Abstract
The fundamental plane of black hole activity is a very important tool to study accretion and jets. However, we found that the SEDs of AGNs and XRBs are different in the 2–10 keV energy band, and it seems inappropriate to use 2–10 keV X-ray luminosities to study the fundamental plane. In this work, we use the luminosity near the peak of the blackbody radiation of the active galactic nuclei and black hole binaries to replace the 2–10 keV luminosity. We re-explore the fundamental plane of black hole activity by using the 2500 luminosity as the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation of AGNs and 1 keV luminosity as the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation of XRBs. We compile samples of black hole binaries and active galactic nuclei with luminosity near the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation and study the fundamental plane between radio luminosity (), the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation (), and black hole mass (). We find that the radio–peak luminosity correlations are and for AGN and XRB, respectively, in the radiatively efficient sample, and and in the radiatively inefficient sample, respectively. Based on the similarities in radio–peak correlations, we further propose a fundamental plane in radio luminosity, the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation, and black hole mass, which is radiatively efficient: with a scatter of = 0.48 dex, and radiatively inefficient: with a scatter of = 0.63 dex. Our results are similar to those of previous studies on the fundamental plane for radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient black hole activity. However, our results exhibit a smaller scatter, so when using the same part of blackbody radiation (i.e., the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation), the fundamental plane becomes a little bit tighter.
1. Introduction
Stellar-mass X-ray binaries (XRBs) and active galactic nuclei (AGNs) capture surrounding material under their own gravity, a process that emits strong radiation, such as radio and X-rays. Radio emission could originate from star formation, disk wind, and jets, and X-ray emission could originate from the corona, accretion disks, and jets [1,2,3]. In addition, the magnetic field is essential for jet formation [4]. It is believed that XRBs and AGNs are scale-invariant across the black hole mass scale and present similar physical properties [5,6,7]. Several studies have pointed out that there may be some sort of connection between the corona and the jets [8,9,10]. However, Ref. [11] posits that there is no connection between the corona and the jets. A tight correlation between the radio and X-ray luminosities was observed in XRBs during their hard states [12,13,14], and this correlation was later extended to AGNs. Considering the mass of the black hole, the authors of Ref. [5] proposed, for the first time, a fundamental plane of black hole activity:
The fundamental plane of black-hole-source activity is often believed to be one of the most prominent pieces of evidence of the similarity of XRBs and AGNs, and it provides an important empirical relation to estimate black hole mass through X-ray luminosity and radio luminosity. Subsequently, the authors of Ref. [15] compiled a bright black hole source with and presented a fundamental plane of radiatively efficient BH sources:
These results support the idea that radio emission is from relativistic jets and X-ray emission is related to the accretion mode and Eddington accretion ratio [16,17]. It is generally accepted that radio emissions come from relativistic jets and X-ray emissions come from the accretion flow or jet base. When the Eddington accretion ratio is relatively high, the most typical model is the disk–corona model, which suggests that X-rays come from the disk–corona system. When the Eddington accretion ratio is relatively small, corresponding to radiatively inefficient accretion modes. The authors of Ref. [18] studied the correlation between the hard X-ray photon indices and the Eddington ratio for six black hole X-ray binaries and found that and show an anti-correlation when is less than a critical luminosity and a positive correlation between and when is higher than a critical luminosity. Similar properties of positive correlation and anti-correlation have been found in AGNs [19,20,21,22]. The results also support the idea that X-ray emissions are related to the accretion mode and Eddington accretion ratio.
However, in these works, the X-ray luminosity of AGNs and XRBs use 2–10 keV luminosity, and by analyzing the spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of AGNs and XRBs, we found that the SEDs of AGNs and XRBs are different in the 2–10 keV energy band, and thus it seems inappropriate to use 2–10 keV X-ray luminosities to study the fundamental plane. For XRBs, the thermal emission from the thin disk peaks in soft X-rays with a peak luminosity roughly around 1 keV. Since the disk temperature in AGNs is cooler compared to that of XRBs, the peak of the AGNs disk appears in the optical/UV band [7,23], with a peak luminosity roughly around 2500 luminosity. In AGNs, there is a non-linear relation between X-ray and optical/UV emissions that is usually parameterized as a dependence between the logarithm of the monochromatic luminosity 2500 and 2 keV () [24,25]. According to this relation, the X-ray luminosity can be converted to 2500 luminosity.
The aim of our work is to use the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation to replace the 2–10 keV luminosity. Although the SED of each AGN and XRB is different, the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation is roughly at 2500 for the AGNs and roughly at 1 keV for the XRBs. Therefore, in this work, we re-explore the fundamental plane of black hole activity using 2500 luminosity as the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation of AGNs and 1 keV luminosity as the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation of XRBs. In terms of the masses of black hole objects, XRBs are homogeneous, with masses of about 3–20 , while AGNs have a broad mass range, with masses of about . The SED of each AGN is different, so different AGN masses have different peak luminosities. Since the disk temperature at 2500 is 0.005 keV, considering the scaling of the black hole accretion disk temperature with the black hole mass [26], we found that the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation of the AGN is 2500 luminosity when its black hole mass is .
This paper is structured as follows: We describe the sample of AGNs and XRBs in Section 2. In Section 3, we present our results and introduce the statistical analysis method. Our discussions are detailed in Section 4. Throughout this paper, we assume the following cosmology for AGNs: = 70 km , , and .
2. Sample
To study the fundamental plane of black hole objects at different scales, we compile a sample with radio luminosity (), the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation (), and black hole mass (). Our total sample consists of radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient samples. Our sample of radiatively efficient AGNs consists of the 64 high-luminosity radio quiet-type I AGNs with ≳ 1% compiled by the authors of Ref. [15] (see Table 1). The and for AGNs show an anti-correlation when are less than a critical luminosity, and a positive correlation between and for AGNs when the Eddington ratios are higher than a critical luminosity, where the critical luminosity is approx ≈1%. To exclude radiatively inefficient sources as much as possible, we therefore only select sources with an Eddington ratio ≳ 1%. We gather from Ref. [27] a subsample of low-luminosity AGNs with measurements of their black hole mass, nuclear radio (5 GHz), and X-ray (2–10 keV) luminosities. The black hole masses in this subsample are mainly calculated based on the empirical relationship ([28,29] review the various ways to estimate black hole masses in detail); in addition, we use other methods to estimate the black hole mass to obtain more reliable black hole masses, as detailed in the references in Table 2. The nuclear radio luminosities of a subsample of the radiatively inefficient AGNs are mainly from Very Large Arrey (VLA) or Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) observations, and the X-ray luminosities are mainly from Chandra or XMM-Newton observations. We obtain the redshift of the radiatively inefficient AGNs from the NED, and calculate the luminosities distance of the AGNs based on our assumed cosmology parameters, which convert the radio fluxes and X-ray fluxes to luminosities. As listed in Table 2, our sample of LLAGNs includes 69 sources.

Table 1.
Data of radiatively efficient AGNs.

Table 2.
Data of radiatively inefficient AGNs.
For the radiatively efficient sample, the AGNs photon index is taken from Ref. [31]. For the radiatively inefficient sample, we assume that the AGNs photon index = 1.8 (a typical value for the X-ray spectrum of AGNs). The 2–10 keV X-rays luminosities are converted to 2 keV X-rays luminosities by the value of AGNs photon index. In AGNs, a non-linear relation between X-ray and optical/UV emission has been found, usually parameterized as a dependence between the logarithm of the monochromatic luminosity at 2500 Å and 2 keV [24]. For the radiatively efficient AGNs, we used the relation:
taken from Ref. [24]. For the radiatively efficient AGNs, we used the relation:
taken from Ref. [25]. Then we plugged the 2 keV into Equations (3) and (4) to obtain the 2500 luminosities for the AGNs.
Our radiatively efficient XRBs are the 134 bright hard-state XRBs compiled by the authors of Ref. [15], the main selection criteria of the subsample of XRBs are the positive correlation and the ≳ 1%, and follow the “outliers” track [55]. For the radiatively inefficient XRBs, we use the Ref. [43] subsample of black hole X-ray binaries, which includes six black hole X-ray binaries, namely GX 339-4, XTE J1118+480, V404 Cyg, XTE J1752-223, H1743-322, and A0620-00. These sources possess simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous radio and X-ray observations, and only sources with ≲ can be selected for inclusion. In this paper, the photon index of the radiatively efficient XRBs is assumed to be 2.1. For the radiatively inefficient sample, we assume that the XRBs photon index = 1.8. The 2–10 keV X-rays luminosities are converted to 1 keV X-rays luminosities by assuming the value of the photon index.
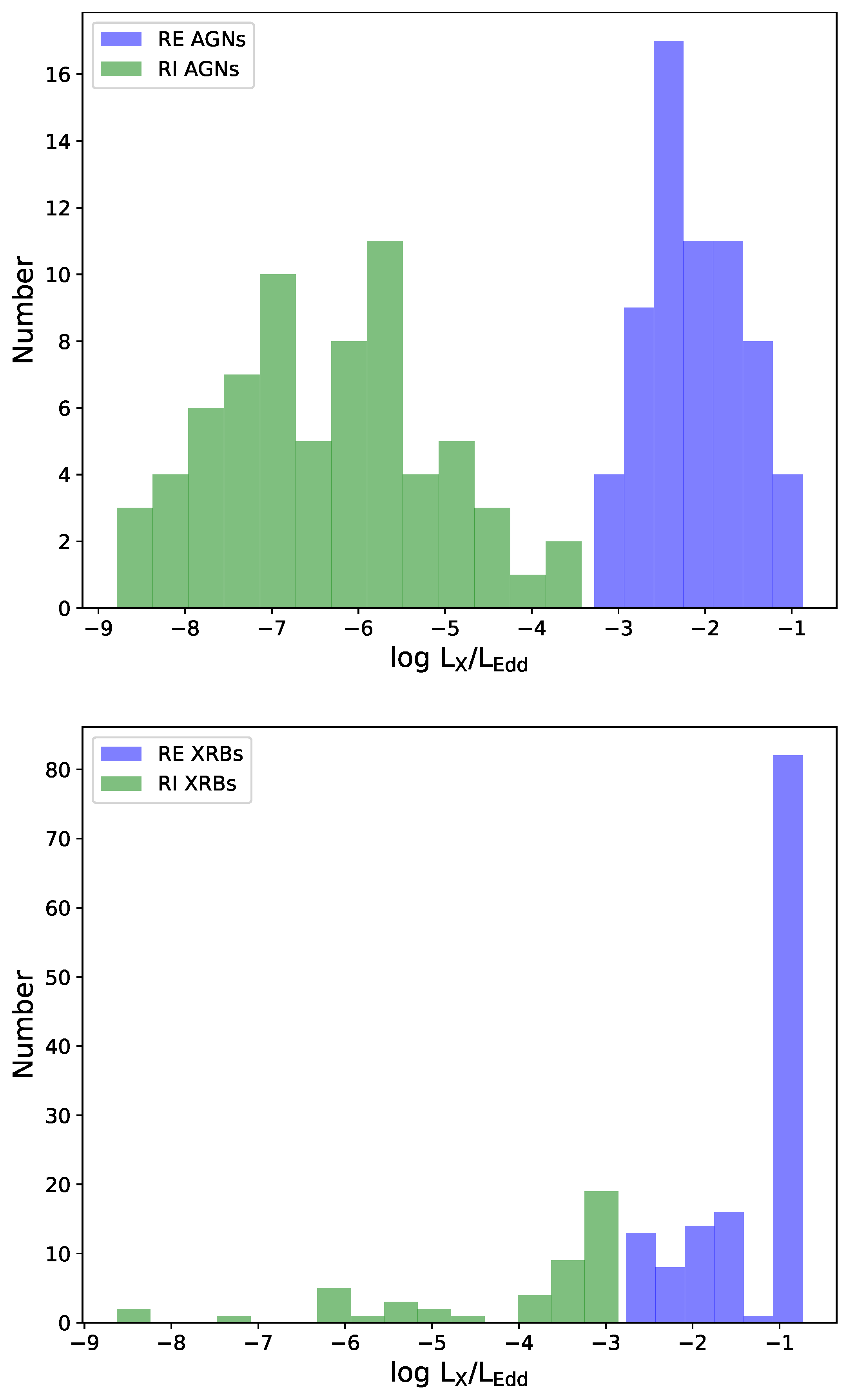
In this work, our final sample used to make the fundamental plane analysis consists of the radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient black hole sources that have available estimates for radio luminosity (), the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation (), and black hole mass (). We utilized the Eddington ratio () to divide radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient sources. As shown in Figure 1, we show the distribution of the Eddington ratio () for the radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient active galactic nuclei and black hole X-ray binaries, respectively. This includes the Eddington ratio for the sample of radiatively efficient AGNs with a median of −2.20, and for radiatively efficient XRBs with a median of −0.90, as well as the Eddington ratio for the sample of radiatively inefficient AGNs with a median of −6.40, and for radiatively inefficient XRBs with a median of −3.35. Our sample of RQ AGNs is limited to those with . This is because RQ AGNs with may have entered a soft state similar to the XRBs, when the radio emission is weak.
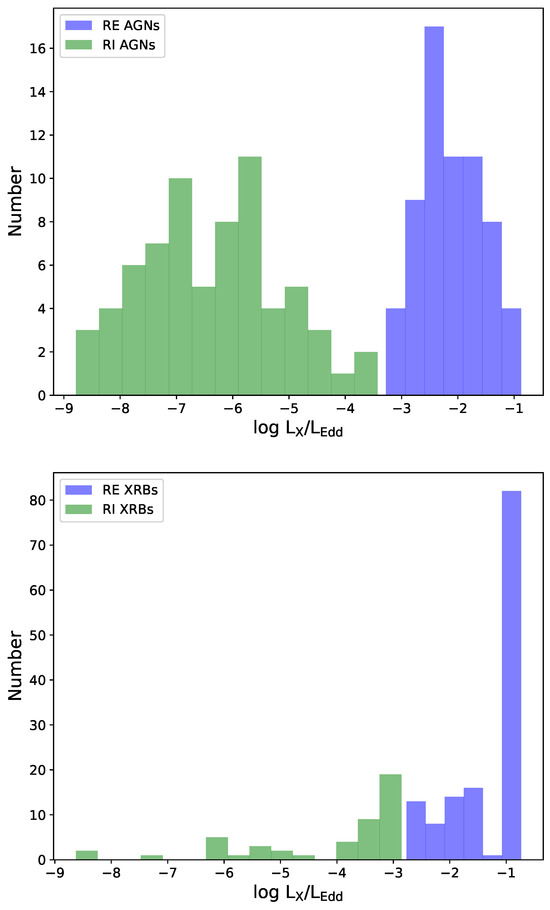
Figure 1.
Distribution of the Eddington ratio for the radiatively efficient (purple histogram) and radiatively inefficient (green histogram) active galactic nuclei and black hole X-ray binaries. The top panel represents the distribution of the Eddington ratio for AGNs in our sample; the bottom panel represents the distribution of the Eddington ratio for XRBs in our sample.
3. Results
We first analyze the correlation between the radio luminosities and the peak luminosities of the blackbody radiation of AGNs and XRBs (the peak luminosities of the blackbody radiation are about 2500 luminosities for AGNs and 1 keV luminosities for XRBs). We use and to examine the radio/peak correlation [45]. In this work, following the fundamental plane proposed in Ref. [5], we defined the fundamental plane of black hole activity as follows:
where is the 5 GHz radio luminosity, is the peak luminosity of the blackbody radiation, and is the black hole mass, the luminosity units are erg and the black hole mass units are . We calculate the coefficients of Equation (5) using a method similar to Ref. [5] and minimize the following statistic, i.e.,
where b is a constant, and the AGNs and XRBs adopt typical observational uncertainties, respectively.
3.1. Sample of Radiatively Efficient Black Hole Sources
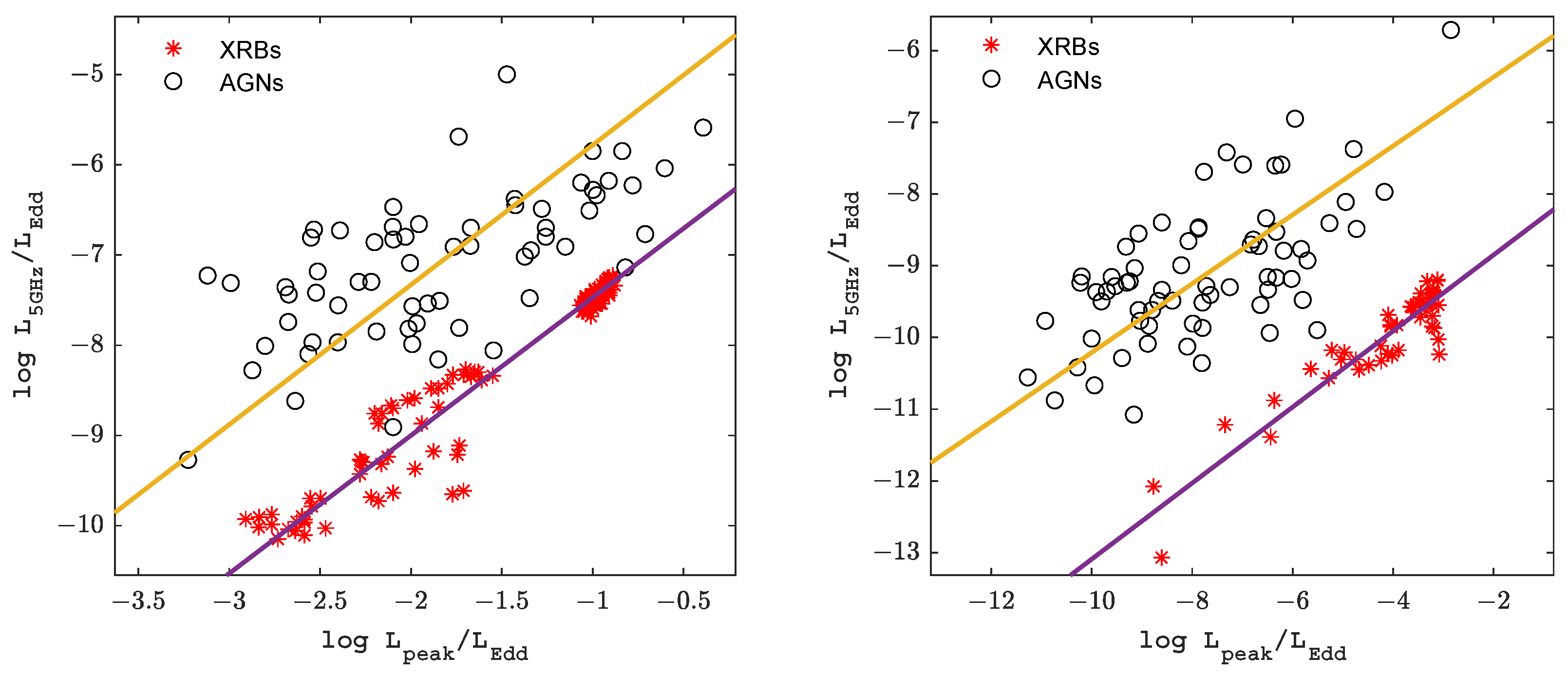
For radiatively efficient black hole objects, as shown in Figure 2, which shows the relationship, we find similar correlations between the radio luminosities and the peak luminosities of the blackbody radiation of AGNs and XRBs, and their best-fit results are as follows:
Equations (7) and (8) represent the best fit for the subsamples of the radiatively efficient AGNs and XRBs, respectively. The uncertainties in the radio luminosities, peak luminosities, and black hole masses of the AGNs adopt typical observational uncertainties, which are = 0.2 dex [56], = 0.3 dex [57], and = 0.4 dex [58]; the typical observational uncertainties for XRBs are = 0.1 dex, = 0.1 dex [14,59], and = 0.15 dex [60], where the uncertainties of XRBs were inferred from the propagation of error method.
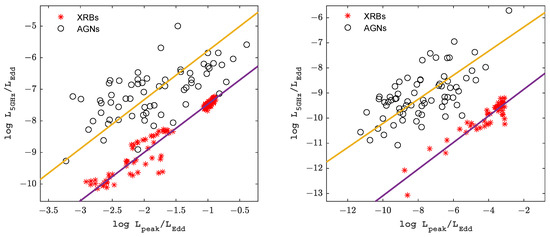
Figure 2.
Eddington-scaled radio–peak correlations for AGNs and XRBs. The left panel represents the radio–peak correlation for radiatively efficient BH sources; the right panel represents the radio–peak correlation for radiatively inefficient BH sources. The solid lines are the best fits for the AGNs and XRBs (see Equations (7), (8), (12) and (13)), respectively.
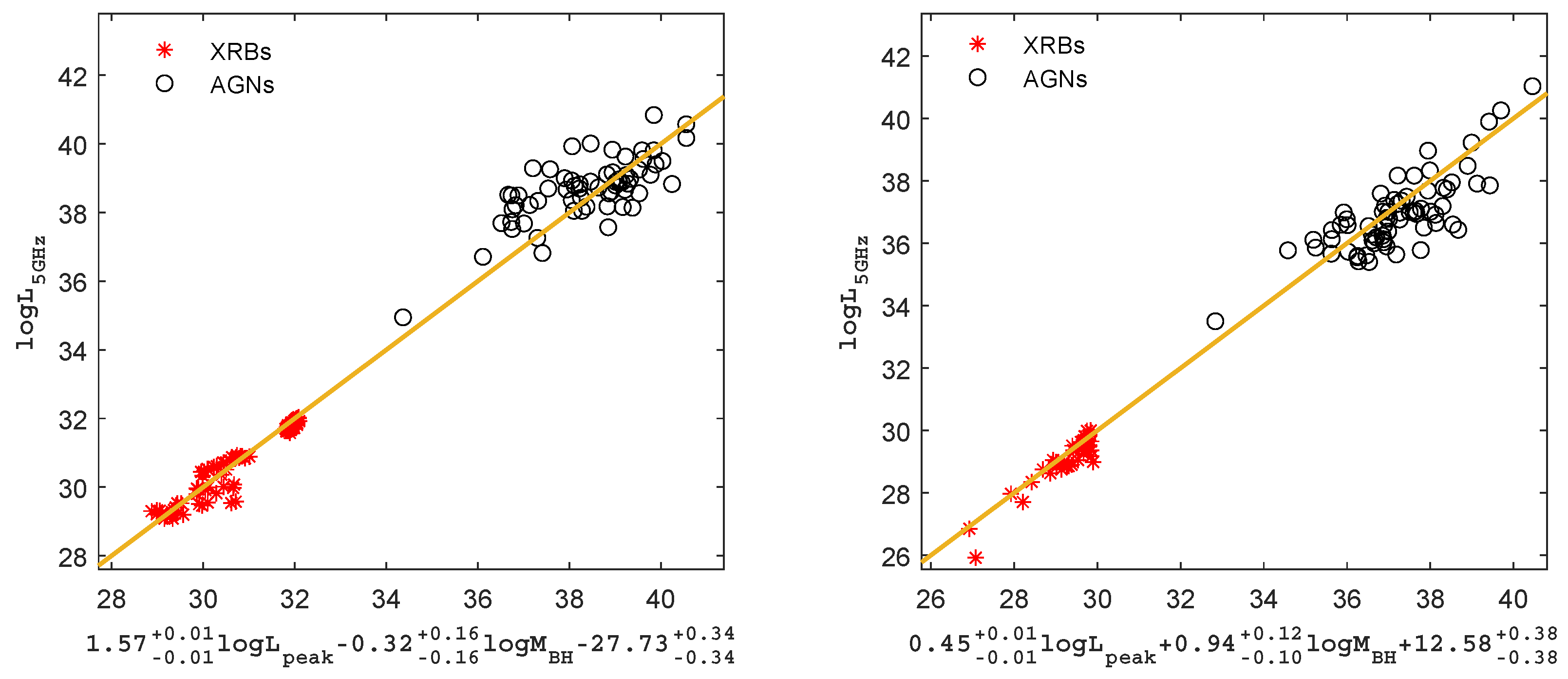
Based on the similarity between the radio luminosities and the peak luminosities of blackbody radiation, the best fits for the fundamental plane of AGNs and XRBs is as follows:
where is 2500 luminosity for AGNs and 1 keV luminosity for XRBs, respectively, and a scatter of = 0.48 dex, the results are shown in Figure 3.
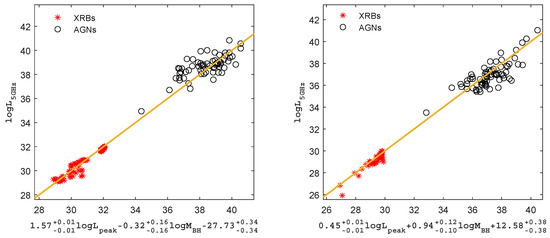
Figure 3.
The fundamental plane of black hole activity for AGNs and XRBs. The left panel represents the fundamental plane for radiatively efficient BH sources; the right panel represents the fundamental plane for radiatively inefficient BH sources. The solid lines are the best fittings.
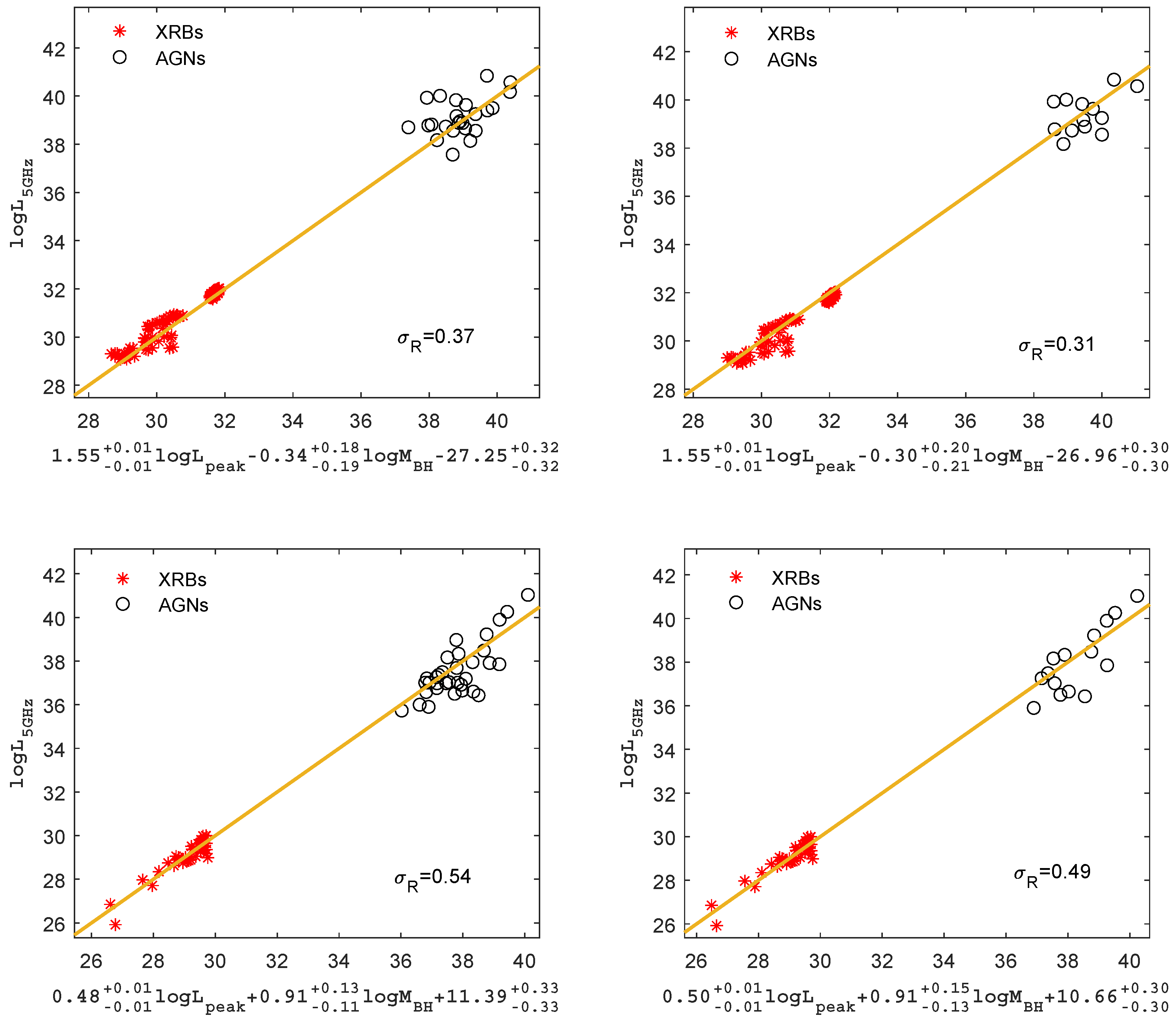
To reduce the additional scatter, we use a subsample of AGNs with a narrow range in black hole mass ( and ), selected from Table 1, to examine the fundamental plane of the AGNs with the black hole mass and XRBs. The results are shown in Figure 4, for the radiatively efficient sample, the best fits for the fundamental plane of the subsample of AGNs with the black hole mass and XRBs are as follows:
with a scatter of = 0.37 dex.The best fits for the fundamental plane of the subsample of AGNs with the black hole mass and XRBs are as follows:
with a scatter of = 0.31 dex.
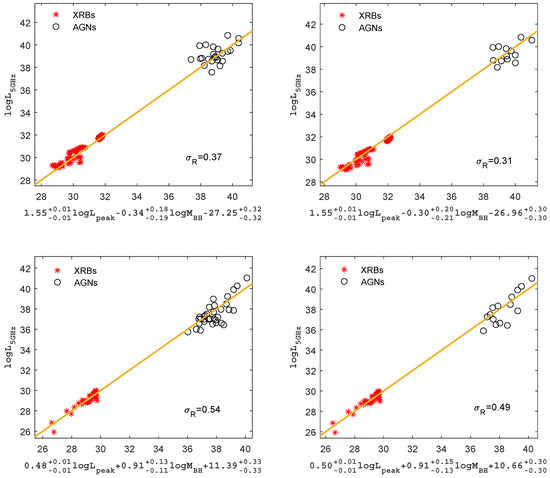
Figure 4.
The fundamental plane of black hole activity for the AGNs with BH mass in narrow range and XRBs. The top panels represent the fundamental plane for radiatively efficient BH sources, the top-left panel represents the fundamental plane for the subsample of AGNs (with the black hole mass ) and XRBs, and the top-right panel represents the fundamental plane for the subsample of AGNs (with the black hole mass ) and XRBs; the bottom panels represent the fundamental plane for radiatively inefficient BH sources, the bottom-left panel represents the fundamental plane for the subsample of AGNs (with the black hole mass ) and XRBs, and the bottom-right panel represents the fundamental plane for the subsample of AGNs (with the black hole mass ) and XRBs. The solid lines are the best fittings.
3.2. Sample of Radiatively Inefficient Black Hole Sources
For radiatively inefficient black hole objects, we use the same analysis, as shown in Figure 2, where the radio luminosities and the peak luminosities of the blackbody radiation of radiatively inefficient black hole objects have a similar correlation, with a best fit as follows:
Equations (12) and (13) represent the best fit for radiatively inefficient AGNs and XRBs subsamples, respectively. The uncertainties in the radio luminosities, peak luminosities, and black hole masses of the AGNs adopt typical observational uncertainties, which are = 0.2 dex [56], = 0.3 dex [57], and = 0.4 dex [58]; the typical observational uncertainties for XRBs are = 0.1 dex, = 0.1 dex [14,59] and = 0.15 dex [60], where the uncertainties of XRBs were inferred from the propagation of error method. The best fits for the fundamental plane of radiatively inefficient black hole objects are as follows:
where is 2500 luminosity for AGNs and 1 keV luminosity for XRBs, respectively, and a scatter of = 0.63 dex; the results are shown in Figure 3.
Similarly, we use a subsample of AGNs with a narrow range in black hole mass ( and ), selected from Table 2, to examine the fundamental plane of the AGNs with the black hole mass and XRBs. The results are shown in Figure 4, for the radiatively inefficient sample, the best fits for the fundamental plane of the subsample of AGNs with the black hole mass and XRBs are as follows:
with a scatter of = 0.54 dex. The best fits for the fundamental plane of the subsample of AGNs with the black hole mass and XRBs are as follows:
with a scatter of = 0.49 dex. The peak luminosity of the AGNs with black hole mass is 2500 . It can be found that after using the subsamples of AGNs with a narrow range in black hole mass ( and ), the fundamental plane becomes a little bit tighter, even though the slope of is roughly unchanged.
4. Discussion
The fundamental plane of black hole activity provides a evidence on disk–jet coupling [5,15], and previous work has mainly investigated the fundamental plane of black hole activity using 5 GHz radio luminosities, 2–10 keV X-ray luminosities, and black hole masses. In this paper, we used the luminosity near the peak of blackbody radiation to replace the 2–10 keV X-ray luminosity; one of the main advantage of using the luminosity near the peak of blackbody radiation to replace the 2–10 keV X-ray luminosity is that 2500 and 1 keV are in the same part of the blackbody radiation. We separately compiled radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient black hole samples that contained the peak luminosity of blackbody radiation. We analyzed the radio–peak luminosity correlations and the fundamental plane for radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient black hole objects, and we found that the radio–peak luminosity of AGNs and XRBs have a similar correlation, and that black hole objects with different radiative efficiencies have different fundamental planes. The reason for the difference may be that they correspond to different accretion modes. In this paper, we adopt the Eddington ratio to distinguish the radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient sources, because the Eddington ratio to some extent reflects the accretion efficiency. So far, a growing number of BH sources have been found to follow a steeper radio/X-ray correlation, namely, ∝, during . The fundamental plane of black hole activity may depend on Eddington ratio; the authors of Ref. [61] found that Eddington ratio dependence for the fundamental plane, and the samples with different Eddington ratios follow different fundamental planes for both radio-quiet AGNs and radio-loud AGNs.
We further selected two subsamples of AGNs with black hole mass in the narrow range ( and ) to study the fundamental plane of black hole objects at different scales. As shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, In the radiatively efficient sample, the fitted slope is and the scatter is dex, and the fitted slopes for the fundamental plane of the subsample of AGNs (black hole mass and , respectively) and XRBs are and , respectively, and the scatter is dex and dex. In the radiatively inefficient sample, the fitted slope is and the scatter is dex, and the fitted slopes for the fundamental plane of the subsample of AGNs (black hole mass and , respectively) and XRBs are and , respectively, and the scatter is dex and dex. We found that after using subsamples of AGNs with a narrow range in black hole mass, the fundamental plane becomes a little bit tighter, even though the slope of is roughly unchanged.
The authors of Ref. [62] found that LLAGNs and low-/hard-state XRBs follow the fundamental plane most tightly, and that Equation (1) should be most suitable for radiatively inefficient accretion model. The authors of Ref. [15] compiled a sample of radiatively efficient black hole sources, consisting of XRB outliers and bright radio-quiet AGNs, and proposed a new fundamental plane of radiatively efficient BH sources, with . In this work, we use the luminosity near the peak of the blackbody radiation of the AGNs and XRBs to replace the 2–10 keV luminosity. In the radiatively efficient sample, the slope of (see Figure 3 and Figure 4) is similar to that of [15], i.e., our work confirms the discovery of [15]. Currently, it is widely recognized that black hole spin may have an impact on the fundamental plane. While we still believe that the accretion disk have a significant effect on the jet power, the spin itself will enter the radio luminosity as a sensitive parameter, introducing scatter in correlation [5]. Therefore, the study of black hole spins may be able to reduce the scatter and obtain a better fit. This will be a focus of our future work.
In the radiatively efficient sample, we find that the radio–peak luminosities of the AGNs and XRBs present a similar correlation slope, and this similar correlation is also present in the radiatively inefficient sample. This is important observational evidence for the coupling of an accretion disk and a jet, and the radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient samples are found to follow different fundamental planes, which may correspond to different accretion physics for the central engine. The mass accretion rate is an important influence parameter for peak and radio luminosity. Through the mass accretion rate, we may be able to bridge both the radiatively efficient and radiatively inefficient fundamental planes. Therefore, exploring the correlations between peak and radio luminosities and mass accretion rates, and thus constructing a unified fundamental plane, will be a focus of our future work. The radio–peak luminosity correlations and the fundamental plane of AGNs and XRBs further suggest that black hole objects at different scales have similar central engines, and that AGNs and XRBs are likely to have similar accretion and jet mechanisms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.-J.D. and Z.Y.; methodology, A.-J.D. and W.-J.Y.; software, Z.Y., W.-J.Y. and Q.-C.L.; validation, Z.Y. and Q.-C.L.; investigation, A.-J.D., Z.Y. and Q.-C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y. and A.-J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.2022SKA0130104, No.12363005), Major Science and Technology Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (No.2022A03013-4).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the referees for insightful comments leading to improvements in the original manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Panessa, F.; Baldi, R.D.; Laor, A.; Padovani, P.; Behar, E.; McHardy, I. The origin of radio emission from radio-quiet AGN. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, M.; Winkel, N.; Vaddi, S.; Torres, M.P.; Gaspari, M.; Smirnova-Pinchukova, I.; O’Dea, C.P.; Combes, F.; Omoruyi, O.; Rose, T.; et al. The Close AGN Reference Survey (CARS): An interplay between radio jets and AGN radiation in the radio-quiet AGN HE0040-1105. Astrophys. J. 2023, 959, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husemann, B.; Scharwächter, J.; Davis, T.A.; Pérez-Torres, M.; Smirnova-Pinchukova, I.; Tremblay, G.R.; Krumpe, M.; Combes, F.; Baum, S.A.; Busch, G.; et al. The Close AGN Reference Survey (CARS)-A massive multi-phase outflow impacting the edge-on galaxy HE 1353- 1917. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Payne, D.G. Hydromagnetic flows from accretion discs and the production of radio jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1982, 199, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merloni, A.; Heinz, S.; Di Matteo, T. A Fundamental Plane of black hole activity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 345, 1057–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcke, H.; Koerding, E.; Markoff, S. A scheme to unify low-power accreting black holes-Jet-dominated accretion flows and the radio/X-ray correlation. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 414, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.J.; Anderson, S.F.; Eracleous, M.; Green, P.J.; Haggard, D.; MacLeod, C.L.; Runnoe, J.C.; Sobolewska, M.A. The analogous structure of accretion flows in supermassive and stellar mass black holes: New insights from faded changing-look quasars. Astrophys. J. 2019, 883, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R.A.; McHardy, I.M.; Baldi, R.D.; Beswick, R.J.; Argo, M.K.; Dullo, B.T.; Knapen, J.H.; Brinks, E.; Fenech, D.M.; Mundell, C.G.; et al. Radio jets in NGC 4151: Where eMERLIN meets HST. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 3842–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panessa, F.; Chiaraluce, E.; Bruni, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Laor, A.; Baldi, R.D.; Behar, E.; McHardy, I.; Tombesi, F.; Vagnetti, F. Hard-X-ray-selected active galactic nuclei–II. Spectral energy distributions in the 5–45 GHz domain. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Méndez, M.; García, F.; Altamirano, D.; Belloni, T.M.; Alabarta, K.; Zhang, L.; Bellavita, C.; Rawat, D.; Ma, R. A NICER look at the jet-like corona of MAXI J1535- 571 through type-B quasi-periodic oscillations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 520, 5144–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, E.; Miller, J.M.; Reynolds, C.; Dai, L. Relativistic reverberation in the accretion flow of a tidal disruption event. Nature 2016, 535, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, S.; Nowak, M.; Fender, R.P.; Tzioumis, A.K.; Markoff, S. Radio/X-ray correlation in the low/hard state of GX 339–4. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 400, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Fender, R.P.; Pooley, G.G. A universal radio–X-ray correlation in low/hard state black hole binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 344, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, S.; Coriat, M.; Brocksopp, C.; Tzioumis, A.K.; Fender, R.P.; Tomsick, J.A.; Buxton, M.M.; Bailyn, C.D. The ‘universal’radio/X-ray flux correlation: The case study of the black hole GX 339- 4. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 428, 2500–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.-J.; Wu, Q.; Cao, X.-F. A new fundamental plane for radiatively efficient black-hole sources. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Cui, W. Radio-X-ray correlation and the “quiescent state” of black hole sources. Astrophys. J. 2005, 629, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markoff, S.; Nowak, M.A.; Wilms, J. Going with the flow: Can the base of jets subsume the role of compact accretion disk coronae? Astrophys. J. 2005, 635, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gu, M. The X-ray spectral evolution in X-ray binaries and its application to constrain the black hole mass of ultraluminous X-ray sources. Astrophys. J. 2008, 682, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemmer, O.; Brandt, W.N.; Netzer, H.; Maiolino, R.; Kaspi, S. The hard X-ray spectral slope as an accretion rate indicator in radio-quiet active galactic nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2006, 646, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-L.; Zhao, Y.-H. Hard X-ray photon index as an indicator of bolometric correction in active galactic nuclei. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 720, L206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichas, M.; Green, P.J.; Constantin, A.; Aldcroft, T.; Kalfountzou, E.; Sobolewska, M.; Hyde, A.K.; Zhou, H.; Kim, D.-W.; Haggard, D.; et al. Empirical links between XRB and AGN accretion using the complete z<0.4 spectroscopic CSC/SDSS catalog. Astrophys. J. 2013, 778, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Constantin, A.; Green, P.; Aldcroft, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Haggard, D.; Barkhouse, W.; Anderson, S.F. Probing the balance of AGN and star-forming activity in the local universe with ChaMP. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolewska, M.A.; Siemiginowska, A.; Gierliński, M. Simulated spectral states of active galactic nuclei and observational predictions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusso, E.; Comastri, A.; Vignali, C.; Zamorani, G.; Brusa, M.; Gilli, R.; Iwasawa, K.; Salvato, M.; Civano, F.; Elvis, M.; et al. The X-ray to optical-UV luminosity ratio of X-ray selected type 1 AGN in XMM-COSMOS. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 512, A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-D. The Relation of Optical/Ultraviolet and X-Ray Emission in Low-luminosity Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2011, 739, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I.; Sunyaev, R.A. Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 24, 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Nagar, N.M.; Falcke, H.; Wilson, A.S. Radio sources in low-luminosity active galactic nuclei-IV. Radio luminosity function, importance of jet power, and radio properties of the complete Palomar sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 435, 521–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliozzi, M.; Williams, J.K.; Akylas, A.; Papadakis, I.E.; Shuvo, O.I.; Halavatkar, A.; Alt, A. Comparing indirect methods for black hole masses in AGN: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, 3417–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormendy, J.; Ho, L.C. Coevolution (or not) of supermassive black holes and host galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 51, 511–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Guainazzi, M.; Matt, G.; Bonilla, N.F.; Ponti, G. CAIXA: A catalogue of AGN in the XMM-Newton archive-I. Spectral analysis. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 495, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-L.; Zhang, S.-N. A comparison of hard X-ray photon indices and iron Kα emission lines in X-ray luminous narrow-and broad-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 713, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.; Bourdarot, G.; Brandner, W.; Cao, Y.; Clénet, Y.; Davies, R.; de Zeeuw, P.T.; Dexter, J.; Drescher, A.; Eckart, A.; et al. Toward measuring supermassive black hole masses with interferometric observations of the dust continuum. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 669, A14. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, C.; Trakhtenbrot, B.; Koss, M.J.; Ueda, Y.; Del Vecchio, I.; Treister, E.; Schawinski, K.; Paltani, S.; Oh, K.; Lamperti, I.; et al. BAT AGN spectroscopic survey. V. X-ray properties of the Swift/BAT 70-month AGN catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2017, 233, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, B.; Iwasawa, K.; Cappi, M.; Dadina, M.; Tombesi, F.; Ponti, G.; Celotti, A.; Miniutti, G. Probing variability patterns of the Fe K line complex in bright nearby AGNs. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 507, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porquet, D.; Reeves, J.N.; O’brien, P.; Brinkmann, W. XMM-Newton EPIC observations of 21 low-redshift PG quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 422, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallimore, J.F.; Axon, D.J.; O’Dea, C.P.; Baum, S.A.; Pedlar, A. A survey of kiloparsec-scale radio outflows in radio-quiet active galactic nuclei. Astron. J. 2006, 132, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panessa, F.; Bassani, L.; Cappi, M.; Dadina, M.; Barcons, X.; Carrera, F.J.; Ho, L.C.; Iwasawa, K. On the X-ray, optical emission line and black hole mass properties of local Seyfert galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 455, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroletti, M.; Panessa, F. The faintest Seyfert radio cores revealed by VLBI. Astron. J. 2009, 706, L260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Ueda, Y.; Ichikawa, K.; Paltani, S.; Boissay, R.; Gandhi, P.; Stalevski, M.; Awaki, H. The narrow Fe Kα line and the molecular torus in active galactic nuclei: An IR/X-ray view. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 567, A142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent-Muehleisen, S.A.; Kollgaard, R.I.; Ryan, P.J.; Feigelson, E.D.; Brinkmann, W.; Siebert, J. Radio-loud active galaxies in the northern ROSAT All-Sky Survey-I. Radio identifications. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1997, 122, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Terashima, Y.; Ho, L.C. Fe K line profile in low-redshift quasars: Average shape and eddington ratio dependence. Astron. J. 2007, 662, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hancock, S.; Young, A.J.; Chainakun, P. X-ray timing and spectral analysis of reverberating active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 514, 5403–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.-J.; Wu, Q. Revisit the Fundamental Plane of black hole activity from sub-Eddington to quiescent state. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, O.; Masegosa, J.; Márquez, I.; Guainazzi, M.; Jiménez-Bailón, E. An X-ray view of 82 LINERs with Chandra and XMM-Newton data. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 506, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.-G.; Yuan, F. Fundamental Plane of Black Hole Activity in the Quiescent Regime. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akylas, A.; Georgantopoulos, I. XMM-Newton observations of Seyfert galaxies from the Palomar spectroscopic survey: The X-ray absorption distribution. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 500, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.W.; Yaqoob, T.; Wang, J.X. Chandra high-energy grating observations of the Fe Kα line core in Type II seyfert galaxies: A comparison with Type I nuclei. Astron. J. 2011, 738, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Gugliucci, N.E.; Fabian, A.C.; Sanders, J.S.; Gentile, G.; Allen, S.W. Magnetic fields in the centre of the Perseus cluster. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 368, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, Y.; Hernàndez-García, L.; Arévalo, P.; López-Navas, E.; Ricci, C.; Koss, M.; Gonzalez-Martin, O.; Baloković, M.; Osorio-Clavijo, N.; García, J.A.; et al. Constraining the X-ray reflection in low accretion-rate active galactic nuclei using XMM-Newton, NuSTAR, and Swift. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 669, A114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, G.; Porquet, D.; Sabra, B.; Reeves, J.N. Study of LINER sources with broad Hα emission. X-ray properties and comparison to luminous AGN and X-ray binaries. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 530, A149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, N.M.; Wilson, A.S.; Falcke, H. Evidence for jet domination of the nuclear radio emission in low-luminosity active galactic nuclei. Astron. J. 2001, 559, L87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zezas, A.; Birkinshaw, M.; Worrall, D.M.; Peters, A.; Fabbiano, G. Chandra observations of NGC 4261 (3C 270): Revealing the jet and hidden active galactic nucleus in a Type 2 LINER. Astron. J. 2005, 627, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullo, B.T.; de Paz, A.G.; Knapen, J.H. Ultramassive Black Holes in the Most Massive Galaxies: M BH–σ versus M BH–R b. Astronomi. J. 2021, 908, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Körding, E.; Coppejans, D.L.; Falcke, H.; Williams, D.; Baldi, R.D.; Mchardy, I.; Beswick, R. 15-GHz radio emission from nearby low-luminosity active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 616, A152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.-F.; Wu, Q.; Dong, A.-J. Different X-ray Spectral evolution for Black hole X-ray Binaries in Dual Tracks of Radio–X-ray Correlation. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.C.; Peng, C.Y. Nuclear luminosities and radio loudness of Seyfert nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2001, 555, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strateva, I.V.; Brandt, W.N.; Schneider, D.P.; Vanden Berk, D.G.; Vignali, C. Soft X-ray and ultraviolet emission relations in optically selected AGN samples. Astron. J. 2005, 130, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Peterson, B.M. Determining central black hole masses in distant active galaxies and quasars. II. Improved optical and UV scaling relationships. Astrophys. J. 2006, 641, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coriat, M.; Corbel, S.; Prat, L.; Miller-Jones, J.C.A.; Cseh, D.; Tzioumis, A.K.; Brocksopp, C.; Rodriguez, J.; Fender, R.P.; Sivakoff, G.R. Radiatively efficient accreting black holes in the hard state: The case study of H1743–322. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-N. Black hole binaries and microquasars. Front. Phys. 2013, 8, 630–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ho, L.C.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, B. The fundamental plane of black hole activity for low-luminosity radio active galactic nuclei across 1<z<4. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.17991. [Google Scholar]
- Körding, E.; Falcke, H.; Corbel, S. Refining the fundamental plane of accreting black holes. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 456, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).