Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Astrophysical Relativistic Jets
Abstract
| Contents | ||
| 1. Introduction......................................................................................................................................................................... | 2 | |
| 1.1. Astrophysical Jets...................................................................................................................................................... | 2 | |
| 1.2. The TRISTAN Code................................................................................................................................................... | 2 | |
| 1.3. Particle-in-Cell Approach and Plasma Instabilities............................................................................................... | 3 | |
| 2. Microscopic and Macroscopic Processes in Plasma Jets................................................................................................ | 5 | |
| 3. PIC Simulations................................................................................................................................................................... | 6 | |
| 3.1. Unmagnetized Jets..................................................................................................................................................... | 6 | |
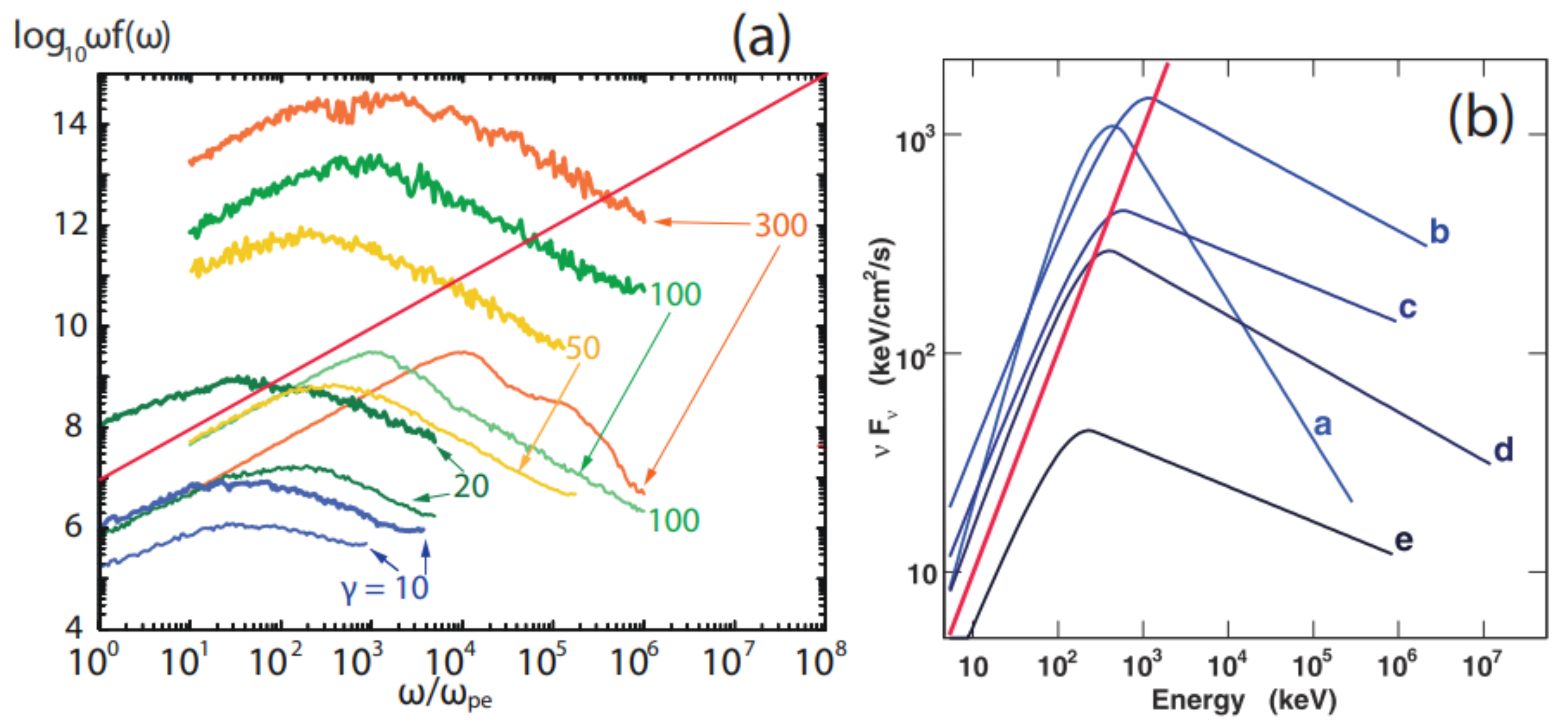
| 3.1.1. Self-Consistent Synthetic Spectra from Shocks........................................................................................... | 6 | |
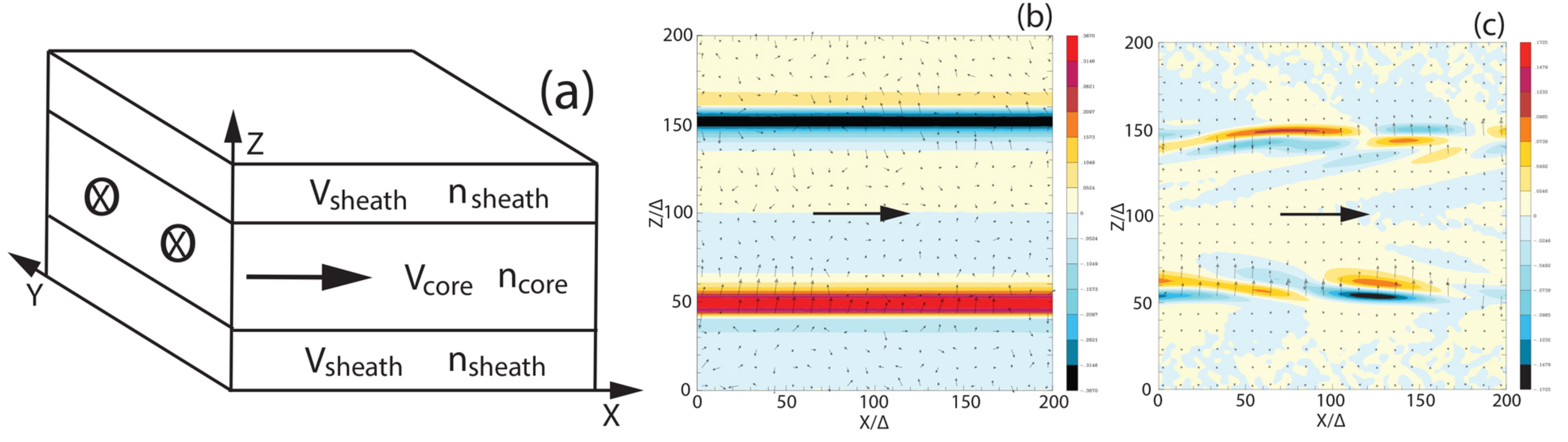
| 3.1.2. Shear Velocity Simulations with the Slab Model and Cylindrical Jets..................................................... | 8 | |
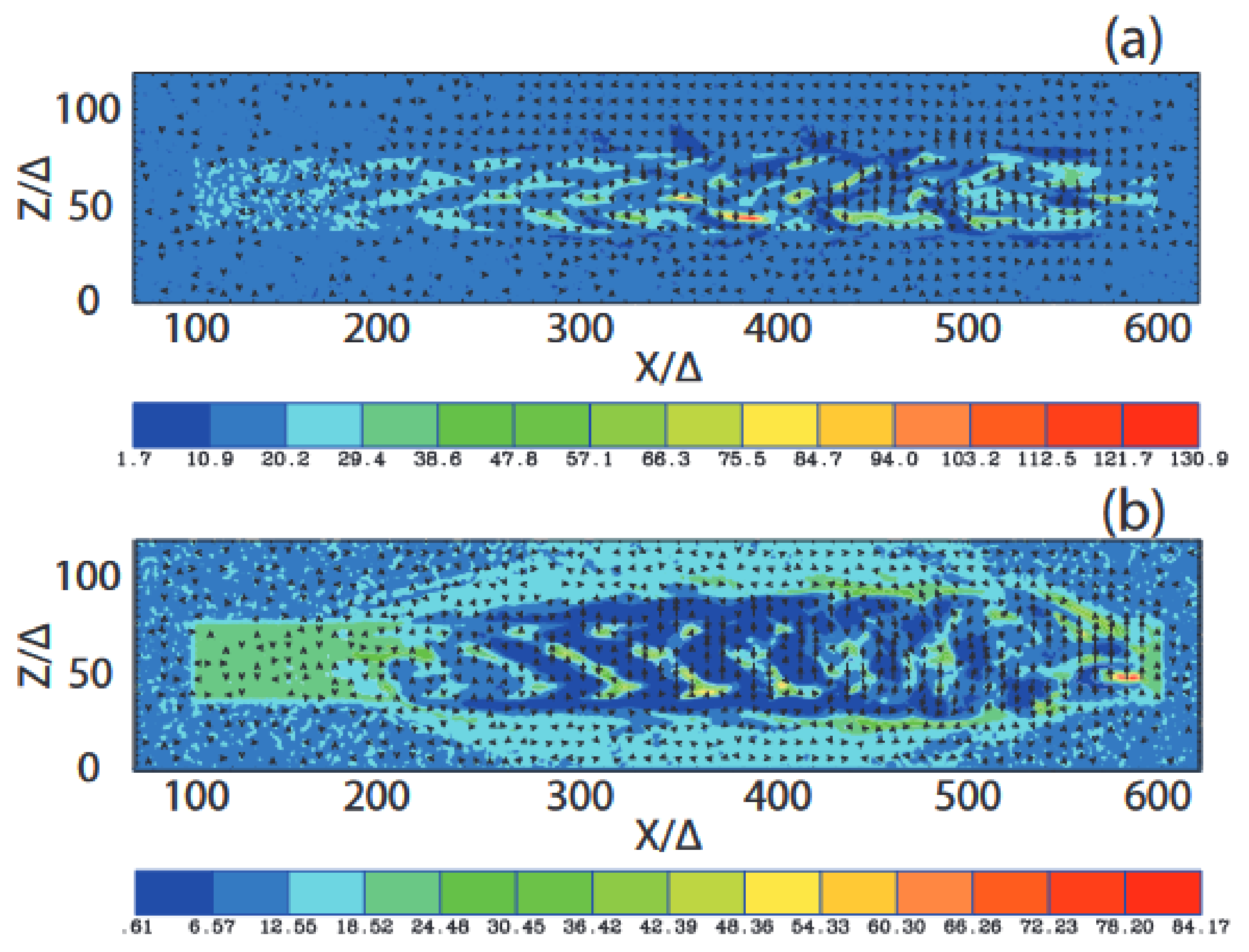
| 3.1.3. Global Simulations of Unmagnetized Relativistic Jets.............................................................................. | 9 | |
| 3.2. Magnetized Jets......................................................................................................................................................... | 12 | |
| 3.2.1. Topology of Relativistic Helical Jets............................................................................................................ | 12 | |
| 3.2.2. Global Simulations with Helical Jets and Large Radii.............................................................................. | 14 | |
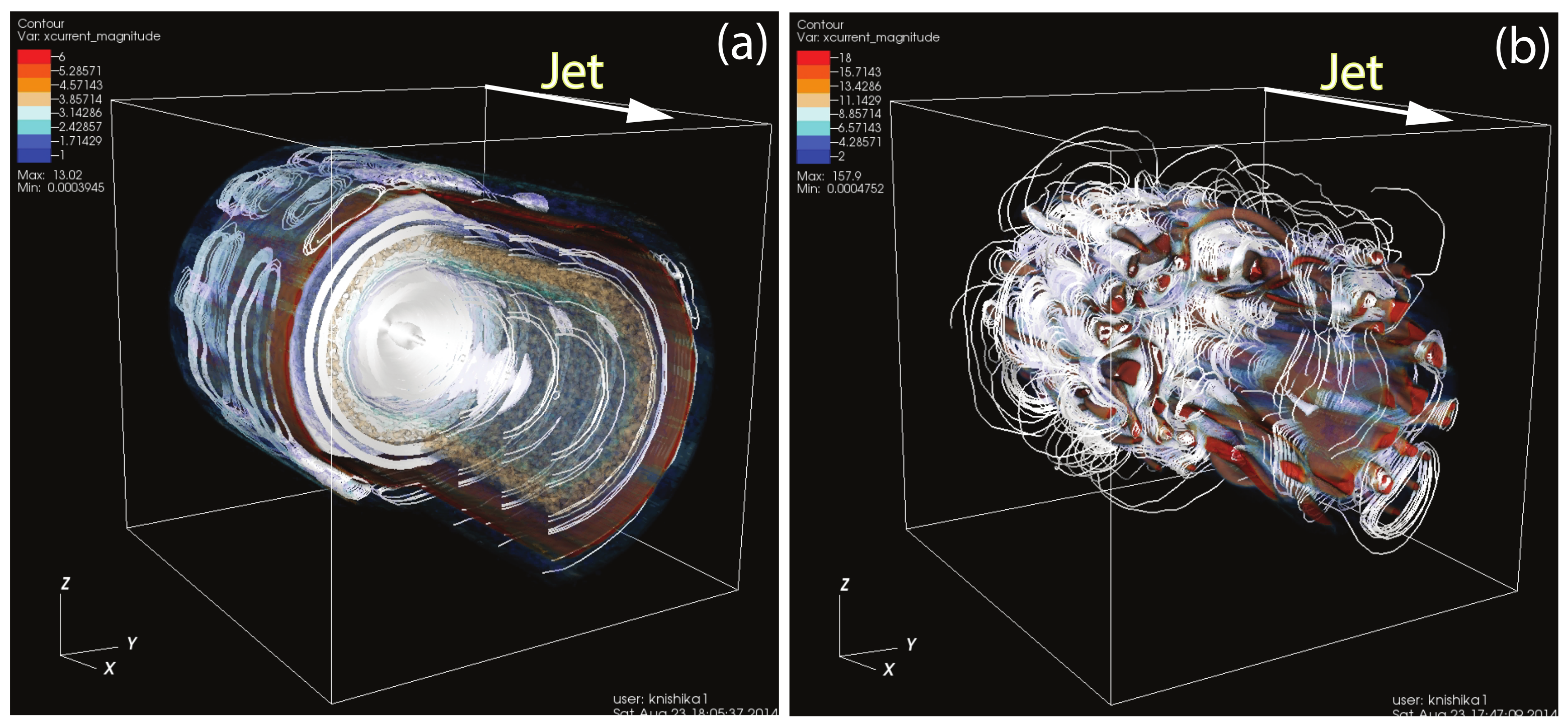
| 3.2.3. Global Jet Simulations with a Toroidal Magnetic Field and a New Injection Scheme........................... | 18 | |
| 4. Summary.............................................................................................................................................................................. | 22 | |
| References................................................................................................................................................................................ | 23 | |
1. Introduction
1.1. Astrophysical Jets
1.2. The TRISTAN Code
1.3. Particle-in-Cell Approach and Plasma Instabilities
2. Microscopic and Macroscopic Processes in Plasma Jets
3. PIC Simulations
3.1. Unmagnetized Jets
3.1.1. Self-Consistent Synthetic Spectra from Shocks
3.1.2. Shear Velocity Simulations with the Slab Model and Cylindrical Jets
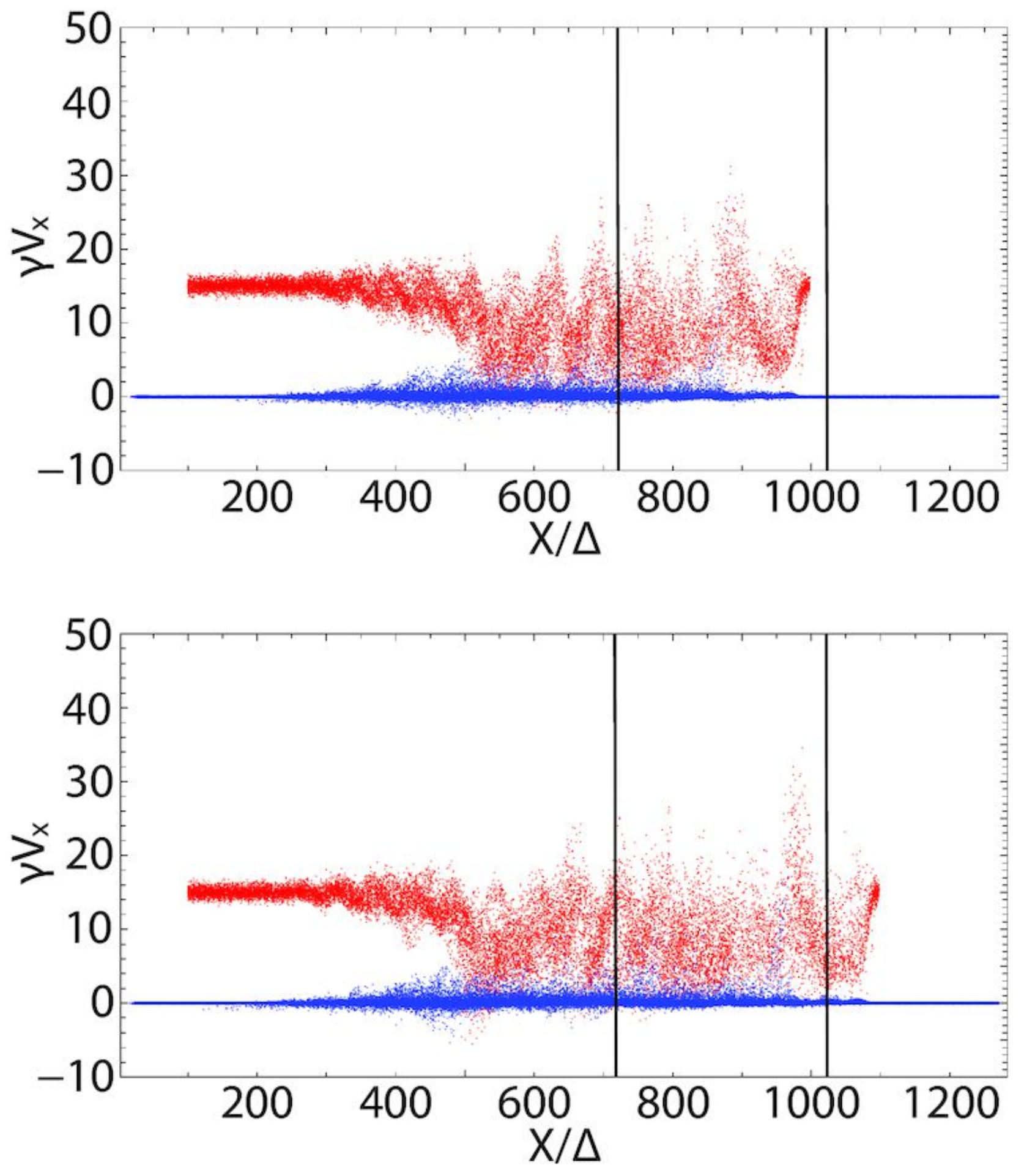
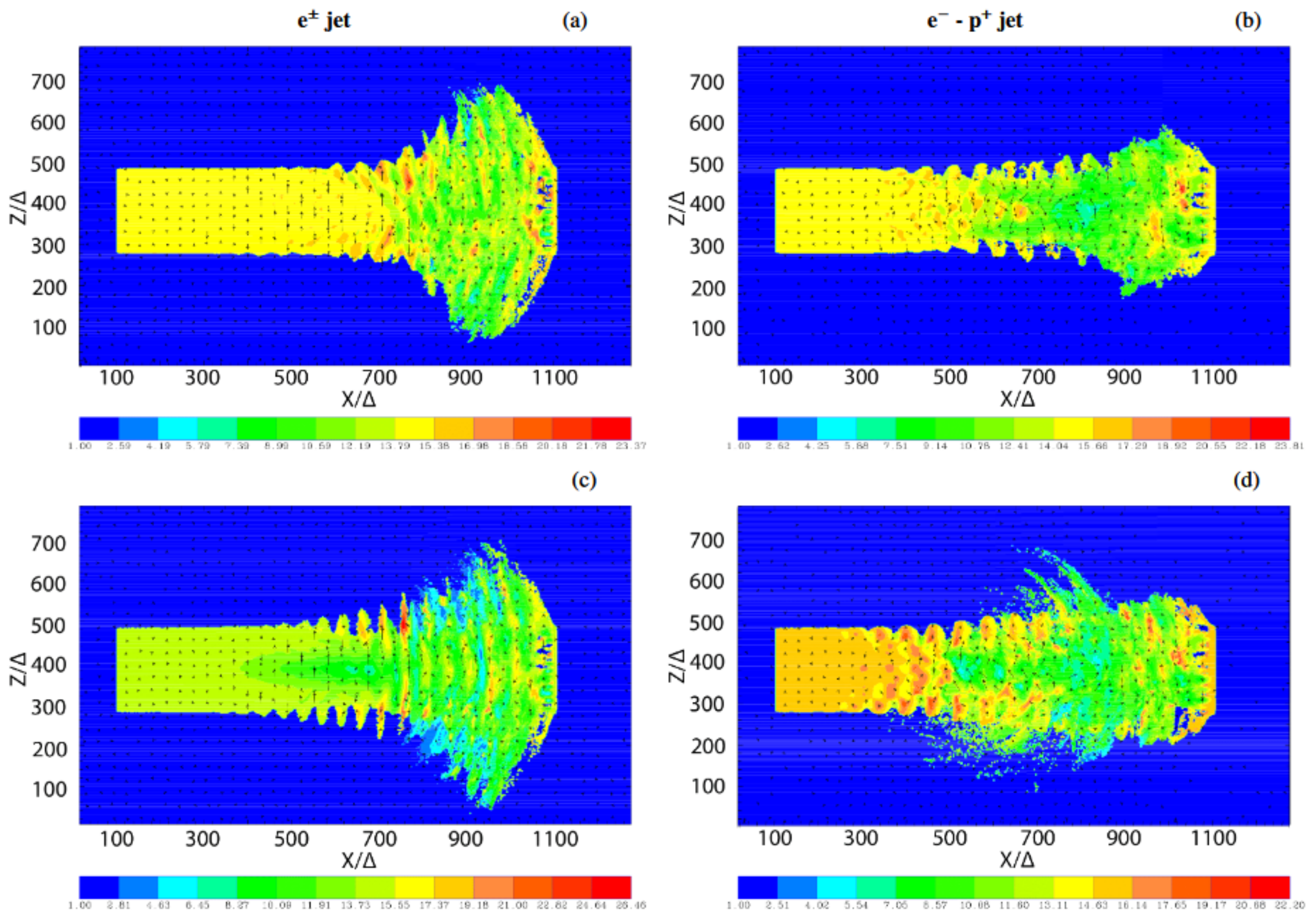
3.1.3. Global Simulations of Unmagnetized Relativistic Jets
- 1.
- Jet electrons are collimated by strong toroidal magnetic fields generated by MI;
- 2.
- Electrons are perpendicularly accelerated along with the jet collimation;
- 3.
- The toroidal magnetic field polarity switches from clockwise to counterclockwise about halfway down the jet.
- 1.
- Jet electrons and positrons mix with the ambient plasma;
- 2.
- Magnetic fields around current filaments generated by a combination of kKHI, MI, and Weibel instability merge and generate density fluctuations;
- 3.
- A larger jet radius is required to properly simulate the jet case, since the jet and ambient particles mix strongly.
3.2. Magnetized Jets
3.2.1. Topology of Relativistic Helical Jets
3.2.2. Global Simulations with Helical Jets and Large Radii
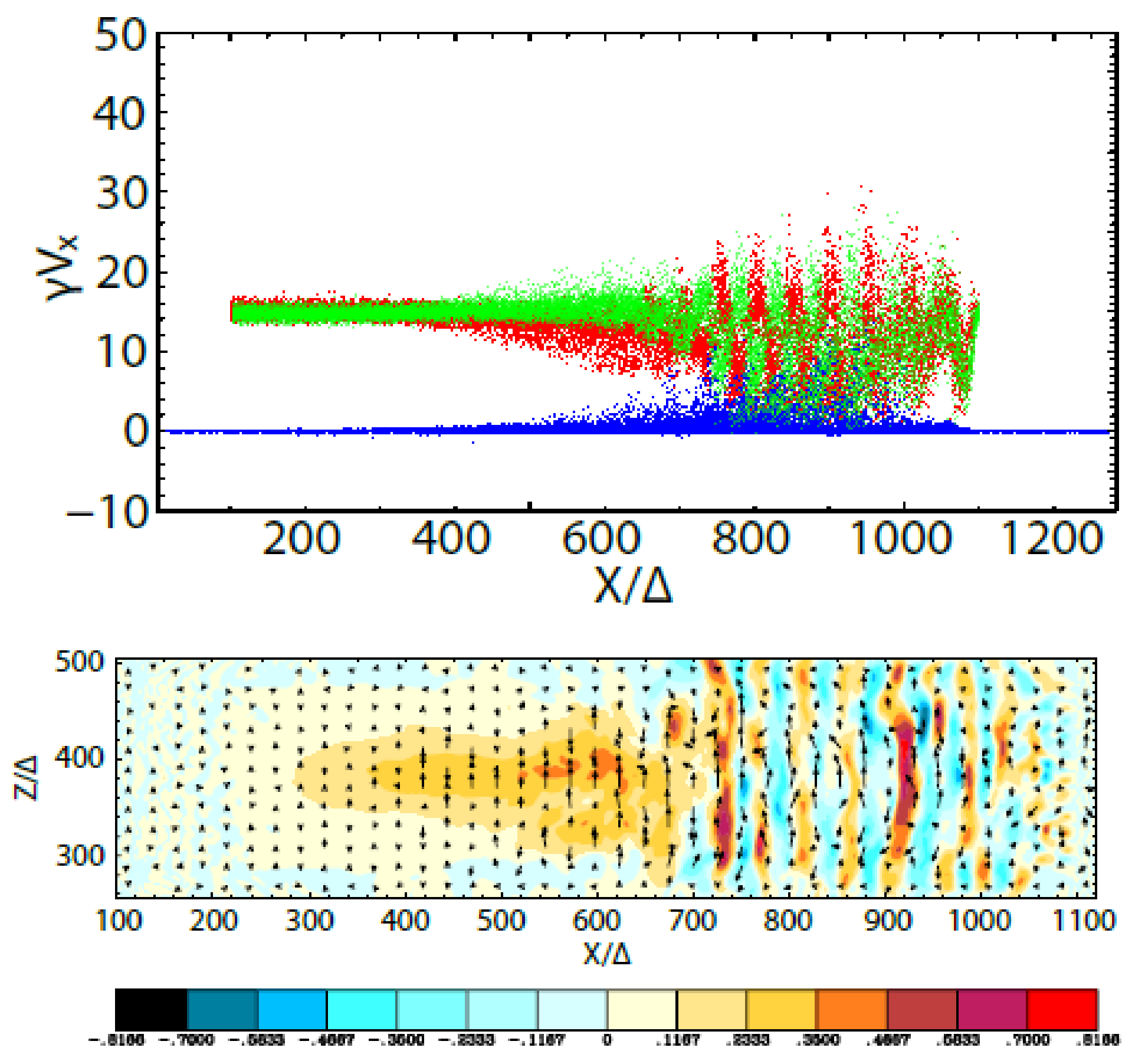
3.2.3. Global Jet Simulations with a Toroidal Magnetic Field and a New Injection Scheme
- 1.
- How does a toroidal magnetic field affect the growth of kKHI, MI, and WI within the jet and in the jet–ambient plasma boundary?
- 2.
- How do jets composed of electrons and positrons and jets composed of electrons and protons evolve in the presence of a large-scale toroidal magnetic field?
- 3.
- How and where are particles accelerated in jets with different plasma compositions?
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blandford, R.; Meier, D.; Readhead, A. Relativistic Jets from Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 467–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, B.; Philippov, A.A. Dissipation of the striped pulsar wind. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 607, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.F.; Fendt, C.; Hardcastle, M.; Nokhrina, E.; Tchekhovskoy, A. Disks and Jets. Gravity, Rotation and Magnetic Fields. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 191, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, N.R.; Marscher, A.P. Faraday Conversion in Turbulent Blazar Jets. Astrophys. J. 2018, 862, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic extraction of energy from Kerr black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punsly, B.; Coroniti, F.V. Ergosphere-driven Winds. Astrophys. J. 1990, 350, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Gravitational Collapse: The Role of General Relativity. Riv. Nuovo Cimento 1969, 1, 252–276. [Google Scholar]
- EHT Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 875, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Shapiro, S.L.; Tsokaros, A. GW170817, general relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations, and the neutron star maximum mass. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peér, A. Energetic and Broad Band Spectral Distribution of Emission from Astronomical Jets. Space Sci. Rev. 2014, 183, 371–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buneman, O. Tristan: The 3-d electromagnetic particle code. In Computer Space Plasma Physics: Simulation Techniques and Software; Matsumoto, H., Omura, Y., Eds.; Terra Scientic Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; pp. 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Messmer, P. Temperature isotropization in solar are plasmas due to the electron rehose instability. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 382, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiec, J.; Pohl, M.; Stroman, T.; Nishikawa, K.-I. Production of Magnetic Turbulence by Cosmic Rays Drifting Upstream of Supernova Remnant Shocks. Astroph. J. 2008, 684, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitkovsky, A. On the structure of relativistic collisionless shocks in electron–ion plasmas. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 673, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, A.; Nishikawa, K.; Pohl, M.; Niemiec, J.; Dutan, I.; Koehn, C.; Mizuno, Y.; MacDonald, N.; Gomez, J.L.; Hirotani, K. 3D PIC Simulations for Relativistic Jets with a Toroidal Magnetic Field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. J. 2021. submitted. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.04158 (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Melzani, M.; Walder, R.; Folini, D.; Winisdoerer, C.; Favre, J.M. Relativistic magnetic reconnection in collisionless ion-electron plasmas explored with particle-in-cell simulations. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 570, A111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Frederiksen, J.T.; Nordlund, A.; Mizuno, Y.; Hardee, P.E.; Niemiec, J.; Gomez, J.L.; Pe’er, A.; Dutan, I.; Meli, A.; et al. Evolution of Global Relativistic Jets: Collimations and Expansion with kKHI and the Weibel Instability. Astrophys. J. 2016, 820, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Mizuno, Y.; Gómez, J.L.; Duţan, I.; Meli, A.; White, C.; Niemiec, J.; Kobzar, O.; Pohl, M.; Pe’er, A.; et al. Microscopic Processes in Global Relativistic Jets Containing Helical Magnetic Fields: Dependence on Jet Radius. Galaxies 2017, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Mizuno, Y.; Gómez, J.L.; Duţan, I.; Meli, A.; Niemiec, J.; Kobzar, O.; Pohl, M.; Sol, H.; MacDonald, N.; et al. Relativistic Jet Simulations of the Weibel Instability in the Slab Model to Cylindrical Jets with Helical Magnetic Fields. Galaxies 2019, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Gomez, J.L.; Dutan, I.; Niemiec, J.; Kobzar, O.; MacDonald, N.; Meli, A.; Pohl, M.; Hirotani, K. Rapid particle acceleration due to recollimation shocks and turbulent magnetic elds in injected jets with helical magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 2652–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, L.; Spitkovsky, A. Relativistic Reconnection: An Efficient Source of Non-thermal Particles. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 783, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Niemiec, J.; Hardee, P.E.; Medvedev, M.; Sol, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Zhang, B.; Pohl, M.; Oka, M.; Hartmann, D.H. Weibel Instability and Associated Strong Fields in a Fully Three-Dimensional Simulation of a Relativistic Shock. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 698, L10–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.-I.; Dutan, I.; Köhn, C.; Mizuno, Y. PIC methods in astrophysics: Simulations of relativistic jets and kinetic physics in astrophysical systems. Living Rev. Comput. Astrophys. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, G.; Tun, B. (Eds.) Rare Event Simulation Using Monte Carlo Methods; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Hesse, M.; Guo, F.; Li, H.; Nakamura, T.K.M. Strongly localized magnetic reconnection by the super-Alfvenic shear flow. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 080701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayburn, D.R. A numerical study of the continuous beam model of extragalactic radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blandford, R.D.; Rees, M.J. A “twin-exhaust” model for double radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 169, 395–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, M.L.; Smarr, L.; Smith, M.D.; Wilson, J.R. Hydrodynamic formation of twin-exhaust jets. Astrophys. J. 1981, 247, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.A.; Norman, M.L.; Burns, J.O. Numerical simulations of a magnetically confined jet. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1986, 311, L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, J.M.; Muller, E. Grid-based Methods in Relativistic Hydrodynamics and Magnetohydrodynamics. Living Rev. Comput. Astrophys. 2015, 1, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, E.S. Spontaneously growing transverse waves in a plasma due to an anisotropic velocity distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1959, 2, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, F.M.; Duffy, P. Particle Acceleration in Shearing Flows: Efficiencies and Limits. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 886, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, I.M.; Lalakos, A.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Fernandez, R.; Foucart, F.; Quataert, E.; Kasen, D. The role of magnetic field geometry in the evolution of neutron star merger accretion discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 490, 4811–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Lazarian, A. Production of the large scale superluminal ejections of the microquasar GRS 1915+105 by violent magnetic reconnection. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 441, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenkhahn, G.; Spruit, H.C. Efficient acceleration and radiation in Poynting flux powered GRB outflows. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 391, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, T.K.; Li, H.; Anantua, R. A Quasi-static Hyper-resistive Model of Ultra-high-energy Cosmic-ray Acceleration by Magnetically Collimated Jets Created by Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2019, 885, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannios, D. UHECRs from magnetic reconnection in relativistic jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, L46–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannios, D. Acceleration and emission of MHD driven, relativistic jets. J. Phys Conf. Ser. 2011, 283, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, J. The effects of sub-shells in highly magnetized relativistic flows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kadowaki, L.H.S.; De Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Stone, J.M. MHD Instabilities in Accretion Disks and Their Implications in Driving Fast Magnetic Reconnection. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, L.H.; Pino, E.M.; Medina-Torrejón, T.E. A Statistical Study of Fast Magnetic Reconnection in Turbulent Accretion Disks and Jets. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.04777 (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Komissarov, S.S. Shock dissipation in magnetically dominated impulsive flows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J.C.; Uzdensky, D.A. A reconnection switch to trigger gamma-ray burst jet dissipation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 573–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, L.; Petropoulou, M.; Giannios, D. Relativistic jets shine through shocks or magnetic reconnection? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzdensky, D.A. Magnetic Reconnection in Extreme Astrophysical Environments. Space Sci. Rev. 2011, 160, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yan, H. The Internal-collision-induced Magnetic Reconnection and Turbulence (ICMART) Model of Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2011, 726, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, W.; Roytershteyn, V.; Karimabadi, H. Influence of Magnetic Shear on the Formation and Interaction of Flux Ropes in Magnetic Reconnection. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Liu, Y.-H.; Daughton, W.; Li, H. Particle Acceleration and Plasma Dynamics during Magnetic Reconnection in the Magnetically Dominated Regime. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Daughton, W.; Zhang, B.; Lloyd-Ronning, N.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, W. Efficient Production of High-energy Nonthermal Particles during Magnetic Reconnection in a Magnetically Dominated Ion-Electron Plasma. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 818, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, H.; Daughton, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.-H. Particle acceleration during magnetic reconnection in a low-beta pair plasma. Phys. Plasmas 2016, 23, 055708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, D.; Milosavljevic, M.; Spitkovsky, A. A flux rope network and particle acceleration in three-dimensional relativistic magnetic reconnection. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimabadi, H.; Roytershteyn, V.; Vu, H.X.; Omelchenko, Y.A.; Scudder, J.; Daughton, W.; Dimmock, A.; Nykyri, K.; Wan, M.; Sibeck, D.; et al. The link between shocks, turbulence, and magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasmas. Phys. Plasmas 2014, 21, 062308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, D.E.; Olson, D.K.; Hesse, M.; Aunai, N.; Kuznetsova, M.; Karimabadi, H.; Daughton, W.; Adrian, M.L. The relation between reconnected flux, the parallel electric field, and the reconnection rate in a three-dimensional kinetic simulation of magnetic reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 122105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenitani, S.; Hoshino, M. Relativistic Particle Acceleration in a Folded Current Sheet. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2005, 618, L111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabuzda, D. Evidence for Helical Magnetic Fields Associated with AGN Jets and the Action of a Cosmic Battery. Galaxies 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A. Launching of Active Galactic Nuclei Jets. In Book Series (ASSL): The Formation and Disruption of Black Hole Jets; Springer: Cham, Switzerlnad, 2015; Volume 414, pp. 45–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ardaneh, K.; Cai, D.; Nishikawa, K.I. Parallel 3D Electromagnetic Particle-In-Cell Simulation for Relativistic Jets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 827, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Piovezan, P.P.; Kadowaki, L.H.S. The role of magnetic reconnection on jet/accretion disk systems. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 518, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannios, D.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Begelman, M.C. Fast TeV variability in blazars: Jets in a jet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, L29–L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, L.; Spitkovsky, A.; Arons, J. The Maximum Energy of Accelerated Particles in Relativistic Collisionless Shocks. Astrophys. J. 2013, 771, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markidis, S.; Lapenta, G.; Delzanno, G.L.; Henri, P.; Goldman, M.V.; Newman, D.L.; Intrator, T.; Laure, E. Signatures of secondary collisionless magnetic reconnection driven by kink instability of a flux rope. Plasma Phys. Control Fusion 2014, 56, 064010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Hardee, P.E.; Nishikawa, K.-I. Spatial Growth of the Current-driven Instability in Relativistic Jets. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Mizuno, Y.; de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M. Spatial Growth of Current-driven Instability in Relativistic Rotating Jets and the Search for Magnetic Reconnection. Astrophys. J. 2016, 824, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.P.; Zrake, J.; Fiuza, F. Nonthermal ion acceleration by the kink instability in nonrelativistic jets. Phys. Plasmas 2019, 26, 072105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davelaar, J.; Philippov, A.A.; Bromberg, O.; Singh, C.B. Particle Acceleration in Kink-unstable Jets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 896, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.P.; Grismayer, T.; Fonseca, R.; Silva, L.O. Transverse electron-scale instability in relativistic shear flows. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 021101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Mizuno, Y.; Niemiec, J.; Kobzar, O.; Pohl, M.; Gomez, J.L.; Dutan, I.; Pe’er, A.; Frederiksen, J.T.; Nordlund, A.; et al. Microscopic processes in global relativistic jets containing helical magnetic fields. Galaxies 2016, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Hardee, P.; Dutan, I.; Zhang, B.; Meli, A.; Choi, E.J.; Min, K.; Niemiec, J.; Mizuno, Y.; Medvedev, M.; et al. Radiation from Particles Accelerated in Relativistic Jet Shocks and Shear flows. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7064. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Hardee, P.E.; Dutan, I.; Niemiec, J.; Medvedev, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Meli, A.; Sol, H.; Zhang, B.; Pohl, M.; et al. Magnetic Field Generation in Core-sheath Jets via the Kinetic Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability. Astrophys. J. 2014, 793, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutan, I.; Nishikawa, K.I.; Mizuno, Y.; Niemiec, J.; Kobzar, O.; Pohl, M.; Gomez, J.L.; Peér, A.; Frederiksen, J.T.; Nordlund, A.; et al. Particle-in-cell simulations of global relativistic jets with helical magnetic fields. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2016, 12, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liska, M.; Hesp, C.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Ingram, A.; van der Klis, M.; Marko, S.B.; Van Moer, M. Disc Tearing and Bardeen-Petterson Alignment in GRMHD Simulations of Highly Tilted Thin Accretion Discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 507, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liska, M.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Quataert, E. Large-scale poloidal magnetic eld dynamo leads to powerful jets in GRMHD simulations of black hole accretion with toroidal field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 3656–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloy, M.A.; Gomez, J.L.; Ibanez, J.M.; Mart, J.M.; Müller, E. Radio Emission from Three dimensional Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets: Observational Evidence of Jet Stratication. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 528, L85–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen-Brown, E.; Lyutikov, M.; Kharb, P. Signatures of large-scale magnetic fields in active galactic nuclei jets: Transverse asymmetries. Mon. Not. R Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, S.P.; McClure-Griths, N.M.; Feain, I.J.; Gaensler, B.M.; Sault, R.J. Broad-band radio circular polarization spectrum of the relativistic jet in PKS B2126-158. Mon. Not. R Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, J.M. Numerical Simulations of Jets from Active Galactic Nuclei. Galaxies 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckmann, M.E.; Shukla, P.K.; Drury, L.O.C. The Formation of a Relativistic Partially Electromagnetic Planar Plasma Shock. Astrophys. J. 2008, 675, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Hardee, P.; Richardson, G.; Preece, R.; Sol, H.; Fishman, G.J. Particle Acceleration in Relativistic Jets Due to Weibel Instability. Astrophys. J. 2003, 595, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Hardee, P.; Hededal, C.B.; Richardson, G.; Preece, R.; Sol, H.; Fishman, G.J. Particle acceleration, magnetic eld generation, and emission in relativistic shocks. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 38, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Mizuno, Y.; Fishman, G.J.; Hardee, P. Particle Acceleration, Magnetic Field Generation, and Associated Emission in Collisionless Relativistic Jets. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2008, 17, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Niemiec, J.; Medvedev, M.; Zhang, B.; Hardee, P.; Nordlund, A.; Frederiksen, J.; Mizuno, Y.; Sol, H.; Pohl, M.; et al. Simulation of Relativistic Shocks and Associated Self-consistent Radiation. In Partially Ionized Plasmas throughout the Cosmos; Florinski, V., Heerikhuisen, J., Zank, G.P., Gallagher, D.L., Eds.; AIP Conference Series; American Institute of Physics: Big Island, HI, USA, 2011; Volume 1366, pp. 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Spitkovsky, A. Particle acceleration in relativistic collisionless shocks: Fermi process at last? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 682, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, M.V.; Loeb, A. Generation of Magnetic Fields in the Relativistic Shock of Gamma-Ray Burst Sources. Astrophys. J. 1999, 526, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.I.; Choi, E.J.; Min, K.W.; Niemiec, J.; Zhang, B.; Hardee, P.; Mizuno, Y.; Medvedev, M.; Nordlund, A.; Frederiksen, J.; et al. Radiation from shock-accelerated particles. In Proceedings of the Gamma-Ray Bursts 2012 Conference (GRB 2012), Munich, Germany, 7–11 May 2012; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Hededal, C.B.; Nishikawa, K.I. The Influence of an Ambient Magnetic Field on Relativistic collisionless Plasma Shocks. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2005, 623, L89–L92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, M.V.; Frederiksen, J.T.; Haugbolle, T.; Nordlund, A. Radiation signatures of sub-Larmor scale magneti fields. Astrophys. J. 2011, 737, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sironi, L.; Spitkovsky, A. Synthetic spectra from particle-in-cell simulations of relativistic collisionless shocks. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, L92–L96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Arimoto, M.; Asano, K.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Band, D.L.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. Fermi Observations of High-Energy Gamma-Ray Emission from GRB 080916C. Science 2009, 323, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.P.; Grismayer, T.; Martins, S.F.; Fiuza, F.; Fonseca, R.A.; Silva, L.O. Large-scale magnetic field generation via the kinetic kelvin-helmholtz instability in unmagnetized scenarios. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Pelletier, G.; Gremillet, L.; Plotnikov, L. Current-driven filamentation upstream of magnetized relativistic collisionless shocks. Mon. Not. R Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.-I.; Hardee, P.; Zhang, B.; Dutan, I.; Medvedev, M.; Choi, E.J.; Min, K.W.; Niemiec, J.; Mizuno, Y.; Nordlund, Å.; et al. Magnetic field generation in a jet sheath plasma via the kinetic Kelvin–Helmholtz instability. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 31, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, D.L.; Koide, S.; Uchida, Y. Magnetohydrodynamic production of relativistic jets. Science 2001, 291, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mościbrodzka, M.; Dexter, J.; Davelaar, J.; Falcke, H. Faraday rotation in GRMHD simulations of the jet launching zone of M87. Mon. Not. R Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, G.; de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Lazarian, A. Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Reconnection and Particle Acceleration: Three-dimensional Effects. Astrophys. J. 2011, 735, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, G.; de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Lazarian, A. Particle Acceleration in Turbulence and Weakly Stochastic Reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 241102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarian, A.; Kowal, G.; Takamoto, M.; de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M.; Cho, J. Theory and Applications of Non-relativistic and Relativistic Turbulent Reconnection. In Magnetic Reconnection. Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Gonzalez, W., Parker, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 427. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, E.P.; Zrake, J.; Fiuza, F. Efficient Nonthermal Particle Acceleration by the Kink Instability in Relativistic Jets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.; Yuan, Y.; Hoshino, M.; Sironi, L. Magnetoluminescence. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 207, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdankin, V.; Uzdensky, D.A.; Werner, G.R.; Begelman, M.C. System-size Convergence of Nonthermal Particle Acceleration in Relativistic Plasma Turbulence. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 867, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisso, L.; Sironi, L. Particle Acceleration in Relativistic Plasma Turbulence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 255101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.L.; Lobanov, A.P.; Bruni, G.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Marscher, A.P.; Jorstad, S.G.; Mizuno, Y.; Bach, U.; Sokolovsky, K.V.; Anderson, J.M.; et al. Probing the innermost regions of agn JETS and their magnetic fields with radioastron. I. Imaging BL lacertae AT 21 μas resolution. Astrophys. J. 2016, 817, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meli, A.; Nishikawa, K.-i. Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Astrophysical Relativistic Jets. Universe 2021, 7, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110450
Meli A, Nishikawa K-i. Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Astrophysical Relativistic Jets. Universe. 2021; 7(11):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110450
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeli, Athina, and Ken-ichi Nishikawa. 2021. "Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Astrophysical Relativistic Jets" Universe 7, no. 11: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110450
APA StyleMeli, A., & Nishikawa, K.-i. (2021). Particle-in-Cell Simulations of Astrophysical Relativistic Jets. Universe, 7(11), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110450





