Abstract
We review and discuss recent results on the search for correlations between astrophysical neutrinos and -ray-detected sources, with many extragalactic studies reporting potential associations with different types of blazars. We investigate possible dependencies on blazar sub-classes by using the largest catalogues and all the multi-frequency data available. Through the study of similarities and differences in these sources we conclude that blazars come in two distinct flavours: LBLs and IHBLs (low-energy-peaked and intermediate-high-energy-peaked objects). These are distinguished by widely different properties such as the overall spectral energy distribution shape, jet speed, cosmological evolution, broad-band spectral variability, and optical polarisation properties. Although blazars of all types have been proposed as neutrino sources, evidence is accumulating in favour of IHBLs being the counterparts of astrophysical neutrinos. If this is indeed the case, we argue that the peculiar observational properties of IHBLs may be indirectly related to proton acceleration to very high energies.
1. Introduction
The discovery of ultra-high energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) established the existence of powerful cosmic accelerators capable of reaching energies millions of times larger than those that can be achieved by the best accelerators on Earth (see ref. [1] and references therein). The interaction of very high-energy cosmic rays (CRs) with matter or radiation in astrophysical contexts results in the production of neutral and charged mesons, which then decay into -rays, high-energy neutrinos and energetic particles, which lose energy in a variety of ways. Neutrinos, -rays (of energy 1 TeV, if not absorbed inside the emitting region or in the host galaxy), and the electromagnetic radiation emitted by secondary particles, are the ‘messengers’ that can reach the Earth undeflected from cosmological distances, providing information about the Universe at extreme energies.
A flow of high-energy neutrinos likely generated in these environments has been detected by the IceCube Observatory (https://icecube.wisc.edu, accessed on 11 December 2021) at the South Pole with energies extending beyond 1 PeV and an energy flux comparable to that observed in the -ray-band [2,3,4]. This facility, however, cannot provide an accurate estimate of the arrival directions of the incoming neutrinos and is not sensitive enough to ensure firm detections of point sources with multiple events. Nevertheless, the absence of any significant anisotropy in the arrival direction of the neutrinos points to a flux that is mostly of extragalactic origin [5]. A number of astrophysical source types have been suggested to be responsible for the observed signal. In particular blazars, long-known as efficient cosmic accelerators, have been proposed as likely sources of high-energy neutrinos (Refs. [6,7,8] and references therein).
In this early phase of multi-messenger astronomy, where the available instrumentation is limited in precision and sensitivity, unambiguous associations would greatly benefit from the detection of high-energy neutrinos together with enhanced activity in some parts of the electromagnetic spectrum of the astrophysical counterpart [9,10]. This condition, however requires that hadronic-related electromagnetic flares are strong enough to outshine the non-thermal radiation generated via different mechanisms, e.g., from accelerated electrons radiating in magnetic fields in the so-called leptonic scenarios [11,12,13]. One such association in space and time was described in ref. [14], which reported a large flare in the -ray and other parts of the spectrum from the blazar PKS 1424−418 in correspondence with the detection of a ∼2 PeV IceCube neutrino. The positional uncertainty of this event (15.9, 50% radius), however, is so large that the a posteriori probability of a chance coincidence was estimated to be about 5%, too large for an unambiguous association.
So far only one astronomical object has been associated with a high-energy astrophysical neutrino with a significance larger than . This is the blazar TXS 0506+056, also known as 5BZB J0509+0541, located in the relatively small uncertainty region of the neutrino IceCube-170922A, detected when the source was undergoing a -ray flare. This result was further strengthened by the discovery of an excess of several lower energy neutrinos from the same direction in a subsequent analysis of IceCube archival data [15,16]. This so-called “neutrino flare” occurred when TXS 0506+056 was in a period of low -ray activity, suggesting that the relationship between astrophysical neutrinos and -ray emission is not straightforward.
2. Blazars
Blazars are the most powerful sources of persistent non-thermal radiation in the Universe [17]. They are a special and rare type of Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN, [18]) with unique characteristics such as the emission of highly variable radiation over the entire electromagnetic spectrum. The most peculiar aspect about blazars is that this radiation originates within a relativistic jet that moves away from the central supermassive black hole and is oriented in the direction of the Earth. This is the very special condition that is responsible for the distinctive features of these sources such as superluminal motion and fast variability (see refs. [17,19,20]).
A few thousand blazars are known. Although these sources have been mostly discovered in the radio, X-ray or -ray bands, they are conventionally sub-classified depending on their optical spectrum as Flat-Spectrum Radio Quasars (FSRQs) and BL Lacertae objects (or BL Lacs), with FSRQs showing broad emission lines like radio-quiet Quasi-Stellar Objects (QSOs), and BL Lacs being featureless or at most displaying very weak emission lines [20]. All blazars emit across the entire electromagnetic spectrum with an energy distribution that, in f vs. space, displays two broad humps, one attributed to synchrotron radiation that rises from radio frequencies and peaks between the far IR and the X-ray band, and the second, more energetic one due to inverse Compton or other mechanisms, that peaks in the low or high-energy -ray band [21]. See ref. [22] for examples of different types of spectral energy distributions (SEDs) including large amounts of multi-frequency data. The peak energy and the relative intensity of the two humps span a wide range of values and have been used to classify blazars depending on the distribution of their power output. On the basis of the rest-frame frequency of their low-energy hump () blazars are classified into low- (LBL/LSP: Hz), intermediate- (IBL/ISP: Hz Hz), and high-energy (HBL/HSP: Hz) peaked sources respectively [23,24]. Extreme blazars are defined by Hz (see ref. [25] for a recent review). In this paper we use the nomenclature LBL, IBL, and HBL as in ref. [22], which is an extension of the codification originally defined in ref. [23] applied to all blazar types, FSRQs and BL Lacs.
Although extremely rare among optical sources, blazars are by far the most common type of objects detected by -ray telescopes outside the Galactic plane [26,27,28]. Given that neutrino production is inevitably associated with the generation of -rays, this peculiarity makes blazars natural candidate neutrino sources. From an observational perspective the situation is however complex since -rays can also be generated in purely leptonic contexts (e.g., synchrotron self-Compton or external inverse Compton [12,29]), and -rays associated to neutrino production could be completely or largely absorbed before they leave the emission region.
3. Astrophysical Neutrinos and Blazars
Blazars have long been considered as probable sources of astrophysical neutrinos [30,31], but statistical searches for neutrino emitters have become possible only recently when sufficient data has been accumulated, mostly from IceCube observations. Investigations of this type have been conducted largely comparing neutrino arrival directions with lists of bright radio or -ray sources or with catalogues of well known blazars and other types of AGN. A search for point sources in the IceCube 10 year data collection, which includes events with energy typically 1 TeV, found an excess of neutrinos at the level from the direction of the local () Seyfert 2 galaxy NGC 1068 and a excess in the northern sky due to significant p-values in the directions of NGC 1068 and three blazars: TXS 0506+056, PKS 1424+240, and GB6 J1542+6129 [4]. A similar work based on the database of the ANTARES neutrino observatory did not lead to the firm detection of point-like sources, with the most prominent excesses found in correspondence of the radio galaxy 3C 403 and the blazar MG3 J225517+2409 [32].
In the radio domain recent papers considered a number of data sets including a complete sample of 8 GHz sources selected from the very large baseline interferometry (VLBI)-based Radio Fundamental Catalogue (RFC), and the list of blazars monitored at various radio frequencies by the MOJAVE project and at the Owens Valley, the Metsähovi, and RATAN-600 Radio Observatories [33,34,35,36]. Possible correlations between radio sources and IceCube neutrinos have been reported in ref. [33], where it is concluded that four radio bright blazars, namely 3C 279, NRAO 530, PKS 1741−4038, and PKS 2145+067, all LBLs, are highly probable high-energy (E TeV) neutrino emitters. However 3C 279, the brightest and the only one of these blazars that is included in the list of objects used for the point source search in the 10-year IceCube data set, is not listed among the objects considered as likely neutrino emitters [4]. In addition, a new analysis based on the same list of 3411 bright radio sources and the updated sample of 10 year of IceCube data [37] did not confirm the results of ref. [34]. A recent investigation aimed at the detection of flare neutrino emission in the 10 year IceCube data set [38] reported a time-dependent neutrino excess in the northern hemisphere at the level of 3 associated with four sources: M87, a giant radio galaxy, TXS 0506+056 and GB6 J1542+6129, two IBL blazars, and NGC 1068. As noted in ref. [39] M87, which has -ray properties similar to those of HBL objects, is also the possible counterpart of the IceCube-141126A track-like event.
The most robust statistical evidence so far for an association between astrophysical neutrinos and blazars remains the case of TXS 0506+056 [9,15,16]. This IBL/HBL type blazar is located well within the ∼0.5 (90% containement) error region of the ∼0.3 PeV event IceCube-170922A that was detected in correspondence with enhanced -ray activity from the source. This already significant result was further strengthened by the detection of a 3.5 excess from the same direction found in a subsequent search of IceCube archival data [15,16]. The corresponding neutrinos were detected between September 2014 and March 2015, when TXS 0506+056 was not undergoing strong -ray activity, implying that the relationship between astrophysical neutrinos and -ray emission is likely complex. A similar, although less striking, event is the case of 3HSP J095507.9+35510, a blazar of the HBL type that is located in the error region of the highly energetic neutrino IceCube-200107A, that was detected during a strong X-ray flare [40].
To find similar cases in existing neutrino data and using all the available multi-frequency information Giommi et al. have carried out a systematic detailed study of 70 public IceCube high-energy neutrino tracks that are well reconstructed and away from the Galactic plane [39]. This effort led to a (post-trial) correlation excess with -ray detected IBLs and HBLs, while no excess was found in correspondence of LBL blazars. This result, together with previous findings, consistently points to growing evidence for a connection between some IceCube neutrinos and IBL and HBL blazars. Moreover, several of the 47 IBLs and HBLs listed in Table 5 of ref. [39], are expected to be new neutrino sources waiting to be identified. Further progress requires optical spectra, which are needed to measure the redshift, and hence the luminosity of the source, determine the properties of the spectral lines, and possibly estimate the mass of the central black hole, , which is the purpose of “The spectra of IceCube Neutrino (SIN) candidate sources” project.
In this framework Paiano et al. [41] presented the spectroscopy of a large fraction of the objects selected in ref. [39], which, together with results taken from the literature, covered % of that sample. This was the first publication of the SIN project whose aim is threefold: (1) to determine the nature of these sources; (2) to model their SEDs using all available multi-wavelength data and subsequently the expected neutrino emission from each blazar; (3) to determine the likelihood of a connection between the neutrino and the blazar using a physical model for the blazar multi-messenger emissions, as done, for example, in refs. [42,43]. In the second SIN paper [44], the sources studied in ref. [41] have been characterised to determine their real nature, and also see if these sources are any different from the rest of the blazar population. Of particular relevance here are the so-called “masquerading” BL Lacs. Padovani et al. [45] showed, in fact, that TXS 0506+056, the first plausible non-stellar neutrino source is, despite appearances, not a blazar of the BL Lac type but instead a masquerading BL Lac. This class was introduced in refs. [46,47] (see also ref. [48]) and includes sources which are in reality FSRQs whose emission lines are washed out by a very bright, Doppler-boosted jet continuum, unlike “real” BL Lacs, which are intrinsically weak-lined objects. This is relevant because “real” BL Lacs and FSRQs belong to different physical classes, i.e., objects without and with high-excitation emission lines in their optical spectra, referred to as low-excitation (LEGs) and high-excitation galaxies (HEGs) [18]. TXS 0506+056, being a HEG, therefore benefits from several radiation fields external to the jet (i.e., the accretion disc, photons reprocessed in the broad-line region or from the dusty torus), which, by providing more targets for the protons might enhance neutrino production as compared to LEGs. This makes masquerading BL Lacs particularly attractive from the point of view of high-energy neutrinos. Padovani et al. [44] have found that the sample considered in [39] has a fraction and possibly as high as 80% of masquerading sources, which is tantalizing.
4. Blazars of Different Types
In the previous section we have shown that experimental evidence is accumulating in favour of blazars being likely neutrino counterparts. Motivated by the possibility that some specific blazar sub-classes may play a role in the emission of astrophysical neutrinos, in this section we use the best available samples and multi-frequency data to review similarities and differences among blazars sub-types.
By definition, LBLs, IBLs and HBLs only differ by the value of in their SEDs. This spread could simply reflect the maximum energy at which particles are accelerated or could be due to other physical processes that determine the shape of the SED.
4.1. Blazar Samples
At present the largest available lists of confirmed blazars are the following:
- The BZCAT catalogue, fifth edition [49], which includes over 3500 objects classified as BZQ (that is showing broad lines typical of QSOs), BZB (BL Lacs with no or very weak lines), BZU (blazars of uncertain type), and BZG (blazars where the optical/IR data in the SED reveals the presence of the host galaxy). BZCAT, being an heterogeneous list of blazars, is not a flux limited sample directly usable for statistical purposes;
- The 3HSP catalogue, which includes 2013 HBL sources [50] with radio flux larger than ∼1 mJy. The sample is not complete at low radio flux densities values;
- The 4LAC-DR2 sample of -ray-selected AGN [51,52], which includes over 3500 blazars of all types, many of which also included in the BZCAT and 3HSP catalogues.
A Sample of IBL Blazars
No well-defined flux limited samples of IBL blazars currently exists. The only large list available is the subset of Fermi 4FGL-DR2 -ray sources classified as ISPs in the 4LAC-DR2 paper [51,52]. The SED classification of 4LAC-DR2 is however not always reliable, especially for IBL sources since at IR/optical frequencies, where IBLs peak, there are emission components not related to the jet, such as the host galaxy or the blue bump, that can sometimes lead to large inaccuracies in the estimation of . To assemble a large and accurately determined sample of -ray -detected IBL blazars we have built the SED of a large fraction of Fermi 4FGL-DR2 blazars through the Open Universe VOU-Blazar tool V1.94 [53], which uses 71 multifrequency catalogues and spectral databases. In particular, we have considered the following samples: (a) all sources classified as ISPs in the 4LAC-DR2 catalogue; (b) blazars classified as HSPs in 4LAC-DR2 that are not included in the 3HSP sample [50]; (c) all sources classified as LSPs in 4FGL-DR2 with Hz. A careful visual inspection of the SED of each candidate allowed us to remove the components that can be related to non-jet emission. A fit to the average multi-frequency non-thermal components led to a sample including 482 sources with between and Hz, and radio flux densities ranging from a few mJy to over 6 Jy at 1.4 GHz. Particular care was also taken in the verification of the redshift of each object as in many cases this parameter was estimated by automatic software that was run on a large number of optical spectra. In some cases warning flags generated by the code have not been taken into account and wrong or inaccurate redshifts have been included in on-line sites and reported in the literature. Our verification was done by visually inspecting published optical spectra, or online SDSS-DR16 spectra, when available. This was useful and necessary since a number of sources with reported medium-high redshifts values in fact showed featureless optical spectra.
Note that this sample of IBL blazars will evolve somewhat in the future depending on the availability of additional multi-frequency data. The table including the details of each IBL blazar in the sample will be made available via the Open Universe platform (https://openuniverse.asi.it, accessed on 11 December 2021). By construction, this is a -ray flux-limited sample. However, considering the observed range of radio to -ray flux ratios for IBLs and the sensitivity of the 4FGL-DR2 catalogue, we expect it to include almost the totality of IBL blazars with radio flux densities mJy.
4.2. LBLs vs. IBLs vs. LBLs
To investigate possible intrinsic differences between LBL, IBL, and HBL blazars we must use samples that are reasonably complete above a common flux limit in the same energy band. Since all blazars in the available lists are radio sources with similar radio spectra, we use a conservative radio flux density limit of 200 mJy, which is sufficiently large to ensure that no objects above this limit are missed in the catalogues listed above.
The IBL and HBL samples can be defined in a straightforward way, since they simply consists of the subset of sources with radio flux density mJy. For the sample of LBL sources we have taken all objects in the BZCAT that are above this flux density limit and are not included in the 3HSP catalogue or in our IBL sample. To ensure uniformity in the radio data, and to avoid the complications of the Galactic plane, we consider the part of the sky covered by the NRAO VLA Sky Survey (NVSS: [54]) (Dec 40) with Galactic latitudes |b| > 10, corresponding to an area of 28,400 square degrees of sky. These selection criteria resulted in HBL, IBL and LBL subsamples that include 38, 114, and 1370 sources, respectively. The total blazar number density N(>200 mJy) therefore is (38 + 114 + 1370)/28,400 = 0.054 deg, a value that is close to that derived from the LogN-LogS of the DXRBS survey [55] for all blazars types. We can therefore assume that these lists are complete at a level that is certainly sufficient for the purpose of finding relevant differences in the three sub-samples.
The relative space density of radio flux-limited ( 200 mJy) LBLs, IBLs and HBLs is shown on the left side of Figure 1. A large gap between LBLs and other blazars types is clearly present. LBLs are over a factor 10 more abundant than IBLs, which are instead only about a factor of two more abundant than HBLs. In this plot LBL sources are all confined in the Log() interval 12–13. Even though some blazars with Log() between 13 and 14 likely exist, from our experience objects possibly located in this frequency interval are rarely observed and their is very difficult to estimate because the flux at these energies is often contaminated by components that are unrelated to the jet, like the dusty torus or emission from the host galaxy. The low number of sources in this frequency bin marks a clear discontinuity between LBLs and the other types of blazars.
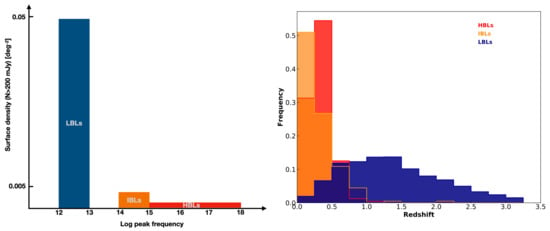
Figure 1.
The surface density (left side) and redshift distributions (right side) of LBL, IBL and HBL blazars with radio flux density larger than 200 mJy.
Another striking discontinuity is evident in the redshift distributions shown on the right side of Figure 1, with the redshifts of both IBLs and HBLs being mostly confined to low values (z 1.0 and peaking below z = 0.5), while those of LBLs reach values larger than 3, with a mean value of 1.44 and a dispersion of 0.8. The large frequency of IBLs in the first redshift bin is due to the still relatively large number of these sources with no redshift estimation (∼30%) due to featureless or unavailable optical spectra, and which therefore are assigned the value of 0. The number of IBL sources with zero redshift will most likely significantly decrease if photometric redshift estimations based on host galaxy signatures in the optical/IR parts of the SED, are carried out as in the case of the 3HSP sample [50]. This sharp discrepancy in the redshift distributions reflects the well known different cosmological evolution between LBL (mostly FSRQs) and HBL blazars. The cosmological evolution of LBLs is strong and similar to that of optically or X-ray selected AGN, which are largely radio quiet QSOs [55,56]. HBLs instead are known to show negative or no evolution [55,57,58]. No conclusive explanation for this low level of evolution in HBLs has been found yet. Since the redshift distribution of IBLs is similar to that of HBLs (Figure 1, right side) it is reasonable to assume that the evolution of IBL blazars is similar or identical to that of HBLs.
LBLs and IBLs/HBLs exhibit sharp differences also from the point of view of SED variability. Large changes of up to factors of 100 or more are commonly observed in HBL blazars (see Figure 4 of ref. [22]) but not in LBLs. Most of the flux variability associated to shifts in HBLs occurs in the X-ray band and is not accompanied by equivalent simultaneous changes at UV or at lower energies. Examples of this behaviour are illustrated in Figure 2 where the data corresponding to high and low states appear in red and green respectively, and all the available data are shown in blue. IBL blazars also show large changes which cause them to occasionally become HBLs during high states. One such example is shown on the left side of Figure 3 for the case of BL Lac, which shifted from typical values around Hz to ∼ Hz during a large flare [59,60]. Several other IBL/HBL transitional sources are known; some of these, e.g., OJ 287, TXS 0506+056, PKS 2005−489, PG 1553+113, are among the blazars that have been frequently observed by Swift, and their SEDs can be found in ref. [22] and online at https://openuniverse.asi.it/blazars/swift/ (accessed on 11 December 2021).
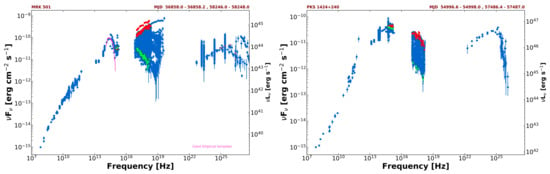
Figure 2.
The SED of the HBL Mrk 501 (left) and the IBL PKS 1424+240 (right) illustrating that most of the variability in these objects is in the X-ray band and translates into large shifts of the energy. Red and green colours represent Swift UVOT and XRT simultaneous data during high and low luminosity states respectively.
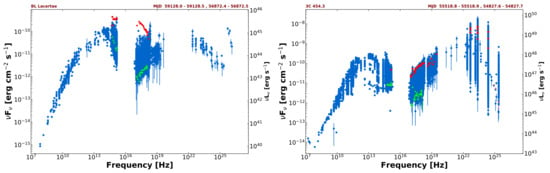
Figure 3.
The SED of the IBL source BL Lac (left), which shifted by a large amount during a strong flare, and the LBL blazar 3C 454.3 (right), which shows large variability of similar amplitude from far IR to the X-ray band, and no large shift. Red and green colours represent Swift UVOT and XRT simultaneous data during high and low luminosity states respectively.
In LBL blazars remains fairly stable between ∼ and ∼ Hz even during large flares since flux variability in these sources seems to occur almost a-chromatically, with similar amplitude at all frequencies from far IR to UV and X-rays [21,22]. One example of such behaviour is shown in the right side of Figure 3 for the case of 3C 454.3. Other examples of LBL blazars with well populated SEDs that follow the same behaviour are 3C 279, PKS 0235+164 and CTA 102 [22] (https://openuniverse.asi.it/blazars/swift/, accessed on 11 December 2021). Blazars also show differences in jet kinematics. LBLs exhibit a wide distribution of apparent jet speeds, with values reaching 30–40c, with jet speeds instead being typically ≲5c and ≲10c for HBL and IBLs respectively [61]. An upcoming paper (Padovani et al., 2022, in preparation) concludes, based on VLBI data, that the two neutrino candidates TXS 0506+056 and PKS 1424+240 have overall parsec-scale properties similar to HBLs and different from those of LBLs.
LBL and HBL blazars also differentiate in their optical polarisation properties, as demonstrated in ref. [62] where the authors studied a sample of X-ray selected BL Lacs (mostly HBLs) and concluded that these objects show a lower level of optical polarisation (with a maximum of ∼10%) and lower duty cycle than radio selected BL Lacs (that are mostly LBLs where the optical flux is dominated by the jet and not by the blue bump and broad lines emission), which are instead characterised by polarisation levels of 30–40% and a high duty cycle [63].
Based on the empirical evidence described above, which reveals strong similarities between IBLs and HBLs properties, and large differences from LBLs, we suggest that blazars come only in two main flavours: LBLs, and IBLs plus HBLs combined, which we propose to collectively call IHBLs. For practical purposes, blazars can be assigned to one of the two sub-classes on the basis of a single value, with LBLs being those with Hz and IHBLs those with Hz.
We stress that LBLs and IHBLs are not simply sub-classes of blazars bureaucratically defined by the value of an observational parameter, but reflect deeply different intrinsic properties, such as cosmological evolution, demographic characteristics, broad-band spectral variability, optical polarisation, and possibly the physical conditions in the emitting regions that in IHBLs might host efficient proton acceleration. Since the cosmological evolution of LBLs is similar to that of optically and X-ray selected radio quiet QSOs, the presence of LBL relativistic jets, at least in first approximation, occurs in QSOs independently of cosmic epoch. The same does not happen in IHBL jets, which instead follow a different evolution. If proton acceleration occurs only (or mostly) in IHBL source it could be that the conditions that enable proton acceleration drive the evolution in these sources.
4.3. Transient Blazars and Neutrino Astronomy
The -ray source 4FGL J1544.3−0649 is a remarkable blazar that remained unnoticed at high energies until May 2017 when it showed a transient-like behaviour brightening to such a level to be detected by Fermi-LAT and the MAXI X-ray sky monitor. The source remained bright for a few months exhibiting an SED typical of bright HBL blazars [64]. This discovery suggests the existence of a population of still undiscovered objects that can occasionally flare and become strong X-ray and -ray sources. If X-ray flares are indeed associated to proton acceleration and neutrino emission, as suggested in ref. [65], these sources could play a significant role in neutrino astronomy. Considering that the expected neutrino flux from 4FGL J1544.3−0649 is the fifth largest in the list of 66 bright blazars considered in ref. [10], blazars that are currently uncatalogued and below detectability in the X-ray and -ray bands could even be a major population of neutrino sources. In this case the identification of the counterpart of many neutrino events would be a very difficult task.
The importance of this possible contribution clearly depends on the abundance of this population of blazars, how often large transient events occur, and how long sources remain in a bright phase. A reliable estimate of the space density and duty cycle of these elusive objects would only be possible through all-sky X-ray or -ray monitors that are significantly more sensitive that those currently in operation. Sensitive all-sky monitors would also easily discover possible high-energy flares from objects in the large localisation errors of neutrino events, providing “smoking-gun” evidence for neutrino-blazar association.
5. Summary and Discussion
Neutrino astronomy is still in a nascent phase, a status characterised by consolidated results on the detection of neutrinos of astrophysical origin, but also by the lack of indisputable evidence about the nature of their electromagnetic counterparts. Some results in this field are sound, such as the absence of anisotropy in the arrival directions of high-energy IceCube neutrinos, which implies a dominant population of extragalactic sources, although a minor Galactic component cannot be excluded. Considering specific associations with known cosmic electromagnetic sources we have shown that a growing number of papers are reporting possible associations of astrophysical neutrinos with AGN, particularly blazars of different types. Substantial theoretical work also demonstrated that neutrino emission mechanisms consistent with the existing data can be accommodated in physical situations that are typical of blazars [6,7,8,42,43,66].
In the following we make some considerations on the nature of the proposed associations with significance larger than 2 for different types of blazars.
As reported in the previous sections correlations of radio-bright AGN with astrophysical neutrinos have been sought extensively [14,33,34,35,36]. Recently, possible statistical associations with specific LBL sources (3C 279, NRAO 530, PKS 1741−038, and PKS 2145+067) have been reported in ref. [33]. These results however were not confirmed by similar works [36,37]. Samples of bright radio sources tends to select LBL objects since IHBL blazars are largely underrepresented in these data sets. For example only 103 out of the 3411 sources (∼) of the complete RFC sub sample with f mJy used in refs. [34,37] are IHBL blazars. A similar proportion is also evident in the surface density comparison plotted on the left part of Figure 1, which refers to blazars with radio flux density larger than 200 mJy at 1.4 GHz. Despite the large surface density of LBL blazars and the multiple statistical searches based on radio-bright sources, no stable significant association with sources of this type has been found. The matching of astrophysical neutrino samples with the position of known -ray-detected blazars, regardless of their radio flux, resulted instead in frequent possible associations with blazars of the IHBL type. Numerous examples of this increasingly reported outcome exist. The following is a list of the most important cases.
- A detailed study of the blazars located in the error regions of a sample of 70 well-reconstructed IceCube tracks found 47 IHBL blazars compared to a background expectation of 26.8, an overabundance equivalent to a 3.2 post trial significance. No excess of LBL blazars was found [39]. This is the statistically most compelling result in favour of IHBLs. Very recently Savard et al. [67], extending this work to 10 additional and newly detected neutrino tracks, confirmed that blazars from the 3HSP catalogue are significantly overrepresented in neutrino error regions.
- The famous blazar TXS 0506+056, currently considered the most reliable source of IceCube neutrinos [9,15,16], is an IHBL source.
- A chance probability of 1 per cent was found in ref. [68] where the authors compared the positions of extreme (IHBL) blazars with those of a sample of IceCube neutrinos. Other types of blazars gave null results.
- The search for point-like sources in the 10 year IceCube sample [4] resulted in a 3.3 excess over the expected background associated with the bright Seyfert 2 galaxy NGC 1068 and the three blazars PKS 1424+240, TXS 0506+056, and GB6 J1542+6129, all of which are bright (fradio 200 mJy) IHBL objects with very similar overall SEDs, as illustrated in Figure 4. A study aimed at finding additional similarities among these three sources will be presented by Padovani et al. (2022), in preparation.
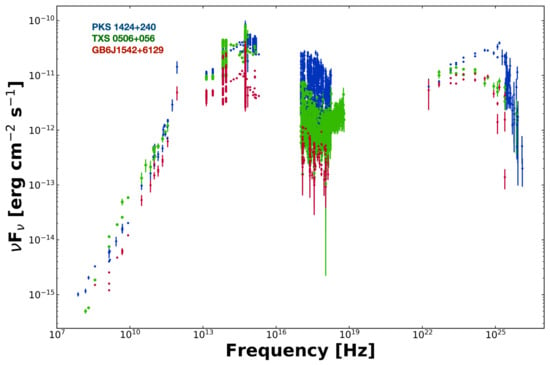 Figure 4. The SED of the three blazars reported as possible neutrino sources in [4]. They are all of the IBL type with remarkably similar flux and overall shape, except in the X-ray band, where small differences in , large variability and non-simultaneous observations cause a large scatter.
Figure 4. The SED of the three blazars reported as possible neutrino sources in [4]. They are all of the IBL type with remarkably similar flux and overall shape, except in the X-ray band, where small differences in , large variability and non-simultaneous observations cause a large scatter. - The IHBL blazar 3HSP J095507.9+35510, located in the error region IceCube-200107A, was undergoing a strong X-ray flare at the time of the neutrino arrival [40].
- The blazar MG3 J225517+2409, a bright IHBL source, has been proposed as the possible counterpart of 5 neutrinos detected by the ANTARES neutrino observatory [32] and the track event IceCube-100608A [39].
- The 2016 detection of three neutrinos within 100 s of each other from the same direction [69] was possibly associated with 3HSP J013632.5+390559, a bright IHBL blazar [39].
- A very recent search for neutrino flare emission in the IceCube 10 year data set [38] reported possible flares at the level of 3 from NGC 1068, two IHBL blazars TXS 0506+056, GB6 J1542+6129, and M87, a giant radio galaxy with -ray properties similar to that of IHBL objects that was already noticed as a possible counterpart of the track IceCube-141126A [39]. The IHBL 1ES1959+650, the next object in order of significance in the list of probable flaring sources of ref. [38], was also noticed as a possible counterpart of three neutrinos detected by AMANDA, the predecessor of IceCube, in 2002 in correspondence of a rare high-energy -ray flare [70].
If the several hints linking IHBLs to astrophysical neutrinos genuinely reflect a particular physical situation in these sources, it could be that the characteristics that distinguish them (e.g., high , no cosmological evolution, slow jet, strongly chromatic variability, low level of optical polarisation) may simply be the observational consequences of proton acceleration to very high energies. The highly variable UV or X-ray radiation that defines IHBLs could then be the direct result of proton synchrotron emission as proposed in refs. [10,65] or of radiation produced by the secondary particles generated in photo hadronic interactions that lose energy on timescales that depend on the specific physical conditions of the emitting region or of its evolution after flares. In this view the existence of IHBL blazars would be strictly connected to proton acceleration in AGN. The still poorly understood low level of cosmological evolution of IHBLs compared to other blazars, might also be connected with the conditions that lead to proton acceleration.
An origin of high-energy neutrinos from a non-evolving and low-density population of sources, such as IHBLs, easily meets the constraint for UHECRs sources not to overproduce the observed -ray background [71]. Intermittent proton acceleration occurring in persistent IHBLs, or in transient blazars like 4FGL J1544.3−0649, would further ease the constraint on the -ray background.
Neutrino multi-messenger astronomy is an exciting new field in rapid evolution where new observational data, possibly of improved localisation accuracy, need to be accumulated to confirm or disprove the hypothesis that IHBL blazars are the preferential site of proton acceleration. Forthcoming observatories like KM3NeT (https://www.km3net.org/, accessed on 11 December 2021) and Baikal-GVD (https://baikalgvd.jinr.ru/, accessed on 11 December 2021) under water neutrino telescopes, the Pacific Ocean Neutrino Experiment (P-ONE) [72], and the future more sensitive IceCube-Gen2 (https://icecube.wisc.edu/science/beyond/, accessed on 11 December 2021) instrument, ideally operating in parallel with a new generation of sensitive all-sky X-ray and -ray detectors, are the facilities that will bring neutrino astronomy into the next phase, settling the question about the role of the different types of AGN in terms of their neutrino and UHECR emission.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The multi-frequency data of all SEDs presented in this work are available through the tools and web pages of the Open Universe platform, e.g., the VOU-BLazars application [53] and the interactive table at https://openuniverse.asi.it/blazars/swift/ (accessed on 11 December 2021).
Acknowledgments
We thank Bia Boccardi for a careful reading of the paper. We acknowledge the use of data, analysis tools and services from the Open Universe platform, the National Extra-galactic Database (NED), and the bibliographic services of the Astrophysics Data System (ADS).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anchordoqui, L.A. Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. Phys. Rep. 2019, 801, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IceCube Collaboration. Evidence for High-Energy Extraterrestrial Neutrinos at the IceCube Detector. Science 2013, 342, 1242856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, A. Characterization of the Astrophysical Diffuse Neutrino Flux with IceCube High-Energy Starting Events. In Proceedings of the 36th International Cosmic Ray Conference (ICRC2019), Madison, WI, USA, 24 July–1 August 2019; Volume 36, p. 1004. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Alispach, C.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; Ansseau, I.; et al. Time-Integrated Neutrino Source Searches with 10 Years of IceCube Data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Alispach, C.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; Ansseau, I.; et al. Search for Sources of Astrophysical Neutrinos Using Seven Years of IceCube Cascade Events. Astrophys. J. 2019, 886, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannheim, K. γ rays and neutrinos from a powerful cosmic accelerator. Phys. Rev. D 1993, 48, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, M.; Halzen, F. High-energy cosmic neutrino puzzle: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 126901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G. High-energy cosmic neutrinos from spine-sheath BL Lac jets. Mon. Not. RAS 2015, 451, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration; Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, eaat1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stathopoulos, S.I.; Petropoulou, M.; Giommi, P.; Vasilopoulos, G.; Padovani, P.; Mastichiadis, A. Probing Neutrino Emission from X-ray Blazar Flares observed with Swift-XRT. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.14632. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisellini, G.; Maraschi, L.; Treves, A. Inhomogeneous synchrotron-self-compton models and the problem of relativistic beaming of BL Lac objects. Astron. Astrophys. 1985, 146, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. A Jet Model for the Gamma-Ray–emitting Blazar 3C 279. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 397, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Begelman, M.C.; Rees, M.J. Comptonization of Diffuse Ambient Radiation by a Relativistic Jet: The Source of Gamma Rays from Blazars? Astrophys. J. 1994, 421, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadler, M.; Krauß, F.; Mannheim, K.; Ojha, R.; Müller, C.; Schulz, R.; Anton, G.; Baumgartner, W.; Beuchert, T.; Buson, S.; et al. Coincidence of a high-fluence blazar outburst with a PeV-energy neutrino event. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration; Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Samarai, I.A.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Neutrino emission from the direction of the blazar TXS 0506+056 prior to the IceCube-170922A alert. Science 2018, 361, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Resconi, E.; Glauch, T.; Arsioli, B.; Sahakyan, N.; Huber, M. Dissecting the region around IceCube-170922A: The blazar TXS 0506+056 as the first cosmic neutrino source. Mon. Not. RAS 2018, 480, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified Schemes for Radio-Loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padovani, P.; Alexander, D.M.; Assef, R.J.; De Marco, B.; Giommi, P.; Hickox, R.C.; Richards, G.T.; Smolčić, V.; Hatziminaoglou, E.; Mainieri, V.; et al. Active galactic nuclei: What’s in a name? Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2017, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blandford, R.; Rees, M. Some comments on radiation mechanisms in Lacertids. In Proceedings of the Pittsburgh Conference on BL Lac Objects, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 24–26 April 1978; Wolfe, A.M., Ed.; University of Pittsburgh Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1978; pp. 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Falomo, R.; Pian, E.; Treves, A. An optical view of BL Lacertae objects. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2014, 22, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giommi, P.; Polenta, G.; Lähteenmäki, A.; Thompson, D.J.; Capalbi, M.; Cutini, S.; Gasparrini, D.; González-Nuevo, J.; León-Tavares, J.; López-Caniego, M.; et al. Simultaneous Planck, Swift, and Fermi observations of X-ray and γ-ray selected blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 541, A160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giommi, P.; Perri, M.; Capalbi, M.; D’Elia, V.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Brandt, C.H.; Pollock, A.M.T.; Arneodo, F.; Di Giovanni, A.; Chang, Y.L.; et al. X-ray spectra, light curves and SEDs of blazars frequently observed by Swift. Mon. Not. RAS 2021, 507, 5690–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Giommi, P. The connection between x-ray- and radio-selected BL Lacertae objects. Astrophys. J. 1995, 444, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Agudo, I.; Ajello, M.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.F.; Angelakis, E.; Arkharov, A.A.; Axelsson, M.; Bach, U.; et al. The Spectral Energy Distribution of Fermi Bright Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 30–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biteau, J.; Prandini, E.; Costamante, L.; Lemoine, M.; Padovani, P.; Pueschel, E.; Resconi, E.; Tavecchio, F.; Taylor, A.; Zech, A. Progress in unveiling extreme particle acceleration in persistent astrophysical jets. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi, S.; Acero, F.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2020, 247, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballet, J.; Burnett, T.H.; Digel, S.W.; Lott, B. Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog Data Release 2. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.11208. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgarelli, A.; Fioretti, V.; Parmiggiani, N.; Verrecchia, F.; Pittori, C.; Lucarelli, F.; Tavani, M.; Aboudan, A.; Cardillo, M.A.; Giuliani, A.N.; et al. Second AGILE catalogue of gamma-ray sources. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F. Canonical high-power blazars. Mon. Not. RAS 2009, 397, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Done, C.; Salamon, M.H.; Sommers, P. High-energy neutrinos from active galactic nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 2697–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, K.; Stanev, T.; Biermann, P.L. Neutrinos from flat-spectrum radio quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 260, L1–L3. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, A.; André, M.; Anghinolfi, M.; Anton, G.; Ardid, M.; Aubert, J.J.; Aublin, J.; Baret, B.; Basa, S.; Belhorma, B.; et al. ANTARES Search for Point Sources of Neutrinos Using Astrophysical Catalogs: A Likelihood Analysis. Astrophys. J. 2021, 911, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavin, A.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Kovalev, Y.A.; Troitsky, S. Observational Evidence for the Origin of High-energy Neutrinos in Parsec-scale Nuclei of Radio-bright Active Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 894, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavin, A.V.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Kovalev, Y.A.; Troitsky, S.V. Directional Association of TeV to PeV Astrophysical Neutrinos with Radio Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovatta, T.; Lindfors, E.; Kiehlmann, S.; Max-Moerbeck, W.; Hodges, M.; Liodakis, I.; Lähteemäki, A.; Pearson, T.J.; Readhead, A.C.S.; Reeves, R.A.; et al. Association of IceCube neutrinos with radio sources observed at Owens Valley and Metsähovi Radio Observatories. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 650, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Vandenbroucke, J.; Pizzuto, A. Testing the AGN Radio and Neutrino correlation using the MOJAVE catalog and 10 years of IceCube Data. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Kamionkowski, M.; Liang, Y.F. Search for high-energy neutrino emission from radio-bright AGN. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 123018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IceCube Collaboration. Search for Multi-flare Neutrino Emissions in 10 yr of IceCube Data from a Catalog of Sources. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 920, L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Glauch, T.; Padovani, P.; Resconi, E.; Turcati, A.; Chang, Y.L. Dissecting the regions around IceCube high-energy neutrinos: Growing evidence for the blazar connection. Mon. Not. RAS 2020, 497, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Padovani, P.; Oikonomou, F.; Glauch, T.; Paiano, S.; Resconi, E. 3HSP J095507.9+355101: A flaring extreme blazar coincident in space and time with IceCube-200107A. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 640, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiano, S.; Falomo, R.; Treves, A.; Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Scarpa, R. The spectra of IceCube neutrino candidate sources–I. Optical spectroscopy of blazars. Mon. Not. RAS 2021, 504, 3338–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Padovani, P.; Mastichiadis, A.; Resconi, E. Photohadronic origin of γ -ray BL Lac emission: Implications for IceCube neutrinos. Mon. Not. RAS 2015, 448, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Oikonomou, F.; Mastichiadis, A.; Murase, K.; Padovani, P.; Vasilopoulos, G.; Giommi, P. Comprehensive Multimessenger Modeling of the Extreme Blazar 3HSP J095507.9+355101 and Predictions for IceCube. Astrophys. J. 2020, 899, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Falomo, R.; Oikonomou, F.; Petropoulou, M.; Glauch, T.; Resconi, E.; Treves, A.; Paiano, S. The Spectra of IceCube Neutrino (SIN) candidate sources-II. Source Characterisation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Padovani, P.; Oikonomou, F.; Petropoulou, M.; Giommi, P.; Resconi, E. TXS 0506+056, the first cosmic neutrino source, is not a BL Lac. Mon. Not. RAS 2019, 484, L104–L108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giommi, P.; Padovani, P.; Polenta, G.; Turriziani, S.; D’Elia, V.; Piranomonte, S. A simplified view of blazars: Clearing the fog around long-standing selection effects. Mon. Not. RAS 2012, 420, 2899–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Padovani, P.; Polenta, G. A simplified view of blazars: The γ-ray case. Mon. Not. RAS 2013, 431, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Foschini, L.; Ghirlanda, G. The transition between BL Lac objects and flat spectrum radio quasars. Mon. Not. RAS 2011, 414, 2674–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, E.; Maselli, A.; Leto, C.; Marchegiani, P.; Perri, M.; Giommi, P.; Piranomonte, S. The 5th edition of the Roma-BZCAT. A short presentation. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 357, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.L.; Arsioli, B.; Giommi, P.; Padovani, P.; Brandt, C.H. The 3HSP catalogue of extreme and high-synchrotron peaked blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 632, A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajello, M.; Angioni, R.; Axelsson, M.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Gonzalez, J.B.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; Bloom, E.D.; et al. The Fourth Catalog of Active Galactic Nuclei Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2020, 892, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, B.; Gasparrini, D.; Ciprini, S. The Fourth Catalog of Active Galactic Nuclei Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope–Data Release 2. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.08406. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.L.; Brandt, C.H.; Giommi, P. The Open Universe VOU-Blazars tool. Astron. Comput. 2020, 30, 100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, J.; Cotton, W.; Greisen, E.; Yin, Q.; Perley, R.; Taylor, G.; Broderick, J. The NRAO VLA Sky Survey. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 1693–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Landt, H.; Perlman, E.S. The Deep X-Ray Radio Blazar Survey. III. Radio Number Counts, Evolutionary Properties, and Luminosity Function of Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2007, 662, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasinger, G.; Miyaji, T.; Schmidt, M. Luminosity-dependent evolution of soft X-ray selected AGN. New Chandra and XMM-Newton surveys. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 441, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Menna, M.T.; Padovani, P. The sedentary multifrequency survey-I. Statistical identification and cosmological properties of high-energy peaked BL Lacs. Mon. Not. RAS 1999, 310, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rector, T.A.; Stocke, J.T.; Perlman, E.S.; Morris, S.L.; Gioia, I.M. The Properties of the X-Ray-selected EMSS Sample of BL Lacertae Objects. Astron. J. 2000, 120, 1626–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prince, R. Broadband study of BL Lac during flare of 2020: Spectral evolution and emergence of HBL component. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.00221. [Google Scholar]
- Sahakyan, N.; Giommi, P. A thirteen-year-long broadband view of BL Lac. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12232. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, M.L.; Homan, D.C.; Hovatta, T.; Kellermann, K.I.; Kiehlmann, S.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Max-Moerbeck, W.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Readhead, A.C.S.; Ros, E.; et al. MOJAVE. XVII. Jet Kinematics and Parent Population Properties of Relativistically Beamed Radio-loud Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jannuzi, B.T.; Smith, P.S.; Elston, R. The Optical Polarization Properties of X-Ray–selected BL Lacertae Objects. Astrophys. J. 1994, 428, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impey, C.D.; Tapia, S. The Optical Polarization Properties of Quasars. Astrophys. J. 1990, 354, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, N.; Giommi, P. The strange case of the transient HBL blazar 4FGL J1544.3−0649. Mon. Not. RAS 2021, 502, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastichiadis, A.; Petropoulou, M. Hadronic X-ray Flares from Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2021, 906, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, X.; Garrappa, S.; Gao, S.; Paliya, V.S.; Franckowiak, A.; Winter, W. Multiwavelength and Neutrino Emission from Blazar PKS 1502 + 106. Astrophys. J. 2021, 912, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, K.; Ruan, J.J.; Haggard, D. Are blazars above the blazar sequence a significant source of IceCube neutrinos? Mon. Not. RAS 2021, 509, 4620–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Resconi, E.; Giommi, P.; Arsioli, B.; Chang, Y.L. Extreme blazars as counterparts of IceCube astrophysical neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icecube Collaboration; Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Multiwavelength follow-up of a rare IceCube neutrino multiplet. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 607, A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halzen, F. The Observation of High-Energy Neutrinos from the Cosmos: Lessons Learned for Multimessenger Astronomy. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.01687. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y.; Taylor, A.; Wang, X.Y.; Aharonian, F. Constraining the redshift distribution of ultrahigh-energy-cosmic-ray sources by isotropic gamma-ray background. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on High Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany, 11–15 July 2016; American Institute of Physics Conference Series. Volume 1792, p. 060005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.; Böhmer, M.; Bosma, J.; Clark, K.; Danninger, M.; Fruck, C.; Gernhäuser, R.; Gärtner, A.; Grant, D.; Henningsen, F.; et al. The Pacific Ocean Neutrino Experiment. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).