A Novel T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody for Treating Mesothelin-Positive Solid Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of the Antibody Library and Selection of Antibodies Binding to rhMSLN
2.2. Generation and Production of anti-CD3ε Antibody
2.3. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.4. Construction of the Fully Humanized Bispecific Expression Vector
2.5. Production and Purification of Bispecific Antibodies
2.6. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.7. Affinity Evaluation and Dual Binding Assay
2.8. T-cell Activation Assay
2.9. Preparation of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
2.10. In Vitro bsAb/hPBMC Cytotoxicity Assay
2.11. In Vivo Study Using a Tumor Xenograft Mouse Model
2.12. Histologic Analysis
2.13. Bispecific Antibodies Pharmacokinetics in Nude Mice
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
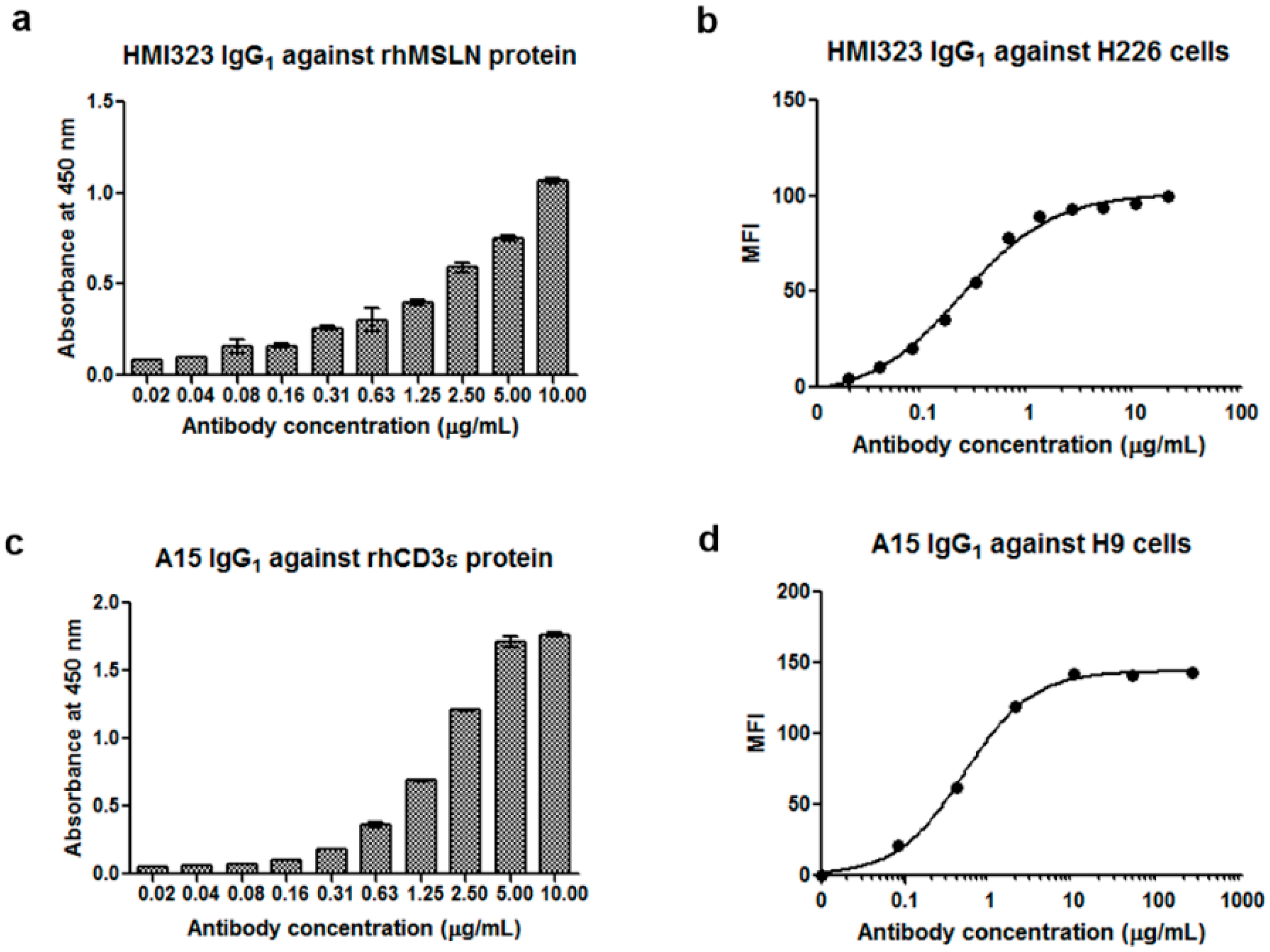
3.1. Generation of Anti-MSLN and Anti-CD3 Monoclonal Antibodies
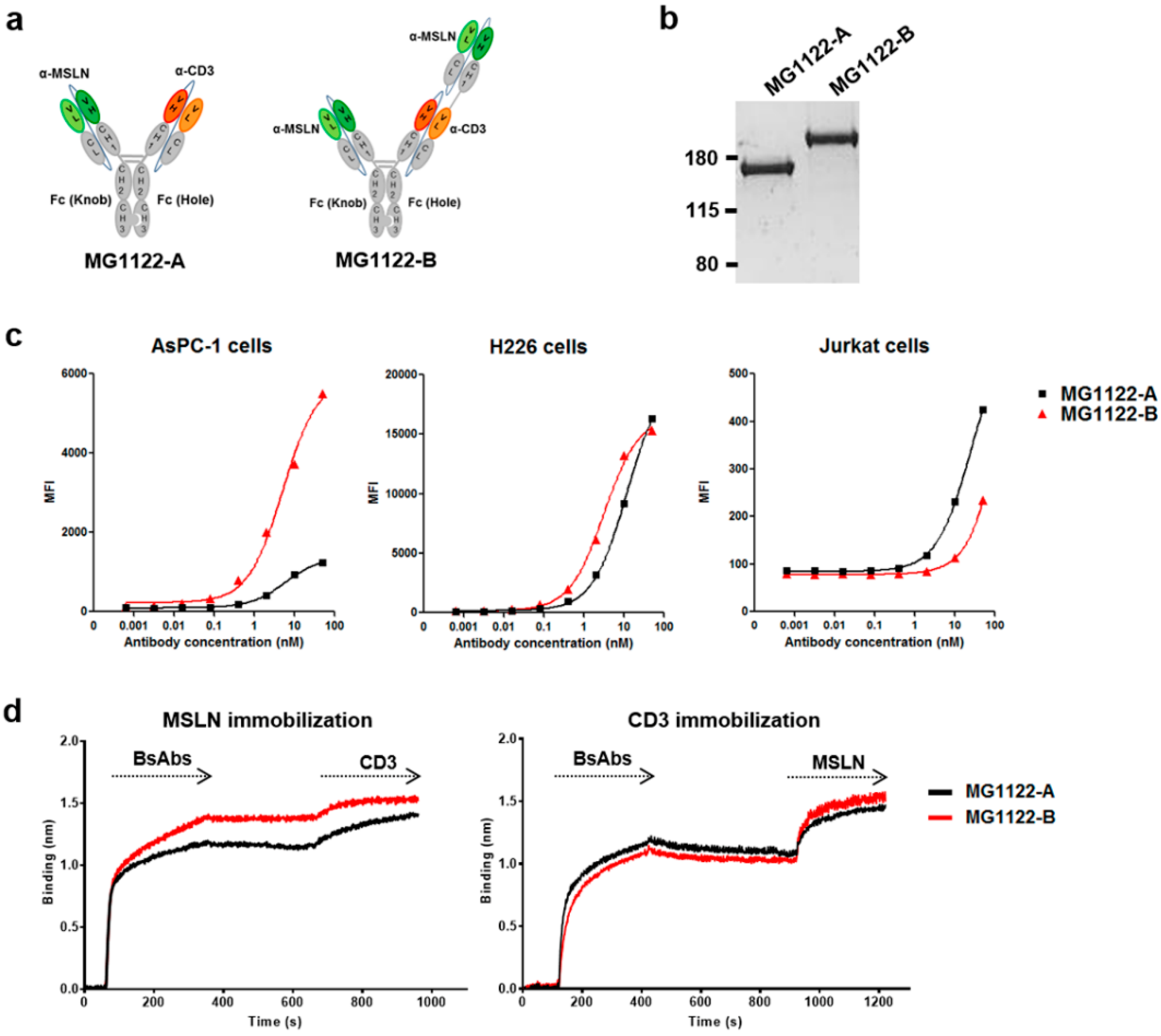
3.2. Construction of Anti-MSLN/CD3 Bispecific Antibodies
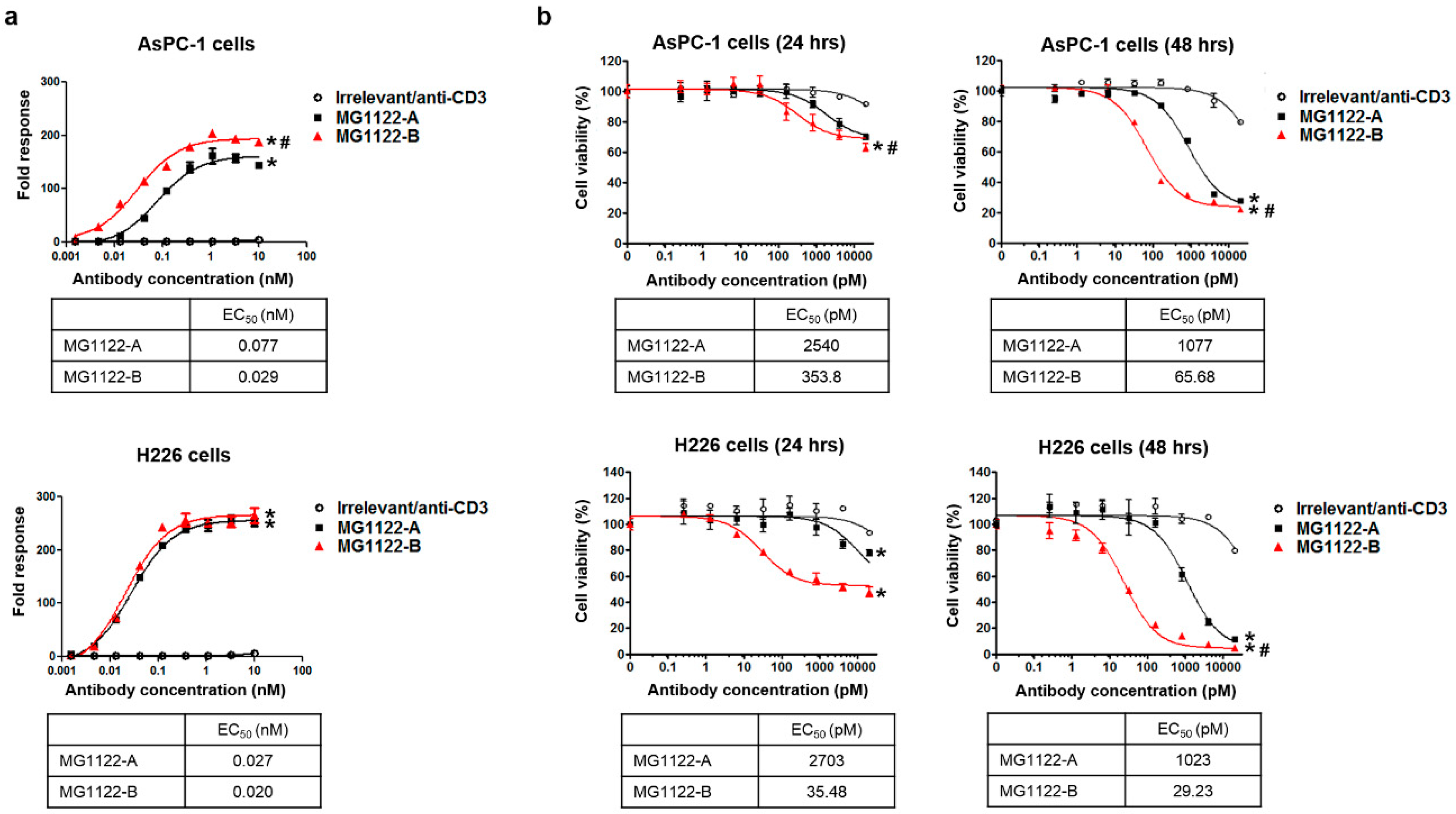
3.3. Characterization of In Vitro Activity of anti-MSLN/CD3 Bispecific Antibodies
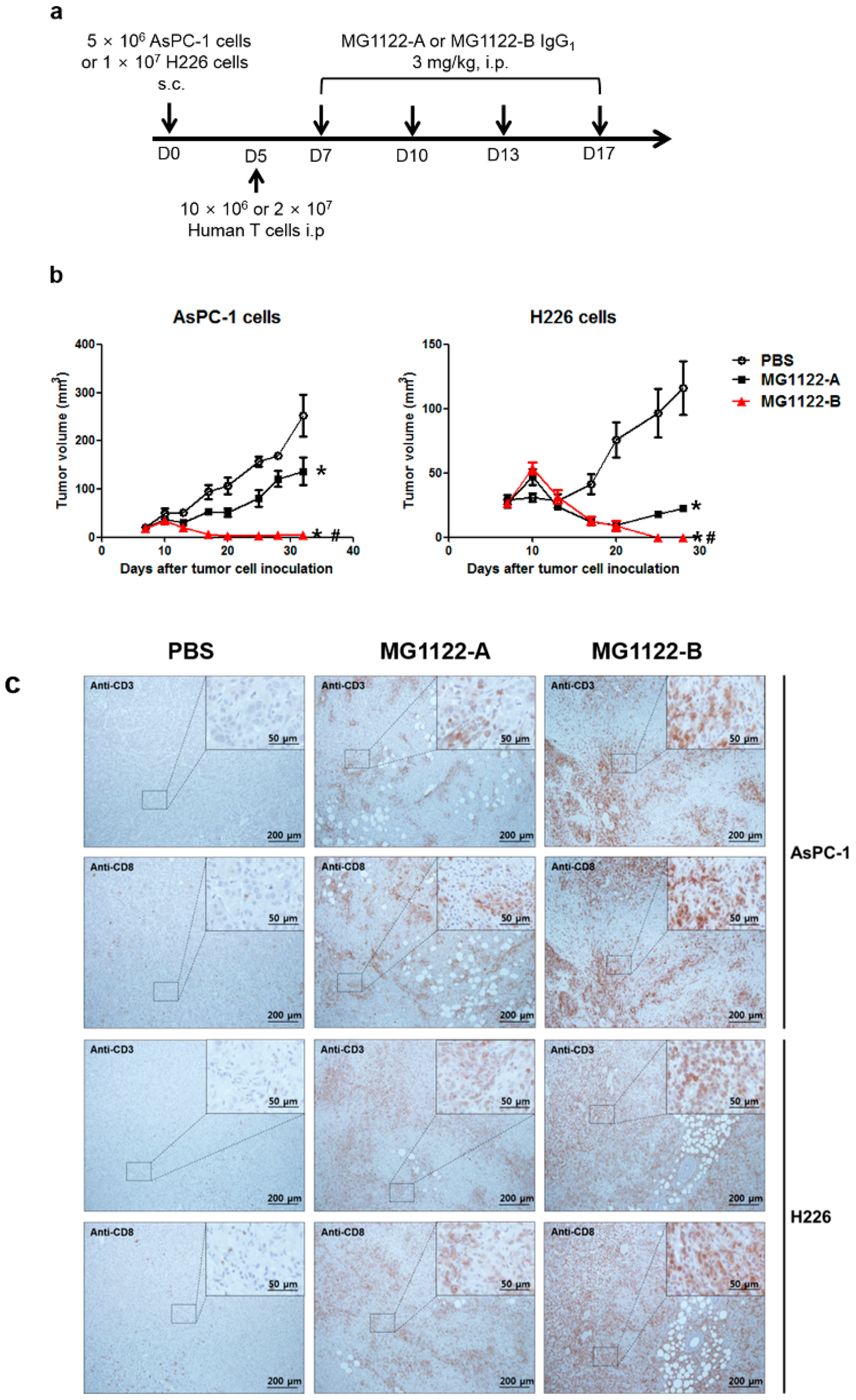
3.4. In Vivo Antitumor Effects of Anti-MSLN/CD3 Bispecific Antibodies in a Tumor Xenograft Mouse Model
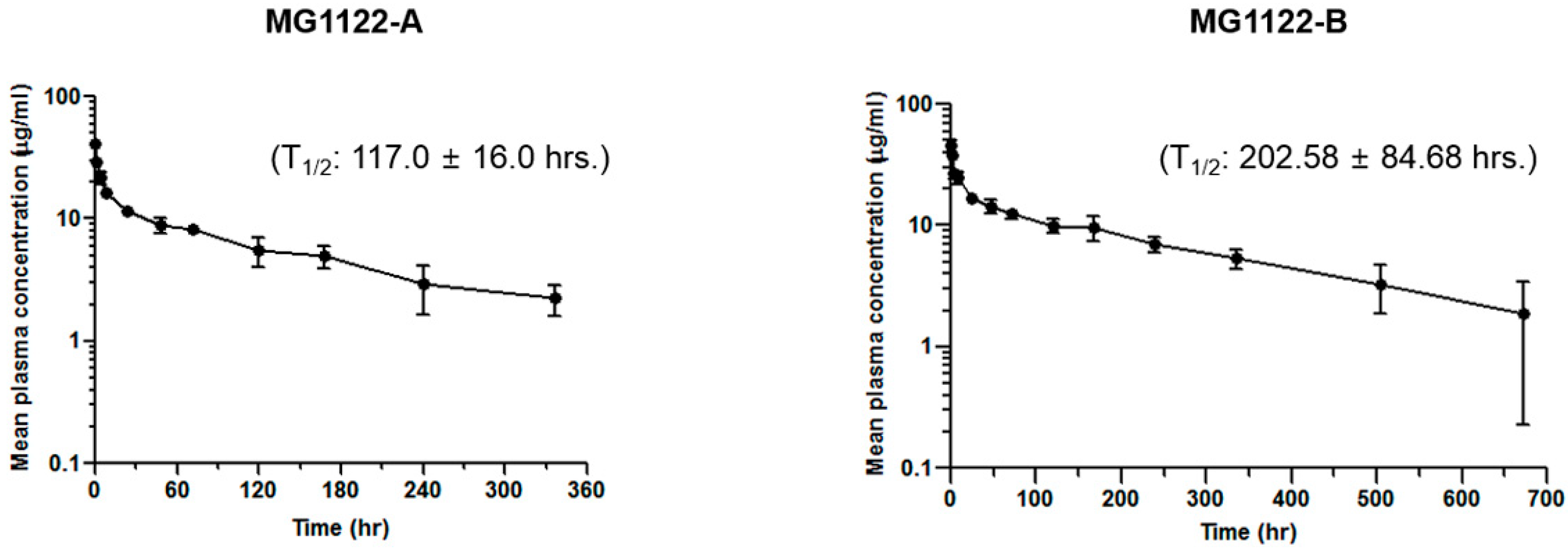
3.5. Anti-MSLN/CD3 Bispecific Antibodies Pharmacokinetics In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Bano, J.; Flores-Flores, R.; Josselin, E.; Goubard, A.; Ganier, L.; Castellano, R.; Chames, P.; Baty, D.; Kerfelec, B. A bispecific antibody-based approach for targeting mesothelin in triple negative breast cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Hung, W.C.; Wang, P.; Paul, C.; Konstantopoulos, K. Mesothelin binding to ca125/muc16 promotes pancreatic cancer cell motility and invasion via mmp-7 activation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Thomas, A.; Alewine, C.; Le, D.T.; Jaffee, E.M.; Pastan, I. Mesothelin immunotherapy for cancer: Ready for prime time? J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, A.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Mesothelin-targeted cars: Driving t cells to solid tumors. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, U.B.; Ellingsen, C.; Schuhmacher, J.; Kristian, A.; Mobergslien, A.; Cruciani, V.; Wickstroem, K.; Schatz, C.A.; Kneip, C.; Golfier, S.; et al. Mesothelin-targeted thorium-227 conjugate (msln-ttc): Preclinical evaluation of a new targeted alpha therapy for mesothelin-positive cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4723–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, D.C.; Eberhardt, W.E. Systemic treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma: New agents in clinical trials raise hope of relevant improvements. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Janmaat, M.L.; Reichert, J.M.; Parren, P. Bispecific antibodies: A mechanistic review of the pipeline. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, S.R.; Baeuerle, P.A. Targeting t cells to tumor cells using bispecific antibodies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacac, M.; Fauti, T.; Sam, J.; Colombetti, S.; Weinzierl, T.; Ouaret, D.; Bodmer, W.; Lehmann, S.; Hofer, T.; Hosse, R.J.; et al. A novel carcinoembryonic antigen t-cell bispecific antibody (cea tcb) for the treatment of solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3286–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayose, Y.; Kudo, T.; Suzuki, M.; Shinoda, M.; Saijyo, S.; Sakurai, N.; Saeki, H.; Fukuhara, K.; Imai, K.; Matsuno, S. Muc1-specific targeting immunotherapy with bispecific antibodies: Inhibition of xenografted human bile duct carcinoma growth. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4205–4212. [Google Scholar]
- Junttila, T.T.; Li, J.; Johnston, J.; Hristopoulos, M.; Clark, R.; Ellerman, D.; Wang, B.E.; Li, Y.; Mathieu, M.; Li, G.; et al. Antitumor efficacy of a bispecific antibody that targets her2 and activates t cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5561–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinklein, N.D.; Pham, D.; Schellenberger, U.; Buelow, B.; Boudreau, A.; Choudhry, P.; Clarke, S.C.; Dang, K.; Harris, K.E.; Iyer, S.; et al. Efficient tumor killing and minimal cytokine release with novel t-cell agonist bispecific antibodies. MAbs 2019, 11, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacac, M.; Klein, C.; Umana, P. Cea tcb: A novel head-to-tail 2:1 t cell bispecific antibody for treatment of cea-positive solid tumors. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1203498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unverdorben, F.; Richter, F.; Hutt, M.; Seifert, O.; Malinge, P.; Fischer, N.; Kontermann, R.E. Pharmacokinetic properties of igg and various fc fusion proteins in mice. MAbs 2016, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlothauer, T.; Herter, S.; Koller, C.F.; Grau-Richards, S.; Steinhart, V.; Spick, C.; Kubbies, M.; Klein, C.; Umana, P.; Mossner, E. Novel human igg1 and igg4 fc-engineered antibodies with completely abolished immune effector functions. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2016, 29, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.; Sustmann, C.; Thomas, M.; Stubenrauch, K.; Croasdale, R.; Schanzer, J.; Brinkmann, U.; Kettenberger, H.; Regula, J.T.; Schaefer, W. Progress in overcoming the chain association issue in bispecific heterodimeric igg antibodies. MAbs 2012, 4, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Schaefer, W.; Regula, J.T. The use of crossmab technology for the generation of bi- and multispecific antibodies. MAbs 2016, 8, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Schaefer, W.; Regula, J.T.; Dumontet, C.; Brinkmann, U.; Bacac, M.; Umana, P. Engineering therapeutic bispecific antibodies using crossmab technology. Methods 2019, 154, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunker, P.; Wartha, K.; Friess, T.; Grau-Richards, S.; Waldhauer, I.; Koller, C.F.; Weiser, B.; Majety, M.; Runza, V.; Niu, H.; et al. Rg7386, a novel tetravalent fap-dr5 antibody, effectively triggers fap-dependent, avidity-driven dr5 hyperclustering and tumor cell apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.J.; Olson, K.; Haber, L.J.; Varghese, B.; Duramad, P.; Tustian, A.D.; Oyejide, A.; Kirshner, J.R.; Canova, L.; Menon, J.; et al. A novel, native-format bispecific antibody triggering t-cell killing of b-cells is robustly active in mouse tumor models and cynomolgus monkeys. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.; Haber, L.; Kelly, M.P.; Vazzana, K.; Canova, L.; Ram, P.; Pawashe, A.; Finney, J.; Jalal, S.; Chiu, D.; et al. A mucin 16 bispecific t cell-engaging antibody for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckinger, A.; Delgado, J.A.; Moser, S.; Moreno, L.; Neuber, B.; Grab, A.; Lipp, S.; Merino, J.; Prosper, F.; Emde, M.; et al. Target expression, generation, preclinical activity, and pharmacokinetics of the bcma-t cell bispecific antibody em801 for multiple myeloma treatment. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanzer, J.M.; Wartha, K.; Moessner, E.; Hosse, R.J.; Moser, S.; Croasdale, R.; Trochanowska, H.; Shao, C.; Wang, P.; Shi, L.; et al. Xgfr*, a novel affinity-matured bispecific antibody targeting igf-1r and egfr with combined signaling inhibition and enhanced immune activation for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. MAbs 2016, 8, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbas, C.F. Phage Display: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Efimov, G.A.; Raats, J.M.H.; Chirivi, R.G.S.; van Rosmalen, J.W.G.; Nedospasov, S.A. Humanization of murine monoclonal anti-htnf antibody: The f10 story. Mol. Biol. 2017, 51, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Tsai, S.; Lo, S.C.; Wear, D.J.; Izadjoo, M.J. Production and characterization of chimeric monoclonal antibodies against burkholderia pseudomallei and b. Mallei using the dhfr expression system. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Ohtomo, T.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Kawai, S.; Koishihara, Y.; Ozaki, S.; Kosaka, M.; Tsuchiya, M. The humanized anti-hm1.24 antibody effectively kills multiple myeloma cells by human effector cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mol. Immunol. 1999, 36, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.S. A heterodimeric fc-based bispecific antibody simultaneously targeting vegfr-2 and met exhibits potent antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2748–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, S.; Kamada, H.; Inoue, M.; Nagano, K.; Mukai, Y.; Higashisaka, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Tsunoda, S. A novel bispecific antibody against human cd3 and ephrin receptor a10 for breast cancer therapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, V.; Rafique, A. Designing binding kinetic assay on the bio-layer interferometry (bli) biosensor to characterize antibody-antigen interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 536, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouquet, H.; Warncke, M.; Scheid, J.F.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Enhanced hiv-1 neutralization by antibody heteroligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberst, M.D.; Fuhrmann, S.; Mulgrew, K.; Amann, M.; Cheng, L.; Lutterbuese, P.; Richman, L.; Coats, S.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Hammond, S.A. Cea/cd3 bispecific antibody medi-565/amg 211 activation of t cells and subsequent killing of human tumors is independent of mutations commonly found in colorectal adenocarcinomas. MAbs 2014, 6, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, T.; Sano, Y.; Komatsu, S.I.; Kamata-Sakurai, M.; Kaneko, A.; Kinoshita, Y.; Shiraiwa, H.; Azuma, Y.; Tsunenari, T.; Kayukawa, Y.; et al. An anti-glypican 3/cd3 bispecific t cell-redirecting antibody for treatment of solid tumors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, A.; Nonomura, C.; Ashizawa, T.; Kondou, R.; Ohshima, K.; Sugino, T.; Mitsuya, K.; Hayashi, N.; Nakasu, Y.; Maruyama, K.; et al. A t-cell-engaging b7-h4/cd3-bispecific fab-scfv antibody targets human breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontermann, R.E.; Brinkmann, U. Bispecific antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurs, F.V.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G.E.; de Groot, D.J.A. A review of bispecific antibodies and antibody constructs in oncology and clinical challenges. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 201, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Albaitero, A.; Xu, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Tran, H.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Scaltriti, M.; Janjigian, Y.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. Overcoming resistance to her2-targeted therapy with a novel her2/cd3 bispecific antibody. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1267891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, J.A.; Su, Z.; Colvin, R.B.; Wong, J.T. Anti-cd3:Anti-il-2 receptor-bispecific mab-mediated immunomodulation. Low systemic toxicity, differential effect on lymphoid tissue, and inhibition of cell-mediated hypersensitivity. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 3674–3682. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Cheung, N.V. T cell engaging bispecific antibody (t-bsab): From technology to therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 182, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandikian, D.; Takahashi, N.; Lo, A.A.; Li, J.; Eastham-Anderson, J.; Slaga, D.; Ho, J.; Hristopoulos, M.; Clark, R.; Totpal, K.; et al. Relative target affinities of t-cell-dependent bispecific antibodies determine biodistribution in a solid tumor mouse model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, T.; Neri, D. Biodistribution studies with tumor-targeting bispecific antibodies reveal selective accumulation at the tumor site. MAbs 2012, 4, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuraszeck, T.; Kasichayanula, S.; Benjamin, J.E. Translation and clinical development of bispecific t-cell engaging antibodies for cancer treatment. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 101, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ciombor, K.K.; Haraldsdottir, S.; Goldberg, R.M. Promising new agents for colorectal cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Kindler, H.L.; Jahan, T.; Bazhenova, L.; Reck, M.; Thomas, A.; Pastan, I.; Parno, J.; O’Shannessy, D.J.; Fatato, P.; et al. Phase ii clinical trial of amatuximab, a chimeric antimesothelin antibody with pemetrexed and cisplatin in advanced unresectable pleural mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5927–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, F.A.; Stickler, M.M.; Razo, J.; DuBridge, R.B. The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: Residual immunogenicity resides in the cdr regions. MAbs 2010, 2, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Cohen, D.; Belmar, N.A.; Choi, D.; Tan, S.S.; Sho, M.; Akamatsu, Y.; Kim, H.; Iyer, R.; Cabel, J.; et al. A bispecific molecule targeting cd40 and tumor antigen mesothelin enhances tumor-specific immunity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1864–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antigen | Clone | ka (1/Ms) | kd (1/s) | KD (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSLN | HMI323 | 3.24 × 105 | 1.58 × 10−3 | 4.87 |
| MG1122-A | 2.04 × 104 | 1.92 × 10−3 | 94.3 | |
| MG1122-B | 9.94 × 104 | 7.74 × 10−4 | 7.79 | |
| CD3 | A15 | 3.90 × 105 | 4.57 × 10−4 | 1.17 |
| MG1122-A | 6.93 × 105 | 9.76 × 10−3 | 14.1 | |
| MG1122-B | 4.61 × 105 | 2.42 × 10−2 | 52.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, A.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Lim, S.; Park, Y.-Y.; Song, E.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, K.; Lim, Y. A Novel T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody for Treating Mesothelin-Positive Solid Tumors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030399
Yoon A, Lee S, Lee S, Lim S, Park Y-Y, Song E, Kim D-S, Kim K, Lim Y. A Novel T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody for Treating Mesothelin-Positive Solid Tumors. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(3):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030399
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Aerin, Shinai Lee, Sua Lee, Sojung Lim, Yong-Yea Park, Eunjung Song, Dong-Sik Kim, Kisu Kim, and Yangmi Lim. 2020. "A Novel T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody for Treating Mesothelin-Positive Solid Tumors" Biomolecules 10, no. 3: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030399
APA StyleYoon, A., Lee, S., Lee, S., Lim, S., Park, Y.-Y., Song, E., Kim, D.-S., Kim, K., & Lim, Y. (2020). A Novel T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody for Treating Mesothelin-Positive Solid Tumors. Biomolecules, 10(3), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030399




