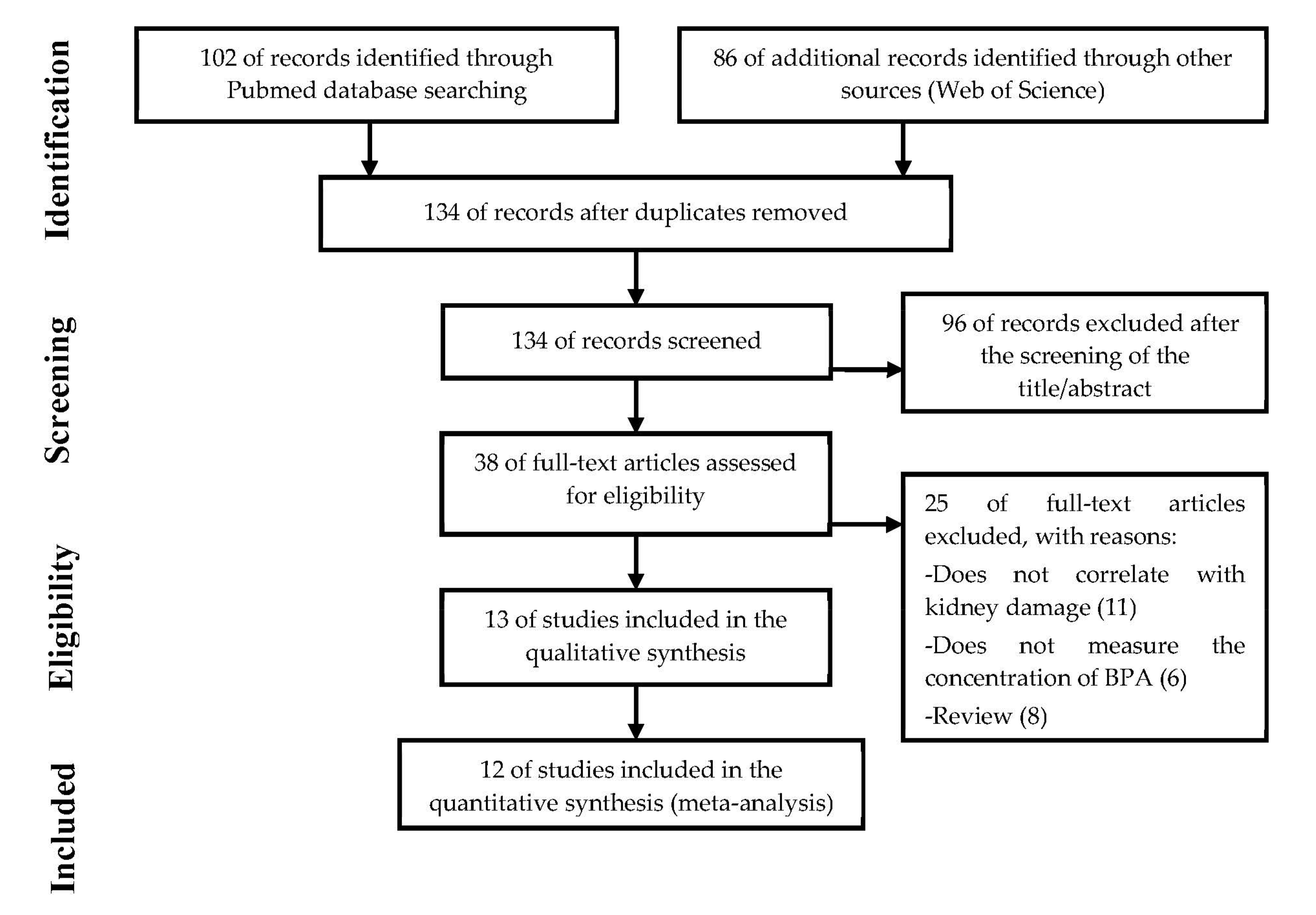
3.1. Selection of Academic Articles
3.2. Study Characteristics
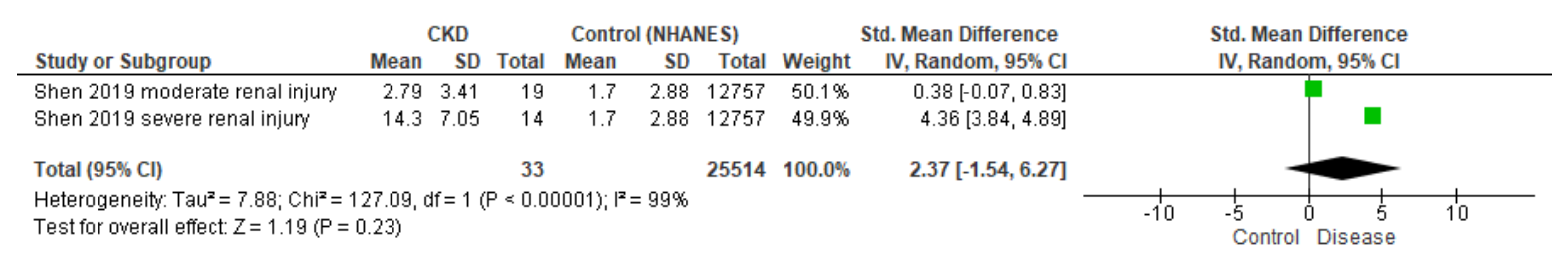
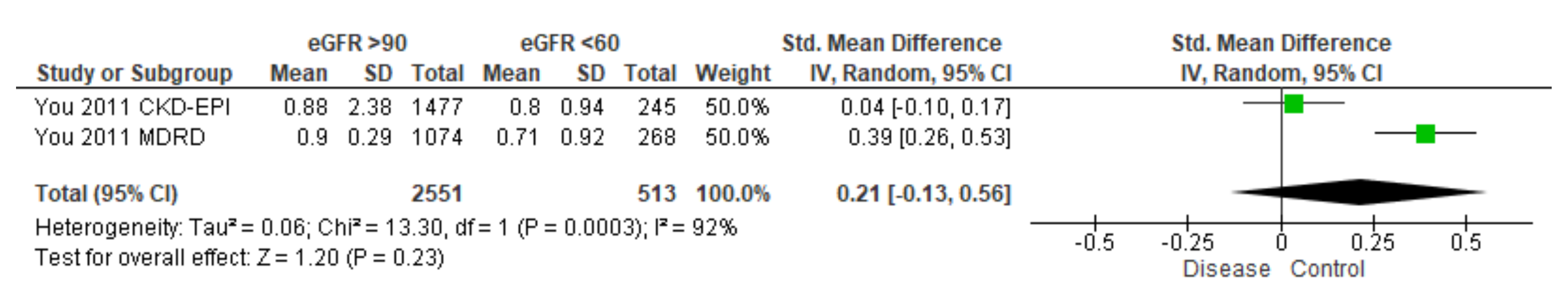
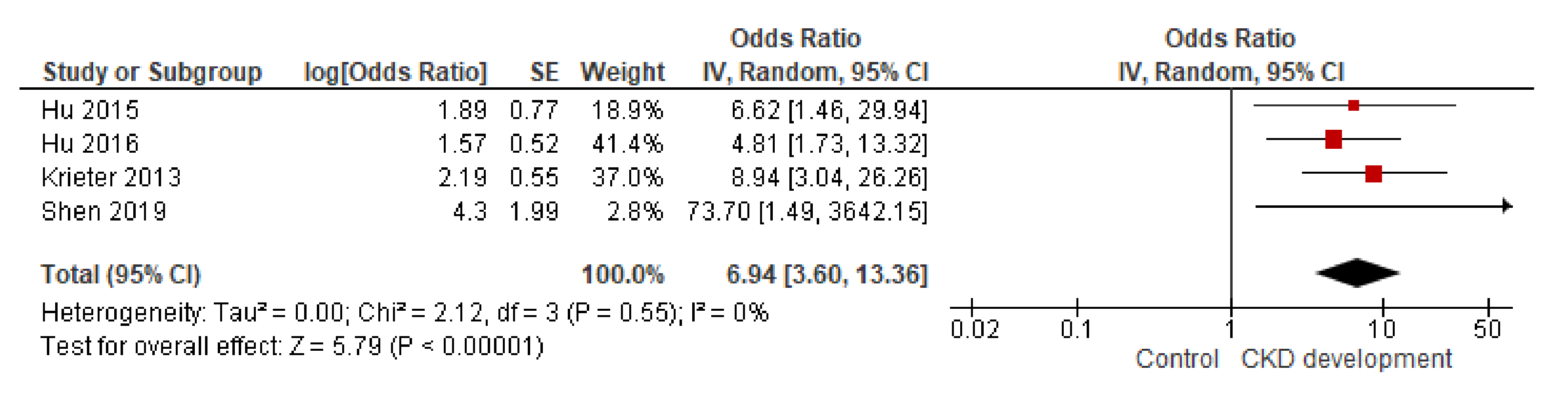
3.3. Meta-Analysis
3.3.1. BPA in Blood
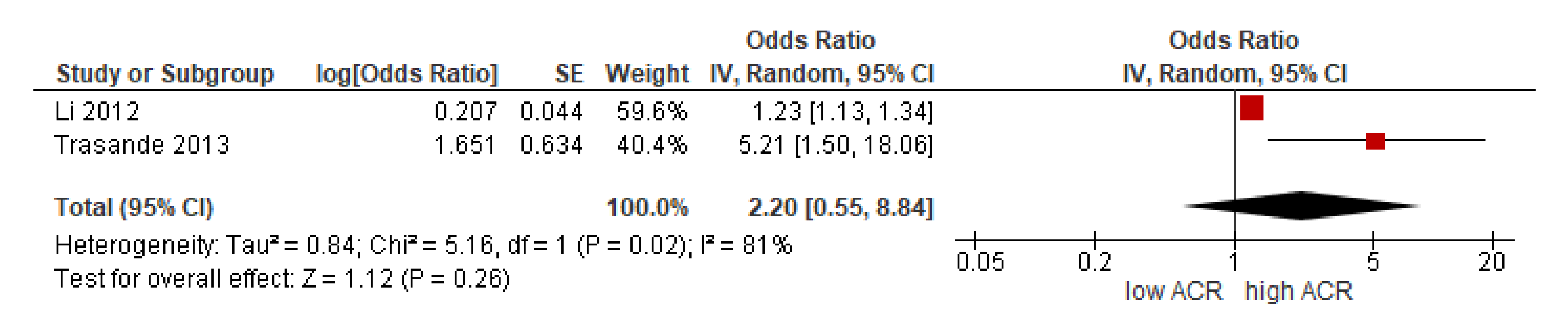
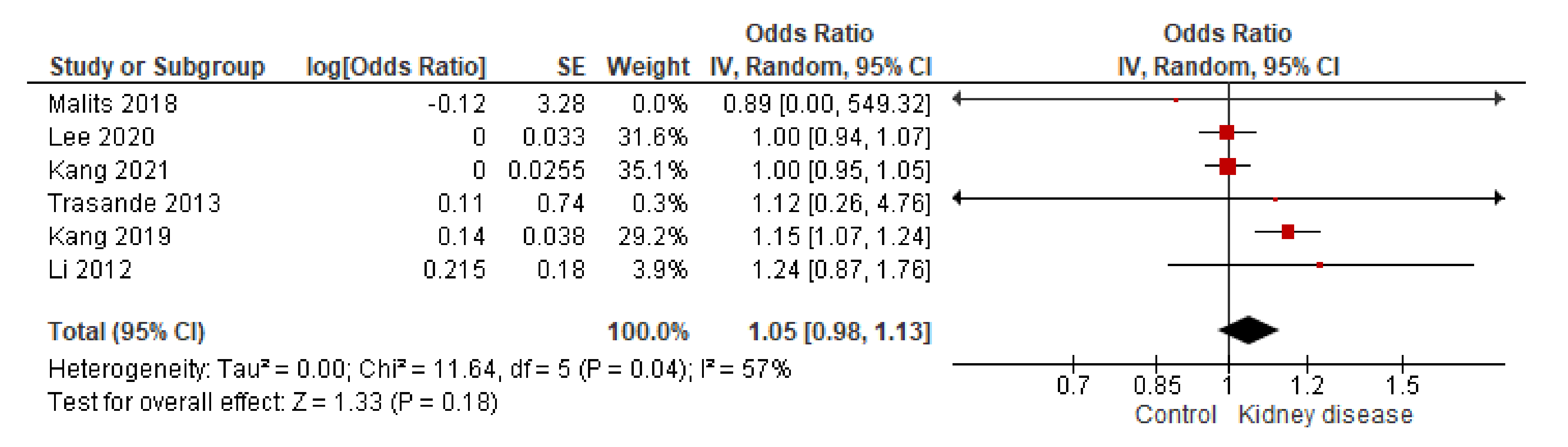
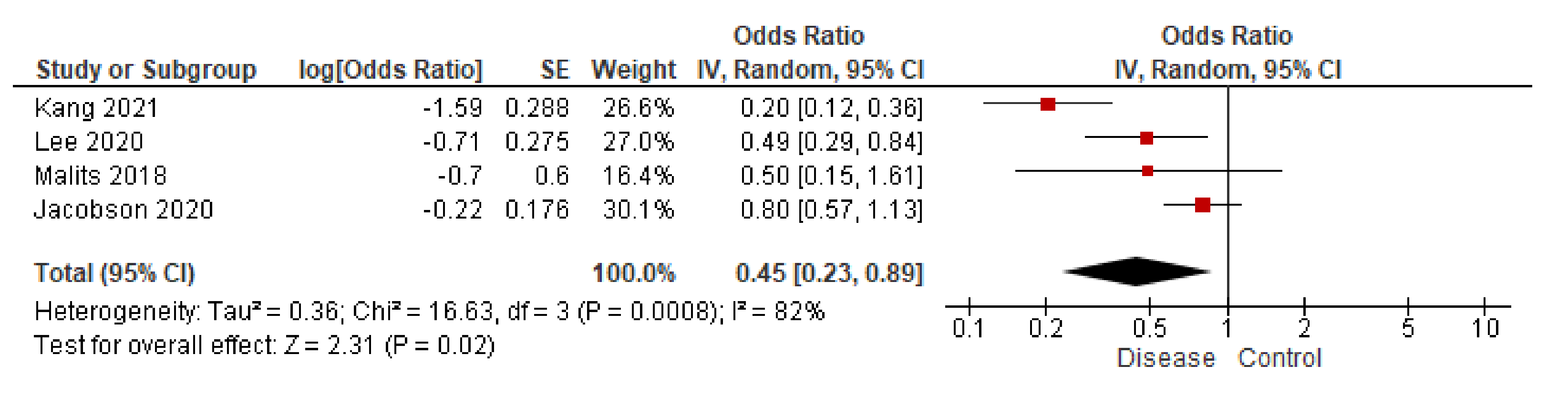
3.3.2. BPA in Urine
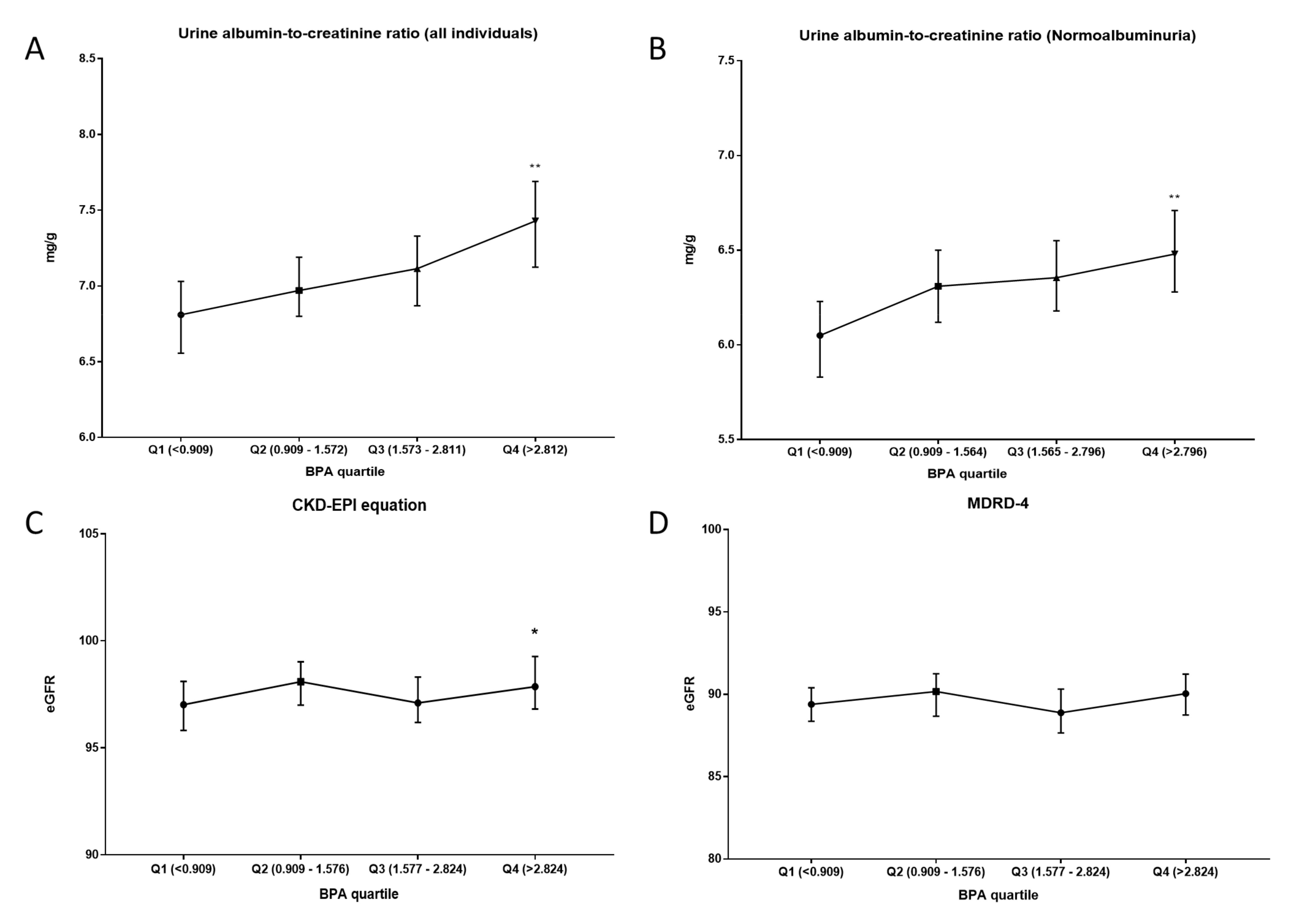
3.4. NHANES 03-16 Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Despite the importance of the BPA-kidney paradigm in the context of human exposure, few works explore the issue.
- In the study of blood BPA and kidney disease, solid evidence correlates high concentrations of BPA in the blood with a greater predisposition to develop kidney disease, at least under pathological conditions.
- In the study of the ACR and urinary BPA, a positive relationship was observed in healthy subjects. The same trend was observed in the NHANES cohort. Similarly, subjects with low-grade albuminuria showed a significant increase in urinary BPA.
- Despite inconsistencies observed in urinary BPA concentration from patients with kidney disease, statistical correlations with eGFR support an important relationship between BPA and glomerular filtration.
- The results, consistent with the experimental models, show interesting evidence that positions BPA as a possible environmental factor inducing kidney damage.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Handbook of Engineering and Specialty Thermoplastics, Volume 3: Polyethers and Polyesters; Thomas, S.; Visakh, P. (Eds.) Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-0-470-63926-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, S.A. The politics of plastics: The making and unmaking of bisphenol a “safety”. Am. J. Public Health 2009, 99 (Suppl. 3), S559–S566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2016, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisch, A.F.; Sheffield, P.E.; Chinn, C.; Edelstein, B.L.; Landrigan, P.J. Bisphenol A and related compounds in dental materials. Pediatrics 2010, 126, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyl, R.W.; Myers, C.B.; Marr, M.C.; Sloan, C.S.; Castillo, N.P.; Veselica, M.M.; Seely, J.C.; Dimond, S.S.; Van Miller, J.P.; Shiotsuka, R.N.; et al. Two-generation reproductive toxicity study of dietary bisphenol a in CD-1 (Swiss) mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 104, 362–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćwiek-Ludwicka, K. Bisphenol A (BPA) in food contact materials—New scientific opinion from EFSA regarding public health risk. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2015, 66, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch-Panadero, E.; Mas, S.; Civantos, E.; Abaigar, P.; Camarero, V.; Ruiz-Priego, A.; Ortiz, A.; Egido, J.; González-Parra, E.; Gonzalez-Parra, E. Bisphenol A is an exogenous toxin that promotes mitochondrial injury and death in tubular cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Yang, S.; Li, T.; Gao, R.; Hu, J.; Luo, T.; Qing, H.; Zhen, Q.; Hu, R.; Li, X.; et al. Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in chronic kidney injury induced by bisphenol-A. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 241, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Parra, E.; Herrero, J.A.; Elewa, U.; Bosch, R.J.; Arduán, A.O.; Egido, J.J.; Arduan, A.O.; Egido, J.J. Bisphenol A in chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Nephrol. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reventun, P.; Sanchez-Esteban, S.; Cook, A.; Cuadrado, I.; Roza, C.; Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Muñoz, C.; Zaragoza, C.; Bosch, R.J.; Saura, M. Bisphenol A induces coronary endothelial cell necroptosis by activating RIP3/CamKII dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea-Herrero, N.; Arenas, M.I.; Muñóz-Moreno, C.; Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; González-Santander, M.; Arribas, I.; Bosch, R.J.R.J.; Munoz-Moreno, C.; Moreno-Gomez-Toledano, R.; Gonzalez-Santander, M.; et al. Bisphenol-A Induces Podocytopathy With Proteinuria in Mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Arenas, M.I.; González-Martínez, C.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Reventún, P.; Di Nunzio, M.; Sánchez-Esteban, S.; Arilla-Ferreiro, E.; Saura, M.; Bosch, R.J. Bisphenol A impaired cell adhesion by altering the expression of adhesion and cytoskeleton proteins on human podocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomza-Marciniak, A.; Stępkowska, P.; Kuba, J.; Pilarczyk, B. Effect of bisphenol A on reproductive processes: A review of in vitro, in vivo and epidemiological studies. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 51–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv-Gal, A.; Flaws, J.A. Evidence for bisphenol A-induced female infertility: A review (2007–2016). Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 827–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pergialiotis, V.; Kotrogianni, P.; Christopoulos-Timogiannakis, E.; Koutaki, D.; Daskalakis, G.; Papantoniou, N. Bisphenol A and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review of the literature. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 3320–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Sabir, S.; Rehman, K. Bisphenol A-induced metabolic disorders: From exposure to mechanism of action. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provvisiero, D.P.; Pivonello, C.; Muscogiuri, G.; Negri, M.; de Angelis, C.; Simeoli, C.; Pivonello, R.; Colao, A. Influence of Bisphenol A on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Li, M.; Liu, A.; Wu, C.; Li, D.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Du, J.; Gao, X.; Hong, Y. Bisphenol A and the Risk of Obesity a Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence. Dose Response 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trasande, L.; Attina, T.M.; Trachtman, H. Bisphenol A exposure is associated with low-grade urinary albumin excretion in children of the United States. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Peng, C.; Gao, R.; Goswami, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, Q.; Cheng, Q.; et al. Serum bisphenol A as a predictor of chronic kidney disease progresion in primary hypertension: A 6-year prospective study. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bi, Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, T.; Xu, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Exposure to bisphenol A is associated with low-grade albuminuria in Chinese adults. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krieter, D.H.; Canaud, B.; Lemke, H.-D.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Morgenroth, A.; von Appen, K.; Dragoun, G.-P.P.; Wanner, C. Bisphenol A in Chronic Kidney Disease. Artif. Organs 2013, 37, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saura, M.; Marquez, S.; Reventun, P.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Arenas, M.I.M.I.; Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Gómez-Parrizas, M.; Muñóz-Moreno, C.; González-Santander, M.; Zaragoza, C.; et al. Oral administration of bisphenol A induces high blood pressure through angiotensin II/CaMKII-dependent uncoupling of eNOS. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4719–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Teppala, S. Urinary bisphenol A and hypertension in a multiethnic sample of US adults. J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 481641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Hong, Y.-C.C. Exposure to bisphenol a from drinking canned beverages increases blood pressure: Randomized crossover trial. Hypertension 2015, 65, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Sanders, A.P.; Saland, J.M.; Wright, R.O.; Arora, M. Environmental exposures and pediatric kidney function and disease: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Goswami, R.; Peng, C.; Gao, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Zhen, Q.; et al. Serum bisphenol A and progression of type 2 diabetic nephropathy: A 6-year prospective study. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 52, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhuang, F.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Bisphenol A analogs in patients with chronic kidney disease and dialysis therapy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro Cochrane Iberoamericano. Manual Cochrane de Revisiones Sistemáticas de Intervenciones versión 5.1.0. In Manual Cochrane de Revisiones Sistemáticas de Intervenciones Versión 5.1.0; Cochrane: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1–639. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, G.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.P.; Lee, J.; Park, H.; Moon, H.-B.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; et al. Urinary metabolites of dibutyl phthalate and benzophenone-3 are potential chemical risk factors of chronic kidney function markers among healthy women. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.; An, J.N.; Lee, J.; Park, H.; Jung, S.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.P.; Choi, K. Association of exposure to phthalates and environmental phenolics with markers of kidney function: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017. Environ. Int. 2020, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Lee, J.P.; Choi, K. Exposure to phthalates and environmental phenols in association with chronic kidney disease (CKD) among the general US population participating in multi-cycle NHANES (2005-2016). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhu, X.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Fan, H.; Chen, J.; Dong, J.; Hao, C.-M.M.; Dai, Q. Renal Function, Bisphenol A, and Alkylphenols: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2003–2006). Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malits, J.; Attina, T.M.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Naidu, M.; Furth, S.; Warady, B.A.; Vento, S.; Trachtman, H.; Trasande, L. Renal Function and exposure to Bisphenol A and phthalates in children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, M.; Attina, T.M.; Naidu, M.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.; Vento, S.; et al. Serially assessed bisphenol A and phthalate exposure and association with kidney function in children with chronic kidney disease in the US and Canada: A longitudinal cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Sánchez-Meca, J.; Marín-Martínez, F.; Botella, J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I 2 Index? Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michels, W.M.; Grootendorst, D.C.; Verduijn, M.; Elliott, E.G.; Dekker, F.W.; Krediet, R.T. Performance of the Cockcroft-Gault, MDRD, and new CKD-EPI formulas in relation to GFR, age, and body size. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poggio, E.D.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Van Lente, F.; Hall, P.M. Performance of the modification of diet in renal disease and Cockcroft-Gault equations in the estimation of GFR in health and in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; He, M. Associations of serum bisphenol A levels with incident chronic kidney disease risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zeeuw, D.; Parving, H.H.; Henning, R.H. Microalbuminuria as an early marker for cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Altman, D.; Antes, G.; Atkins, D.; Barbour, V.; Barrowman, N.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyzes: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.B. Concentrations of bisphenol A and its associations with urinary albumin creatinine ratios across the various stages of renal function. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9946–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Arenas, M.I.; Sánchez-Esteban, S.; Cook, A.; Saura, M.; Bosch, R.J. Critical Analysis of Human Exposure to Bisphenol a and its Novel Implications on Renal, Cardiovascular and Hypertensive Diseases. In Hot Topics in Endocrinology and Metabolism [Working Title]; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, S.; Egido, J.; González-Parra, E.; Mas, S.; Egido, J.; González-Parra, E. Importancia del bisfenol A, una toxina urémica de origen exógeno, en el paciente en hemodiálisis. Nefrologia 2017, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teeguarden, J.G.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Doerge, D.R.; Churchwell, M.I.; Gunawan, R.; Graham, M.K. Twenty-Four Hour Human Urine and Serum Profiles of Bisphenol A during High-Dietary Exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, E.B.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Slitt, A.L.; King, R. Bisphenol A sulfonation is impaired in metabolic and liver disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 292, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, K.; Gagne, M.; Nong, A.; Aylward, L.L.; Hays, S.M. Biomonitoring Equivalents for bisphenol A (BPA). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 58, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkel, W.; Colnot, T.; Csanady, G.A.; Filser, J.G.; Dekant, W.; Vokel, W.; Colnot, T.; Csanady, G.A.; Filser, J.G.; Dekant, W.; et al. Metabolism and kinetics of bisphenol a in humans at low doses following oral administration. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkel, W.; Bittner, N.; Dekant, W. Detection of bisphenol A in human urine by LC-MS/MS. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 197, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Doerge, D.R.; Twaddle, N.C.; Woodling, K.A.; Fisher, J.W. Pharmacokinetics of bisphenol A in neonatal and adult rhesus monkeys. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 248, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Yu, S.H.; Lee, C.B.; Park, Y.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, D.S. Effects of bisphenol A on cardiovascular disease: An epidemiological study using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2016 and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinodh Kumar, B.; Mohan, T. Retrospective comparison of estimated GFR using 2006 MDRD, 2009 CKD-EPI and cockcroft-gault with 24 hour urine creatinine clearance. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, BC09–BC12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N (%) | Age, Years | Urinary BPA, ng/mL | Urinary BPA, µg/g Creat. | MDRD-4 (eGFR) | CKD-EPI (eGFR) | Ratio alb./Creat. | Serum Creat., mg/dL | Serum Albumin, g/dL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 6238 (48.49%) | 47 (46–48) | 1.8 (1.7–1.9) | 1.4 (1.37–1.44) | 88.52 (87.92–89.12) | 95.25 (94.55–96.05) | 6.06 (5.9–6.21) | 0.98 (0.97–0.99) | 4.4 (4.4–4.4) |
| Female | 6519 (51.10%) | 46 (45–46) | 1.6 (1.5–1.6) | 1.75 (1.71–1.78) | 90.75 (89.88–91.57) | 99.94 (99.18–100.7) | 7.98 (7.78–8.15) | 0.73 (0.72–0.74) | 4.2 (4.2–4.2) |
| Total | 12757 (100%) | 46 (46–47) | 1.7 (1.6–1.7) | 1.57 (1.55–1.6) | 89.96 (88.97–90.21) | 97.48 (96.99–98.09) | 7.06 (6.95–7.18) | 0.85 (0.84–0.85) | 4.3 (4.3–4.3) |
| p-value | 0.0642 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Group | Urinary BPA, µg/g Creatinine | n | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney disease | 1.784 (1.5–2) | 320 | 0.016 |
| The rest of the cohort | 1.563 (1.538–1.591) | 11,572 | |
| Dialysis treatment | 2.9 (1.744–3.75) | 24 | 0.031 |
| Non-dialysis kidney patient | 1.677 (1.458–1.942) | 296 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Arenas, M.I.; Vélez-Vélez, E.; Coll, E.; Quiroga, B.; Bover, J.; Bosch, R.J. Bisphenol a Exposure and Kidney Diseases: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and NHANES 03–16 Study. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11071046
Moreno-Gómez-Toledano R, Arenas MI, Vélez-Vélez E, Coll E, Quiroga B, Bover J, Bosch RJ. Bisphenol a Exposure and Kidney Diseases: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and NHANES 03–16 Study. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(7):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11071046
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno-Gómez-Toledano, Rafael, María I. Arenas, Esperanza Vélez-Vélez, Elisabeth Coll, Borja Quiroga, Jordi Bover, and Ricardo J. Bosch. 2021. "Bisphenol a Exposure and Kidney Diseases: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and NHANES 03–16 Study" Biomolecules 11, no. 7: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11071046
APA StyleMoreno-Gómez-Toledano, R., Arenas, M. I., Vélez-Vélez, E., Coll, E., Quiroga, B., Bover, J., & Bosch, R. J. (2021). Bisphenol a Exposure and Kidney Diseases: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and NHANES 03–16 Study. Biomolecules, 11(7), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11071046







