Abstract
The growing database of exoplanets has shown us the statistical characteristics of various exoplanet populations, providing insight towards their origins. Observational evidence suggests that the process by which gas giants are conceived in the stellar disk may be disparate from that of smaller planets. Using NASA’s Exoplanet Archive, we analyzed the relationships between planet mass and stellar metallicity, as well as planet mass and stellar mass for low-mass exoplanets (MP < 0.13 MJ) orbiting spectral class G, K, and M stars. We performed further uncertainty analysis to confirm that the exponential law relationships found between the planet mass, stellar mass, and the stellar metallicity cannot be fully explained by observation biases alone.
1. Introduction
Until the first exoplanets were discovered nearly three decades ago, most studies have generally focused on the properties of gas giants, due to biases in early detection methods such as radial velocity towards large planets [1]. In comparison, relatively less is known about the sizeable, yet elusive, population of small planets. Data on planets smaller than the size of Neptune has recently become more accessible with transit photometry, enabling significant statistical analyses of small planets. Accordingly, the field has begun expanding from studying mostly gas giants to exploring sub-Neptune-like planets as well.
Recent work [2,3,4] has studied the frequency of planets as a function of stellar metallicity, and has also discussed [5] stellar metallicity among giant planets. These, and several subsequent studies, have established a strong correlation between the number of giant gas planets in an extrasolar system, and the metallicity of their host stars. This is explained by a core accretion model of planetary formation [6]: to form giant planets, enough solid surface density is needed to reach a critical core mass and the stellar metallicity is the threshold for formation. Based on a database with almost entirely giant planets, this model is consistent with the conclusion that exoplanets are more likely to be found around metal-rich stars [2].
Besides the occurrence–metallicity correlation, a further analysis was discussed in a previous study [7], pointing out the correlation between a planet’s initial mass and its host star’s metallicity. Given a high metallicity environment, more giant planets are likely to form, but for all ranges of metallicity, the mass distribution is similar. This result is reasonable since, as planetary evolution proceeds, the gaseous envelope composes a majority of the giant planet’s mass—not solids. As a result, although the occurrence of giant planets increases with metallicity, we cannot easily conclude that the mass also follows the same pattern. In fact, a recent study [8] showed that the heavy element enrichment of giant planets relative to their host star’s metallicity correlates negatively with planet mass, which suggests that the mass of giant planets does not increase with star metallicity.
Early studies [7,9] suggested that the occurrence–metallicity correlation is weaker for sub-Neptune planets, which is also confirmed by a recent analysis [3] pointing out that this relation is weaker for low-mass planets. The relationship between the stellar metallicity and the planet mass has also been discussed previously [10], in which only the relation for large mass planets was analyzed due to the limited sample size. Recently, with a larger data sample, studies began to focus on the relationship between the planet radius or the planet mass and the stellar metallicity [11,12] for low-mass planets. This raises the question: Where is the expected planetary mass increase for small planets orbiting metal-rich stars? To answer this question, the relationship between the mass of individual low-mass planets and stellar metallicity needs to be examined directly, rather than the frequency of planet occurrence. With analysis of the stellar metallicity–stellar mass relation, it is reasonable for us to study the planet mass–stellar metallicity relation based on the recent research of the planet mass–stellar mass relation [11,13]. Recent work [1] presented a metallicity–mass-period diagram of low-mass exoplanets, identifying a potential correlation between the mass of each planet and stellar metallicity. However, no mathematical relationship has been established. Our paper reexamines this metallicity–mass correlation by proposing a regression model to explain the trend, and analyzes the effect of observational bias and data uncertainty.
2. Data
Using the NASA Exoplanet Archive (https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/ (accessed on 1 February 2021)) with over 4300 confirmed exoplanets, we selected a subset of low-mass planets according to three criteria: (1) the projected mass of the planet is <0.13 Jupiter-mass (MJ); (2) its host star is class G, K, or M; and (3) the percentage of uncertainty of the planet’s mass measurement is <100%. The range of planets encompassed by these conditions roughly represents the population of sub-gas giant exoplanets. A major source of uncertainty from radial velocity measurements is noise from stellar activity, and it is shown in a recent study [14] that hotter main sequence stars emit greater stellar jitter. Thus, the host stars of the sample are limited to later type (G, K, M) spectral classes to reduce the relative effect of stellar noise on radial velocity (RV) oscillations induced by small exoplanets. In total, 253 planets fitting the conditions were used in this study.
3. Results
3.1. The Planet Mass–Stellar Metallicity Relation
The focus of this study is to reexamine the relationship between the mass of low-mass planets and stellar metallicity, and to analyze whether the relationship can be explained with observation biases. Figure 1 is the scatter plot for planet mass against stellar metallicity. Two groups of exoplanets emerge: high-mass planets > 0.13 MJ and low-mass planets < 0.13 MJ. Note that we also considered eight different cutoffs from 0.08 MJ to 0.22 MJ; however, there were no significant changes with these different values in the two distributions (see Figure A1 in the Appendix A).
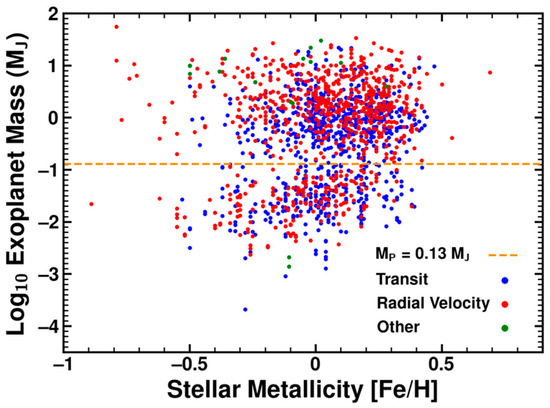
Figure 1.
Scatter plot of mass against stellar metallicity for all 253 exoplanets. Unit of exoplanet mass is Jupiter-mass. Unit of stellar metallicity is [Fe/H]. The dotted orange line shows the mass cutoff line for low-mass planets.
About 58% of the low-mass exoplanets and 46% of the high-mass exoplanets were detected by transit photometry, while 42% of the low-mass and 53% of the high-mass planets were detected through radial velocity detection. This suggests that the observed group distinction is not solely due to biases in the detection method. While the high-mass planets show no correlation with stellar metallicity, the low-mass planets exhibit a linear relationship with metallicity, as isolated in Figure 2.
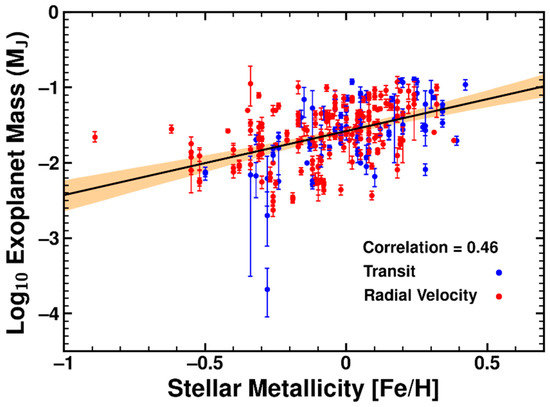
Figure 2.
Linear regression with 95% confidence interval for the mass–metallicity scatter plot of the low-mass exoplanets. Unit of exoplanet mass is Jupiter-mass with error margins taken from the NASA exoplanet archive. Unit of stellar metallicity is [Fe/H].
To test if this observed trend is significant, a linear regression was performed. The mass–metallicity regression follows the exponential-law equation:
where M is the mass of planet, MJ is Jupiter’s mass, a = 0.026 ± 0.0029, b = 0.85 ± 0.20 with 95% confidence, and [Fe/H] denotes the metallicity of the host star. We considered the possibility that the observed trend could be a result of biases inherent to each detection method. A two-dimensional two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test [15] was performed on both groups with a resulting p-value of 0.08, which does not provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the two planet populations are significantly different. Furthermore, planets detected by transit photometry and radial velocity follow the regression line with correlation coefficients of 0.53 and 0.41, respectively, over the same metallicity range, suggesting that the relation cannot be entirely attributed to differences in detection methods.
Though some of our sample is discovered by transit photometry, they must undergo follow-up radial velocity observation to obtain the mass measurement (Only 23 planets in our sample are missing the RV amplitude). Another concern is the correlation between stellar mass and stellar metallicity affecting radial velocity measurements. Although metallicity does not directly affect radial velocity measurements, it is correlated with stellar mass [1], which is a variable in the equation for the semi-amplitude (K1) of a radial velocity oscillation below:
where m, M, P, i, and e are the mass of the planet, mass of the star, period, inclination, and eccentricity, respectively [16]. Using Kepler’s third law, and assuming a circular orbit and a constant orbital semimajor axis, gives the detectability relation,
between projected planet mass and stellar mass. The inclination (i) is randomly distributed so that it has no impact on the statistical analysis. From Figure 3, we can see that stellar mass increases approximately linearly with stellar metallicity for this group of low-mass exoplanets, a result that is supported by recent studies [17,18]. To show that this mass–metallicity correlation does not explain the exponential law trend; we assume a perfect linear correlation between stellar mass and stellar metallicity and perform a linear regression to compute K1, in terms of metallicity. To estimate the amplitude, we assume circular orbits (e = 0) and a constant semi-major axis (a) as 0.1 AU. Figure 3 shows the contours of constant RV amplitude along with the exoplanet population in the mass-period plane. Equation (1) follows a steeper exponential trend than Equation (3), a power relation, which is shown in the right panel of Figure 3. Furthermore, the distribution of real RV magnitude of each planet shows no relevance to the exponential trend. Therefore, there is not sufficient evidence to attribute the planet mass–stellar metallicity trend to star mass–metallicity correlations.
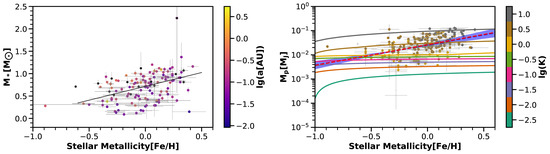
Figure 3.
Left panel: stellar mass versus stellar metallicity for low-mass exoplanets. Unit of stellar mass is solar-mass. Unit of stellar metallicity is [Fe/H]. Right panel: planet mass versus stellar metallicity. The contour lines mark constant radial velocity amplitudes, which are computed based on the linear relationship of stellar mass and metallicity and the assumption of e = 0 and a = 0.1 AU, while the color of the dots indicate the RV (radial velocity) magnitudes of each planet, which is calculated by the properties (stellar mass, planetary mass, semi-major axis) obtained from the NASA Exoplanet Archive website. The dashed blue line is our regression results with the 95% confidence interval shown by the shadow area.
3.2. The Planet Mass–Stellar Mass Relation
In addition to the mass–metallicity trend, a significant mass–mass relation was also found. Shown in Figure 4, planet mass against stellar mass for the same set of exoplanets was plotted with a linear regression following the equation:
with a = 0.039 ± 0.0052 and b = 0.92 ± 0.17 with 95% confidence. Like the mass–metallicity regression, the b slope value for Equation (4) is significantly higher than expected if the trend were due to radial velocity stellar mass scaling. We over-plot the detectability lower bound as the dotted blue line in Figure 4 by using limiting K1 values for 10 m telescopes [14] and assuming head-on inclination with no eccentricity. The selected population lies well above the bound, suggesting that detectability does not fully explain the trend.
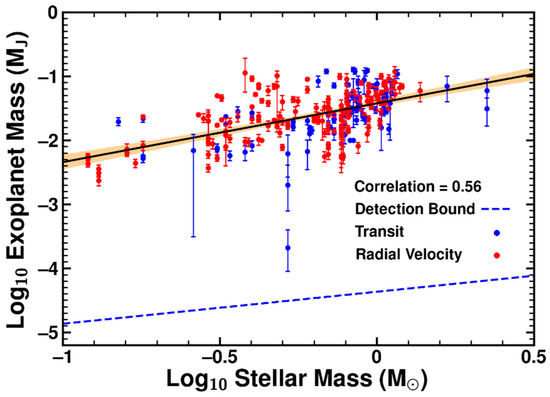
Figure 4.
Linear regression with 95% confidence interval for mass–mass scatter plot of low-mass exoplanets and lower bound detectability. Unit of exoplanet mass is Jupiter-mass with error margins taken from the NASA exoplanet archive. Unit of stellar mass is solar-mass.
To further investigate potential multicollinearity effects of the stellar mass–metallicity relation on this regression, we performed principal component (PC) analysis on stellar metallicity and mass. PC1 and PC2 capture 68% and 32% of the total variance, respectively. In Figure 5, we plot stellar mass and stellar metallicity against the principal components. Although they exhibit somewhat similar distributions along the first principal axis, a two-dimensional Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) test gives a p-value of 5.0 × 10−10, indicating that they are significantly different. The difference of distributions is much more apparent along the second principal axis, as metallicity correlates to PC2 much stronger than mass, suggesting that a large amount of variance in the data is unaccounted for when considering stellar mass or metallicity alone. It is thus highly unlikely that either the planet mass–stellar metallicity trend or the planet mass–stellar mass trend is caused by multicollinearity between stellar parameters.
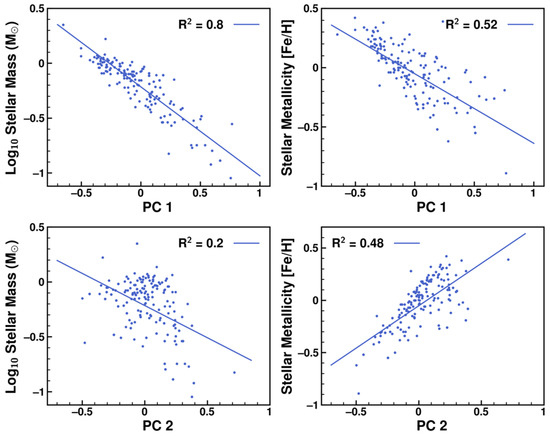
Figure 5.
Scatter plots of stellar mass and stellar metallicity versus principal components. Unit of stellar mass is solar-mass. Unit of stellar metallicity is [Fe/H]. The linear regression gives the R2 value between each principal component and each stellar parameter.
3.3. Uncertainty Analysis
In our analysis, planet mass is referring to projected mass () for those planets without inclination information. It will not influence the linear trend, given that the inclinations (i) are randomly distributed, though the absolute value of the index (a and b) would change if our sample is full of . However, our sample contains both the projected mass () and the accurate mass (M), which could lead to discrepancy between the two subjects.
To investigate the impact of this discrepancy on our conclusion, we make up the difference by simply translating into its average value of accurate mass, (⟨M⟩). The distribution function for i is given by , so the average value of is equal to π/4. As a consequence, the average value of mass is [19]. We multiply the data points of by and show them in Figure 6, as well as the data points of M. The linear regression for the sample contains accurate mass, and projected mass is shown in red in Figure 6, while the linear regression for the sample contains accurate mass, and estimated average mass () is shown in the blue. The overlapping 95% confidence intervals show that there is no significance difference between the two, suggesting that our conclusion is not affected by M and differences.
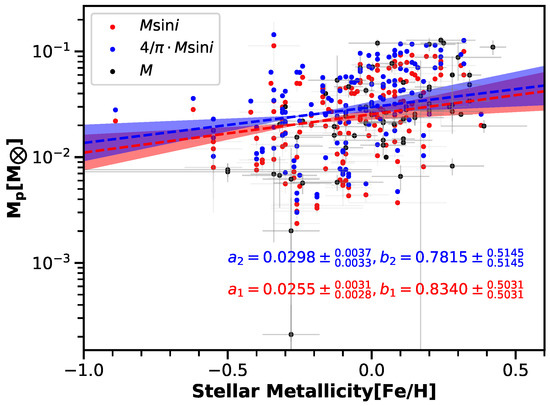
Figure 6.
The scatter plot of planetary mass versus metallicity. The mass is given in different ways. The black dots mark those from accurate measurements, M; the red dots mark the measurement value, while the blue dots mark data points of multiplied by . The red and blue dashed lines represent the fitting curve from linear regression for the sample of and , respectively, as do the texts and the shadow regions (95% confidence interval) in two colors.
As is the lower limit of the real mass (M), it is sufficient to show the trend of the lower boundary of the planetary mass for a given stellar metallicity. Figure 2 indicates the existence of a linear lower boundary, and we can determine the boundary by following the method proposed by the recent study [20]. Firstly, we compute the cumulative distribution function of planetary masses over a succession of metallicity bins, which contain 53 data points equally (only the last bin contains 54 data points). Secondly, the ‘minimum mass’ of the bin is set at different limits (3%, 4%, 5%, and 6%) of this cumulative distribution, as shown by Figure 7. Thirdly, we conduct a linear regression for the minimum mass. For the cutoff limit of 3%, which is accepted by [20], we determine the lower boundary as increasing linearly from 0.0003 MJ to 0.0159 MJ, as shown in Figure 8, where the shadow zone indicates a planet desert below the mass lower boundary. To test the sensitivity to the choice of the chosen cutoff limit, we also apply 4%, 5%, and 6% as the minimum mass limit and got a similar linear boundary (Figure 8). The lower limit of this boundary ranges from 0.0003 MJ to 0.0005 MJ, and the upper limit ranges from 0.0159 MJ to 0.0199 MJ. The linear correlation coefficient varies from 1.18 to 1.24, with the relative uncertainty of 5%, which consolidates our conclusion of the lower boundary.
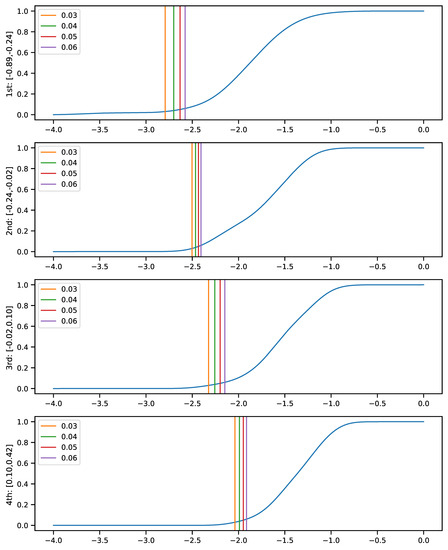
Figure 7.
The cumulative distribution function of planetary masses over a succession of metallicity bins from the bottom to the top, with each bin containing 53 data points, except for the last bin, which has 54 data points. The ranges of the bins are shown on the left y-label. The vertical lines mark the “minimum mass” of the bin as set at the 3%, 4%, 5%, or 6% limit of this cumulative distribution, as shown in the legend.
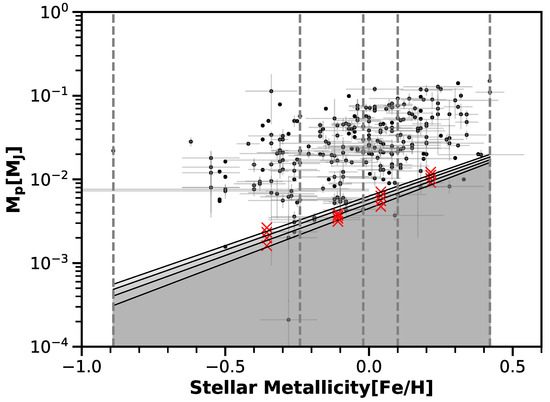
Figure 8.
The gray dashed lines mark the four bins, and the red crosses mark the minimum mass of the bin with different cutoff limits of 3%, 4%, 5%, and 6% separately. The lower boundary is computed by linear regression of the minimum mass and the shadow zone indicates the planet desert below the mass lower boundary.
To determine the lower boundary of the planetary mass for a given boundary, we divide the sample into four subsets regarding a succession of metallicity bins. The first 3 bins contain 53 data points and the last bin contains 54. For each bin, we compute the cumulative distribution function of planetary masses when the ‘minimum mass’ of the bin is set at different (3%, 4%, 5%, 6%) limits for this cumulative distribution, as shown by Figure 7. It shows that the results are not sensitive to the value of the cutoff point, which validifies our conclusion of the existence of the lower limit.
The above analysis suggests the correlation between the planet mass and stellar metallicity is unlikely to be explained by observation biases. The same is true for the planet mass versus stellar mass relation.
4. Discussion
An increase in small planet mass associated with higher stellar metallicity is consistent with the core accretion model of planet formation, wherein dense elements provide matter for solid cores in earlier stages of accretion. Recent work [20] proposed an upper limit to the mass of Neptune-like planets based on stellar metallicity and orbital period in favor of the in-situ formation theory. Our results agree with this finding, but also raise the intriguing possibility that planetary mass may be mathematically tied to stellar metallicity. Currently, the in-situ core accretion model does not account for a potential exponential law relation. The existence of such a trend may suggest that the mass of low-mass planets may be roughly modeled as a function of its host star parameters; the accretion process that leads to the formation of small planets may result in planets whose masses are proportional to the properties of protoplanetary disks—including star metallicity and mass. Due to the relatively low correlation of both trends identified, much more observational data on low-mass planets is needed to confirm this relation.
Another intriguing observation is the apparent difference of properties between gas giant and low-mass planets. While gas giants tend to increase in frequency but not necessarily mass around more metal-rich stars, smaller planets tend to increase in mass; however, there has been no solid evidence that an increase in frequency occurs as well. The disparity between these two populations hints at an undiscovered characteristic of the planetary accretion process. Since terrestrial planets generally have an upper limit of mass before they accrete gaseous envelopes [21], the lack of a correlation between gas giant mass and stellar metallicity gives reason to believe that the solid cores of gas giants have upper mass limits as well. Otherwise, the total mass of gas giant planets would be expected to increase with stellar metallicity, but this is not the case.
The planet mass–stellar mass relation largely agrees with in situ planet formation theories [22]. Since stellar mass is strongly correlated with the mass of its protoplanetary disk [23], the basic expectation is that total planet mass correlates positively with stellar mass—this condition is fulfilled by the observed trend. If planetary mass can indeed be mathematically modeled using stellar parameters, the power law relationship identified may provide insight towards the accretion process.
Although the solid mass of small planets may decrease slightly on average as stellar mass increases [24], the total mass of small planets increases on average (Figure 4). This might imply that the gaseous envelopes of sub-Neptunian planets increase with stellar mass, while the solid core mass decreases, on average. Further studies including the orbital distance of planets may be illuminating, since gas envelope accretion is believed to only be possible at a critical distance from the star [25].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H.J. and D.Z.; methodology, J.H.J., D.Z. and X.J.; software, D.Z. and X.J.; validation, J.H.J., B.X. and K.A.F.; formal analysis, J.H.J., D.Z. and X.J.; investigation, D.Z. and J.H.J.; resources, J.H.J.; data curation, D.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Z. and J.H.J.; writing—review and editing, J.H.J., X.J., B.X. and K.A.F.; visualization, D.Z. and X.J.; supervision, J.H.J.; project administration, J.H.J.; funding acquisition, J.H.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the NASA Exoplanet Research Program NNH18ZDA001N-2XRP.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This article has been approved for unlimited release by the Document Review Services at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), California Institute of Technology. Record: URS298316; Submitted by author: Jonathan H Jiang on 01/31/2021; Document Type: Journal Article; Title: Revisiting the Planet Mass and Stellar Metallicity Relation for Low-Mass Exoplanets Orbiting GKM Class Stars; The JPL clearance number is CL#21-1542.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study are available to download from the NASA Exoplanet Archive (https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/ (accessed on 1 February 2021)), operated by Caltech under contract with NASA. The computed data underlying this article are described in the article. For additional questions regarding the data and code sharing, please contact the corresponding author at Jonathan.H.Jiang@jpl.nasa.gov.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with NASA. We also acknowledge the funding support from the NASA Exoplanet Research Program NNH18ZDA001N-2XRP. We thank Sheldon Zhu for helpful comments and discussions during the development of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
In this study, we accept 0.13 Jupiter-mass as the cutoff, which is a subjective threshold estimated from the visual gap apparent in Figure A1, taking previous literature on low-mass exoplanets as reference (e.g., [1], which has a cutoff at 0.094 Jupiter-mass). We also considered eight different cutoffs from 0.08 MJ to 0.22 MJ; however, it can be seen from the results that R2 are not very sensitive to the threshold regardless. It is suggested that the correlation holds even with many different cuts.
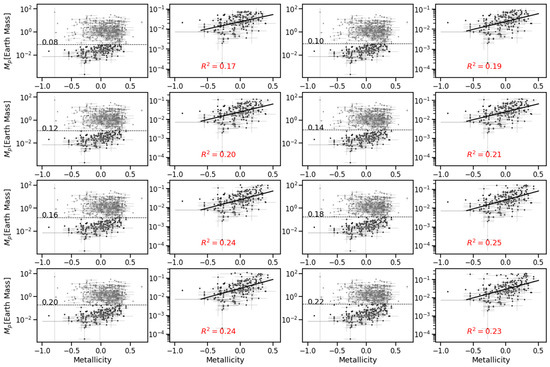
Figure A1.
The first and third columns show scatter plots for planetary mass against the metallicity of planets satisfying our criterion (2) and (3). The gray dots represent the high-mass planets, of which the masses are above different cutoffs as shown by the gray horizontal lines, while the black dots represent the low-mass planets, of which the masses are lower than the cutoffs. The linear regressions for those low-mass planets are shown to the left and the fitting scores (R2) are shown on the figure.
References
- Sousa, S.G.; Adibekyan, V.; Santos, N.C.; Mortier, A.; Barros, S.C.C.; Delgado-Mena, E.; Demangeon, O.; Israelian, G.; Faria, J.P.; Figueira, P.; et al. The metallicity–period–mass diagram of low-mass exoplanets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 3981–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.C.; Israelian, G.; Mayor, M. Spectroscopic [Fe/H] for 98 extra-solar planet-host stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 415, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.T.; Casagrande, L.; Ireland, M.J.; Lin, J. Confirming known planetary trends using a photometrically selected Kepler sample. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 501, 5309–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W. Influence of Stellar Metallicity on Occurrence Rates of Planets and Planetary Systems. Astrophys. J. 2019, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.C. Confirming the Metal-Rich Nature of Stars with Giant Planets. arXiv 2001, arXiv:astro-ph/0109018v1. [Google Scholar]
- Pollack, J.B.; Hubickyj, O.; Bodenheimer, P.; Lissauer, J.J.; Podolak, M.; Greenzweig, Y. Formation of the Giant Planets by Concurrent Accretion of Solids and Gas. ICARUS 1996, 124, 62–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordanisi, C. Extrasolar planet population synthesis -IV. Correlations with disk metallicity, mass, and lifetime. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 541, A97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorngren, D.P.; Fortney, J.J.; Murray-Clay, R.A.; Lopez, E.D. The Mass–Metallicity Relation for Giant Planets. Astrophys. J. 2016, 831, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udry, S.; Santos, N.C. Statistical Properties of Exoplanets. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 45, 397–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, L.; Cunha, K.; Smith, V.V.; De Araújo, F.X.; Schuler, S.C.; De La Reza, R. Stellar Parameters and Metallicities of Stars Hosting Jovian and Neptunian Mass Planets: A Possible Dependence of Planetary Mass on Metallicity. Astrophys. J. 2010, 720, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Mass and mass scalings of super-Earths. Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, B.J.; Petigura, E.A. The California-Kepler Survey. VII. Precise Planet Radii Leveraging Gaia DR2 Reveal the Stellar Mass Dependence of the Planet Radius Gap. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.A.; Huber, D.; Gaidos, E.; Van Saders, J.L.; Weiss, L.M. The Gaia–Kepler Stellar Properties Catalog. II. Planet Radius Demographics as a Function of Stellar Mass and Age. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavchan, P. Radial Velocity Prospects Current and Future: A White Paper Report prepared by the Study Analysis Group 8 for the Exoplanet Program Analysis Group (ExoPAG). arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.01770. [Google Scholar]
- Fasano, G.; Franceschini, A. A multidimensional version of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1987, 225, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddock, G.F. The Derivation of the Radial Velocity Equation. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1913, 25, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leethochawalit, N.; Kirby, E.N.; Moran, S.M.; Ellis, R.S.; Treu, T. Evolution of the Stellar Mass–Metallicity Relation. I. Galaxies in thez∼ 0.4 Cluster Cl0024. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, R.M.; Kauffmann, G.; Guo, Q. The relation between metallicity, stellar mass and star formation in galaxies: An analysis of observational and model data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovis, C.; Fischer, D. Radial Velocity Techniques for Exoplanets; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Courcol, B.; Bouchy, F.; Deleuil, M. An upper boundary in the mass-metallicity plane of exo-Neptunes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammer, H.; Stökl, A.; Erkaev, N.V.; Dorfi, E.A.; Odert, P.; Güdel, M.; Kulikov, Y.N.; Kislyakova, K.G.; Leitzinger, M. Origin and loss of nebula-captured hydrogen envelopes from ‘sub’- to ‘super-Earths’ in the habitable zone of Sun-like stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 3225–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.J. A Brief Overview of Planet Formation. In Handbook of Exoplanets; Deeg, H., Belmonte, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S.M.; Rosenfeld, K.A.; Kraus, A.L.; Wilner, D.J. The mass dependence between protoplanetary disks and their stellar hosts. Astrophys. J. 2013, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, G.D. Planet Populations as a Function of Stellar Properties. In Handbook of Exoplanets; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Montmerle, T.; Augereau, J.-C.; Chaussidon, M.; Gounelle, M.; Marty, B.; Morbidelli, A. Solar System Formation and Early Evolution: The First 100 Million Years. In From Suns to Life: A Chronological Approach to the History of Life on Earth; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).