D-Aspartate Upregulates DAAM1 Protein Levels in the Rat Testis and Induces Its Localization in Spermatogonia Nucleus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experiments
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. Preparation of Total Protein Extracts from Rat Testis and GC-1 Cells and Western Blotting Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Nuclear Protein Extracts from Rat Testis and Western Blotting Analysis
2.5. Immunofluorescence Analysis on Rat Testis
2.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis on GC-1
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
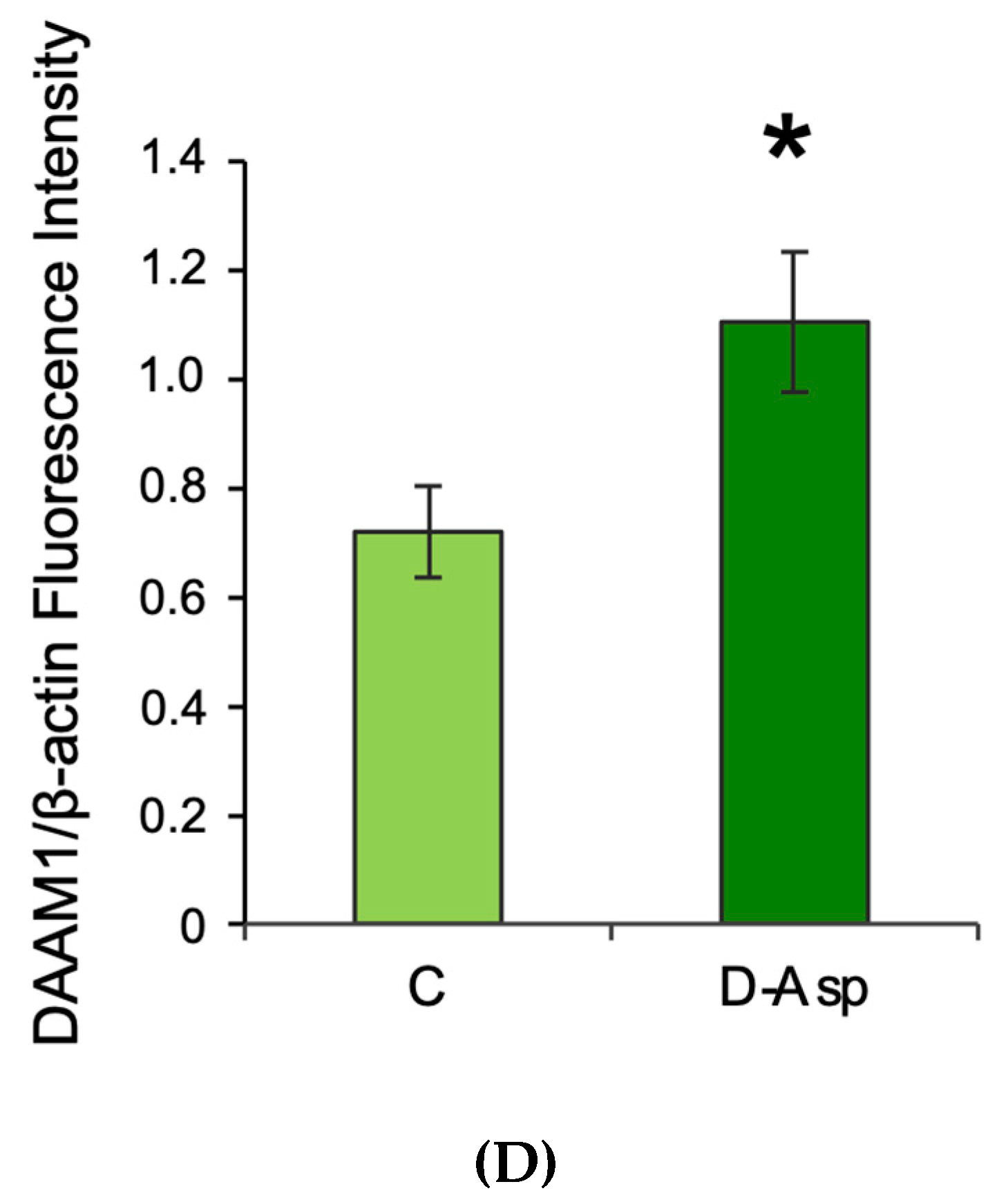
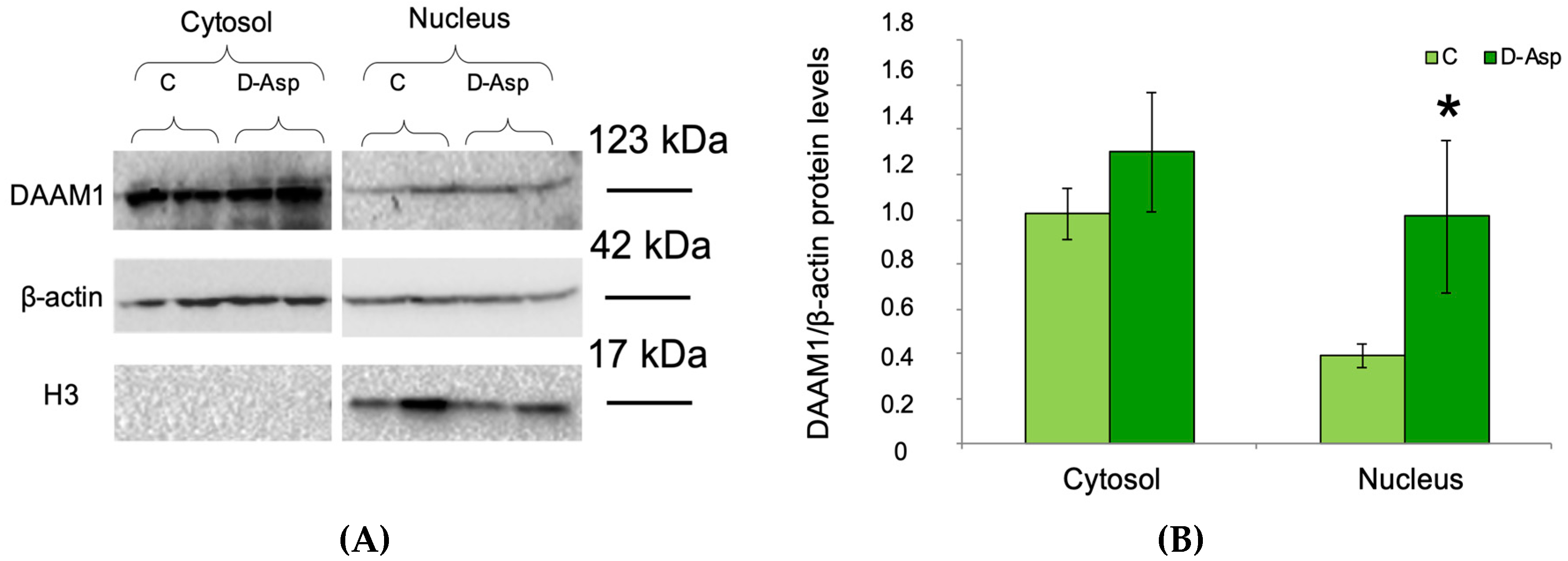
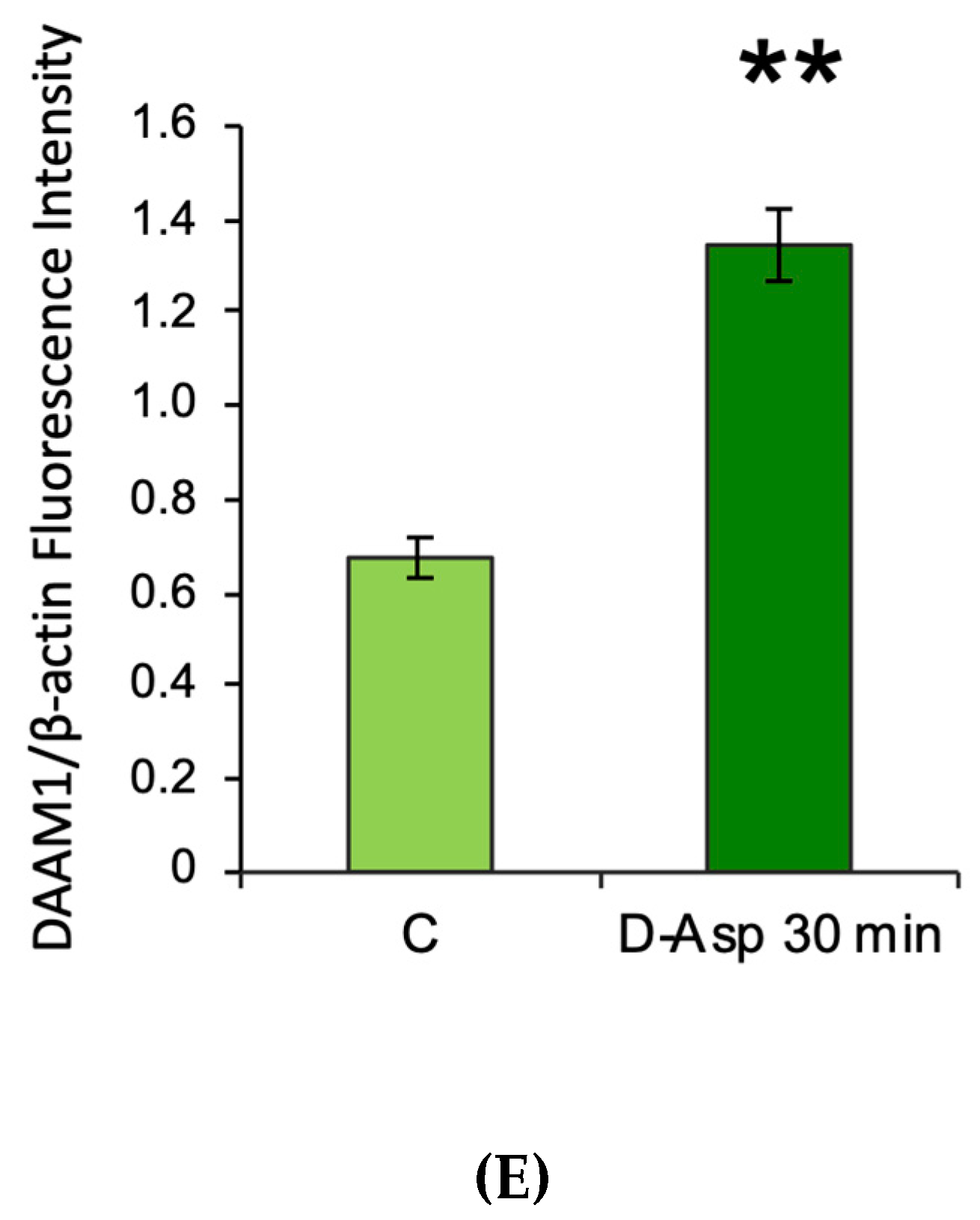
3.1. Effects of Oral Administration of D-Asp on Testicular DAAM1 Protein Levels and Localization
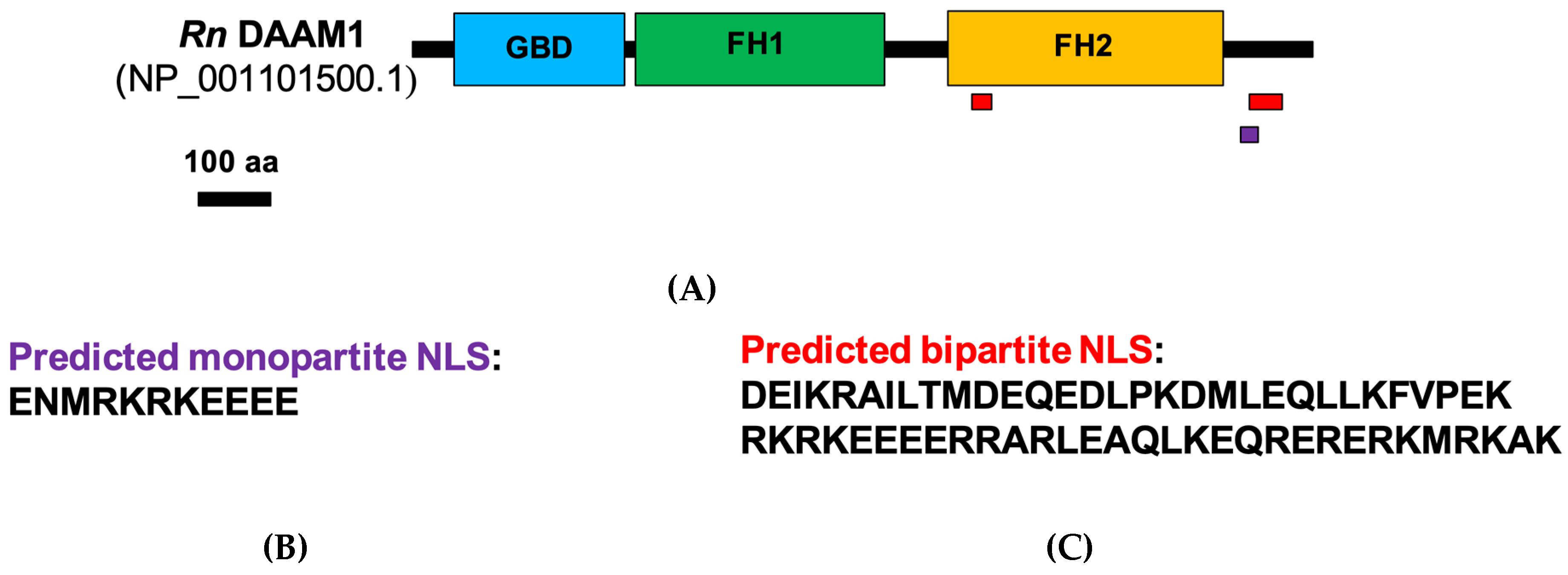
3.2. DAAM1 Nuclear Localization: Bioinformatics and Biochemical Analysis
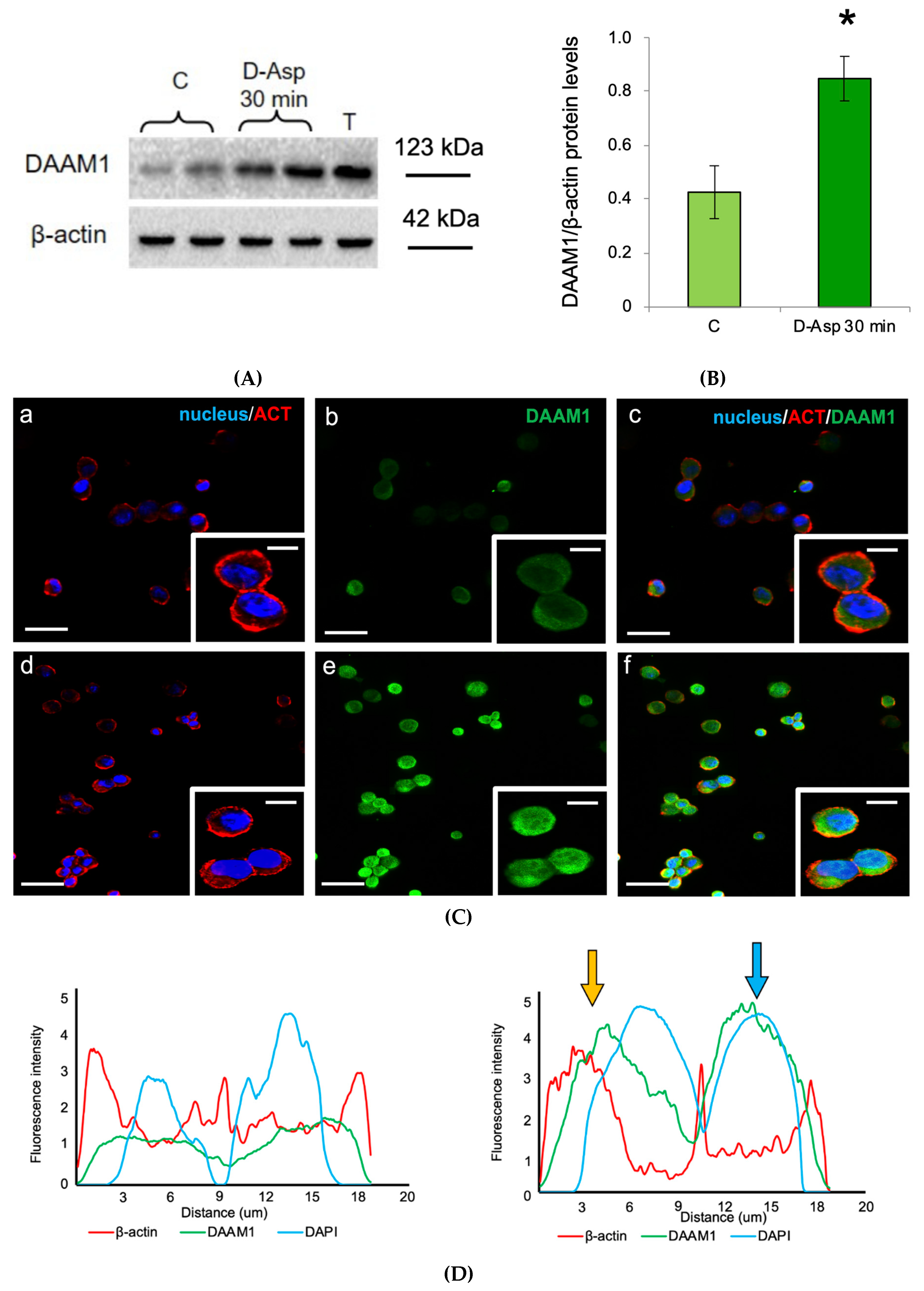
3.3. Effects of D-Asp on DAAM1 Protein Levels and Localization in Mouse GC-1 Cells
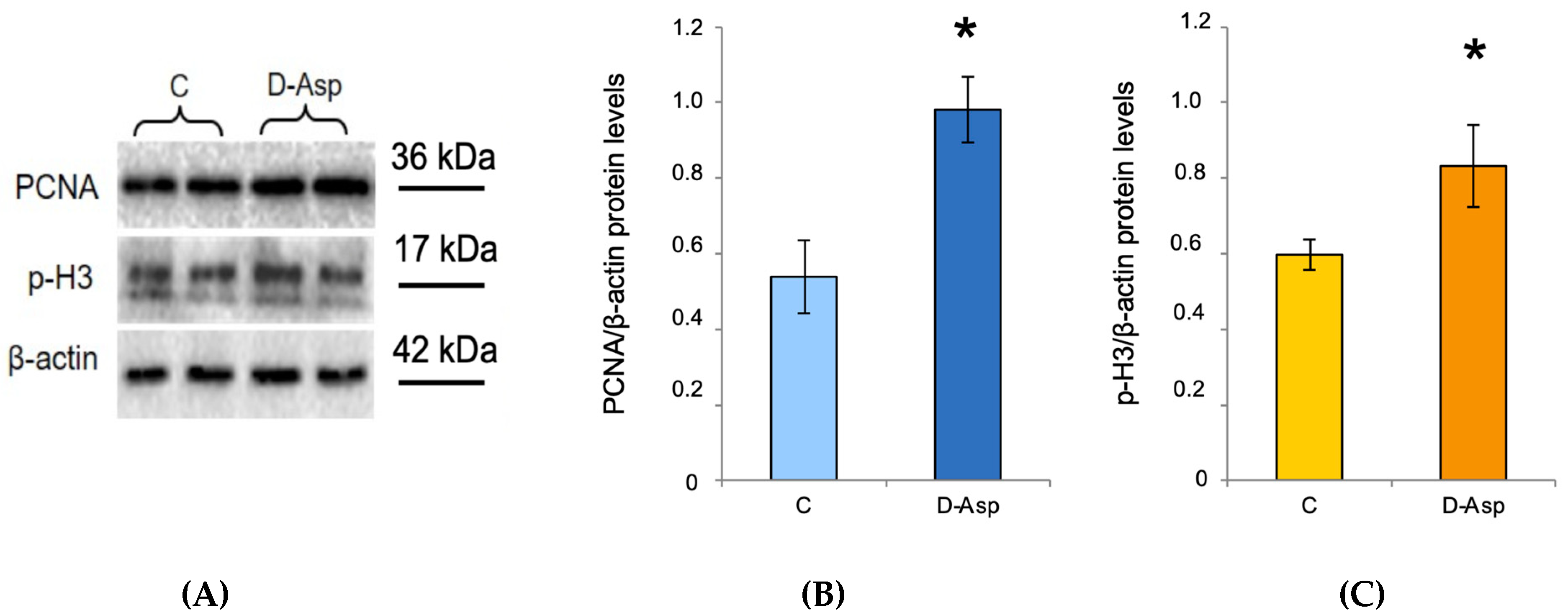
3.4. Effects of Oral Administration of D-Asp on Testicular PCNA and p-H3 Protein Levels
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLean, D.J.; Friel, P.J.; Johnston, D.S.; Griswold, M.D. Characterization of Spermatogonial Stem Cell Maturation and Differentiation in Neonatal Mice1. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, M.; Fasano, C.; Minucci, S.; Serino, I.; Sinisi, A.A.; Dale, B.; Di Matteo, L. DAAM1 and PREP are involved in human spermatogenesis. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2020, 32, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.S.; Shakes, D.C. Spermatogenesis. In Germ Cell Development in C. elegans; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 757, pp. 171–203. [Google Scholar]
- Pariante, P.; Dotolo, R.; Venditti, M.; Ferrara, D.; Donizetti, A.; Aniello, F.; Minucci, S. Prothymosin alpha expression and localization during the spermatogenesis of Danio rerio. Zygote 2015, 24, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, M.; Minucci, S. Prothymosin alpha expression in the vertebrate testis: A comparative review. Zygote 2017, 25, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergoli, M.; Venditti, M.; Piccillo, E.; Minucci, S.; Politano, L. Study of Expression of Genes Potentially Responsible for Reduced Fitness in Patients With Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 and Identification of New Biomarkers of Testicular Function. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 87, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.Q.; Garbers, D.L. Male Germ Cell Specification and Differentiation. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flück, C.E.; Pandey, A.V. Steroidogenesis of the testis—New genes and pathways. In Annales d’endocrinologie; Elsevier Masson: Paris, France, 2014; Volume 75, pp. 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Walker, W.H. The regulation of spermatogenesis by androgens. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.J. Molecular regulation of steroidogenesis in endocrine Leydig cells. Steroids 2015, 103, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, G. d-Aspartic acid: An endogenous amino acid with an important neuroendocrine role. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 53, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, M.M.; Santillo, A.; Baccari, G.C. Current knowledge of d-aspartate in glandular tissues. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuchi, T.; Homma, H. Free D-Aspartate in Mammals. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, N.; Shi, T.; Sweedler, J.V. D-Aspartate acts as a signaling molecule in nervous and neuroendocrine systems. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrone, L.; Di Giovanni, M.; Di Fiore, M.M.; Baccari, G.C.; Santillo, A. Effects of D-Aspartate Treatment on D-Aspartate Oxidase, Superoxide Dismutase, and Caspase 3 Activities in Frog (Rana esculenta) Tissues. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamanna, C.; Assisi, L.; Botte, V.; Di Fiore, M.M. Involvement of D-Asp in P450 aromatase activity and estrogen receptors in boar testis. Amino Acids 2006, 32, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamanna, C.; Assisi, L.; Vittoria, A.; Botte, V.; Di Fiore, M.M. d-Aspartic acid and nitric oxide as regulators of androgen production in boar testis. Theriogenology 2007, 67, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Chieffi, P.; Burrone, L.; Baccari, G.C.; Longobardi, S.; Di Fiore, M.M. d-aspartate affects NMDA receptor-extracellular signal–regulated kinase pathway and upregulates androgen receptor expression in the rat testis. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillo, A.; Chieffi Baccari, G.; Falvo, S.; Di Giacomo Russo, F.; Venditti, M.; Di Fiore, M.M. Effects of D-aspartate on sex hormone-dependent tissues in Pelophylax esculentus. In Amphibians: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Cannon, L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Chieffi Baccari, G.; Di Giacomo Russo, F.; Rosati, L.; Di Fiore, M.M. Testis and brain steroidogenesis during the reproductive cycle of Pelophylax esculentus. In Amphibians: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Cannon, L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giovanni, M.; Burrone, L.; Baccari, G.C.; Topo, E.; Santillo, A. Distribution of free D-aspartic acid and D-aspartate oxidase in frogRana esculentatissues. J. Exp. Zoöl. Part A: Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2010, 313, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, A.; Di Fiore, M.M.; Fisher, G.; Milone, A.; Seleni, A.; D’Aniello, S.; Perna, A.F.; Ingrosso, D. Occurrence of D-aspartic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid in rat neuroendocrine tissues and their role in the modulation of luteinizing hormone and growth hormone release. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topo, E.; Soricelli, A.; D’Aniello, A.; Ronsini, S.; D’Aniello, G. The role and molecular mechanism of D-aspartic acid in the release and synthesis of LH and testosterone in humans and rats. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, M.M.; Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Longobardi, S.; Baccari, G.C. Molecular Mechanisms Elicited by d-Aspartate in Leydig Cells and Spermatogonia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, M.M.; Burrone, L.; Santillo, A.; Chieffi Baccari, G. Endocrine activity of D-aspartate in nonmammalian animals. In D-Amino Acids: Physiology, Metabolism, and Application; Yoshimura, T., Nishikawa, T., Homma, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore, M.M.; Boni, R.; Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Gallo, A.; Esposito, S.; Baccari, G.C. D-Aspartic Acid in Vertebrate Reproduction: Animal Models and Experimental Designs. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Homma, H.; Lee, J.-A.; Imai, K. D-Aspartate stimulation of testosterone synthesis in rat Leydig cells. FEBS Lett. 1999, 444, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Homma, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Imai, K. Stimulation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (STAR) gene expression by D-aspartate in rat Leydig cells. FEBS Lett. 1999, 454, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Chieffi, P.; Di Fiore, M.M.; Senese, R.; Baccari, G.C. D-Aspartate Induces Proliferative Pathways in Spermatogonial GC-1 Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 231, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Di Fiore, M.M.; Russo, F.D.G.; Chieffi, P.; Usiello, A.; Pinelli, C.; Baccari, G.C. AMPA receptor expression in mouse testis and spermatogonial GC-1 cells: A study on its regulation by excitatory amino acids. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 11044–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Homma, H.; Lee, J.-A.; Fukushima, T.; Santa, T.; Tashiro, K.; Iwatsubo, T.; Imai, K. Localization ofd-Aspartic Acid in Elongate Spermatids in Rat Testis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 351, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kageyama, S.; Nagasawa, M.; Wada, A.; Murai, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Hanada, E.; Agata, Y.; Kawauchi, A. The Effect of d-Aspartate on Spermatogenesis in Mouse Testis1. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, G.; Ronsini, S.; Guida, F.; Spinelli, P.; D’Aniello, A. Occurrence of D-aspartic acid in human seminal plasma and spermatozoa: Possible role in reproduction. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 84, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, A.; Di Cosmo, A.; Di Cristo, C.; Annunziato, L.; Petrucelli, L.; Fisher, G. Involvement of D-Aspartic acid in the synthesis of testosterone in rat testes. Life Sci. 1996, 59, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillo, A.; Venditti, M.; Minucci, S.; Baccari, G.C.; Falvo, S.; Rosati, L.; Di Fiore, M.M. D-Asp upregulates PREP and GluA2/3 expressions and induces p-ERK1/2 and p-Akt in rat testis. Reproduction 2019, 158, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotolo, R.; Kim, J.D.; Pariante, P.; Minucci, S.; Diano, S. Prolyl Endopeptidase (PREP) is Associated With Male Reproductive Functions and Gamete Physiology in Mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 231, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, M.; Minucci, S. Subcellular Localization of Prolyl Endopeptidase during the First Wave of Rat Spermatogenesis and in Rat and Human Sperm. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 67, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, M.; Chemek, M.; Minucci, S.; Messaoudi, I. Cadmium-induced toxicity increases prolyl endopeptidase (PREP) expression in the rat testis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, I.; Zeitschel, U.; Rudolph, T.; Rahfeld, J.-U.; Gerhartz, B.; Bigl, V.; DeMuth, H.-U.; Roßner, S.; Ruiz-Carrillo, D. Subcellular localization suggests novel functions for prolyl endopeptidase in protein secretion. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, M.; Aniello, F.; Santillo, A.; Minucci, S. Study on PREP localization in mouse seminal vesicles and its possible involvement during regulated exocytosis. Zygote 2019, 27, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mao, B.; Wu, S.; Lian, Q.; Ge, R.-S.; Silvestrini, B.; Cheng, C.Y. Regulation of spermatid polarity by the actin- and microtubule (MT)-based cytoskeletons. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 81, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariante, P.; Dotolo, R.; Venditti, M.; Ferrara, D.; Donizetti, A.; Aniello, F.; Minucci, S. First Evidence of DAAM1 Localization during the Post-Natal Development of Rat Testis and in Mammalian Sperm. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 2172–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, D.R. Molecular details of formin-mediated actin assembly. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, S.; Baccaria, G.C.; Spaziano, G.; Rosati, L.; Venditti, M.; Di Fiore, M.M.; Santillo, A.; Di Flore, M.M. StAR protein and steroidogenic enzyme expressions in the rat Harderian gland. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2018, 341, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.-C.; Narisawa, S.; Hess, R.; Millán, J.L. Immortalization of germ cells and somatic testicular cells using the SV40 large T antigen. Exp. Cell Res. 1992, 201, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillo, A.; Pinelli, C.; Burrone, L.; Baccari, G.C.; Di Fiore, M.M. d-Aspartic acid implication in the modulation of frog brain sex steroid levels. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 181, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemek, M.; Venditti, M.; Boughamoura, S.; Mimouna, S.B.; Messaoudi, I.; Minucci, S. Involvement of testicular DAAM1 expression in zinc protection against cadmium-induced male rat reproductive toxicity. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Sato, A.; Khadka, D.; Bharti, R.; Diaz, H.; Runnels, L.; Habas, R. Mechanism of activation of the Formin protein Daam1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 105, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosugi, S.; Hasebe, M.; Tomita, M.; Yanagawa, H. Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10171–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Duan, F.; Zhou, X.; Pan, H.; Li, R. Differential responses of GC-1 spermatogonia cells to high and low doses of bisphenol A. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Fan, R.; et al. Melatonin promotes the proliferation of GC-1 spg cells by inducing metallothionein-2 expression through ERK1/2 signaling pathway activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65627–65641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, E.M.; Gildenberg, M.S.; Washington, T. The Many Roles of PCNA in Eukaryotic DNA Replication. Enzymes 2016, 39, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, S.; Corces, V.G. Phosphorylation of histone H3: A balancing act between chromosome condensation and transcriptional activation. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moujaber, O.; Stochaj, U. The Cytoskeleton as Regulator of Cell Signaling Pathways. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Iwasa, M.; Aihara, T.; Maéda, Y.; Narita, A. The nature of the globular- to fibrous-actin transition. Nature 2009, 457, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.D. Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesarone, M.A.; DuPage, A.G.; Goode, B.L. Unleashing formins to remodel the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönichen, A.; Geyer, M. Fifteen formins for an actin filament: A molecular view on the regulation of human formins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2010, 1803, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, R.; Cobellis, G.; Chioccarelli, T.; Ciaramella, V.; Migliaccio, M.; Fasano, S.; Pierantoni, R.; Meccariello, R. Kisspeptins, Estrogens and Male Fertility. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 4070–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fiore, M.M.; Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Baccari, G.C.; Venditti, M.; Russo, F.D.G.; Lispi, M.; D’Aniello, G. Sex hormone levels in the brain of d -aspartate-treated rats. C. R. Biol. 2018, 341, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunleavy, J.; O’Bryan, M.K.; Stanton, P.G.; O’Donnell, L. The cytoskeleton in spermatogenesis. Reproduction 2019, 157, R53–R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanegashima, K.; Zhao, H.; Dawid, I.B. WGEF activates Rho in the Wnt–PCP pathway and controls convergent extension in Xenopus gastrulation. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlow, F.; Topczewski, J.; Sepich, D.; Solnica-Krezel, L. Zebrafish Rho Kinase 2 Acts Downstream of Wnt11 to Mediate Cell Polarity and Effective Convergence and Extension Movements. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habas, R.; Kato, Y.; He, X. Wnt/Frizzled Activation of Rho Regulates Vertebrate Gastrulation and Requires a Novel Formin Homology Protein Daam1. Cell 2001, 107, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, L.A.; Goda, Y. Actin in action: The interplay between the actin cytoskeleton and synaptic efficacy. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, S.N.; Haber, M.; Murai, K.K.; Dunn, R.J. Localization of the Diaphanous-related formin Daam1 to neuronal dendrites. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 447, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, F.; Salinas, P.C. Wnt proteins as modulators of synaptic plasticity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 53, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrar, S.; Jia, Z. Molecular mechanisms coordinating functional and morphological plasticity at the synapse: Role of GluA2/N-cadherin interaction-mediated actin signaling in mGluR-dependent LTD. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giovanni, M.; Topo, E.; Santillo, A.; D’Aniello, A.; Baccari, G.C. d-Aspartate binding sites in rat Harderian gland. Amino Acids 2009, 38, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Percipalle, P. An actin-based nucleoskeleton involved in gene regulation and genome organization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsior, S.M.; Platz, S.; Buchmeier, S.; Scheer, U.; Jockusch, B.M.; Hinssen, H. Conformational difference between nuclear and cytoplasmic actin as detected by a monoclonal anti-body. J. Cell. Sci. 1999, 112, 797–809. [Google Scholar]
- Grzanka, A.; Grzanka, A.; Orlikowska, M. Fluorescence and ultrastructural localization of actin distribution patterns in the nucleus of HL-60 and K-562 cell lines treated with cytostatic drugs. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 11, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schoenenberger, C.-A.; Buchmeier, S.; Boerries, M.; Sütterlin, R.; Aebi, U.; Jockusch, B. Conformation-specific antibodies reveal distinct actin structures in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelpsch, D.J.; Tootle, T. Nuclear Actin: From Discovery to Function. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2018, 301, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüven, T.; Hartmann, E.; Görlich, D. Exportin 6: A novel nuclear export receptor that is specific for profilin·actin complexes. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5928–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopie, J.; Skarp, K.-P.; Rajakylä, E.K.; Tanhuanpää, K.; Vartiainen, M.K. Active maintenance of nuclear actin by importin 9 supports transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E544–E552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, R.; Vartiainen, M.K. To be or not to be assembled: Progressing into nuclear actin filaments. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, T.; Innocenti, M. New nuclear and perinuclear functions of formins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.C.; Leder, P. Genetic Evidence That Formins Function within the Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23472–23477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Copeland, J.W.; Fasnacht, M.; Etchberger, J.F.; Liu, J.; Honig, B.; Hobert, O. An unusual Zn-finger/FH2 domain protein controls a left/right asymmetric neuronal fate decision in C. elegans. Development 2006, 133, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, S.J.; Green, B.J.; Burchat, S.; Papalia, G.A.; Banner, D.; Copeland, J.W. The Diaphanous Inhibitory Domain/Diaphanous Autoregulatory Domain Interaction Is Able to Mediate Heterodimerization between mDia1 and mDia2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30120–30130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, D.; Liu, Z.X.; Sellin, L.; Spokes, K.; Zeller, R.; Cantley, L.G. Hepatocyte growth factor induces MAPK-dependent formin IV translocation in renal epithelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar]
- Ménard, I.; Gervais, F.G.; Nicholson, D.W.; Roy, S. Caspase-3 cleaves the formin-homology-domain-containing protein FHOD1 during apoptosis to generate a C-terminal fragment that is targeted to the nucleolus. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 1863–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarlink, C.; Wang, H.; Grosse, R. Nuclear Actin Network Assembly by Formins Regulates the SRF Coactivator MAL. Science 2013, 340, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyheröinen, S.; Vartiainen, M.K. Nuclear actin dynamics in gene expression and genome organization. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisis, N.; Krasinska, L.; Harker, B.; Urbach, S.; Rossignol, M.; Camasses, A.; Dewar, J.; Morin, N.; Fisher, D. Initiation of DNA replication requires actin dynamics and formin activity. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3212–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venditti, M.; Santillo, A.; Falvo, S.; Di Fiore, M.M.; Chieffi Baccari, G.; Minucci, S. D-Aspartate Upregulates DAAM1 Protein Levels in the Rat Testis and Induces Its Localization in Spermatogonia Nucleus. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050677
Venditti M, Santillo A, Falvo S, Di Fiore MM, Chieffi Baccari G, Minucci S. D-Aspartate Upregulates DAAM1 Protein Levels in the Rat Testis and Induces Its Localization in Spermatogonia Nucleus. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050677
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenditti, Massimo, Alessandra Santillo, Sara Falvo, Maria Maddalena Di Fiore, Gabriella Chieffi Baccari, and Sergio Minucci. 2020. "D-Aspartate Upregulates DAAM1 Protein Levels in the Rat Testis and Induces Its Localization in Spermatogonia Nucleus" Biomolecules 10, no. 5: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050677
APA StyleVenditti, M., Santillo, A., Falvo, S., Di Fiore, M. M., Chieffi Baccari, G., & Minucci, S. (2020). D-Aspartate Upregulates DAAM1 Protein Levels in the Rat Testis and Induces Its Localization in Spermatogonia Nucleus. Biomolecules, 10(5), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050677







