Abstract
Continuous gravitational waves are long-lasting forms of gravitational radiation produced by persistent quadrupolar variations of matter. Standard expected sources for ground-based interferometric detectors are neutron stars presenting non-axisymmetries such as crustal deformations, r-modes or free precession. More exotic sources could include decaying ultralight boson clouds around spinning black holes. A rich suite of data-analysis methods spanning a wide bracket of thresholds between sensitivity and computational efficiency has been developed during the last decades to search for these signals. In this work, we review the current state of searches for continuous gravitational waves using ground-based interferometer data, focusing on searches for unknown sources. These searches typically consist of a main stage followed by several post-processing steps to rule out outliers produced by detector noise. So far, no continuous gravitational wave signal has been confidently detected, although tighter upper limits are placed as detectors and search methods are further developed.
1. Introduction
The search for continuous gravitational-wave signals (CWs), long-duration forms of gravitational radiation, is one of the endeavours of gravitational-wave astronomy. These signals are produced by long-standing quadrupolar variations, such as rapidly spinning neutron star (NSs) sustaining a crustal deformation, undergoing an r-mode instability or in free precession [1,2,3,4], as well as more exotic sources such as the annihilation of ultra-light boson clouds around spinning black holes [5,6,7,8] or compact dark matter objects (CDOs) in the Solar System [9].
Detecting a CW signal could shed some light on NS physics, as well as open a new channel to test general relativity (extra polarizations, Lorentz violations) or detect dark matter [10,11,12,13,14]. No confident CW detection has been reported to date. The current product of CW searches are source-agnostic upper limits on the nominal CW amplitude . These results can then be mapped into different astrophysical scenarios, such as the ellipticity of nearby NSs, the mass of ultralight bosons around black holes [15,16], or the nearby population of planetary-mass primordial black hole binaries [17,18].
The present document reviews search methods and pipelines employed to look for CW signals in the observing runs performed by the second generation of ground-based interferometric detectors (advanced detectors). Reviews on the physical mechanisms of CW emission by NSs can be found in [1,2,3,4]. Basic data analysis techniques are discussed in [19]. Finally, [20] discusses the main results of previous CW searches up to 2017.
The standard CW signal model consists of a quasi-monochromatic source emitting gravitational waves at a certain frequency . For the case of a NS sustaining a certain ellipticity, corresponds to twice the spinning frequency of the star. Further time derivatives of the frequency arise due to different physical mechanisms affecting the source, such as energy emission as gravitational or electromagnetic radiation. In the case of sources in binary systems, the orbital motion induces a Doppler modulation.
Regardless of the specific intrinsic frequency modulation of the source, CW signals as seen from Earth are Doppler-modulated due to the detector motion around the Solar System barycenter (SSB). For a source with a given intrinsic frequency evolution , the detector-frame frequency is given by
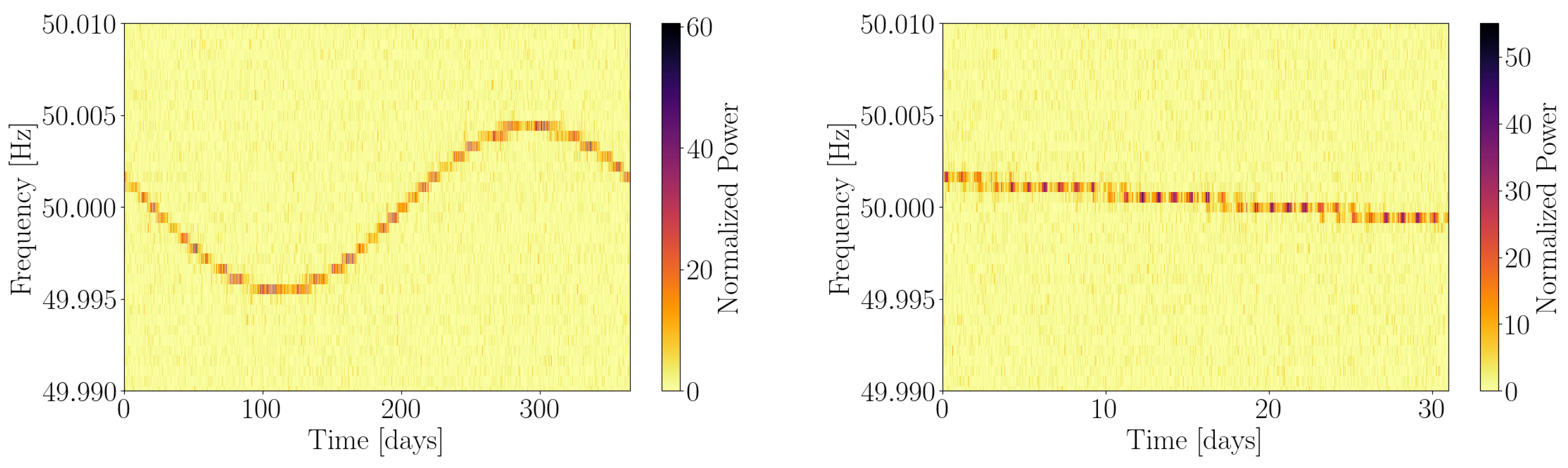
where the phase-evolution parameters include the CW frequency and the sky position of the source , as well as any other parameter describing the intrinsic frequency evolution of the signal. refers to the detector velocity expressed as a fraction of the speed of light, and contains both the daily and yearly motion of Earth around the SSB, of orders and , respectively. The yearly modulations can be clearly seen in the left panel of Figure 1; the daily modulation is contained within a frequency bin.
Figure 1.
Data spectrogram showing the response of an Earth-bound detector to a passing CW signal emitted by an isolated source. The left panel displays the one-year evolution of the detector response, while the right panel zooms in on a month-long period. Frequency modulations correspond to the yearly translation of Earth around the SSB (the daily Doppler modulation is contained within a frequency bin). Amplitude modulations correspond to the change in antenna-pattern functions throughout a day.
The amplitude of a CW signal is described using four parameters, namely, the initial CW phase , the spherical angles describing the orientation of the source , and the nominal gravitational wave amplitude . The response of a ground-based detector to a passing CW is better described in terms of the so-called JKS representation [21]
where the four time-independent depend on the four amplitude parameters and the antenna-pattern response of the detector is contained in the four quadratures , which only depend on the phase-evolution parameters. The basic effect of the antenna-pattern response on a CW signal is a daily amplitude modulation, clearly visible in Figure 1.
As opposed to the short signals produced by compact binary coalescences (CBCs), with typical durations between a few minutes and less than a second for current detectors, CW signals are expected to last for years, spanning several observing runs of the current and future generation of ground-based interferometric detectors [22,23,24,25,26]. This difference in duration is crucial in terms of detecting and estimating the parameters of a CW signal.
Modelled searches are usually performed using matched filtering [27], comparing the datastream to a set of templates in order to find a high correlation. Due to the typical duration of a CW signal (spanning the entire observing run), the required number of templates to perform a blind search is prohibitively high even for current computing standards [28,29,30].
The standard strategy, in a broad sense, is to reduce the effective length of the datastream by performing matched filtering over shorter segments; the segment-wise results can then be combined into a final statistic. These kind of schemes are usually referred to as semicoherent searches [19]: the segment-wise analysis is typically referred to as coherent, as it compares the phase evolution of a signal with the datastream throughout a coherence time . The resulting coherent filters are then combined incoherently (ignoring phase information) into a final detection statistic. This incoherent combination allows to recover part of the sensitivity lost due to the split of the initial datastream; the final sensitivity, however, is lower than that of a fully coherent search.
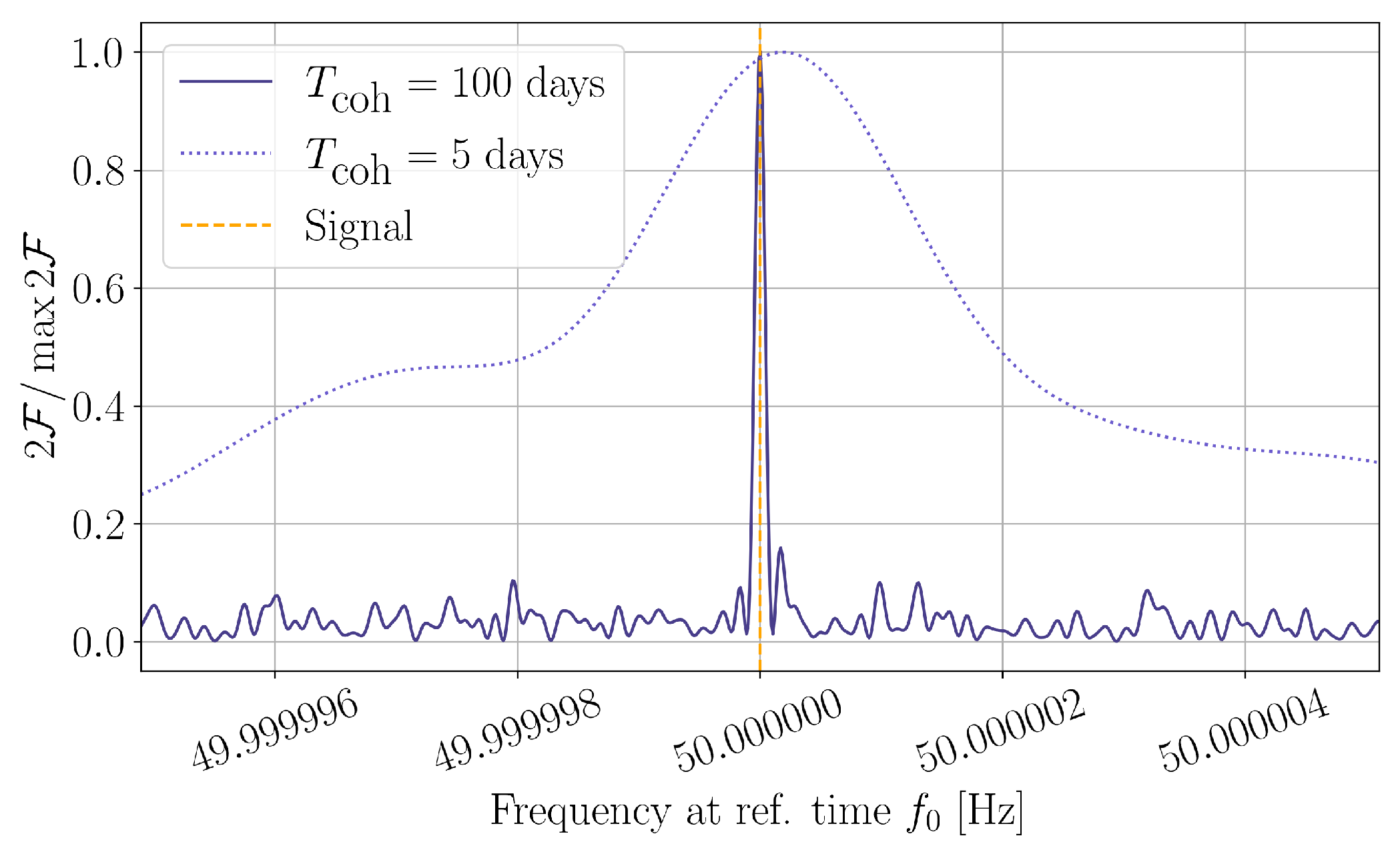
Figure 2 illustrates the principle of operation of semicoherent searches. By comparing shorter streams of data, a looser constraint is imposed when comparing phase-evolution templates. As a result, the characteristic width of detection-statistic peaks widens, reducing the required number of templates to ensure a good covering of the parameter space. This strategy is at the core of multi-stage approaches such as those discussed in Section 4.
Figure 2.
Effect of different values of on one of the standard detection statistics for CW searches, the -statistic (see Section 2.1). Longer coherence times impose a greater penalization to deviations with respect to the signal model; as a result, peaks tend to become narrower around the true signal parameters.
Parameter estimation, on the other hand, is positively affected by the long signal durations. Typical frequency resolutions are under a mHz for initial stages, achieving nHz resolution at fully coherent follow-ups using a year of data. Sky localization is also significantly improved. If we think of CBC sky localization, neglecting contributions from antenna-pattern amplitude modulations and higher GW modes, the problem is basically that of determining the direction a GW pulse came from, which can be solved by means of measuring the pulse from N detectors and finding the overlapping sky-positions [31]. The case of CW signals is much simpler, as they are not just single pulses, but continuously arrive at the detector as it moves around the SSB. Due to this movement, a single interferometric detector receiving a CW signal at different positions with respect to the SSB is essentially equivalent to an arbitrary large set of different detectors receiving the same pulse from a source. Hence, for CW sources, sharp sky localization can be achieved using a single detector by simply extending the duration of an observing run.
CW searches require a very fine parameter-space resolution in order not to miss a signal, increasing the computing cost of a matched-filtered search up to unaffordable figures [28]. As a result, searches for CW signals from unknown sources tend to follow a hierarchical approach [32,33,34,35,36,37,38]: wide parameter-space regions are analysed using a less-constraining statistic so that a coarser template bank can be used, see Figure 2. Interesting regions are then typically small enough to follow up using a more sensitive statistic. A quantitative description of this strategy can be found in [39].
The structure of this work goes as follows: in Section 2 we review the main search methods and pipelines employed to search for CW signals from unknown sources during the era of the advanced detectors. Section 3 discusses different post-processing stages employed by said searches; these include both specific prescriptions to select interesting candidates (e.g., clusterings) and consistency arguments to assess the overlap of a specific set of templates with instrumental disturbances. Section 4 reviews follow-up strategies to further analyse interesting candidates. So far, no search has claimed a confident CW detection, reporting instead constraints on the maximum detectable amplitude achieved. Different approaches to constructing said constraints are listed in Section 5. Finally, a summary of the reviewed methods is presented in Section 6.
2. Wide Parameter-Space Search Pipelines
We present a review of methods and pipelines employed to date to search for CW signals from unknown sources during the era of the advanced detectors. Specifically, we consider three kinds of searches for unknown sources: (i) blind searches, with weak prior assumptions about possible source parameters [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]; (ii) spot-light searches, focused at sky regions harbouring an interesting population of objects whose exact frequency is unknown, such as globular clusters or the Galactic Center (GC) [55,56]; and (iii) directed searches, targeting specific celestial objects compatible with a CW source, such as supernova remnants (SNRs) or low-mass X-ray binaries (LMXBs) [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69].
2.1. -Statistic Searches
The -statistic is a standard detection statistic for CW signals. Initially derived as a maximum-likelihood estimator with respect to amplitude parameters [21,70], it was later rederived in a Bayesian context as a Bayes factor, gauging the presence (or lack) of a signal in a Gaussian noise data stream, in which amplitude parameters are marginalized using a rather unphysical set of amplitude priors [71,72,73,74,75,76]. This detection statistic can be extended for more generic types of sources, such as binary white-dwarf systems [77] or the inspiral phase of binary black-hole coalescences [78].
Semicoherent searches balance sensitivity and computing cost by choosing a suitable number of coherent segments whose combination into a semicoherent quantity can be performed in an efficient manner. The basic “stack-slide” procedure used for many -statistic semicoherent searches [32,33,34,79] is to set up a template bank in each coherent segment to compute the segment-wise coherent detection statistic. Then, in the semicoherent stage, the semicoherent detection statistic is computed on a finer template bank by combining results from the segment-wise coherent detection statistics. This template bank refinement can be seen as a consequence of using multiple coherent segments: the greater the number of coherent templates to be combined, the greater the resulting number of distinct semicoherent segments. Discussion on the specifics of template bank refinements are deferred to Section 2.1.1 and Section 2.1.2.
We discuss three different implementations of semicoherent -statistic searches, namely the Global Correlation Transform hierarchical search (GCT), Weave and Time-domain -statistic. They mainly diverge in the manner of constructing semicoherent quantities, taking different trade-offs in terms of computing cost, memory requirement and robustness to non-Gaussianities. We note, however, that fully coherent searches for targets at a specific sky position, such as supernova remnants [59,66], are still performed nowadays.
2.1.1. GCT Hierarchical Search
Detection statistics (and the -statistic in particular) present a set of characteristic correlations across the CW parameter-space due to some level of degeneracy present in CW signals [80]. Understanding the structure of said correlations offers a simple method to reuse coherent -statistic values to construct a semicoherent statistic, reducing the overall computing cost of the search. The GCT introduces a set of coordinates defined by the intersection of parameter-space correlation surfaces to identify nearby parameter-space points where the -statistic achieves a high value due to the presence of a signal [81,82,83].
Due to its interesting trade-off between sensitivity and computational cost [84], semicoherent GCT searches have been used by the Einstein@Home project to perform deep searches throughout different observing runs [40,49,61,62,69]. Einstein@Home searches distribute the computational load of a search across a volunteer-computing network using BOINC [85] to analyse a large number of parameter-space candidates.
At the core of the GCT search there are combinations of -statistic values computed at different coherent segments containing data from one or multiple detectors. These are combined into the semicoherent -statistic using a finer template bank with refinement only on the spindown parameters [82]. This allows for the easy implementation of Bayesian extensions over the semicoherent -statistic, such as the “line-robust” or statistics [86,87,88,89], which combine -statistics from different detectors to suppress single-detector artifacts.
No general computing model is available for the GCT search, requiring extensive software-injection campaigns in order to numerically tune the sensitivity of a search to the available computing resources [36]. As discussed in Section IV B of [90], this is due to a core assumption in [32,82,83] neglecting refinements in the sky parameter-space. Further developments in the field, discussed in Section 2.1.2, proposed a new strategy to solve this problem. For the case of directed searches, however, optimal setup strategies are available [91].
2.1.2. Weave
Local parameter-space structure can be understood in terms of the mismatch [92,93]. Given a signal parametrised by a set of parameters , the parameter-space mismatch quantifies the fractional loss of (squared) signal-to-noise ratio produced by an arbitrary parameter-space off-set with respect to the true signal parameters:
In a neighbourhood of , the mismatch can be expressed in terms of a quadratic form as
where the symmetric 2-rank tensor plays the role of a Riemannian metric in the parameter-space.
It was quickly realized that, for the case of flat parameter-spaces, the metric offers a complete description of the parameter-space, allowing for the easy construction of optimal setups [29,94]; alas, the standard CW parameter-space (specifically, the sky-position subspace) presents a non-trivial structure resulting in a curved parameter-space.
Weave [90] represents the coming together of a number of search strategies. It implements, for the first time, a semicoherent search with a well-understood computational model based on a flat parameter-space metric. The setup is capable of constructing template banks at the suitable resolution to achieve an optimal computing cost [30,90,95,96]. Setting up Weave requires only a list of time stamps delimiting semicoherent segments, a coherent mismatch , with which single-segment template banks will be constructed, and a semicoherent mismatch , to setup the semicoherent template bank. The identification of a template from the semicoherent bank to its corresponding ensemble of coherent templates is handled by the Weave code using the coherent parameter-space metric to identify the nearest neighbor in each segment. In a sense, Weave retains the general characteristics of the GCT search, mainly being an engine to combine coherent -statistics, but, as opposed to it, Weave requires no extensive numerical calibration to be deployed using an optimal setup.
The success of Weave as an all-sky search, however, is related to the characteristics of the -statistic’s parameter-space structure. As discussed in depth in [96,97], the optimal setup for a realistic computing budget tends to yield semicoherent mismatch values well beyond the validity of the metric approximation (i.e., ). Nevertheless, empirical studies [96] show that in this regime the -statistic actually falls off more slowly than predicted by the metric, meaning the resulting template bank will contain more templates than strictly required. An alternative approach circumventing the empirical characterization of the regime is discussed in [94,98,99].
Despite achieving a better sensitivity than the GCT search at a fixed computing cost, the increased memory requirements of Weave make it so far unsuitable for its deployment on Einstein@Home [84]. Nonetheless, its sensitivity and setup flexibility have already been proven in the implementation of a novel CW search strategy [51].
2.1.3. Time-Domain -Statistic
Both GCT and Weave searches rely on a common implementation of the -statistic [100], publicly available under LALSuite [101]. The Time-domain -statistic pipeline [102] uses a different implementation, based on the -statistic’s time-dependent behaviour throughout the observing run. Instead of computing semicoherent quantities, it focuses on significant parameter-space points at coherent-segment level, looking for coincident candidates across different time segments and detectors. Using this coincidence criterion (which we review in more depth in Section 3), the pipeline automatically becomes robust to strong instrumental features, since they tend to overlap with different parameter-space regions as an observing run progresses.
This particular implementation of the -statistic uses its own template bank setup in order to optimize the number of fast Fourier transform (FFT) computations [103,104], which normally takes a significant part of the overall computing cost of the search. Further improvements at parameter-estimation level are optimization algorithms to resolve the characteristic frequency multi-modality of the -statistic [105] and the inclusion of machine-learning algorithms to filter out non-astrophysical candidates [106].
2.2. Fourier-Transform-Based Searches
The efficiency of -statistic searches stems from the marginalization with respect to amplitude parameters, removing four parameter-space dimensions from the search [29]. Semicoherent pipelines, moreover, assume amplitude parameters to be independent across different coherent segments. This approach makes it difficult to search for amplitude parameters, such as specific CW polarizations.
An alternative family of methods use Fourier transforms of short data segments (Short Fourier Transforms, SFTs) as the basic unit of operation. The duration of an SFT is typically such that CW signals are contained within a single frequency bin. For an isolated NS, this length is about 30 min [107], although the exact value depends on the considered frequency range. We note that SFTs themselves can, in some situations, corresponds to coherent segments of a semicoherent search; in such cases, the effective coherent length is proportional to the SFT length.
In order to construct a detection statistic , Fourier transform amplitudes are combined using a set of weights (effectively a kernel) taking into account source polarization, antenna-pattern amplitude modulations, Doppler modulations and relative phase deviations across different detectors:
where parameters other than time dependency have been kept implicit for the sake of simplicity. Frequency modulations are assumed to be contained within the specific set of Fourier amplitudes being combined, although can be configured to increase robustness against different kinds of spectral leakage by including neighbouring frequency bins into the kernel [39,108].
We review two families of searches stemming from Equation (5), depending on whether their primary target is to increase the robustness against deviations from the intended CW model (PowerFlux & Falcon) or to improve sensitivity by increasing the effective amount of data used (Cross-Correlation).
2.2.1. PowerFlux & Falcon
The PowerFlux pipeline [109,110,111,112] estimates power from a CW source depending on its sky position. The basic implementation [41,42,54] uses a diagonal kernel to combine Fourier power from each SFT. In this case, the role of is to diminish the contribution of unfavourable frequency bins (due to high noise floors or a low antenna-pattern response) to the total weighted Fourier power. Since the final statistic ignores relative phase shifts between SFTs, this corresponds to a semicoherent search for a specific CW polarization.
Loosely coherent methods [39,113,114] exploit the flexibility of Equation (5) to set up a kernel to account for unmodeled phase shifts, be it due to parameter-space mismatches or unaccounted physics such as small binary orbital modulations [115]. To do so, phases are allowed to drift at most by a specific amount across contiguous data segments, obtaining as a result [39]
where data are assumed to come from a single detector for the sake of simplicity. (The framework presented in [39] is flexible enough to treat data from multiple detectors.) This simple kernel illustrates the principle of operation of loosely coherent searches: if , behaves like a delta function and phases among contiguous segments are uncorrelated, effectively performing a semicoherent search; if , and phases are correlated throughout the full data stream, performing a fully coherent search. Tuning to intermediate value allows to trade sensitivity and computing cost: low values involve simpler kernels (less non-zero terms), easing the computing cost of Equation (5) but imposing tighter constraints with respect to the chosen CW model. A discussion on physically relevant values can be found in [39], whereas an efficient implementation of low- kernels can be found in [113,114].
Due to its high computing cost, the initial implementation of loosely coherent methods on PowerFlux was mainly used on directed searches, such as spot-light surveys [55] or follow-up stages (see Section 4). An efficient implementation, Falcon, was later developed to perform all-sky searches throughout O1 [43,44] and O2 [46,47,48], setting competitive constraints on the nearby population of Galactic neutron stars.
2.2.2. Cross-Correlation
The Cross-Correlation search [116,117,118], implemented in the LALSuite library [101], closes the sensitivity gap between semicoherent and coherent searches by increasing the effective amount of data using the correlation of Fourier amplitudes at different times.
Although initially designed to look for stochastic GW backgrounds, CW signals are a perfect target to be looked at for using Cross-Correlation, as they are long-lasting and deterministic. This allows to use not only the cross-correlation of different instruments during a certain period of time, but also the cross-correlation of data segments at different periods of time. In the context of CW searches, Cross-Correlation searches have been employed to look for specific high-priority targets, such as CW emission from the LMXB system Scorpius X-1 [58,67]. Complementarily, searches for stochastic GW backgrounds, such as the Radiometer search [119,120,121], are able also to constrain CW amplitudes from specific sky locations, such as those of SNRs, LMXBs such as Scorpius X-1 or the Galactic Center [122,123,124].
To do so, the kernel is constructed following the expected correlation of a signal across different stretches of data at different times and detectors. Specifically, only amplitudes within a certain time range are combined together. As opposed to PowerFlux and Falcon, however, polarization angles are averaged out using uniform priors. The parameter plays a similar role to that of (see Section 2.2.1) in terms of trading computing cost and sensitivity: longer increases the number of cross-correlations to perform, but also imposes a tighter constraint with respect to the specified CW model. Latest developments on this pipeline include the use of re-sampling techniques to accelerate its evaluation [125] and the use of shear parameter-space transform to optimize the setup of template banks [118].
2.3. Hough-Transform Semicoherent Searches
Loud instrumental features in the data tend to saturate detection statistics due to their strong resemblance to CW signals along short periods of time. This problem pushed forward the development of methods capable of suppressing narrow-band features in the data, such as the application of the Hough transform to the search for CW signals.
The basic idea is to limit the contribution of each semicoherent segment to a bounded quantity, which contributes by a limited amount to the overall statistic. This is done by binarising a power-like quantity (whitened Fourier power formatted as SFTs, as discussed in Section 2.2, or the -statistic) into ones and zeroes using a predetermined threshold [107]. Such a binarisation, however, comes at the cost of ignoring noise-floor variations and antenna-pattern amplitude modulations, meaning highly contaminated frequency bands around low-sensitivity sky positions will contribute the same amount as clean frequency bands at the most favoured sky positions. This problem is usually solved by introducing a set of weights into the detection statistic [126,127].
The Hough transform [128] can be used to identify shapes in binarised images. Given a parameter-space parametrizing a family of curves, each set of parameters is assigned a score, the number count, proportional to the number of pixels in the image consistent with the corresponding curve. In CW searches, the parameter space is typically the set of phase-evolution parameters, according to which the data spectrogram is traversed adding (weighted) ones and zeroes depending on whether each frequency bin contains excess power or not.
Hough-transform-based searches have been widely used during the latest all-sky searches [41,42,45,50,52,53]. We discuss the two main implementations of the Hough transform for CW searches, SkyHough and FrequencyHough.
2.3.1. SkyHough
The SkyHough pipeline was the initial implementation of the Hough transform to the search for CW signals [107,129]. Due to the Earth’s movement around the SSB, a CW signal arriving at the detector at a certain time t with a given frequency has a very specific set of sky positions from which it could have originated. Said sky positions take the shape of thick annuli (“circles in the sky”) [80,107,130] which, for consistency, can be described themselves as one/zero regions in the sky patch. The binarisation of the data spectrogram, thus, gets mapped into the selection and summation of sky patches containing different selected annuli.
The “circles in the sky” are weakly affected by local changes in ; hence, once computed for a specific frequency, these structures can be saved into a look-up table (LUT) to analyse several frequency bins. The use of LUTs, on the other hand, affects the maximum sensitivity of SkyHough since only an approximated frequency-evolution track is being used. Further developments on the pipeline include the re-analysis of interesting candidates using the exact frequency-evolution track and using more sensitive statistics in order to improve parameter estimation [131,132]. Additionally, the combination of LUTs can be easily accelerated using GPU parallelization [133].
The use of LUTs depends on a basic set of CW parameters, namely frequency and sky position, meaning it can be arbitrarily extended to look for different types of CW signals as long as the source’s intrinsic and extrinsic frequency evolutions are uncoupled from the Earth’s Doppler modulation. This includes transient-like CW signals, such as those produced by newborn NSs [134], or NSs in binary systems [133].
2.3.2. FrequencyHough
FrequencyHough is another pipeline based on the Hough transform [135,136]. As opposed to SkyHough, binarized spectrograms are mapped onto the frequency and spindown subspace . In this case, sky position is fixed for all the analysed templates. This presents two main advantages with respect to SkyHough. First, it allows to increase frequency resolution independently of other parameters, resulting in a better parameter recovery. Second, all candidates analysed at once are related to the same sky position. As a result, sky regions where templates tend to overlap with instrumental features can be dealt with in a simpler manner [137,138]. This different mapping, however, limits the generalization possibilities of FrequencyHough to linear relations between parameters.
This search is usually combined with different data formats: wide parameter-space searches are usually run using the so-called Short Fourier Data Base (SFDB) [139], which includes time-domain cleaning of raw data to reduce the effect of transient noise. For searches at a specific parameter-space region at hand, such as supernova remnants, the Galactic center or a specific outlier from a wider search, Band Sampled Data (BSD) [140,141] is used to efficiently apply heterodyning filters, reducing the computing cost of analysing such a local parameter-space region.
Several generalizations of these methods have been developed in order to look for other kinds of source. Power-law frequency evolution was covered using a generalization of FrequencyHough [142], allowing to search for binary neutron star merger remnants [143]. A study on the suitability of FrequencyHough to probe planetary-mass primordial black holes was presented in [17]. A method to conduct all-sky searches for CWs from the evaporation of boson clouds around spinning black holes was developed in [144], using the BSD framework [140,141]. A related method to place constraints on dark-photon dark matter interacting directly with GW interferometers was developed in [145] and applied in [146].
2.4. Viterbi Searches
CW signals could contain stochastic contributions (spin wandering) whose behaviour would not be well represented by the standard model introduced in Equation (1). This could affect objects in both isolated and binary systems [147,148], and should be taken into account in order to describe the underlying physics.
A simple approach is to describe the frequency-evolution model itself as a stochastic process, namely a Markov Chain (MC), and infer the most likely instantaneous frequency of a signal from the data. This is usually developed under the framework of Hidden Markov Models (HMM) [149,150,151,152,153], but an equivalent description can be made using Bayesian probability [154]. As discussed in [12], the search for ultralight boson-cloud evaporation around spinning black holes could also benefit from this kind of approach. A specific example of such a search, directed toward Cygnus X-1 using Advanced LIGO O2 data, was presented in [16].
Given a set of measurements at discrete times , we want to infer the instantaneous frequency of a signal in the data . This problem can be readily expressed as an inference one on f by means of Bayes theorem [155]
where the sampling distribution of different measurements has been (conservatively) factored assuming logical independence. The prior probability distribution on the instantaneous frequency is usually specified in terms of the initial frequency and the transition probabilities of the MC
is generally taken as a uniform distribution over the searched frequency band; the choice of transition probabilities (thus prior probabilities) and sampling distribution is dependent upon the method and source of interest, as summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of CW searches based on a MC implemented via the Viterbi algorithm. Transition probabilities (second column) and other details of each specific pipeline are discussed in the text.
Regardless of the astrophysical scope, searches using a MC evolution model (Equation (7)) obtain the most likely (maximum-posterior) frequency-evolution path using the Viterbi algorithm [159]
Two basic choices exist for transition probabilities [152], depending on whether the dominant frequency-drift time-scale is given by the source’s spin wandering or secular spindown. The former allows transitions to any neighbouring frequency bin at each time step. The latter uses a so-called biased HMM: given a frequency at bin j, the following frequency bin must be equal or lower, ; the specific number of bins is usually between two and three [65,156].
Since no template bank is involved, Viterbi searches are able to benefit from a wide variety of detection statistics at a small tuning cost. Specifically, binary modulations can be easily folded in using the -statistic, which improves over the -statistic [160] by combining frequency side-bands using complex weights. In order to track phase information, Viterbi 3.0 uses an efficient implementation of the -statistic [71,72] first proposed in [113].
Finally, the SOAP pipeline [154] uses Bayesian spectral analysis to avoid relying on the -statistic, looking for CW signals displaying a sinusoidal behaviour during short periods of time. To do so, the sampling distribution is taken proportional to the data’s Schuster periodogram [161], adding an extra hypothesis to increase the robustness against strong monochromatic features in the data. This pipeline assumes the CW signal frequency is contained in a single frequency bin; as a result, the maximum recoverable spindown corresponds to that of a NS with a small ellipticity, in an analogous manner to the latest Falcon searches [46,47,48].
2.5. Machine Learning
The use of machine-learning (ML) techniques in the search for CW signals follows one of two trends: either to classify and summarize the results of a search’s main stage, as discussed in Section 3.2, or to substitute the search step itself, acting as a detection statistic. A recent review on ML applications in GW data analysis in general can be found in [162].
A first approach is to train a classifier directly over Fourier-transformed raw time-series data to distinguish the presence of a signal within background noise. The specific data format is dependent upon the signals being looked for: for CW signals, which last for long periods of time over narrow frequency bands. In [163,164], a convolutional neural network (CNN) is trained on the real and imaginary parts of short-time Fourier transforms. Slight variations on this proposal were employed to look for postmerger signals. These signals, compared to CW signals, last a shorter period of time over a wider frequency band [165]. In order to reflect the non-trivial time dependency of the signal, Ref. [166] took Fourier transforms using shorter time durations, finally using the data spectrogram as input for, again, a CNN.
The second approach takes a less radical point of view. Instead of starting from raw data, machine learning algorithms are applied on the output of a search pipeline to construct a new detection statistic [167,168]. This approach could be beneficial, as the output of search pipelines typically enhances signal features across the output parameter space. The specific format with which the output data is better represented, however, remains a point of discussion.
Further applications of ML to post-process the output of a search [106,169,170] will be covered in Section 3.2.
3. Post-Processing Strategies
The main stage of a wide parameter-space search usually returns the loudest templates in terms of a specific detection statistic. A good portion of these templates are correlated, either because their corresponding time-frequency evolution tracks sweep over similar data or because of the presence of non-Gaussianities in the data, producing broad parameter-space artifacts [88,171,172]. The idea behind post-processing stages is to reduce the number of candidates into an affordable quantity to be followed up.
Complementarily, veto strategies can be applied in order to reduce further the number of candidates resulting from a search. A veto is a simple method to assess the consistency of a CW candidate with respect to a signal hypothesis. The outcome is usually a boolean answer; as opposed to a post-processing or follow-up stage, the primary objective is to quickly reject an inconsistent CW candidate at a low computing cost.
The following subsections summarize common post-processing strategies employed in contemporary CW searches. After a brief overview of coincidence and clustering steps, we review four families of vetoes. Other techniques employed in previous searches can be found in [137].
3.1. Coincidences
In a network of gravitational-wave detectors with a comparable level of sensitivity, a CW signal is expected to produce significant candidates in the analysis of every detector’s data. Imposing a coincidence criterion, that is, focusing on common parameter-space regions highlighted in every single dataset, reduces the false-alarm probability of the search, as noise fluctuations are less likely to be coincident across different detectors than CW signals [102]. This approach obeys a robustness versus sensitivity trade-off, as combining data from different detectors into a single analysis increases the sensitivity of a search without increasing the required number of templates to be evaluated, keeping the computing budget under control [93].
This approach has been widely employed in FrequencyHough and SkyHough searches. In both cases, a parameter-space distance, based on an Euclidean ansatz, is used to identify close-by candidates in each detector’s results. Other searches, such as Time-domain -statistic, PowerFlux, or Falcon, impose coincidence criteria based on the overlap of enhanced parameter-space regions across both datasets, rather than using a parameter-space distance.
In particular, as discussed in Section 2, Time-domain -statistic is the most prominent user of this strategy [102]. As opposed to other semicoherent searches, it does not combine coherent segments into a semicoherent statistic, but looks for coincident candidates across multiple segments (including different detectors), reducing the overall false-alarm probability of the search.
3.2. Parameter-Space Clustering
Another option is to group together nearby templates according to some notion of distance. This process, usually referred to as clustering in the data analysis literature, has been extensively employed by PowerFlux, Einstein@Home, FrequencyHough, and SkyHough, using different implementations, both in terms of clustering strategy and parameter-space distance [40,41,42,45,49,50,52]. Clustering is typically implemented using an unsupervised approach [130,173]: the parameter-space and the clustering algorithm itself act as prior information to construct meaningful groupings of the resulting template bank. Supervised ML approaches [106,169,170], aimed at identifying specific parameter-space structures, have also been proposed.
Unsupervised approaches try to unveil structure from a data set. Prior information is encoded both in terms of the distance used to compare nearby candidates and the linkage criteria. The resulting clusters are sieved through selection criteria which can take into account parameters like the maximum significance in the cluster or its number of elements. We focus our exposition on the choice of parameter-space distance; a complete description of the clustering algorithms themselves is given in the corresponding references.
Initial implementations, used by FrequencyHough and SkyHough [41,42,50] assumed a Euclidean parameter-space distance on the CW signal parameters
pairing candidates within a certain distance threshold to form the final clusters. The exact parameters and parameter-space resolutions are search-dependent.
A more informative approach, still based on a Euclidean ansatz, was proposed in [173]. In this case, clusters are classified according to topographic parameters by projecting detection statistics over planes, namely over the frequency-spindown plane and the ecliptic plane. Instead of using the basic CW parameters, distance was computed after projecting the sky position of the candidate onto the ecliptic plane, thus allowing a greater variance around the ecliptic, where sky localization tends to become more uncertain [80,107].
These distance measures are effective for local analyses, but quickly become unreliable whenever more involved parameter-space structures such as correlated parameters with periodic boundaries come into play, as is the case for signals from sources in binary systems [174]. A parameter-space distance for a generic, quasi-monochromatic CW signal was proposed in [130] using the instantaneous detector-frame frequency associated to a CW template . Concretely, the distance between two templates and can be defined as the average mismatch between their corresponding detector-frame frequency tracks throughout an observing run
This prescription is consistent with the -statistic’s parameter-space correlations and can be simplified into a discrete sum for a faster implementation [52,53,130].
Candidate post-processing, and clustering in particular, is also a suitable step in which machine learning strategies are able to deliver an improvement of sensitivity. As opposed to raw data, on which CW signals are typically a subdominant contribution, the structures produced by different features in the data on the parameter space of a search are suitable to be classified using a supervised approach, as long as a clear classification of the features at hand is available. To date, two approaches have been proposed.
The first one [106], framed within the Time-domain -statistic pipeline, uses a convolutional network to classify different representations of the main search’s output into three possible classes, namely, noisy bands containing Gaussian-like noise, narrow spectral artifacts, and CW signals. A similar (albeit more manual) approach was reported in [40].
The second approach is developed as an alternative to the clustering algorithm employed in Einstein@Home searches [169,170]. In this case, a neural network is trained to recognize signal-induced patterns on a certain projection of the parameter space in order to identify typical structures associated to CW signals. The training set is produced by manually identifying software-injected signals using an image editing tool.
3.3. Detector-Consistency Vetoes
The first family of vetoes tests the consistency of a CW candidate across the network of GW detectors. The basic implementation is formulated as follows: given a CW candidate with parameters p and N detectors, a detection statistic is computed using data from each detector alone and combining the datasets from all detectors at once . Then, a function of single-detector statistics is compared to the multi-detector statistics in order to decide whether the candidate behaves consistently with a CW signal or not. The decision boundary, usually expressed in terms of the difference , can be calibrated by means of a software-injection campaign. As discussed in [86,87,88,89], the and detection statistics are a Bayesian approach to this implementation of the detector-consistency veto. In their implementation [40,49,175], however, the information is processed during search-time, discarding inconsistent candidates at an earlier stage and potentially improving the detection of marginally significant signals.
An example of detector-consistency vetoes can be found in the SkyHough contribution to [41], where F was taken to be the expected multi-detector statistic computed from the single-detector statistics including the varying noise floors but ignoring the antenna pattern modulations. Another example is found in the Weave search [51], where F is simply the maximum detection statistic over all the involved detectors. A slight variation was employed in the BinarySkyHough analysis of early O3 data [52,53], where the detection statistic of one of the LIGO detectors was compared against the other one. This was motivated due to the asymmetric behaviour of said detectors during the third observing run, with H1 being more affected by noise disturbances than L1.
3.4. Vetoes
The second family of vetoes considers the behaviour of a putative CW signal within a particular dataset, namely, whether the detection statistic accumulates throughout the observing run in a way which is more consistent with an instrumental artefact than an astrophysical signal. This is the idea behind the veto, initially proposed in [176] for CBC signals and later implemented for CW signals in [177]. In this case, the dataset is partitioned into p segments over which a detection statistic is computed . These segment-wise statistics are then compared to the expected segment-wise statistics under the presence of a signal in Gaussian noise, usually characterized by a mean and standard deviation and , and combined into a chi-squared discriminant
Under the assumption of Gaussian noise, this discriminant follows a distribution with degrees of freedom; real-data applications, however, must calibrate this test using a suitable injection campaign [41]. In [52,53], extreme deviations of the segment-wise detection statistic were used to identify stretches of data in which the CW template showed a great degree of overlap with an instrumental feature; this approach is equivalent to using a discriminant in the limit of a very strong sample .
3.5. Vetoing Narrow Spectral Features
The third family of vetoes relies on detector characterization to identify frequency bands in which an instrumental feature is present. CW searches integrate long periods of time looking for quasi-monochromatic signals concentrated around a fraction of a Hertz. Quite often, those narrow bands are populated by narrow spectral features (lines) due to instrumental or environmental disturbances (defective power supplies, blinking LEDs, wind blowing, local fauna interacting with the detector...) which, under very general conditions, are able to mimic the effect produced by a CW signal in the detector, usually producing a large number of candidates in a search [171,178,179]. Catalogues listing narrow spectral features and their cause (if known) for the latest runs of the advanced detectors are publicly available [180,181,182,183,184,185,186]. These kinds of features are generally not a problem for CBC searches, as those signals sweep wide frequency bands in a relatively short time duration, although noise subtraction techniques are applied in severe cases [187,188].
A common approach, usually referred to as the (known) line veto (see, e.g., [41,42,45,52]), is to check whether the frequency evolution of a CW candidate overlaps with any frequency band containing such instrumental features, in which case the candidate is discarded. This requires a high degree of manual intervention, as line catalogues must be created and properly understood, and incurs the risk of removing a genuine signal candidate due to an unfortunate line crossing at a potentially insignificant period of the run.
The DM-off veto was proposed in [189] as a hypothesis-test version of the line veto: it compares the significance of a CW candidate, which includes Doppler modulations due to the Earth’s movement around the SSB, versus the significance obtained after analysing its surrounding frequency band using an unmodulated template bank (i.e., without Doppler Modulation, hence DM-off). This veto was applied with great success in [40]. As happens with the detector-consistency veto and the statistic [88], the DM-off veto can be refactored as a detection statistic in a Bayesian framework to construct a proper line-robust statistic: instead of testing against a single-detector artefact, the hypothetical statistic would test against an ensemble of monochromatic and unmodulated signals in any number of detectors [178].
Alternatively, as performed in [40,49,190], frequency bins in the data containing lines can be replaced by Gaussian noise drawn from the distribution of neighbouring bins to suppress the presence of candidates, preventing any candidate of instrumental origin from polluting the search results. This process is generally performed on SFT data before starting a search.
Short-duration loud instrumental glitches also present a problem to CW searches, as they tend to degrade the noise floor across a wide frequency band. This sort of artefact, however, is typically dealt with before starting a search using a cleaning procedure such as gating [139,179,191,192].
3.6. Null-Hypothesis Vetoes
The fourth family of vetoes are essentially a reformulation of the standard null-hypothesis test, in which a CW candidate is deemed as uninteresting if it is consistent enough with respect to the background noise distribution. A simple proposal, usually referred to as off-sourcing [64,193], is to evaluate a CW candidate on nearly independent noise realizations by shifting its sky position away. This is based on the fact that detector artefacts tend to imprint wider parameter-space regions with significant templates than CW signals. Off-sourced time-frequency tracks are able to break signal-induced correlations while still being affected by instrumental disturbances. The resulting distribution is a proxy of the noise hypothesis’s sampling distribution and can be used to construct significance arguments about the CW candidate of interest.
This veto was adapted by [51] to evaluate the final surviving candidate of a search. In their use case, however, they considered the distribution of the loudest candidate from a CW search, that is, considering the number of trials performed by evaluating a template bank on a data stream. Such a distribution has been previously studied in the CW literature [194,195], but it was not until recently that a method applicable to a generic CW search based on extreme value theory was proposed [172].
Steps towards a fully Bayesian treatment of loudest-candidate null-hypothesis vetoes were taken in [38], which proposed a Bayes factor to evaluate the loudest candidate of a CW search, , whose noise-hypothesis component was constructed fitting a Gumbel distribution to the loudest outliers of off-sourced template banks. This approach was used to develop a complete hierarchical follow-up framework, discussed in Section 4.2.
4. Follow-up
Follow-up stages are contextualized within a hierarchical search, as discussed in the introduction. They improve the parameter estimation of a CW candidate by imposing tighter constrains on its expected behaviour. This leads to the factual use of simple follow-up stages as signal-consistency veto strategies. Base search stages construct less sensitive detection statistics by effectually using less constraining CW signal models. For example, a semicoherent search, in which phase information is contained in discrete, non-overlapping segments, is insensitive to arbitrary phase jumps between coherence segments. In this sense, the sensitivity loss with respect to a fully coherent search is due to the increased trials factor of this looser family of signal models [43].
There are two ways in which follow-ups may be performed. Following the notation established in [33], we refer to them as fresh data mode (FDM) and recycling data mode (RDM). As their names suggest, FDM looks for a CW candidate in a new dataset containing brand new information; RDM, on the other hand, re-analyses the same dataset using a different method. The typical example of FDM is to look for a CW candidate obtained in a certain observing run using data from subsequent observing runs [40,54,62]. Examples of RMD include, for example, multi-stage semicoherent or loosely coherent searches aiming towards a fully coherent search in a restricted parameter space region [36,37,38,39].
Most CW searches are conducted focusing on a single dataset, usually the latest available observing run of the advanced detectors. Hence, follow-up strategies operate on RDM (even though sometimes FDM assumptions are used for simplicity, as they turn out more conservative and simpler to implement [195,196]). Nevertheless, this sort of strategy could be detrimental towards detecting a CW signal, as standard RDM operations leading to effectively longer coherence time may lose candidates affected by some form of unmodelled behaviour, such as glitches [197,198] or accretion-induced spin wandering [148]. Strict FDM must be used in order for a search to follow up a CW candidate with a consistent signal model. Looking into previous observing runs, on the other hand, runs into a sensitivity problem, as marginal candidates may end up completely lost due to the lower quality of the detectors. Examples of searches in which a FDM follow-up looked into a posterior observing run include [40,55].
4.1. Single-Stage Follow-up
The simplest follow-up strategy calibrates a threshold on a different (more sensitive) detection statistic according to some prescription and compares it to the score returned by reanalysing the CW candidate. As opposed to a veto, this approach points towards evaluating the consistency (or discrepancy) of the CW candidate with respect to a certain population of signals.
The standard FrequencyHough follow-up as employed in [41,45] belongs to this category: baseline Fourier transform length is increased, imposing tighter constraints on the signal model and discarding short-duration candidates. Later searches also make use of the BSD framework [140,141]. Similar strategies, in this case using the fully coherent -statistic, were proposed in [199,200].
In order to overcome the curse of dimensionality, BinarySkyHough searches [50,52,53] employ an MCMC-based follow-up implemented in PyFstat [37,38,201]. The multi-detector -statistic [21,70] is used to allow for arbitrarily long coherence times. In this sense, following up a CW candidate is equivalent to sampling the posterior probability distribution of the phase-evolution parameters given a data stream [37]
where the prior probability distribution represents the parameter-space region of interest identified by a search. The result of this grid-less approach is the -statistic evaluated at the loudest candidate of the parameter space at a negligible mismatch. This approach generalizes that of [199,200], which specializes in the single-stage fully-coherent follow-up of CW candidates.
As discussed in Section 4.2, the use of MCMC methods simplifies the setup of a generic multi-stage follow-up, as no calibration of parameter-space grids is required. The onus in this case is on the search pipeline to deliver a small-enough prior support for the MCMC to converge. This can always be achieved by starting from a shorter coherence time [37], at the expense of increasing the number of follow-up stages.
A similar strategy is used by the Time-domain -statistic follow-up, focusing on the optimization aspect of the procedure. In this case, a max-finding algorithm such as [202] is employed to travel around the parameter space. The result, as with PyFstat, are the most favoured signal parameters, corresponding to the ones reporting the loudest -statistic value.
4.2. Multi-Stage Follow-up
As discussed in Section 1, multi-stage follow-ups are the natural continuation to a wide parameter-space search after identifying interesting parameter-space regions. Given a data stream, each subsequent follow-up stage operates in RDM, gradually increasing the coherence time with respect to previous stages and, as a consequence, imposing a tighter version of the selected signal model. The effect on a CW candidate is twofold: first, non-astrophysical CW-like artefacts tend to get rejected as coherence time increases (though, as earlier discussed, this could have detrimental effects on more complex CW signals too); second, increasing coherence time results in a refinement in parameter-space resolution, improving the parameter estimation of the candidate at hand. This last effect must be considered carefully, as it also implies an increased number of templates to analyse, quickly becoming unaffordable if parameter-space regions are not gradually narrowed down.
We start by discussing the follow-up strategy introduced in [36], which was applied as a generic follow-up to multiple CW searches with minor modifications [40,41,42,49]. This example is paradigmatic in the sense that it fully exposes the two main challenges of a multi-stage setup. A similar approach, albeit at much smaller scale, was employed to follow-up SkyHough results in [45]. First, one must set up a proper set of parameter-space grids such that CW signals are not lost due to a bad parameter-space covering. If an analytical model of the follow-up method at hand is not available, as is the case in [36], one must resort to an extensive software injection campaign to construct a suitable setup. Second, a criterion must be set up to select/reject CW candidates after performing different stages. If the detection statistic’s behaviour across different stages is well understood (see, e.g., [196]), an analytical criterion can be derived from first principles; otherwise, a software injection campaign must be used to calibrate a rejection criterion.
Latest developments on the follow-up of CW candidates [37,38] are able to simplify the setup for the -statistic, although further work is required for its application to generic detection statistics. As discussed in Section 4.1, the use of MCMC samplers simplifies the setup due to their lack of grids: if a CW signal is within the prior support, parameter-space samplers can get arbitrarily close to the injection parameters given enough time to wander around the prior volume. This argument can be posed quantitatively in terms of the so-called coherence time ladder [37], which make use of the parameter-space metric to increase the parameter-space resolution in a controlled manner. Since the follow-up is typically a local analysis, rough estimates of the number of templates using typical parameter-space resolutions are usually a valid approximation [198].
Proper comparison of detection statistics from different stages in a Bayesian framework is currently restricted to the -statistic [196], as the sampling distribution under a signal hypothesis must be known given a (squared) signal-to-noise ratio . This result was used in [38] to propose , a (meta) Bayes factor (as the -statistic itself is a Bayes factor) evaluating the result of a multi-stage follow-up, pushing forward the development of a fully-Bayesian follow-up of CW candidates. In this case, the probability under the noise hypothesis was derived from a combination of off-sourcing and extreme value theory [172]. The use of detection statistics (Bayes factors) as data proxies to construct Bayesian arguments is also discussed in [195,203].
An alternative family of follow-up methods were developed under the name of loose coherence [39,113,114], already introduced in Section 2.2.1. In this case, instead of following the ad hoc recipe of increasing coherence time until a fully-coherent search is achieved, phase information across neighbouring time segments is gradually correlated in a controlled manner by combining (complex) Fourier amplitudes. As opposed to semicoherent methods, which allow for arbitrary phase jumps at the border of a segment, loosely coherent methods allow for phase shifts within pre-specified ranges, depending on the required robustness of the method. Under this framework, semicoherent methods are rediscovered imposing delta-correlation between phases at consecutive time segments. This follow-up approach is fully integrated within the PowerFlux and Falconsearches [41,42,43,44,46,47,55].
5. Upper Bounds on
Since no CW detection has been reported to date, the main data product of CW searches are bounds on the nominal gravitational-wave amplitude produced by a population of sources consistent with the target signal model. As discussed in Section 1, astrophysical information can be extracted from this quantity by taking different assumptions, such as the maximum allowed ellipticity from a galactic neutron star at a certain distance from the detector.
Two basic approaches are pursued at production level to derive said upper bounds, depending on whether the aim is for a strict frequentist upper limit or population-based sensitivity estimations. The calibration and establishment of upper bounds of any kind usually involves an extensive software injection campaign in real data with a non-negligible computing cost; for this reason, a common approach lies in between both extrema, quoting a proper estimation at a definite set of representative frequency bands and interpolating the results across the rest of the spectrum.
Population-based sensitivity estimations are based on estimating the false-dismissal probability of a search given a certain setup (be it a threshold at a fixed false-alarm probability or a more intricate procedure). The detection probability amplitude corresponds then to the amplitude associated to a false dismissal of after properly marginalizing with respect to other amplitude parameters using a set of priors reflecting the studied source distribution [194]. In practise [40,41,42,45,49,50,52], detection probabilities are usually estimated numerically by means of an injection recovery campaign.
Strict frequentist upper limits, on the other hand, return a conservative estimate of the upper bound, in the sense that false-dismissal probability is at most . An example of this kind is the universal statistic procedure [204], which is able to construct strict frequentist upper limits regardless of the underlying noise distribution. This procedure has been extensively combined with the PowerFlux and Falcon pipelines to efficiently produce robust upper limits under different GW polarization assumptions [41,42,43,44,46,47,55].
To date, all wide parameter-space searches have made use of one of these two upper bounds to report on their results. These upper bounds, however, describe the probability of detecting a signal given an ensemble of equivalent noise realizations, rather than the range where a signal could be found given the data stream at hand. Work towards reporting the latter, Bayesian upper bounds, for wide parameter-space searches was developed in [195,203].
6. Summary
We reviewed the methods employed by current wide parameter-space searches for continuous gravitational waves from unknown sources conducted on advanced-detector data. The most widespread approach consists of a hierarchical setup in which parameter-space regions are analysed using more sensitive (and consequently more expensive) methods as they are gradually narrowed down. Detecting a CW signal requires both an instrumental and computational effort to confidently unveil such a weak signal using the current generation of gravitational-wave detectors. The use of multiple methods taking different trade-offs in sensitivity and robustness against instrumental artefacts provides an ideal environment to pursue new strategies towards CW detection and parameter estimation. For the sake of completeness, Table 2 provides a comprehensive summary of the search methods reviewed in the present work.

Table 2.
Summary of CW search methods covered by the present review, grouped by scope and observing run.
Funding
This work was supported by European Union FEDER funds, the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, and the Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación grants PID2019-106416GB-I00/AEI/MCIN/10.13039/501100011033, RED2018-102661-T, RED2018-102573-E, Comunitat Autònoma de les Illes Balears through the Conselleria de Fons Europeus, Universitat i Cultura and the Direcció General de Política Universitaria i Recerca with funds from the Tourist Stay Tax Law ITS 2017-006 (PRD2018/24, PRD2020/11), Generalitat Valenciana (PROMETEO/2019/071), EU COST Actions CA18108, CA17137, CA16214, and CA16104. R.T. is supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Universidades (ref. FPU 18/00694). D.K. is supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (ref. BEAGAL 18/00148) and cofinanced by the Universitat de les Illes Balears.
Acknowledgments
We thank Karl Wette, Keith Riles, Ornella J. Piccinni, and the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Continuous Wave working group for useful suggestions. This paper has been assigned document number LIGO-P2100408.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lasky, P.D. Gravitational Waves from Neutron Stars: A Review. Publ. Astron. Soc. Austral. 2015, 32, e034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glampedakis, K.; Gualtieri, L. Gravitational waves from single neutron stars: An advanced detector era survey. Astrophys. Space Sci. Libr. 2018, 457, 673–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieniawska, M.; Bejger, M. Continuous gravitational waves from neutron stars: Current status and prospects. Universe 2019, 5, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, B.; Schwenzer, K. Gravitational waves from isolated neutron stars. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03137. [Google Scholar]
- Essig, R. Working Group Report: New Light Weakly Coupled Particles. In Proceedings of the Community Summer Study 2013: Snowmass on the Mississippi, CSS2013, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 29 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R.; Ghosh, S.; Barausse, E.; Berti, E.; Cardoso, V.; Dvorkin, I.; Klein, A.; Pani, P. Gravitational wave searches for ultralight bosons with LIGO and LISA. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 064050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.; Ghosh, S.; Barausse, E.; Berti, E.; Cardoso, V.; Dvorkin, I.; Klein, A.; Pani, P. Stochastic and resolvable gravitational waves from ultralight bosons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 131101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.J.; Baryakhtar, M.; Papa, M.A.; Tsuna, D.; Kawanaka, N.; Eggenstein, H.B. Characterizing the continuous gravitational-wave signal from boson clouds around Galactic isolated black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 063020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.J.; Papa, M.A.; Reddy, S. Gravitational waves from compact dark matter objects in the solar system. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 800, 135072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isi, M.; Weinstein, A.J.; Mead, C.; Pitkin, M. Detecting Beyond-Einstein Polarizations of Continuous Gravitational Waves. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 082002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isi, M.; Pitkin, M.; Weinstein, A.J. Probing Dynamical Gravity with the Polarization of Continuous Gravitational Waves. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isi, M.; Sun, L.; Brito, R.; Melatos, A. Directed searches for gravitational waves from ultralight bosons. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 084042, Erratum in 2020, 102, 049901.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Gao, Y.; Shao, L. Precession of spheroids under Lorentz violation and observational consequences for neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 084028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Gao, Y.; Shao, L. Signatures of Lorentz Violation in Continuous Gravitational-Wave Spectra of Ellipsoidal Neutron Stars. Galaxies 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, C.; D’Antonio, S.; Astone, P.; Frasca, S.; Intini, G.; La Rosa, I.; Leaci, P.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Miller, A.L.; Muciaccia, F.; et al. Direct constraints on ultra-light boson mass from searches for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Brito, R.; Isi, M. Search for ultralight bosons in Cygnus X-1 with Advanced LIGO. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 063020, Erratum in 2020, 102, 089902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Clesse, S.; De Lillo, F.; Bruno, G.; Depasse, A.; Tanasijczuk, A. Probing planetary-mass primordial black holes with continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Dark Univ. 2021, 32, 100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Aggarwal, N.; Clesse, S.; De Lillo, F. Constraints on planetary and asteroid-mass primordial black holes from continuous gravitational-wave searches. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.06188. [Google Scholar]
- Prix, R. Gravitational Waves from Spinning Neutron Stars. In Neutron Stars and Pulsars; Becker, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 357, Chapter 24; pp. 651–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riles, K. Recent searches for continuous gravitational waves. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 32, 1730035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaranowski, P.; Krolak, A.; Schutz, B.F. Data analysis of gravitational-wave signals from spinning neutron stars. 1. The Signal and its detection. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasi, J.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.; Abernathy, M.R.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Advanced LIGO. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 074001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acernese, F.; Agathos, M.; Agatsuma, K.; Aisa, D.; Allemandou, N.; Allocca, A.; Amarni, J.; Astone, P.; Balestri, G.; Ballardin, G.; et al. Advanced Virgo: A second-generation interferometric gravitational wave detector. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, T.; Ando, M.; Arai, K.; Arai, Y.; Araki, S.; Araya, A.; Aritomi, N.; Asada, H.; Aso, Y.; Atsuta, S. KAGRA: 2.5 Generation Interferometric Gravitational Wave Detector. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, M.; Van Den Broeck, C.; Bartolo, N.; Belgacem, E.; Bertacca, D.; Bizouard, M.A.; Branchesi, M.; Clesse, S.; Foffa, S.; García-Bellido, J.; et al. Science Case for the Einstein Telescope. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 2000, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitze, D.; Adhikari, R.X.; Ballmer, S.; Barish, B.; Barsotti, L.; Billingsley, G.; Brown, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Coyne, D.; Eisenstein, R.; et al. Cosmic Explorer: The U.S. Contribution to Gravitational-Wave Astronomy beyond LIGO. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2019, 51, 035. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agathos, M.; et al. A guide to LIGO–Virgo detector noise and extraction of transient gravitational-wave signals. Class. Quant. Grav. 2020, 37, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, P.R.; Creighton, T.; Cutler, C.; Schutz, B.F. Searching for periodic sources with LIGO. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 57, 2101–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R. Template-based searches for gravitational waves: Efficient lattice covering of flat parameter spaces. Class. Quant. Grav. 2007, 24, S481–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K. Lattice template placement for coherent all-sky searches for gravitational-wave pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 122010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairhurst, S. Source localization with an advanced gravitational wave detector network. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, P.R.; Creighton, T. Searching for periodic sources with LIGO II: Hierarchical searches. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, C.; Gholami, I.; Krishnan, B. Improved stack-slide searches for gravitational-wave pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R.; Shaltev, M. Search for Continuous Gravitational Waves: Optimal StackSlide method at fixed computing cost. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltev, M. Optimizing the StackSlide setup and data selection for continuous-gravitational-wave searches in realistic detector data. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 044058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, M.A.; Eggenstein, H.B.; Walsh, S.; Di Palma, I.; Allen, B.; Astone, P.; Bock, O.; Creighton, T.D.; Keitel, D.; Machenschalk, B.; et al. Hierarchical follow-up of subthreshold candidates of an all-sky Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves on LIGO sixth science run data. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.; Prix, R. Hierarchical multistage MCMC follow-up of continuous gravitational wave candidates. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 103020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, R.; Keitel, D.; Sintes, A.M. Application of a hierarchical MCMC follow-up to Advanced LIGO continuous gravitational-wave candidates. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 084012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V. On blind searches for noise dominated signals: A loosely coherent approach. Class. Quant. Grav. 2010, 27, 205017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. First low-frequency Einstein@Home all-sky search for continuous gravitational waves in Advanced LIGO data. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. All-sky Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the O1 LIGO Data. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 062002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Full Band All-sky Search for Periodic Gravitational Waves in the O1 LIGO Data. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V.; Papa, M.A. Sensitivity improvements in the search for periodic gravitational waves using O1 LIGO data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V.; Papa, M.A. Results from an Extended Falcon All-Sky Survey for Continuous Gravitational Waves. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. All-sky search for continuous gravitational waves from isolated neutron stars using Advanced LIGO O2 data. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V.; Papa, M.A. Results from the First All-Sky Search for Continuous Gravitational Waves from Small-Ellipticity Sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dergachev, V.; Papa, M.A. Results from high-frequency all-sky search for continuous gravitational waves from small-ellipticity sources. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 063019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V.; Papa, M.A. Search for continuous gravitational waves from small-ellipticity sources at low frequencies. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 043003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steltner, B.; Papa, M.A.; Eggenstein, H.B.; Allen, B.; Dergachev, V.; Prix, R.; Machenschalk, B.; Walsh, S.; Zhu, S.J.; Kwang, S. Einstein@Home All-sky Search for Continuous Gravitational Waves in LIGO O2 Public Data. Astrophys. J. 2021, 909, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covas, P.B.; Sintes, A.M. First all-sky search for continuous gravitational-wave signals from unknown neutron stars in binary systems using Advanced LIGO data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 191102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wette, K.; Dunn, L.; Clearwater, P.; Melatos, A. Deep exploration for continuous gravitational waves at 171–172 Hz in LIGO second observing run data. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 083020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, A.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. All-sky search in early O3 LIGO data for continuous gravitational-wave signals from unknown neutron stars in binary systems. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 064017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, R. An all-sky search in early O3 LIGO data for continuous gravitational-wave signals from unknown neutron stars in binary systems. In Proceedings of the 55th Rencontres de Moriond on Gravitation, online, 9–11 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, A.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. All-sky search for continuous gravitational waves from isolated neutron stars in the early O3 LIGO data. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 082004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V.; Papa, M.A.; Steltner, B.; Eggenstein, H.B. Loosely coherent search in LIGO O1 data for continuous gravitational waves from Terzan 5 and the galactic center. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 084048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinni, O.J.; Astone, P.; D’Antonio, S.; Frasca, S.; Intini, G.; La Rosa, I.; Leaci, P.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Miller, A.; Palomba, C. Directed search for continuous gravitational-wave signals from the Galactic Center in the Advanced LIGO second observing run. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 082004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Search for gravitational waves from Scorpius X-1 in the first Advanced LIGO observing run with a hidden Markov model. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Upper Limits on Gravitational Waves from Scorpius X-1 from a Model-Based Cross-Correlation Search in Advanced LIGO Data. Astrophys. J. 2017, 847, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C. Searches for Continuous Gravitational Waves from 15 Supernova Remnants and Fomalhaut b with Advanced LIGO. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 122, Erratum in 2021, 918, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. Search for gravitational waves from Scorpius X-1 in the second Advanced LIGO observing run with an improved hidden Markov model. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 122002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Papa, M.A.; Singh, A.; Eggenstein, H.-B.; Zhu, S.J.; Dergachev, V.; Hu, Y.; Prix, R.; Machenschalk, B.; Beer, C.; et al. Results from an Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves from Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr. and G347.3. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 024063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, M.A.; Ming, J.; Gotthelf, E.V.; Allen, B.; Prix, R.; Dergachev, V.; Eggenstein, H.B.; Singh, A.; Zhu, S.J. Search for Continuous Gravitational Waves from the Central Compact Objects in Supernova Remnants Cassiopeia A, Vela Jr., and G347.3–0.5. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millhouse, M.; Strang, L.; Melatos, A. Search for gravitational waves from 12 young supernova remnants with a hidden Markov model in Advanced LIGO’s second observing run. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 083025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, H.; Clearwater, P.; Melatos, A.; Dunn, L. Search for gravitational waves from five low mass X-ray binaries in the second Advanced LIGO observing run with an improved hidden Markov model. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 023006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Sun, L. Search for continuous gravitational waves from Fomalhaut b in the second Advanced LIGO observing run with a hidden Markov model. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 023020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, L.; Owen, B.J. Directed searches for continuous gravitational waves from twelve supernova remnants in data from Advanced LIGO’s second observing run. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 083023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Papa, M.A.; Krishnan, B.; Watts, A.L. Search for Continuous Gravitational Waves from Scorpius X-1 in LIGO O2 Data. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 906, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, A.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. Searches for continuous gravitational waves from young supernova remnants in the early third observing run of Advanced LIGO and Virgo. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Papa, M.A.; Eggenstein, H.B.; Machenschalk, B.; Steltner, B.; Prix, R.; Allen, B.; Behnke, O. Results from an Einstein@Home search for continuous gravitational waves from G347.3 at low frequencies in LIGO O2 data. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.02808. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, C.; Schutz, B.F. The Generalized F-statistic: Multiple detectors and multiple GW pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 063006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R.; Krishnan, B. Targeted search for continuous gravitational waves: Bayesian versus maximum-likelihood statistics. Class. Quant. Grav. 2009, 26, 204013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.T.; Prix, R.; Cutler, C.J.; Willis, J.L. New Coordinates for the Amplitude Parameter Space of Continuous Gravitational Waves. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R.; Giampanis, S.; Messenger, C. Search method for long-duration gravitational-wave transients from neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurandhar, S.; Krishnan, B.; Willis, J.L. Marginalizing the likelihood function for modeled gravitational wave searches. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.08163. [Google Scholar]
- Bero, J.J.; Whelan, J.T. An Analytic Approximation to the Bayesian Detection Statistic for Continuous Gravitational Waves. Class. Quant. Grav. 2019, 36, 015013, Erratum in 2019, 36, 049601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K. Geometric Approach to Analytic Marginalisation of the Likelihood Ratio for Continuous Gravitational Wave Searches. Universe 2021, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R.; Whelan, J.T. F-statistic search for white-dwarf binaries in the first Mock LISA Data Challenge. Class. Quant. Grav. 2007, 24, S565–S574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppel, D. The multi-detector F-statistic metric for short-duration non-precessing inspiral gravitational-wave signals. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.B. A Study of Recycled Pulsars in Globular Clusters. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R.; Itoh, Y. Global parameter-space correlations of coherent searches for continuous gravitational waves. Class. Quant. Grav. 2005, 22, S1003–S1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletsch, H.J. Parameter-space correlations of the optimal statistic for continuous gravitational-wave detection. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletsch, H.J.; Allen, B. Exploiting global correlations to detect continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 181102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletsch, H.J. Parameter-space metric of semicoherent searches for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.; Wette, K.; Papa, M.A.; Prix, R. Optimizing the choice of analysis method for all-sky searches for continuous gravitational waves with Einstein@Home. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 082004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.P. BOINC: A Platform for Volunteer Computing. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.01699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D.; Prix, R.; Papa, M.A.; Leaci, P.; Siddiqi, M. Search for continuous gravitational waves: Improving robustness versus instrumental artifacts. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 064023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D.; Prix, R. Line-robust statistics for continuous gravitational waves: Safety in the case of unequal detector sensitivities. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D. Robust semicoherent searches for continuous gravitational waves with noise and signal models including hours to days long transients. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 084024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D. Distinguishing transient signals and instrumental disturbances in semi-coherent searches for continuous gravitational waves with line-robust statistics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 716, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K. Parameter-space metric for all-sky semicoherent searches for gravitational-wave pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 082003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Krishnan, B.; Papa, M.A.; Aulbert, C.; Fehrmann, H. Optimal directed searches for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 064011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, B.J. Search templates for gravitational waves from inspiraling binaries: Choice of template spacing. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, 6749–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R. Search for continuous gravitational waves: Metric of the multi-detector F-statistic. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 023004, Erratum in 2007, 75, 069901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B. Optimal template banks. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 042005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K.; Prix, R. Flat parameter-space metric for all-sky searches for gravitational-wave pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K. Empirically extending the range of validity of parameter-space metrics for all-sky searches for gravitational-wave pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 122002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K.; Walsh, S.; Prix, R.; Papa, M.A. Implementing a semicoherent search for continuous gravitational waves using optimally-constructed template banks. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 123016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B. Spherical ansatz for parameter-space metrics. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Shoom, A.A. Template banks based on Zn and An* lattices. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.11631. [Google Scholar]
- Prix, R. The F-Statistic and Its Implementation in ComputeFstatistic_v2. 2006. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T0900149/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- LIGO Scientific Collaboration. LIGO Algorithm Library—LALSuite; Free Software (GPL), 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasi, J.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.; Abernathy, M.R.; Accadia, T.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; et al. Implementation of an F-statistic all-sky search for continuous gravitational waves in Virgo VSR1 data. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 165014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarski, A.; Jaranowski, P. Banks of templates for all-sky narrow-band searches of gravitational waves from spinning neutron stars. Class. Quant. Grav. 2015, 32, 145014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poghosyan, G.; Matta, S.; Streit, A.; Bejger, M.; Królak, A. Architecture, implementation and parallelization of the software to search for periodic gravitational wave signals. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2015, 188, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieniawska, M.; Bejger, M.; Krolak, A. Follow-up procedure for gravitational wave searches from isolated neutron stars using the time-domain F-statistic method. Class. Quant. Grav. 2019, 36, 225008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, F.; Bejger, M.; Ciecielag, P. Convolutional neural network classifier for the output of the time-domain F-statistic all-sky search for continuous gravitational waves. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 025016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, B.; Sintes, A.M.; Papa, M.A.; Schutz, B.F.; Frasca, S.; Palomba, C. The Hough transform search for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Papa, M.A.; Schutz, B.F. Optimal strategies for sinusoidal signal detection. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V. Description of PowerFlux Algorithms and Implementation. 2006. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T050186/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Dergachev, V. Description of PowerFlux 2 Algorithms and Implementation. 2011. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T1000272/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Dergachev, V.; Riles, K. PowerFlux Polarization Analysis. 2006. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T050187/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Mendell, G.; Wette, K. Using generalized PowerFlux methods to estimate the parameters of periodic gravitational waves. Class. Quant. Grav. 2008, 25, 114044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dergachev, V. Loosely coherent searches for sets of well-modeled signals. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 062003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V. Loosely coherent searches for medium scale coherence lengths. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.02351. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Papa, M.A.; Dergachev, V. Characterizing the sensitivity of isolated continuous gravitational wave searches to binary orbits. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 024058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurandhar, S.; Krishnan, B.; Mukhopadhyay, H.; Whelan, J.T. Cross-correlation search for periodic gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.T.; Sundaresan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Peiris, P. Model-Based Cross-Correlation Search for Gravitational Waves from Scorpius X-1. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.J.; Whelan, J.T.; Wofford, J.K.; Wette, K. Template Lattices for a Cross-Correlation Search for Gravitational Waves from Scorpius X-1. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.16142. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Dhurandhar, S.; Souradeep, T.; Lazzarini, A.; Mandic, V.; Bose, S.; Ballmer, S. Gravitational wave radiometry: Mapping a stochastic gravitational wave background. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, A.; Dalvi, P.; Mitra, S. Fast Gravitational Wave Radiometry using Data Folding. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, A.; Suresh, J.; Mitra, S. Very fast stochastic gravitational wave background map making using folded data. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Directional Limits on Persistent Gravitational Waves from Advanced LIGO’s First Observing Run. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 121102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abraham, S.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; et al. Directional limits on persistent gravitational waves using data from Advanced LIGO’s first two observing runs. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. All-sky, all-frequency directional search for persistent gravitational-waves from Advanced LIGO’s and Advanced Virgo’s first three observing runs. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.09834. [Google Scholar]
- Meadors, G.D.; Krishnan, B.; Papa, M.A.; Whelan, J.T.; Zhang, Y. Resampling to accelerate cross-correlation searches for continuous gravitational waves from binary systems. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 044017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, C.; Astone, P.; Frasca, S. Adaptive Hough transform for the search of periodic sources. Class. Quant. Grav. 2005, 22, S1255–S1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, B.; Sintes, A.M. Hough Search with Improved Sensitivity. 2007. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T070124-x0/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Hough, P.V. Method and Means for Recognizing Complex Patterns. U.S. Patent US3069654A, 18 December 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Sintes, A.M.; Krishnan, B. Improved hough search for gravitational wave pulsars. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 32, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, R.; Keitel, D.; Sintes, A.M. Time-frequency track distance for comparing continuous gravitational wave signals. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 064053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho de la Jordana, L. Hierarchical Hough all-sky search for periodic gravitational waves in LIGO S5 data. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 228, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covas, P.B. Searching for Continuous Gravitational Waves with Advanced LIGO. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de les Illes Balears, Palma, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Covas, P.B.; Sintes, A.M. New method to search for continuous gravitational waves from unknown neutron stars in binary systems. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.; Keitel, D.; Sintes, A.M. Adaptive transient Hough method for long-duration gravitational wave transients. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 104067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Astone, P.; D’Antonio, S.; Frasca, S.; Palomba, C. Detection of periodic gravitational wave sources by Hough transform in the f versus f(.) plane. Class. Quant. Grav. 2008, 25, 184015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astone, P.; Colla, A.; D’Antonio, S.; Frasca, S.; Palomba, C. Method for all-sky searches of continuous gravitational wave signals using the frequency-Hough transform. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaci, P. Methods to filter out spurious disturbances in continuous-wave searches from gravitational-wave detectors. Phys. Scr. 2015, 2015. 90, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intini, G.; Leaci, P.; Astone, P.; Antonio, S.D.; Frasca, S.; Rosa, I.L.; Miller, A.; Palomba, C.; Piccinni, O. A Doppler-modulation based veto to discard false continuous gravitational-wave candidates. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 225007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astone, P.; Frasca, S.; Palomba, C. The short FFT database and the peak map for the hierarchical search of periodic sources. Class. Quant. Grav. 2005, 22, S1197–S1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinni, O.J.; Astone, P.; D’Antonio, S.; Frasca, S.; Intini, G.; Leaci, P.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Miller, A.; Palomba, C.; Singhal, A. A new data analysis framework for the search of continuous gravitational wave signals. Class. Quant. Grav. 2019, 36, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinni, O.J.; Frasca, S. The Band-Sampled-Data collection for the search of continuous gravitational wave signals. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Astone, P.; D’Antonio, S.; Frasca, S.; Intini, G.; La Rosa, I.; Leaci, P.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Muciaccia, F.; Palomba, C.; et al. Method to search for long duration gravitational wave transients from isolated neutron stars using the generalized frequency-Hough transform. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Search for gravitational waves from a long-lived remnant of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, S.; Palomba, C.; Astone, P.; Frasca, S.; Intini, G.; La Rosa, I.; Leaci, P.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Miller, A.; Muciaccia, F.; et al. Semicoherent analysis method to search for continuous gravitational waves emitted by ultralight boson clouds around spinning black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 103017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Astone, P.; Bruno, G.; Clesse, S.; D’Antonio, S.; Depasse, A.; De Lillo, F.; Frasca, S.; La Rosa, I.; Leaci, P.; et al. Probing new light gauge bosons with gravitational-wave interferometers using an adapted semicoherent method. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. Constraints on dark photon dark matter using data from LIGO’s and Virgo’s third observing run. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.13085. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, G.; Jones, D.I.; Prix, R. Effect of timing noise on targeted and narrow-band coherent searches for continuous gravitational waves from pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 062009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Messenger, C.; Riles, K. Accretion-induced spin-wandering effects on the neutron star in Scorpius X-1: Implications for continuous gravitational wave searches. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 043016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, S.; Sun, L.; Melatos, A.; Moran, W.; Evans, R.J. Hidden Markov model tracking of continuous gravitational waves from a neutron star with wandering spin. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, S.; Clearwater, P.; Melatos, A.; Sun, L.; Moran, W.; Evans, R.J. Hidden Markov model tracking of continuous gravitational waves from a binary neutron star with wandering spin. II. Binary orbital phase tracking. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Melatos, A.; Suvorova, S.; Moran, W.; Evans, R.J. Hidden Markov model tracking of continuous gravitational waves from young supernova remnants. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 043013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Melatos, A.; Lasky, P.D. Tracking continuous gravitational waves from a neutron star at once and twice the spin frequency with a hidden Markov model. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melatos, A.; Clearwater, P.; Suvorova, S.; Sun, L.; Moran, W.; Evans, R.J. Hidden Markov model tracking of continuous gravitational waves from a binary neutron star with wandering spin. III. Rotational phase tracking. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, J.; Messenger, C.; Woan, G. Generalized application of the Viterbi algorithm to searches for continuous gravitational-wave signals. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 023006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaynes, E.T. Probability Theory: The Logic of Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniwal, D.; Clearwater, P.; Dunn, L.; Melatos, A.; Ottaway, D. Search for continuous gravitational waves from ten H.E.S.S. sources using a hidden Markov model. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. Search for continuous gravitational waves from 20 accreting millisecond X-ray pulsars in O3 LIGO data. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.09255. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Melatos, A. Application of hidden Markov model tracking to the search for long-duration transient gravitational waves from the remnant of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viterbi, A. Error bounds for convolutional codes and an asymptotically optimum decoding algorithm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut, L.; Messenger, C.; Melatos, A.; Owen, B.J. Implementation of the frequency-modulated sideband search method for gravitational waves from low mass X-ray binaries. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretthorst, G.L. Bayesian Spectrum Analysis and Parameter Estimation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cuoco, E.; Powell, J.; Cavaglià, M.; Ackley, K.; Bejger, M.; Chatterjee, C.; Coughlin, M.; Coughlin, S.; Easter, P.; Essick, R.; et al. Enhancing Gravitational-Wave Science with Machine Learning. Mach. Learn. Sci. Tech. 2021, 2, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreissigacker, C.; Sharma, R.; Messenger, C.; Zhao, R.; Prix, R. Deep-Learning Continuous Gravitational Waves. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 044009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreissigacker, C.; Prix, R. Deep-Learning Continuous Gravitational Waves: Multiple detectors and realistic noise. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, N.; Lasky, P.D. The evolution of binary neutron star post-merger remnants: A review. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2021, 53, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Astone, P.; D’Antonio, S.; Frasca, S.; Intini, G.; La Rosa, I.; Leaci, P.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Muciaccia, F.; Mitidis, A.; et al. How effective is machine learning to detect long transient gravitational waves from neutron stars in a real search? Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 062005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.S.; Tanaka, T. Use of an excess power method and a convolutional neural network in an all-sky search for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 084049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, J.; Messenger, C.; Woan, G. Robust machine learning algorithm to search for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 083024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtipour, B.; Papa, M.A. Deep learning for clustering of continuous gravitational wave candidates. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 064009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtipour, B.; Papa, M.A. Deep learning for clustering of continuous gravitational wave candidates II: Identification of low-SNR candidates. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 064027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covas, P.B.; Effler, A.; Goetz, E.; Meyers, P.M.; Neunzert, A.; Oliver, M.; Pearlstone, B.L.; Roma, V.J.; Schofield, R.M.S.; Adya, V.B.; et al. Identification and mitigation of narrow spectral artifacts that degrade searches for persistent gravitational waves in the first two observing runs of Advanced LIGO. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 082002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, R.; Modafferi, L.M.; Keitel, D.; Sintes, A.M. Empirically estimating the distribution of the loudest candidate from a gravitational-wave search. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.12032. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Papa, M.A.; Eggenstein, H.B.; Walsh, S. Adaptive clustering procedure for continuous gravitational wave searches. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 082003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaci, P.; Prix, R. Directed searches for continuous gravitational waves from binary systems: Parameter-space metrics and optimal Scorpius X-1 sensitivity. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Results of the deepest all-sky survey for continuous gravitational waves on LIGO S6 data running on the Einstein@Home volunteer distributed computing project. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B. χ2 time-frequency discriminator for gravitational wave detection. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho de la Jordana, L.; Sintes, A.M. A χ2 veto for continuous gravitational wave searches. Class. Quant. Grav. 2008, 25, 184014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D. Improving Robustness of Continuous-Gravitational-Wave Searches against Signal-Like Instrumental Artefacts and a Concept for an Octahedral Gravitational-Wave Detector in Space. Ph.D. Thesis, Leibniz University Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Areeda, J.S.; Berger, B.K.; Bruntz, R.; Effler, A.; Essick, R.C.; Fisher, R.P.; Godwin, P.; Goetz, E.; Helmling-Cornell, A.F.; et al. LIGO detector characterization in the second and third observing runs. Class. Quant. Grav. 2021, 38, 135014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GWOSC-O1 Instrumental Lines. 2021. Available online: https://www.gw-openscience.org/o1speclines/ (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- GWOSC-O2 Instrumental Lines. 2021. Available online: https://www.gw-openscience.org/o2speclines/ (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- GWOSC-O3a Instrumental Lines. 2021. Available online: https://www.gw-openscience.org/O3/o3aspeclines/ (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Goetz, E.; Neunzert, A.; Riles, K.; Mateas, A.; Kandhasamy, S.; Tasson, J.; Barschaw, C.; Middleton, H.; Hughey, S.; Mueller, L.; et al. O3a Lines and Combs in C00 Data. 2020. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/T2000719/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Goetz, E.; Neunzert, A.; Riles, K.; Mateas, A.; Kandhasamy, S.; Tasson, J.; Barschaw, C.; Middleton, H.; Hughey, S.; Mueller, L.; et al. Unidentified O3a Lines and Combs in C00 Data. 2020. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/T2000720/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Goetz, E.; Neunzert, A.; Riles, K.; Mateas, A.; Kandhasamy, S.; Tasson, J.; Barschaw, C.; Middleton, H.; Hughey, S.; Mueller, L.; et al. O3 Lines and Combs Found in Self-Gated C01 Data. 2021. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T2100153/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Goetz, E.; Neunzert, A.; Riles, K.; Mateas, A.; Kandhasamy, S.; Tasson, J.; Barschaw, C.; Middleton, H.; Hughey, S.; Mueller, L.; et al. Unidentified O3 Lines and Combs Found in Self-Gated C01 Data. 2021. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/T2100154/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Driggers, J.C.; Vitale, S.; Lundgren, A.P.; Evans, M.; Kawabe, K.; Dwyer, S.E.; Izumi, K.; Schofield, R.M.S.; Effler, A.; Sigg, D.; et al. Improving astrophysical parameter estimation via offline noise subtraction for Advanced LIGO. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Massinger, T.J.; Lundgren, A.P.; Driggers, J.C.; Urban, A.L.; Nuttall, L.K. Improving the Sensitivity of Advanced LIGO Using Noise Subtraction. Class. Quant. Grav. 2019, 36, 055011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.J.; Papa, M.A.; Walsh, S. New veto for continuous gravitational wave searches. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 124007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D.; Woan, G.; Pitkin, M.; Schumacher, C.; Pearlstone, B.; Riles, K.; Lyne, A.G.; Palfreyman, J.; Stappers, B.; Weltevrede, P. First search for long-duration transient gravitational waves after glitches in the Vela and Crab pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 064058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweizig, J.; Riles, K. Information on Self-Gating of h(t) Used in O3 Continuous-Wave and Stochastic Searches. 2021. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T2000384/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Steltner, B.; Papa, M.A.; Eggenstein, H.B. Identification and removal of non-Gaussian noise transients for gravitational wave searches. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.09933. [Google Scholar]
- Isi, M.; Mastrogiovanni, S.; Pitkin, M.; Piccinni, O.J. Establishing the significance of continuous gravitational-wave detections from known pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 123027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wette, K. Estimating the sensitivity of wide-parameter-space searches for gravitational-wave pulsars. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreissigacker, C.; Prix, R.; Wette, K. Fast and Accurate Sensitivity Estimation for Continuous-Gravitational-Wave Searches. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 084058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prix, R. Coherent F-Statistic on Semi-Coherent Candidate. 2019. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T1700236/public (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Ashton, G.; Prix, R.; Jones, D.I. Statistical characterization of pulsar glitches and their potential impact on searches for continuous gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 063004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.; Prix, R.; Jones, D.I. A semicoherent glitch-robust continuous-gravitational-wave search method. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 063011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltev, M.; Prix, R. Fully coherent follow-up of continuous gravitational-wave candidates. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 084057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltev, M.; Leaci, P.; Papa, M.A.; Prix, R. Fully coherent follow-up of continuous gravitational-wave candidates: An application to Einstein@Home results. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 124030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keitel, D.; Tenorio, R.; Ashton, G.; Prix, R. PyFstat: A Python package for continuous gravitational-wave data analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A Simplex Method for Function Minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rover, C.; Messenger, C.; Prix, R. Bayesian versus frequentist upper limits. In PHYSTAT 2011; CERN: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergachev, V. Novel universal statistic for computing upper limits in an ill-behaved background. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).