Abstract
We review a special class of supergravity model that interpolates all the single-dilaton truncations of the maximal gauged supergravity. We also provide explicit non-extremal, charged black hole solutions and their supersymmetric limits, asymptotic charges, thermodynamics and boundary conditions. We also discuss a suitable Hamilton–Jacobi formulation and related BPS flow equations for the supersymmetric configurations, with an explicit form for the superpotential function. Finally, we briefly analyze certain models within the class under consideration as consistent truncations of the maximal, gauged supergravity in four dimensions.
1. Introduction
Anti-de Sitter (AdS) black hole configurations are an intriguing field of research due to the role they play in high energy theory as well as in the phenomenology of the AdS/CFT conjecture [1]. The latter exploits a surprising geometric picture (‘holographic duality’) for dimensional conformal quantum field theories living at the boundary of a dual (super)gravity model in D dimensions, also providing a concrete ‘recipe’ for relating the bulk gravity model with the dual field theory at its boundary.1 The correspondence can then be exploited to gain new insights into both of the dual theories since stable AdS solutions would describe conformal critical points of the gauge theory at the boundary. This turns out to be a realization of the holographic principle [2], being the description of the bulk AdS spacetime encoded on the dual conformal gauge field theory. Moreover, the energy scale of the boundary theory is related to the radial direction of the bulk spacetime [3,4] so that the geometric radial flow can be (holographically) interpreted as the renormalization group flow of the dual quantum field theory [5,6], the UV perturbation appearing as boundary conditions on the supergravity fields at large radius.
In light of the above discussion, AdS black hole solutions can provide a powerful framework to reveal specific features about a dual, strongly coupled gauge theory, providing then a possible description of many condensed matter phenomena. The thermodynamic properties of AdS black holes were first analyzed in [7] and subsequently extended to various other AdS black hole configurations [8,9,10,11,12]. These studies describe how black holes feature specific phase structures, giving rise to critical phenomena analogous to other common thermodynamic systems. Of particular interest are black hole solutions preserving a certain amount of supersymmetry, since they allow mapping a weak (string) coupling description of the system thermodynamics to the strong-coupling regime, where a formulation in terms of a black hole configuration is valid [13]. Moreover, these solutions can be exploited to study the BPS attractor flows in AdS spacetime [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
Gauged Supergravities and Black Holes
The analysis of stationary black hole configurations was motivated by the study of classical general relativity solutions as well as by a deeper understanding of the mentioned AdS/CFT duality. For instance, in general relativity, these kind of solutions are important for clarifying relevant aspects of no-hair theorems [28], the role of scalar charges for black hole thermodynamics [29,30,31,32], and other specific features related to the stability of the theory [33,34,35].
In general, the construction of black hole solutions in gauged supergravity theories is a fundamental groundwork for (phenomenologically realistic) cosmological models, supporting an effective cosmological constant term as well as a suitable scalar potential and related scalar mass contributions. In this regard, gauged supergravity theories in four dimensions provide realistic quantum field models featuring a non-trivial scalar potential: the latter could lift the moduli degeneracy and select a consistent vacuum state for our universe. Moreover, an embedding of the scalar potential itself in a supergravity model is important, since many physical aspects of the theory can be better understood.
On the other hand, from the perspective of the AdS/CFT duality, the discovery of one-parameter family of maximal four-dimensional supergravity theories [36] led to significant progresses toward understanding the vacuum properties and the structure of the dual field theories [37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Together with the original model [44], other gauged supergravities have been developed, exploiting the presence of a dyonic embedding tensor [45,46,47]; these models feature a richer vacuum structure and scalar field dynamics with respect to the original theory.
Several procedures have been proposed in order to obtain exact, regular hairy [23,47,48,49,50,51,52] and supersymmetric black hole solutions [25,53,54] for a general scalar potential. The mentioned studies also seem to suggest that an important condition for the existence of hairy black hole solutions is the presence of suitable scalar field self-interaction properties, together with an appropriate gravitational interaction determining the near-horizon behavior as well as the far-region hair physics.2 This also implies a probable connection between the integrability of the equations of motion and the explicit form of the scalar potential.
In the following we will review exact charged hairy black hole solutions in gauged , supergravity of [55].3 These hairy black hole configurations feature a scalar potential whose specific form is connected with the existence of exact solutions and, in turn, with a black hole solution generating technique. The dilatonic scalar field features generalized boundary conditions preserving the conformal isometries of Anti-de Sitter spacetime: these conditions can be interpreted, according to the holographic dictionary, as perturbing the boundary (UV critical point) with multi-trace deformations of the dual conformal field theory [58]. In particular, the mixed boundary conditions for the scalar would correspond to adding a triple-trace operator to the dual field theory action.
Below, we will provide the explicit expressions for two different families of non-extremal black hole solutions, analyzing the duality relation between them. We will then consider the thermodynamic properties of the solutions together with the analysis of the related boundary conditions. We will also analyze which conditions for the parameters give rise to (non-singular) BPS configurations. In a separate section, we will exploit an Hamilton–Jacobi formalism for our new class of black holes, characterizing their dynamics in terms of a first-order description. Finally, we will briefly discuss specific models (within the new general class under consideration) as consistent truncations of the maximal , gauged supergravity.
2. The Model
Let us consider an extended supergravity theory in , coupled to vector multiplets and no hypermultiplets, in the presence of Fayet–Iliopoulos terms (FI-terms).
The model describes vector fields , () and complex scalar fields (). The bosonic gauged Lagrangian has the standard form
and is defined in terms of the vector field strengths . The complex scalars span a special Kähler manifold [59,60,61] and feature non-minimal coupling to the vector fields through the matrices , , while the form of the scalar potential explicitly depends on the FI-terms.
The presence of a non-trivial scalar potential comes from the gauging of a -symmetry of the corresponding ungauged model (without FI-terms) and implies the existence of minimal couplings of the vectors to the fermion fields only.
2.1. Single-Dilaton Truncation
Let us now focus on a model with no hypermultiplets and a single vector multiplet () with a single complex scalar field z () [47,55]. The geometry of the special Kähler manifold is characterized by a prepotential function with explicit form:
The coordinate z is identified with the ratio , in a local patch in which . For special values of n, this model can be reduced to a consistent truncation of the STU model4.
If we set , the holomorphic section of the model reads:
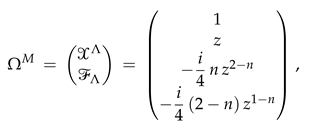 and, in the special coordinate frame, the lower components
and, in the special coordinate frame, the lower components  can be expressed as the gradient with respect to the upper entries of the prepotential function,
can be expressed as the gradient with respect to the upper entries of the prepotential function,  . The Kähler potential is expressed as
The theory is then deformed with the introduction of dyonic, electric–magnetic FI-terms. The latter are defined by a constant symplectic vector , encoding the gauge parameters of the model. The scalar potential can be then obtained from [47,55]
where
. The Kähler potential is expressed as
The theory is then deformed with the introduction of dyonic, electric–magnetic FI-terms. The latter are defined by a constant symplectic vector , encoding the gauge parameters of the model. The scalar potential can be then obtained from [47,55]
where
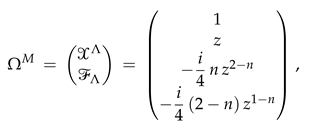
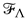 can be expressed as the gradient with respect to the upper entries of the prepotential function,
can be expressed as the gradient with respect to the upper entries of the prepotential function, 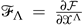 . The Kähler potential is expressed as
. The Kähler potential is expressed as
The matrix is a symplectic, symmetric, negative definite matrix, expressed in terms of and as
and satisfies [69,70]
The scalar manifold is endowed with a flat symplectic bundle and it is possible to associate with each point of this space the matrix , thus determining a metric on the symplectic fiber. Being defined in terms of the coupling matrices , in the bosonic Lagrangian (1), the matrix also encodes the information about the non-minimal couplings between the scalars and the vectors of the theory.
If we express the scalar field as
the truncation to the dilaton field (i.e., setting the axion ) is consistent provided:5
After the restriction to the dilaton, the scalar metric reads:
and is positive for . We then express in terms of n as
so that the kinetic term for is canonically normalized.
As a function of the dilaton field only, the scalar potential has the following explicit form [47,55]:
2.1.1. Vacua
Let us make the change of variable
in the potential (15), using also the consistent truncation condition (11)
The resulting potential has the form:
where
with the condition , to ensure the reality of the solution.
If we want to find the vacua of the theory, we have to solve the equation
where the derivative of the potential has the form:
with
A first vacuum solution is given by
while other vacuum configurations come from the solutions of the equation
The above Equation (24) has a variable number of solutions, depending on the range of values to which the number n belongs. Table 1 summarizes the number, types and mass of vacuum solutions for each possible interval of values of n [47].

Table 1.
Vacuum types.
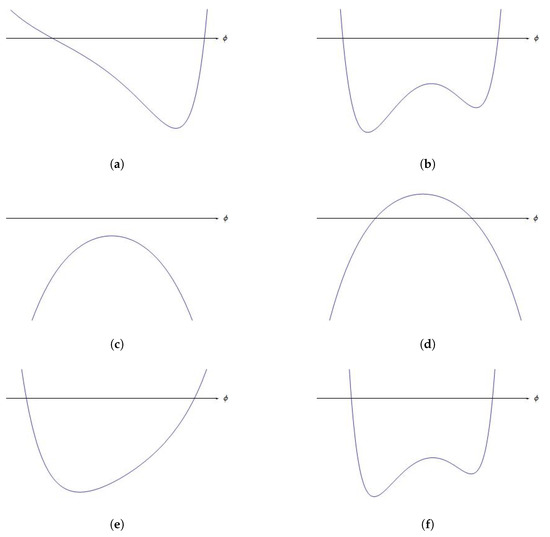
Figure 1.
Vacua potential graphics.
2.1.2. Redefinitions
We now consider the shift
and redefine the FI-terms as:
having also introduced the quantity
together with the parameters , s and
expressed in terms of the AdS radius L. The above definitions ensure the existence of an AdS vacuum without further constrains on the original FI-terms components [55].
The truncation to the dilaton is consistent provided Equations (11) and (12) are satisfied. The former, in the new parametrization (26), is rewritten as
which is solved, excluding and , either for (pure electric FI-terms) or for : since we are interested in dyonic FI-terms configurations, we will restrict ourselves to the latter case.
After the shift (25), the scalar field z is expressed as
and the same redefinition in the potential (with ) yields
where .
After the restriction to the dilaton, the matrix vanishes, while the takes a diagonal form and, if we define the canonically normalized gauge fields
the action takes the explicit form
3. Results
3.1. Hairy Black Hole Solutions
Now we consider two distinct families of solutions, which we refer to as electric and magnetic, respectively [55].
3.1.1. Family 1 – Electric Solutions
A first family of solutions is given by
where is an integration constant and is the metric on the -surfaces with constant scalar curvature . 6
- Boundary conditions, mass and thermodynamics for the electric solutions.
We now consider the change of coordinates [55]
to make contact with AdS canonical coordinates in the asymptotic limit, the + (−) sign holding for (). The corresponding asymptotic behavior of the scalar field is
The coefficients of the leading and subleading coefficients read
and correspond to AdS invariant boundary conditions, namely a triple-trace deformation in the boundary theory preserving the boundary conformal symmetry. The asymptotic expansion of the spacetime (36) in the new coordinates reads [55]
where
The black hole mass can be read-off from the above expansion and reads7
where . The energy density of the system [72] is expressed as
the dual boundary field theory living then on a manifold of radius L. The temperature and the entropy are given by
where . Finally, the physical charges and electric potentials are
and it is possible to verify that these quantities satisfy the first law of thermodynamics:8
3.1.2. Family 2 – Magnetic Solutions
A second family of solutions is given by
The electric and magnetic solutions are related to each other by means of electromagnetic duality
and the corresponding transformation of the electromagnetic fields (see also Section 4.1). In each of the two families, the asymptotic region is found for . The geometry and scalar field are singular at and and, therefore, the configuration features two inequivalent, disjoint geometries for or .
- Boundary conditions, mass and thermodynamics for the magnetic solutions.
The metric of the magnetic family can be obtained from the electric solutions by means of the transformation
and, therefore, the same analysis performed for the electric family can be exploited in the magnetic frame. In the latter case, the scalar asymptotic leading and subleading coefficients satisfy
which correspond again to AdS invariant boundary conditions (triple-trace deformation in the boundary theory). We introduce the quantity [55]
where the + (−) corresponds to () and express the black hole mass as
The magnetic charges and potentials are given by
and it is possible to verify that the above quantities satisfy the first law of thermodynamics:
3.1.3. Case or
The action in this special case9 has the explicit form
The scalar potential coming from (5) in the limit is redefined through the shift
and writing the FI-terms as:
while the field strengths have the form
The above Lagrangian yields a consistent truncation of the minimal coupling supergravity [74] (corresponding to the case) if the constraints (11), (12) are satisfied. In particular, the latter explicitly reads
The theory features an explicit dyonic solution of the form [55]
and the above constraint (61) requires
4. Discussion
4.1. Duality Relation between the Two Families of Solutions
The two families of solutions can be related by an electric–magnetic duality symmetry.10 The transformation of the non-dynamical of amounts to a change in the theory, the duality being then interpreted as an equivalence between different models. Consider a generic theory described by the Lagrangian (1), the scalar potential given by Equation (5). Let us introduce the magnetic field strengths
and the symplectic field strength vector
The special Kähler manifold spanned by the scalars has a flat symplectic bundle structure, the matrix acting as a metric on the symplectic fiber. With each isometry of the scalar manifold, it can be associated a constant symplectic matrix such that, if is the action of on the scalars, transforms as [69,70]:
having suppressed symplectic indices. Then, if we transform correspondingly the Maxwell fields and the FI-terms ,
the equations of motion are left invariant.
Aside from the above duality, it is possible to redefine and as [55]:
where is a generic real, invertible matrix. This amounts to a change of basis in the symplectic fiber and does not alter the physics of the model. We can apply this mechanism to our truncated single-dilaton model, taking care that the transformations do not turn on the truncated axion . The absence of the latter implies , while the isometries of the dilaton can be expressed as
being a constant. The transformation (74) was used in Section 2.1.2 to reabsorb the dependence of the FI-terms, the latter then depending only on . This was then followed by the redefinition (73) of the field strengths and terms. If we now focus on the duality transformation (75), it is possible to verify that the associated transformation is given by matrix . In particular, we find:
and, applying shift symmetry (74) and the above redefinition, the new FI-terms have the form
Now it is possible to prove that the scalar potential satisfies
or, equivalently
only depending on . Then, if the electric solution
solves the field equations with parameter , the magnetic configuration
is a solution with parameter .
4.2. Supersymmetric Solutions
Now we want to study supersymmetryc configurations for our model, imposing the vanishing of the SUSY variations [75] (see Appendix A). First, it is useful to make a change of coordinates that puts metric (36) in the standard form
This can be achieved through the change of coordinate
c being an integration constant.
4.2.1. Family 1
The scalar field z in the new parametrization has the form
while the electric–magnetic charges explicitly read
The solution is supersymmetric if the following relations are satisfied:
4.2.2. Family 2
The scalar field z reads
while the electric–magnetic charges are
The solution is supersymmetric if
The supersymmetric magnetic condition can be obtained from the supersymmetric electric condition by means of the duality transformation
4.3. Old and New Solutions
Here we briefly mention already known configurations as particular cases of our new general solutions [55].
4.3.1. Duff–Liu
The Duff and Liu solution [65] features singular supersymmetric configurations, while some of their non-extremal solutions can be put in relation with our model for special values of the parameter. The theory under consideration is the well known STU model of gauged supergravity with three scalar fields , , .
The model. If we equal the three scalars, , we obtain the so-called model. The latter coincides with our formulation (33) for .
The or model. In this case, we set . The STU model then reduces to the model, coinciding with our (57). The Duff–Liu configuration can be recovered from our solution provided either the magnetic or the electric charges are set to zero.
4.3.2. Cacciatori–Klemm
This model was important since it provided the first non singular supersymmetric black holes in AdS [14].
The model. The spherically symmetric, purely magnetic supersymmetric solution can be obtained from our prepotential (2) with , corresponding to , and pure magnetic FI-terms.
4.4. New BPS Black Holes with Finite Area
4.4.1. Family 1: BPS Electric Black Holes
The electric family has BPS black holes of finite area for . In this case, we find [55]:
and it is possible to verify that is an even function of , , so that we can restrict our analysis to the interval.
Keeping in mind that the spacetime has disjoint and inequivalent geometries for and (the asymptotic region being located at ), we can characterize the location of the horizon as follows
- k = 0:
- in the flat case the location of the horizon is very simple (see the above (91)) and it follows that and , so we conclude that only exists;
- k = −1:
- in the hyperbolic case, always exists while the solution exists provided ;
- k = +1:
- for spherical black hole only exists, provided .
Using BPS conditions (86), we can write the explicit form for the physical charges and electric potentials for the supersymmetric solutions as [55]:
having fixed . The mass of the electric BPS black hole configuration is given by
and it is then verified the extremality condition
4.4.2. Family 2: BPS Magnetic Black Holes
We can again restrict to the case, and verify that this family has BPS black holes of finite area for (electric gauging). In this case, the metric for the magnetic solution is the same than for the electric one, implying a coinciding analysis about the location of the horizons. The extremality of the magnetic solutions is the same as for the electric solutions when the electric charges and potentials are interchanged by their magnetic counterparts.
4.5. Hamilton–Jacobi Formulation
If we consider a stationary dilatonic black hole configuration with radial dependence for the scalar field, , the most general metric ansatz, with spherical or hyperbolic symmetry, has the form (82),
We can obtain the equations of motion coming from the bosonic gauged Lagrangian (1), with the above metric ansatz, from a one-dimensional effective action that, apart from total derivative terms, has the form
where the prime stands for derivative with respect to r and where we can define an effective potential
in terms of the scalar potential V and the (charge-dependent) black hole potential . The latter can be written in the symplectically covariant form [75,76,77]
in terms of the magnetic and electric charges and scalar-dependent matrix . The black hole potential (98) can also be schematically rewritten in terms of the central charges as [75,76,77]
Once given the effective action, one can make use of the Hamilton–Jacobi formalism and derive a system of first-order equations (flow equations) for the warp factors , and scalar fields .
Flow equations
If we collectively denote the metric and scalar degrees of freedom characterizing the solution by , we can rewrite the effective Lagrangian of Equation (96) as
with
The conjugate momenta are obtained from
while the Hamiltonian can be written as
together with the energy conservation constraint .
Let us now consider a BPS configuration. If a superpotential function can be defined for the latter, then the radial evolution of the system can be described in terms of equations of the form
BPS hairy black hole. The superpotential function for our electric solution has the explicit form
where is written in terms of the central charge and complex superpotential obtained from the geometry of the supergravity Kähler manifold [75]. The above superpotential correctly satisfies equations (104) for the hairy black hole configuration, namely
when evaluated on the solution.
4.6. Truncations
4.6.1. Uncharged Case
The infinitely many theories defined by the model under consideration comprise all the possible one-dilaton consistent truncations of the -deformed, gauged maximal supergravities [36,42,45,46,69,70,78,79]11.
Let us consider the following truncation to gravity and scalar field sector of the maximal supergravity [81,82]:
with 7 independent scalars (, ) and scalar potential
where
A single-scalar field reduction preserving can be obtained through [55]
having defined:
that also implies
With the above choices, we can obtain a consistent truncation of the -rotated gauged maximal supergravity. The corresponding action is invariant under , and and reduces, in the absence of vector fields, to the action (33) upon identifications:
or, changing into in (112),
We conclude that our new single-scalar models with vanishing vector fields coincide with gauged -deformed maximal supergravity truncations to a singlet sector, with respect to the following subgroups of the gauging [55]:
In particular, or correspond to models which can be embedded in the STU truncation of the gauged supergravity. Therefore, the new black hole solutions, in the absence of electric and magnetic charges, can all be embedded in the maximal theory.
4.6.2. Charged Case
Now we consider charged solutions and their possible embedding in the dyonic, gauged maximal supergravity [55].
- case.
Let us consider first the case. These solutions describe gravity coupled to one scalar and two vector fields. The latter, when identified with their counterparts in the maximally supersymmetric theory, should not excite other fields in the model: this requires the condition in our solution12, again with the presence of seven independent scalar fields (, ) parameterizing the Cartan subalgebra of .
Then, we want to further truncate the model to a single scalar , singlet with respect to the subgroup of . The two vector fields of the charged solution are identified with two of the 28 vectors of the maximal theory that do not source the six scalars we want to vanish. We then express as [55]:
The equations for the six scalars () are satisfied when , while enters the kinetic terms of the vector fields as in (33), with , after identifying the two vectors and as:
in terms of the of the maximal theory and the generators ().13 The two field strengths in (33) can be in turn identified with the of the maximal theory as [55]:
In the case, the same generators are gauged by linear combinations of and of the form
which amounts to gauging in a different symplectic frame, with electric vector fields (the hat denoting indices in the new -rotated symplectic frame). The related symplectic vector of electric and magnetic field strengths in the new frame is obtained from the relation [55]:
while the deformed kinetic matrix is expressed in terms of the in the original frame as:
After the truncation, the vector kinetic terms in the new symplectic frame will depend on through the restrictions to . The dependence can be disposed of at the level of field equations and Bianchi identities, since the latter depend on only in symplectic-invariant contractions with the matrix and its derivatives. The dependence of the terms involving the vector field strengths can be undone redefining the latter, which amounts to express them in terms of their counterparts in the original frame ( and their magnetic duals) through the matrix E. Upon these redefinitions, the bosonic field equations of the truncated model coincide with those obtained from the action (33), with , provided we identify [55]:
The embedding of the model in the maximal theory will be studied in the future. In the remaining cases or , our solutions can be extended to charged solutions within gauged supergravity within the bosonic part of the STU truncation of it.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank M. Trigiante, A. Anabalon, D. Astefanesei for discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Supersymmetric Black Hole Solutions
In order to obtain supersymmetric configurations, we have to impose the vanishing of the SUSY transformations in addition to solving the equations of motion.
The relevant supersymmetry variations can be expressed as:
with .14 The covariant derivatives are written as
with
and, in the chosen parametrization, we also have [75]:
having used properties
The kinetic matrix is defined as
and can be expressed in terms of the prepotential as [84]
with , . We emphasize that, in the special coordinate frame, the whole Lagrangian can be written in terms of the holomorphic prepotential function (if any) and its derivatives.
From an explicit computation of the supersymmetry variations (A1), we find the following relations for the warp factors [75]
and for the scalars
the above covariant derivative acting on objects with weight , and having introduced two projectors relating the spinor components as [15,16,75,85]
The choice of phase turns out to be irrelevant from the physical point of view (due to the presence of the symmetry), while it will amount to putting the symplectic sections of the vector multiplet moduli space in a particular frame [15,16].
The Killing spinors must satisfy the relations [75]
where we have
and the following expression for the phase holds [75]:
The chosen type of Killing spinors explicitly break 3/4 of the supersymmetry, i.e., the solution is 1/4 BPS, meaning that only 2 supercharges are preserved, corresponding to the 2 degrees of freedom of the complex function parameterizing the , Killing spinors [15,16].
Finally, from the SUSY variations we obtain the property [75]
and, using also the ansatz
for the symplectic vector, we find for the components:
together with the relation
Notes
| 1 | The boundary theory is located at the UV critical point and is it possible to employ a UV/IR connection, which relates gravity degrees of freedom at large (small) radius with the corresponding counterparts in the dual field theory at high (low) energy regime. |
| 2 | Scalar self-interactions could be relevant for dynamic and thermodynamic stability of the configuration: naively, we can imagine the condition for the existence of hairy solutions as if the self-interaction of the scalar and the gravitational interaction were to combine such that the near-horizon hair did not collapse into the black hole, while the far-region hair did not escape to infinity. |
| 3 | These new solutions generalize the uncharged configurations of [47,51,56,57]. |
| 4 | The STU model [62,63,64] is a supergravity coupled to vector multiplets and characterized, in a suitable symplectic frame, by the prepotential , together with symmetric scalar manifold of the form spanned by the three complex scalars (); this model is in turn a consistent truncation of the maximal theory in four dimensions with gauge group [65,66,67,68]. |
| 5 | The conditions come from the consistency of the axion field equations after the truncation. |
| 6 | The explicit form of the solution makes the uncharged limit well-defined, giving the hairy black hole configurations of [47]; the result should be not taken for granted, since in the standard literature the uncharged limit gives either Schwarzschild or Schwarzschild–AdS spacetime. |
| 7 | Since the solution preserves conformal symmetry at the boundary, the mass can be directly extracted from the metric [30,31,71]. |
| 8 | We do not have to modify the 1st law with the contribution of scalar charges having preserved the boundary conformal symmetry [30,31,73]. |
| 9 | This particular class of solutions is noteworthy as it can be embedded in gauged supergravity [74]. |
| 10 | The latter is a non-perturbative (global) symmetry of the ungauged theory and is extended to the gauged one if the constant tensor is made to transform under it as well [69,70]. |
| 11 | The construction of these models was carried out by exploiting the freedom in the initial choice of the symplectic frame of the maximal theory, that is, gauging a group in different symplectic frames by rotating the original one [44,80] making use of a suitable symplectic matrix, thus obtaining a one-parameter class of inequivalent theories (-deformed models). |
| 12 | , label the 28 vectors of the maximal theory, while m, n are the symplectic indices of the 56 electric and magnetic charges. |
| 13 | We explicitly have , , [55]. |
| 14 | For the gamma-matrices we can use the conventions of App. A of [83]. |
References
- Maldacena, J.M. The Large N limit of superconformal field theories and supergravity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1999, 38, 1113–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susskind, L. The World as a hologram. J. Math. Phys. 1995, 36, 6377–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peet, A.W.; Polchinski, J. UV/IR relations in AdS dynamics. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 59, 065011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susskind, L.; Witten, E. The Holographic bound in anti-de Sitter space. arXiv 1998, arXiv:hep-th/9805114. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, J.; Verlinde, E.P.; Verlinde, H.L. On the holographic renormalization group. JHEP 2000, 08, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, J. The Holographic renormalization group. Fortsch. Phys. 2001, 49, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.; Page, D.N. Thermodynamics of Black Holes in anti-De Sitter Space. Commun. Math. Phys. 1983, 87, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamblin, A.; Emparan, R.; Johnson, C.V.; Myers, R.C. Charged AdS black holes and catastrophic holography. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 60, 064018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamblin, A.; Emparan, R.; Johnson, C.V.; Myers, R.C. Holography, thermodynamics and fluctuations of charged AdS black holes. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 60, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetic, M.; Gubser, S.S. Phases of R charged black holes, spinning branes and strongly coupled gauge theories. JHEP 1999, 04, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarelli, M.M.; Cognola, G.; Klemm, D. Thermodynamics of Kerr-Newman-AdS black holes and conformal field theories. Class. Quant. Grav. 2000, 17, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalón, A.; Astefanesei, D.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. Instability of supersymmetric black holes via quantum phase transitions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:hep-th/2105.08771. [Google Scholar]
- Strominger, A.; Vafa, C. Microscopic origin of the Bekenstein-Hawking entropy. Phys. Lett. 1996, B379, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciatori, S.L.; Klemm, D. Supersymmetric AdS(4) black holes and attractors. JHEP 2010, 01, 085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, K.; Looyestijn, H.; Vandoren, S. BPS black holes in N = 2 D = 4 gauged supergravities. JHEP 2010, 08, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, K.; Vandoren, S. Static supersymmetric black holes in AdS4 with spherical symmetry. JHEP 2011, 04, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, K.; Toldo, C.; Vandoren, S. On BPS bounds in D = 4 N = 2 gauged supergravity. JHEP 2011, 12, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldo, C.; Vandoren, S. Static nonextremal AdS4 black hole solutions. JHEP 2012, 09, 048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, D.D.K.; Compère, G. Dyonic AdS black holes in maximal gauged supergravity. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecchi, A.; Hristov, K.; Klemm, D.; Toldo, C.; Vaughan, O. Rotating black holes in 4d gauged supergravity. JHEP 2014, 01, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecchi, A.; Halmagyi, N. Supersymmetric black holes in AdS4 from very special geometry. JHEP 2014, 04, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Pang, Y.; Pope, C. An ω deformation of gauged STU supergravity. JHEP 2014, 04, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faedo, F.; Klemm, D.; Nozawa, M. Hairy black holes in N=2 gauged supergravity. JHEP 2015, 11, 045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Marrani, A.; Petri, N.; Santoli, C. BPS black holes in a non-homogeneous deformation of the stu model of N = 2, D = 4 gauged supergravity. JHEP 2015, 09, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, S.; Klemm, D.; Petri, N. Supersymmetric black holes and attractors in gauged supergravity with hypermultiplets. JHEP 2015, 06, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hristov, K.; Katmadas, S.; Toldo, C. Rotating attractors and BPS black holes in AdS4. JHEP 2019, 01, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, N.; Faedo, F.; Klemm, D.; Ramírez, P.F. Rotating black holes in the FI-gauged N = 2, D = 4 ℂPn model. JHEP 2019, 03, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, T. Towards a Novel no-hair Theorem for Black Holes. Phys. Rev. 2006, D74, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, T.; Maeda, K. Stability and thermodynamics of AdS black holes with scalar hair. Phys. Rev. 2005, D71, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A.; Astefanesei, D.; Martinez, C. Mass of asymptotically anti–de Sitter hairy spacetimes. Phys. Rev. 2015, D91, 041501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A.; Astefanesei, D.; Choque, D.; Martinez, C. Trace Anomaly and Counterterms in Designer Gravity. JHEP 2016, 03, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Pope, C.N.; Wen, Q. Thermodynamics of AdS Black Holes in Einstein-Scalar Gravity. JHEP 2015, 03, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, T.; Hollands, S. Stability in designer gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2005, 22, 5323–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsel, A.J.; Hertog, T.; Hollands, S.; Marolf, D. A Tale of two superpotentials: Stability and instability in designer gravity. Phys. Rev. 2007, D75, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, T.; Horowitz, G.T.; Roberts, M.M. New stability results for Einstein scalar gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 205007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dall’Agata, G.; Inverso, G.; Trigiante, M. Evidence for a family of SO(8) gauged supergravity theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 201301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghese, A.; Dibitetto, G.; Guarino, A.; Roest, D.; Varela, O. The SU(3)-invariant sector of new maximal supergravity. JHEP 2013, 1303, 082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrio, J.; Varela, O. Electric/magnetic duality and RG flows in AdS4/CFT3. JHEP 2014, 1401, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallerati, A.; Samtleben, H.; Trigiante, M. The > 2 supersymmetric AdS vacua in maximal supergravity. JHEP 2014, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghese, A.; Guarino, A.; Roest, D. All G2 invariant critical points of maximal supergravity. JHEP 2012, 1212, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, H.; Nozawa, M. Classification and stability of vacua in maximal gauged supergravity. JHEP 2013, 01, 045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, A. On new maximal supergravity and its BPS domain-walls. JHEP 2014, 02, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, A. CSOc superpotentials. Nucl. Phys. 2015, B900, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, B.; Nicolai, H. N = 8 Supergravity. Nucl. Phys. 1982, B208, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agata, G.; Inverso, G. On the Vacua of N = 8 Gauged Supergravity in 4 Dimensions. Nucl. Phys. 2012, B859, 70–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agata, G.; Inverso, G. De Sitter vacua in N = 8 supergravity and slow-roll conditions. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 718, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anabalón, A.; Astefanesei, D.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. Hairy Black Holes and Duality in an Extended Supergravity Model. JHEP 2018, 04, 058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneaux, M.; Martinez, C.; Troncoso, R.; Zanelli, J. Black holes and asymptotics of 2+1 gravity coupled to a scalar field. Phys. Rev. 2002, D65, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.; Troncoso, R.; Zanelli, J. Exact black hole solution with a minimally coupled scalar field. Phys. Rev. 2004, D70, 084035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, T.; Maeda, K. Black holes with scalar hair and asymptotics in N = 8 supergravity. JHEP 2004, 07, 051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A. Exact Black Holes and Universality in the Backreaction of non-linear Sigma Models with a potential in (A)dS4. JHEP 2012, 06, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.H.; Lu, H.; Wen, Q. Scalar Hairy Black Holes in General Dimensions. Phys. Rev. 2014, D89, 044014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agata, G.; Gnecchi, A. Flow equations and attractors for black holes in N = 2 U(1) gauged supergravity. JHEP 2011, 03, 037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnecchi, A.; Toldo, C. On the non-BPS first order flow in N = 2 U(1)-gauged Supergravity. JHEP 2013, 03, 088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A.; Astefanesei, D.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. New non-extremal and BPS hairy black holes in gauged N = 2 and N = 8 supergravity. JHEP 2021, 04, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A.; Astefanesei, D. Black holes in ω-defomed gauged N = 8 supergravity. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 732, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A.; Astefanesei, D.; Choque, D.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. Exact holographic RG flows in extended SUGRA. JHEP 2021, 04, 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, E. Multitrace operators, boundary conditions, and AdS/CFT correspondence. arXiv 2001, arXiv:hep-th/0112258. [Google Scholar]
- Strominger, A. Special Geometry. Commun. Math. Phys. 1990, 133, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger, J.; Witten, E. Matter Couplings in N = 2 Supergravity. Nucl. Phys. B 1983, 222, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, E.; Van Proeyen, A. = 2 Supergravity in D = 4, 5, 6 Dimensions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, M.J.; Liu, J.T.; Rahmfeld, J. Four-dimensional string-string-string triality. Nucl. Phys. B 1996, 459, 125–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrndt, K.; Kallosh, R.; Rahmfeld, J.; Shmakova, M.; Wong, W.K. STU black holes and string triality. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 6293–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrndt, K.; Lust, D.; Sabra, W.A. Stationary solutions of N = 2 supergravity. Nucl. Phys. B 1998, 510, 264–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, M.; Liu, J.T. Anti-de Sitter black holes in gauged N = 8 supergravity. Nucl. Phys. B 1999, 554, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoli, L.; D’Auria, R.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. Extremal Limits of Rotating Black Holes. JHEP 2013, 1305, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoli, L.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. On Extremal Limits and Duality Orbits of Stationary Black Holes. JHEP 2014, 01, 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoli, L.; D’Auria, R.; Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. On D = 4 Stationary Black Holes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 474, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallerati, A.; Trigiante, M. Introductory Lectures on Extended Supergravities and Gaugings. Springer Proc. Phys. 2016, 176, 41–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigiante, M. Gauged Supergravities. Phys. Rept. 2017, 680, 1–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneaux, M.; Martinez, C.; Troncoso, R.; Zanelli, J. Asymptotic behavior and Hamiltonian analysis of anti-de Sitter gravity coupled to scalar fields. Annals Phys. 2007, 322, 824–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.C. Stress tensors and Casimir energies in the AdS / CFT correspondence. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 60, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabalon, A.; Andrade, T.; Astefanesei, D.; Mann, R. Universal Formula for the Holographic Speed of Sound. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 781, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciani, J.F. Coupling of O(2) Supergravity with Several Vector Multiplets. Nucl. Phys. B 1978, 132, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallerati, A. Constructing black hole solutions in supergravity theories. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2020, A34, 1930017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, S.; Gibbons, G.W.; Kallosh, R. Black holes and critical points in moduli space. Nucl. Phys. 1997, B500, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoli, L.; D’Auria, R.; Ferrara, S.; Trigiante, M. Extremal black holes in supergravity. Lect. Notes Phys. 2008, 737, 661–727. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Agata, G.; Inverso, G.; Marrani, A. Symplectic Deformations of Gauged Maximal Supergravity. JHEP 2014, 07, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inverso, G. Electric-magnetic deformations of D = 4 gauged supergravities. JHEP 2016, 03, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, B.; Nicolai, H. N=8 Supergravity with Local SO(8) x SU(8) Invariance. Phys. Lett. B 1982, 108, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetic, M.; Gubser, S.; Lu, H.; Pope, C. Symmetric potentials of gauged supergravities in diverse dimensions and Coulomb branch of gauge theories. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 086003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetic, M.; Lu, H.; Pope, C.; Sadrzadeh, A. Consistency of Kaluza-Klein sphere reductions of symmetric potentials. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoli, L.; Cerchiai, B.L.; D’Auria, R.; Gallerati, A.; Noris, R.; Trigiante, M.; Zanelli, J. N-extended D = 4 supergravity, unconventional SUSY and graphene. JHEP 2020, 01, 084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, M.K.; Zumino, B. Duality Rotations for Interacting Fields. Nucl. Phys. 1981, B193, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romans, L. Supersymmetric, cold and lukewarm black holes in cosmological Einstein-Maxwell theory. Nucl. Phys. B 1992, 383, 395–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).