On the Properties of the Power-Law Cosmological Solutions in Lovelock Gravity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Model
- We leave only the highest Lovelock contribution—indeed, since we are interested in the high-curvature regime, terms with higher orders in curvature will dominate those with lower, such that the latter could be omitted;
- We employ the power-law ansatz , with being the Kasner exponent.
- Power sum
- Elementary symmetric polynomialsFor practical purposes it may be better to use a recursive analog of (10)—with all at hand from the beginning, calculate one after another:
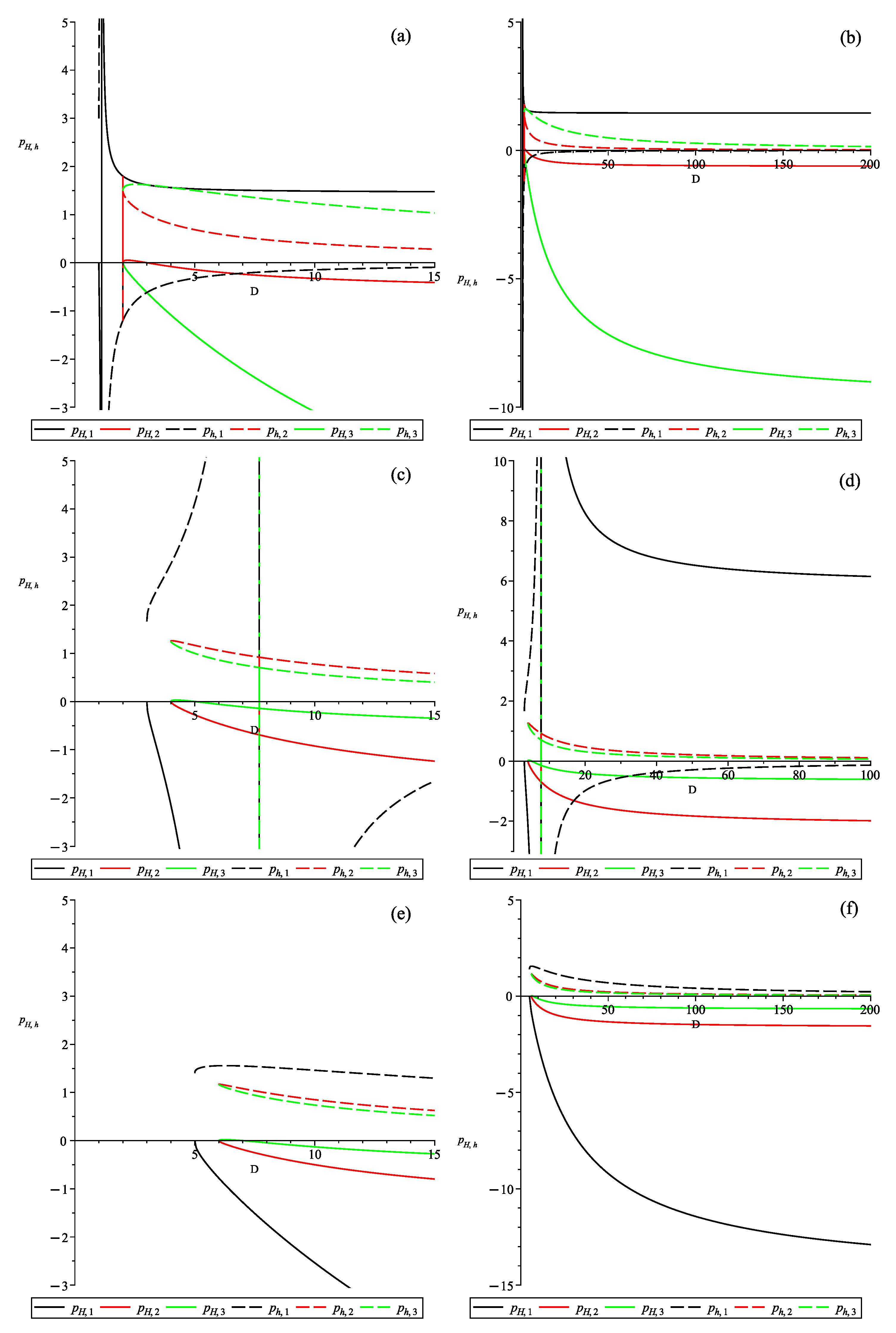
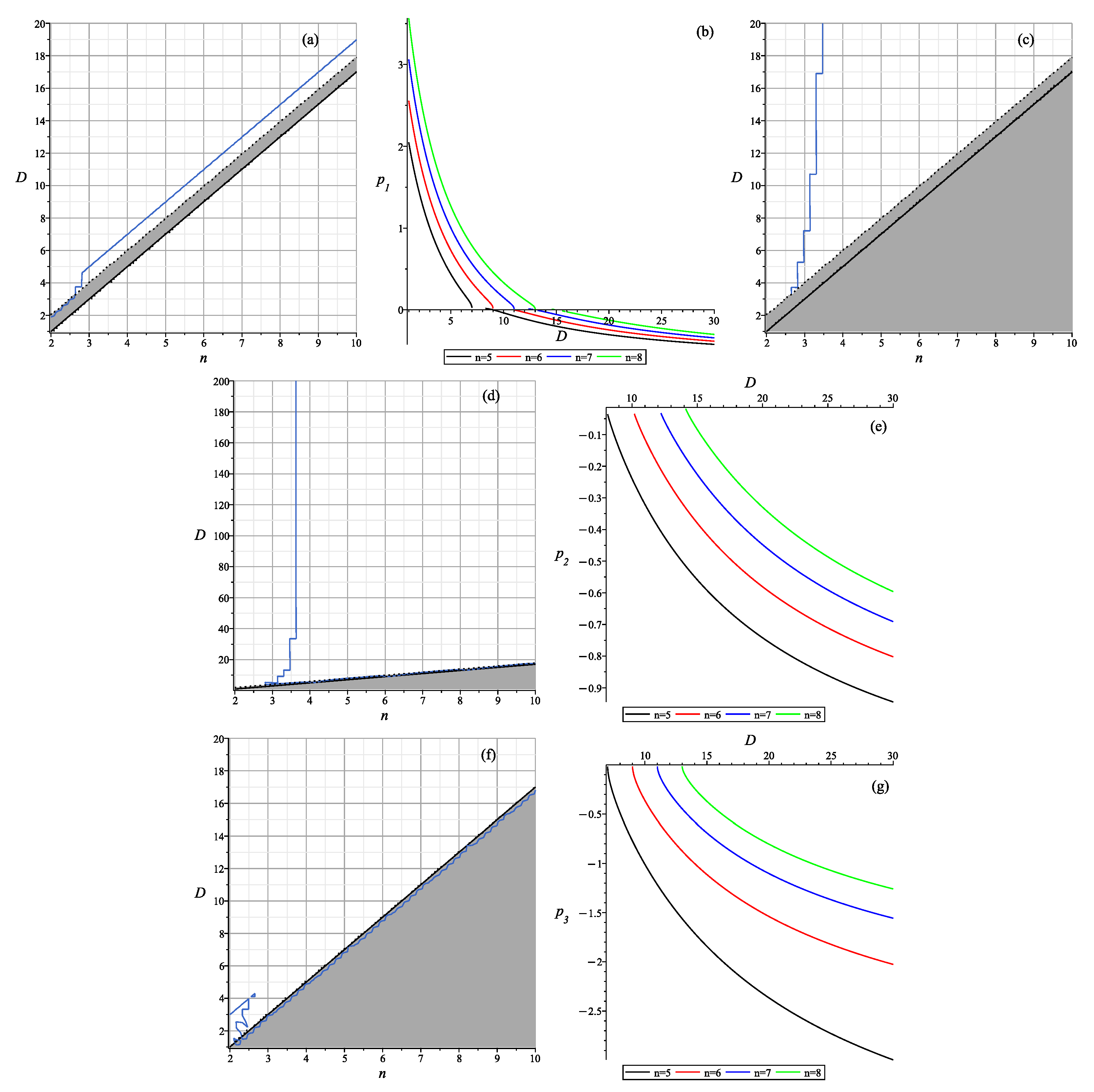
3. Particular n Cases
3.1. (Gauss–Bonnet)
- At , all solutions of the cubic part of are trivial, leaving us with only the solution;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are , such that there is only one non-trivial solution in addition to the solution;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are such that there are two non-trivial solutions in addition to the solution, with one of them being able to describe realistic compactification.
- ;
- ;
- .
3.2. (Cubic Lovelock)
- At , all solutions of the cubic part of are trivial, leaving us with only the solution;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are , such that there is only one non-trivial solution in addition to , but it has a contracting three-dimensional subspace, making it unrealistic;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are , such that there are two non-trivial solutions in addition to , but both of them have a contracting three-dimensional subspace, making them unrealistic;
- At there are three distinct solutions of the cubic part of , but all of them have a contracting three-dimensional subspace, making all of them unrealistic.
- ;
- ;
- .
3.3.
- At , all solutions of the cubic part of are trivial, leaving us with only the solution;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are , such that there is only one non-trivial solution in addition to , but it has a contracting three-dimensional subspace, making it unrealistic;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are , such that there are two non-trivial solutions in addition to , but both of them have a contracting three-dimensional subspace, making them unrealistic.
- ;
- ;
- .
3.4. Conclusions
4. General n Case
- At , all solutions of the cubic part of are trivial, leaving us with only the solution;
- At , solutions of the cubic part of are , such that there is only one non-trivial solution in addition to , but it has a contracting three-dimensional subspace for , making it unrealistic;
- At solutions of the cubic part of aresuch that there are two non-trivial solutions in addition to , but for , both of them have a contracting three-dimensional subspace, making them unrealistic.
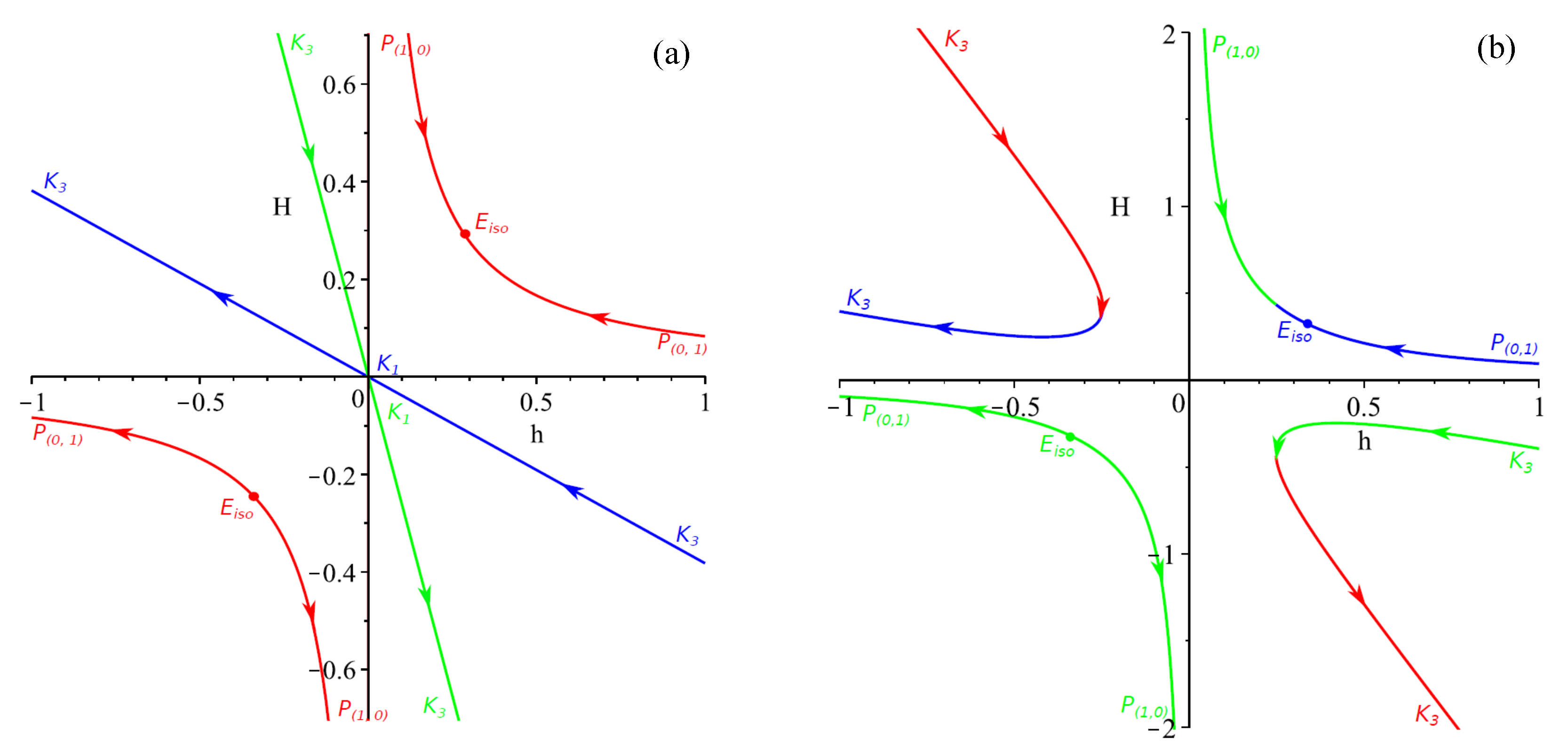
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordström, G. Über die Möglichkeit, das Elektromagnetische Feld und das Gravitationsfeld zu vereiningen. Phys. Z. 1914, 15, 504–506. [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza, T. Zum Unitätsproblem der Physik. Sit. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. 1921, K1, 966. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, O. Quantentheorie und fünfdimensionale Relativitätstheorie. Z. Phys. 1926, 37, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, O. The Atomicity of Electricity as a Quantum Theory Law. Nature 1926, 118, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherk, J.; Schwarz, J.H. Dual Models for Nonhadrons. Nucl. Phys. B 1974, 81, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelas, P.; Horowitz, G.T.; Strominger, A.; Witten, E. Vacuum configurations for superstrings. Nucl. Phys. B 1985, 258, 46–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiebach, B. Curvature squared terms and string theories. Phys. Lett. B 1985, 156, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumino, B. Gravity theories in more than four dimensions. Phys. Rep. 1986, 137, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelock, D. Einstein Tensor and Its Generalizations. J. Math. Phys. 1971, 12, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Hoissen, F. Spontaneous compactification with quadratic and cubic curvature terms. Phys. Lett. B 1985, 163, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deruelle, N.; Fariña-Busto, L. Lovelock gravitational field equations in cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1990, 41, 3696–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Hoissen, F. Dimensionally continued Euler forms: Kaluza-Klein cosmology and dimensional reduction. Class. Quant. Gravity 1986, 3, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena Marugán, G.A. Dynamically generated four-dimensional models in Lovelock cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1992, 46, 4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Makarenko, A.N.; Obukhov, V.V.; Osetrin, K.E.; Filippov, A.E. Stationary vs. singular points in an accelerating FRW cosmology derived from six-dimensional Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 644, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.I.; Ohta, N. Inflation from superstring and M-theory compactification with higher order corrections. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 063520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.I.; Ohta, N. Cosmic acceleration with a negative cosmological constant in higher dimensions. JHEP 2014, 1406, 095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, F.; Giacomini, A.; Pavluchenko, S.A. Dynamical compactification in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity from geometric frustration. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 064044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, F.; Giacomini, A.; Pavluchenko, S.A. Cosmological dynamics in higher-dimensional Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2014, 46, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, F.; Giacomini, A.; Pavluchenko, S.A.; Toporensky, A. Friedmann dynamics recovered from compactified Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet cosmology. Gravit. Cosmol. 2018, 24, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.; Toporensky, A. Effects of spatial curvature and anisotropy on the asymptotic regimes in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Giacomini, A.; Pavluchenko, S.A.; Toporensky, A. Cosmological solutions in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity with static curved extra dimensions. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Pavluchenko, S.A. Some aspects of the cosmological dynamics in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2021, 36, 2150092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Giacomini, A.; Toporensky, A. Dynamic compactification with stabilized extra dimensions in cubic Lovelock gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2018, 50, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Giacomini, A.; Toporensky, A. Anisotropic cosmological dynamics in Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity: An example of dynamical compactification in 7+1 dimensions. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2020, 52, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Toporensky, A. Stability Analysis of Compactification in 3rd Order Lovelock Gravity. Gravit. Cosmol. 2023, 29, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Toporensky, A. Splitting into two isotropic subspaces as a result of cosmological evolution in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Gravit. Cosmol. 2019, 25, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Brassel, B.P.; Maharaj, S.D. Dust Universes in Higher Dimensions with Gauss–Bonnet Corrections. Universe 2025, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, A. Universal cosmological solutions in Lovelock gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2025, 85, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulware, D.G.; Deser, S. String-generated gravity models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 55, 2656–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.T. Symmetric Solutions to the Gauss-Bonnet Extended Einstein Equations. Nucl. Phys. B 1986, 268, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Anti-de-Sitter black hole thermodynamics in higher derivative gravity and new confining–deconfining phases in dual CFT. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 521, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Ogushi, S. Friedmann-Robertson-Walker brane cosmological equations from the five-dimensional bulk (A)dS black hole. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2002, 17, 4809–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetic, M.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Black Hole Thermodynamics and Negative Entropy in deSitter and Anti-deSitter Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Nucl. Phys. B 2002, 628, 295–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.G. Gauss-Bonnet black holes in AdS spaces. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 084014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, T.; Maeda, H. Spacetime structure of static solutions in Gauss-Bonnet gravity: Neutral case. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, T.; Maeda, H. Spacetime structure of static solutions in Gauss-Bonnet gravity: Charged case. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadhich, N.; Pons, J.M. On static black holes solutions in Einstein and Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet gravity with topology Sn × Sn. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilshire, D.L. Spherically symmetric solutions of Einstein-Maxwell theory with a Gauss-Bonnet term. Phys. Lett. B 1986, 169, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.C.; Simon, J.Z. Black-hole thermodynamics in Lovelock gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 38, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.G. A Note on Thermodynamics of Black Holes in Lovelock Gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 582, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grain, J.; Barrau, A.; Kanti, P. Exact Results for Evaporating Black Holes in Curvature-Squared Lovelock Gravity: Gauss-Bonnet Greybody Factors. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 104016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.G.; Ohta, N. Black holes in pure Lovelock gravities. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camanho, X.O.; Edelstein, J.D. A Lovelock black hole bestiary. Class. Quant. Gravity 2013, 30, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadhich, N.; Pons, J.M.; Prabhu, K. On the static Lovelock black holes. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2013, 45, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H. Final fate of spherically symmetric gravitational collapse of a dust cloud in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, M.; Maeda, H. Effects of Lovelock terms on the final fate of gravitational collapse: Analysis in dimensionally continued gravity. Class. Quant.Gravity 2006, 23, 1779–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H. Effects of Gauss–Bonnet term on the final fate of gravitational collapse. Class. Quant. Gravity 2006, 23, 2155–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadhich, N.; Ghosh, S.G.; Jhingan, S. Gravitational collapse in pure Lovelock gravity in higher dimensions. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 084024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Farhangkhah, N. Asymptotically flat radiating solutions in third order Lovelock gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 064015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reall, H.S.; Tanahashi, N.; Way, B. Shock formation in Lovelock theories. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 044013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, H. Cosmological solutions of the extended Einstein gravity with the Gauss-Bonnet term. Phys. Lett. B 1986, 179, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirnos, I.V.; Pavluchenko, S.A.; Toporensky, A.V. New features of flat (4+1)-dimensional cosmological model with a perfect fluid in Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Gravitat. Cosmol. 2010, 16, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. On exponential cosmological type solutions in the model with Gauss-Bonnet term and variation of gravitational constant. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernazarov, K.K.; Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. On exponential solutions in the Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet cosmology, stability and variation of G. Gravit. Cosmol. 2016, 22, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D. On stable exponential solutions in Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet cosmology with zero variation of G. Gravit. Cosmol. 2016, 22, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernazarov, K.K.; Ivashchuk, V.D. Stable exponential cosmological solutions with zero variation of G in the Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet model with a Λ-term. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. Stable exponential cosmological solutions with two factor spaces in the Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet model with a Λ-term. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2018, 50, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. Exact exponential cosmological solutions with two factor spaces of dimension m in EGB model with a Λ-term. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2018, 16, 1950025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernazarov, K.K.; Ivashchuk, V.D. Examples of Stable Exponential Cosmological Solutions with Three Factor Spaces in EGB Model with a Λ-Term. Gravit. Cosmol. 2019, 25, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. Exponential cosmological solutions with two factor spaces in EGB model with Λ = 0 revisited. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernazarov, K.K.; Ivashchuk, V.D. Stable exponential cosmological solutions with three different Hubble-like parameters in EGB model with a Λ-term. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S. Exponential cosmological solutions in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet gravity with two subspaces: General approach. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.10423. [Google Scholar]
- Chirkov, D.; Pavluchenko, S.; Toporensky, A. Exact exponential solutions in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet flat anisotropic cosmology. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 29, 1450093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Pavluchenko, S.; Toporensky, A. Constant volume exponential solutions in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet flat anisotropic cosmology with a perfect fluid. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2014, 46, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A.; Toporensky, A.V. Note on properties of exact cosmological solutions in Lovelock gravity. Gravitat. Cosmol. 2014, 20, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.; Pavluchenko, S.; Toporensky, A. Non-constant volume exponential solutions in higher-dimensional Lovelock cosmologies. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2015, 47, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Stability analysis of the exponential solutions in Lovelock cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 104017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D. On stability of exponential cosmological solutions with nonstatic volume factor in the Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, D.M.; Toporensky, A.V. On stable exponential cosmological solutions in the EGB model with a cosmological constant in dimensions D = 5,6,7,8. Gravit. Cosmol. 2017, 23, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernazarov, K.K.; Ivashchuk, V.D. Stable exponential cosmological solutions with zero variation of G and three different Hubble-like parameters in the Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet model with a Λ-term. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. Stable exponential cosmological solutions with 3- and l-dimensional factor spaces in the Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet model with a Λ-term. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D.; Kobtsev, A.A. On stable exponential cosmological solutions with two factor spaces in (1 + m + 2)-dimensional Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet model with Λ-term. Phil. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2022, 380, 20210177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deruelle, N. On the approach to the cosmological singularity in quadratic theories of gravity: The Kasner regimes. Nucl. Phys. B 1989, 327, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A.; Toporensky, A.V. A note on differences between (4+1)- and (5+1)-dimensional anisotropic cosmology in the presence of the Gauss-Bonnet term. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2009, 24, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V.D. On anisotropic Gauss-Bonnet cosmologies in (n + 1) dimensions, governed by an n-dimensional Finslerian 4-metric. Gravitat. Cosmol. 2010, 16, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchuk, V. On cosmological-type solutions in multi-dimensional model with Gauss-Bonnet term. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2010, 7, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirnos, I.V.; Makarenko, A.N.; Pavluchenko, S.A.; Toporensky, A.V. The nature of singularity in multidimensional anisotropic Gauss-Bonnet cosmology with a perfect fluid. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2010, 42, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. General features of Bianchi-I cosmological models in Lovelock gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. The dynamics of the flat anisotropic models in the Lovelock gravity. I: The even-dimensional case. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 104021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Cosmological dynamics of spatially flat Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet models in various dimensions. Vacuum case. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 024046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Cosmological dynamics of spatially flat Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet models in various dimensions: Low-dimensional Λ-term case. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 084019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Cosmological dynamics of spatially flat Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet models in various dimensions: High-dimensional Λ-term case. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Realistic compactification in spatially flat vacuum cosmological models in cubic Lovelock gravity: Low-dimensional case. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Realistic compactification in spatially flat vacuum cosmological models in cubic Lovelock gravity: High-dimensional case. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Realistic Compactification Models in Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet Gravity. Particles 2018, 1, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavluchenko, S.A. Cosmological Models in Lovelock Gravity: An Overview of Recent Progress. Universe 2024, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camanho, X.O.; Dadhich, N.; Molina, A. Pure Lovelock Kasner metrics. Class. Quant. Gravity 2015, 32, 175016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, I.G. Symmetric Functions and Hall Polynomials, 2nd ed.; Oxford mathematical monographs; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavluchenko, S. On the Properties of the Power-Law Cosmological Solutions in Lovelock Gravity. Universe 2025, 11, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11120390
Pavluchenko S. On the Properties of the Power-Law Cosmological Solutions in Lovelock Gravity. Universe. 2025; 11(12):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11120390
Chicago/Turabian StylePavluchenko, Sergey. 2025. "On the Properties of the Power-Law Cosmological Solutions in Lovelock Gravity" Universe 11, no. 12: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11120390
APA StylePavluchenko, S. (2025). On the Properties of the Power-Law Cosmological Solutions in Lovelock Gravity. Universe, 11(12), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11120390





