Reconciling the Waiting Time Peaks Variations of Repeating FRBs with an Eccentric Neutron Star–White Dwarf Binary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. NS-WD Binary Model
3. Stable Mass Transfer
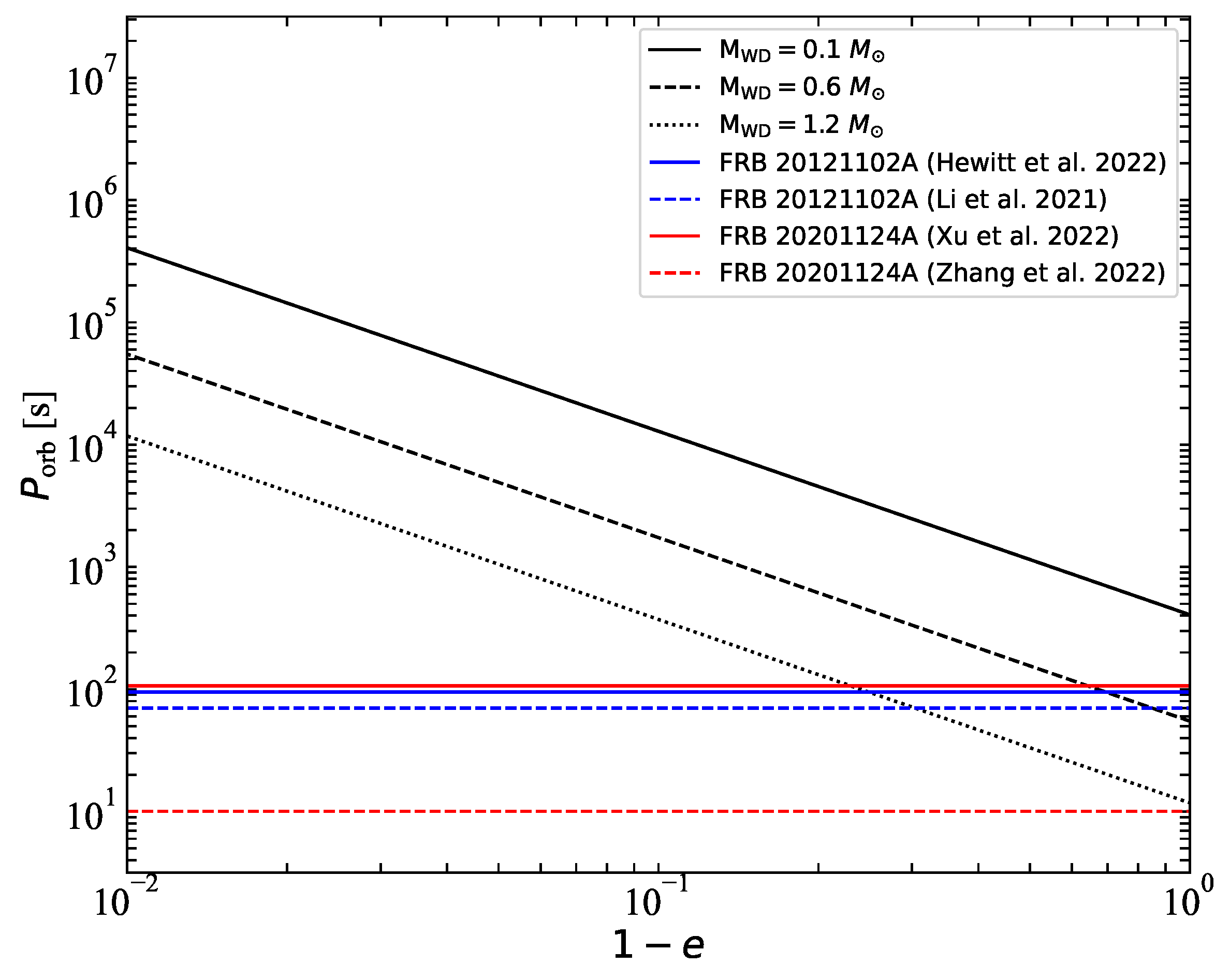
3.1. Orbital Period
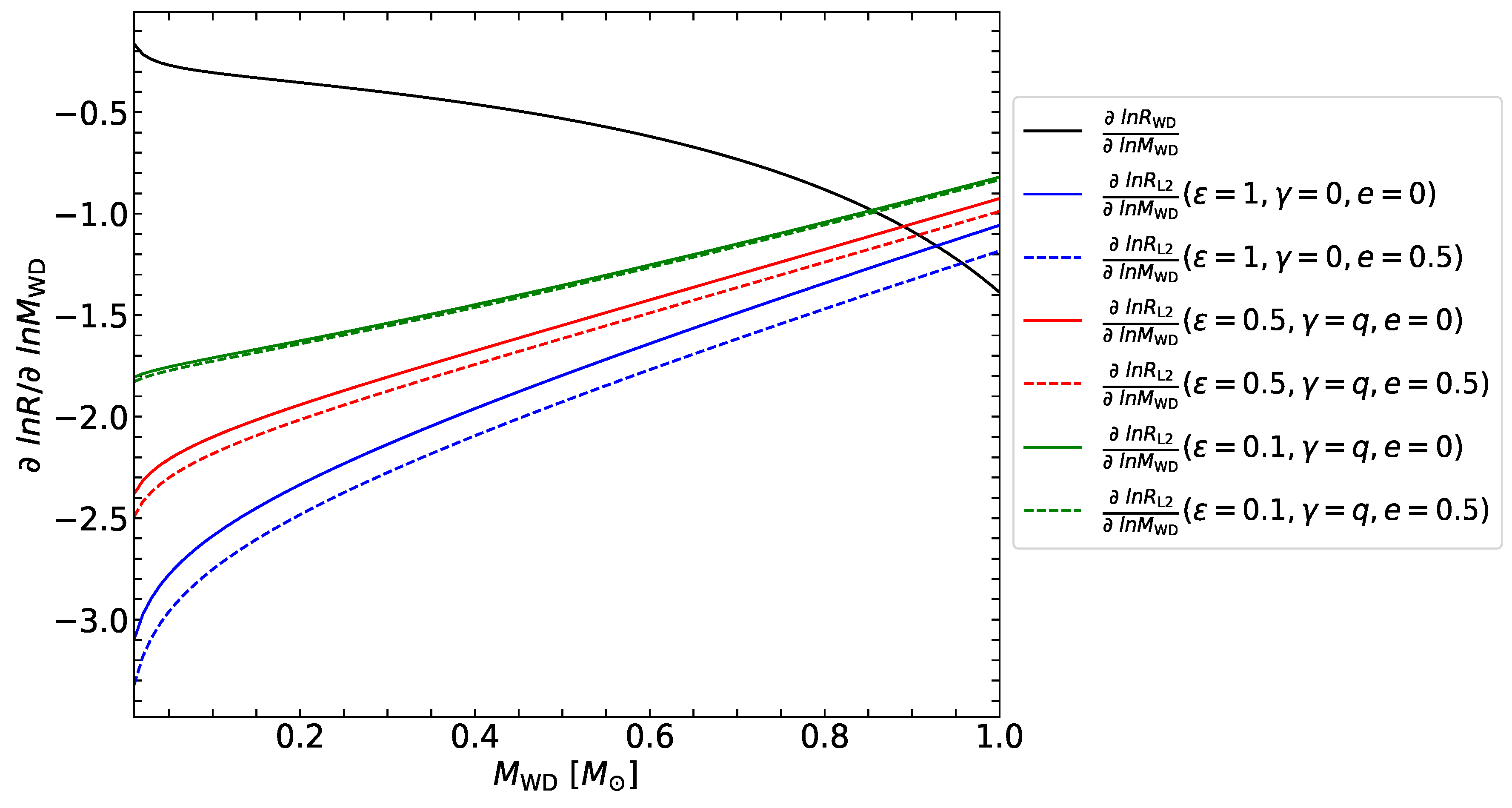
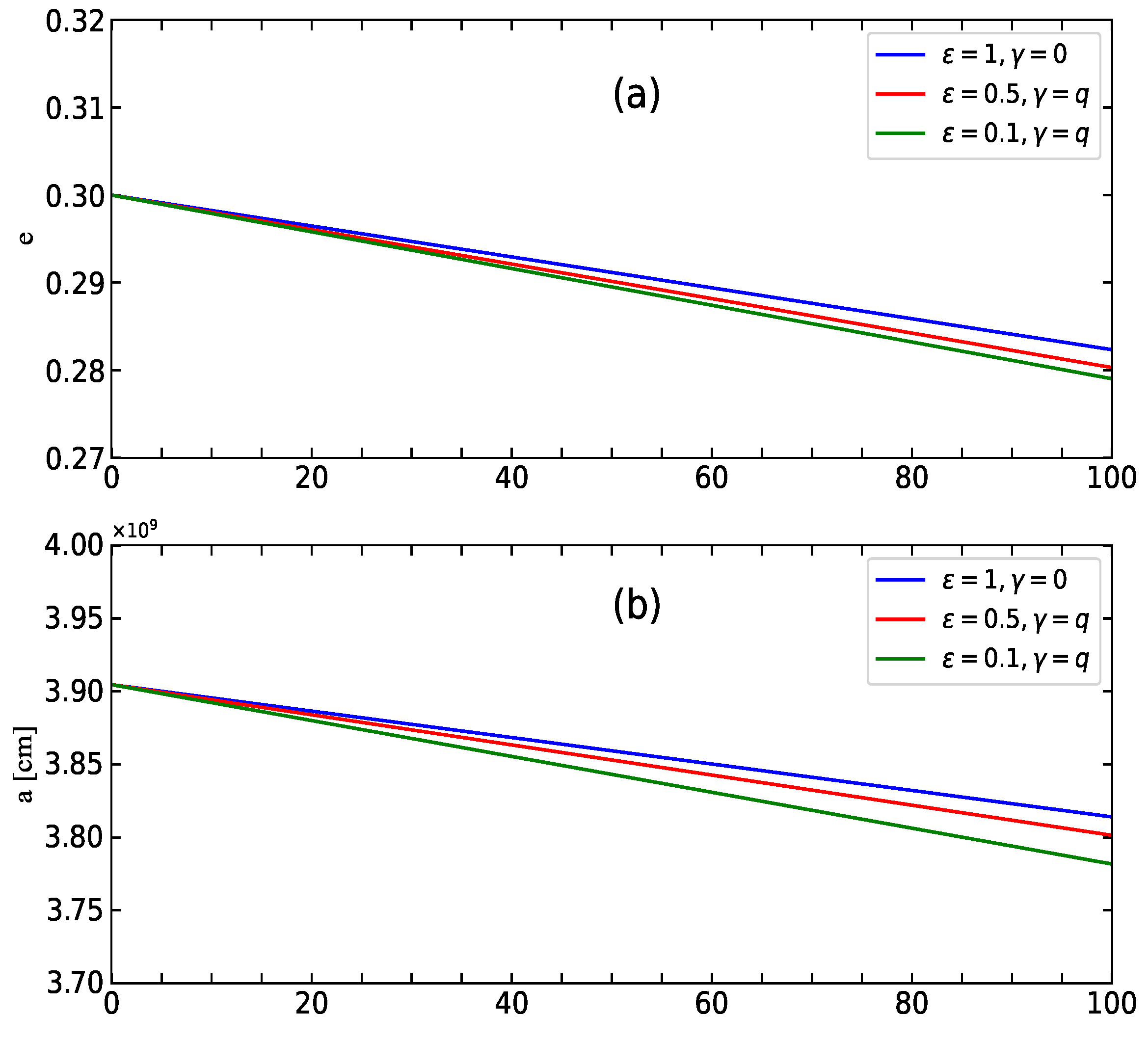
3.2. Orbital Evolution of NS-WD Binary
3.3. Mass Transfer Rate
3.4. Results
4. Unstable Mass Transfer
4.1. FRB 20121102A
4.2. FRB 20201124A
5. Conclusions and Discussion
- In the case of stable mass transfer (e.g., ), although the short-term Roche lobe overflow can significantly shorten the orbital period of the NS-WD binary, the magnitude of the orbital period shrinkage cannot fully account for the observed reductions in the long-duration wait time peaks of FRBs 20121102A and 20201124A (see Section 3).
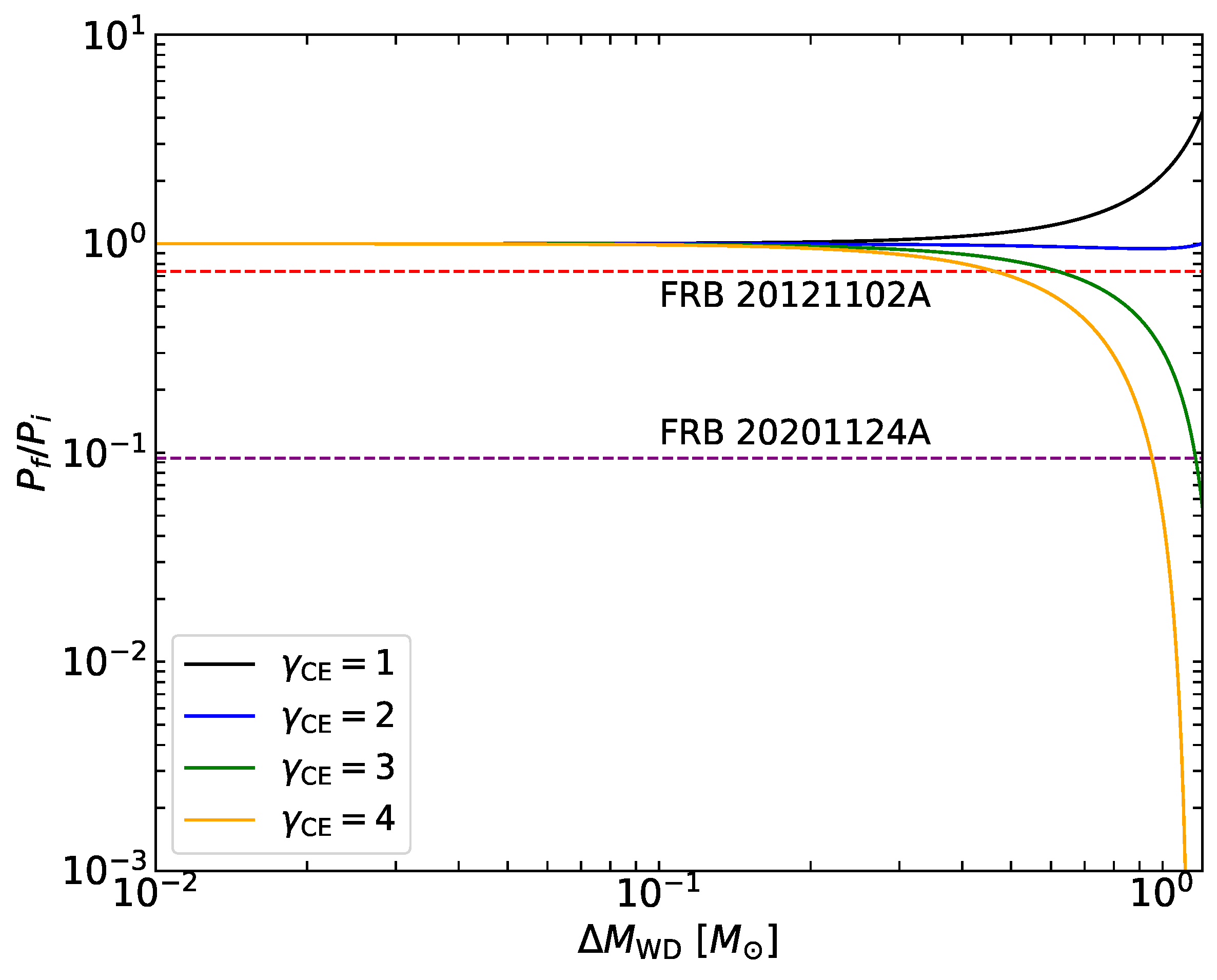
- The CE ejections provide an additional and more efficient mechanism for angular momentum loss in the system with a massive WD (e.g., ). By applying the -mechanism to the CE ejections, the variations in the orbital period of the NS-WD binary, which are comparable to the changes in the wait time peaks of two repeaters, can be reconstructed with ranging between 3 and 4. Furthermore, our analysis also suggests distinct evolutionary pathways for the two sources; for FRB 20121102A, the binary likely undergoes a combination of CE ejection and Roche lobe overflow, while for FRB 20201124A the system may experience multiple CE ejections (see Figure 4, Section 4).
- For FRB 20121102A, the remnant WD mass falls below the critical mass after the CE phase. Stable mass transfer occurs when the WD fills its Roche lobe at the periastron. For FRB 20201124A, the final binary system consisting of an NS and a stripped O-Ne WD should be in a circular orbit. Following the complete ejection of the WD envelope, the remaining mass transfer rate decreases significantly, leading to a sharp decrease in the event rate of FRB 20201124A (see Section 4.1 and Section 4.2).
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CE | Common Envelope |
| CHIME | Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment |
| FAST | Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope |
| FRB | Fast Radio Burst |
| GRB | Gamma Ray Burst |
| LISA | Laser Interferometer Space Antenna |
| NS | Neutron Star |
| WD | White Dwarf |
| WT | Waiting Time |
| 1 | https://www.chime-frb.ca/catalog (accessed on 20 April 2025) [8]. |
| 2 | The length of the activity window depends on observing frequency. For example, the activity phase of the bursts detected by LOFAR in the 110–188 MHz is ∼, whereas the activity window of bursts detected by CHIME/FRB (400–800 MHz) is ∼ of the activity cycle [15]. |
| 3 | This repeater was first discovered by CHIME/FRB [35]. |
| 4 | |
| 5 | https://www.chime-frb.ca/repeaters/FRB20201124A (accessed on 20 April 2025). |
| 6 |
References
- Cordes, J.M.; Chatterjee, S. Fast Radio Bursts: An Extragalactic Enigma. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 417–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, E.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Lorimer, D.R. Fast radio bursts. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2019, 27, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, E.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Lorimer, D.R. Fast radio bursts at the dawn of the 2020s. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2022, 30, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcote, B.; Nimmo, K.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Tendulkar, S.P.; Bassa, C.G.; Paragi, Z.; Keimpema, A.; Bhardwaj, M.; Karuppusamy, R.; Kaspi, V.M.; et al. A repeating fast radio burst source localized to a nearby spiral galaxy. Nature 2020, 577, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, S.D.; Bannister, K.W.; Bhandari, S.; Deller, A.T.; Ekers, R.D.; Glowacki, M.; Gordon, A.C.; Gourdji, K.; James, C.W.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; et al. A luminous fast radio burst that probes the Universe at redshift 1. Science 2023, 382, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, C.D.; Ravi, V.; Belov, K.V.; Hallinan, G.; Kocz, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; McKenna, D.L. A fast radio burst associated with a Galactic magnetar. Nature 2020, 587, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.C. et al. [The CHIME/FRB Collaboration] A bright millisecond-duration radio burst from a Galactic magnetar. Nature 2020, 587, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M. et al. [The CHIME/FRB Collaboration] The First CHIME/FRB Fast Radio Burst Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2021, 257, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.Q.; Xie, W.J.; Deng, C.M.; Li, L.; Dai, Z.G.; Zhang, H.M. Can a Single Population Account for the Discriminant Properties in Fast Radio Bursts? Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Gu, W.M.; Sun, M.Y.; Yi, T. One-off and Repeating Fast Radio Bursts: A Statistical Analysis. Astrophys. J. 2022, 939, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.H.; Zhang, C.M.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.W.; Peng, B.; Zhu, W.W.; Strom, R.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, N.; Wu, Q.D.; et al. Luminosity distribution of fast radio bursts from CHIME/FRB Catalog 1 by means of the updated Macquart relation. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2022, 367, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, J.W.T.; Spitler, L.G.; Seymour, A.D.; Cordes, J.M.; Michilli, D.; Lynch, R.S.; Gourdji, K.; Archibald, A.M.; Bassa, C.G.; Bower, G.C.; et al. FRB 121102 Bursts Show Complex Time-Frequency Structure. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 876, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. The physical mechanisms of fast radio bursts. Nature 2020, 587, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. The physics of fast radio bursts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2023, 95, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Bassa, C.G.; Pleunis, Z.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Chawla, P.; Keane, E.F.; Kondratiev, V.; Michilli, D.; Nimmo, K. Propagation effects at low frequencies seen in the LOFAR long-term monitoring of the periodically active FRB 20180916B. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 9872–9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M. et al. [The CHIME/FRB Collaboration] Periodic activity from a fast radio burst source. Nature 2020, 582, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Law, C.J.; Wharton, R.S.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Bower, G.C.; Cordes, J.M.; Tendulkar, S.P.; Bassa, C.G.; Demorest, P.; et al. A direct localization of a fast radio burst and its host. Nature 2017, 541, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcote, B.; Paragi, Z.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Keimpema, A.; van Langevelde, H.J.; Huang, Y.; Bassa, C.G.; Bogdanov, S.; Bower, G.C.; Burke-Spolaor, S.; et al. The Repeating Fast Radio Burst FRB 121102 as Seen on Milliarcsecond Angular Scales. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 834, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwade, K.M.; Mickaliger, M.B.; Stappers, B.W.; Morello, V.; Agarwal, D.; Bassa, C.G.; Breton, R.P.; Caleb, M.; Karastergiou, A.; Keane, E.F.; et al. Possible periodic activity in the repeating FRB 121102. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 3551–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruces, M.; Spitler, L.G.; Scholz, P.; Lynch, R.; Seymour, A.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Gouiffés, C.; Hilmarsson, G.H.; Kramer, M.; Munjal, S. Repeating behaviour of FRB 121102: Periodicity, waiting times, and energy distribution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 500, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.G.; Zhong, S.Q. Periodic Fast Radio Bursts as a Probe of Extragalactic Asteroid Belts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 895, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.M.; Yi, T.; Liu, T. A neutron star-white dwarf binary model for periodically active fast radio burst sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 497, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutikov, M.; Barkov, M.V.; Giannios, D. FRB Periodicity: Mild Pulsars in Tight O/B-star Binaries. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 893, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.M.; Zhong, S.Q.; Dai, Z.G. An Accreting Stellar Binary Model for Active Periodic Fast Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2021, 922, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Gu, W.M.; Fu, J.B.; Weng, S.S.; Wang, J.F.; Sun, M.Y. Repeating Ultraluminous X-Ray Bursts and Repeating Fast Radio Bursts: A Possible Association? Astrophys. J. 2022, 937, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Q.; Chen, H.Y.; Gu, W.M.; Yi, T. Effects of Gravitational-wave Radiation of Eccentric Neutron Star-White Dwarf Binaries on the Periodic Activity of Fast Radio Burst Sources. Astrophys. J. 2022, 929, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniamini, P.; Wadiasingh, Z.; Metzger, B.D. Periodicity in recurrent fast radio bursts and the origin of ultralong period magnetars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 3390–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, Y.; Beloborodov, A.M.; Bransgrove, A. Precessing Flaring Magnetar as a Source of Repeating FRB 180916.J0158+65. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 895, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zou, Y.C. Orbit-induced Spin Precession as a Possible Origin for Periodicity in Periodically Repeating Fast Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 893, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Gu, W.M.; Sun, M.; Liu, T.; Yi, T. Reconciling the 16.35-day Period of FRB 20180916B with Jet Precession. Astrophys. J. 2021, 921, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, N.; Metzger, B.D.; Beniamini, P.; Margalit, B.; Renzo, M.; Sironi, L.; Kovlakas, K. Periodic Fast Radio Bursts from Luminous X-ray Binaries. Astrophys. J. 2021, 917, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, P.; Zhu, W.W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.X.; Duan, R.; Zhang, Y.K.; Feng, Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Chatterjee, S.; et al. A bimodal burst energy distribution of a repeating fast radio burst source. Nature 2021, 598, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Niu, J.R.; Chen, P.; Lee, K.J.; Zhu, W.W.; Dong, S.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, J.C.; Wang, B.J.; Xu, J.W.; et al. A fast radio burst source at a complex magnetized site in a barred galaxy. Nature 2022, 609, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Wang, P.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Tsai, C.W.; Niu, C.H.; Luo, R.; Yao, J.M.; Zhu, W.W.; et al. FAST Observations of an Extremely Active Episode of FRB 20201124A. II. Energy Distribution. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 22, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanman, A.E.; Andersen, B.C.; Chawla, P.; Josephy, A.; Noble, G.; Kaspi, V.M.; Bandura, M.; Boyle, P.J.; Brar, C.; Breitman, D.; et al. A Sudden Period of High Activity from Repeating Fast Radio Burst 20201124A. Astrophys. J. 2022, 927, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.R.; Zhu, W.W.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, D.J.; Zhang, Y.K.; Jiang, J.C.; Han, J.L.; Li, D.; Lee, K.J.; et al. FAST Observations of an Extremely Active Episode of FRB 20201124A. IV. Spin Period Search. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 22, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, D.M.; Snelders, M.P.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Nimmo, K.; Jahns, J.N.; Spitler, L.G.; Gourdji, K.; Hilmarsson, G.H.; Michilli, D.; Ould-Boukattine, O.S.; et al. Arecibo observations of a burst storm from FRB 20121102A in 2016. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 3577–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.C.; Wang, W.Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.W.; Zhang, C.F.; Wang, B.J.; Zhou, D.J.; Zhang, Y.K.; Niu, J.R.; Lee, K.J.; et al. FAST Observations of an Extremely Active Episode of FRB 20201124A. III. Polarimetry. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 22, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.J.; Han, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Lee, K.J.; Zhu, W.W.; Li, D.; Jing, W.C.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Jiang, J.C.; et al. FAST Observations of an Extremely Active Episode of FRB 20201124A: I. Burst Morphology. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 22, 124001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.; Olsson, E.; Davies, M.B. A new type of long gamma-ray burst. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 374, L34–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.C.; Bandura, K.; Bhardwaj, M.; Boyle, P.J.; Breitman, D.; Cassanelli, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Chawla, P.; Cliche, J.F.; Cubranic, D.; et al. Sub-second periodicity in a fast radio burst. Nature 2022, 607, 256–259. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.M.; Dong, Y.Z.; Liu, T.; Ma, R.Y.; Wang, J.F. A Neutron Star-White Dwarf Binary Model for Repeating Fast Radio Burst 121102. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 823, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczyński, B. Evolutionary Processes in Close Binary Systems. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1971, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbunt, F.; Rappaport, S. Mass Transfer Instabilities Due to Angular Momentum Flows in Close Binaries. Astrophys. J. 1988, 332, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, T.R.; Nelemans, G.; Steeghs, D. Mass transfer between double white dwarfs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 350, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, P.C. Gravitational Radiation and the Motion of Two Point Masses. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepinsky, J.F.; Willems, B.; Kalogera, V.; Rasio, F.A. Interacting Binaries with Eccentric Orbits. II. Secular Orbital Evolution due to Non-conservative Mass Transfer. Astrophys. J. 2009, 702, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haaften, L.M.; Nelemans, G.; Voss, R.; Wood, M.A.; Kuijpers, J. The evolution of ultracompact X-ray binaries. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubow, S.H.; Shu, F.H. Gas dynamics of semidetached binaries. Astrophys. J. 1975, 198, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webbink, R.F. Stellar evolution and binaries. Interact. Bin. Stars 1985, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Sberna, L.; Toubiana, A.; Miller, M.C. Golden Galactic Binaries for LISA: Mass-transferring White Dwarf Black Hole Binaries. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepinsky, J.F.; Willems, B.; Kalogera, V.; Rasio, F.A. Interacting Binaries with Eccentric Orbits: Secular Orbital Evolution Due to Conservative Mass Transfer. Astrophys. J. 2007, 667, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosopoulou, F.; Kalogera, V. Orbital Evolution of Mass-transferring Eccentric Binary Systems. II. Secular Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2016, 825, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.F. Fast, Ultraluminous X-Ray Bursts from Tidal Stripping of White Dwarfs by Intermediate-mass Black Holes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 871, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrick, A.; Davies, M.B.; Church, R.P. Mass transfer in white dwarf-neutron star binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 3556–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.W.; Ge, H.W.; Chen, X.F.; Chen, H.L. Binary Population Synthesis. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Liu, Z.W.; Han, Z.W. Binary stars in the new millennium. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2024, 134, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livio, M.; Soker, N. The Common Envelope Phase in the Evolution of Binary Stars. Astrophys. J. 1988, 329, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webbink, R.F. Double white dwarfs as progenitors of R Coronae Borealis stars and type I supernovae. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1984, 277, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J. The evolution of cataclysmic and low-mass X-ray binaries. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1984, 54, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelemans, G.; Verbunt, F.; Yungelson, L.R.; Portegies Zwart, S. Reconstructing the evolution of double helium white dwarfs: Envelope loss without spiral-in. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 360, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Nelemans, G.; Yungelson, L.R.; Portegies Zwart, S.F.; Verbunt, F. Population synthesis for double white dwarfs. I. Close detached systems. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 365, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.W. X-ray binaries in globular clusters. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1975, 199, L143–L145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tout, C.A.; Eggleton, P.P. Tidal enhancement by a binary companion of stellar winds from cool giants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1988, 231, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. A “Cosmic Comb” Model of Fast Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 836, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsten, F.; Ould-Boukattine, O.S.; Herrmann, W.; Gawroński, M.P.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Lu, W.; Snelders, M.P.; Chawla, P.; Yang, J.; Blaauw, R.; et al. A link between repeating and non-repeating fast radio bursts through their energy distributions. Nat. Astron. 2024, 8, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.Q.; Dai, Z.G. Magnetars from Neutron Star-White Dwarf Mergers: Application to Fast Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michilli, D.; Seymour, A.; Hessels, J.W.T.; Spitler, L.G.; Gajjar, V.; Archibald, A.M.; Bower, G.C.; Chatterjee, S.; Cordes, J.M.; Gourdji, K.; et al. An extreme magneto-ionic environment associated with the fast radio burst source FRB 121102. Nature 2018, 553, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Dai, Z.G.; Cheng, K.S. Repeating fast radio burst 20201124A originates from a magnetar/Be star binary. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, N.; Metzger, B.D. Radio Nebulae from Hyperaccreting X-Ray Binaries as Common-envelope Precursors and Persistent Counterparts of Fast Radio Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2022, 937, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ai, S.K.; Zhang, B.B.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.K.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Yin, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Lü, H.J. A long-duration gamma-ray burst with a peculiar origin. Nature 2022, 612, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.Q.; Li, L.; Dai, Z.G. GRB 211211A: A Neutron Star-White Dwarf Merger? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 947, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Seoane, P.; Andrews, J.; Arca Sedda, M.; Askar, A.; Baghi, Q.; Balasov, R.; Bartos, S.S.; Bellovary, J.; Berry, C.P.L.; Berti, E.; et al. Astrophysics with the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. Living Rev. Relativ. 2023, 26, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Cao, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Qu, Y.H.; Niu, J.R.; Zhu, W.W.; Han, J.L.; et al. FAST Observations of FRB 20220912A: Burst Properties and Polarization Characteristics. Astrophys. J. 2023, 955, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, U.; Roy, J.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Dudeja, C.; Kudale, S. Low-frequency, wideband study of an active repeater, FRB 20240114A, with the GMRT. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.09749. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Dai, Z.G.; Wu, X.F. The Propagation of Fast Radio Bursts in the Magnetosphere Shapes Their Waiting-time and Flux Distributions. Astrophys. J. 2024, 962, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.W.; Niu, J.R.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zhou, D.J.; Xu, H.; Wang, P.; Niu, C.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, S.; et al. Hyper-active repeating fast radio bursts from rotation modulated starquakes on magnetars. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.16626. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.-Y. Reconciling the Waiting Time Peaks Variations of Repeating FRBs with an Eccentric Neutron Star–White Dwarf Binary. Universe 2025, 11, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050133
Chen H-Y. Reconciling the Waiting Time Peaks Variations of Repeating FRBs with an Eccentric Neutron Star–White Dwarf Binary. Universe. 2025; 11(5):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050133
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hao-Yan. 2025. "Reconciling the Waiting Time Peaks Variations of Repeating FRBs with an Eccentric Neutron Star–White Dwarf Binary" Universe 11, no. 5: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050133
APA StyleChen, H.-Y. (2025). Reconciling the Waiting Time Peaks Variations of Repeating FRBs with an Eccentric Neutron Star–White Dwarf Binary. Universe, 11(5), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11050133





