Dynamical Black Holes and Accretion-Induced Backreaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dynamics of Spherically Symmetric Spacetimes
2.1. General Setup
2.2. Dynamics of the Misner–Sharp Mass
- the initial mass at the reference radius ;
- the accumulated energy flux through the 2-sphere at from to ;
- the final energy contained between the 2-spheres at and r.
3. Near-Horizon Approximation Scheme
3.1. Existence of Future Trapping Horizons
3.2. General Model
3.3. Perfect Fluid Model
4. Perturbative Scheme for Accretion
4.1. Perturbations near a Trapping Horizon
4.2. Accretion-Induced Shifts in Trapping Horizons
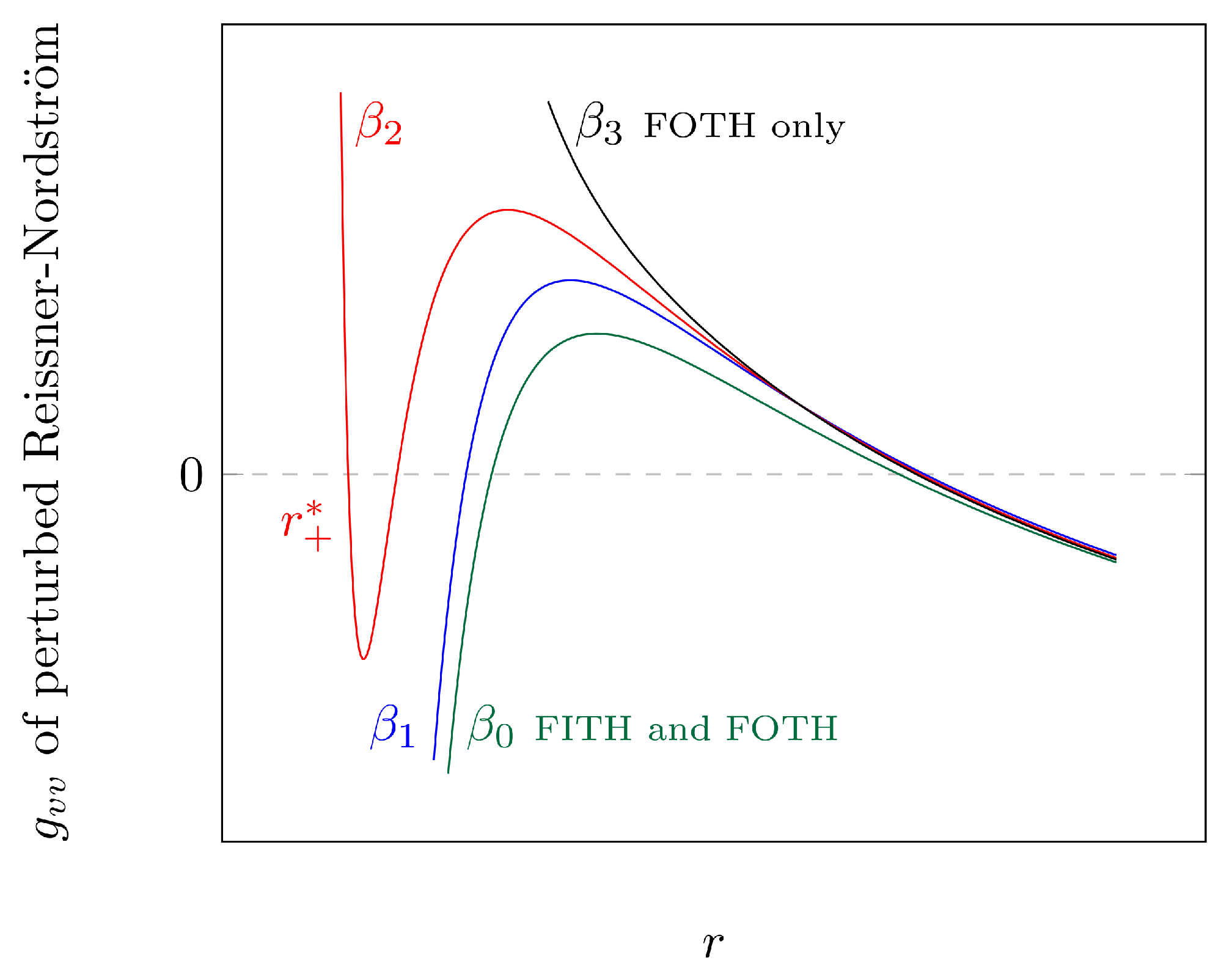
5. On the Presence of Future Inner Trapping Horizons
6. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Future Trapping Horizons
| 1 | The investigation of null congruences is useful for the study of trapping horizons, but the expansion scalar can also be defined for timelike congruences. |
References
- Krishnan, B. Fundamental properties and applications of quasi-local black hole horizons. Class. Quant. Grav. 2008, 25, 114005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, J.L.; Gourgoulhon, E. Mass and angular momentum in general relativity. In Mass and Motion in General Relativity; Blanchet, L., Spallicci, A., Whiting, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 87–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, S.A. General laws of black-hole dynamics. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misner, C.; Sharp, D. Relativistic equations for adiabatic, spherically symmetric gravitational collapse. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, W.C.; Misner, C.W. Observer time as a coordinate in relativistic spherical hydrodynamics. Astrophys. J. 1966, 143, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Krishnan, B. Isolated and dynamical horizons and their applications. Living Rev. Rel. 2004, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, G.; Visser, M. Kodama time: Geometrically preferred foliations of spherically symmetric spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 044027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, I. Black-hole boundaries. Can. J. Phys. 2005, 83, 1073–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, G.; Nakamura, K.; Oshiro, Y.; Tomimatsu, A. Surface gravity in dynamical spherically symmetric spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.B. Black holes and black hole thermodynamics without event horizons. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2009, 41, 1539–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.B.; Yeom, D. Spherically symmetric trapping horizons, the Misner-Sharp mass and black hole evaporation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2009, 24, 5261–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.B.; Yoon, J.H. Dynamical surface gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2008, 25, 085010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V. Embedding black holes and other inhomogeneities in the universe in various theories of gravity: A short review. Universe 2018, 4, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Physical observability of horizons. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 127502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVittie, G.C. The mass-particle in an expanding universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1933, 93, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Giulini, D. Generalization of McVittie’s model for an inhomogeneity in a cosmological spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 043521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, K.; Abdelqader, M. More on McVittie’s Legacy: A Schwarzschild-de Sitter black and white hole embedded in an asymptotically ΛCDM cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 044045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V.; Moreno, A.F.Z.; Prain, A. The charged McVittie spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, A.; Guariento, D.C.; Molina, C. Cosmological black holes and white holes with time-dependent mass. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 084043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Molina, C.; Lima, J.A.S. Dynamical model for primordial black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 123516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakurta, S.N.G. Kerr metric in an expanding universe. Indian J. Phys. B 1981, 55, 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, P.C. The gravitational field of a radiating star. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. Sect. A 1951, 33, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, P.C. ‘Newtonian’ time in general relativity. Nature 1953, 171, 260–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, R.L. Radiating Vaidya metric imbedded in de Sitter space. Phys. Rev. D 1985, 31, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, T.L.; Molina, C.; Lima, J.A.S. Black-hole evaporation for cosmological observers. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.08114. [Google Scholar]
- Babichev, E.; Dokuchaev, V.; Eroshenko, Y. Backreaction of accreting matter onto a black hole in the Eddington-Finkelstein coordinates. Class. Quant. Grav. 2012, 29, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Black holes do evaporate thermally. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1981, 46, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.A. Gravitational energy in spherical symmetry. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.A. Unified first law of black-hole dynamics and relativistic thermodynamics. Class. Quant. Grav. 1998, 15, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.A.; Di Criscienzo, R.; Nadalini, M.; Vanzo, L.; Zerbini, S. Local Hawking temperature for dynamical black holes. Class. Quant. Grav. 2009, 26, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V. Cosmological and Black Hole Apparent Horizons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, H. Conserved energy flux for the spherically symmetric system and the backreaction problem in the black hole evaporation. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1980, 63, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.; Poloský, J. Exact Space-Times in Einstein’s General Relativity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnor, W.B.; Vaidya, P.C. Spherically symmetric radiation of charge in Einstein-Maxwell theory. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1970, 1, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Structure of space-time. In Battelle Rencontres—1967 Lectures in Mathematics and Physics; DeWitt, C.M., Wheeler, J.A., Eds.; W. A. Benjamin: Seattle, WA, USA, 1968; pp. 121–235. [Google Scholar]
- Matzner, R.; Zamorano, N.; Sandberg, V. Instability of the Cauchy horizon of Reissner-Nordström black holes. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 19, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, E.; Israel, W. Internal structure of black holes. Phys. Rev. D 1990, 41, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ori, A. Inner structure of a charged black hole: An exact mass-inflation solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Filippo, F.; Carballo-Rubio, R.; Liberati, S.; Pacilio, C.; Visser, M. On the inner horizon instability of non-singular black holes. Universe 2022, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Filippo, F.; Liberati, S.; Visser, M. Mass inflation without Cauchy horizons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 181402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargueño, P.; Medina, S.; Nowakowski, M.; Batic, D. Quantum-mechanical corrections to the Schwarzschild black-hole metric. Europhys. Lett. 2017, 117, 60006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, W. Models of evaporating black holes. I. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, W. Models of evaporating black holes. II. Effects of the outgoing created radiation. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, T.d.L.; Molina, C.; Baldiotti, M.C. Dynamical Black Holes and Accretion-Induced Backreaction. Universe 2025, 11, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070202
Campos TdL, Molina C, Baldiotti MC. Dynamical Black Holes and Accretion-Induced Backreaction. Universe. 2025; 11(7):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070202
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Thiago de L., C. Molina, and Mario C. Baldiotti. 2025. "Dynamical Black Holes and Accretion-Induced Backreaction" Universe 11, no. 7: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070202
APA StyleCampos, T. d. L., Molina, C., & Baldiotti, M. C. (2025). Dynamical Black Holes and Accretion-Induced Backreaction. Universe, 11(7), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11070202






