Abstract
In the present article, we investigate the physical acceptability of the spatially homogeneous and isotropic Friedmann–Lemâitre–Robertson–Walker line element filled with two fluids, with the first being pressureless matter and the second being different types of holographic dark energy. This geometric and material content is considered within the gravitational field equations of the (where T is the torsion scalar and the B is the boundary term) gravity in Hubble’s cut-off. The cosmological parameters, such as the Equation of State (EoS) parameter, during the cosmic evolution, are calculated. The models are stable throughout the universe expansion. The region in which the model is presented is dependent on the real parameter of holographic dark energies. For all , the models vary from CDM era to the quintessence era.
1. Introduction
The amazing disclosure of the increasing expansion of the universe is one of the energizing advancement areas of cosmology. This enormous change in cosmic history has been demonstrated from a differing set of high-precision observational information amassed from different cosmic sources [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The quickening paradigm is considered a result of a fascinating kind of entity, named dark energy.
Dark energy might anticipate the final eventual fate of the universe; its striking highlights are, as yet, unknown. To investigate such an astounding idea, various methodologies have been introduced. Among the different dynamical dark energy models, the essential applicant is the cosmological constant . However, this experiences enormous incidents and fine-tuning problems [7,8]. As a result of this, different dynamical dark energy models have been recommended, such as K-essence [9,10], phantom energy [11,12], quintessence [13], Chaplygin gas [14,15,16] and holographic dark energy (HDE) models [17,18,19,20,21].
Here, we are particularly concerned with HDE. Inspired by black hole thermodynamics [22,23], the holographic principle states that all of the information contained in a volume of space can be represented as a hologram, which corresponds with a theory regarding the boundary of that space [24]. The most successful realization of the holographic principle is the AdS/CFT correspondence, as can be observed in the seminal reference [25]. With applications in different fields of physics, e.g., nuclear physics [26] and cosmology [27], at present, it is believed that the holographic principle should be a fundamental principle of quantum gravity.
The cosmological constant problem mentioned above [7,8] may nearly be a quantum gravity issue. In this way, as the most fundamental principle of quantum gravity, the holographic principle should play an essential role in solving it. In fact, in [17], the first HDE model was proposed, where the holographic principle applies to cosmic acceleration. Such a model of dark energy density relies on two physical quantities on the universe’s boundary: the reduced Planck mass and a cosmological length scale (which can be taken as the future event horizon of the universe). It was suggested that, in the case of a system with ultraviolet cutoff, given by , for a region of size L, the total energy should not exceed the mass of a black hole of the same size. This results in the HDE density being defined as , with C being a constant, being the reduced Planck mass and G being the Newtonian gravitational constant.
Several works exist in the literature in which the eminent authors have discussed the different kinds of HDE by using the holographic principle and dimensional analysis [28,29,30]. Wang et al. [31] derived the general formula for the energy density of HDE and defined the HDE model’s properties, in which the future event horizon is chosen as the characteristic length scale. Pourhassan et al. [32] used observational data to perform cosmography for this holographic model based on fluid/gravity duality. They also obtained the HDE from the fluid/gravity duality constraint through cosmological observations. Sharma et al. [33] calculated the EoS and the deceleration parameter of the Tsallis HDE model to understand cosmological evolution by exploring the interacting Tsallis HDE model in a non-flat universe, with an infrared cut-off as the apparent horizon. By choosing the relationship between interacting dark matter and different HDE fluid environment models, Shekh and Ghaderi [34] have developed a Hypersurface-homogeneous cosmological model of the universe with interacting dark matter and other HDE fluid environment models. It should be a function with a unit of the inverse of cosmic time by considering a constant deceleration parameter corresponding to a purely accelerating model towards . In early and late periods of cosmic evolution, interacting fluids such as dark matter, holographic, and Renyi HDE fluids demonstrate dominance in Hubble’s and Granda–Oliveros cut-offs, respectively.
Different kinds of infrared (IR) cut-offs have been considered in HDE models, e.g., Hubble’s horizon [35,36], event horizon [37], particle horizon [38], conformal universe age [39,40], Ricci scalar radius [41] and Granda–Oliveros cutoff f [42]. Such HDE models with different IR cutoffs can explain the ongoing situation of the increasing speed of universe expansion in agreement with present-day observational information.
Recently, several cosmological phenomena have been discussed using Renyi and Tsallis entropies, proposed in [43,44] as generalizations of the Bekenstein entropy [22]. Such generic entropy formulations can be used in different forms to approach the DE question. From these formulations, the Renyi [45], Tsallis [29] and Sharma–Mittal HDE models [46] have been proposed.
In [47], the Renyi HDE model was examined, with the IR cutoff considered as the Hubble horizon. The examination was made through analysis of the growth rate of perturbations and statefinder hierarchy. In [48], the effects of considering different IR cutoffs, such as the particle horizon, the Ricci horizon and the Granda–Oliveros cutoff in Tsallis HDE, were explored. Observational constraints of the Tsallis HDE model were obtained in [49]. The approach developed in [47] was applied to the Sharma–Mittal HDE model in [50].
To complement the evasion possibilities of the cosmological fine-tuning problem quoted in References [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] and their presented applications, alternative gravity theories must be mentioned. Alternative gravity theories generalize the Einstein–Hilbert action, allowing it to depend generically on the Ricci scalar R and other scalars. Some quite interesting dark energy models have been derived from such formulations, e.g., based on [51,52,53] and gravity theories [54,55,56,57,58,59], with being the trace of the energy-momentum tensor.
Another possibility, which has recently drawn theoretical cosmologists’ attention, is teleparallel gravity [60,61,62,63,64,65]. While in the General Relativity framework, the metric contains the gravitational potentials as responsible for the curvature of space–time, in the teleparallel framework, the gravitational fields are represented by the torsion tensor and the curvature is not important.
Particularly, in [66], the gravity was proposed, with T being the torsion scalar and B the boundary term. Such a formulation was shown to be quite generic in the following sense. If the function is assumed to be independent of the boundary term, the gravity [67,68] is retrieved. Likewise, for a particular form of the function , the teleparallel equivalent of gravity is obtained.
In the following, we quote some interesting references concerning applications of the gravity. Zubair et al. investigated the cosmic evolution in-depth in [69]. From the different functional forms of the function , they have reconstructed de Sitter, power-law, phantom and even standard cosmological models. Extra polarization states of gravitational waves were obtained by Capozziello et al. in [70]. Bahamonde and Capozziello adopted the Noether symmetry approach to study dynamical systems in [71], while Bahamonde et al. analyzed the thermodynamics in gravity in [72].
Energized by the above references, in this article, we investigate the Renyi, Tsallis and Sharma–Mittal HDE models in the gravity under Hubble’s cutoff.
2. The Gravity Field Equations
The gravity action is given as follows [66]
where is the determinant of the tetrad components, , G is the Newtonian gravitational constant, the speed of light c is taken as 1, is a function of the torsion scalar T and boundary term , in which and is the matter action.
By varying the action given in the equation above with respect to the tetrad, the field equations are obtained as
where and . The matter distribution is assumed to be the combination of pressureless matter and isotropic dark energy in the form
which are, respectively, given as
where is the energy density of matter, whereas and are the pressure and energy density of HDE fluid, with , where is the four-velocity vector of the fluid.
The EoS parameter is defined as
After parameterizing the energy-momentum tensor of dark energy , it can be expressed as follows
where , and are the directional EoS parameters on and z axis, respectively.
3. Metric, Friedman-Like Equations and Power Law Expansion Solutions
We consider the spatially homogeneous and isotropic Friedman–Lemâitre–Robertson–Walker line-element in the form
where a is the scale factor of the universe, are the comoving coordinates and we have taken a null spatial curvature .
The components of (2) for the line element (8) with the stress-energy tensor (3) can be written as
where H is the Hubble parameter and the overhead dot represents the differentiation with respect to the cosmic time.
The torsion scalar for the metric (8) is written as
It is related to the Ricci scalar as
The boundary term for metric (8) is obtained as
Since field Equations (9) and (10) have four unknowns and are highly nonlinear, an extra condition is needed to completely solve the system. Here, we use the volumetric power law expansion as [73]
where and are both constants. For different values of , different phases of the evolution of the model are predicted. For , a decelerated phase of the universe expansion is expected, while for , an accelerated phase is expected.
Keeping the relation in mind, we obtain the following time–redshift relation
4. Physical Acceptability of the Gravity Holographic Dark Energy Models
4.1. Renyi Holographic Dark Energy Model with Hubble’s Horizon Cutoff
The energy density of Renyi HDE is characterized as follows [73]
with d and constants. Here, by considering the Hubble horizon as a candidate for the IR-cutoff, i.e., , the Renyi HDE density from Equation (17) is
In view of Equation (16), the expression for the Renyi HDE provided in Equation (18) becomes, in terms of the redshift,
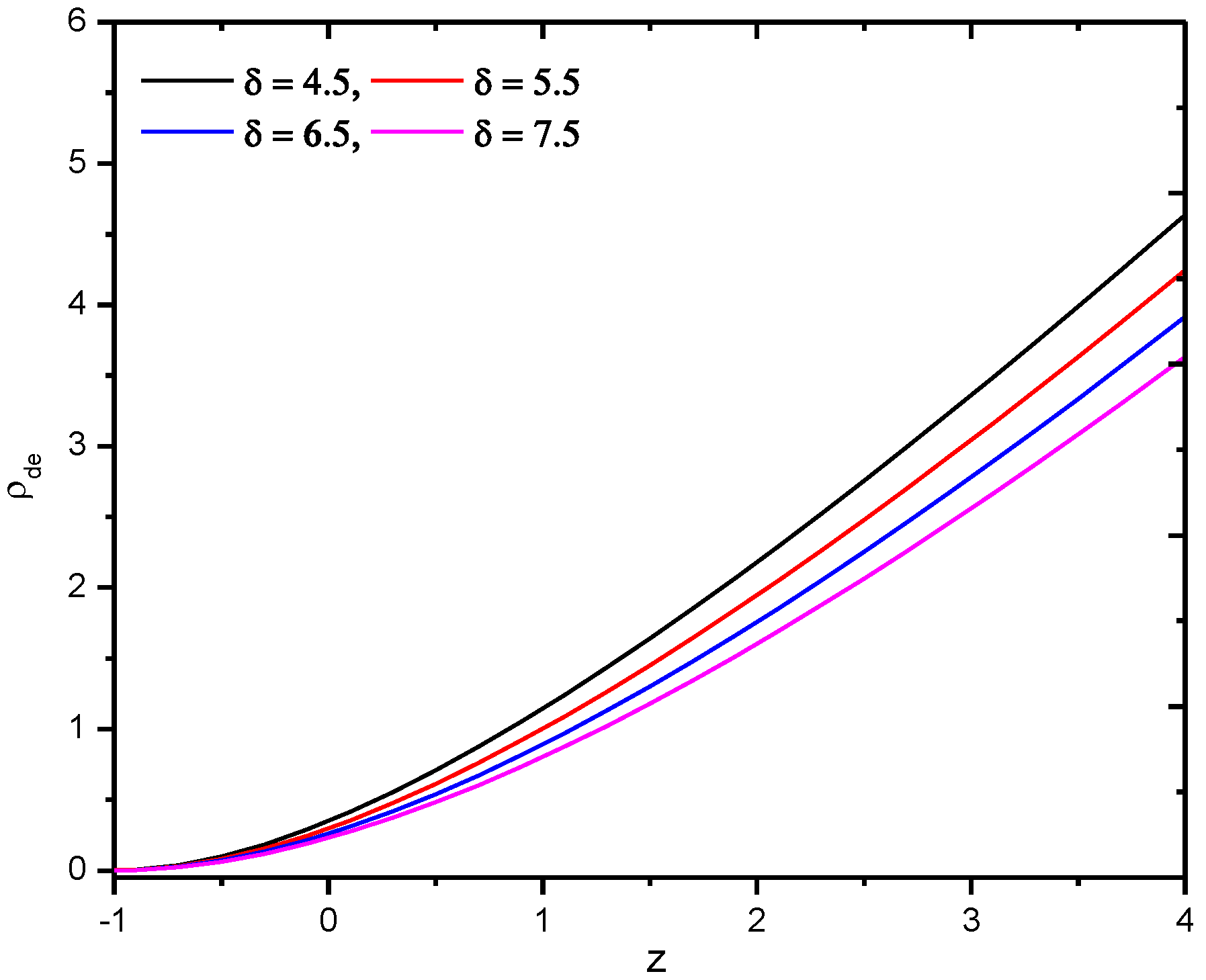
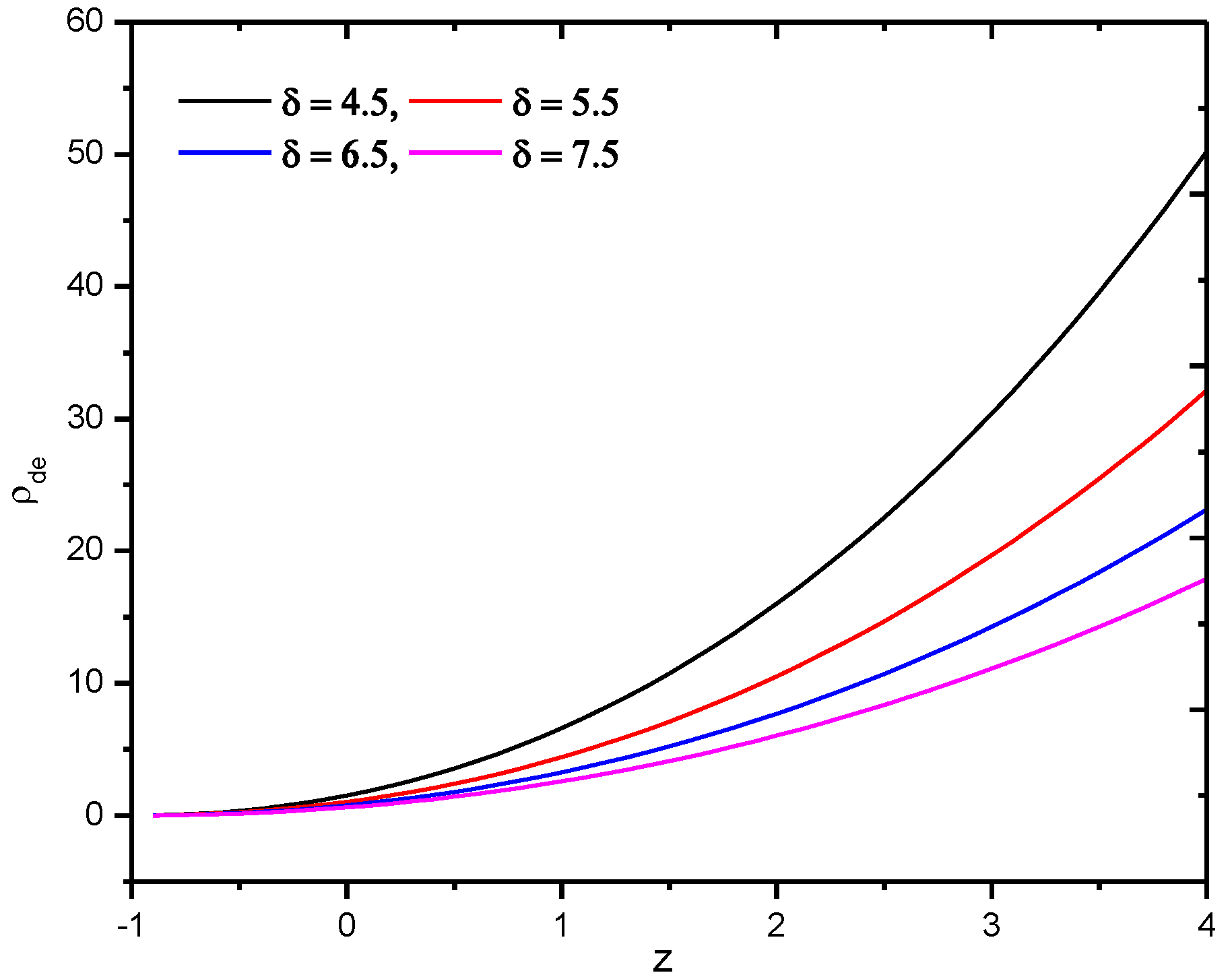
The behavior of Renyi HDE density with Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for an appropriate choice of constants, especially , appears in Figure 1.
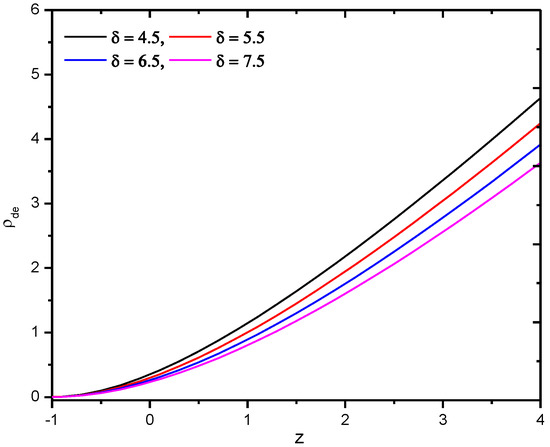
Figure 1.
Behavior of Renyi holographic dark energy density with Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants and .
Using Equations (9) and (19), the energy density of pressureless matter is obtained as
with and being constants.
The EoS parameter of Renyi HDE is obtained as
The behavior of the EoS parameter of Renyi HDE gravity model versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants, especially for , is shown in Figure 2. It is observed that for all , the value of is −1, hence it is CDM model, and for it approaches the Quintessences region.
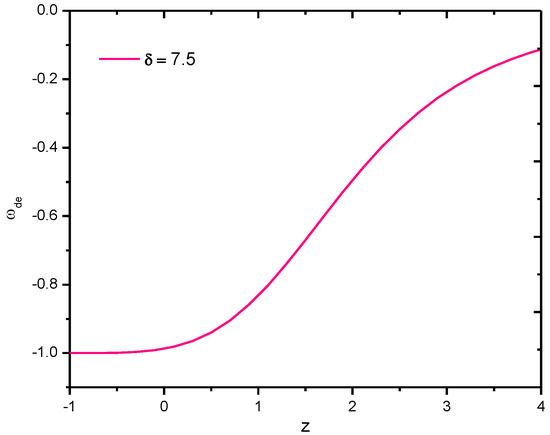
Figure 2.
Behavior of EoS parameter of Renyi holographic dark energy density of gravity model in Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants , , , , and .
4.2. Tsallis Holographic Dark Energy Model with Hubble’s Horizon Cutoff
The energy density of Tsallis holographic dark energy is characterized as follows [73]
Here, is a constant. By considering the Hubble horizon as a candidate for the IR-cutoff, i.e., , the Tsallis HDE density from Equation (22) is
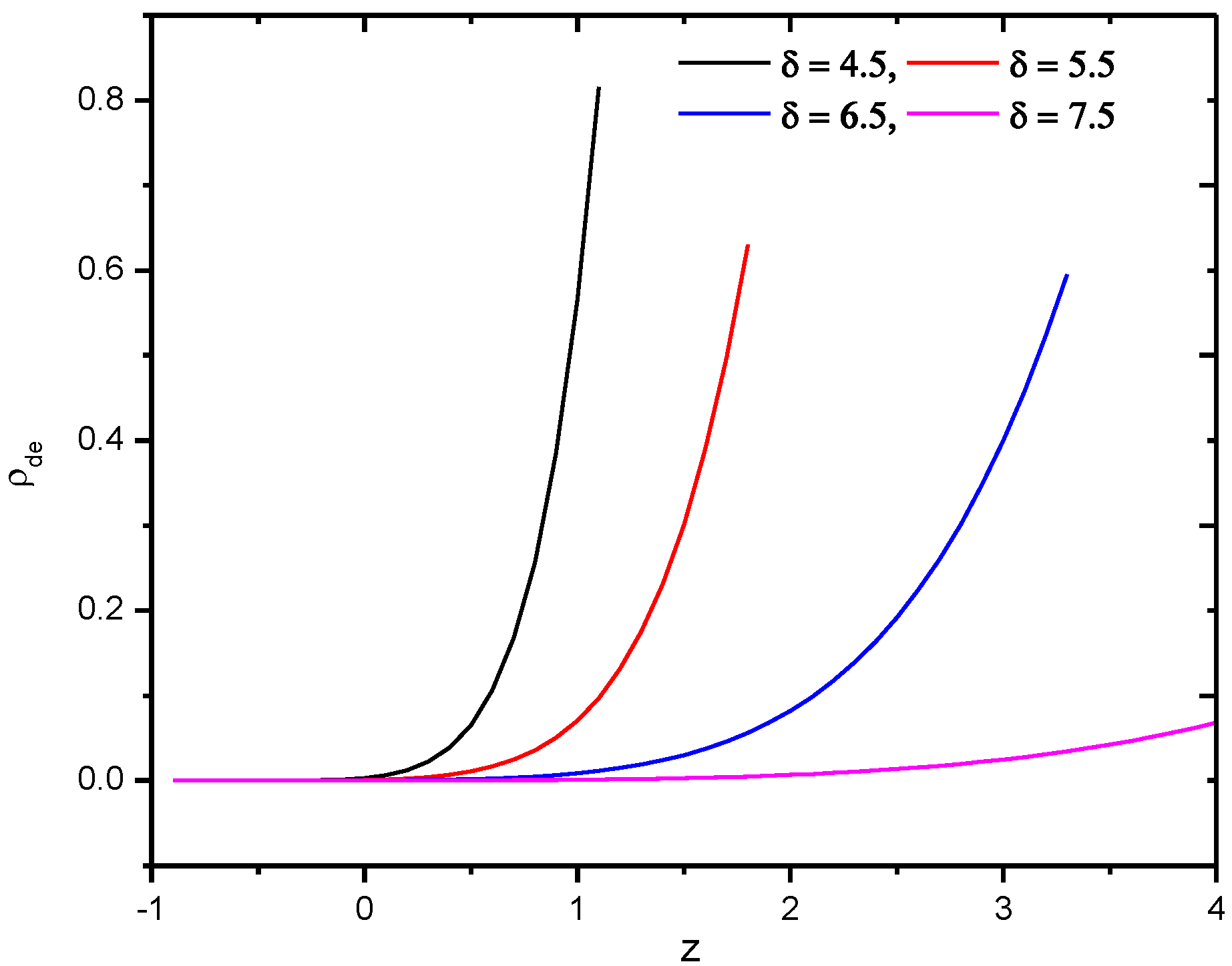
Its behavior as a function of redshift can be seen in Figure 3.
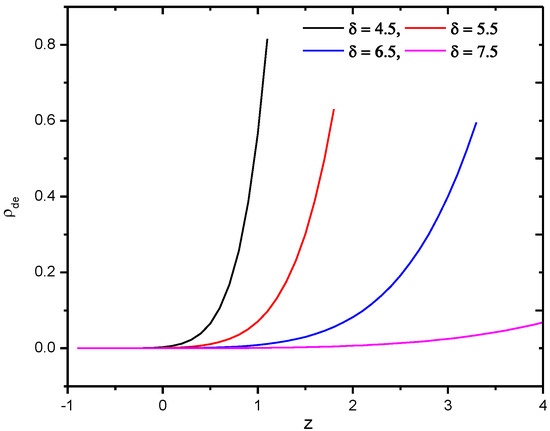
Figure 3.
Behavior of Tsallis holographic dark energy density of gravity model in Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants and .
The EoS parameter of Tsallis HDE is obtained as
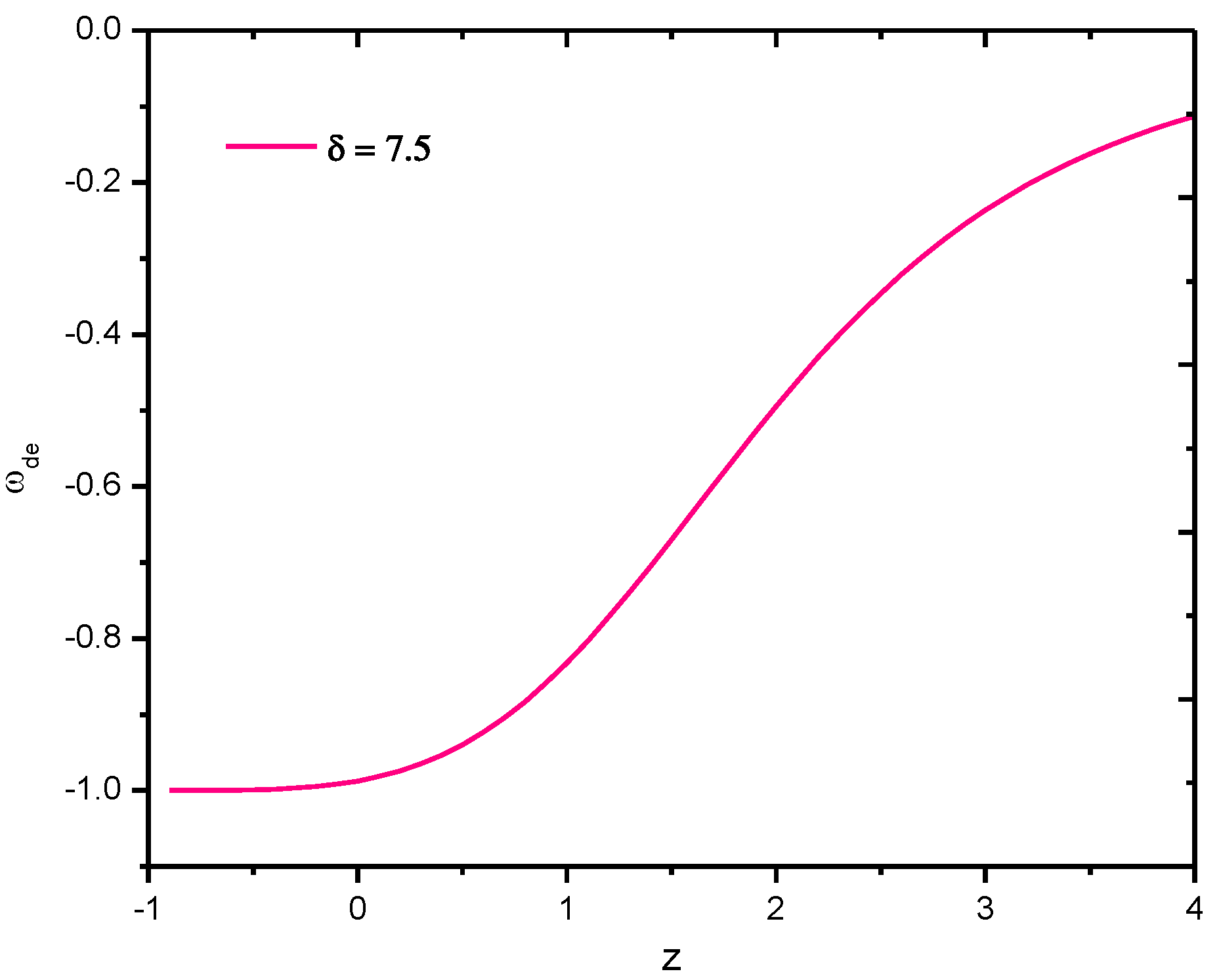
The behavior of the EoS parameter of Tsallis HDE of gravity model versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants, especially for , is clearly shown in Figure 4. It is observed that for all (here, negative redshift, i.e., , is the blueshift which represents the present model of the universe), the value of is −1, hence it is the CDM model and further, for , it approaches the Quintessences region.
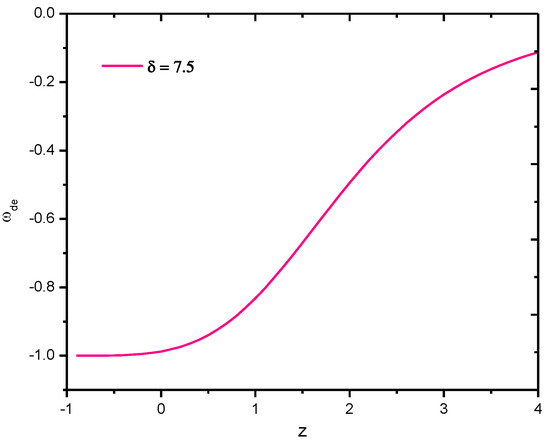
Figure 4.
Behavior of EoS parameter of Tsallis holographic dark energy density of gravity model in Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants , , , , , and .
4.3. Sharma–Mittal Holographic Dark Energy Model with Hubble’s Horizon Cutoff
The energy density of Sharma–Mittal HDE is characterized as follows [73]
where . Here, by considering Hubble horizon as a candidate for IR-cutoff, i.e., , the Sharma–Mittal HDE density from Equation (27) is
Its evolution in redshift can be seen in the figure below Figure 5.
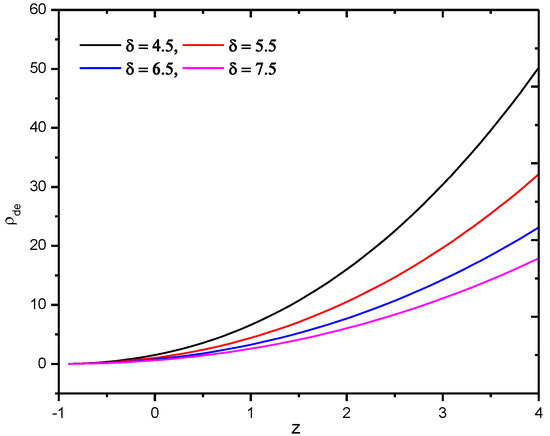
Figure 5.
Behavior of Sharma–Mittal holographic dark energy density of gravity model in Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants , , , , , and .
The EoS parameter of Sharma–Mittal HDE is obtained as
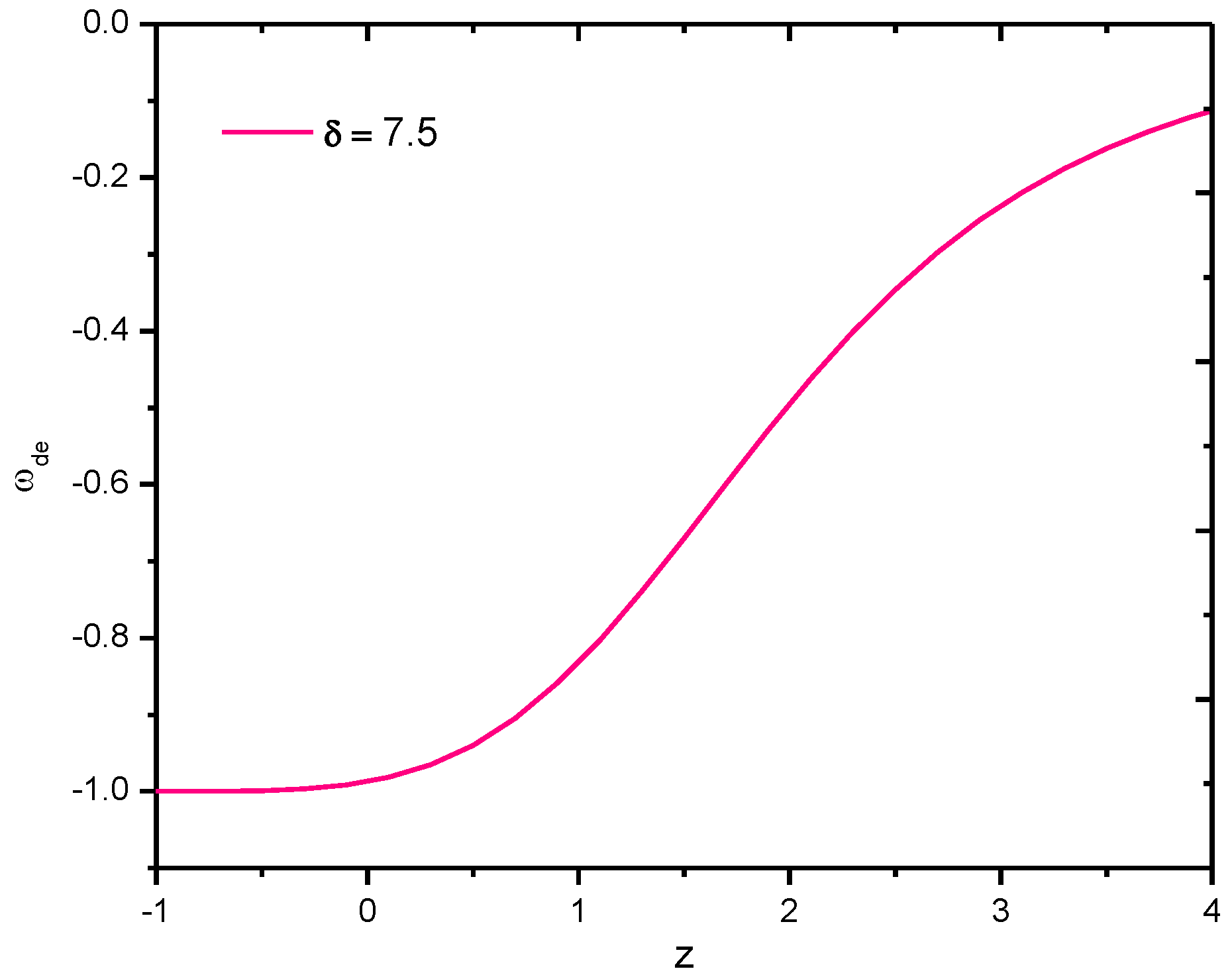
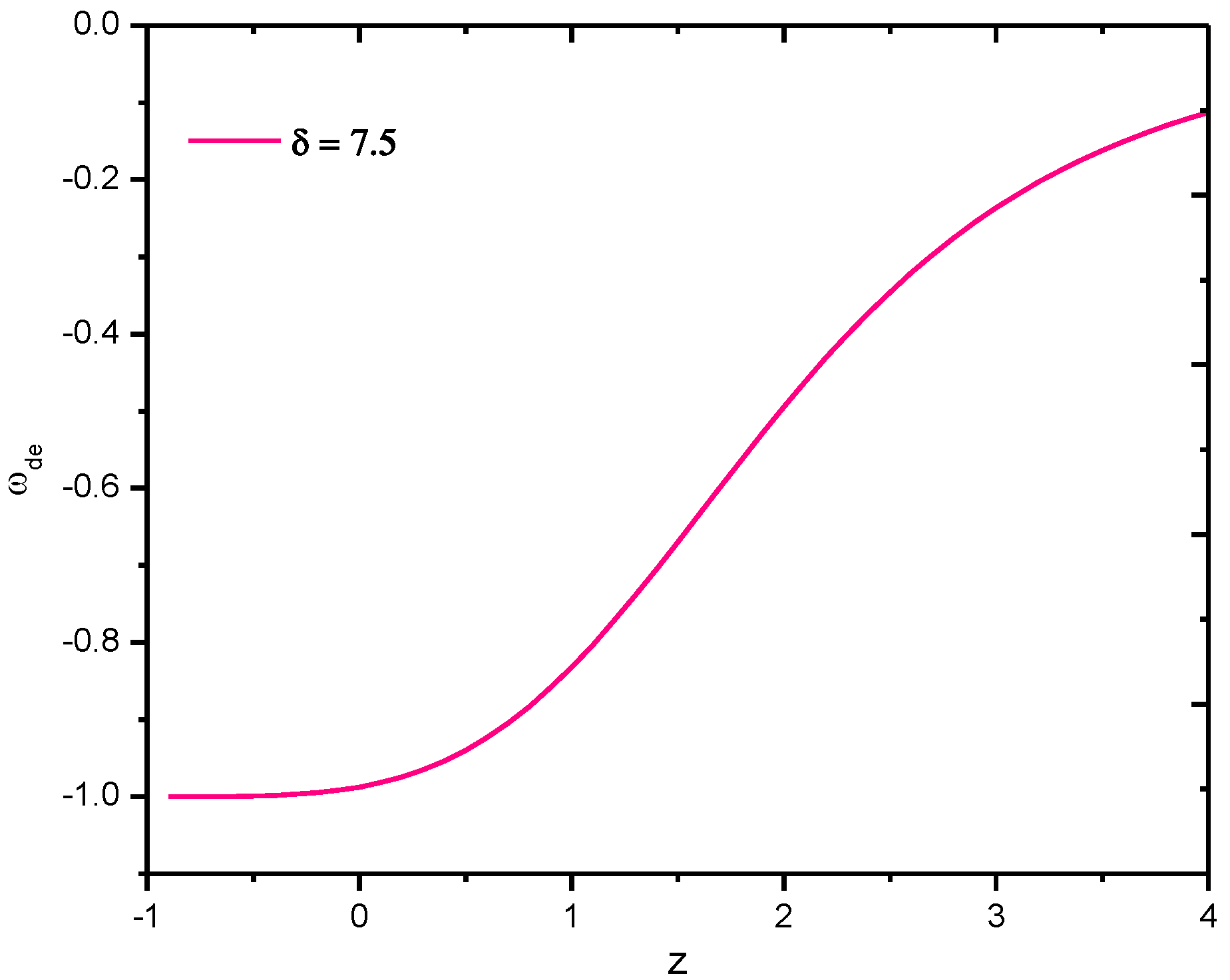
The behavior of the EoS parameter of Sharma–Mittal holographic dark energy of gravity model versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants, especially for , is shown in Figure 6 above. It is observed that for all , the value of is −1, hence it is CDM model, and further, for , it approaches the Quintessences region.
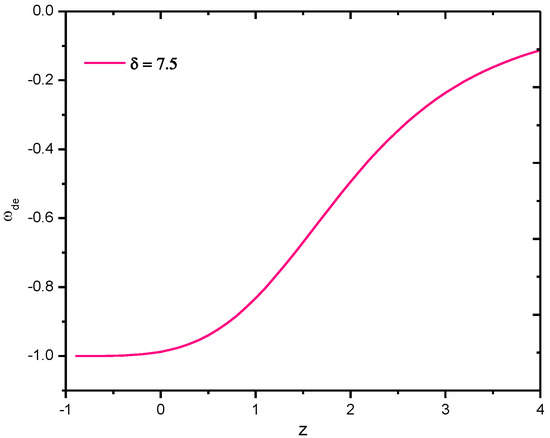
Figure 6.
Behavior of EoS parameter of Sharma–Mittal holographic dark energy gravity model in Hubble’s horizon cutoff versus redshift for the appropriate choice of constants , , , , , and .
5. Discussion
The holographic principles need the degrees of freedom of a spatial region to reside not in the interior of an ordinary quantum field theory, but on the surface of the region, along with a number of degrees of freedom per unit area no greater than 1 per Planck area. Hence, the entropy of a region must not go beyond its area in Planck units [74].
The holographic principle was applied to cosmology in [74], and since then, many HDE models have appeared. In addition to those mentioned previously, see [75,76,77,78,79,80,81].
In the present article, we have chosen to work with HDE models in the theory of gravity. We have analyzed three different possibilities within this context, the Renyi, Tsallis and Sharma–Mittal HDE models, and observed that, in all possibilities for all , the value of is −1, hence it is CDM model, and further, for , it approaches the Quintessences region, which indicates the cosmic acceleration of the universe.
Author Contributions
S.H.S.: Writing—Original draft preparation, Investigation, Graph plotting, P.H.R.S.M.: Methodology, Formal analysis, Conceptualization, Writing, P.K.S.: Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Validation, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Riess, A.G.; Strolger, L.-G.; Tonry, J.; Casertano, S.; Ferguson, H.C.; Mobasher, B.; Challis, P.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jha, S.; Li, W.; et al. Type Ia Supernova Discoveries at z>1 from the Hubble Space Telescope: Evidence for past deceleration and constraints on dark energy evolution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astier, P.; Pain, R. Observational evidence of the accelerated expansion of the universeL’acceleration de l’expansion de l’Univers du point de vue de l’observation. Compt. Rend. Phys. 2012, 13, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-R.; Zhang, T.-J.; Pen, U.-L. Method for Direct Measurement of Cosmic Acceleration by 21-cm Absorption Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 041303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haridasu, B.S.; Luković, V.V.; D’Agostino, R.; Vittorio, N. Strong evidence for an accelerating Universe. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 600, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.; Hayden, B. Is the expansion of the universe accelerating? all signs point to yes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 833, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentham, N. Distance measurements as a probe of cosmic acceleration. Month. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2001, 326, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The cosmological constant problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J. The phenomenological approach to modeling the dark energy. Compt. Rend. Phys. 2012, 13, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.; Steinhardt, P.J. Essentials of k-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T. Tracking K-essence. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 063514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.R.; Kamionkowski, M.; Weinberg, N.N. Phantom Energy: Dark Energy with ω<1 Causes a Cosmic Doomsday. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 071301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Diíaz, P. You need not be afraid of phantom energy. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 021303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, I.; Wang, L.; Steinhardt, P.J. Quintessence, Cosmic Coincidence, and the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Finelli, F.; Burigana, C.; Carturan, D. WMAP and the generalized Chaplygin gas. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys. 2003, 7, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.C.; Bertolami, O.; Sen, A.A. Generalized Chaplygin gas, accelerated expansion, and dark-energy-matter unification. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 043507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keresztes, Z.; Gergely, L.A.; Kamenshchik, A.Y.; Gorini, V.; Polarski, D. Soft singularity crossing and transformation of matter properties. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 88, 023535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. A Model of holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 603, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, D.; Zimdahl, W. Holographic dark energy and cosmic coincidence. Phys. Lett. B 2005, 628, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.G.; Li, M. The holographic dark energy in a Non-flat Universe. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys. 2004, 8, 013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.G.; Gong, Y. Supernova Constraints on a holographic dark energy model. arXiv 2004, arXiv:astro-ph/0403590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y. Extended holographic dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 064029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekenstein, J.D. Black holes and entropy. Phys. Rev. D 1973, 7, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.W. Particle creation by black holes. Comm. Math. Phys. 1975, 43, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, G. Dimensional reduction in quantum gravity. arXiv 1993, arXiv:gr-qc/9310026. [Google Scholar]
- Maldacena, J.M. The large-N limit of super conformal field theories and super gravity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1999, 38, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Rajagopal, K.; Wiedemann, U.A. Wilson loops in heavy ion collisions and their calculation in AdS/CFTJ. J. High Energy Phys. 2007, 3, 066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strominger, A. The dS/CFT correspondence. J. High Energy Phys. 2001, 10, 034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.A. Tsallis, Renyi and Sharma–Mittal holographic dark energy models in DGP brane-world. Phys. Dark Univ. 2019, 26, 100349. [Google Scholar]
- Tavayef, M.; Sheykhi, A.; Bamba, K.; Moradpour, H. Tsallis holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 781, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, Y.; Mandal, S.; Sahoo, P.K.; Reddy, D.R.K. Observational constraint on interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy in logarithmic Brans–Dicke theory. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Holographic dark energy. Phys. Rep. 2017, 696, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, B.; Bonilla, A.; Faizal, M.; Abreu, E.M.C. Holographic dark energy from fluid/gravity duality constraint by cosmological observations. Phys. Dark Univ. 2018, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.K.; Dubey, V.C.; Pradhan, A. Diagnosing interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy in the non-flat universe. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2020, 17, 2050032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekh, S.H.; Ghaderi, K. Hypersurface-homogeneous space–time with interacting holographic model of dark energy with Hubble’s and Granda–Oliveros IR cut-off. Phys. Dark Univ. 2021, 31, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Holographic dark energy model with Hubble horizon as an IR cut-off. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys. 2009, 9, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gong, Y.; Chen, X. Dynamical behavior of the extended holographic dark energy with the Hubble horizon. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 083536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, Y.; Remmen, G.N. Area law unification and the holographic event horizon. J. High Ener. Phys. 2018, 2018, 063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, H.M. The particle versus the future event horizon in an interacting holographic dark energy model. J. Cosm. Astrop. Phys 2007, 2, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.P.; Wu, Y.L. Holographic dark energy model characterized by the conformal-age-like length. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2012, 27, 1250085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.P.; Wu, Y.L. Cosmological constraint and analysis on holographic dark energy model characterized by the conformal-age-like length. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2012, 27, 1250130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.K.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, J.-L.; Duan, P.-F. Generalized holographic Ricci dark energy and generalized second law of thermodynamics in Bianchi Type I universe. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2015, 47, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodam-Mohammadi, A.; Pasqua, A.; Malekjani, M.; Khomenko, I.; Monshizadeh, M. Statefinder diagnostic of logarithmic entropy corrected holographic dark energy with Granda-Oliveros IR cut-off. Astrophys. Spa. Sci. 2013, 345, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renyi, A. Probability Theory; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Stallis, C. Possible generalization of Boltzmann-Gibbs entropy. J. Stat. Phys. 1988, 52, 479. [Google Scholar]
- Moradpour, H.; Moosavi, S.A.; Lobo, I.P.; Morais Graça, J.P.; Jawad, A.; Salako, I.G. Thermodynamic approach to holographic dark energy and the Rényi entropy. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 829. [Google Scholar]
- Sayahian, S.J.; Moosavi, S.A.; Moradpour, H.; Morais Graça, J.P.; Lobo, I.P.; Salako, I.G.; Jawad, A. Generalized entropy formalism and a new holographic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 780, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.C.; Sharma, U.K.; Mamon, A.A. Interacting Rényi holographic dark energy in the Brans-Dicke theory. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 6658862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, M.A.; Sheykhi, A.; Moradpour, H.; Bamba, K. Note on Tsallis holographic dark energy. Eur. Phys. J. 2018, 78, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, E. Observational constraints on interacting Tsallis holographic dark energy model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.K.; Dubey, V.C. Exploring the Sharma–Mittal holographic dark energy models with different diagnostic tools. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Polarski, D.; Tsujikawa, S. Are f(R) Dark Energy Models Cosmologically Viable? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 131302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Gannouji, R.; Polarski, D.; Tsujikawa, S. Conditions for the cosmological viability of f(R) dark energy models. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Cardone, V.F.; Troisi, A. Reconciling dark energy models with f(R) theories. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 043503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffou, E.H.; Kpadonou, A.V.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Houndjo, M.J.S.; Tossa, J. Cosmological viable f(R,T) dark energy model: Dynamics and stability. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 356, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houndjo, M.J.S. Reconstruction of f(R,T) gravity describing matter dominated and accelerated phases. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2012, 21, 1250003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Chand, A.; Pradhan, A. Dark energy models in f(R,T) theory with variable deceleration parameter. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2016, 55, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirhashchi, H.; Pradhan, A.; Jaiswal, R. Two-Fluid Dark Energy Models in Bianchi Type-III Universe with Variable Deceleration Parameter. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.H.R.S.; Sahoo, P.K. The simplest non-minimal matter–geometry coupling in the f(R,T) cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Sahoo, P.; Bishi, B.K. Anisotropic cosmological models in f(R,T) gravity with variable deceleration parameter. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2017, 14, 1750097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combi, L.; Romero, G.E. Is Teleparallel gravity really equivalent to reneral relativity? Annal. Phys. 2018, 530, 1700175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, H.I.; Pereira, J.G. Torsion gravity: A Reappraisal. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2004, 13, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf, J.W. The teleparallel equivalent of general relativity. Annal. Phys. 2013, 525, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, K.; Abdolmaleki, A. Generalized second law of thermodynamics in f(T) gravity. JCAP 2012, 04, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harko, T.; Francisco, F.S.L.; Otalora, G.; Saridakis, E.N. f(T) gravity and cosmology. JCAP 2014, 12, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, T.M.; Amani, A. Stability and interacting f(T) gravity with modified Chaplygin gas. Can. J. Phys. 2017, 95, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, S.; Boehmer, C.G.; Wright, M. Modified teleparallel theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M.; Saridakis, E.N. f(T) teleparallel gravity and cosmology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sotiriou, T.P.; Barrow, J.D. f(T) gravity and local Lorentz invariance. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 064035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Waheed, S.; Fayyaz, M.A.; Ahmad, I. Energy constraints and the phenomenon of cosmic evolution in the f(T,B) framework. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Capriolo, M.; Caso, L. Weak field limit and gravitational waves in f(T,B) teleparallel gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, S.; Capozziello, S. Noether symmetry approach in f(T,B) teleparallel cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, S.; Zubair, M.; Abbas, G. Thermodynamics and cosmological reconstruction in f(T,B) gravity. Phys. Dark Univ. 2018, 19, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Debnath, U. Tsallis, Rényi and Sharma-Mittal holographic and new agegraphic dark energy models in D-dimensional fractal universe. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, W.; Susskind, L. Holography and Cosmology. arXiv 1998, arXiv:hep-th/9806038. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.-G. Holographic dark energy model from Ricci scalar curvature. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 043511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, S.; Fabris, J.C.; Herrera, R.; Zimdahl, W. Holographic dark-energy models. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 123006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.R. Interacting holographic dark energy model in non-flat universe. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 642, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.R.; Vagenas, E.C. The cosmological dynamics of interacting holographic dark energy model. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2009, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Farooq, M.U.; Rashid, M.A. Generalized holographic dark energy model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2009, 61, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Holographic-dark-energy model with non-minimal coupling. Europhys. Lett. 2005, 71, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, Y.S.; Seo, M.G. Origin of holographic dark energy models. Phys. Lett. B 2009, 671, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).