Recent Advances in Understanding R-Process Nucleosynthesis in Metal-Poor Stars and Stellar Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Signatures of the r-Process in Stars
3. Astrophysical Sites for the Production of r-Process Elements
3.1. Neutron Star Mergers
3.2. Core-Collapse Supernovae
3.3. Other Sites
4. Astrophysical Environments for Studying the r-Process
4.1. Dwarf Galaxies
4.2. Globular Clusters
4.3. Galactic Stars
5. Looking Ahead
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Recently, the i-process has been suggested to also contribute a portion of the heaviest elements, particularly at the lowest metallicities (see [26] and references therein). |
| 2 | Delayed decay is the process by which unstable, neutron-rich nuclei produced during the r-process undergo decay after neutron flux ceases, transforming into more stable elements and shaping the final abundance pattern. |
| 3 | [Fe/H] = (N(Fe)/N(H))⋆ − (N(Fe)/N(H))⊙, where N(Fe) and N(H) represent the number densities of iron and hydrogen, respectively. [X/Y] = (N(X)/N(Y))⋆ − (N(X)/N(Y))⊙, where N(X) and N(Y) represent the number densities of elements X and Y, respectively. For sun, [Fe/H]⊙ is defined as zero to set a reference point or benchmark. |
References
- Beers, T.C.; Preston, G.W.; Shectman, S.A. A search for stars of very low metal abundance. I. Astron. J. 1985, 90, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, T.C.; Preston, G.W.; Shectman, S.A. A search for stars of very low metal abundance. II. Astron. J. 1992, 103, 1987–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliam, A.; Preston, G.W.; Sneden, C.; Searle, L. Spectroscopic Analysis of 33 of the Most Metal Poor Stars. II. Astron. J. 1995, 109, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, T.C.; Christlieb, N. The Discovery and Analysis of Very Metal-Poor Stars in the Galaxy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 43, 531–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromm, V.; Yoshida, N.; Hernquist, L.; McKee, C.F. The formation of the first stars and galaxies. Nature 2009, 459, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frebel, A.; Norris, J.E. Near-Field Cosmology with Extremely Metal-Poor Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 53, 631–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, J.J.; Sneden, C.; Lawler, J.E.; Aprahamian, A.; Wiescher, M.; Langanke, K.; Martínez-Pinedo, G.; Thielemann, F.K. Origin of the heaviest elements: The rapid neutron-capture process. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2021, 93, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, C.; Karakas, A.I.; Lugaro, M. The Origin of Elements from Carbon to Uranium. Astrophys. J. 2020, 900, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, H.; Reyes, A.D.B.; Best, A.; Brown, E.F.; Chatziioannou, K.; Chipps, K.A.; Deibel, C.M.; Ezzeddine, R.; Galloway, D.K.; Hansen, C.J.; et al. Horizons: Nuclear astrophysics in the 2020s and beyond. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 2022, 49, 110502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christlieb, N. Finding the Most Metal-poor Stars of the Galactic Halo with the Hamburg/ESO Objective-prism Survey (with 6 Figures). Rev. Mod. Astron. 2003, 16, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkenburg, E.; Martin, N.; Youakim, K.; Aguado, D.S.; Allende Prieto, C.; Arentsen, A.; Bernard, E.J.; Bonifacio, P.; Caffau, E.; Carlberg, R.G.; et al. The Pristine survey—I. Mining the Galaxy for the most metal-poor stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 2587–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sivarani, T.; Susmitha, A.; Beers, T.C.; Giridhar, S.; Surya, A.; Masseron, T. Chemical Composition of Two Bright, Extremely Metal-poor Stars from the SDSS MARVELS Pre-survey. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacio, P.; Molaro, P.; Sivarani, T.; Cayrel, R.; Spite, M.; Spite, F.; Plez, B.; Andersen, J.; Barbuy, B.; Beers, T.C.; et al. First stars VII—Lithium in extremely metal poor dwarfs. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 462, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masseron, T.; Johnson, J.A.; Lucatello, S.; Karakas, A.; Plez, B.; Beers, T.C.; Christlieb, N. Lithium Abundances in Carbon-enhanced Metal-poor Stars. Astrophys. J. 2012, 751, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sivarani, T.; Beers, T.C.; Susmitha, A.; Nayak, P.K.; Pandey, J.C. Li Distribution, Kinematics, and Detailed Abundance Analysis among Very Metal-poor Stars in the Galactic Halo from the HESP-GOMPA Survey. Astrophys. J. 2022, 937, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frebel, A. From Nuclei to the Cosmos: Tracing Heavy-Element Production with the Oldest Stars. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2018, 68, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christlieb, N.; Beers, T.C.; Barklem, P.S.; Bessell, M.; Hill, V.; Holmberg, J.; Korn, A.J.; Marsteller, B.; Mashonkina, L.; Qian, Y.Z.; et al. The Hamburg/ESO R-process Enhanced Star survey (HERES). I. Project description, and discovery of two stars with strong enhancements of neutron-capture elements. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 428, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barklem, P.S.; Christlieb, N.; Beers, T.C.; Hill, V.; Bessell, M.S.; Holmberg, J.; Marsteller, B.; Rossi, S.; Zickgraf, F.J.; Reimers, D. The Hamburg/ESO R-process enhanced star survey (HERES). II. Spectroscopic analysis of the survey sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 439, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira Mello, C.; Hill, V.; Barbuy, B.; Spite, M.; Spite, F.; Beers, T.C.; Caffau, E.; Bonifacio, P.; Cayrel, R.; François, P.; et al. High-resolution abundance analysis of very metal-poor r-I stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 565, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.T.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Beers, T.C.; Placco, V.M.; Roederer, I.U.; Frebel, A.; Sakari, C.M.; Simon, J.D.; Thompson, I.B. The R-process Alliance: First Release from the Southern Search for R-process-enhanced Stars in the Galactic Halo. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakari, C.M.; Placco, V.M.; Farrell, E.M.; Roederer, I.U.; Wallerstein, G.; Beers, T.C.; Ezzeddine, R.; Frebel, A.; Hansen, T.; Holmbeck, E.M.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: First Release from the Northern Search for r-process-enhanced Metal-poor Stars in the Galactic Halo. Astrophys. J. 2018, 868, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Frebel, A.; Chiti, A.; Hinojisa, K.; Placco, V.M.; Ji, A.P.; Beers, T.C.; Hansen, T.T.; Roederer, I.U.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: First Magellan/MIKE Release from the Southern Search for R-process-enhanced Stars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmbeck, E.M.; Hansen, T.T.; Beers, T.C.; Placco, V.M.; Whitten, D.D.; Rasmussen, K.C.; Roederer, I.U.; Ezzeddine, R.; Sakari, C.M.; Frebel, A.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: Fourth Data Release from the Search for R-process-enhanced Stars in the Galactic Halo. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2020, 249, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Ezzeddine, R.; Allende Prieto, C.; Aria, N.; Shah, S.P.; Beers, T.C.; Frebel, A.; Hansen, T.T.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Placco, V.M.; et al. The R-process Alliance: Fifth Data Release from the Search for R-process-enhanced Metal-poor Stars in the Galactic Halo with the GTC. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 274, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielemann, F.K.; Eichler, M.; Panov, I.V.; Wehmeyer, B. Neutron Star Mergers and Nucleosynthesis of Heavy Elements. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2017, 67, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choplin, A.; Siess, L.; Goriely, S.; Martinet, S. The intermediate neutron capture process. V. The i-process in AGB stars with overshoot. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 684, A206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration]; [Virgo Collaboration] Estimating the Contribution of Dynamical Ejecta in the Kilonova Associated with GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Hansen, C.J.; Selsing, J.; Koch, A.; Malesani, D.B.; Andersen, A.C.; Fynbo, J.P.U.; Arcones, A.; Bauswein, A.; Covino, S.; et al. Identification of strontium in the merger of two neutron stars. Nature 2019, 574, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmbeck, E.M.; Frebel, A.; McLaughlin, G.C.; Mumpower, M.R.; Sprouse, T.M.; Surman, R. Actinide-rich and Actinide-poor r-process-enhanced Metal-poor Stars Do Not Require Separate r-process Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2019, 881, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sivarani, T.; Beers, T.C. Abundance Analysis of New r-process-enhanced Stars from the HESP–GOMPA Survey. Astrophys. J. 2020, 899, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanajo, S.; Fujibayashi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Actinide-Boosting r Process in Black-Hole–Neutron-Star Merger Ejecta. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 241201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, A.P.; Frebel, A.; Chiti, A.; Simon, J.D. R-process enrichment from a single event in an ancient dwarf galaxy. Nature 2016, 531, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.P.; Frebel, A. From Actinides to Zinc: Using the Full Abundance Pattern of the Brightest Star in Reticulum II to Distinguish between Differentr-process Sites. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.P.; Simon, J.D.; Roederer, I.U.; Magg, E.; Frebel, A.; Johnson, C.I.; Klessen, R.S.; Magg, M.; Cescutti, G.; Mateo, M.; et al. Metal Mixing in the r-process Enhanced Ultrafaint Dwarf Galaxy Reticulum II. Astron. J. 2023, 165, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmerer, J.; Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Collier, J.; Woolf, V.M.; Lawler, J.E. The Rise of the s-Process in the Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2004, 617, 1091–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Gallino, R. Neutron-capture elements in the early galaxy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 241–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Beniamini, P.; Piran, T. Neutron star mergers as sites of r-process nucleosynthesis and short gamma-ray bursts. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2018, 27, 1842005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.C.; Bessell, M.S.; Frebel, A.; Casey, A.R.; Asplund, M.; Jacobson, H.R.; Lind, K.; Norris, J.E.; Yong, D.; Heger, A.; et al. A single low-energy, iron-poor supernova as the source of metals in the star SMSS J031300.36-670839.3. Nature 2014, 506, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Ivans, I.I.; Fuller, G.M.; Burles, S.; Beers, T.C.; Lawler, J.E. Evidence of Multiple R-Process Sites in the Early Galaxy: New Observations of CS 22892-052. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 533, L139–L142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrel, R.; Hill, V.; Beers, T.C.; Barbuy, B.; Spite, M.; Spite, F.; Plez, B.; Andersen, J.; Bonifacio, P.; François, P.; et al. Measurement of stellar age from uranium decay. Nature 2001, 409, 691–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frebel, A.; Johnson, J.L.; Bromm, V. Probing the formation of the first low-mass stars with stellar archaeology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 380, L40–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M.; Frebel, A.; Ji, A.P.; Placco, V.M.; Ezzeddine, R.; Roederer, I.U.; Hattori, K.; Beers, T.C.; Meléndez, J.; Hansen, T.T.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: A Very Metal-poor, Extremely r-process-enhanced Star with [Eu/Fe] = +2.2, and the Class of r-III Stars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Beers, T.C.; Hattori, K.; Placco, V.M.; Hansen, T.T.; Ezzeddine, R.; Frebel, A.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Sakari, C.M. The R-Process Alliance: 2MASS J22132050–5137385, the Star with the Highest-known r-process Enhancement at [Eu/Fe] = +2.45. Astrophys. J. 2024, 971, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, Y.; Beers, T.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Wanajo, S.; Roederer, I.U.; Tanaka, M.; Chiba, M.; Saitoh, T.R.; Placco, V.M.; Hansen, T.T.; et al. The -process Alliance: Enrichment of R-process Elements in a Simulated Milky Way-like Galaxy. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.11943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.T.; Andersen, J.; Nordström, B.; Beers, T.C.; Yoon, J.; Buchhave, L.A. The role of binaries in the enrichment of the early Galactic halo. I. r-process-enhanced metal-poor stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 583, A49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hill, V.; Plez, B.; Cayrel, R.; Beers, T.C.; Nordström, B.; Andersen, J.; Spite, M.; Spite, F.; Barbuy, B.; Bonifacio, P.; et al. First stars. I. The extreme r-element rich, iron-poor halo giant CS 31082-001. Implications for the r-process site(s) and radioactive cosmochronology. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 387, 560–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashonkina, L.; Christlieb, N.; Eriksson, K. The Hamburg/ESO R-process Enhanced Star survey (HERES). X. HE 2252-4225, one more r-process enhanced and actinide-boost halo star. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmbeck, E.M.; Beers, T.C.; Roederer, I.U.; Placco, V.M.; Hansen, T.T.; Sakari, C.M.; Sneden, C.; Liu, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Cowan, J.J.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: 2MASS J09544277+5246414, the Most Actinide-enhanced R-II Star Known. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 859, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placco, V.M.; Almeida-Fernandes, F.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Roederer, I.U.; Mardini, M.K.; Hayes, C.R.; Venn, K.; Chiboucas, K.; Deibert, E.; Gamen, R.; et al. SPLUS J142445.34-254247.1: An r-process-enhanced, Actinide-boost, Extremely Metal-poor Star Observed with GHOST. Astrophys. J. 2023, 959, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Vassh, N.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Mumpower, M.R.; Surman, R.; Cowan, J.J.; Beers, T.C.; Ezzeddine, R.; Frebel, A.; Hansen, T.T.; et al. Element abundance patterns in stars indicate fission of nuclei heavier than uranium. Science 2023, 382, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielemann, F.K.; Arcones, A.; Käppeli, R.; Liebendörfer, M.; Rauscher, T.; Winteler, C.; Fröhlich, C.; Dillmann, I.; Fischer, T.; Martinez-Pinedo, G.; et al. What are the astrophysical sites for the r-process and the production of heavy elements? Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2011, 66, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Shigeyama, T. The Origins of Light and Heavy R-process Elements Identified by Chemical Tagging of Metal-poor Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 795, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Beers, T.C.; Ezzeddine, R.; Sivarani, T.; Nayak, P.K.; Pandey, J.C.; Saraf, P.; Susmitha, A. A chemodynamical analysis of bright metal-poor stars from the HESP-GOMPA survey—Indications of a non-prevailing site for light r-process elements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 529, 2191–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, M.; Karakas, A.I.; Stancliffe, R.J.; Meyer, B.S.; Lugaro, M. Learning about the Intermediate Neutron-capture Process from Lead Abundances*. Astrophys. J. 2019, 887, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Simon, J.D.; Contreras, C.; Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Morrell, N.; et al. Light curves of the neutron star merger GW170817/SSS17a: Implications for r-process nucleosynthesis. Science 2017, 358, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, A.; Radice, D.; Bernuzzi, S. AT 2017gfo: An Anisotropic and Three-component Kilonova Counterpart of GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shappee, B.J.; Simon, J.D.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Morrell, N.; Prieto, J.L.; Kasen, D.; Holoien, T.W.S.; Kollmeier, J.A.; Kelson, D.D.; et al. Early spectra of the gravitational wave source GW170817: Evolution of a neutron star merger. Science 2017, 358, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmbeck, E.M.; Andrews, J.J. Total r-process Yields of Milky Way Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2024, 963, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Metzger, B.D. Three-Dimensional General-Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Remnant Accretion Disks from Neutron Star Mergers: Outflows and r-Process Nucleosynthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 231102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehmeyer, B.; Fröhlich, C.; Côté, B.; Pignatari, M.; Thielemann, F.K. Using failed supernovae to constrain the Galactic r-process element production. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.F.; Lippuner, J.; Duez, M.D.; Faber, J.A.; Foucart, F.; Lombardi, J.C., Jr.; Ning, S.; Ott, C.D.; Ponce, M. The influence of neutrinos on r-process nucleosynthesis in the ejecta of black hole-neutron star mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 3907–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Wanajo, S.; Prantzos, N. Neutron Star Mergers as the Origin of r-process Elements in the Galactic Halo Based on the Sub-halo Clustering Scenario. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 804, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoz, D.; Nakar, E. The Neutron Star Merger Delay-time Distribution, R-process “Knees,” and the Metal Budget of the Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2025, 982, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, C.; Mandel, I.; Belczynski, K.; Goriely, S.; Janka, T.H.; Just, O.; Ruiter, A.J.; Vanbeveren, D.; Kruckow, M.U.; Briel, M.M.; et al. Can Neutron Star Mergers Alone Explain the r-process Enrichment of the Milky Way? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 943, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levan, A.J.; Gompertz, B.P.; Salafia, O.S.; Bulla, M.; Burns, E.; Hotokezaka, K.; Izzo, L.; Lamb, G.P.; Malesani, D.B.; Oates, S.R.; et al. Heavy-element production in a compact object merger observed by JWST. Nature 2024, 626, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Li, L.X.; Chen, Q.H.; Hu, R.C.; Liang, E.W. Neutron star mergers as the dominant contributor to the production of heavy r-process elements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc 2024, 529, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbidge, E.M.; Burbidge, G.R.; Fowler, W.A.; Hoyle, F. Synthesis of the Elements in Stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1957, 29, 547–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.G.W. Nuclear Reactions in Stars and Nucleogenesis. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1957, 69, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliam, A. Barium Abundances in Extremely Metal-poor Stars. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Takiwaki, T.; Thielemann, F.K. The r-process Nucleosynthesis in the Various Jet-like Explosions of Magnetorotational Core-collapse Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibagaki, S.; Kajino, T.; Mathews, G.J.; Chiba, S.; Nishimura, S.; Lorusso, G. Relative Contributions of the Weak, Main, and Fission-recycling r-process. Astrophys. J. 2016, 816, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Sawai, H.; Takiwaki, T.; Yamada, S.; Thielemann, F.K. The Intermediate r-process in Core-collapse Supernovae Driven by the Magneto-rotational Instability. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 836, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, B.; Roberts, L.F. Proto-neutron star convection and the neutrino-driven wind: Implications for the r-process. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 520, 3986–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Röpke, F.K.; Fryer, C.; Ruiter, A.J.; Seitenzahl, I.R.; Nittler, L.R.; Ohlmann, S.T.; Reifarth, R.; Pignatari, M.; Belczynski, K. Remnants and ejecta of thermonuclear electron-capture supernovae—Constraining oxygen-neon deflagrations in high-density white dwarfs. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, A74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Röpke, F.K.; Pakmor, R.; Seitenzahl, I.R.; Ohlmann, S.T.; Edelmann, P.V.F. Do electron-capture supernovae make neutron stars?—First multidimensional hydrodynamic simulations of the oxygen deflagration. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 593, A72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouqi, K.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Rosswog, S.; Kratz, K.-L. Correlations of r-process elements in very metal-poor stars as clues to their nucleosynthesis sites. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 663, A70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; O’Connor, E.P.; Couch, S.M.; Leung, S.C.; Nomoto, K. Hydrodynamic simulations of electron-capture supernovae: Progenitor and dimension dependence. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 513, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Parthasarathy, M. The r- and s- process nuclei in the early history of the galaxy: HD 122563. Astrophys. J. 1983, 267, 757–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, S.; Aoki, W.; Ishimaru, Y.; Wanajo, S.; Ryan, S.G. Neutron-Capture Elements in the Very Metal Poor Star HD 122563. Astrophys. J. 2006, 643, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xylakis-Dornbusch, T.; Hansen, T.T.; Beers, T.C.; Christlieb, N.; Ezzeddine, R.; Frebel, A.; Holmbeck, E.; Placco, V.M.; Roederer, I.U.; Sakari, C.M.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: Analysis of limited-r stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 688, A123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, A.R.; Schlaufman, K.C. The Universality of the Rapid Neutron-capture Process Revealed by a Possible Disrupted Dwarf Galaxy Star. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcones, A.; Montes, F. Production of Light-element Primary Process Nuclei in Neutrino-driven Winds. Astrophys. J. 2011, 731, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumpower, M.R.; Jaffke, P.; Verriere, M.; Randrup, J. Primary fission fragment mass yields across the chart of nuclides. Phys. Rev. C 2020, 101, 054607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Burrows, A. Supernova Explosions of the Lowest-mass Massive Star Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2024, 969, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.; Obergaulinger, M.; Aloy, M.Á.; Gabler, M.; Arcones, A.; Thielemann, F.K. Magnetorotational supernovae: A nucleosynthetic analysis of sophisticated 3D models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 518, 1557–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Müller, B.; Powell, J. Nucleosynthesis in the Innermost Ejecta of Magnetorotational Supernova Explosions in Three Dimensions. Astrophys. J. 2024, 969, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Sprouse, T.M.; Fryer, C.L.; Ryan, B.R.; Dolence, J.C.; Mumpower, M.R.; Surman, R. Full Transport General Relativistic Radiation Magnetohydrodynamics for Nucleosynthesis in Collapsars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.; Metzger, B.D. Signatures of r-process Enrichment in Supernovae from Collapsars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 939, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Barnes, J.; Metzger, B.D. Collapsars as a major source of r-process elements. Nature 2019, 569, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abohalima, A.; Frebel, A. JINAbase—A Database for Chemical Abundances of Metal-poor Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 238, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescutti, G.; Chiappini, C.; Hirschi, R.; Meynet, G.; Frischknecht, U. The s-process in the Galactic halo: The fifth signature of spinstars in the early Universe? Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantzos, N.; Abia, C.; Limongi, M.; Chieffi, A.; Cristallo, S. Chemical evolution with rotating massive star yields—I. The solar neighbourhood and the s-process elements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 3432–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frebel, A.; Ji, A.P. Observations of R-Process Stars in the Milky Way and Dwarf Galaxies. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.09188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, J.J.; Rose, W.K. Production of C-14 and neutrons in red giants. Astrophys. J. 1977, 212, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissenkov, P.A.; Herwig, F.; Woodward, P.; Andrassy, R.; Pignatari, M.; Jones, S. The i-process yields of rapidly accreting white dwarfs from multicycle He-shell flash stellar evolution models with mixing parametrizations from 3D hydrodynamics simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 4258–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Beers, T.C.; Placco, V.M.; Rasmussen, K.C.; Carollo, D.; He, S.; Hansen, T.T.; Roederer, I.U.; Zeanah, J. Observational Constraints on First-star Nucleosynthesis. I. Evidence for Multiple Progenitors of CEMP-No Stars. Astrophys. J. 2016, 833, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnachie, A.W. The Observed Properties of Dwarf Galaxies in and around the Local Group. Astron. J. 2012, 144, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.D. The Faintest Dwarf Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 375–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnachie, A.W.; Venn, K.A. Revised and New Proper Motions for Confirmed and Candidate Milky Way Dwarf Galaxies. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drlica-Wagner, A.; Bechtol, K.; Mau, S.; McNanna, M.; Nadler, E.O.; Pace, A.B.; Li, T.S.; Pieres, A.; Rozo, E.; Simon, J.D.; et al. Milky Way Satellite Census. I. The Observational Selection Function for Milky Way Satellites in DES Y3 and Pan-STARRS DR1. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.L.; Hansen, T.; Simon, J.D.; Li, T.S.; Bernstein, R.A.; Kuehn, K.; Pace, A.B.; DePoy, D.L.; Palmese, A.; Pieres, A.; et al. Chemical Abundance Analysis of Tucana III, the Second r-process Enhanced Ultra-faint Dwarf Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2019, 882, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.; Hansen, C.J.; Arcones, A. Extreme r-process Enhanced Stars at High Metallicity in Fornax*. Astrophys. J. 2021, 912, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchesi, R.; Jablonka, P.; Skúladóttir, Á.; Lardo, C.; Mashonkina, L.; Primas, F.; Venn, K.; Hill, V.; Minniti, D. Extremely metal-poor stars in the Fornax and Carina dwarf spheroidal galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 686, A266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, Y.; Saitoh, T.R.; Fujii, M.S.; Kaneko, K.; Beers, T.C. SIRIUS: Identifying Metal-poor Stars Enriched by a Single Supernova in a Dwarf Galaxy Cosmological Zoom-in Simulation Resolving Individual Massive Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2025, 980, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, R.P. On the nonhomogeneity of metal abundances in stars of globular clusters and satellite subsystems of the Galaxy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 17, 309–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.C. Evidence from sodium-abundance variations among red giants of M13 for inhomogeneities in the protocluster gas. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1980, 237, L87–L91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, R.P.; Sneden, C.; Smith, G.H.; Shetrone, M.D.; Langer, G.E.; Pilachowski, C.A. Proton Capture Chains in Globular Cluster Stars.II.Oxygen, Sodium, Magnesium, and Aluminum Abundances in M13 Giants Brighter Than the Horizontal Branch. Astron. J. 1997, 113, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, R.; Sneden, C.; Carretta, E. Abundance Variations Within Globular Clusters. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 42, 385–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, R.G.; Carretta, E.; Bragaglia, A. Multiple populations in globular clusters. Lessons learned from the Milky Way globular clusters. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2012, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, R.; Bragaglia, A.; Carretta, E.; D’Orazi, V.; Lucatello, S.; Sollima, A. What is a globular cluster? An observational perspective. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2019, 27, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, E.; Bragaglia, A.; Gratton, R.; Lucatello, S. Na-O anticorrelation and HB. VIII. Proton-capture elements and metallicities in 17 globular clusters from UVES spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 505, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, E.; Bragaglia, A.; Gratton, R.G.; Lucatello, S.; Catanzaro, G.; Leone, F.; Bellazzini, M.; Claudi, R.; D’Orazi, V.; Momany, Y.; et al. Na-O anticorrelation and HB. VII. The chemical composition of first and second-generation stars in 15 globular clusters from GIRAFFE spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 505, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotto, G. Observations of multiple populations in star clusters. In Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union, Volume 4, Symposium S258: The Ages of Stars; Mamajek, E.E., Soderblom, D.R., Wyse, R.F.G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; Volume 258, pp. 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, A.P.; Piotto, G.; Renzini, A.; Marino, A.F.; Bedin, L.R.; Vesperini, E.; D’Antona, F.; Nardiello, D.; Anderson, J.; King, I.R.; et al. The Hubble Space Telescope UV Legacy Survey of Galactic globular clusters—IX. The Atlas of multiple stellar populations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 464, 3636–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, A.P.; Marino, A.F.; Da Costa, G.S.; Lagioia, E.P.; D’Antona, F.; Goudfrooij, P.; Jerjen, H.; Massari, D.; Renzini, A.; Yong, D.; et al. Multiple populations in globular clusters and their parent galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 491, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, A.P.; Marino, A.F. Multiple Populations in Star Clusters. Universe 2022, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Kraft, R.P.; Shetrone, M.D.; Smith, G.H.; Langer, G.E.; Prosser, C.F. Star-To-Star Abundance Variations Among Bright Giants in the Metal-Poor Globular Cluster M15. Astron. J. 1997, 114, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Johnson, J.; Kraft, R.P.; Smith, G.H.; Cowan, J.J.; Bolte, M.S. Neutron-Capture Element Abundances in the Globular Cluster M15. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 536, L85–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, K.; Honda, S.; Aoki, W.; Kajino, T.; Mathews, G.J. Neutron-Capture Elements in the Metal-poor Globular Cluster M15. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 641, L117–L120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobeck, J.S.; Kraft, R.P.; Sneden, C.; Preston, G.W.; Cowan, J.J.; Smith, G.H.; Thompson, I.B.; Shectman, S.A.; Burley, G.S. The Abundances of Neutron-capture Species in the Very Metal-poor Globular Cluster M15: A Uniform Analysis of Red Giant Branch and Red Horizontal Branch Stars. Astron. J. 2011, 141, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, C.C.; Hill, V.; Sobeck, J.; Carretta, E. Ba and Eu abundances in M 15 giant stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Shigeyama, T. Enrichment history of r-process elements shaped by a merger of neutron star pairs. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 565, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.N.; Duggan, G.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Macias, P. The Stars in M15 Were Born with the r-process. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 891, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarumi, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Inoue, S. Internal R-process Abundance Spread of M15 and a Single Stellar Population Model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 921, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Sneden, C. Heavy-element Dispersion in the Metal-poor Globular Cluster M92. Astron. J. 2011, 142, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Thirupathi, S.; Beers, T.C.; Susmitha, A. A high-resolution spectroscopic study of two new Na- and Al-rich field giants–likely globular cluster escapees in the Galactic halo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.G. No Heavy-element Dispersion in the Globular Cluster M92. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 740, L38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Thompson, I.B. Detailed abundances of 15 stars in the metal-poor globular cluster NGC 4833. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 3889–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.N.; Ji, A.P.; Kovalev, M. r-process Abundance Patterns in the Globular Cluster M92. Astrophys. J. 2023, 958, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera Garcia, J.; Sakari, C.M.; Roederer, I.U.; Evans, D.W.; Silva, P.; Mateo, M.; Song, Y.Y.; Kremin, A.; Bailey, J.I.; Walker, M.G. Abundances of Neutron-capture Elements in 62 Stars in the Globular Cluster Messier 15. Astrophys. J. 2024, 967, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Ezzeddine, R.; Placco, V.M.; Frebel, A.; Aguado, D.S.; Roederer, I.U. Probing Abundance Variations among Multiple Stellar Populations in the Metal-Poor Globular Cluster NGC 2298 using Gemini-South/GHOST. Astron. J. 2025, 170, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, R.; Griffin, R.; Gustafsson, B.; Vieira, T. HD 115444—A Barium star of extreme population II. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1982, 198, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alencastro Puls, A.; Kuske, J.; Hansen, C.J.; Lombardo, L.; Visentin, G.; Arcones, A.; Fernandes de Melo, R.; Reichert, M.; Bonifacio, P.; Caffau, E.; et al. Chemical Evolution of R-process Elements in Stars (CERES): IV. An observational run-up of the third r-process peak with Hf, Os, Ir, and Pt. Astron. Astrophys. 2025, 693, A294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Lawler, J.E.; Den Hartog, E.A.; Placco, V.M.; Surman, R.; Beers, T.C.; Ezzeddine, R.; Frebel, A.; Hansen, T.T.; Hattori, K.; et al. The R-process Alliance: A Nearly Complete R-process Abundance Template Derived from Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of the R-process-enhanced Metal-poor Star HD 222925. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2022, 260, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaia Collaboration; Prusti, T.; de Bruijne, J.H.J.; Brown, A.G.A.; Vallenari, A.; Babusiaux, C.; Bailer-Jones, C.A.L.; Bastian, U.; Biermann, M.; Evans, D.W.; et al. The Gaia mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Hattori, K.; Valluri, M. Kinematics of Highly r-process-enhanced Field Stars: Evidence for an Accretion Origin and Detection of Several Groups from Disrupted Satellites. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudin, D.; Shank, D.; Beers, T.C.; Yuan, Z.; Limberg, G.; Roederer, I.U.; Placco, V.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Dietz, S.; Rasmussen, K.C.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: Chemodynamically Tagged Groups of Halo r-process-enhanced Stars Reveal a Shared Chemical-evolution History. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Okuno, A.; Roederer, I.U. Finding r-II Sibling Stars in the Milky Way with the Greedy Optimistic Clustering Algorithm. Astrophys. J. 2023, 946, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, D.; Beers, T.C.; Placco, V.M.; Gudin, D.; Catapano, T.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Ezzeddine, R.; Roederer, I.U.; Sakari, C.M.; Frebel, A.; et al. The R-Process Alliance: Chemodynamically Tagged Groups. II. An Extended Sample of Halo r-process-enhanced Stars. Astrophys. J. 2023, 943, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berczik, P.; Ishchenko, M.; Sobodar, O.; Mardini, M. Cosmological insights into the early accretion of r-process-enhanced stars: II. Dynamical identification of lost members of Reticulum II. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 692, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.J.; Shi, J.; Yan, H.L.; Chen, T.Y.; Allende Prieto, C.; Beers, T.C.; Liu, S.; Li, C.Q.; Ding, M.Y.; Tang, Y.J.; et al. Discovery of an Extremely r-process-enhanced Thin-disk Star with [Eu/H] = +0.78. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 970, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Lawler, J.E.; Burles, S.; Beers, T.C.; Fuller, G.M. Europium Isotopic Abundances in Very Metal Poor Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 566, L25–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aoki, W.; Honda, S.; Beers, T.C.; Sneden, C. Measurement of the Europium Isotope Ratio for the Extremely Metal poor, r-Process-enhanced Star CS 31082-001. Astrophys. J. 2003, 586, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, A.J.; Ryan, S.G.; Hosford, A.; García Pérez, A.E.; Aoki, W.; Honda, S. The barium isotopic fractions in five metal-poor stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.P.; Koposov, S.E.; Allende Prieto, C.; Manser, C.J.; Kizhuprakkat, N.; Myers, A.D.; Dey, A.; Gänsicke, B.T.; Li, T.S.; Rockosi, C.; et al. Overview of the DESI Milky Way Survey. Astrophys. J. 2023, 947, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, R.S.; Agertz, O.; Berbel, A.A.; Aird, J.; Alexander, D.A.; Amarsi, A.; Anders, F.; Andrae, R.; Ansarinejad, B.; Ansorge, W.; et al. 4MOST: Project overview and information for the First Call for Proposals. Messenger 2019, 175, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Trager, S.C.; Dalton, G.B.; Aguerri, J.A.L.; Drew, J.E.; Falcón-Barroso, J.; Gänsicke, B.T.; Hill, V.; Iovino, A.; Pieri, M.M.; et al. The wide-field, multiplexed, spectroscopic facility WEAVE: Survey design, overview, and simulated implementation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 530, 2688–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, M.; Ellis, R.S.; Chiba, M.; Greene, J.E.; Aihara, H.; Arimoto, N.; Bundy, K.; Cohen, J.; Doré, O.; Graves, G.; et al. Extragalactic science, cosmology, and Galactic archaeology with the Subaru Prime Focus Spectrograph. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 66, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, O.A.; Mucciarelli, A.; Origlia, L.; Schultheis, M.; Caffau, E.; Di Matteo, P.; Randich, S.; Recio-Blanco, A.; Zoccali, M.; Bonifacio, P.; et al. MOONS Surveys of the Milky Way and its Satellites. Messenger 2020, 180, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, C.; Wolf, C.; Onken, C.A.; Beers, T.C.; Casagrande, L.; Mackey, D.; Da Costa, G.S.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; et al. Milky Way Tomography with the SkyMapper Southern Survey. II. Photometric Recalibration of SMSS DR2. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Beers, T.C.; Wolf, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Onken, C.A.; Yuan, H.; Shank, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Shi, J.; et al. Beyond Spectroscopy. I. Metallicities, Distances, and Age Estimates for Over 20 Million Stars from SMSS DR2 and Gaia EDR3. Astrophys. J. 2022, 925, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yuan, H.; Niu, Z.; Yang, L.; Beers, T.C.; Huang, Y. Stellar Loci. V. Photometric Metallicities of 27 Million FGK Stars Based on Gaia Early Data Release 3. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2022, 258, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, H.; Xiang, M.; Duan, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Beers, T.C.; Galarza, C.A.; Daflon, S.; Fernández-Ontiveros, J.A.; et al. J-PLUS: Stellar parameters, C, N, Mg, Ca, and [α/Fe] abundances for two million stars from DR1. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 659, A181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Beers, T.C.; Yuan, H.; Tan, K.F.; Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Li, H.N.; Zhao, J.K.; et al. Beyond Spectroscopy. II. Stellar Parameters for over 20 Million Stars in the Northern Sky from SAGES DR1 and Gaia DR3. Astrophys. J. 2023, 957, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Yuan, H.; López-Sanjuan, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, B.; Beers, T.C.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Alcaniz, J.; et al. J-PLUS: Photometric Recalibration with the Stellar Color Regression Method and an Improved Gaia XP Synthetic Photometry Method. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 269, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Beers, T.C.; Xiao, K.; Yuan, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Gu, H.; Hong, J.; Liu, J.; Fan, Z.; Coelho, P.; et al. J-PLUS: Beyond Spectroscopy. III. Stellar Parameters and Elemental-abundance Ratios for Five Million Stars from DR3. Astrophys. J. 2024, 974, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yuan, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, K.; Huang, Y.; Beers, T.C.; Hong, J. Stellar Loci. VII. Photometric Metallicities of 5 Million FGK Stars Based on GALEX GR6+7 AIS and Gaia EDR3. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 271, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Beers, T.C.; Huang, B.; Xu, S.; Yang, L.; Almeida-Fernandes, F.; Perottoni, H.D.; Limberg, G.; et al. S-PLUS: Photometric Recalibration with the Stellar Color Regression Method and an Improved Gaia XP Synthetic Photometry Method. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2024, 271, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, G.; Yang, H.; Beers, T.C.; Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. The Stellar Abundances and Galactic Evolution Survey (SAGES). II. Machine Learning–based Stellar Parameters for 21 Million Stars from the First Data Release. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2025, 277, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Beers, T.C. Stellar Parameters for over 50 Million Stars from SMSS DR4 and Gaia DR3. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2025, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, Y.; Beers, T.C.; Xiao, K.; Liu, J.; Jia, L.; Han, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. Photometric Stellar Parameters for 195,478 Kepler Input Catalog Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2025, 277, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W.; Fan, Z.; Tan, K.F.; Li, C.; Zuo, F. The SAGE photometric survey: Technical description. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, H.; Tan, K.; et al. The Stellar Abundances and Galactic Evolution Survey (SAGES). I. General Description and the First Data Release (DR1). Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 268, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.C.; Schmidt, B.P.; Bessell, M.S.; Conroy, P.G.; Francis, P.; Granlund, A.; Kowald, E.; Oates, A.P.; Martin-Jones, T.; Preston, T.; et al. The SkyMapper Telescope and The Southern Sky Survey. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2007, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onken, C.A.; Wolf, C.; Bessell, M.S.; Chang, S.W.; Luvaul, L.C.; Tonry, J.L.; White, M.C.; Da Costa, G.S. SkyMapper Southern Survey: Data release 4. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2024, 41, e061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes de Oliveira, C.; Ribeiro, T.; Schoenell, W.; Kanaan, A.; Overzier, R.A.; Molino, A.; Sampedro, L.; Coelho, P.; Barbosa, C.E.; Cortesi, A.; et al. The Southern Photometric Local Universe Survey (S-PLUS): Improved SEDs, morphologies, and redshifts with 12 optical filters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 241–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenarro, A.J.; Moles, M.; Cristóbal-Hornillos, D.; Marín-Franch, A.; Ederoclite, A.; Varela, J.; López-Sanjuan, C.; Hernández-Monteagudo, C.; Angulo, R.E.; Vázquez Ramió, H.; et al. J-PLUS: The Javalambre Photometric Local Universe Survey. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 622, A176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perottoni, H.D.; Placco, V.M.; Almeida-Fernandes, F.; Herpich, F.R.; Rossi, S.; Beers, T.C.; Smiljanic, R.; Amarante, J.A.S.; Limberg, G.; Werle, A.; et al. The S-PLUS Ultra-Short Survey: First data release. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 691, A138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoli, S.; Marín-Franch, A.; Varela, J.; Vázquez Ramió, H.; Abramo, L.R.; Cenarro, A.J.; Dupke, R.A.; Vílchez, J.M.; Cristóbal-Hornillos, D.; González Delgado, R.M.; et al. The miniJPAS survey: A preview of the Universe in 56 colors. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 653, A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.O.; Chiti, A.; Limberg, G.; Pace, A.; Cerny, W.; Rossi, S.; Carlin, J.L.; Stringfellow, G.; Placco, V.; Atzerberg, K.; et al. The DECam MAGIC Survey: A Wide-field Photometric Metallicity Study of the Sculptor Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.03593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LSST Science Collaboration; Abell, P.A.; Allison, J.; Anderson, S.F.; Andrew, J.R.; Angel, J.R.P.; Armus, L.; Arnett, D.; Asztalos, S.J.; Axelrod, T.S.; et al. LSST Science Book, Version 2.0. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0912.0201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezić, Ž.; Kahn, S.M.; Tyson, J.A.; Abel, B.; Acosta, E.; Allsman, R.; Alonso, D.; AlSayyad, Y.; Anderson, S.F.; Andrew, J.; et al. LSST: From Science Drivers to Reference Design and Anticipated Data Products. Astrophys. J. 2019, 873, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumpower, M.R.; Surman, R.; McLaughlin, G.C.; Aprahamian, A. The impact of individual nuclear properties on r-process nucleosynthesis. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2016, 86, 86–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, C.J. Neutron rich matter in the laboratory and in the heavens after GW170817. Ann. Phys. 2019, 411, 167992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
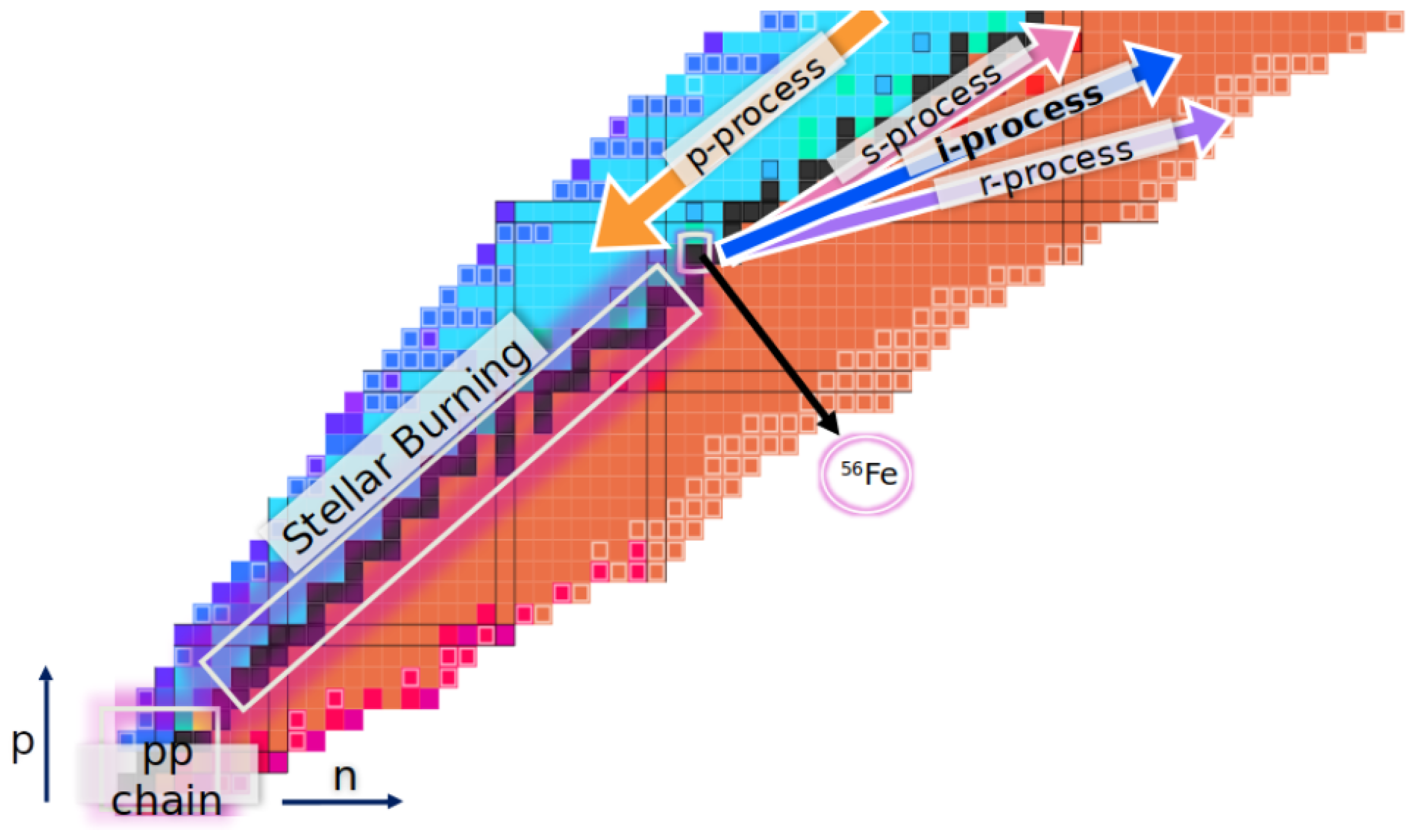
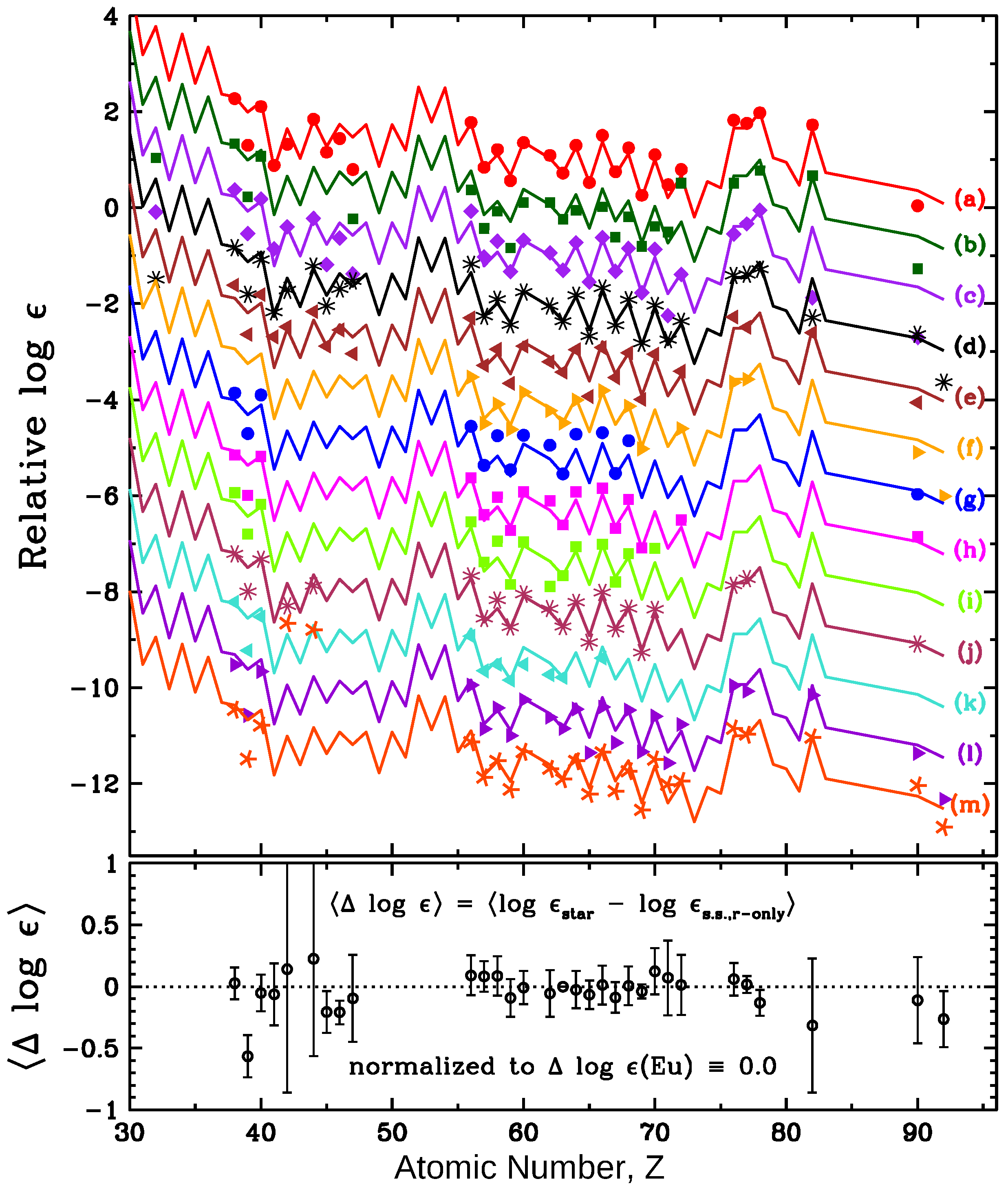

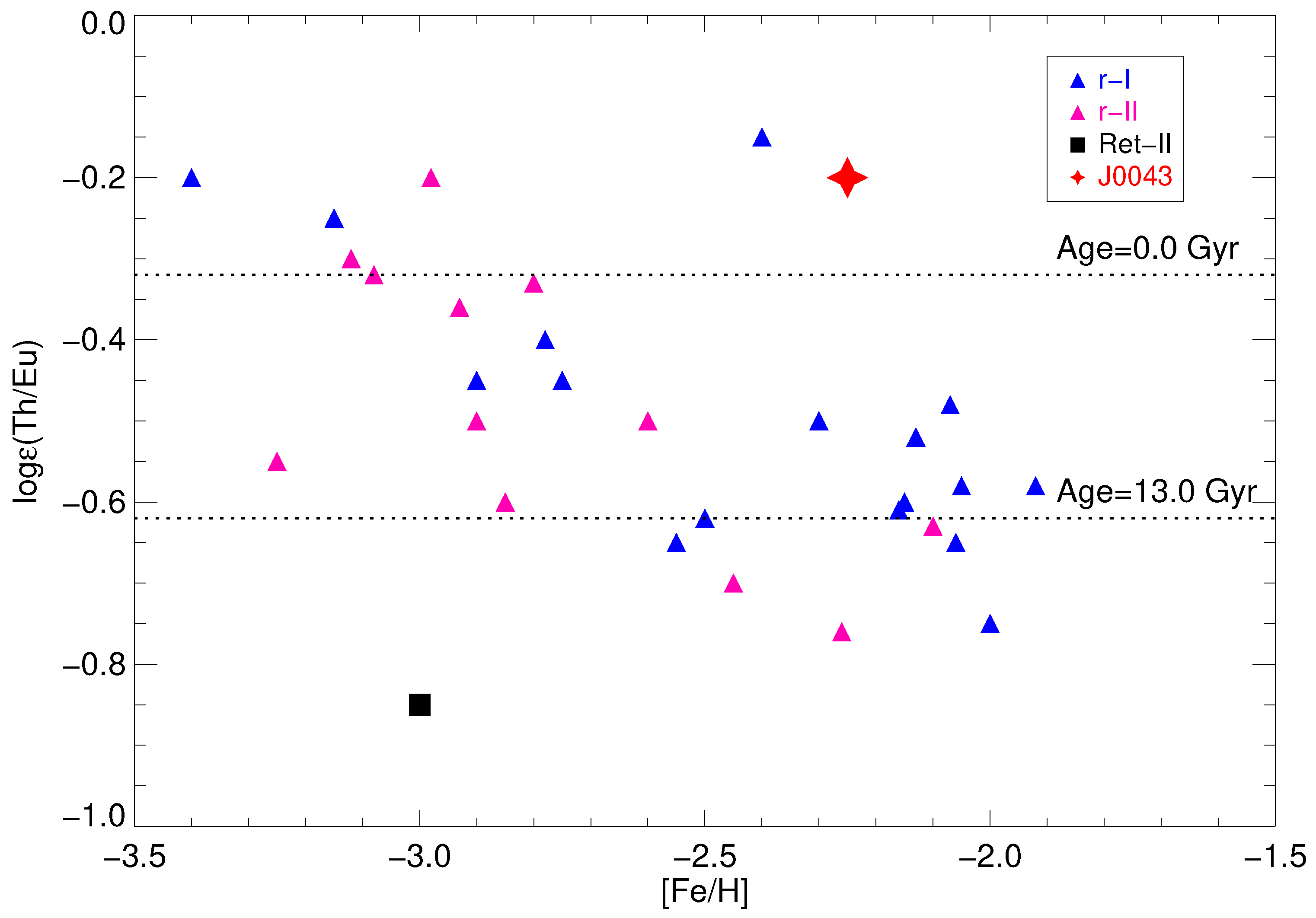
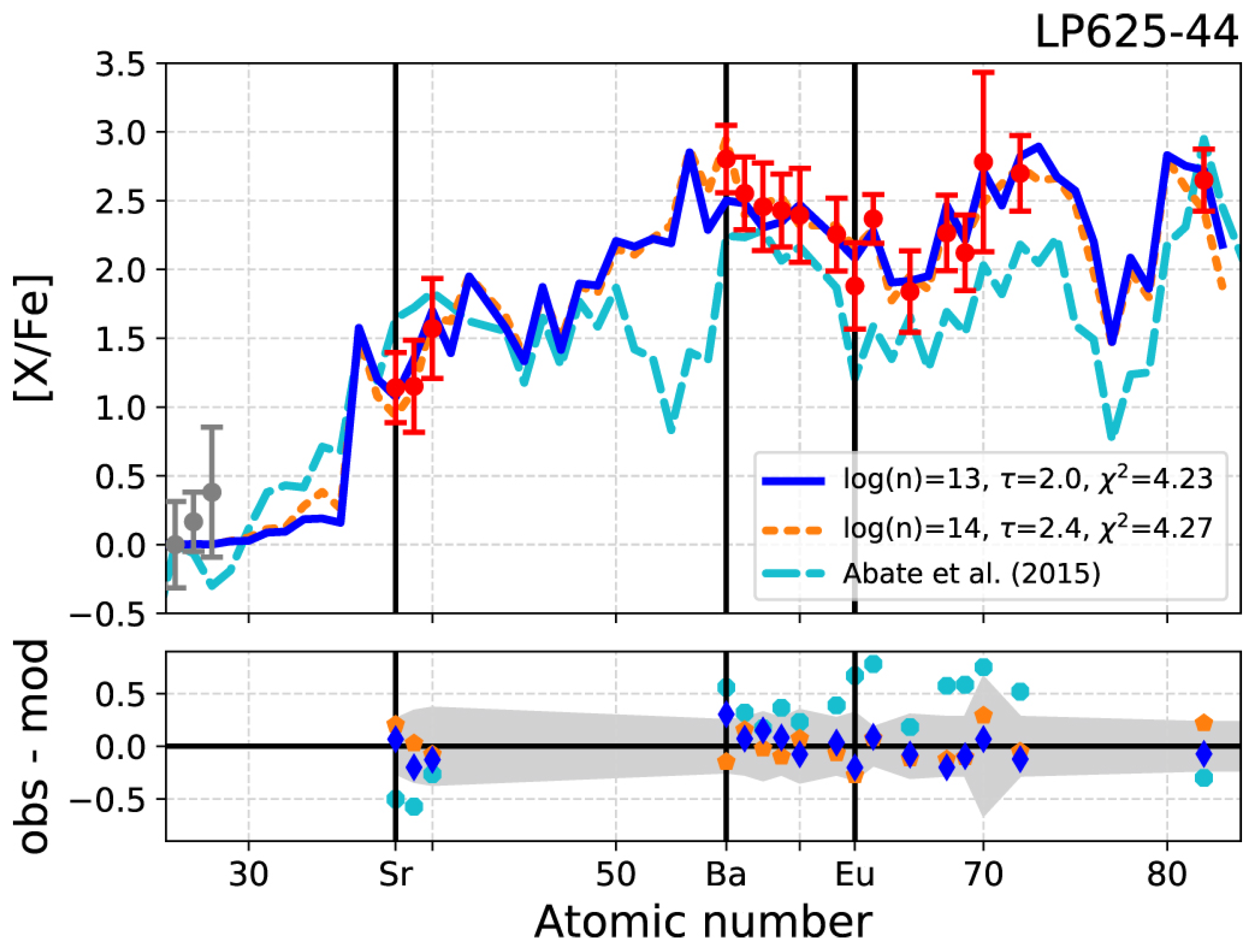
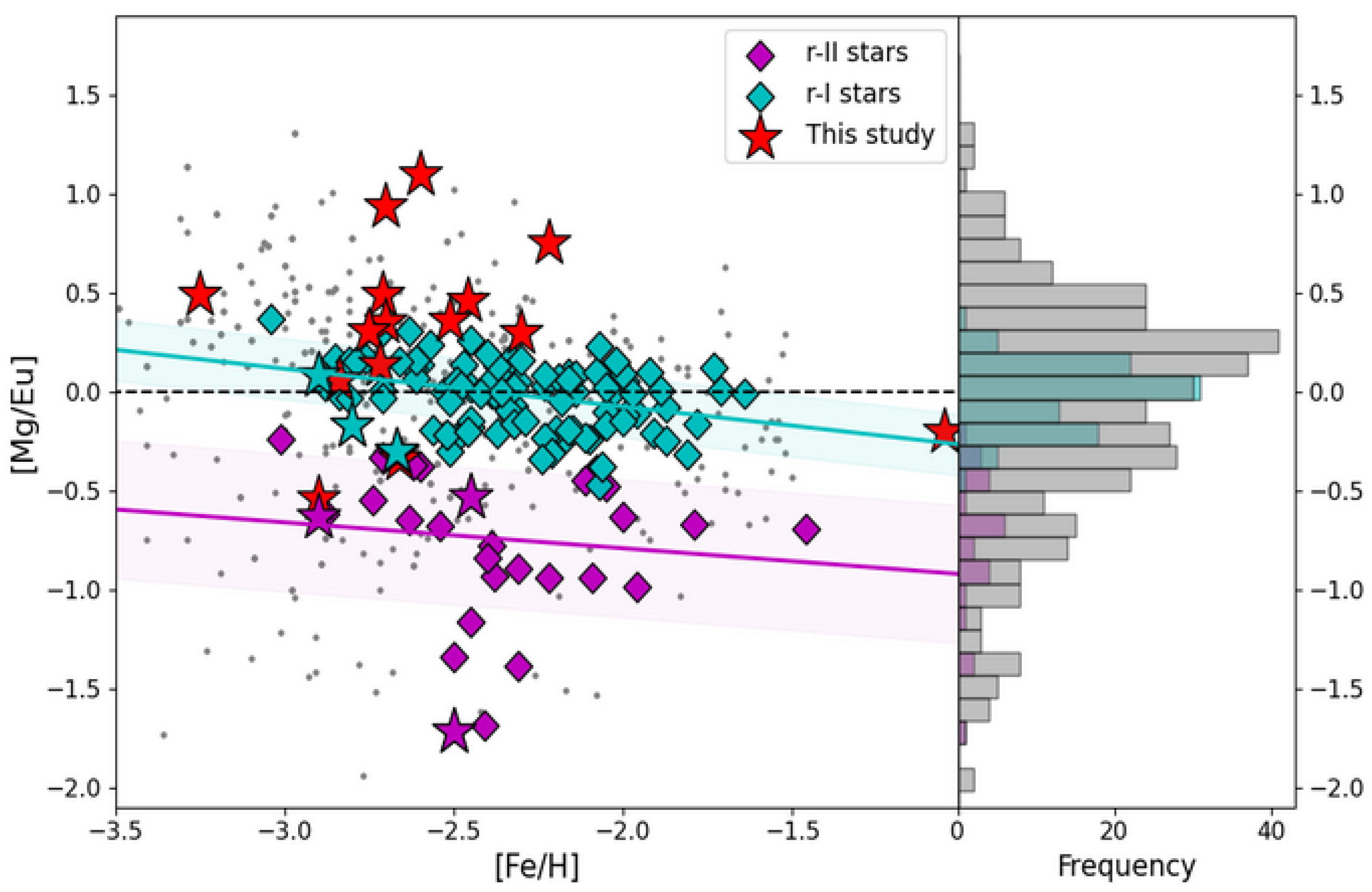
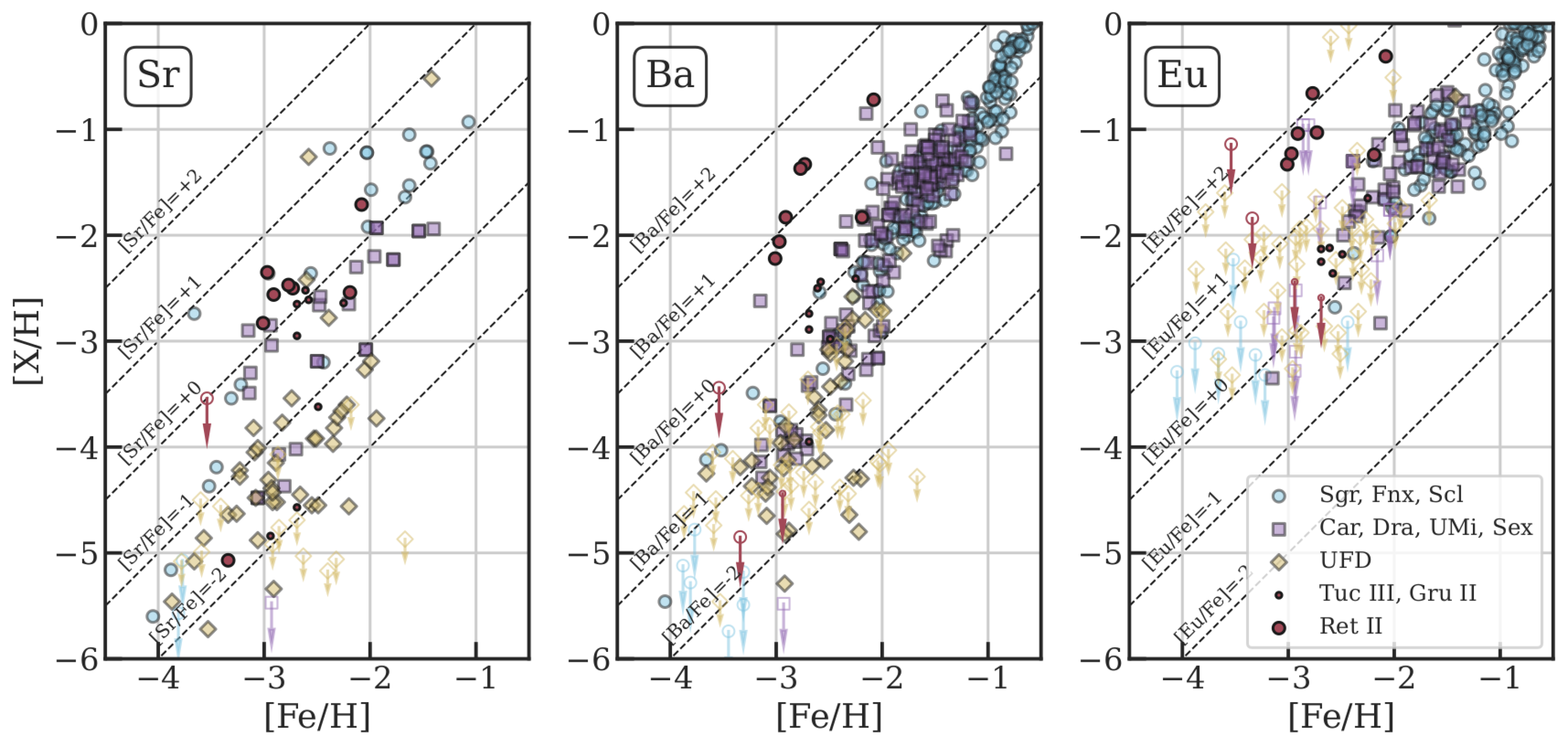
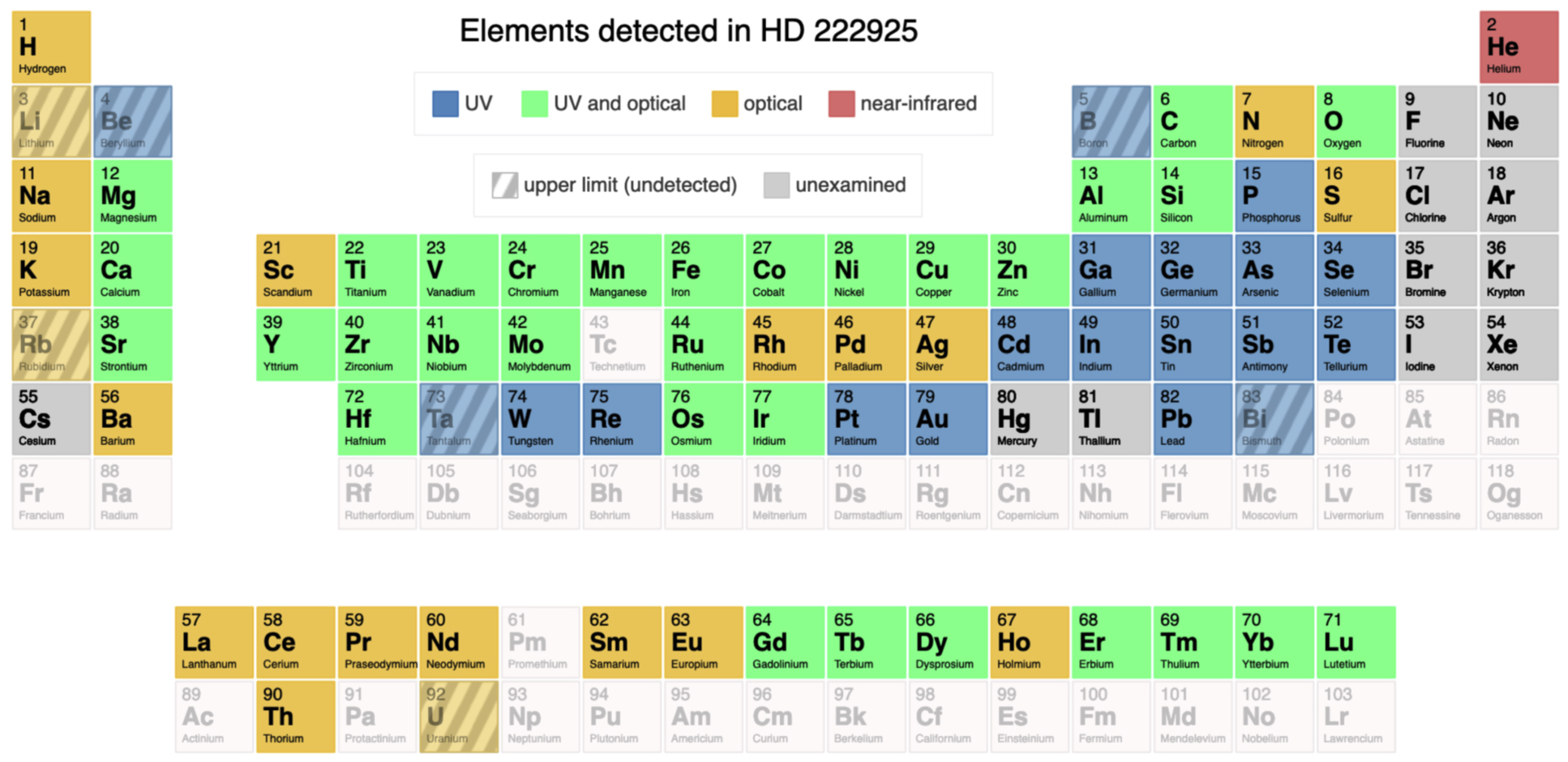
| Description | Definition | Abbreviation |
| Solar | ||
| Metal-poor | MP | |
| Very metal-poor | VMP | |
| Extremely metal-poor | EMP | |
| Ultra metal-poor | UMP | |
| Hyper metal-poor | HMP | |
| Mega metal-poor | MMP | |
| Septa metal-poor | SMP | |
| Octa metal-poor | OMP | |
| Giga metal-poor | GMP | |
| Signature | Criteria | Abbreviation |
| r-process-enhanced | and | r-I |
| and | r-II | |
| limited r-process | , , and | |
| s-process: | , ; also | s |
| r- and s-process | and | |
| i-process | and | i |
| carbon-enhanced | CEMP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bandyopadhyay, A.; Beers, T.C. Recent Advances in Understanding R-Process Nucleosynthesis in Metal-Poor Stars and Stellar Systems. Universe 2025, 11, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070229
Bandyopadhyay A, Beers TC. Recent Advances in Understanding R-Process Nucleosynthesis in Metal-Poor Stars and Stellar Systems. Universe. 2025; 11(7):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070229
Chicago/Turabian StyleBandyopadhyay, Avrajit, and Timothy C. Beers. 2025. "Recent Advances in Understanding R-Process Nucleosynthesis in Metal-Poor Stars and Stellar Systems" Universe 11, no. 7: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070229
APA StyleBandyopadhyay, A., & Beers, T. C. (2025). Recent Advances in Understanding R-Process Nucleosynthesis in Metal-Poor Stars and Stellar Systems. Universe, 11(7), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070229






