Abstract
IceCube measures a diffuse neutrino flux comparable to the Waxman-Bahcall bound, which suggests the possibility that the ultra-high energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) have a common origin with diffuse high energy neutrinos. We propose high energy gamma-ray and/or neutrino observations toward the arrival directions of UHECRs to search for the sources and test this possibility. We calculate the detection probability of gamma-ray/neutrino sources, and find that the average probability per UHECR of >10 EeV is ∼10% if the sensitivity of the gamma-ray or neutrino telescope is ∼10 erg cm s and the source number density is ∼10 Mpc. Future gamma-ray and neutrino observations toward UHECRs, e.g., by LHAASO-WCDA, CTA, IceCube/Gen2, are encouraged to constrain the density of UHECR sources or even identify the sources of UHECRs.
1. Introduction
The origin of ultra-high energy cosmic rays (≳10 eV; UHECRs) is still an open question [1,2]. Because cosmic rays are charged particles, their arrival directions will be affected by magnetic field during propagation, which makes it difficult to locate the UHECR sources by their arrival directions directly. The sample size is another difficulty of searching sources by UHECR observations. The cosmic ray flux above the cosmic ray spectral “ankle” is small and there is a cutoff feature at the highest energies [3,4]. The ankle might be attributed to the transition from Galactic to extra-galactic components [5,6], or the “dip” due to the electron pair production in cosmic ray propagation [7]. The cutoff may be caused by interactions of UHECRs with the cosmic background radiation, known as Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin (GZK) cutoff [8,9], however, the maximum energy of particle acceleration [10] in the sources may also lead to such cutoff. These features of cosmic ray energy spectrum indicate that UHECRs may come from extra-galactic sources.
Cosmic rays may produce high energy gamma-rays and neutrinos via pion production processes, when cosmic rays interact with background photons or matter. This makes it possible to build a connection between UHECRs and gamma-rays or neutrinos. Neutral particles are not deflected by magnetic fields, pointing back to the sources. Moreover, neutrinos hardly interact with other matter, which makes them a special kind of astrophysical messengers [11,12].
High energy astrophysical neutrinos are discovered by the IceCube neutrino detector [13,14], opening a window to high energy neutrino astronomy. The IceCube measured neutrino flux [15] is comparable to the Waxman-Bahcall bound [16,17], ∼2 × 10 GeV cm s sr, which is an upper bound for the extra-galactic neutrino flux derived from the observed UHECR flux and assuming all the UHECR energy are converted to pions. Such coincidence may suggest that the UHECRs and high energy neutrinos are produced in the same or related processes [18]. The cosmic ray particles resulting in secondary neutrinos lose energy efficiently in the sources or the environment by pion production, thus the neutrino flux from charged pion decay can be comparable to the Waxman-Bahcall bound.
In this work, we assume a common origin of UHECRs and the high energy neutrinos, and suggest an observation strategy that search for gamma-ray and neutrino sources at UHECR directions. We calculate the probability of the detection of gamma-ray or neutrino sources in the UHECR directions.
2. Physical Picture and Assumption
We adopt the following physical picture for the emission of gamma-ray and neutrinos associated with UHECR sources, and some assumptions in the calculation of the gamma-ray and neutrino emission.
2.1. UHECR Sources as Gamma-Ray and Neutrino Sources
We assume the UHECRs are dominantly protons, although there is debate of proton versus heavy nucleus composition. In this case, the spectral cut-off feature at highest energy is well explained by the GZK effect, and the observed spectral index above eV is consistent with explained by shock acceleration [19].
We assume UHECRs and the high energy neutrino producing cosmic rays are accelerated by the same sources. The UHECRs escape from the sources and their environment, e.g., the host galaxy, promptly due to their large rigidity, while the cosmic rays with lower energy are trapped in the host galaxy. These trapped cosmic rays interact with matter, e.g., the interstellar medium, in the host galaxy and lose most of their energy in pion production process, then neutrinos and gamma-rays can be produced by pion decay. In this situation, we naturally expect a diffuse neutrino flux from UHECR sources roughly equal to the Waxman-Bahcall bound, and IceCube diffuse neutrino flux is mainly contributed by these UHECR associated neutrinos.
The host galaxies emit both high energy neutrinos and gamma-rays. Neutrinos come from charged pion decay, , and the following muon decay, . Neutral pions are also produced in pion production process, and they quickly decay to high energy gamma-rays, . In this picture, high energy neutrinos and gamma-rays are well connected in arrival directions and flux with UHECRs, if UHECRs do not change their directions in propagation, which is the case as shown below.
2.2. Spatial and Temporal Association of UHECRs with Gamma-Ray/Neutrino Signals
Consider the propagation of protons with energy E in the magnetic field with strength B and correlation length . After travel a distance d, the typical angle deflection of the proton is ∼, where is Lamour radius of the proton [20], i.e., ∼. It is expected to observe gamma-ray and neutrino point sources toward the UHECR directions within few degree separation.
Due to the deflection, the arrival time of UHECRs will be delayed relative to a photon emitted in the same time by a typical delay time, ∼∼ for E∼ and a distance d∼, The arrival time will spread in a timescale similar to , if the UHECRs are produced by explosive events rather than steady sources.
We assume the diffuse neutrino flux measured by IceCube can be accounted for by UHECR sources and their environments. Thus we expect to observe gamma-rays and neutrinos from the UHECR directions in the same time for steady sources—however, even for explosive sources of UHECRs, this is also very likely. For the low energy cosmic rays to be trapped in the source environment, say the source’s host galaxy, and lose energy significantly in pion production, it may be required that the energy loss time scale is larger than the escape time scale of cosmic rays, thus the gamma-ray and neutrino emission duration will be the energy loss time of cosmic rays, ∼∼, given cross section ∼ for protons, medium density ∼, much larger than the UHECR spreading time. We expect to find a persistent source of gamma-rays or neutrinos around the direction of a detected UHECR.
3. Method and Formula
The way to estimate the probability of finding correlated gamma-ray and neutrino sources is shown in this section.
3.1. Horizon for Gamma-Ray and Neutrino Sources
Both gamma-ray and neutrino source detection are limited by the sensitivity of telescopes. In addition, high energy gamma-rays from extra-galactic sources are attenuated due to the absorption by the extra-galactic background light (EBL), . So only sources within some “horizon” can be detected.
The horizon is determined by the typical luminosity of the source. For gamma-ray sources, the typical specific gamma-ray luminosity, , of a single source related to UHECRs can be derived via , i.e.,
where is the source number density in the local universe, is the Hubble timescale of the universe, is a coefficient accounting for the redshift evolution of the UHECR production rate density and we take ≃ 3 for redshift evolution following the star formation rate [16], and is the total flux of gamma-ray from UHECR sources when EBL absorption is neglected.
The neutrino and gamma-ray are both from pion decays. We assume in interactions, pion number ratio is :::1:1. Each gamma-ray gains of energy of a , while each neutrino gains of energy of a . Then we have , and . So high energy gamma-ray flux (without EBL absorption) from UHECR sources can be scaled with neutrino flux as
with . From the latest results of IceCube observations, we have [21] for single flavor (we have assumed equal flavor ratio for the three neutrino flavors).
Considering the EBL absorption for high energy gamma-rays, the maximum redshift of the gamma-ray sources that can be detected is determined by equation
Here is the optical depth of high energy gamma-rays due to EBL absorption, for which we adopt the observational results from [22]. is the integral sensitivity of gamma-ray telescope at gamma-ray energy above and is the luminosity distance (we adopt the standard CDM cosmological model). The sensitivity and the source number density are two parameters that decide the maximum redshift.
The horizon for neutrino source searching can be derived similarly. Due to the very weak interactions with the background matter, the universe is transparent to neutrinos, thus the neutrino horizon can be solved out via
where is the neutrino telescope sensitivity, and the typical specific neutrino luminosity for a single source can be obtained by
3.2. Detection Probability
We propose to use gamma-ray and/or neutrino telescopes to observe the directions of the detected UHECRs, and estimate the average probability to detect a gamma-ray and/or neutrino source for per UHECR.
For an UHECR detector array with the effective area and the observational time , the total number of UHECRs that are detected above some energy E is the integration of the UHECR production rate over the universe history,
where is the specific production rate density of UHECRs as function of cosmic ray energy E and at redshift z, dV/dz is the comoving volume per unit redshift, and accounts for the GZK effect (see below).
To account for the GZK effect, consider an “optical depth” , where is the comoving distance and is the energy loss length due to GZK effect. Following [23], we take , with t being the energy loss time of UHECRs in the Cosmic Microwave Background, which is parameterized as , with , , , and .
Given the telescope horizon, the number of detected UHECRs that are originated from sources within the horizon, i.e., within the maximum redshift, is
The ratio between the above two gives the average probability of finding a source from each detected UHECR with energy above E,
4. Results
Based on the method and assumptions above, we calculate the horizon distance and the source detection probability. We consider observations of gamma-rays above 2 TeV with telescope sensitivity in the range of about –. For neutrino observations, the sensitivity for neutrino source detection at >100 TeV is also about . The horizons for gamma-ray and neutrino telescopes are shown in Figure 1 for various source density . The gamma-ray horizon is roughly scaling with the sensitivity as . And we find that the horizon is <100 Mpc for high energy gamma-ray sources. The EBL absorption does not affect the horizon significantly, and the limitation on the gamma-ray source detection is mainly determined by the telescope sensitivity.
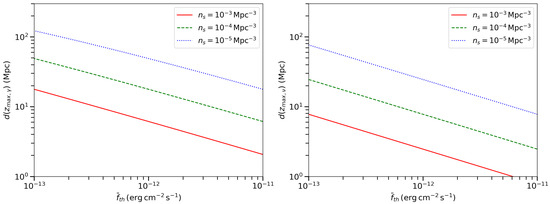
Figure 1.
The horizon distance as a function of telescope sensitivities. Left panel: observation of >2 TeV gamma-rays. Right panel: observation of >100 TeV neutrinos. The three lines from top to bottom correspond to three source number densities, , , and .
For the UHECR production rate and spectrum, we take for particle acceleration in collisionless shocks [19], and , comparable to star formation rate evolution and active galactic nuclei redshift distribution [24]. As for the effective area of the UHECR array we assume the energy dependence following the Auger experiment [25], i.e., beyond , the detection reaches a full efficiency and is a constant independent of E.
With the horizons derived, the probability of source detection per UHECR can be calculated. Three parameters determine the detection probability: the sensitivity, source number density and the lower limit of cosmic ray energy. The first two parameters affect the horizon together by their product, , because the maximum redshift can be seperated from and in Equations (3) and (4). The dependence of the detection probability on the product, , is shown in Figure 2. A larger source number density leads to lower luminosity, and then smaller detection probability. A better gamma-ray or neutrino telescope sensitivity surely leads to a higher probability.
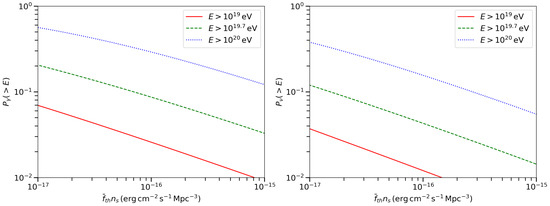
Figure 2.
Average detection probability for gamma-ray/neutrino sources toward UHECR directions as a function of the product of source number density and the gamma-ray/neutrino telescope sensitivity. Left panel: observation of >2 TeV gamma-rays. Right panel: observation of >100 TeV neutrinos. The three lines correspond to three lower limits of cosmic ray energy, , and .
Prediction for LHAASO-WCDA and IceCube can be obtained from Figure 2. For the WCDA sensitivity of [26] and assuming a source number density of , the detection probability of gamma-ray sources at the directions of UHECRs with energy above can be quite high, (>10∼. Similar probability is obtained for neutrino source searching with IceCube, which has a typical sensitivity of [27].
In Figure 3 we show the dependence of the detection probability on the energy lower limit of UHECRs sample, assuming . The probability increases with cosmic ray energy. For higher energy cosmic rays, the GZK effect will suppress UHECR flux from distant sources, leading to a higher detection probability for gamma-ray or neutrino sources. Above energy , GZK cutoff suppresses the observed UHECR flux more significantly, and lead to a fast increasing of detection probability.
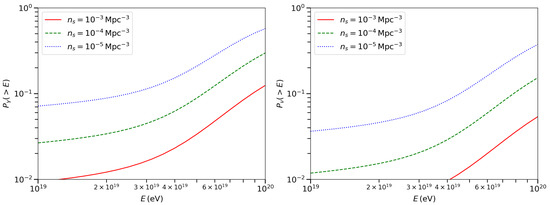
Figure 3.
Average detection probability for gamma-ray/neutrino sources toward UHECR directions as a function of the lower limit of the cosmic ray energy. Left panel: observation of >2 TeV gamma-rays. Right panel: observation of >100 TeV neutrinos. The three lines correspond to three source number densities, , , and . The sensitivity is assumed to be for both gamma-ray and neutrino telescopes.
5. Conclusions and Discussion
In this work, we show a picture for UHECR source bearing galaxies as high energy gamma-ray and neutrino sources, motivated by the coincidence of IceCube neutrino flux and Waxman-Bahcall bound. We estimate the probability of detecting gamma-ray or neutrino sources around UHECR directions. The detection probability for different parameters, including the lower limit of UHECR energy, the source number density and the sensitivity of gamma-ray and neutrino telescopes, is estimated. We find that the average probability per UHECR is about for detecting gamma-ray sources at the directions of UHECRs with energy , for a gamma-ray telescope with a sensitivity of and if the source density number density is . This implies that it needs a UHECR sample containing about 10 events of to find a gamma-ray source. The probability for neutrino source detection is found to be in the same order of for the same parameter setting, because the gamma-ray and neutrino emission is well connected in the flux and spectrum.
The model can be used for both steady sources and transient sources of UHECRs. For steady sources, the source number density in our model and calculation just means their number density. For example, starbusrt galaxies are one kind of potential sources for UHECRs [28]. Number density of starburst galaxies is about , and they can be seen as steady sources. When the gamma-ray telescope sensitivity is , we have probability to find gamma-ray source at direction of a UHECR with energy , if source number density is at a level of that for starburst galaxies. For transient sources, gamma-ray and neutrino emission from their host galaxies still last ∼. The production, , is an average number density for transient sources. But these transient events often occur repeatedly in their host galaxies, and we consider the host galaxies as the gamma-ray and neutrino sources. To get the number density of host galaxies, the average number density of the sources should multiply a factor , where is the typical time interval between two transient events. So we can use ∼ as the source number density for transient sources. Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are candidate sources for UHECRs [20,29,30], and they are transient events. Event rate of GRB is about ∼∼, if we consider the beaming effect. When we take the time interval ∼, we get source number density for GRBs is ∼. For source number density at this level, an UHECR sample with energy above is needed to get a detection probability.
We consider protons as the main composition of UHECRs. A heavier composition will affect our results. For heavy nuclei, the Lamour radius will be smaller, , which lead to a stronger deflection. The typical deflection angle for heavy nuclei is Z times as large as that for proton, . It is hard to find gamma-rays or neutrino sources in a small region around UHECR direction when the UHECRs composition is too heavy. And if the search is in a larger region, there will be more noise and false positive signals.
When we calculate the typical gamma-ray luminosity of single source in Section 3.1, we consider the high energy gamma-rays all from decay. Besides the gamma-rays hadronic process, there are other leptonic processes, Inverse-Compton and synchrotron radiation of electrons, producing high energy gamma-rays. We assume gamma-rays from decay typically account for a fraction f () of the total gamma-ray luminosity, while the calculation in Section 3 and Section 4 just takes . When leptonic components contribute significantly, the gamma-ray luminosity should be modified by multiplying a factor of . The effect of this modification is the same as multiplying a factor f on source number density or on telescope sensitivity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Z.L. and Q.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.L., X.T. and Q.Z.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, Z.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11773003, U1931201) and the China Manned Space Project (CMS-CSST-2021-B11).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Tianqi Huang and Kai Wang for helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nagano, M.; Watson, A.A. Observations and implications of the ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2000, 72, 689–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, K.; Olinto, A.V. The Astrophysics of Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic Rays. ARA&A 2011, 49, 119–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.U.; Abu-Zayyad, T.; Allen, M.; Amman, J.F.; Archbold, G.; Belov, K.; Belz, J.W.; Ben Zvi, S.Y.; Bergman, D.R.; Blake, S.A.; et al. First Observation of the Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin Suppression. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Aguirre, C.; Allard, D.; Allekotte, I.; Allen, J.; Allison, P.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; Ambrosio, M.; et al. Observation of the Suppression of the Flux of Cosmic Rays above 4 × 1019 eV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 061101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, D.; Parizot, E.; Olinto, A.V. On the transition from galactic to extragalactic cosmic-rays: Spectral and composition features from two opposite scenarios. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 27, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Budnik, R.; Waxman, E. The energy production rate & the generation spectrum of UHECRs. J. Cosmology Astropart. Phys. 2009, 2009, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezinsky, V.; Gazizov, A.; Grigorieva, S. On astrophysical solution to ultrahigh energy cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 043005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greisen, K. End to the Cosmic-Ray Spectrum? Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, G.T.; Kuz’min, V.A. Upper Limit of the Spectrum of Cosmic Rays. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 1966, 4, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Hillas, A.M. The Origin of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays. ARA&A 1984, 22, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halzen, F.; Hooper, D. High-energy neutrino astronomy: The cosmic ray connection. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2002, 65, 1025–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E. High energy cosmic ray and neutrino astronomy. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1101.1155. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Abbasi, R.; Abdou, Y.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Altmann, D.; Auffenberg, J.; Bai, X.; et al. First Observation of PeV-Energy Neutrinos with IceCube. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 021103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IceCube Collaboration. Evidence for High-Energy Extraterrestrial Neutrinos at the IceCube Detector. Science 2013, 342, 1242856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Alispach, C.; Alves, A.A.; Amin, N.M.; Andeen, K.; et al. IceCube high-energy starting event sample: Description and flux characterization with 7.5 years of data. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E.; Bahcall, J. High energy neutrinos from astrophysical sources: An upper bound. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 59, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcall, J.; Waxman, E. High energy astrophysical neutrinos: The upper bound is robust. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Waxman, E.; Thompson, T.; Loeb, A. The energy production rate density of cosmic rays in the local universe is ∼1044–45 erg Mpc−3 yr−1 at all particle energies. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1311.0287. [Google Scholar]
- Blandford, R.; Eichler, D. Particle acceleration at astrophysical shocks: A theory of cosmic ray origin. Phys. Rep. 1987, 154, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E. Cosmological Gamma-Ray Bursts and the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stettner, J. Measurement of the diffuse astrophysical muon-neutrino spectrum with ten years of IceCube data. In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2019), Madison, Wisconsin, 24 July–1 August 2019; Volume 36, p. 1017. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G. The extragalactic background light revisited and the cosmic photon-photon opacity. A&A 2017, 603, A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E. Cosmological Origin for Cosmic Rays above 1019 eV. ApJ 1995, 452, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, B.J.; Terlevich, R.J. The cosmological evolution of the QSO luminosity density and of the star formation rate. MNRAS 1998, 293, L49–L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Ahn, E.J.; Allard, D.; Allekotte, I.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; Ambrosio, M.; Anchordoqui, L.; et al. Trigger and aperture of the surface detector array of the Pierre Auger Observatory. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. A 2010, 613, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; della Volpe, D.; Liu, S.; Bi, X.; Chen, Y.; D’Ettorre Piazzoli, B.; Feng, L.; Jia, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; et al. The Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) Science Book (2021 Edition). arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.02773. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Alispach, C.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; Ansseau, I.; et al. Time-Integrated Neutrino Source Searches with 10 Years of IceCube Data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.N.; Kusenko, A.; Nagataki, S.; Zhang, B.B.; Yang, R.Z.; Fan, Y.Z. Monte Carlo Bayesian search for the plausible source of the Telescope Array hotspot. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 043011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Ioka, K.; Nagataki, S.; Nakamura, T. High-energy cosmic-ray nuclei from high- and low-luminosity gamma-ray bursts and implications for multimessenger astronomy. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 023005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietri, M. The Acceleration of Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays in Gamma-Ray Bursts. ApJ 1995, 453, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
