Differential Impacts of Environmentally Relevant Microplastics on Gut Barrier Integrity in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet Versus Normal Chow Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animal and Experimental Scheme
2.3. Tissue Collection and Histological Observation
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. qPCR Analysis
2.6. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.7. SCFAs Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
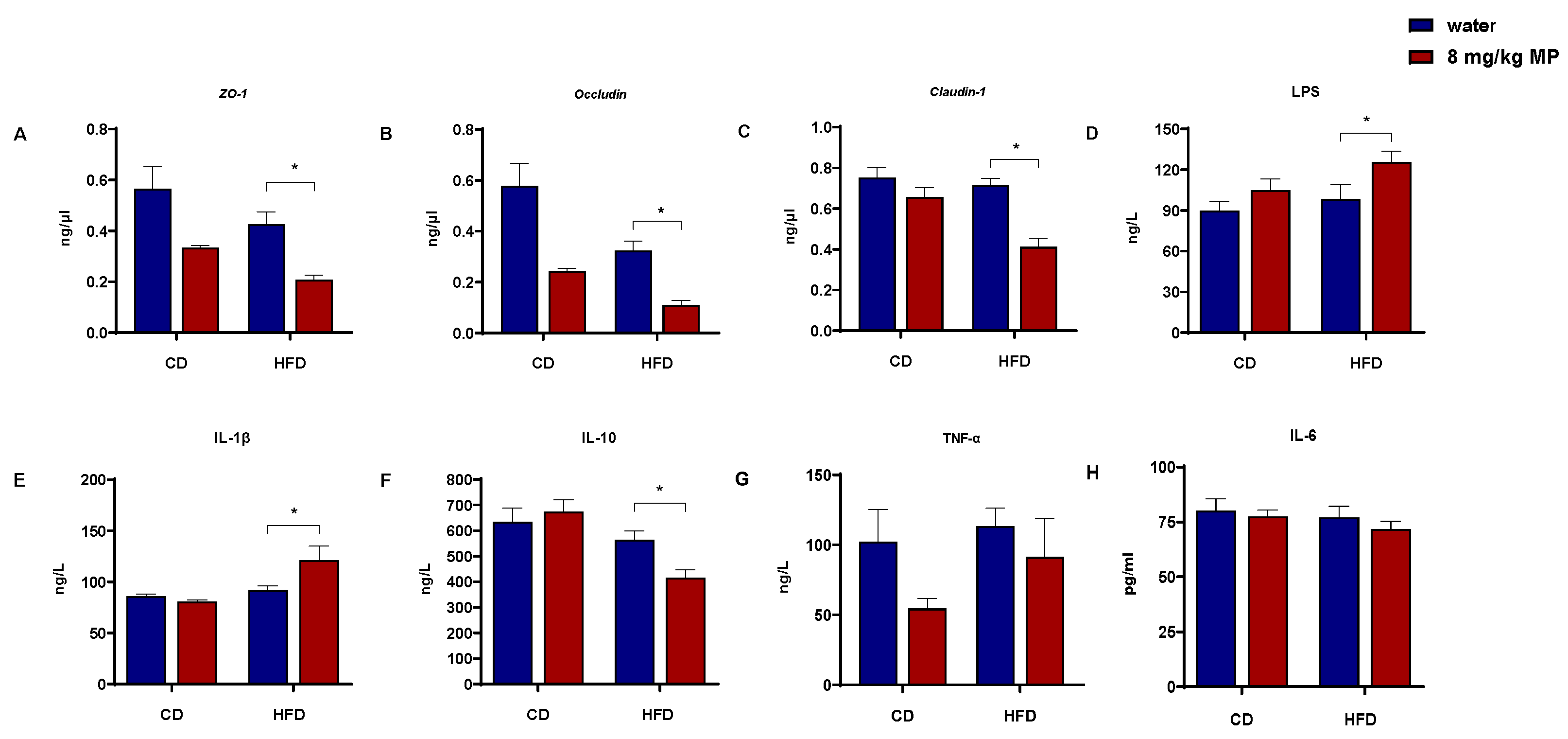
3.1. Levels of Inflammatory Factors and Barrier Protein Gene Transcription
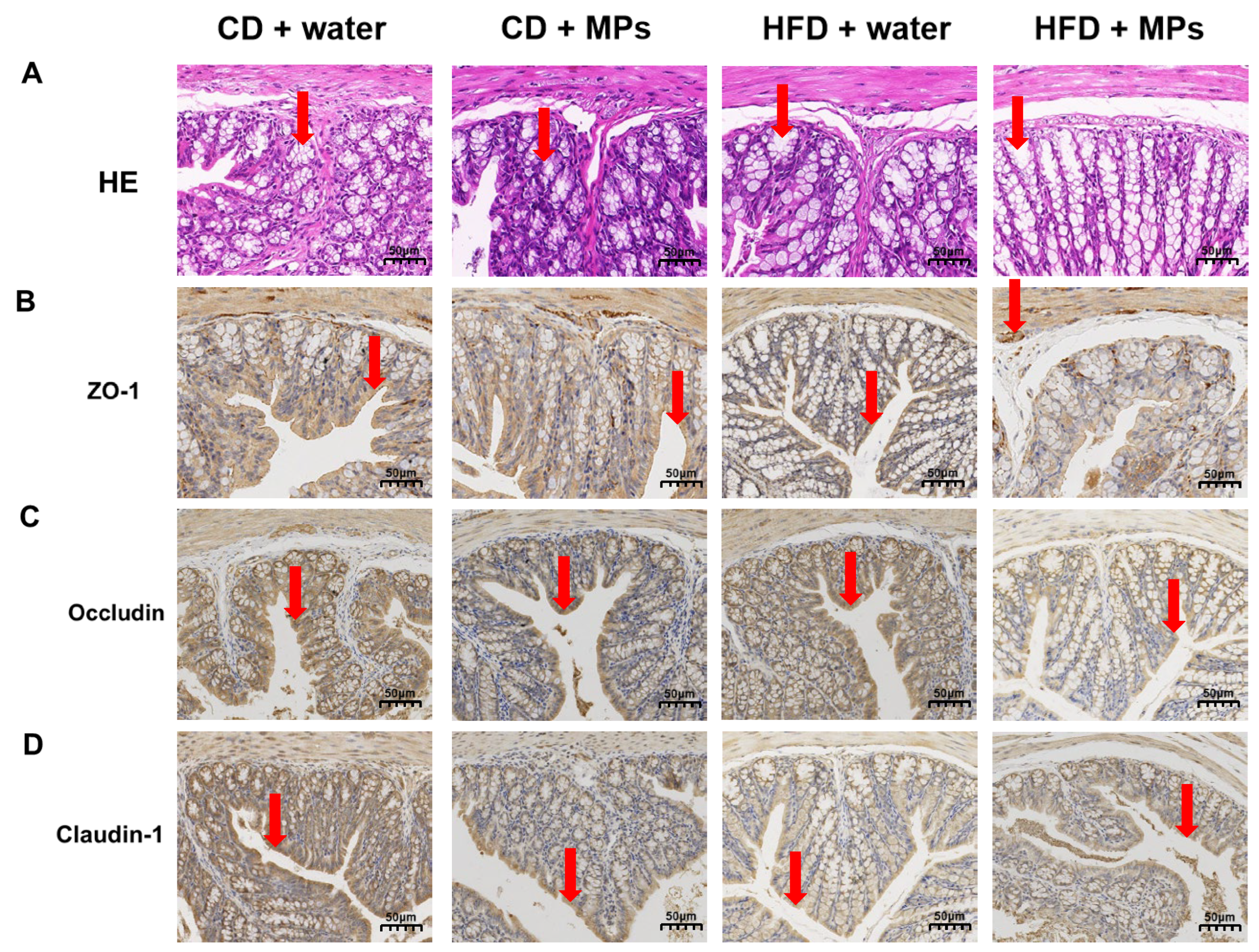
3.2. Morphology in the Colon
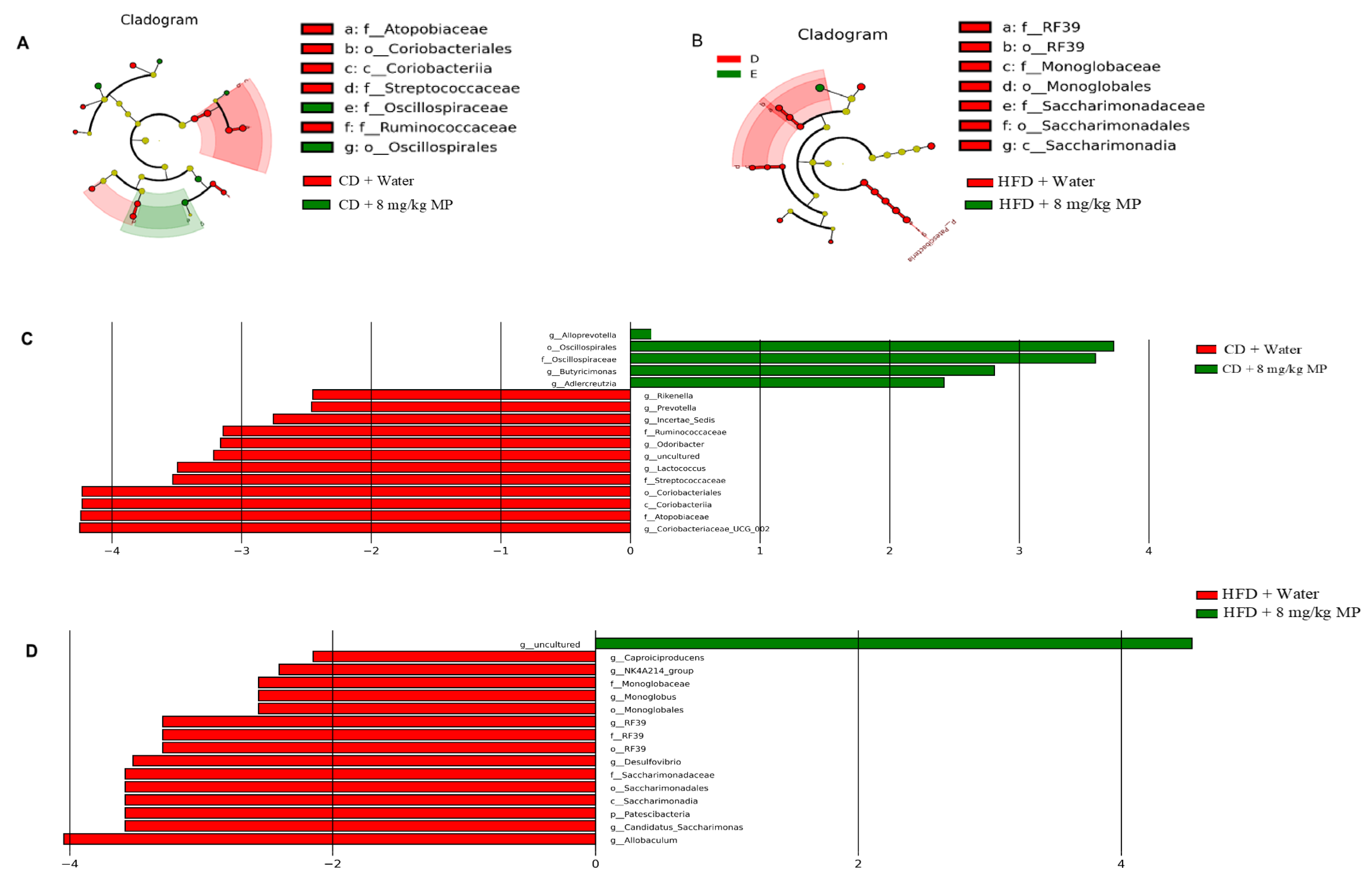
3.3. Composition and Diversity of the Gut Microbiota
3.4. Changes in the Gut Microbiota
3.5. Short-Chain Fatty Acids
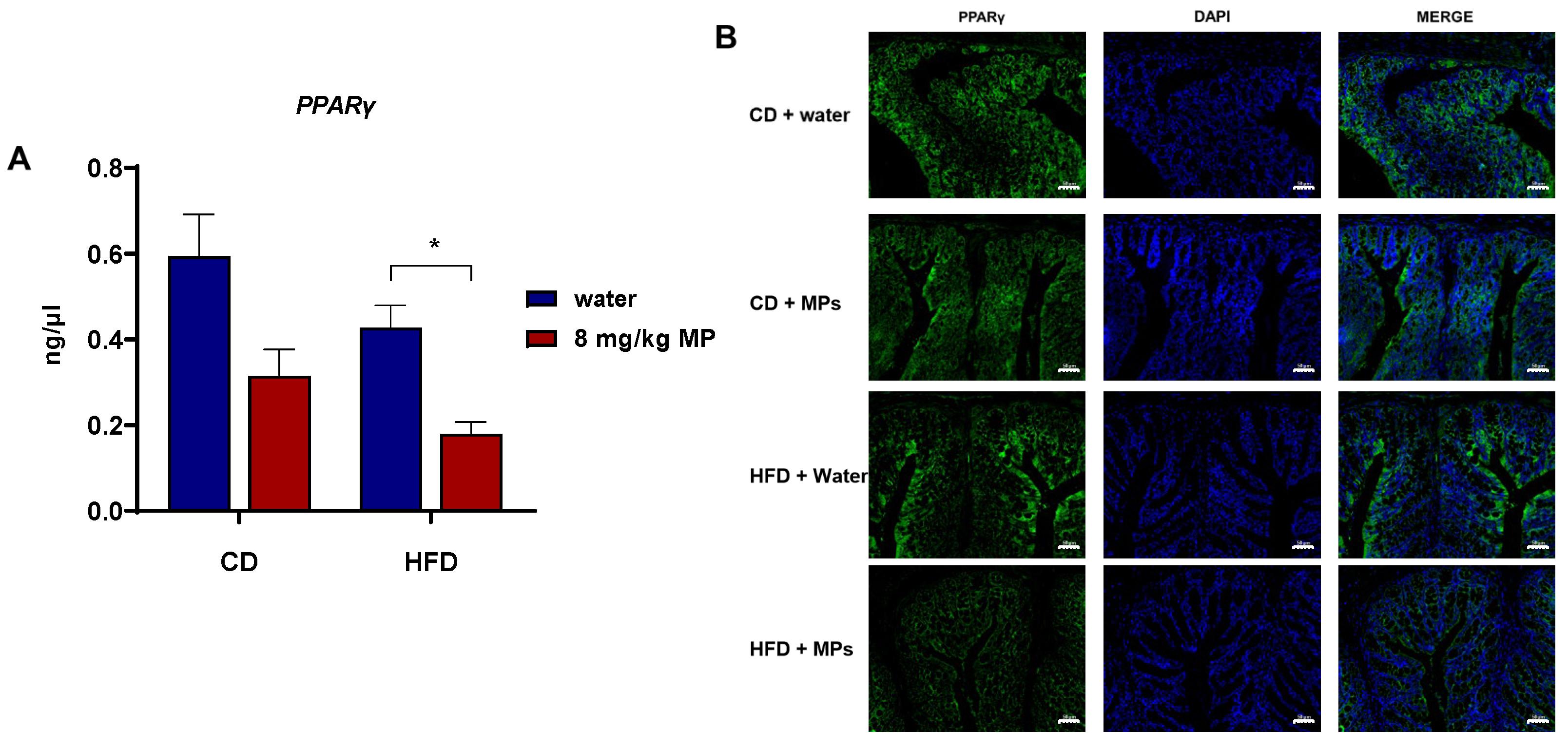
3.6. Expression of PPARγ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPs | Microplastics |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| CD | Chow diet |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinate Analysis |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäuerlein, P.S.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Pieke, E.N.; Ter Laak, T.L. Fate of microplastics in the drinking water production. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhdoumi, P.; Hossini, H.; Pirsaheb, M. A review of microplastic pollution in commercial fish for human consumption. Rev. Environ. Health 2023, 38, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarer, S. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in drinking water treatment plants, distribution systems, water from refill kiosks, tap waters and bottled waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Ren, S.-Y.; Ni, H.-G. Incidence of microplastics in personal care products: An appreciable part of plastic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.R.; Wright, S.J.; Gant, T.W. A critical review of microplastics toxicity and potential adverse outcome pathway in human gastrointestinal tract following oral exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2023, 385, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shi, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Jabeen, K.; Kolandhasamy, P. Microplastic Pollution in Table Salts from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13622–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Ekvall, M.T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Linse, S.; Malmendal, A.; Cedervall, T. Altered behavior, physiology, and metabolism in fish exposed to polystyrene nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, W.; Hu, F.; Song, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, J. Prolonged oral ingestion of microplastics induced inflammation in the liver tissues of C57BL/6J mice through polarization of macrophages and increased infiltration of natural killer cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene microplastics affect the distribution of gut microbiota and inflammation development in mice. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lv, M.; Li, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Sun, X.; Han, X.; Chen, L. The distinct toxicity effects between commercial and realistic polystyrene microplastics on microbiome and histopathology of gut in zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Sun, M.; Zhou, M.; Chang, Z.; Li, L. Polyvinyl chloride microplastics induce growth inhibition and oxidative stress in Cyprinus carpio var. larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, R.; Zhou, X.; Xu, C. Intestinal Barrier Function-Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Interactions and Possible Role of Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Whitley, C.S.; Haribabu, B.; Jala, V.R. Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function by Microbial Metabolites. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 1463–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Xing, M.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. Are Microplastics Toxic? A Review from Eco-Toxicity to Effects on the Gut Microbiota. Metabolites 2023, 13, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleu, S.; Machiels, K.; Raes, J.; Verbeke, K.; Vermeire, S. Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.S.G.; Jensen, B.B.; Theil, P.K.; Nielsen, T.S.; Knudsen, K.E.B.; Purup, S. Effect of butyrate and fermentation products on epithelial integrity in a mucus-secreting human colon cell line. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Du, Y.; Guan, H.; Jia, J.; Zhu, N.; Shi, Y.; Rong, S.; Yuan, W. Butyrate ameliorates skeletal muscle atrophy in diabetic nephropathy by enhancing gut barrier function and FFA2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signals. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Jiang, Z.; Cai, H.; Li, Y.; Mo, Q.; Deng, L.; Zhong, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Kang, J.X.; et al. Modulation of the Gut Microbiota during High-Dose Glycerol Monolaurate-Mediated Amelioration of Obesity in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. MBio 2020, 11, e00190-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoli, R.; Mattace Raso, G.; Lama, A.; Pirozzi, C.; Santoro, A.; Di Guida, F.; Sanges, M.; Aksoy, E.; Calignano, A.; D’Arienzo, A.; et al. Preventive and therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus paracasei B21060-based synbiotic treatment on gut inflammation and barrier integrity in colitic mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, G.; Yao, S.; Ullah, A.; Fang, S.; Guo, E.; Bo, Y. Polystyrene microplastics impair brown and beige adipocyte function via the gut microbiota-adipose tissue crosstalk in high-fat diet mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Bao, L.; Yang, Z.; Wu, B.; Si, R.; Zhao, W.; Peng, C.; et al. Polystyrene microplastic exposure induces insulin resistance in mice via dysbacteriosis and pro-inflammation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Hale, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Doses of Large Polystyrene Microplastics Disturbs Lipid Homeostasis via Bowel Function Interference. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15805–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Bognar, Z.; Csabai-Tanics, T.; Obodo, B.N.; Szekeres-Bartho, J. Allergic Disposition of IVF-Conceived Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Barker, D.F.; Barve, S.S.; McClain, C.J. The type of dietary fat modulates intestinal tight junction integrity, gut permeability, and hepatic toll-like receptor expression in a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Pan, Y.; He, J.; Pang, X.; Shao, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ye, J.; et al. Toxic vascular effects of polystyrene microplastic exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Majima, S.; Senmaru, T.; Ushigome, E.; Nakanishi, N.; Asano, M.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. Oral Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics of Mice on a Normal or High-Fat Diet and Intestinal and Metabolic Outcomes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, R.S.; Moncada, M.; Aryana, K.J. Leaky Gut and the Ingredients That Help Treat It: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Leaky gut: Mechanisms, measurement and clinical implications in humans. Gut 2019, 68, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ye, J.; Zeng, S.; Yang, C. Florfenicol alleviated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in Ctenopharyngodon idella through inhibiting toll/NF-κB signaling pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-M.; Byeon, E.; Jeong, H.; Kim, M.-S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, J.-S. Different effects of nano- and microplastics on oxidative status and gut microbiota in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielian, T.; Bearden, E.D.; Baldwin, A.C.; Esen, N. IL-1 and TNF-alpha play a pivotal role in the host immune response in a mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus-induced experimental brain abscess. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Diversity, metabolism and microbial ecology of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Ling, T.W.; Korecka, A.; Li, Y.; D’Arienzo, R.; Bunte, R.M.; Berger, T.; Arulampalam, V.; Chambon, P.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Absence of intestinal PPARγ aggravates acute infectious colitis in mice through a lipocalin-2-dependent pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Ding, Z.; Xu, M.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Xing, M.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Differential Impacts of Environmentally Relevant Microplastics on Gut Barrier Integrity in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet Versus Normal Chow Diet. Metabolites 2025, 15, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080557
Niu H, Yang Y, Zhou Y, Ma X, Ding Z, Xu M, Wu L, Li X, Xing M, Zhang Q, et al. Differential Impacts of Environmentally Relevant Microplastics on Gut Barrier Integrity in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet Versus Normal Chow Diet. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080557
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Huixia, Ying Yang, Yuting Zhou, Xue Ma, Zhehao Ding, Manjin Xu, Lizhi Wu, Xueqing Li, Mingluan Xing, Qin Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Differential Impacts of Environmentally Relevant Microplastics on Gut Barrier Integrity in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet Versus Normal Chow Diet" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080557
APA StyleNiu, H., Yang, Y., Zhou, Y., Ma, X., Ding, Z., Xu, M., Wu, L., Li, X., Xing, M., Zhang, Q., Chen, H., Tao, X., Mo, Z., Chen, Z., Tu, P., & Lou, X. (2025). Differential Impacts of Environmentally Relevant Microplastics on Gut Barrier Integrity in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet Versus Normal Chow Diet. Metabolites, 15(8), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080557







