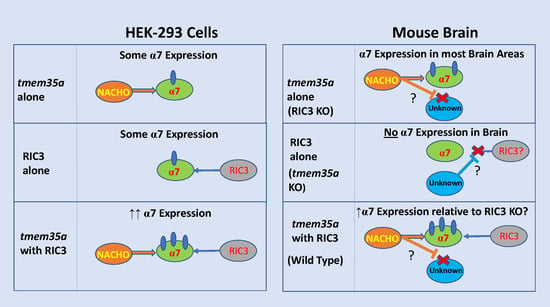
Why Does Knocking Out NACHO, But Not RIC3, Completely Block Expression of α7 Nicotinic Receptors in Mouse Brain?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Reagents, Antibodies, and Cell Lines
2.3. Cell Transfections and Western Blots (WBs)
2.4. [125I]-Labeled-αBGT Binding Assay
2.5. Generation of ric3 KO and tmem35a KO Mice, Brain Dissections and Preparation of Mouse Macrophages
2.6. 125. I-α-Bungarotoxin (αBGT) Autoradiography
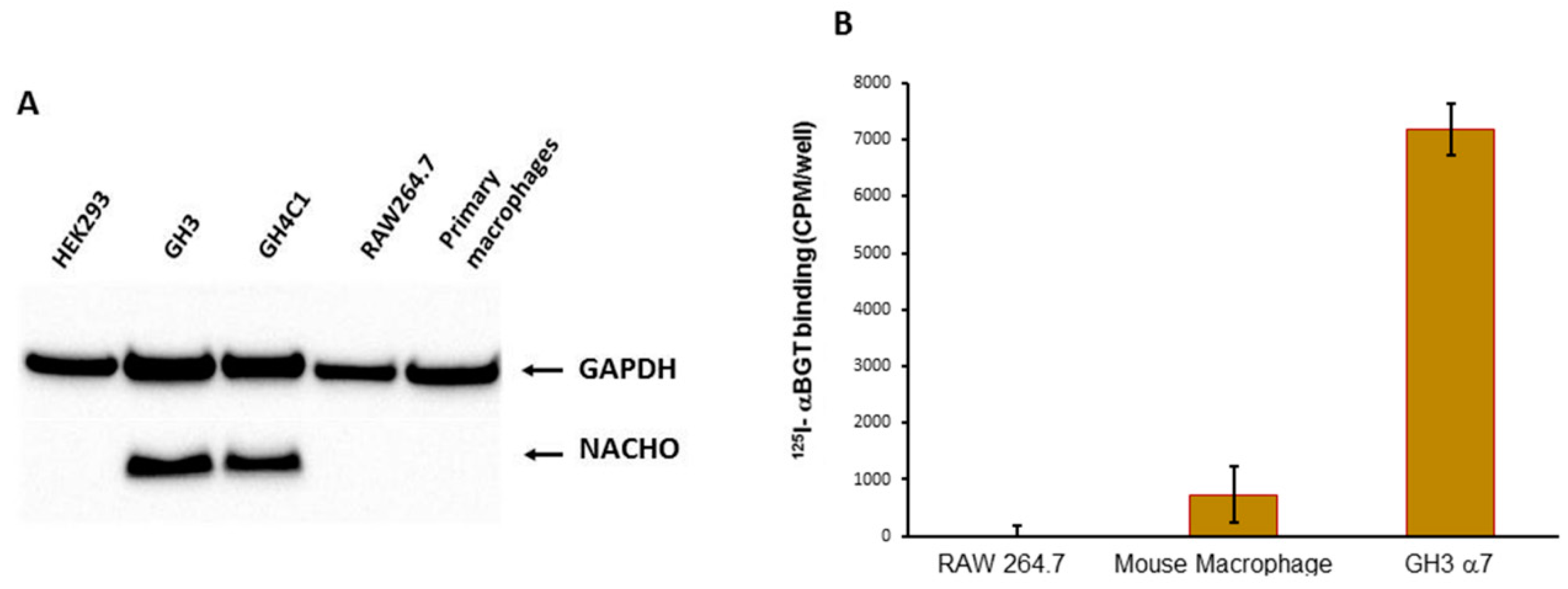
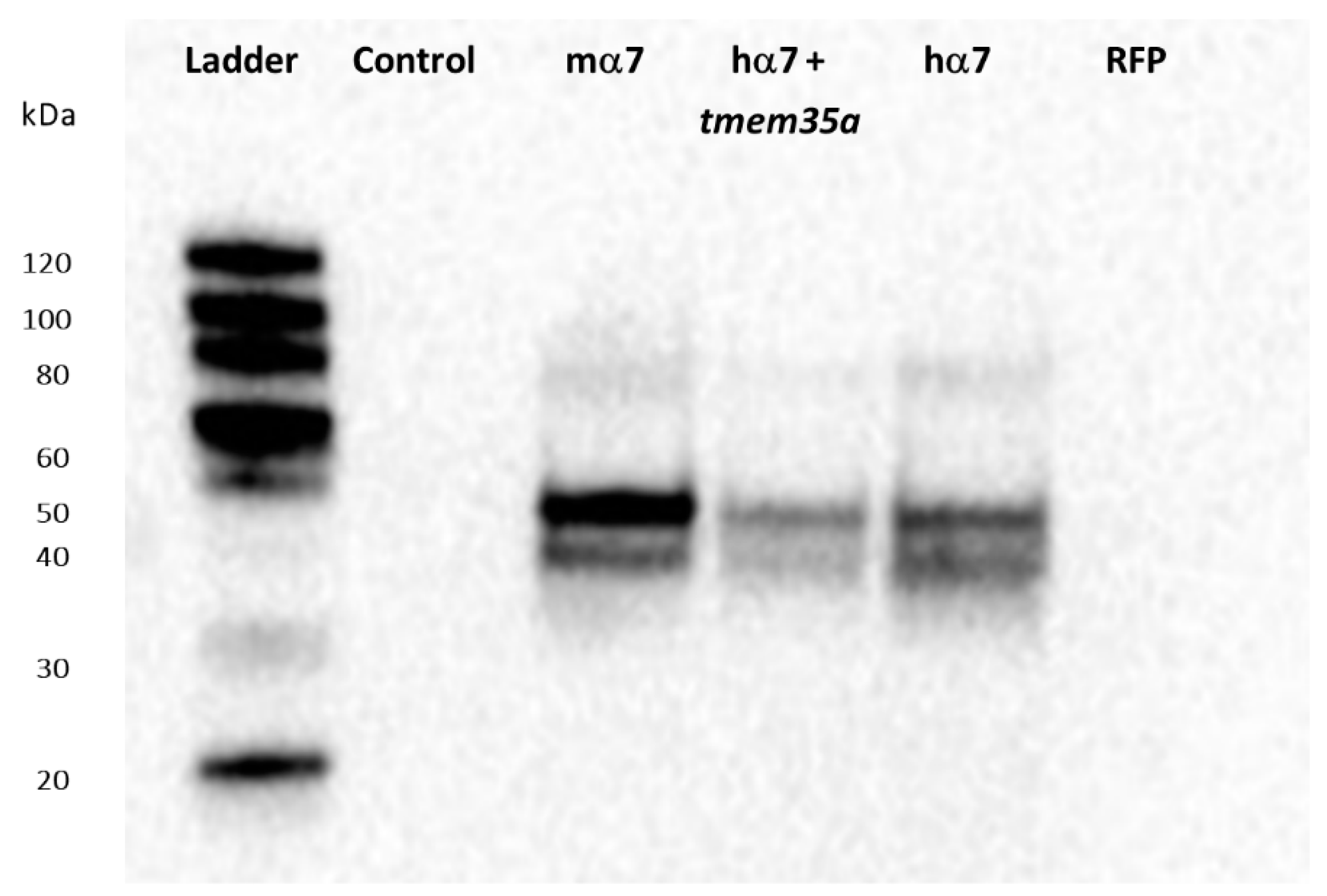
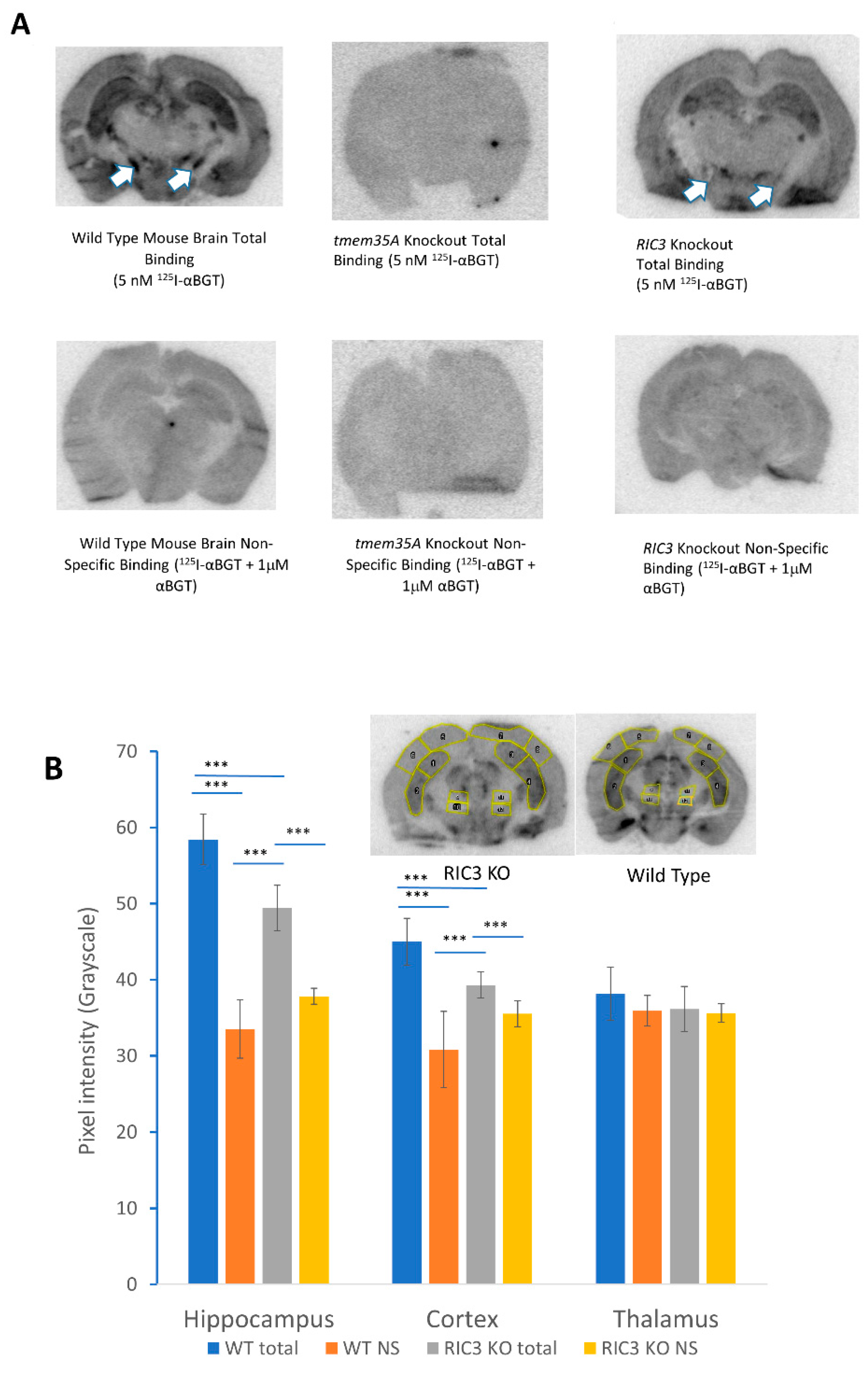
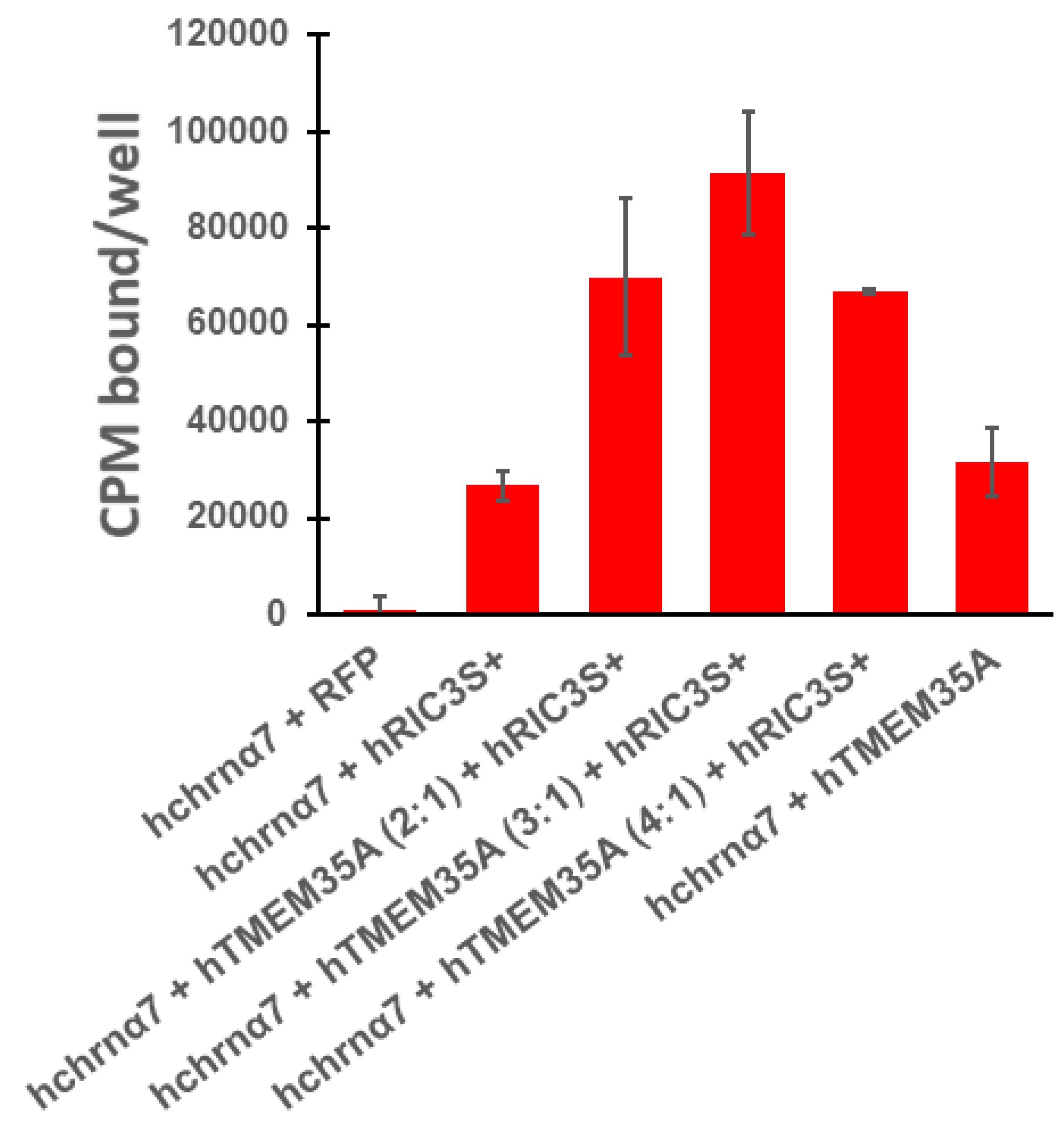
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zoli, M.; Pucci, S.; Vilella, A.; Gotti, C. Neuronal and Extraneuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, N.S.; Harkness, P.C. Assembly and trafficking of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (Review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 2008, 25, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Matta, J.A.; Lord, B.; Harrington, A.W.; Sutton, S.W.; Davini, W.B.; Bredt, D.S. Brain alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Assembly Requires NACHO. Neuron 2016, 89, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, J.A.; Gu, S.; Davini, W.B.; Lord, B.; Siuda, E.R.; Harrington, A.W.; Bredt, D.S. NACHO Mediates Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Function throughout the Brain. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.S. RIC-3: A nicotinic acetylcholine receptor chaperone. Br. J. Pharm. 2008, 153, S177–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treinin, M. RIC-3 and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Biogenesis, properties, and diversity. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.G.; Alfonso, A.; Nguyen, M.; Crowell, J.A.; Johnson, C.D.; Rand, J.B. A genetic selection for Caenorhabditis elegans synaptic transmission mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12593–12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevi, S.; Yassin, L.; Eshel, M.; Sala, F.; Sala, S.; Criado, M.; Treinin, M. Conservation within the RIC-3 gene family. Effectors of mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34411–34417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.V.; Georgieff, M.K.; Engeland, W.C. Sodium depletion increases sympathetic neurite outgrowth and expression of a novel TMEM35 gene-derived protein (TUF1) in the rat adrenal zona glomerulosa. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4852–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.C.; Dimova, J.G.; Dakoji, S.; Yuan, L.L.; Gewirtz, J.C.; Tran, P.V. Deletion of novel protein TMEM35 alters stress-related functions and impairs long-term memory in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R166–R178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koperniak, T.M.; Garg, B.K.; Boltax, J.; Loring, R.H. Cell-specific effects on surface alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression revealed by over-expression and knockdown of rat RIC3 protein. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herber, D.L.; Severance, E.G.; Cuevas, J.; Morgan, D.; Gordon, M.N. Biochemical and histochemical evidence of nonspecific binding of alpha7nAChR antibodies to mouse brain tissue. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.W.; Wonnacott, S. Why doesn’t nicotinic ACh receptor immunoreactivity knock out? Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, N.; Mechawar, N.; Jones, I.; Gochberg-Sarver, A.; Orr-Urtreger, A.; Plomann, M.; Salas, R.; Molles, B.; Marubio, L.; Roth, U.; et al. Evaluating the suitability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies for standard immunodetection procedures. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommel, F.R.; Raghavan, B.; Paddenberg, R.; Kummer, W.; Tumala, S.; Lochnit, G.; Gieler, U.; Peters, E.M. Suitability of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor alpha7 and Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor 3 Antibodies for Immune Detection: Evaluation in Murine Skin. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2015, 63, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, B.K.; Loring, R.H. Evaluating Commercially Available Antibodies for Rat alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2017, 65, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.W.; Loring, R.H.; Aizenman, E.; Zigmond, R.E. Autoradiographic localization of putative nicotinic receptors in the rat brain using 125I-neuronal bungarotoxin. J. Neurosci. 1991, 11, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishtala, S.N.; Mnatsakanyan, N.; Pandhare, A.; Leung, C.; Jansen, M. Direct interaction of the resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase type 3 protein with the serotonin receptor type 3A intracellular domain. J. Neurochem. 2016, 137, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.K.; Loring, R.H. GTS-21 has cell-specific anti-inflammatory effects independent of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, L.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.Y.; Martin, F.; Grant, D.; Solloway, M.; Parker, L.; Ye, W.; et al. A mouse knockout library for secreted and transmembrane proteins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen Mouse Brain Atlas. 2004. Available online: https://mouse.brain-map.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, J.K.; Sagher, D.; Krivoshein, A.V.; Criado, M.; Jefford, G.; Green, W.N. Ric-3 promotes alpha7 nicotinic receptor assembly and trafficking through the ER subcompartment of dendrites. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 10112–10126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baez-Pagan, C.A.; Delgado-Velez, M.; Lasalde-Dominicci, J.A. Activation of the Macrophage alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Control of Inflammation. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2015, 10, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horenstein, N.A.; Papke, R.L. Anti-inflammatory Silent Agonists. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, M.J.; Blattman, S.B.; Barrantes, F.J.; Lukas, R.J.; Hawrot, E. Resistance to Inhibitors of Cholinesterase 3 (Ric-3) Expression Promotes Selective Protein Associations with the Human alpha7-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Interactome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M. Reproducibility crisis: Blame it on the antibodies. Nature 2015, 521, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, L.; Andrade, J.; Odeberg, J.; Uhlen, M. The epitope space of the human proteome. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Ben-Ami, H.; Biala, Y.; Farah, H.; Elishevitz, E.; Battat, E.; Treinin, M. Receptor and subunit specific interactions of RIC-3 with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 12329–12336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Tang, X.Q.; Wang, Z.Z. Mouse RIC-3, an endoplasmic reticulum chaperone, promotes assembly of the alpha7 acetylcholine receptor through a cytoplasmic coiled-coil domain. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12625–12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, T.W.; Graveley, B.R. Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature 2010, 463, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudemont, B.; Popa, A.; Parmley, J.L.; Rocher, V.; Blugeon, C.; Necsulea, A.; Meyer, E.; Duret, L. The fitness cost of mis-splicing is the main determinant of alternative splicing patterns. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredenina, T.; Ferraro, T.; Terstappen, G.C.; Caricasole, A.; Roncarati, R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human variant of RIC-3, a putative chaperone of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biosci. Rep. 2008, 28, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, Y.; Treinin, M. Regulation of RIC-3 and of nAChR expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5662–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr-Urtreger, A.; Goldner, F.M.; Saeki, M.; Lorenzo, I.; Goldberg, L.; De Biasi, M.; Dani, J.A.; Patrick, J.W.; Beaudet, A.L. Mice deficient in the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor lack alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites and hippocampal fast nicotinic currents. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 9165–9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteaker, P.; Davies, A.R.; Marks, M.J.; Blagbrough, I.S.; Potter, B.V.; Wolstenholme, A.J.; Collins, A.C.; Wonnacott, S. An autoradiographic study of the distribution of binding sites for the novel alpha7-selective nicotinic radioligand [3H]-methyllycaconitine in the mouse brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerbach, D.; Lingenhohl, K.; Dobbins, P.; Mosbacher, J.; Corbett, N.; Nozulak, J.; Hoyer, D. Coupling of human nicotinic acetylcholine receptors alpha 7 to calcium channels in GH3 cells. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

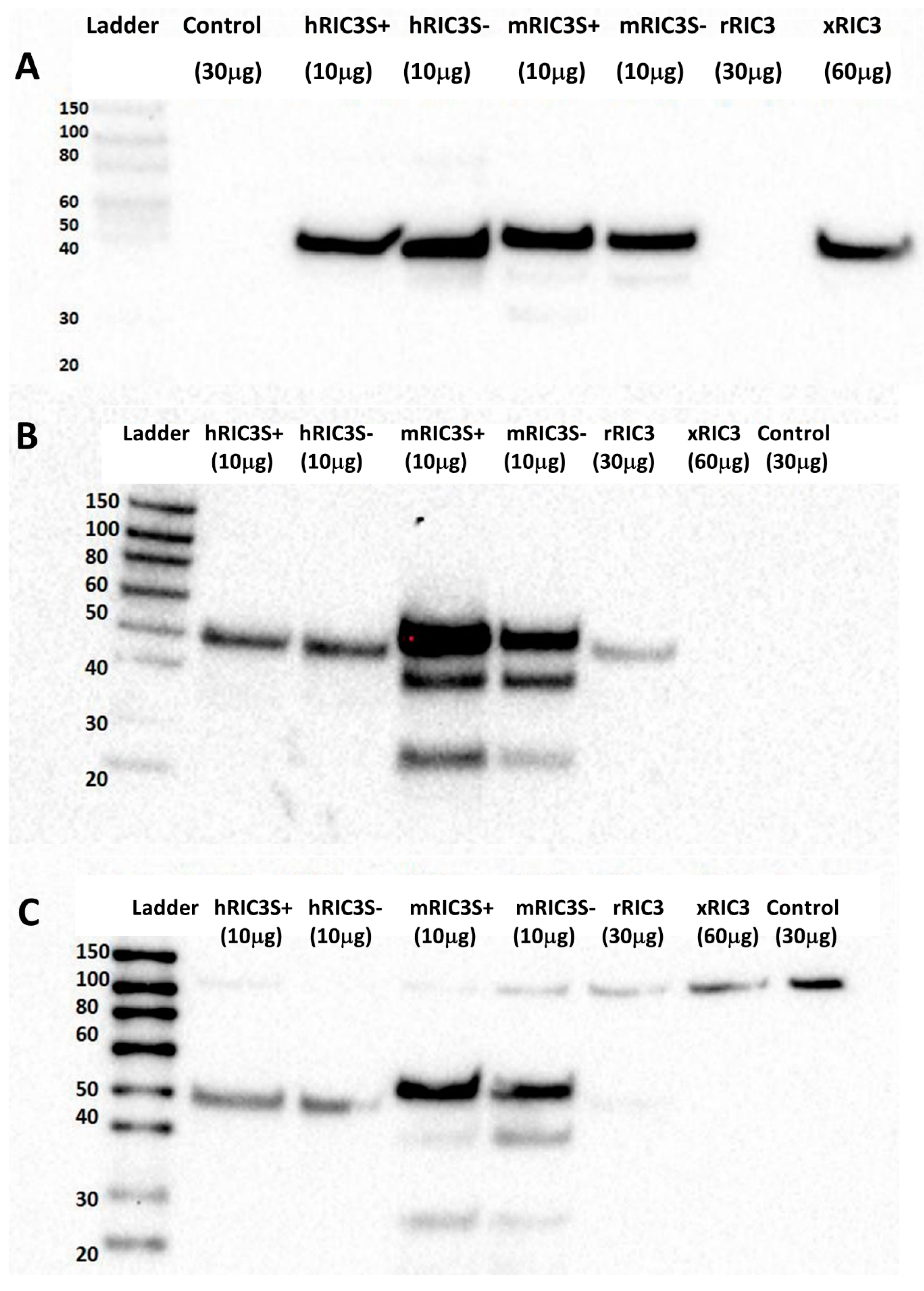
| Primary Antibody * | Company | Catalog Number | Lot Number(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Human RIC3 | Abcam | ab112911 | GR99507-5 |
| Anti-Human RIC3 ** | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-377408 | H3117 |
| Anti-Human RIC3 | Thermofisher | PA5-48432 | SF2408204A |
| Anti-Human RIC3 | Thermofisher/Invitrogen | PA5-64196 | SL2490062C, TE2576142A |
| Anti-Mouse RIC3 *** | Alomone Labs | ANC-020 | ANC020AN0125 |
| Anti-Human RIC3 **** | Novus Biologicals | H00079608-B01P | H6291 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deshpande, A.; Vinayakamoorthy, R.M.; Garg, B.K.; Thummapudi, J.P.; Oza, G.; Adhikari, K.; Agarwal, A.; Dalvi, P.; Iyer, S.; Thulasi Raman, S.; et al. Why Does Knocking Out NACHO, But Not RIC3, Completely Block Expression of α7 Nicotinic Receptors in Mouse Brain? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030470
Deshpande A, Vinayakamoorthy RM, Garg BK, Thummapudi JP, Oza G, Adhikari K, Agarwal A, Dalvi P, Iyer S, Thulasi Raman S, et al. Why Does Knocking Out NACHO, But Not RIC3, Completely Block Expression of α7 Nicotinic Receptors in Mouse Brain? Biomolecules. 2020; 10(3):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030470
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeshpande, Anish, Remitha M. Vinayakamoorthy, Brijesh K. Garg, Jaya Prakash Thummapudi, Gauri Oza, Ketaki Adhikari, Aayush Agarwal, Parnika Dalvi, Swetha Iyer, Sarulatha Thulasi Raman, and et al. 2020. "Why Does Knocking Out NACHO, But Not RIC3, Completely Block Expression of α7 Nicotinic Receptors in Mouse Brain?" Biomolecules 10, no. 3: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030470
APA StyleDeshpande, A., Vinayakamoorthy, R. M., Garg, B. K., Thummapudi, J. P., Oza, G., Adhikari, K., Agarwal, A., Dalvi, P., Iyer, S., Thulasi Raman, S., Ramesh, V., Rameshbabu, A., Rezvaya, A., Sukumaran, S., Swaminathan, S., Tilak, B., Wang, Z., Tran, P. V., & Loring, R. H. (2020). Why Does Knocking Out NACHO, But Not RIC3, Completely Block Expression of α7 Nicotinic Receptors in Mouse Brain? Biomolecules, 10(3), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030470