Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Risk Across the Lifespan
Abstract
1. Introduction
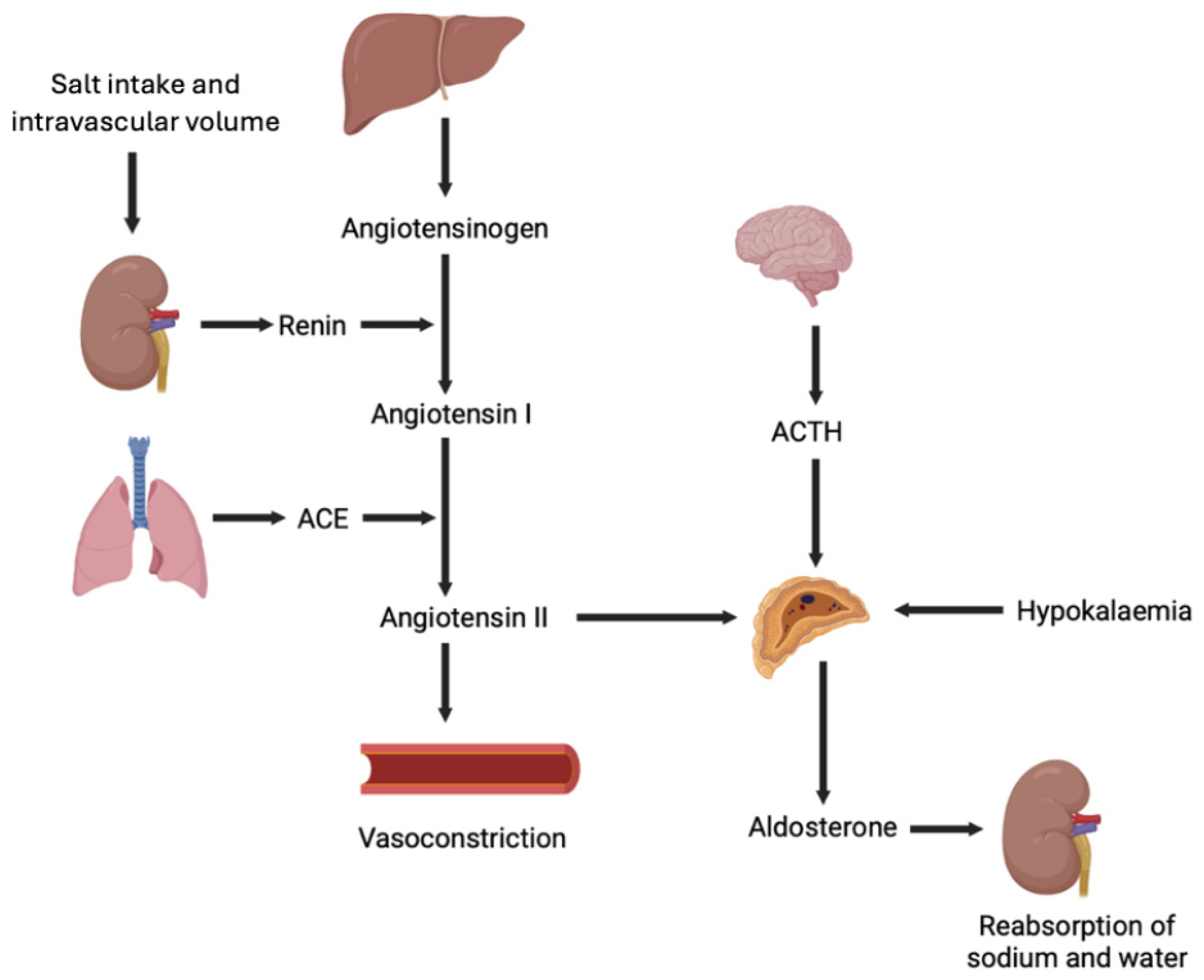
2. Aldosterone: A Hormone in the Cardiovascular System
3. Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Risk in Early Life
4. Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Health During Adolescence and Young Adulthood
5. Subclinical Primary Aldosteronism and Cardiovascular Risk Among Adults
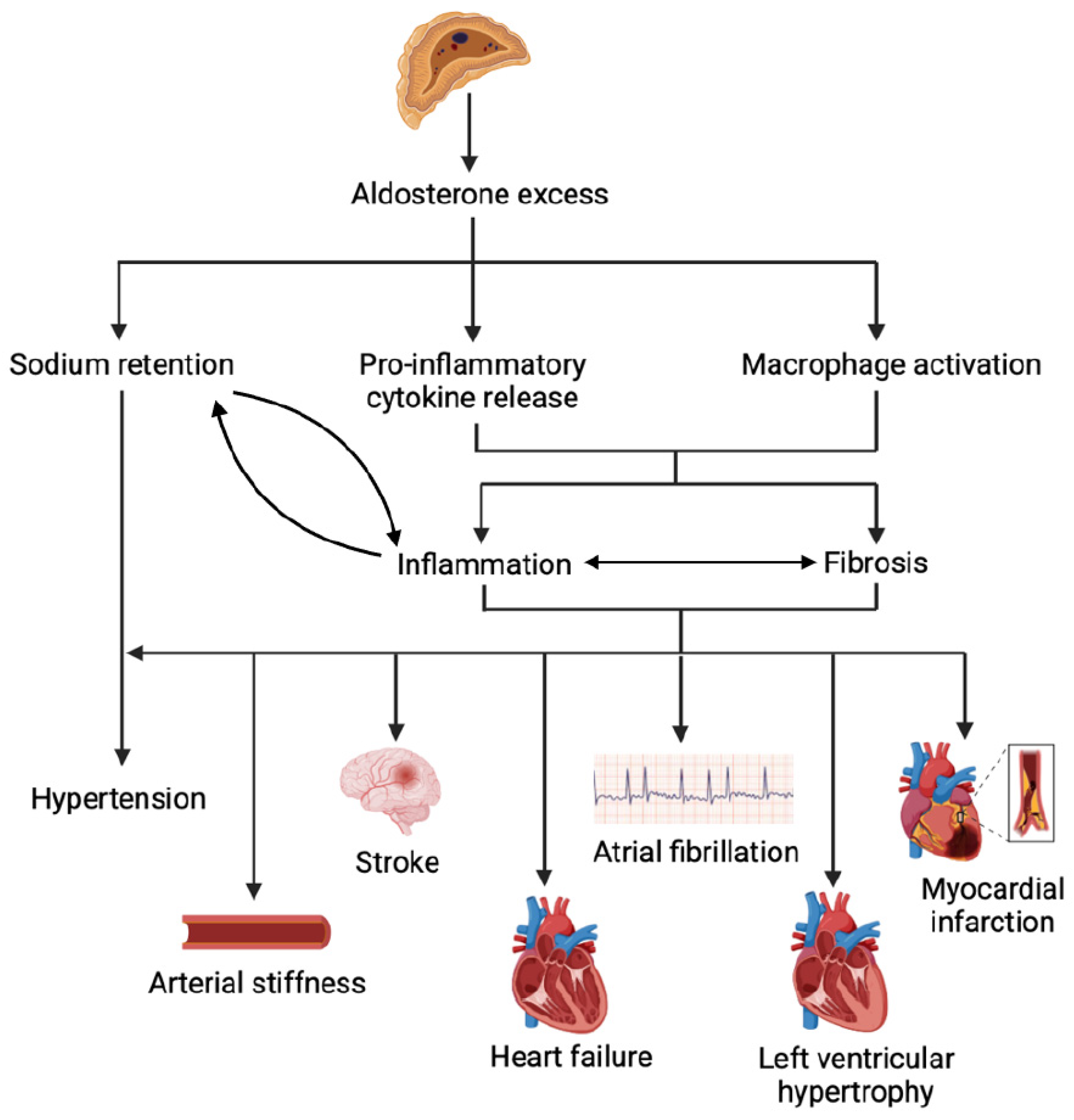
6. Aldosterone Excess in Adulthood: A Multidimensional Disease Beyond Blood Pressure
6.1. Hypertension and Arterial Stiffness
6.2. Myocardial Infarction and Stroke
6.3. Atrial Fibrillation and Other Cardiac Arrhythmias
6.4. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
6.5. Cardiac Fibrosis and Heart Failure
7. Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Funder, J.W. Aldosterone and Mineralocorticoid Receptors-Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Makhanova, N.; Caron, K.; Lopez, M.L.; Gomez, R.A.; Smithies, O.; Kim, H.S. Homeostatic responses in the adrenal cortex to the absence of aldosterone in mice. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2650–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kloet, E.R.; Van Acker, S.A.; Sibug, R.M.; Oitzl, M.S.; Meijer, O.C.; Rahmouni, K.; de Jong, W. Brain mineralocorticoid receptors and centrally regulated functions. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticone, S.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Moretti, C.; Williams, T.A.; Veglio, F.; Gaita, F.; Mulatero, P. Cardiovascular events and target organ damage in primary aldosteronism compared with essential hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudrand, R.; Guarda, F.J.; Fardella, C.; Hundemer, G.; Brown, J.; Williams, G.; Vaidya, A. Continuum of Renin-Independent Aldosteronism in Normotension. Hypertension 2017, 69, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Wijkman, M.O.; Claggett, B.L.; Shah, A.M.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E.; Wang, Z.; Yu, B.; Boerwinkle, E.; et al. Cardiac Structure and Function Across the Spectrum of Aldosteronism: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Goldwater, D.; Allison, M.; Seeman, T.; Kestenbaum, B.R.; Watson, K.E. Serum Aldosterone Concentration, Blood Pressure, and Coronary Artery Calcium: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Hypertension 2020, 76, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Luque-Fernandez, M.A.; Allison, M.A.; Baudrand, R.; Ix, J.H.; Kestenbaum, B.; de Boer, I.H.; Vaidya, A. The Spectrum of Subclinical Primary Aldosteronism and Incident Hypertension: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananda, R.A.; Gwini, S.; Beilin, L.J.; Schlaich, M.P.; Stowasser, M.; Young, M.J.; Adler, B.; Fuller, P.J.; Mori, T.A.; Yang, J. Relationship Between Renin, Aldosterone, Aldosterone-to-Renin Ratio and Arterial Stiffness and Left Ventricular Mass Index in Young Adults. Circulation 2024, 150, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaich, M.P.; Schobel, H.P.; Hilgers, K.; Schmieder, R.E. Impact of aldosterone on left ventricular structure and function in young normotensive and mildly hypertensive subjects. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 85, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundemer, G.L.; Agharazii, M.; Madore, F.; Vaidya, A.; Brown, J.M.; Leung, A.A.; Kline, G.A.; Larose, E.; Piché, M.E.; Crean, A.M.; et al. Subclinical Primary Aldosteronism and Cardiovascular Health: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Circulation 2024, 149, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, A.F.; Yang, J.; Vaidya, A. Primary aldosteronism—A multidimensional syndrome. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ghorayeb, N.; Bourdeau, I.; Lacroix, A. Role of ACTH and Other Hormones in the Regulation of Aldosterone Production in Primary Aldosteronism. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spät, A.; Hunyady, L. Control of aldosterone secretion: A model for convergence in cellular signaling pathways. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 489–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funder, J.W. Mineralocorticoid receptors: Distribution and activation. Heart Fail. Rev. 2005, 10, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, U.; Hyman, R.; Smith, T.W.; Medford, R.M. Aldosterone-mediated regulation of Na+, K(+)-ATPase gene expression in adult and neonatal rat cardiocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 12058–12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénitah, J.P.; Vassort, G. Aldosterone upregulates Ca(2+) current in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunda, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Hinek, A. Aldosterone induces elastin production in cardiac fibroblasts through activation of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors in a mineralocorticoid receptor-independent manner. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockand, J.D.; Meszaros, J.G. Aldosterone stimulates proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts by activating Ki-RasA and MAPK1/2 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H176–H184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoshi, M.P.; Yan, X.; Okoshi, K.; Nakayama, M.; Schuldt, A.J.; O’Connell, T.D.; Simpson, P.C.; Lorell, B.H. Aldosterone directly stimulates cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. J. Card. Fail. 2004, 10, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehling, M.; Neylon, C.B.; Fullerton, M.; Bobik, A.; Funder, J.W. Nongenomic effects of aldosterone on intracellular Ca2+ in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1995, 76, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagawa, Y.; Saino, T.; Matsuura, M.; Satoh, Y. The effects of diuretics on intracellular Ca2+ dynamics of arteriole smooth muscles as revealed by laser confocal microscopy. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 42, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, N.; Nakanishi, S.; Tanabe, S. Aldosterone affects blood flow and vascular tone regulated by endothelium-derived NO: Therapeutic implications. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruthi, D.; McCurley, A.; Aronovitz, M.; Galayda, C.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Jaffe, I.Z. Aldosterone promotes vascular remodeling by direct effects on smooth muscle cell mineralocorticoid receptors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callera, G.E.; Touyz, R.M.; Tostes, R.C.; Yogi, A.; He, Y.; Malkinson, S.; Schiffrin, E.L. Aldosterone activates vascular p38MAP kinase and NADPH oxidase via c-Src. Hypertension 2005, 45, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrop, H.; Höcherl, K.; Kurtz, A.; Schweda, F.; Todorov, V.; Wagner, C. Physiology of kidney renin. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 607–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; de Vries, R.; Saxena, P.R.; Schalekamp, M.A.; Danser, A.H. Vasoconstriction by in situ formed angiotensin II: Role of ACE and chymase. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 44, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Aguayo, A.; Aglony, M.; Bancalari, R.; Avalos, C.; Bolte, L.; Garcia, H.; Loureiro, C.; Carvajal, C.; Campino, C.; Inostroza, A.; et al. Birth weight is inversely associated with blood pressure and serum aldosterone and cortisol levels in children. Clin. Endocrinol. 2012, 76, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minette, M.S.; Hoyer, A.W.; Pham, P.P.; DeBoer, M.D.; Reller, M.D.; Boston, B.A. Cardiac function in congenital adrenal hyperplasia: A pattern of reversible cardiomyopathy. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 1193–1198.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falhammar, H.; Frisén, L.; Hirschberg, A.L.; Norrby, C.; Almqvist, C.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Nordenström, A. Increased Cardiovascular and Metabolic Morbidity in Patients with 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: A Swedish Population-Based National Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotanidou, E.; Giza, S.; Tsinopoulou, V.-R.; Vogiatzi, M.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A. Diagnosis and Management of Endocrine Hypertension in Children and Adolescents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 5591–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretchmer, N.; Dickinson, W.A.; McNamara, H.; Karl, R. Primary aldosteronism in a 9-year-old child. Pediatrics 1959, 23, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, A.; Bergstein, J.; Grim, C.E.; Yum, M.N.; Weinberger, M.H. Childhood Primary Aldosteronism Due to an Adrenal Adenoma: Preoperative Localization by Adrenal Vein Catheterization. Pediatrics 1980, 65, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Richey, P.A.; DiSessa, T.G.; Alpert, B.S.; Jones, D.P. Blood aldosterone-to-renin ratio, ambulatory blood pressure, and left ventricular mass in children. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, T.M.; Appel, L.J.; Holmes, K.W.; Fivush, B.; Miller, E.R., 3rd. Association Between Adiposity and Left Ventricular Mass in Children with Hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2016, 18, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; May Gwini, S.; Beilin, L.J.; Schlaich, M.; Stowasser, M.; Young, M.J.; Fuller, P.J.; Mori, T.A. Relationship Between the Aldosterone-to-Renin Ratio and Blood Pressure in Young Adults: A Longitudinal Study. Hypertension 2021, 78, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Gona, P.N.; Salton, C.J.; Chuang, M.L.; Levy, D.; Manning, W.J.; O’Donnell, C.J. Left Ventricular Structure and Risk of Cardiovascular Events: A Framingham Heart Study Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Toit, W.L.; Schutte, A.E.; Gafane-Matemane, L.F.; Kruger, R.; Mels, C.M.C. The renin-angiotensin-system and left ventricular mass in young adults: The African-PREDICT study. Blood Press. 2021, 30, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murro, D.G.; Beavers, M.; Harshfield, G.A.; Kapuku, G.K. Aldosterone contributes to elevated left ventricular mass in black boys. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.E.; Haas, A.V.; Rosner, B.; Adler, G.K.; Williams, G.H. Elevated Blood Pressure and Aldosterone Dysregulation in Young Black Women Versus White Women on Controlled Sodium Diets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e773–e779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbacher, S.; Mongiat, M.; Bernasconi, R.; Blum, S.; Meyre, P.; Krisai, P.; Ceylan, S.; Risch, M.; Risch, L.; Conen, D. Aldosterone-to-renin ratio and blood pressure in young adults from the general population. Am. Heart J. 2020, 222, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluwe, B.; Pohlman, N.; Kesireddy, V.; Zhao, S.; Tan, Y.; Kline, D.; Brock, G.; Odei, J.B.; Effoe, V.S.; Tcheugui, J.B.E.; et al. The role of aldosterone and ideal cardiovascular health in incident cardiovascular disease: The Jackson heart study. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 14, 100494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthakis, V.; Enserro, D.M.; Murabito, J.M.; Polak, J.F.; Wollert, K.C.; Januzzi, J.L.; Wang, T.J.; Tofler, G.; Vasan, R.S. Ideal cardiovascular health: Associations with biomarkers and subclinical disease and impact on incidence of cardiovascular disease in the Framingham Offspring Study. Circulation 2014, 130, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; Heizhati, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hong, J.; Wu, T. Aldosterone is Associated with New-onset Cerebrovascular Events in Patients with Hypertension and White Matter Lesions: A Cohort Study. Endocr. Pract. 2024, 30, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freminville, J.B.; Gardini, M.; Cremer, A.; Camelli, S.; Baron, S.; Bobrie, G.; Gosse, P.; Boulestreau, R.; Gebara, N.; Doublet, J.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Secondary Hypertension in Young Adults. Hypertension 2024, 81, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananda, R.A.; Gwini, S.M.; Long, K.M.; Lai, J.H.; Chen, G.; Russell, G.M.; Stowasser, M.; Fuller, P.J.; Yang, J. Diagnostic Delay and Disease Burden in Primary Aldosteronism: An International Patient Survey. Hypertension 2024, 81, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.Y.; Shen, J.; Fuller, P.J.; Yang, J. Current pattern of primary aldosteronism diagnosis: Delayed and complicated. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 47, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, C.; Colussi, G.; Nadalini, E.; Chiuch, A.; Baroselli, S.; Lapenna, R.; Sechi, L.A. Cardiovascular outcomes in patients with primary aldosteronism after treatment. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowasser, M.; Gordon, R.D. Primary Aldosteronism: Changing Definitions and New Concepts of Physiology and Pathophysiology Both Inside and Outside the Kidney. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1327–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.K.; Värri, E.; Matikainen, N.; Koskela, J.; Tikkakoski, A.J.; Kähönen, M.; Niemelä, O.; Mustonen, J.; Nevalainen, P.I.; Pörsti, I. Primary aldosteronism: Higher volume load, cardiac output and arterial stiffness than in essential hypertension. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queisser, N.; Schupp, N. Aldosterone, oxidative stress, and NF-κB activation in hypertension-related cardiovascular and renal diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutouyrie, P.; Chowienczyk, P.; Humphrey, J.D.; Mitchell, G.F. Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 864–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannemann, A.; Wallaschofski, H.; Lüdemann, J.; Völzke, H.; Markus, M.R.; Rettig, R.; Lendeckel, U.; Reincke, M.; Felix, S.B.; Empen, K.; et al. Plasma aldosterone levels and aldosterone-to-renin ratios are associated with endothelial dysfunction in young to middle-aged subjects. Atherosclerosis 2011, 219, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.S.; Sung, S.H.; Liao, C.W.; Pan, C.T.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, Z.W.; Wu, V.C.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, H.M.; Lin, Y.H. Aldosterone Induces Vascular Damage. Hypertension 2019, 74, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.N.; Young, M.J.; Evans, M.A.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Chrissobolis, S. Aldosterone-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain are mediated by the endothelial cell mineralocorticoid receptor. Brain Res. 2016, 1637, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidar, S.; Kaplan, M.; Pavlotzky, E.; Coleman, R.; Hayek, T.; Hamoud, S.; Aviram, M. Aldosterone administration to mice stimulates macrophage NADPH oxidase and increases atherosclerosis development: A possible role for angiotensin-converting enzyme and the receptors for angiotensin II and aldosterone. Circulation 2004, 109, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.X.; Chen, X.Q.; Sun, X.N.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, W.C.; Zheng, X.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shi, H.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Li, C.; et al. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Deficiency in Macrophages Inhibits Atherosclerosis by Affecting Foam Cell Formation and Efferocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzolla, V.; Armani, A.; Mammi, C.; Moss, M.E.; Pagliarini, V.; Pontecorvo, L.; Antelmi, A.; Fabbri, A.; Rosano, G.; Jaffe, I.Z.; et al. Essential role of ICAM-1 in aldosterone-induced atherosclerosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 232, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Chen, S.S.; Quinn, M.T.; Weber, K.T. Aldosterone-induced inflammation in the rat heart: Role of oxidative stress. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.W.; Chou, C.H.; Wu, X.M.; Chen, Z.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, Y.Y.; Wu, V.C.; Rose-John, S.; Hung, C.S.; Lin, Y.H. Interleukin-6 plays a critical role in aldosterone-induced macrophage recruitment and infiltration in the myocardium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Han, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, H.; Qi, Y.; Du, J. Macrophage-stimulated cardiac fibroblast production of IL-6 is essential for TGF β/Smad activation and cardiac fibrosis induced by angiotensin II. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, A.P.; Bagley, J.; Chen, W.S.; Galayda, C.; Nickerson, H.; Armani, A.; Caprio, M.; Carmeliet, P.; Jaffe, I.Z. Aldosterone increases early atherosclerosis and promotes plaque inflammation through a placental growth factor-dependent mechanism. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraaijenhof, J.M.; Nurmohamed, N.S.; Tzolos, E.; Meah, M.; Geers, J.; Kaiser, Y.; Kroon, J.; Hovingh, G.K.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Dweck, M.R. Interleukin 6 plasma levels are associated with progression of coronary plaques. Open Heart 2024, 11, e002773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seccia, T.M.; Letizia, C.; Muiesan, M.L.; Lerco, S.; Cesari, M.; Bisogni, V.; Petramala, L.; Maiolino, G.; Volpin, R.; Rossi, G.P. Atrial fibrillation as presenting sign of primary aldosteronism: Results of the Prospective Appraisal on the Prevalence of Primary Aldosteronism in Hypertensive (PAPPHY) Study. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denham, N.C.; Pearman, C.M.; Caldwell, J.L.; Madders, G.W.P.; Eisner, D.A.; Trafford, A.W.; Dibb, K.M. Calcium in the Pathophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reil, J.C.; Hohl, M.; Selejan, S.; Lipp, P.; Drautz, F.; Kazakow, A.; Münz, B.M.; Müller, P.; Steendijk, P.; Reil, G.H.; et al. Aldosterone promotes atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemers, P.; Hamdi, H.; Guedj, K.; Suffee, N.; Farahmand, P.; Popovic, N.; Claus, P.; LePrince, P.; Nicoletti, A.; Jalife, J.; et al. Atrial fibrillation is associated with the fibrotic remodelling of adipose tissue in the subepicardium of human and sheep atria. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzeshka, M.S.; Lip, G.Y.; Snezhitskiy, V.; Shantsila, E. Cardiac Fibrosis in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, Y.; Ramirez, R.J.; Kaur, K.; Salvador-Montañés, O.; Ponce-Balbuena, D.; Ramos-Mondragón, R.; Ennis, S.R.; Guerrero-Serna, G.; Berenfeld, O.; Jalife, J. Eplerenone Reduces Atrial Fibrillation Burden Without Preventing Atrial Electrical Remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F. Regulation of Potassium Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Rinehart, J.; Zhang, J.; Moeckel, G.; Castañeda-Bueno, M.; Stiegler, A.L.; Boggon, T.J.; Gamba, G.; Lifton, R.P. Mineralocorticoid receptor phosphorylation regulates ligand binding and renal response to volume depletion and hyperkalemia. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, S.M.; LaPointe, N.M.; Kramer, J.M.; Califf, R.M. What clinicians should know about the QT interval. JAMA 2003, 289, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.N.; Qu, Z.; Shivkumar, K. Electrophysiology of Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e004667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, R.; Tsurutani, Y.; Nakatsue, T.; Hirataka, A.; Nakai, K.; Saito, J. Lethal Arrhythmia Induced by Severe Hypokalemia with Primary Aldosteronism: A Case Report and Literature Review. Intern. Med. 2024, 63, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan, T.; Bergfeldt, L. Left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertension: Its arrhythmogenic potential. Heart 2005, 91, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Sone, M.; Inagaki, N.; Kawashima, A.; Takeda, Y.; Yoneda, T.; Kurihara, I.; Itoh, H.; Tsuiki, M.; Ichijo, T.; et al. Nadir Aldosterone Levels After Confirmatory Tests Are Correlated with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Primary Aldosteronism. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ori, Y.; Chagnac, A.; Korzets, A.; Zingerman, B.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Bergman, M.; Gafter, U.; Salman, H. Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with primary aldosteronism/low-renin hypertension on low-dose spironolactone. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Andrés, N.; Martin-Fernandez, B.; Rossignol, P.; Zannad, F.; Lahera, V.; Fortuno, M.A.; Cachofeiro, V.; Díez, J. A role for cardiotrophin-1 in myocardial remodeling induced by aldosterone. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H2372–H2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muiesan, M.L.; Salvetti, M.; Paini, A.; Agabiti-Rosei, C.; Monteduro, C.; Galbassini, G.; Belotti, E.; Aggiusti, C.; Rizzoni, D.; Castellano, M.; et al. Inappropriate left ventricular mass in patients with primary aldosteronism. Hypertension 2008, 52, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, E.K.; Morgan, J.; Kennaway, D.R.; Bienvenu, L.A.; Rickard, A.J.; Delbridge, L.M.D.; Fuller, P.J.; Clyne, C.D.; Young, M.J. Deoxycorticosterone/Salt-Mediated Cardiac Inflammation and Fibrosis Are Dependent on Functional CLOCK Signaling in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2906–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Liao, C.W.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, C.W.; Pan, C.T.; Chen, Z.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, L.C.; Chang, Y.R.; Wu, V.C.; et al. Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients with Primary Aldosteronism: A Propensity Score-Matching Follow-Up Study with Tissue Doppler Imaging. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenča, D.; Melenovský, V.; Stehlik, J.; Staněk, V.; Kettner, J.; Kautzner, J.; Adámková, V.; Wohlfahrt, P. Heart failure after myocardial infarction: Incidence and predictors. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.; Rutten, F.H.; Lee, M.M.; Hawkins, N.M.; Petrie, M.C. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Everything the clinician needs to know. Lancet 2024, 403, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, A.L.; Tanaka, A.; Sorescu, D.; Liu, H.; Jeong, E.M.; Sturdy, M.; Walp, E.R.; Dudley, S.C., Jr.; Sutliff, R.L. Diastolic dysfunction is associated with cardiac fibrosis in the senescence-accelerated mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H824–H831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, C.H.; Xu, T.Y.; Xu, J.Z.; Zhu, L.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.G. Non-invasive left ventricular pressure-strain loop study on cardiac fibrosis in primary aldosteronism: A comparative study with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wu, T.; Wang, W.; Cheng, W.; Wan, S.; Tian, H.; Chen, T.; Sun, J.; Ren, Y. CMR-Verified Myocardial Fibrosis Is Associated with Subclinical Diastolic Dysfunction in Primary Aldosteronism Patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 672557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redheuil, A.; Blanchard, A.; Pereira, H.; Raissouni, Z.; Lorthioir, A.; Soulat, G.; Vargas-Poussou, R.; Amar, L.; Paul, J.L.; Helley, D.; et al. Aldosterone-Related Myocardial Extracellular Matrix Expansion in Hypertension in Humans: A Proof-of-Concept Study by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelbert, E.B.; Sabbah, H.N.; Butler, J.; Gheorghiade, M. Employing Extracellular Volume Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Measures of Myocardial Fibrosis to Foster Novel Therapeutics. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, e005619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Shah, R.V.; Neilan, T.G.; Mitchell, R.; Moreno, H., Jr.; Kwong, R.; Jerosch-Herold, M. Cardiac magnetic resonance assessment of interstitial myocardial fibrosis and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in hypertensive mice treated with spironolactone. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.M.; Xu, J.Z.; Tang, X.F.; Gao, P.J. Comparison of left ventricular structure and function in primary aldosteronism and essential hypertension by echocardiography. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puar, T.H.; Cheong, C.K.; Foo, R.S.Y.; Saffari, S.E.; Tu, T.M.; Chee, M.R.; Zhang, M.; Ng, K.S.; Wong, K.M.; Wong, A.; et al. Treatment of Primary Aldosteronism and Reversal of Renin Suppression Improves Left Ventricular Systolic Function. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 916744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Vaduganathan, M.; Claggett, B.; Jhund, P.S.; Desai, A.S.; Henderson, A.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Pitt, B.; Senni, M.; et al. Finerenone in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.F., Jr. Diagnosis and treatment of primary aldosteronism: Practical clinical perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, G.K.; Stowasser, M.; Correa, R.R.; Khan, N.; Kline, G.; McGowan, M.J.; Mulatero, P.; Murad, M.H.; Touyz, R.M.; Vaidya, A.; et al. Primary Aldosteronism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, 2453–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorselaars, W.; Nell, S.; Postma, E.L.; Zarnegar, R.; Drake, F.T.; Duh, Q.Y.; Talutis, S.D.; McAneny, D.B.; McManus, C.; Lee, J.A.; et al. Clinical Outcomes After Unilateral Adrenalectomy for Primary Aldosteronism. JAMA Surg. 2019, 154, e185842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkhof, P.; Bärfacker, L. 30 YEARS OF THE MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: 60 years of research and development. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 234, T125–T140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Zannad, F.; Remme, W.J.; Cody, R.; Castaigne, A.; Perez, A.; Palensky, J.; Wittes, J. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, N.; Dobson, J.; Wilson, S.; Dahlöf, B.; Sever, P.S.; Wedel, H.; Poulter, N.R. Effect of spironolactone on blood pressure in subjects with resistant hypertension. Hypertension 2007, 49, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaine, J.; Beauchemin, C.; Ramos, E. Use, tolerability and compliance of spironolactone in the treatment of heart failure. BMC Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, H.K.; Ménard, J.; White, W.B.; Young, W.F., Jr.; Williams, G.H.; Williams, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; McInnes, G.T.; Connell, J.M.; MacDonald, T.M. A double-blind, randomized study comparing the antihypertensive effect of eplerenone and spironolactone in patients with hypertension and evidence of primary aldosteronism. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Filippatos, G.; Claggett, B.L.; Desai, A.S.; Jhund, P.S.; Henderson, A.; Brinker, M.; Kolkhof, P.; Schloemer, P.; Lay-Flurrie, J.; et al. Finerenone in heart failure and chronic kidney disease with type 2 diabetes: FINE-HEART pooled analysis of cardiovascular, kidney and mortality outcomes. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 3758–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, J.; He, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Shen, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Patients with Primary Aldosteronism: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation 2025, 151, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcu, A.F.; Freeman, M.W.; Bancos, I.; Ben-Shlomo, A.; Hamidi, O.; Hamrahian, A.H.; Huang, W.; Kirschner, L.S.; Sam, R.; Mallappa, A.; et al. Phase 2a Study of Baxdrostat in Primary Aldosteronism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 393, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.W.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Marshall, W.; Pater, M.; Isaacsohn, J.; Pearce, C.; Murphy, B.; Alp, N.; Srivastava, A.; Bhatt, D.L.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of Baxdrostat for Treatment-Resistant Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffin, L.J.; Kopjar, B.; Melgaard, C.; Wolski, K.; Ibbitson, J.; Bhikam, S.; Weir, M.R.; Ofili, E.O.; Mehra, R.; Luther, J.M.; et al. Lorundrostat Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Hauske, S.J.; Canziani, M.E.; Caramori, M.L.; Cherney, D.; Cronin, L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hugo, C.; Nangaku, M.; Rotter, R.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of aldosterone synthase inhibition with and without empagliflozin for chronic kidney disease: A randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ananda, R.A.; Mori, T.A.; Yang, J. Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Risk Across the Lifespan. Metabolites 2025, 15, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080553
Ananda RA, Mori TA, Yang J. Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Risk Across the Lifespan. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080553
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnanda, Roshan A., Trevor A. Mori, and Jun Yang. 2025. "Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Risk Across the Lifespan" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080553
APA StyleAnanda, R. A., Mori, T. A., & Yang, J. (2025). Aldosterone and Cardiovascular Risk Across the Lifespan. Metabolites, 15(8), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080553






