Curvature Invariants for Lorentzian Traversable Wormholes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method to Compute the Invariants
3. Morris and Thorne Wormhole
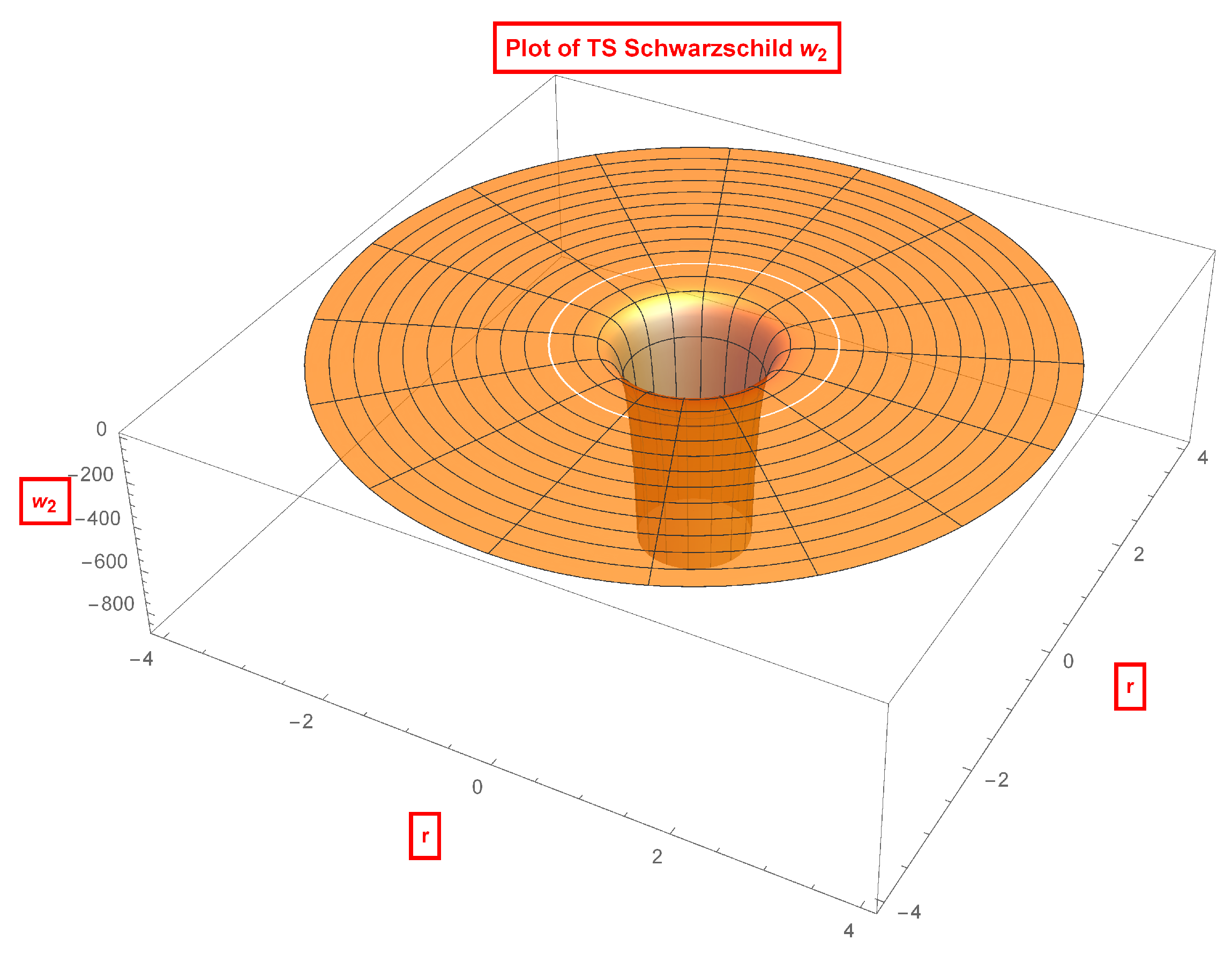
4. Thin-Shell Schwarzschild Wormhole
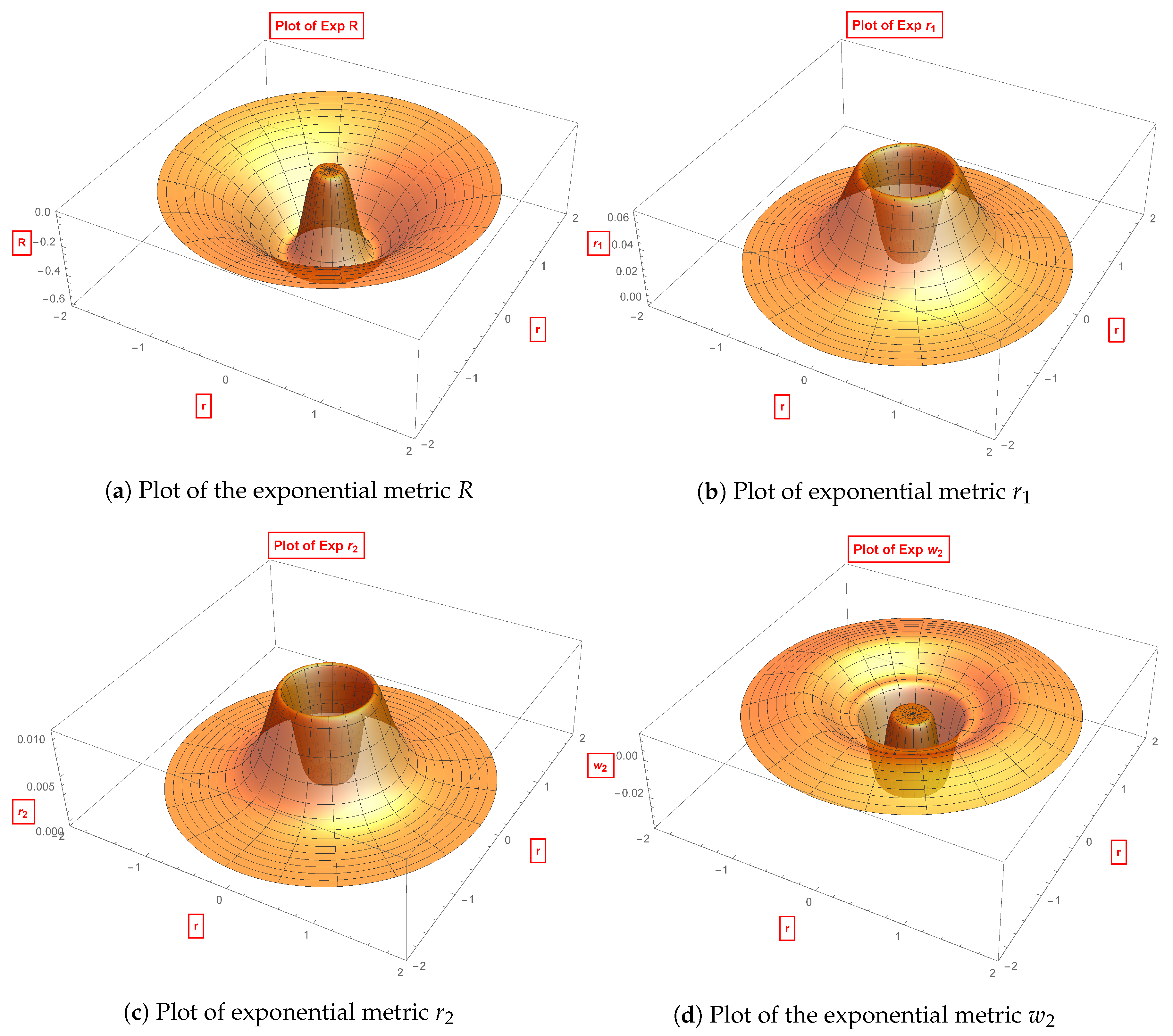
5. The Exponential Metric
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, M.S.; Thorne, K.S. Wormholes in spacetime and their use for interstellar travel: A tool for teaching general relativity. Am. J. Phys. 1988, 56, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.S.; Thorne, K.S.; Yurtsever, U. Wormholes, time machines, and the weak energy conditions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, H.G. Ether flow through a drainhole: A particle model in general relativity. J. Math. Phys. 1973, 14, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.A. Scalar-tensor theory and scalar charge. Acta Phys. Pol. 1973, 4, 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, M. Lorentzian Wormholes: From Einstein to Hawking; AIP Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Penrose, R.; Rindler, W. Spinors and Space-Time; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zakhary, E.; McIntosh, C.B.G. A Complete Set of Riemann Invariants. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1997, 29, 539–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffel, E.B. Ueber die Transformation der homogenen Differentialausdrücke zweiten Grades. J. Angew. Math. 1869, 70, 46–70. [Google Scholar]
- Stephani, H.; Kramer, D.; MacCallum, M.A.H.; Hoenselaers, C.; Herlt, E. Exact Solutions of Einstein’s Field Equations; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- D’Inverno, R.C. Introducing Einstein’s Relativity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, S. Spacetime and Geometry: An Introduction to General Relativity, 1st ed.; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Groen, O.; Hervik, S. Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity: With Modern Applications in Cosmology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 538. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini, C.; Bini, D.; Capozziello, S.; Ruffini, R. Second order scalar invariants of the Riemann tensor: Applications to black hole space-times. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2002, 11, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.; Hervik, S.; Pelavas, N. Spacetimes characterized by their scalar curvature invariants. Class. Quantum Gravity 2009, 26, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, M.A.H. Spacetime invariants and their uses. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.06857v1. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, R.C.; Overduin, J.; Wilcomb, K. A New Way to See Inside Black Holes. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1512.02762v2. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.G.; Campanelli, M. Making use of geometrical invariants in black hole collisions. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 127501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, M.A.H. On singularities, horizons, invariants, and the results of Antoci, Liebscher and Mihich (GRG 38, 15 (2006) and earlier). Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2006, 38, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdelqader, M.; Lake, K. Invariant characterization of the Kerr spacetime: Locating the horizon and measuring the mass and spin of rotating black holes using curvature invariants. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 084017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.N.; Shoom, A.A. Local Invariants Vanishing on Stationary Horizons: A Diagnostic for Locating Black Holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 141102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coley, A.; McNutt, D. Identification of black hole horizons using scalar curvature invariants. Class. Quantum Gravity 2018, 35, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonserm, P.; Ngampitipan, T.; Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Exponential metric represents a traversable wormhole. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 084048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnese, A.G.; La Camera, M. Traceless stress energy and traversable wormholes. Nuovo Cim. B 2002, 117, 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Korolev, R.V.; Sushkov, S.V. Exact wormhole solutions with nonminimal kinetic coupling. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 124025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, J.; McLenaghan, R.G. Algebraic invariants of the Riemann tensor in a four-dimensional Lorentzian space. J. Math. Phys. 1991, 32, 3135–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carot, J.; Costa, J.D. On the Geometry of Warped Spacetimes. Class. Quantum Gravity 1993, 10, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosuosso, K.; Pollney, D.; Pelavas, N.; Musgrave, P.; Lake, K. Invariants of the Riemann tensor for class B warped product spacetimes. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1998, 115, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.S.N. Wormhole Basics. In Wormholes, Warp Drives and Energy Conditions; Fundamental Theories of Physics; Lobo, F.S.N., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 189, pp. 11–33. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, D.; MacCallum, M.A.H.; Gregoris, D.; Forget, A.; Coley, A.; Chavy-Waddy, P.C.; McNutt, D.D. Cartan Invariants and Event Horizon Detection, Extended Version. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2018, 50, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcubierre, M. The warp drive: hyper-fast travel within general relativity. Class. Quantum Gravity 1994, 11, L73–L77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. | Warped products of class B are line elements of the form subject to the restriction . Class spacetimes include all spherical, planar, and hyperbolic spacetimes and contain all spacetime line elements considered in this paper [26]. |
| 2. | The syzygies reveal either all independent irreducible algebraic relations among the set of invariants or that no set exists [9]. |

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mattingly, B.; Kar, A.; Julius, W.; Gorban, M.; Watson, C.; Ali, M.; Baas, A.; Elmore, C.; Shakerin, B.; Davis, E.; et al. Curvature Invariants for Lorentzian Traversable Wormholes. Universe 2020, 6, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6010011
Mattingly B, Kar A, Julius W, Gorban M, Watson C, Ali M, Baas A, Elmore C, Shakerin B, Davis E, et al. Curvature Invariants for Lorentzian Traversable Wormholes. Universe. 2020; 6(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleMattingly, Brandon, Abinash Kar, William Julius, Matthew Gorban, Cooper Watson, MD Ali, Andrew Baas, Caleb Elmore, Bahram Shakerin, Eric Davis, and et al. 2020. "Curvature Invariants for Lorentzian Traversable Wormholes" Universe 6, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6010011
APA StyleMattingly, B., Kar, A., Julius, W., Gorban, M., Watson, C., Ali, M., Baas, A., Elmore, C., Shakerin, B., Davis, E., & Cleaver, G. (2020). Curvature Invariants for Lorentzian Traversable Wormholes. Universe, 6(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6010011






