Evolution of the Early Universe in Einstein–Cartan Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Field Equation
3. Phase Space Analysis
4. Inflation
4.1.
4.2.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hehl, F.; von der Heyde, P.; Kerlick, G.; Nester, J. General relativity with spin and torsion: Foundations and prospects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1976, 48, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F. On the kinematics of the torsion of space-time. Found. Phys. 1985, 15, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.; McCrea, J.; Mielke, E.; Neeman, Y. Metric-affine gauge theory of gravity: Field equations, noether identities, world spinors, and breaking of dilation invariance. Phys. Rep. 1995, 258, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lledo, M.; Sommovigo, L. Torsion formulation of gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2010, 27, 065014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyssenhoff, J.; Raabe, A. Relativistic dynamics of spin-fluids and spin-particles. Acta Phys. Pol. 1947, 9, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov, Y.; Korotky, V. The Weyssenhoff fluid in Einstein-Cartan theory. Class. Quantum Gravity 1987, 4, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, L.; Krisch, J. Spinning fluid cosmologies in Einstein-Cartan theory. Class. Quantum Gravity 1994, 11, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Berredo-Peixoto, G.; De Freitas, E. On the cosmological effects of the Weyssenhoff spinning fluid in the Einstein-Cartan framework. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2009, 24, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, B.; Jalalzadeh, S. Signature transition in Einstein-Cartan cosmology. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 726, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.; von der Heyde, P.; Kerlick, G. General relativity with spin and torsion and its deviations from Einstein’s theory. Phys. Rev. D 1974, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurgaliev, I.; Ponomariev, W. The earliest evolutionary stages of the universe and space-time torsion. Phys. Lett. 1983, 130B, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M. Spin-dominated inflation in the Einstein-Cartan theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poplawski, N. Big bounce from spin and torsion. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2012, 44, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, G.; Poplawski, N. Big bounce and closed universe from spin and torsion. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atazadeh, K. Stability of the Einstein static universe in Einstein-Cartan theory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 6, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, P.; Yu, H. Emergent scenario in the Einstein-Cartan theory. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, N. Cosmology with torsion: An alternative to cosmic inflation. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 694, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, N. Matter-antimatter asymmetry and dark matter from torsion. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 084033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawski, N. Nonsingular, big-bounce cosmology from spinor-torsion coupling. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 107502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, K.; Nester, J.; Yo, H. Torsion cosmology and the accelerating universe. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 023522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.; Orazi, E.; Pradisi, G. Einstein-Cartan pseudoscalaron inflation. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Kamada, K.; Mukaida, K. Quantum corrections to Higgs inflation in Einstein-Cartan gravity. JHEP 2024, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Hong, M.; Mukaida, K. Starobinsky inflation and beyond in Einstein-Cartan gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, M.; Rubio, J. Higgs-Dilaton inflation in Einstein-Cartan gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 5, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaposhnikov, M.; Shkerin, A.; Timiryasov, I.; Zell, S. Higgs inflation in Einstein-Cartan gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, M.; Rubio, J. Preheating in Einstein-Cartan Higgs Inflation: Oscillon formation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 12, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, F.; Frenkel, J.; Martins-Filho, S.; McKeon, D. Quantization of Einstein-Cartan theory in the first order form. Ann. Phys. 2024, 462, 169607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isichei, R.; Magueijo, J. Minisuperspace quantum cosmology from the Einstein-Cartan path integral. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 023526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, M.; Akhshabi, S.; Shadmehri, M. Gravitational slip parameter and gravitational waves in Einstein-Cartan theory. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Izaurieta, F.; Riveros, C.; Salgado, G.; Valdivia, O. Gravitational waves in Einstein-Cartan theory: On the effects of dark matter spin tensor. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 40, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, E.; De Falco, V. Gravitational waves at the first post-Newtonian order with the Weyssenhoff fluid in Einstein-Cartan theory. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battista, E.; De Falco, V. First post-Newtonian generation of gravitational waves in Einstein-Cartan theory. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 084067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhshabi, S.; Zamani, S. Cosmological distances and Hubble tension in Einstein-Cartan theory. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2023, 55, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Khunt, A.; Hasmani, A. A study of Morris-Thorne wormhole in Einstein-Cartan theory. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2024, 21, 06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensh, S.; Liberati, S. Raychaudhuri equations and gravitational collapse in Einstein-Cartan theory. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 084073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Bonder, Y. Signature of Einstein-Cartan theory. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 849, 138431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, V.; Battista, E.; Usseglio, D.; Capozziello, S. Radiative losses and radiation-reaction effects at the first post-Newtonian order in Einstein-Cartan theory. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, V.; Battista, E. Analytical results for binary dynamics at the first post-Newtonian order in Einstein-Cartan theory with the Weyssenhoff fluid. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 064032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, E.; De Falco, V.; Usseglio, D. First post-Newtonian N-body problem in Einstein-Cartan theory with the Weyssenhoff fluid: Lagrangian and first integrals. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, S.; Pozdnyakov, S.; Zubkov, M. High energy scattering in Einstein-Cartan gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Banerjee, N. Dynamical systems study of Chameleon scalar field. Ann. Phys. 2015, 356, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Khyllep, W.; Tamanini, N. Cosmological dynamics of scalar fields with kinetic corrections: Beyond the exponential potential. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 063004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Sur, S. Dynamical system analysis of dark energy models in scalar coupled metric-torsion theories. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, J.; Gomez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Perez, J. Dynamical dark energy: Scalar fields and running vacuum. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 32, 1750054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Frolov, A. Cosmological dynamics in f(R) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 124036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yu, H. The dynamical behavior of f(T) theory. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 692, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H. Dynamics of Teleparallel Dark Energy. Phys. Lett. B 2012, 712, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Khyllep, W.; Saridakis, E.; Tamanini, N.; Vagnozzi, S. Cosmological dynamics of mimetic gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 2, 041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Tu, F. Phase space analysis of the Umami Chaplygin model. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2021, 36, 2150052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.; Vagenas, E. The Cosmological dynamics of interacting holographic dark energy model. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2009, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Roy, N. Stability analysis of a holographic dark energy model. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2015, 47, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Tu, F. Stability analysis of a Tsallis holographic dark energy model. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 36, 175001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargach, A.; Bargach, F.; Ouali, T. Dynamical system approach of non-minimal coupling in holographic cosmology. Nucl. Phys. B 2019, 940, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, B.; Tu, F.; Chen, J. Dynamical analysis and statefinder of Barrow holographic dark energy. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R. Phase space analysis of Tsallis agegraphic dark energy. Gen. Relat. Gravit. 2021, 53, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R. Phase space analysis of barrow agegraphic dark energy. Universe 2022, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millano, A.; Jusufi, K.; Leon, G. Phase space analysis of the bouncing universe with stringy effects. Phys. Lett. B 2023, 841, 137916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, A. The inflationary universe: A possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A. A new inflationary universe scenario: A possible solution of the horizon, flatness, homogeneity, isotropy and primordial monopole problems. Phys. Lett. B 1982, 108, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.; Chibisov, G. Quantum fluctuations and a nonsingular universe. JETP Lett. 1981, 33, 532. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, A.; Challinor, A.; Lasenby, A. Efficient computation of CMB anisotropies in closed FRW models. Astrophys. J. 2000, 538, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardeau, F.; Colombi, S.; Gaztanaga, E.; Scoccimarro, R. Large-scale structure of the universe and cosmological perturbation theory. Phys. Rep. 2002, 367, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Cosmology; Oxford Univ. Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2018 results. X. Constraints on inflation. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, W. Modular invariant slow roll inflation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 10, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragavendra, H.; Sarkar, A.; Sethi, S. Constraining ultra slow roll inflation using cosmological datasets. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 7, 088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdeeva, E.; Skugoreva, M.; Toporensky, A.; Vernov, S. New slow-roll approximations for inflation in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 9, 050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, H.; Lin, W. Inflation and reheating predictions in f(T)-gravity. Phys. Dark Univ. 2024, 44, 101482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiase, G.; Luciano, G.; Sheykhi, A. Slow-roll inflation and growth of perturbations in Kaniadakis modification of Friedmann cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, B.; Moradpour, H.; Shabani, H. Slow-roll inflation and reheating in Rastall theory. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 42, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.; Mandal, S.; Sahoo, P. Slow-roll inflation in f(T,T) modified gravity. Chin. Phys. C 2023, 47, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, C.; Racioppi, A.; Tomberg, E. Slow-roll inflation in Palatini F(R) gravity. J. High Energ. Phys. 2022, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karciauskas, M.; Diaz, J. Slow-roll inflation in the Jordan frame. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 083526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Reyimuaji, Y.; Zhang, X. Slow-roll inflation in f(R,T) gravity with a RT mixing term. Phys. Dark Univ. 2022, 38, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Shokri, M. Slow-roll inflation in f(Q) non-metric gravity. Phys. Dark Univ. 2022, 37, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forconi, M.; Giare, W.; Valentino, E.; Melchiorri, A. Cosmological constraints on slow roll inflation: An update. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Chen, C.; Fu, C. Primordial black holes and stochastic gravitational wave background from inflation with a noncanonical spectator field. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 083537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamonal, M. Slow-roll inflation in f(R,T) gravity and a modified Starobinsky-like inflationary model. Phys. Dark Univ. 2021, 31, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wu, P.; Yu, H. Primordial black holes and oscillating gravitational waves in slow-roll and slow-Climb inflation with an intermediate noninflationary phase. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 043527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, K.; Arapoglu, A.; Yukselci, A. Formalizing slow-roll inflation in scalar-tensor theories of gravitation. Phys. Dark Univ. 2020, 30, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wu, P.; Yu, H. Primordial Black Holes from Inflation with Nonminimal Derivative Coupling. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 063532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, L.; Jimenez, D. Probing dark matter signals in neutrino telescopes through angular power spectrum. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 9, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Espinoza, M.; Otalora, G.; Videla, N.; Saavedra, J. Slow-roll inflation in generalized scalar-torsion gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 8, 029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, L.; Jimenez, D. Slow-roll inflation with exponential potential in scalar-tensor models. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Gong, Y.; Sabir, M. Inflation with Gauss-Bonnet coupling. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 083521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadio, R.; Giugno, A.; Giusti, A. Corpuscular slow-roll inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 024041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintsov, S.; Oikonomou, V. Reconstruction of slow-roll F(R) gravity inflation from the observational indices. Ann. Phys. 2018, 388, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebzadeh, B.; Rezazadeh, K.; Karami, K. Brans-Dicke inflation in light of the Planck 2015 data. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 7, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Gao, Q.; Gong, Y. Inflation with non-minimally derivative coupling. Int. J. Mode. Phys. A 2015, 30, 1545004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.; Lee, B.; Lee, W.; Tumurtushaa, G. Observational constraints on slow-roll inflation coupled to a Gauss-Bonnet term. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 063527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Gong, Y.; Li, T.; Ye, T. Simple single field inflation models and the running of spectral index. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2014, 57, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antusch, S.; Nolde, D. BICEP2 implications for single-field slow-roll inflation revisited. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 5, 035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Schwarz, D. Slow-roll inflation with a Gauss-Bonnet correction. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 123520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M. Slow-roll Inflation with the Gauss-Bonnet and Chern-Simons Corrections. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 11, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, S.; Ketov, S.; Watanabe, N. Slow-roll inflation in the (R + R4) gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2010, 27, 145016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, B.; Zhang, K. Holographic inflation and holographic dark energy from entropy of the anti-de Sitter black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2025, 85, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøn, Ø. Consequences of the Improved Limits on the Tensor-to-Scalar Ratio from BICEP/Planck, and of Future CMB-S4 Measurements, for Inflationary Models. Universe 2022, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, C.; Chan, N.; Lazkoz, R. Dynamics of dark energy models and centre manifolds. Phys. Lett. B 2012, 714, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Khyllep, W.; Tamanini, N. Scalar-Fluid interacting dark energy: Cosmological dynamics beyond the exponential potential. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 023515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Khyllep, W.; Zonunmawia, H. Cosmological dynamics of the general non-canonical scalar field models. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannan, J.; Boyce, W.; Mckibben, M. Differential Equations: An Introduction to Modern Methods and Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.; Ringeval, C.; Vennin, V. Encyclopædia Inflationaris: Opiparous Edition. Phys. Dark Univ. 2014, 5–6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, D. TASI Lectures on Inflation. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0907.5424. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Wu, P.; Yu, H. Stability of the Einstein static Universe in the scalar-tensor theory of gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2016, 33, 215011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, B. CMB power spectrum for emergent scenario and slow expansion in scalar-tensor theory of gravity. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 41, 101262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Tu, F.; Zhang, R. Emergent scenario in mimetic gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 195002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, P.; Yu, H. Stability of Einstein static universe in gravity theory with a non-minimal derivative coupling. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Kang, S. On the stability of Einstein static universe in general scalar-tensor theory with non-minimal derivative coupling. Ann. Phys. 2018, 399, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, P.; Yu, H.; Luo, L. Stability of Einstein static state universe in the spatially flat branemodels. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 758, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; Waseem, A. Inhomogeneous perturbations and stability analysis of the Einstein static universe in f(R,T) gravity. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
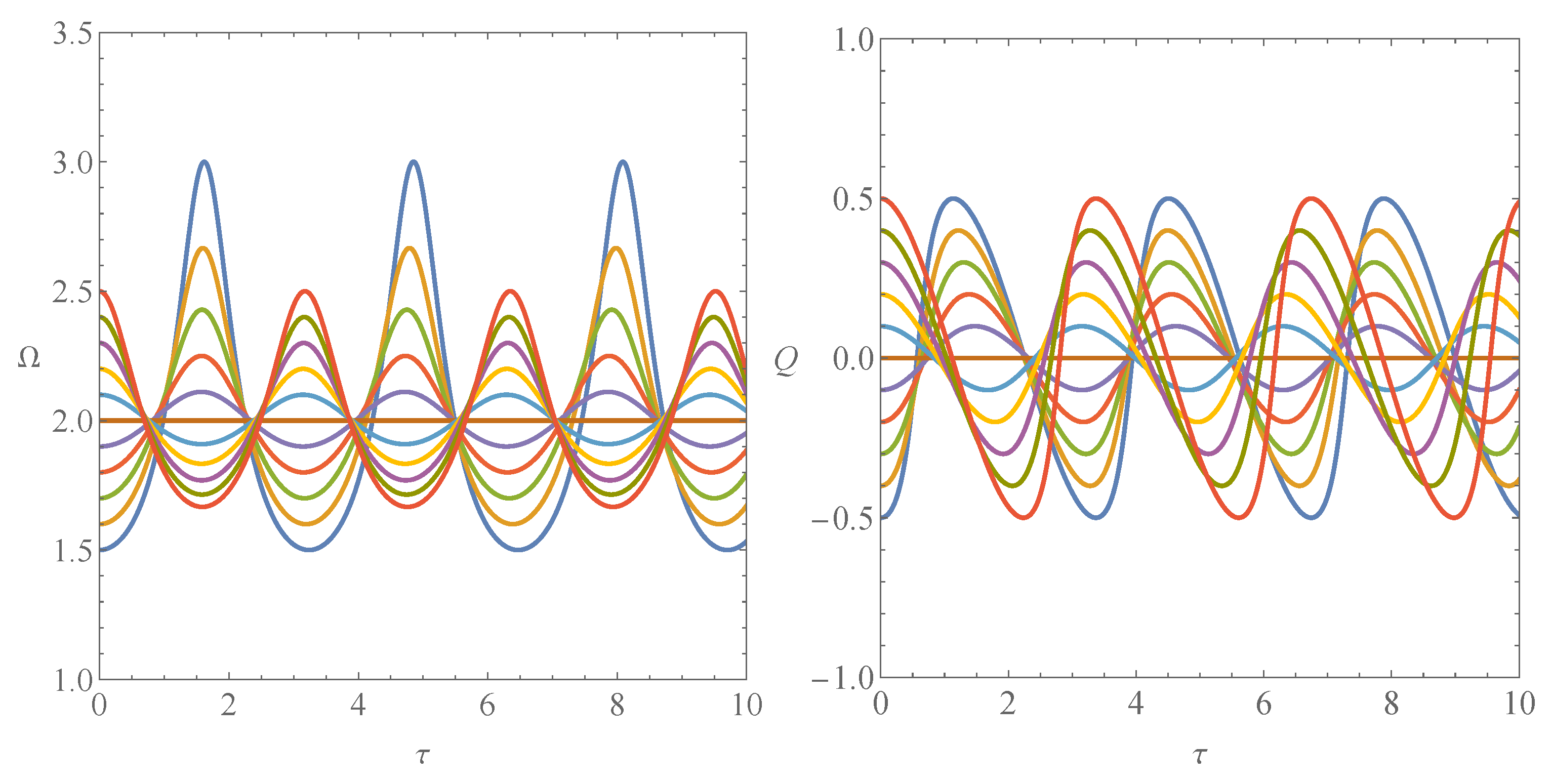
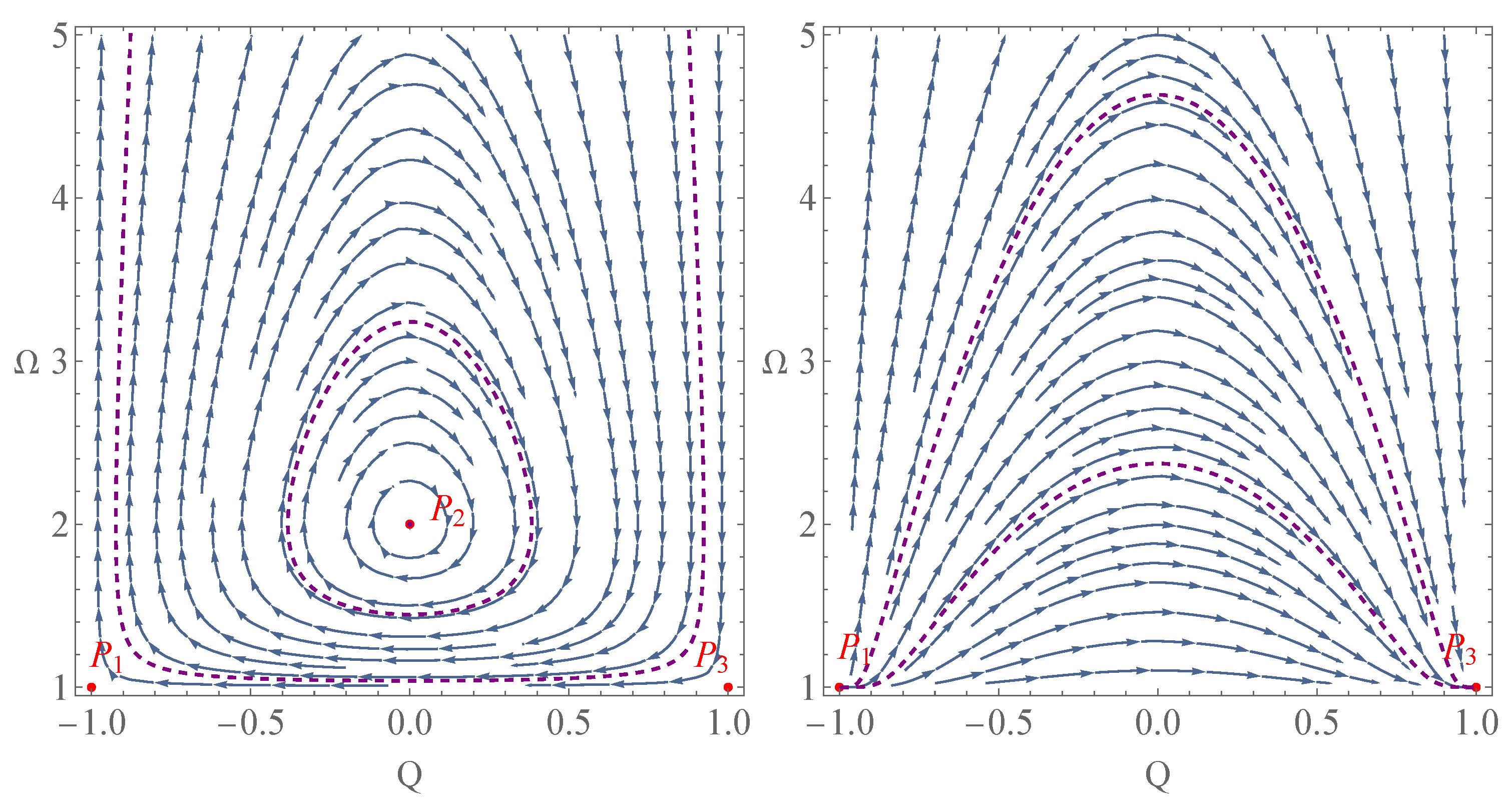
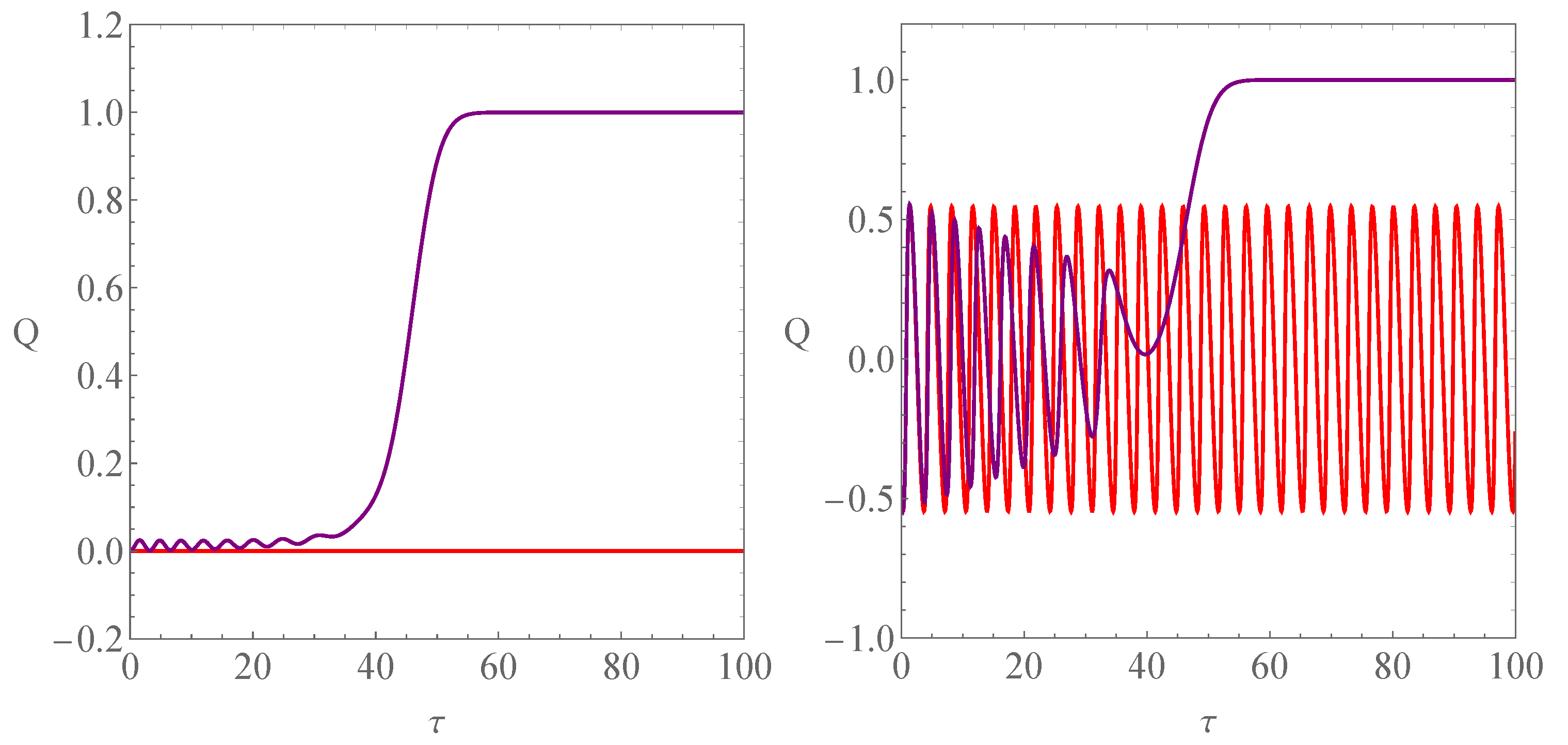

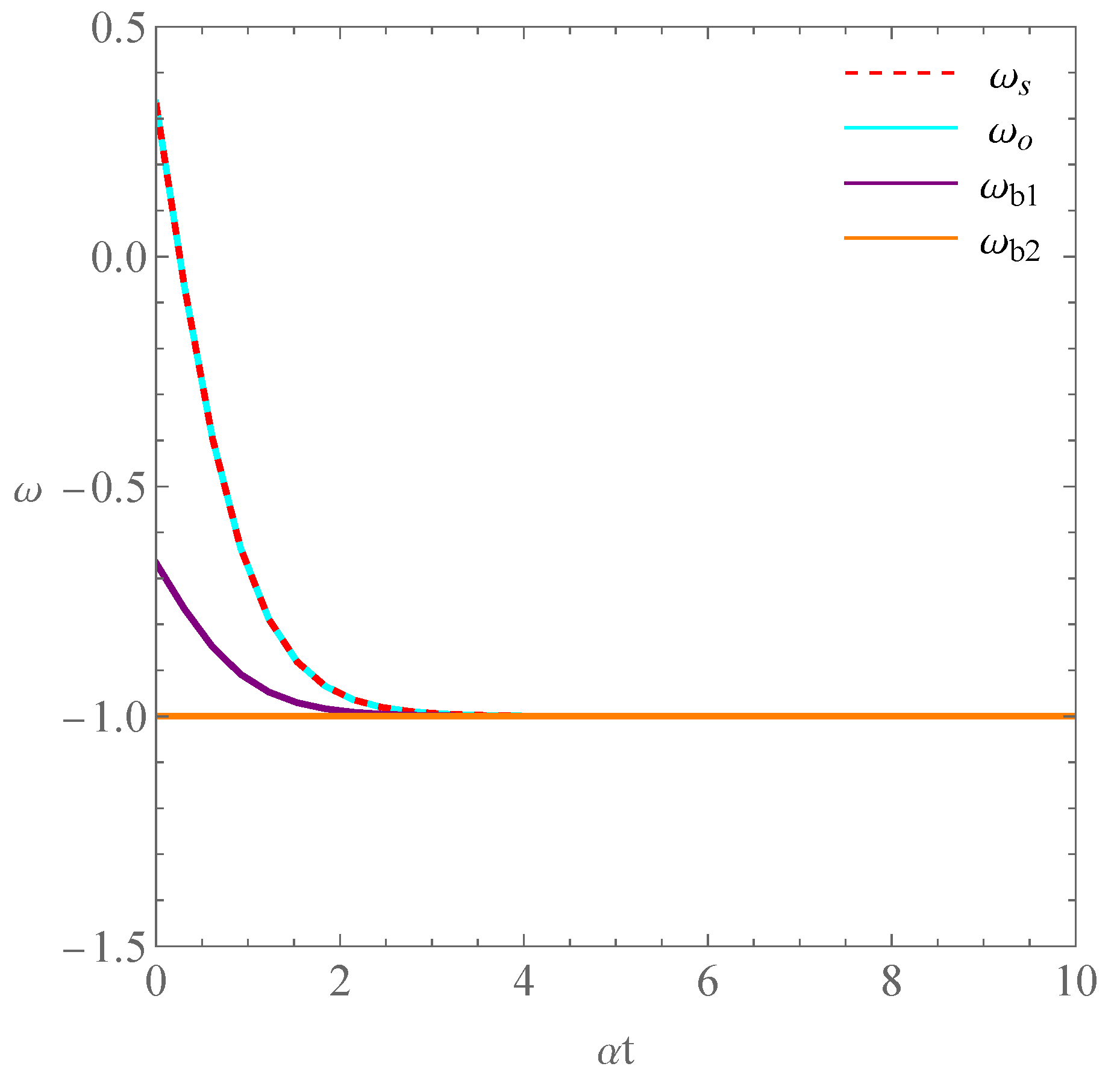
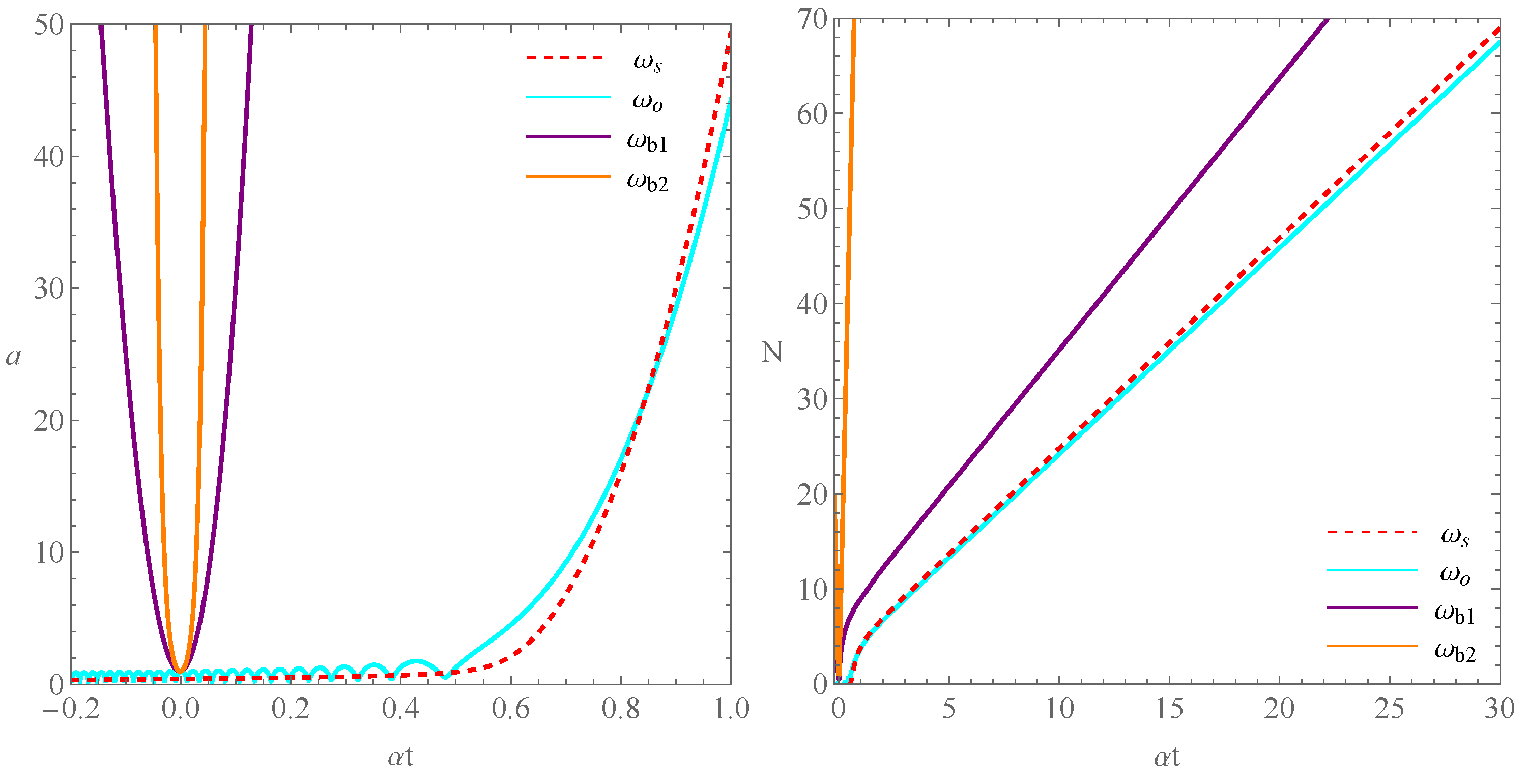
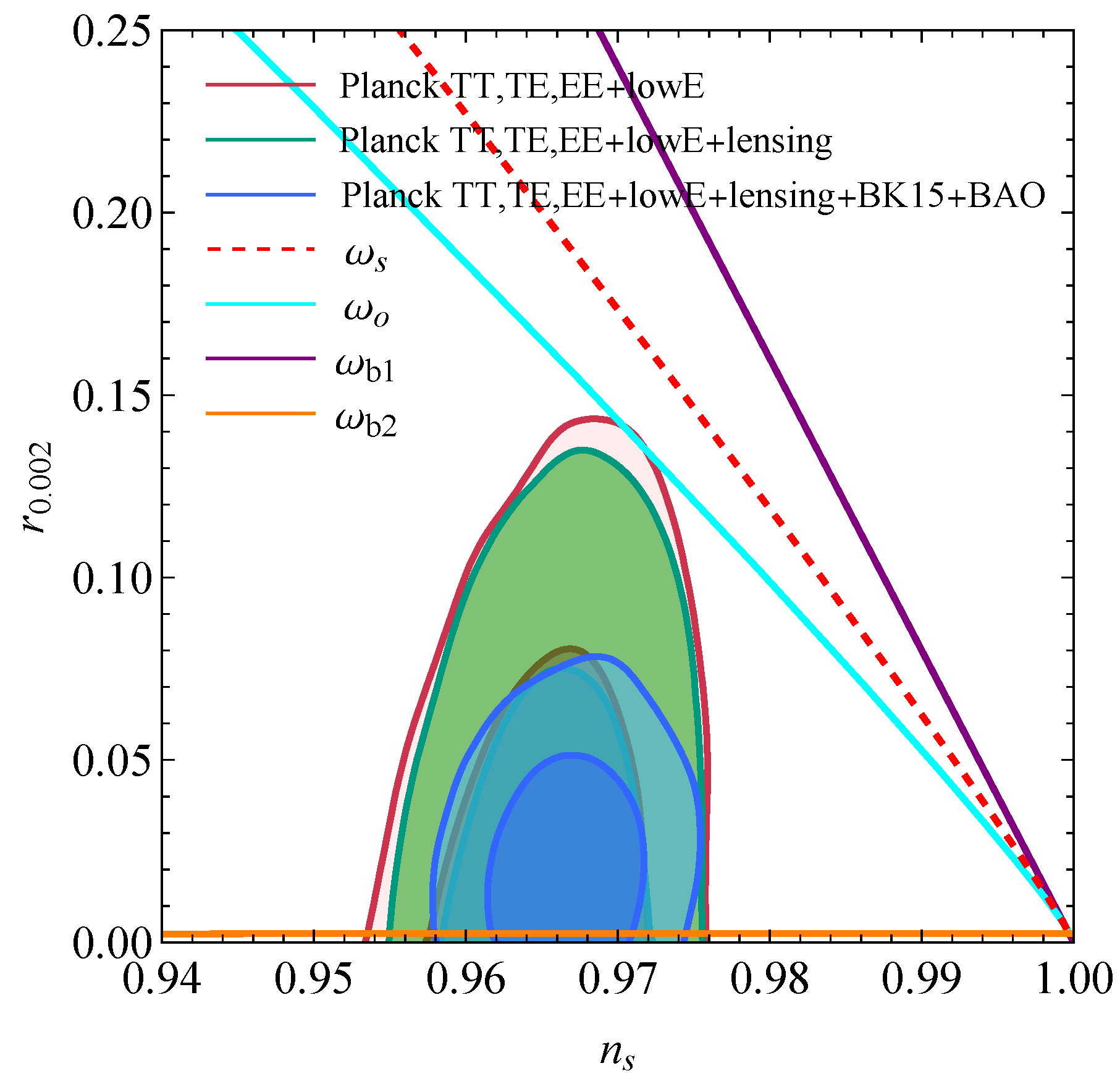
| Existence | Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||||
| 0 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, B.; Zhang, K. Evolution of the Early Universe in Einstein–Cartan Theory. Universe 2025, 11, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050147
Huang Q, Huang H, Xu B, Zhang K. Evolution of the Early Universe in Einstein–Cartan Theory. Universe. 2025; 11(5):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050147
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qihong, He Huang, Bing Xu, and Kaituo Zhang. 2025. "Evolution of the Early Universe in Einstein–Cartan Theory" Universe 11, no. 5: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050147
APA StyleHuang, Q., Huang, H., Xu, B., & Zhang, K. (2025). Evolution of the Early Universe in Einstein–Cartan Theory. Universe, 11(5), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050147






