Selected Results on Variable Stars Observed by TESS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Introducing the TESS Space Telescope
- Exoplanet discoveryThe primary mission of TESS is to discover exoplanets around the brightest stars in the sky. Unlike its predecessor, the Kepler Space Telescope, which mainly focused on a small, distant FoV, TESS scans a much larger portion of the sky, enabling the detection of relatively small planets around nearby stars. This makes verification follow-up observations easier and provides prime targets for future observations by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST; [10]) and other ground-based telescopes.
- Stellar variability and asteroseismologyBeyond exoplanet discovery, TESS also contributes significantly to stellar astrophysics by observing variable stars. The mission enables researchers to analyse stellar oscillations through asteroseismology, which helps to determine the internal structures of stars, and also to study stellar flares, binary systems, and other astrophysical phenomena.
3. Stars Showing Extrinsic Light Variations
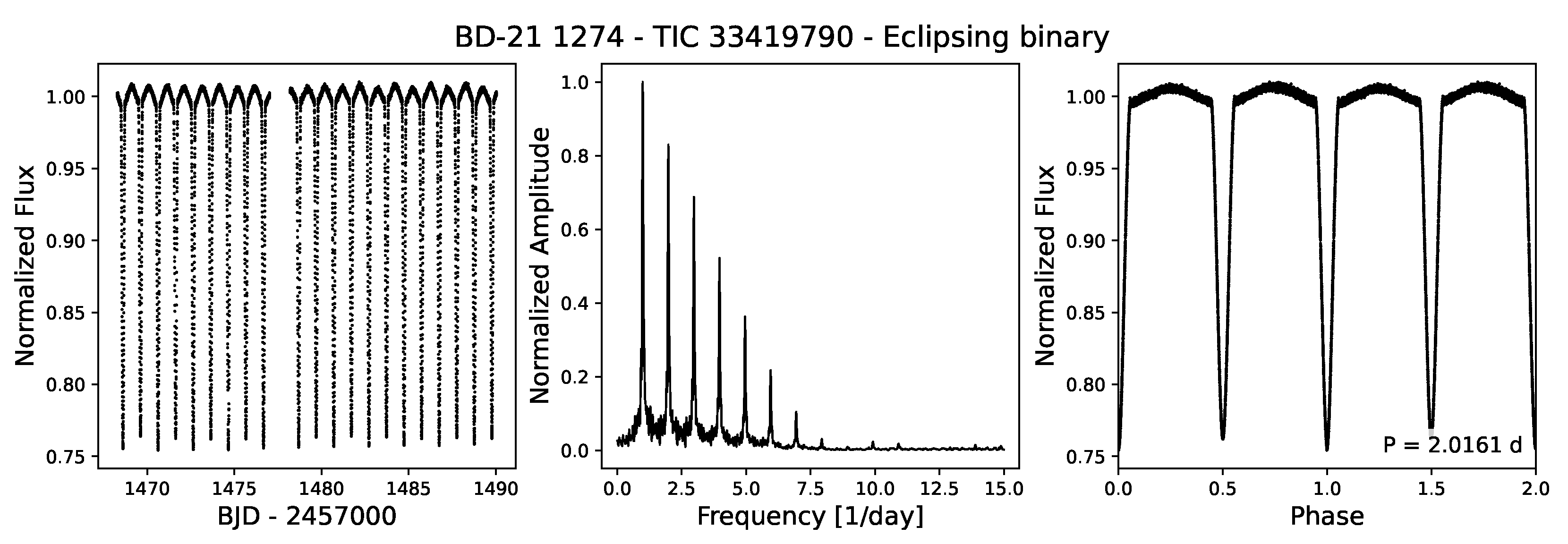
3.1. Eclipsing Binaries
3.2. Transiting Exoplanets
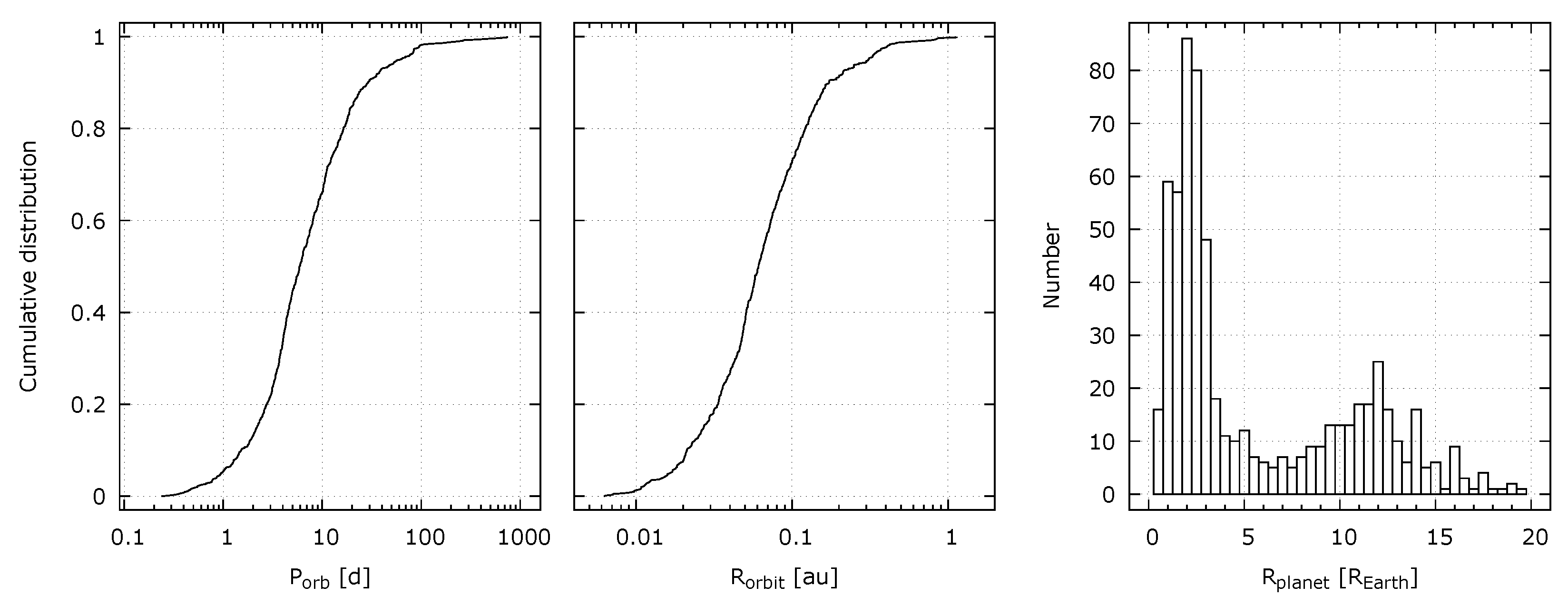
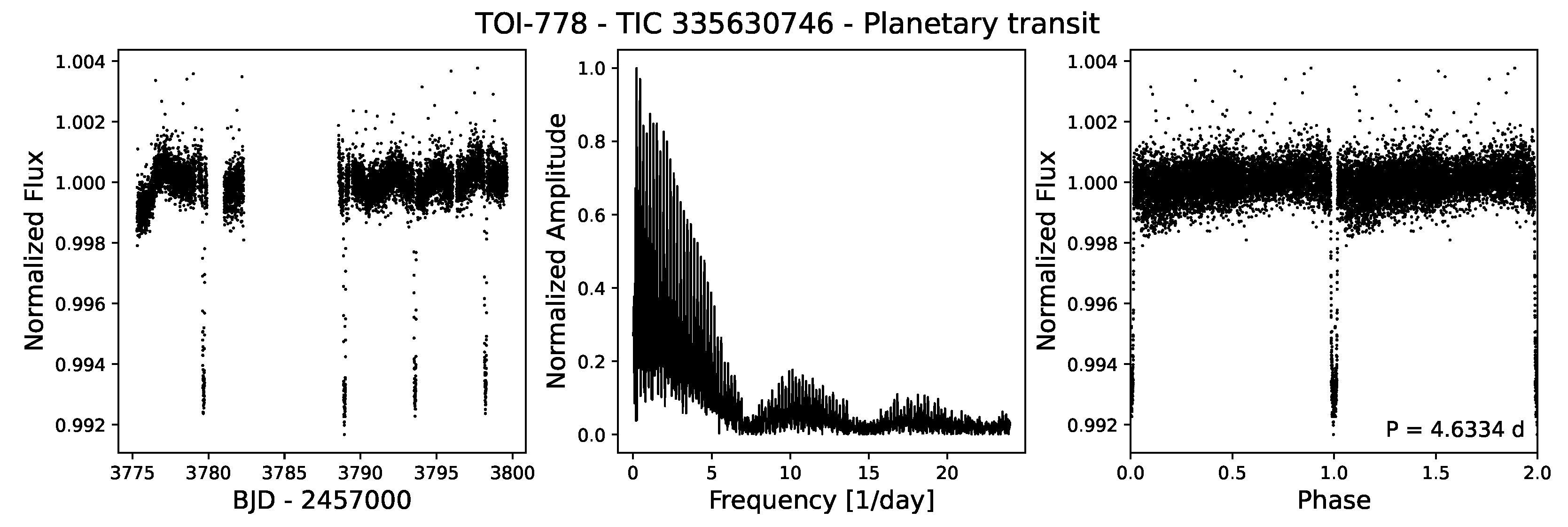
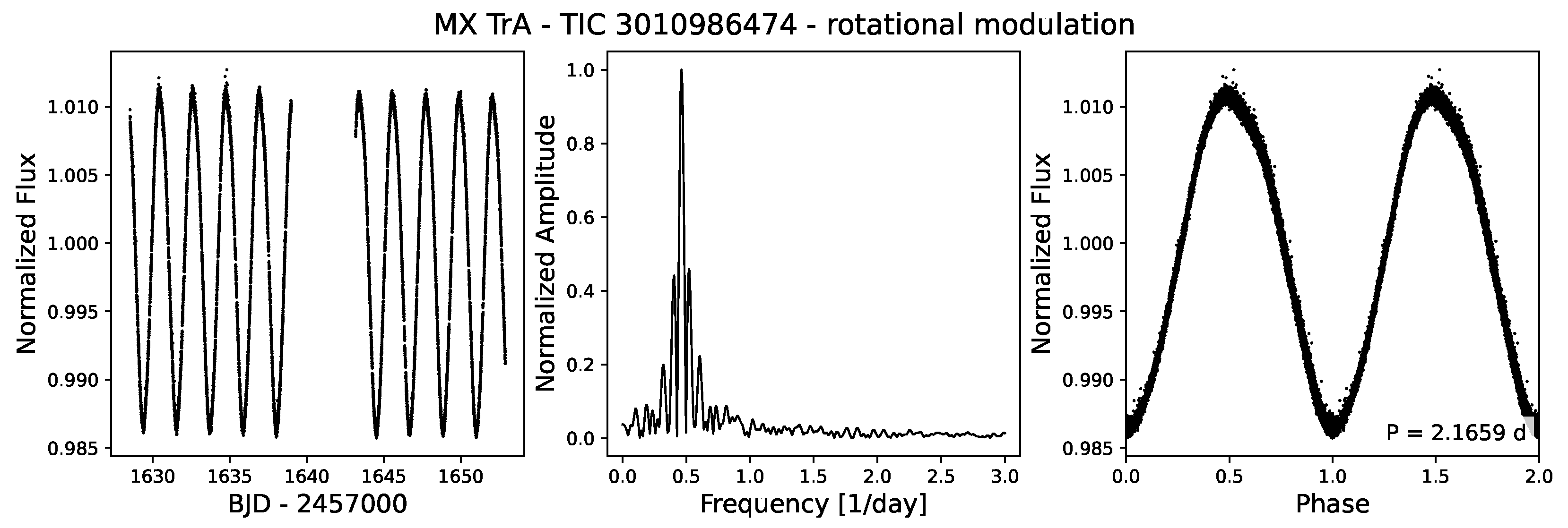
3.3. Light Variations by Stellar Rotation
4. Stars Showing Intrinsic Light Variations
4.1. Eruptive Variables
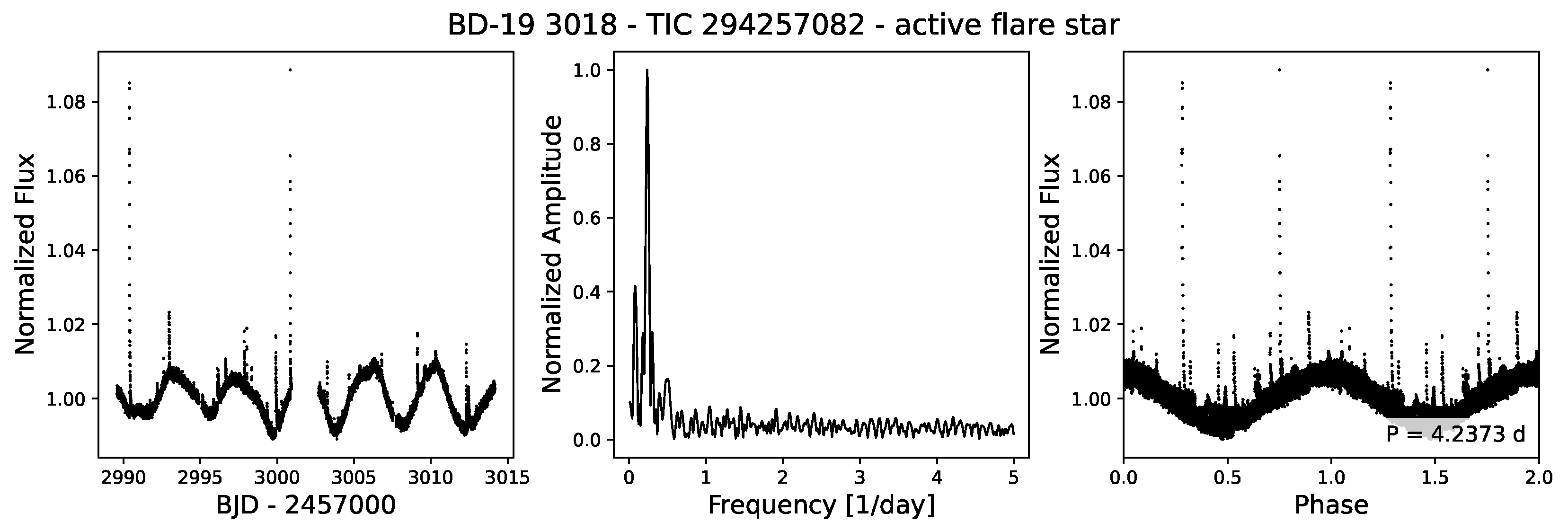
4.1.1. Flare Stars
4.1.2. Wolf–Rayet Stars and Luminous Blue Variables
4.2. Cataclysmic Variables
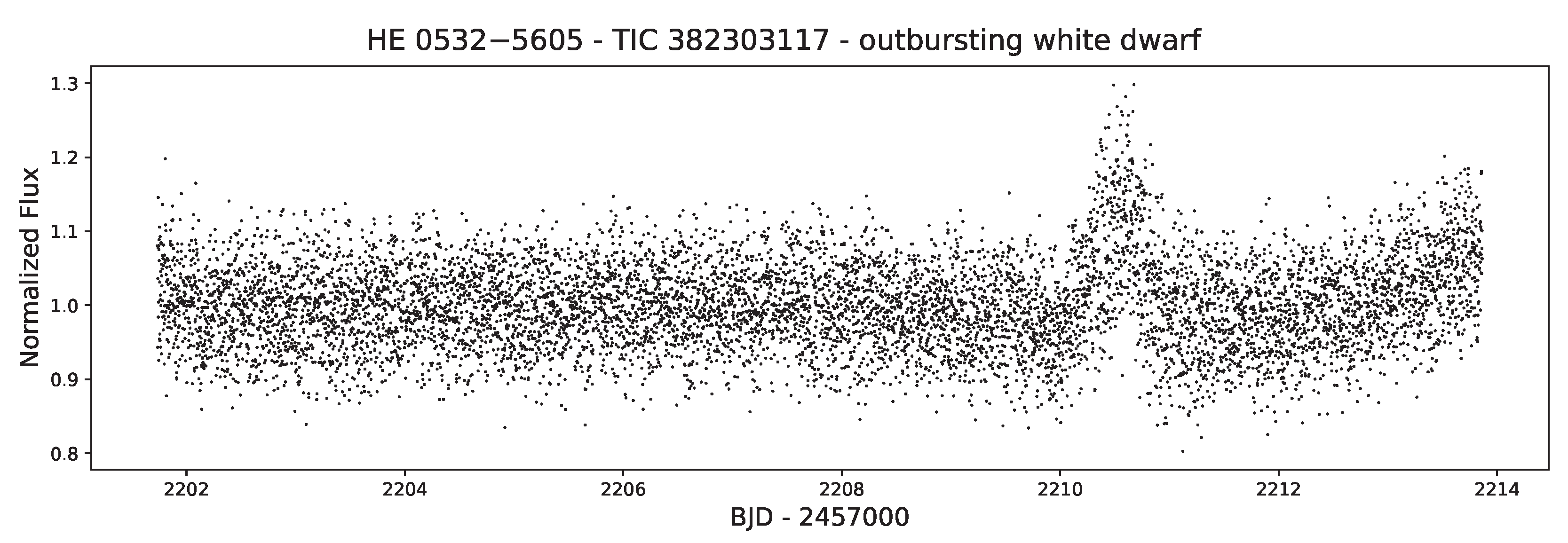
4.2.1. Dwarf Novae and Novae
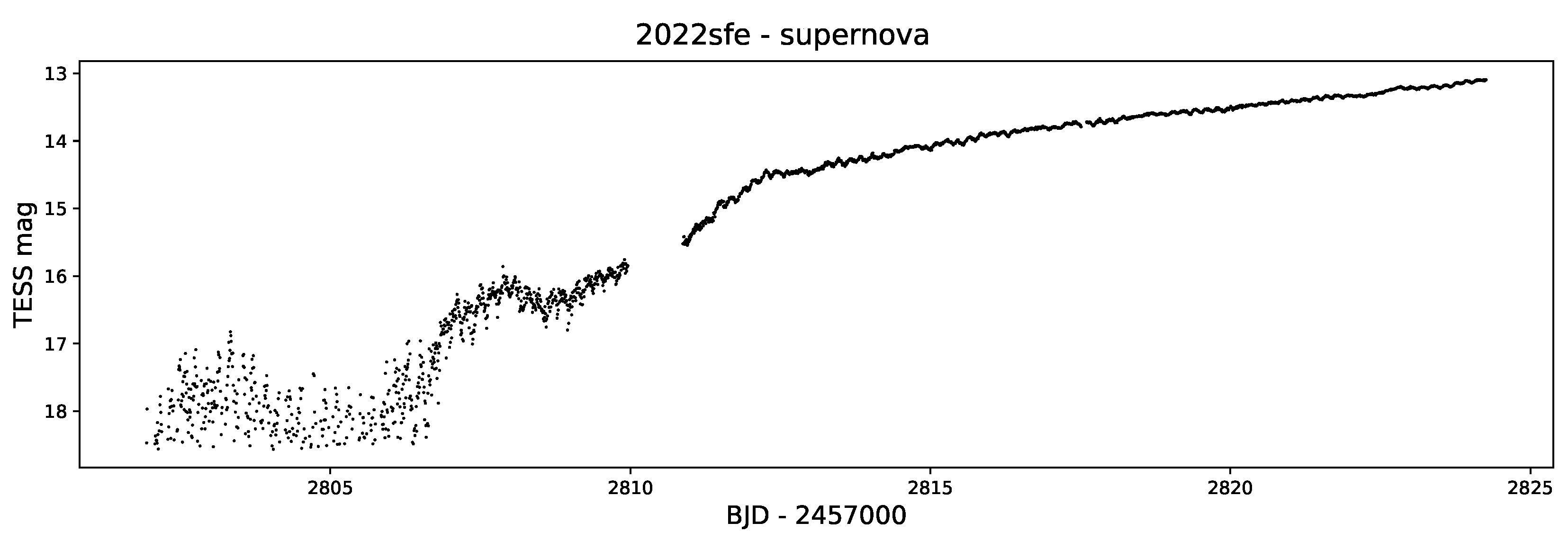
4.2.2. Supernovae
4.3. Stellar Pulsation
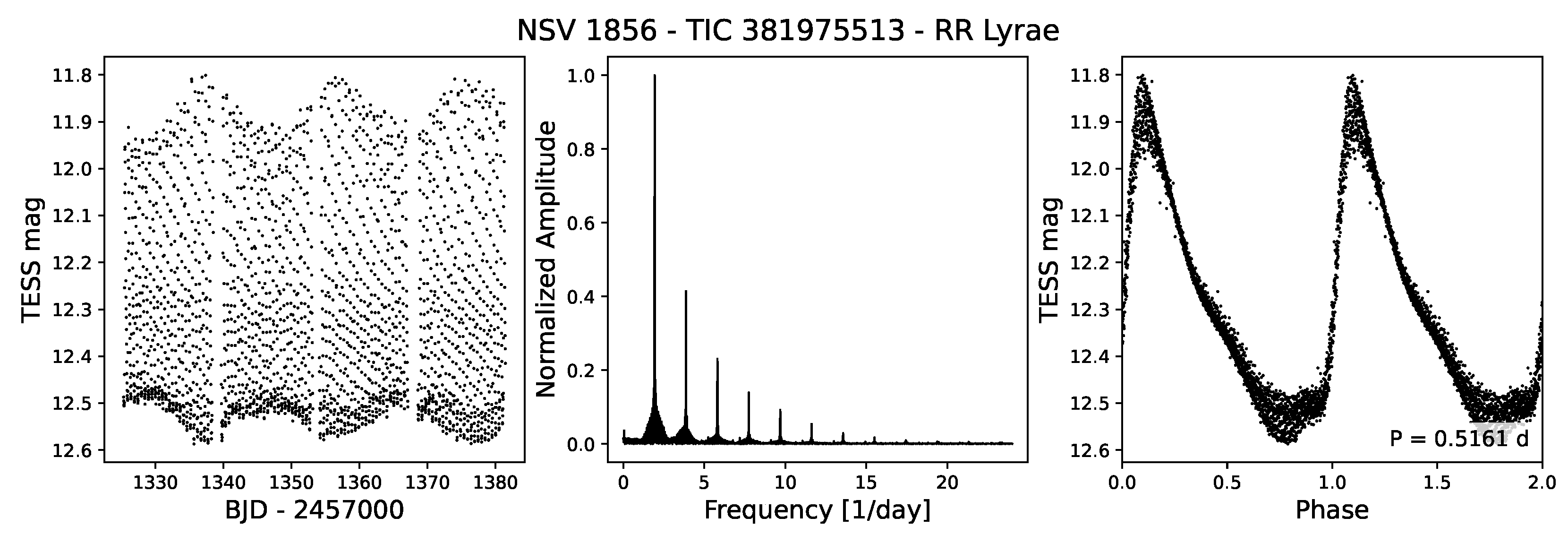
4.3.1. RR Lyrae Stars
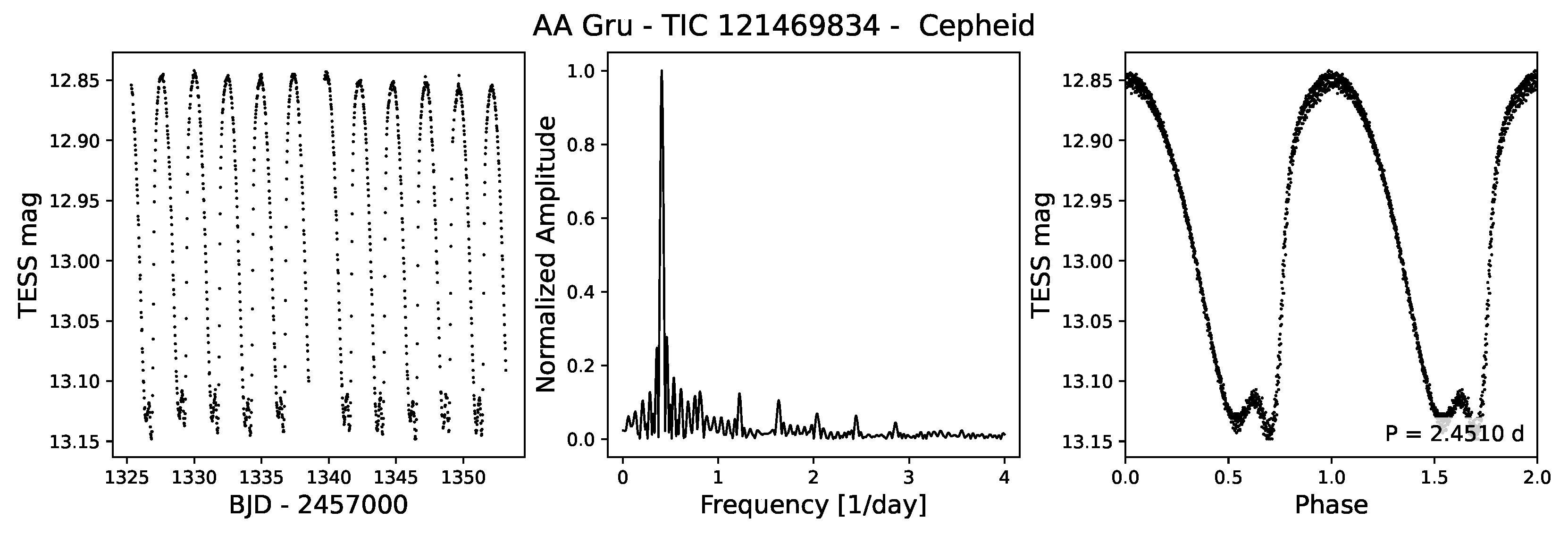
4.3.2. Cepheid Pulsators
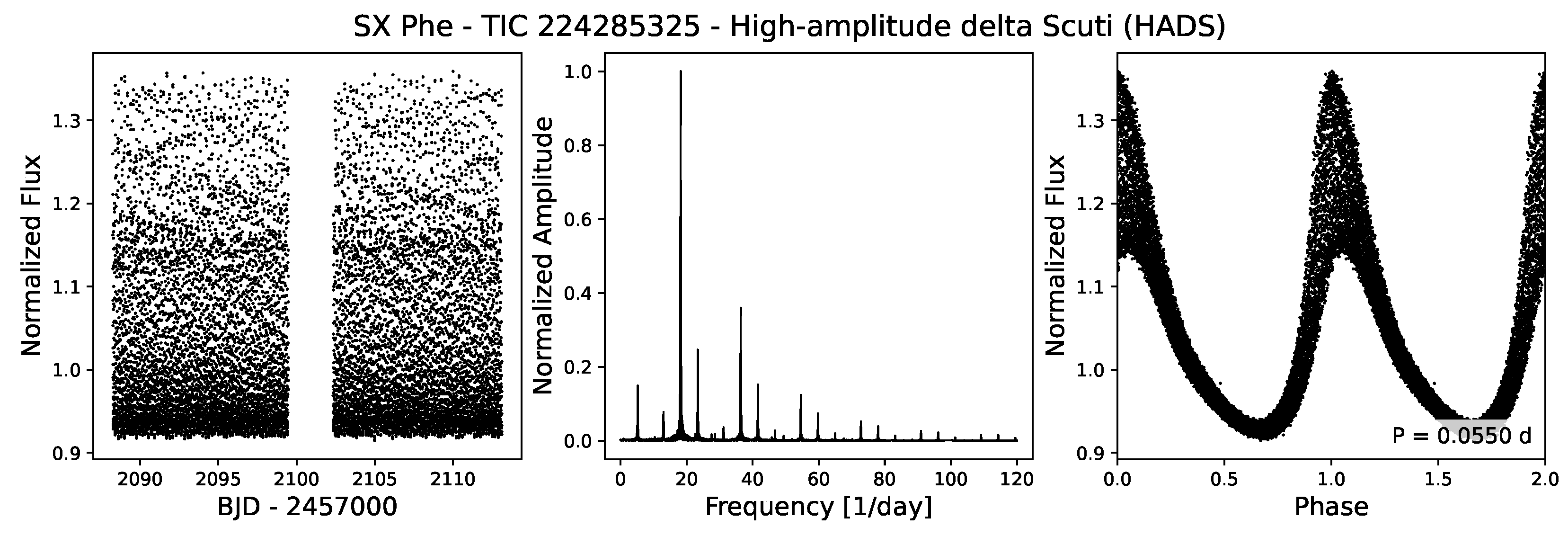
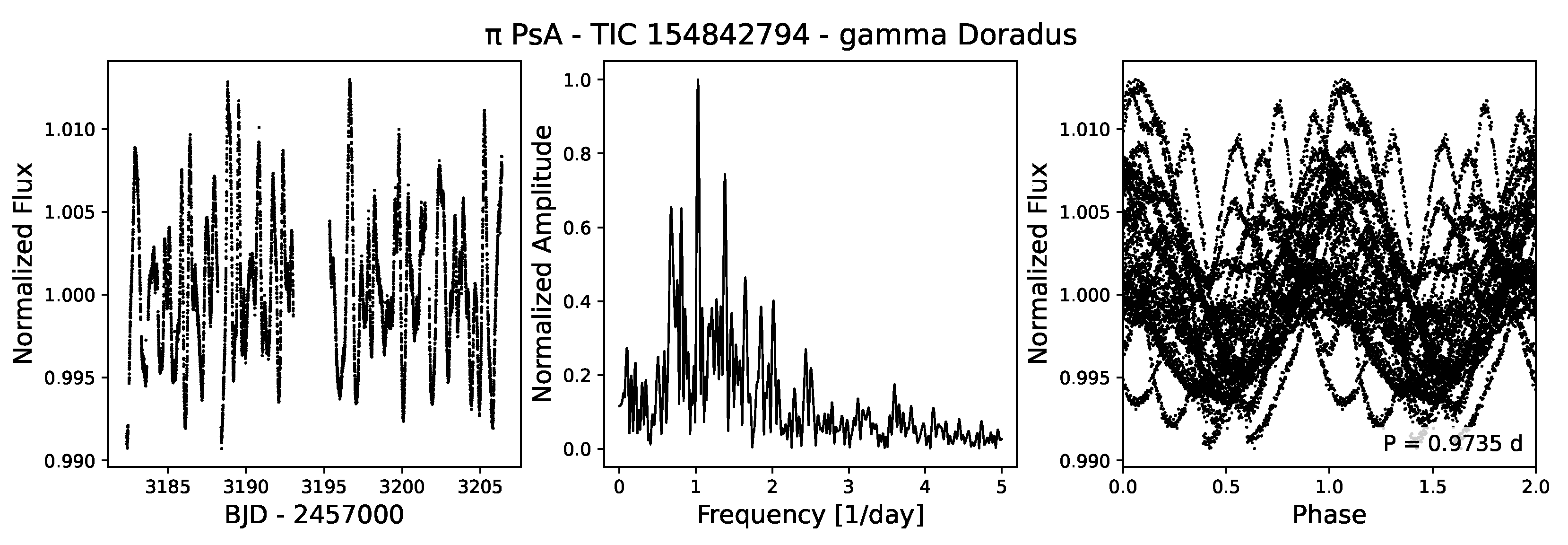
4.3.3. Scuti and Doradus Variables
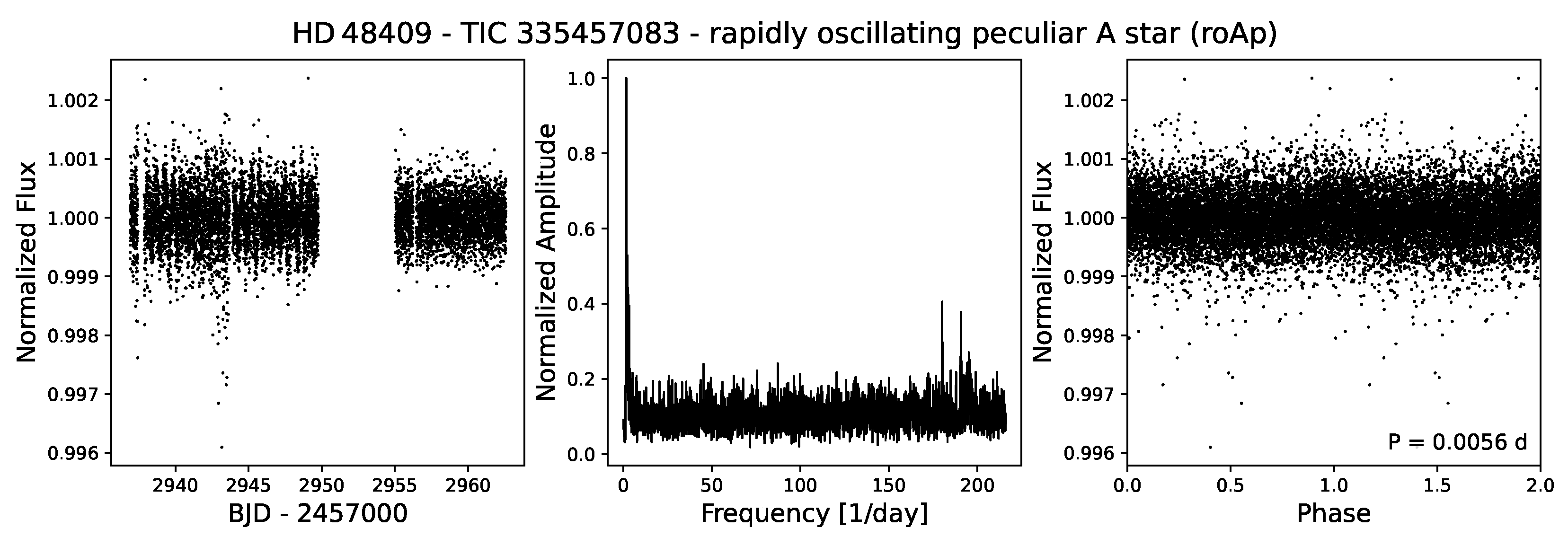
4.3.4. roAp Stars
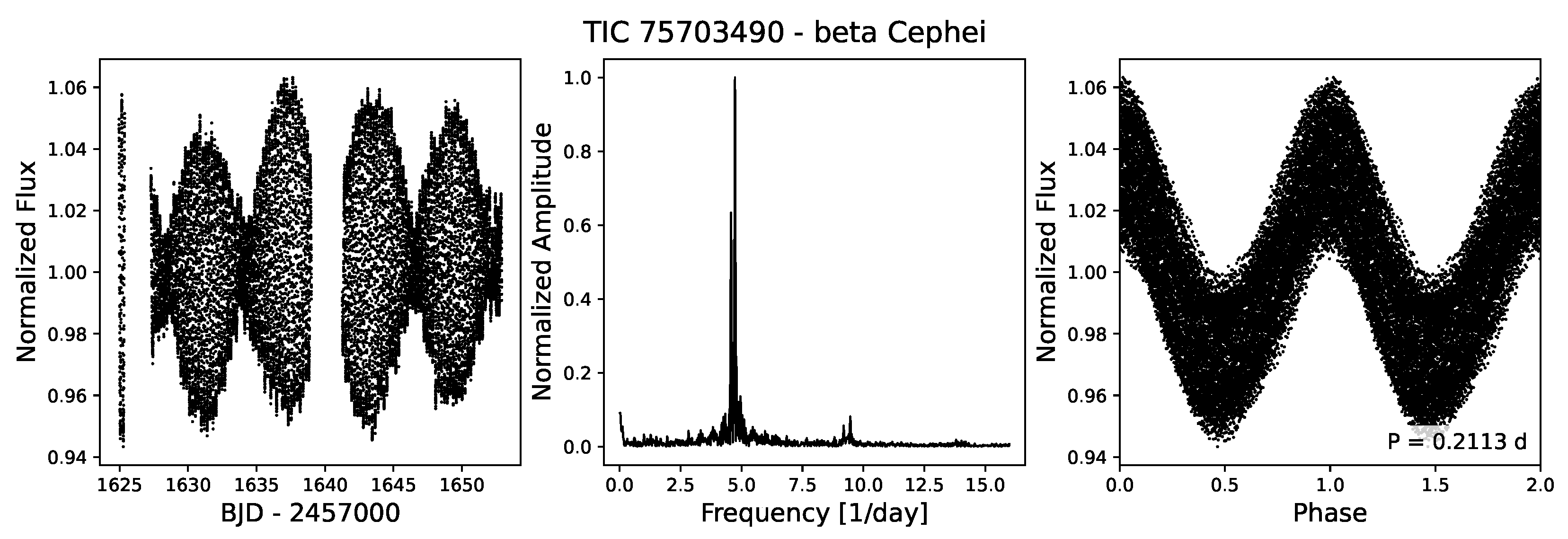
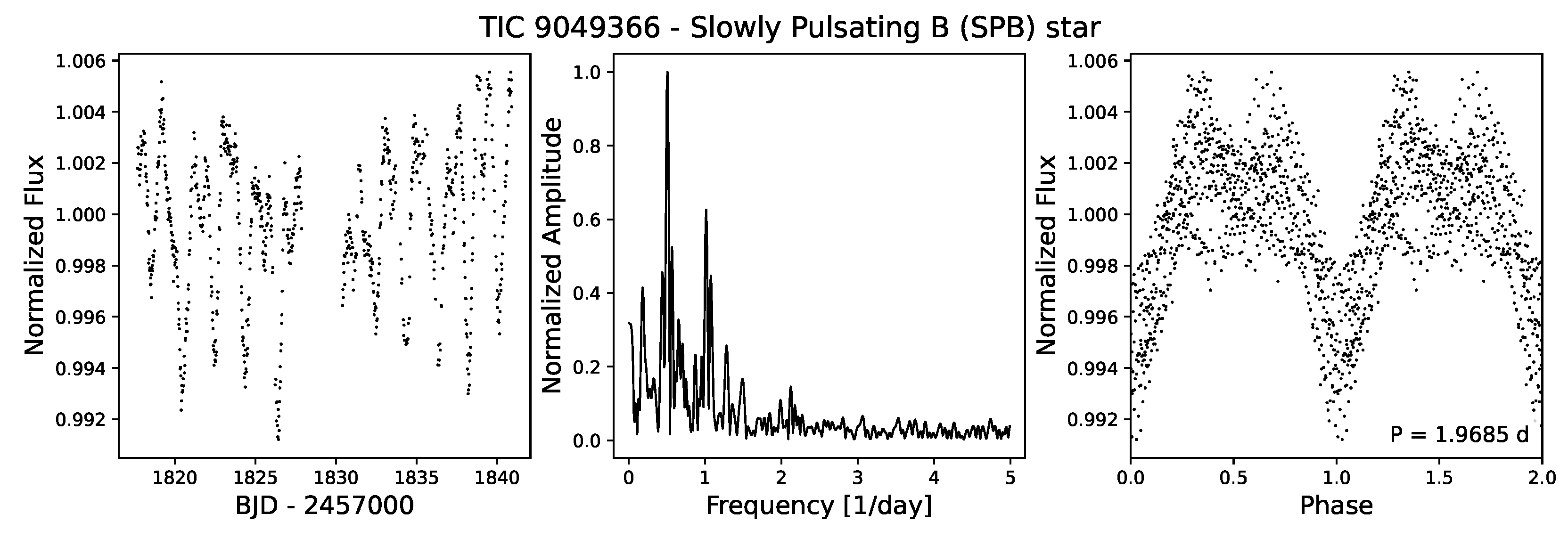
4.3.5. Cep and Slowly Pulsating B-Stars
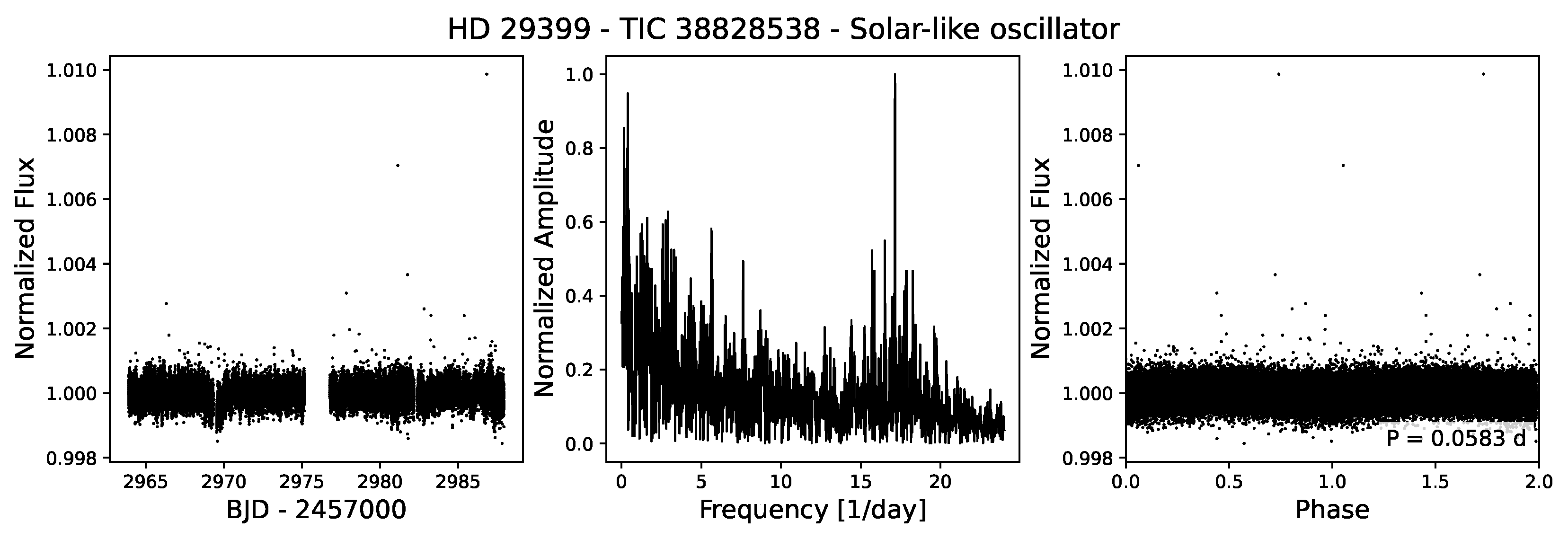
4.3.6. Solar-like Oscillations
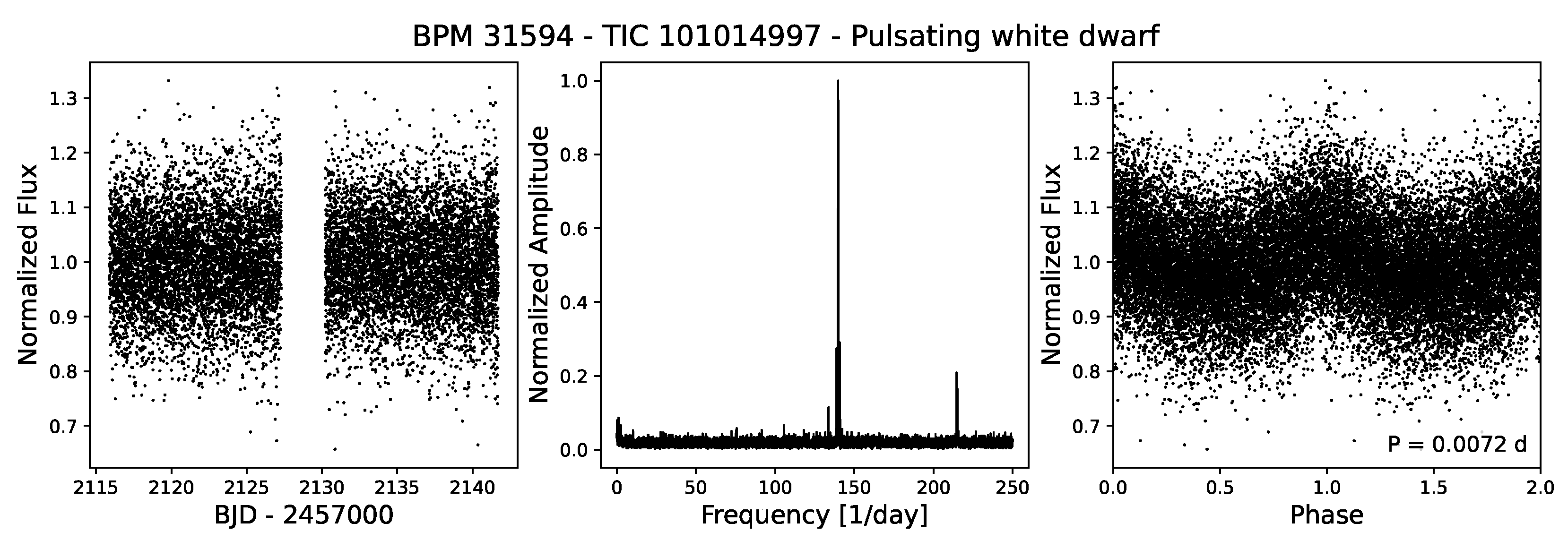
4.3.7. Pulsating White Dwarfs
4.3.8. Pulsating Hot Subdwarf Stars
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/docs/counts_detail.html, accessed on 1 June 2025. |
| 2 | see note 1 above. |
| 3 | https://tess.mit.edu/followup/, accessed on 1 June 2025. |
References
- Zima, W. The Campaigns of the Delta Scuti Network. Delta Scuti Star Newsl. 1997, 11, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Nather, R.E.; Winget, D.E.; Clemens, J.C.; Hansen, C.J.; Hine, B.P. The Whole Earth Telescope: A New Astronomical Instrument. Astrophys. J. 1990, 361, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.; Matthews, J.; Kuschnig, R.; Johnson, R.; Rucinski, S.; Pazder, J.; Burley, G.; Walker, A.; Skaret, K.; Zee, R.; et al. The MOST Asteroseismology Mission: Ultraprecise Photometry from Space. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglin, A.; Auvergne, M.; Barge, P.; Deleuil, M.; Catala, C.; Michel, E.; Weiss, W.; COROT Team. Scientific Objectives for a Minisat: CoRoT. In Proceedings of the CoRoT Mission Pre-Launch Status-Stellar Seismology and Planet Finding; Fridlund, M., Baglin, A., Lochard, J., Conroy, L., Eds.; ESA Special Publication: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 1306, p. 33. [Google Scholar]
- Borucki, W.J.; Koch, D.; Basri, G.; Batalha, N.; Brown, T.; Caldwell, D.; Caldwell, J.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Cochran, W.D.; DeVore, E.; et al. Kepler Planet-Detection Mission: Introduction and First Results. Science 2010, 327, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, R.L.; Brown, T.M.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Kjeldsen, H.; Aerts, C.; Appourchaux, T.; Basu, S.; Bedding, T.R.; Chaplin, W.J.; Cunha, M.S.; et al. Kepler Asteroseismology Program: Introduction and First Results. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2010, 122, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.B.; Sobeck, C.; Haas, M.; Still, M.; Barclay, T.; Mullally, F.; Troeltzsch, J.; Aigrain, S.; Bryson, S.T.; Caldwell, D.; et al. The K2 Mission: Characterization and Early Results. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2014, 126, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, G.R.; Winn, J.N.; Vanderspek, R.; Latham, D.W.; Bakos, G.Á.; Bean, J.L.; Berta-Thompson, Z.K.; Brown, T.M.; Buchhave, L.; Butler, N.R.; et al. Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2014: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave; Oschmann, J.M., Jr., Clampin, M., Fazio, G.G., MacEwen, H.A., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9143, p. 914320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauer, H.; Aerts, C.; Cabrera, J.; Deleuil, M.; Erikson, A.; Gizon, L.; Goupil, M.; Heras, A.; Walloschek, T.; Lorenzo-Alvarez, J.; et al. The PLATO mission. Exp. Astron. 2025, 59, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.P.; Mather, J.C.; Abbott, R.; Abell, J.S.; Abernathy, M.; Abney, F.E.; Abraham, J.G.; Abraham, R.; Abul-Huda, Y.M.; Acton, S.; et al. The James Webb Space Telescope Mission. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2023, 135, 068001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodricke, J. A series of observations on, and a discovery of, the period of the variation of the light of the bright star in the head of Medusa, called Algol. In a letter from John Goodricke, Esq. to the Rev. Anthony Shepherd, D. D. F. R. S. and Plumian Professor at Cambridge. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 1783, 73, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prša, A.; Kochoska, A.; Conroy, K.E.; Eisner, N.; Hey, D.R.; IJspeert, L.; Kruse, E.; Fleming, S.W.; Johnston, C.; Kristiansen, M.H.; et al. TESS Eclipsing Binary Stars. I. Short-cadence Observations of 4584 Eclipsing Binaries in Sectors 1-26. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2022, 258, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJspeert, L.W.; Tkachenko, A.; Johnston, C.; Garcia, S.; De Ridder, J.; Van Reeth, T.; Aerts, C. An all-sky sample of intermediate- to high-mass OBA-type eclipsing binaries observed by TESS. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 652, A120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJspeert, L.W.; Tkachenko, A.; Johnston, C.; Aerts, C. Statistical view of orbital circularisation with 14 000 characterised TESS eclipsing binaries. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 691, A242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, V.B.; Powell, B.P.; Fornear, A.U.; Di Fraia, M.Z.; Gagliano, R.; Jacobs, T.L.; de Lambilly, J.S.; Durantini Luca, H.A.; Majewski, S.R.; Omohundro, M.; et al. The TESS Ten Thousand Catalog: 10,001 uniformly-vetted and -validated Eclipsing Binary Stars detected in Full-Frame Image data by machine learning and analyzed by citizen scientists. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.05631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, B.P.; Kostov, V.B.; Rappaport, S.A.; Borkovits, T.; Zasche, P.; Tokovinin, A.; Kruse, E.; Latham, D.W.; Montet, B.T.; Jensen, E.L.N.; et al. TIC 168789840: A Sextuply Eclipsing Sextuple Star System. Astron. J. 2021, 161, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handler, G.; Kurtz, D.W.; Rappaport, S.A.; Saio, H.; Fuller, J.; Jones, D.; Guo, Z.; Chowdhury, S.; Sowicka, P.; Kahraman Aliçavuş, F.; et al. Tidally trapped pulsations in a close binary star system discovered by TESS. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, R.; Rappaport, S.A.; Powell, B.; Handler, G.; Omohundro, M.; Gagliano, R.; Kostov, V.; Fuller, J.; Kurtz, D.W.; Zhang, V.; et al. TIC 435850195: The Second Triaxial Tidally Tilted Pulsator. Astrophys. J. 2024, 975, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chontos, A.; Murphy, J.M.A.; MacDougall, M.G.; Fetherolf, T.; Van Zandt, J.; Rubenzahl, R.A.; Beard, C.; Huber, D.; Batalha, N.M.; Crossfield, I.J.M.; et al. The TESS-Keck Survey: Science Goals and Target Selection. Astron. J. 2022, 163, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, A.S.; Lubin, J.; Beard, C.; Akana Murphy, J.M.; Rubenzahl, R.; Hill, M.L.; Crossfield, I.J.M.; Chontos, A.; Robertson, P.; Isaacson, H.; et al. The TESS-Keck Survey. XX. 15 New TESS Planets and a Uniform RV Analysis of All Survey Targets. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 272, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.T.; Addison, B.C.; Okumura, J.; Vach, S.; Errico, A.; Heitzmann, A.; Rodriguez, J.E.; Wright, D.J.; Clerté, M.; Brown, C.J.; et al. Spinning up a Daze: TESS Uncovers a Hot Jupiter Orbiting the Rapid Rotator TOI-778. Astron. J. 2023, 165, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.A.; Barclay, T.; Schlieder, J.E.; Quintana, E.V.; Hord, B.J.; Kostov, V.B.; Lopez, E.D.; Rowe, J.F.; Hoffman, K.; Walkowicz, L.M.; et al. The First Habitable-zone Earth-sized Planet from TESS. I. Validation of the TOI-700 System. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.A.; Vanderburg, A.; Rodriguez, J.E.; Hord, B.J.; Clement, M.S.; Barclay, T.; Quintana, E.V.; Schlieder, J.E.; Kane, S.R.; Jenkins, J.M.; et al. A Second Earth-sized Planet in the Habitable Zone of the M Dwarf, TOI-700. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 944, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivshina, E.S.; Winn, J.N. TESS Transit Timing of Hundreds of Hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2022, 259, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, G.; Dimitrov, D.; Fernández, M.; Sota, A.; Nowak, G.; Ohlert, J.; Nikolov, G.; Bukowiecki, Ł.; Hinse, T.C.; Pallé, E.; et al. Departure from the constant-period ephemeris for the transiting exoplanet WASP-12. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipping, D.; Solano-Oropeza, D.; Yahalomi, D.A.; Li, M.; Poddar, A.; Zhang, X. Near-circular orbits for planets with Earth-like sizes and instellations around M and K dwarf stars. Nat. Astron. 2025, 9, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernàndez-Carnerero, À.; Sànchez-Marrè, M.; Morales, J.C. Additive Attention for Vetting Transiting Exoplanet Candidates. Astron. J. 2025, 170, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiscale, S.; Inno, L.; Rotundi, A.; Ciaramella, A.; Ferone, A.; Magliano, C.; Cacciapuoti, L.; Kostov, V.; Quintana, E.V.; Covone, G.; et al. DART-Vetter: A Deep Learning Tool for Automatic Triage of Exoplanet Candidates. Astron. J. 2025, 170, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallue, C.J.; Vanderburg, A. Identifying Exoplanets with Deep Learning: A Five-planet Resonant Chain around Kepler-80 and an Eighth Planet around Kepler-90. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadegan, H.; Martinho, M.J.S.; Wilkens, L.S.; Jenkins, J.M.; Smith, J.C.; Caldwell, D.A.; Twicken, J.D.; Gerum, P.C.L.; Walia, N.; Hausknecht, K.; et al. ExoMiner: A Highly Accurate and Explainable Deep Learning Classifier That Validates 301 New Exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, I.L.; Angus, R.; David, T.; Curtis, J.; Hattori, S.; Lu, Y.L. Methods for the Detection of Stellar Rotation Periods in Individual TESS Sectors and Results from the Prime Mission. Astron. J. 2024, 167, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claytor, Z.R.; van Saders, J.L.; Cao, L.; Pinsonneault, M.H.; Teske, J.; Beaton, R.L. TESS Stellar Rotation up to 80 Days in the Southern Continuous Viewing Zone. Astrophys. J. 2024, 962, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.; Gehrels, N.; Baltay, C.; Bennett, D.; Breckinridge, J.; Donahue, M.; Dressler, A.; Gaudi, B.S.; Greene, T.; Guyon, O.; et al. Wide-Field InfrarRed Survey Telescope-Astrophysics Focused Telescope Assets WFIRST-AFTA 2015 Report. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.03757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, Y.; Potravnov, I.; Romanovskaya, A.; Ryabchikova, T. Modeling the TESS Light Curve of Ap Si Star MX TrA. Universe 2024, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samus’, N.N.; Kazarovets, E.V.; Durlevich, O.V.; Kireeva, N.N.; Pastukhova, E.N. General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1. Astron. Rep. 2017, 61, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.; Ramsay, G.; Doyle, J.G. Superflares and variability in solar-type stars with TESS in the Southern hemisphere. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 3596–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, M.N.; Zhan, Z.; Seager, S.; Rimmer, P.B.; Ranjan, S.; Stassun, K.G.; Oelkers, R.J.; Daylan, T.; Newton, E.; Kristiansen, M.H.; et al. Stellar Flares from the First TESS Data Release: Exploring a New Sample of M Dwarfs. Astron. J. 2020, 159, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Meng, G.; Han, X.L.; Misra, P.; Yang, J.; Pi, Q. Properties of flare events based on light curves from the TESS survey. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 669, A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seli, B.; Vida, K.; Oláh, K.; Görgei, A.; Soós, S.; Pál, A.; Kriskovics, L.; Kővári, Z. Stellar flare morphology with TESS across the main sequence. Astron. Astrophys. 2025, 694, A161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazé, Y.; Rauw, G.; Gosset, E. Red noise and pulsations in evolved massive stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 5038–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, A. TESS light curves of cataclysmic variables -II- Superhumps in old novae and novalike variables. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 352–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.B.; Qian, S.B.; Zhu, L.Y.; Dong, A.J.; Zhi, Q.J.; Liao, W.P.; Zhao, E.G.; Han, Z.T.; Liu, W.; Zang, L.; et al. First discovery of quasi-periodic oscillations in the dwarf nova HS 2325+8205 based on TESS photometry. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 518, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch, A. TESS light curves of cataclysmic variables-I-Unknown periods in long-known stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 514, 4718–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallely, P.J.; Fausnaugh, M.; Jha, S.W.; Tucker, M.A.; Eweis, Y.; Shappee, B.J.; Kochanek, C.S.; Stanek, K.Z.; Chen, P.; Dong, S.; et al. ASASSN-18tb: A most unusual Type Ia supernova observed by TESS and SALT. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 2372–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallely, P.J.; Kochanek, C.S.; Stanek, K.Z.; Fausnaugh, M.; Shappee, B.J. High-cadence, early-time observations of core-collapse supernovae from the TESS prime mission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 500, 5639–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygieł, D.M.; Pojmański, G.; Pilecki, B. Galactic Fundamental Mode RR Lyrae Stars. Period-Amplitude Diagram, Metallicities and Distribution. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 59, 137–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaia Collaboration; Brown, A.G.A.; Vallenari, A.; Prusti, T.; de Bruijne, J.H.J.; Babusiaux, C.; Biermann, M.; Creevey, O.L.; Evans, D.W.; Eyer, L.; et al. Gaia Early Data Release 3. Summary of the contents and survey properties. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 649, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, L.; Bódi, A.; Pál, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Hambsch, F.J.; Benkő, J.M.; Derekas, A.; Ebadi, M.; Joyce, M.; Hasanzadeh, A.; et al. First Results on RR Lyrae Stars with the TESS Space Telescope: Untangling the Connections between Mode Content, Colors, and Distances. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2022, 258, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkő, J.M.; Plachy, E.; Netzel, H.; Bódi, A.; Molnár, L.; Pál, A. Time series analysis of bright TESS RRc stars: Additional modes, phase variations, and more. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 521, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalik, P.; Smolec, R.; Kolenberg, K.; Molnár, L.; Kurtz, D.W.; Szabó, R.; Benkő, J.M.; Nemec, J.M.; Chadid, M.; Guggenberger, E.; et al. Kepler photometry of RRc stars: Peculiar double-mode pulsations and period doubling. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 2348–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sódor, Á.; Skarka, M.; Liška, J.; Bognár, Z. KIC 2831097-a 2-yr-orbital-period RR Lyrae binary candidate. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachy, E.; Pál, A.; Bódi, A.; Szabó, P.; Molnár, L.; Szabados, L.; Benkő, J.M.; Anderson, R.I.; Bellinger, E.P.; Bhardwaj, A.; et al. TESS Observations of Cepheid Stars: First Light Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2021, 253, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalski, A.; Szymański, M.K.; Szymański, G. OGLE-IV: Fourth Phase of the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 65, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, J.A.; Kaye, A.B.; Bradley, P.A.; Cox, A.N.; Neuforge, C. Driving the Gravity-Mode Pulsations in γ Doradus Variables. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 542, L57–L60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoci, V.; Cunha, M.S.; Bowman, D.M.; Murphy, S.J.; Kurtz, D.W.; Bedding, T.R.; Borre, C.C.; Christophe, S.; Daszyńska-Daszkiewicz, J.; Fox-Machado, L.; et al. The first view of δ Scuti and γ Doradus stars with the TESS mission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 490, 4040–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balona, L.A.; Dziembowski, W.A. Kepler observations of δ Scuti stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 417, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balona, L.A.; Guzik, J.A.; Uytterhoeven, K.; Smith, J.C.; Tenenbaum, P.; Twicken, J.D. The Kepler view of γ Doradus stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 3531–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.W. 12.15 Minute Light Variations in Przybylski’s Star, HD 101065. Inf. Bull. Var. Stars 1978, 1436, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.M.; Bugnet, L. Asteroseismology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.01715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.J.; Saio, H.; Takada-Hidai, M.; Kurtz, D.W.; Shibahashi, H.; Takata, M.; Hey, D.R. On the first δ Sct-roAp hybrid pulsator and the stability of p and g modes in chemically peculiar A/F stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 4272–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D.L.; Cunha, M.S.; Lares-Martiz, M.; Kurtz, D.W.; Antoci, V.; Barceló Forteza, S.; De Cat, P.; Derekas, A.; Kayhan, C.; Ozuyar, D.; et al. TESS Cycle 2 observations of roAp stars with 2-min cadence data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 9548–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D.L.; Cunha, M.S.; Kurtz, D.W.; Antoci, V.; Hey, D.R.; Bowman, D.M.; Kobzar, O.; Buzasi, D.L.; Kochukhov, O.; Niemczura, E.; et al. TESS cycle 1 observations of roAp stars with 2-min cadence data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, 1073–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.P. Theory of Stellar Pulsation. (PSA-2); Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1980; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Unno, W.; Osaki, Y.; Ando, H.; Saio, H.; Shibahashi, H. Nonradial Oscillations of Stars; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, C.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Kurtz, D.W. Asteroseismology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.d.; Qian, S.b.; Zhu, L.y.; Liu, L.; Li, L.j.; Zang, L. Observational Properties of 155 O- and B-type Massive Pulsating Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 265, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankov, A.; Handler, G. Catalog of Galactic β Cephei Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2005, 158, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigulski, A. Pulsating Stars in the ASAS-3 Database. I. beta Cephei Stars. AIP Conf. Proc. 2005, 55, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, C.I.; Handler, G. β Cephei Pulsators in Eclipsing Binaries Observed with TESS. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 272, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaia Collaboration; De Ridder, J.; Ripepi, V.; Aerts, C.; Palaversa, L.; Eyer, L.; Holl, B.; Audard, M.; Rimoldini, L.; Brown, A.G.A.; et al. Gaia Data Release 3. Pulsations in main sequence OBAF-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 674, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, D.; Aerts, C. Confronting sparse Gaia DR3 photometry with TESS for a sample of around 60000 OBAF-type pulsators. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 688, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzewski, D.J.; Vanrespaille, M.; Aerts, C.; Guo, Z.; Hey, D.; De Ridder, J. Mode identification and ensemble asteroseismology of 119 β Cep stars detected by Gaia light curves and monitored by TESS. Astron. Astrophys. 2025, 698, A253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.H.; Chu, Y.Q.; Li, G.P.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.P.; Su, H.J.; Yao, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Xing, X.Z.; et al. The Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST). Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 12, 1197–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.d.; Qian, S.b.; Zhu, L.y.; Li, L.j. A Catalog of New Slowly Pulsating B-type Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 268, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, W.H.; Miglio, A.; Chaplin, W.J.; Stassun, K.G.; García, R.; González-Cuesta, L.; Mathur, S.; Appourchaux, T.; Benomar, O.; Buzasi, D.L.; et al. Solar-like oscillations and ellipsoidal variations in TESS observations of the binary 12 Boötis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 516, 3709–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, S.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Long, L.; Li, M.; Sun, T.; Ye, L. Detection of Solar-like Oscillations in Subgiant and Red Giant Stars Using 2 minute Cadence TESS Data. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 271, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedding, T.R.; Mosser, B.; Huber, D.; Montalbán, J.; Beck, P.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Elsworth, Y.P.; García, R.A.; Miglio, A.; Stello, D.; et al. Gravity modes as a way to distinguish between hydrogen- and helium-burning red giant stars. Nature 2011, 471, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, E.; Nielsen, M.B.; Chaplin, W.J.; Ball, W.H.; Davies, G.R.; Bedding, T.R.; Buzasi, D.L.; Chontos, A.; Huber, D.; Kayhan, C.; et al. Catalogue of solar-like oscillators observed by TESS in 120-s and 20-s cadence. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 669, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winget, D.E.; Kepler, S.O. Pulsating white dwarf stars and precision asteroseismology. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 157–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córsico, A.H.; Althaus, L.G.; Miller Bertolami, M.M.; Kepler, S.O. Pulsating white dwarfs: New insights. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2019, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, Z.; Kawaler, S.D.; Bell, K.J.; Schrandt, C.; Baran, A.S.; Bradley, P.A.; Hermes, J.J.; Charpinet, S.; Handler, G.; Mullally, S.E.; et al. TESS first look at evolved compact pulsators. Known ZZ Ceti stars of the southern ecliptic hemisphere as seen by TESS. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 638, A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, Z.; Sódor, Á.; Clark, I.R.; Kawaler, S.D. ZZ Ceti stars of the southern ecliptic hemisphere re-observed by TESS. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 674, A204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.D.; Kepler, S.O.; Hermes, J.J.; Amaral, L.A.; Uzundag, M.; Bognár, Z.; Bell, K.J.; VanWyngarden, M.; Baran, A.; Pelisoli, I.; et al. Discovery of 74 new bright ZZ Ceti stars in the first three years of TESS. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 511, 1574–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.D.; Kepler, S.O.; Oliveira da Rosa, G.; Hermes, J.J. Thirty-two New Bright ZZ Ceti Stars from TESS: Adding Cycles 4 and 5. Astrophys. J. 2025, 984, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Tout, C.A.; Chen, X.; Kruckow, M.U.; Chen, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z. The Common Envelope Evolution Outcome-A Case Study on Hot Subdwarf B Stars. Astrophys. J. 2022, 933, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, G.; Brassard, P.; Charpinet, S.; Green, E.M.; Randall, S.K.; Van Grootel, V. A preliminary look at the empirical mass distribution of hot B subdwarf stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 539, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffer, R.A.; Bergeron, P.; Koester, D.; Liebert, J. Atmospheric Parameters of Field Subdwarf B Stars. Astrophys. J. 1994, 432, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.M.; Fontaine, G.; Hyde, E.A.; For, B.Q.; Chayer, P. Systematics of Hot Subdwarfs Obtained from a Large Low Resolution Survey. In Proceedings of the Hot Subdwarf Stars and Related Objects, Bamberg, Germany, 23–27 July 2007; Heber, U., Jeffery, C.S., Napiwotzki, R., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series. Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 392, p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Heber, U. Hot Subdwarf Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 211–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heber, U. Hot Subluminous Stars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2016, 128, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.S.; Van Grootel, V.; Østensen, R.H.; Worters, H.L.; Sahoo, S.K.; Sanjayan, S.; Charpinet, S.; Nemeth, P.; Telting, J.H.; Kilkenny, D. Short-period pulsating hot-subdwarf stars observed by TESS. I. Southern ecliptic hemisphere. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 669, A48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Maxted, P.F.L.; Marsh, T.R.; Ivanova, N. The origin of subdwarf B stars-I. The formation channels. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 336, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Maxted, P.F.L.; Marsh, T.R. The origin of subdwarf B stars-II. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 341, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, B.; Rood, R.T.; O’Connell, R.W. Ultraviolet Radiation from Evolved Stellar Populations. I. Models. Astrophys. J. 1993, 419, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpinet, S.; Fontaine, G.; Brassard, P.; Dorman, B. The Potential of Asteroseismology for Hot, Subdwarf B Stars: A New Class of Pulsating Stars? Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 471, L103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpinet, S.; Fontaine, G.; Brassard, P.; Chayer, P.; Rogers, F.J.; Iglesias, C.A.; Dorman, B. A Driving Mechanism for the Newly Discovered Class of Pulsating Subdwarf B Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1997, 483, L123–L126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, D.; Koen, C.; O’Donoghue, D.; Stobie, R.S. A new class of rapidly pulsating star-I. EC 14026-2647, the class prototype. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 285, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.M.; Fontaine, G.; Reed, M.D.; Callerame, K.; Seitenzahl, I.R.; White, B.A.; Hyde, E.A.; Østensen, R.; Cordes, O.; Brassard, P.; et al. Discovery of A New Class of Pulsating Stars: Gravity-Mode Pulsators among Subdwarf B Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 583, L31–L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Pigulski, A.; Kozieł, D.; Ogłoza, W.; Silvotti, R.; Zoła, S. Multicolour photometry of Balloon 090100001: Linking the two classes of pulsating hot subdwarfs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 360, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, S.; Huber, J.; Dreizler, S.; Heber, U.; O’Toole, S.J.; Green, E.M.; Fontaine, G. HS 0702+6043: A star showing both short-period p-mode and long-period g-mode oscillations. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 445, L31–L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpinet, S.; Brassard, P.; Fontaine, G.; Van Grootel, V.; Zong, W.; Giammichele, N.; Heber, U.; Bognár, Z.; Geier, S.; Green, E.M.; et al. TESS first look at evolved compact pulsators. Discovery and asteroseismic probing of the g-mode hot B subdwarf pulsator EC 21494-7018. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 632, A90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.S.; Charpinet, S.; Østensen, R.H.; Reed, M.D.; Van Grootel, V.; Lyu, C.; Telting, J.H.; Németh, P. Short-period pulsating hot subdwarf stars observed by TESS. II. Northern ecliptic hemisphere. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 686, A65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzundag, M.; Vučković, M.; Németh, P.; Miller Bertolami, M.; Silvotti, R.; Baran, A.S.; Telting, J.H.; Reed, M.; Shoaf, K.A.; Østensen, R.H.; et al. Asteroseismic analysis of variable hot subdwarf stars observed with TESS. I. The mean g-mode period spacings in hot subdwarf B stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 651, A121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzundag, M.; Krzesinski, J.; Pelisoli, I.; Németh, P.; Silvotti, R.; Vučković, M.; Dawson, H.; Geier, S. A comprehensive search for hot subdwarf stars using Gaia and TESS. I. Pulsating hot subdwarf B stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 684, A118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bognár, Z.; Sódor, Á. Selected Results on Variable Stars Observed by TESS. Universe 2025, 11, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11090319
Bognár Z, Sódor Á. Selected Results on Variable Stars Observed by TESS. Universe. 2025; 11(9):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11090319
Chicago/Turabian StyleBognár, Zsófia, and Ádám Sódor. 2025. "Selected Results on Variable Stars Observed by TESS" Universe 11, no. 9: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11090319
APA StyleBognár, Z., & Sódor, Á. (2025). Selected Results on Variable Stars Observed by TESS. Universe, 11(9), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11090319





