Serum Metabolomic Signatures in Nonhuman Primates Treated with a Countermeasure and Exposed to Partial- or Total-Body Radiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
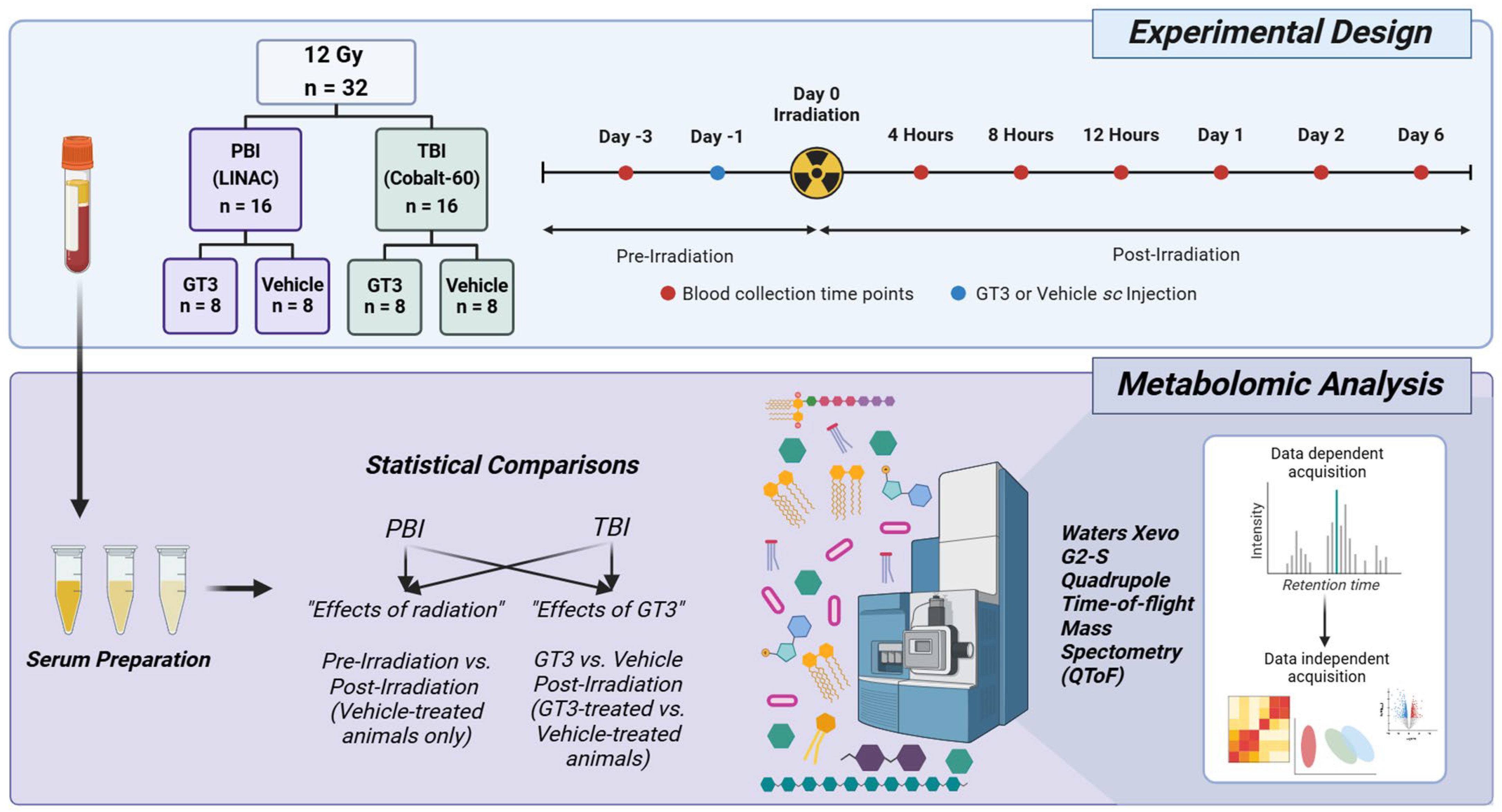
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Animals
2.3. Drug Preparation and Administration
2.4. Radiation Exposure
2.4.1. Partial-Body Radiation Exposure
2.4.2. Total-Body Radiation Exposure
2.5. Blood Sample Collection
2.6. Sample Preparation and Metabolomic Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
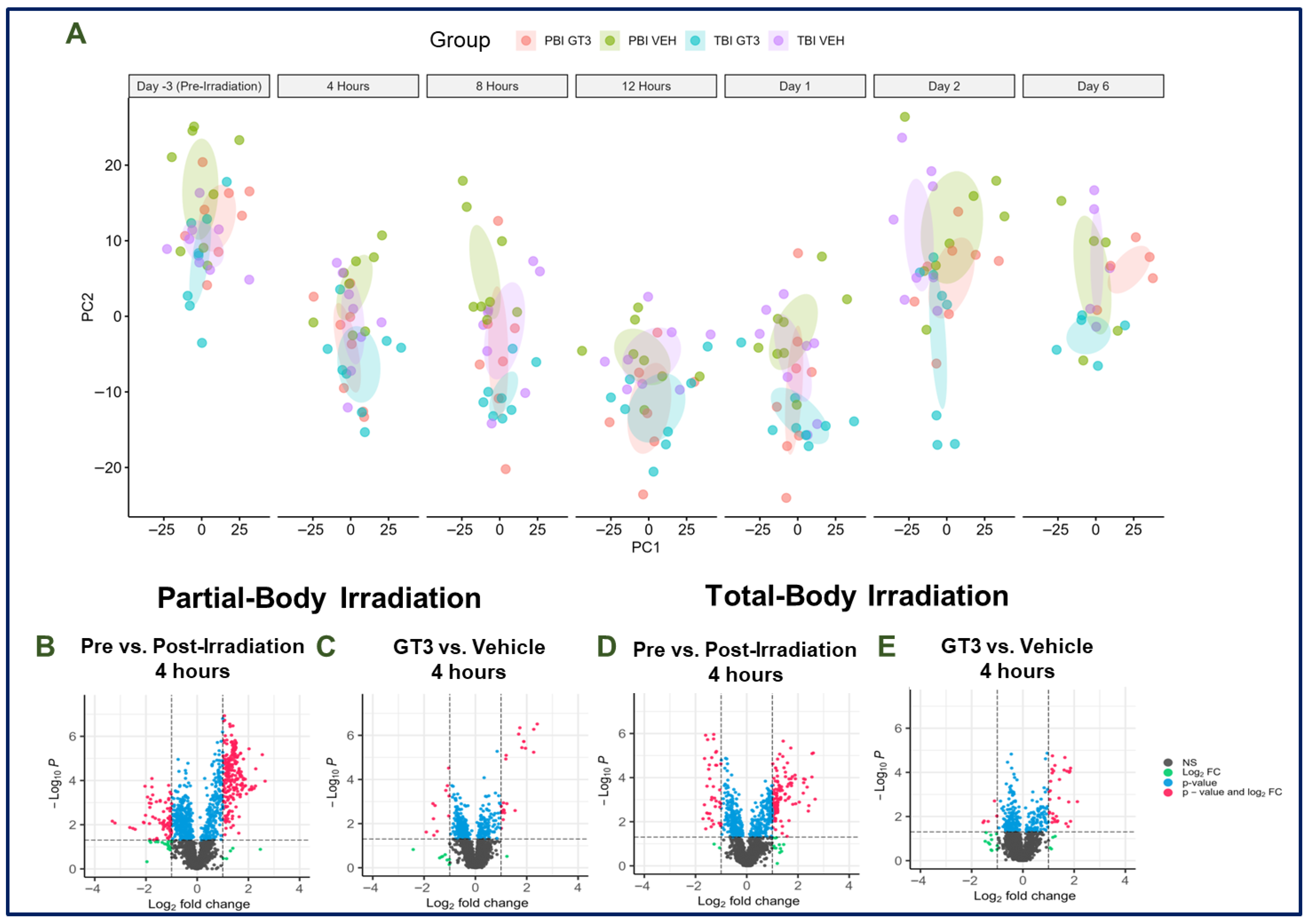
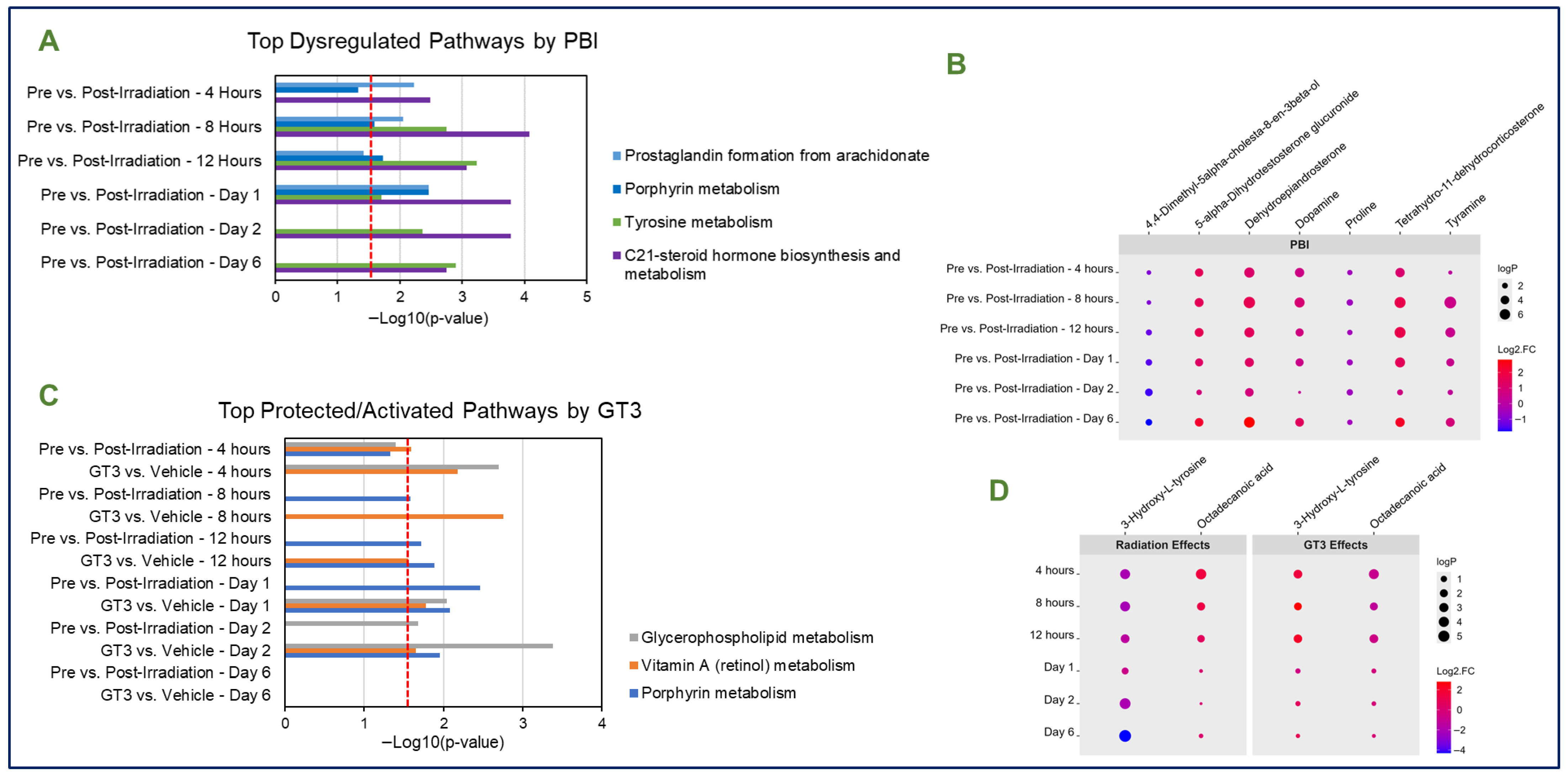
3.1. Effects of Partial-Body Radiation on Metabolomic Profiles
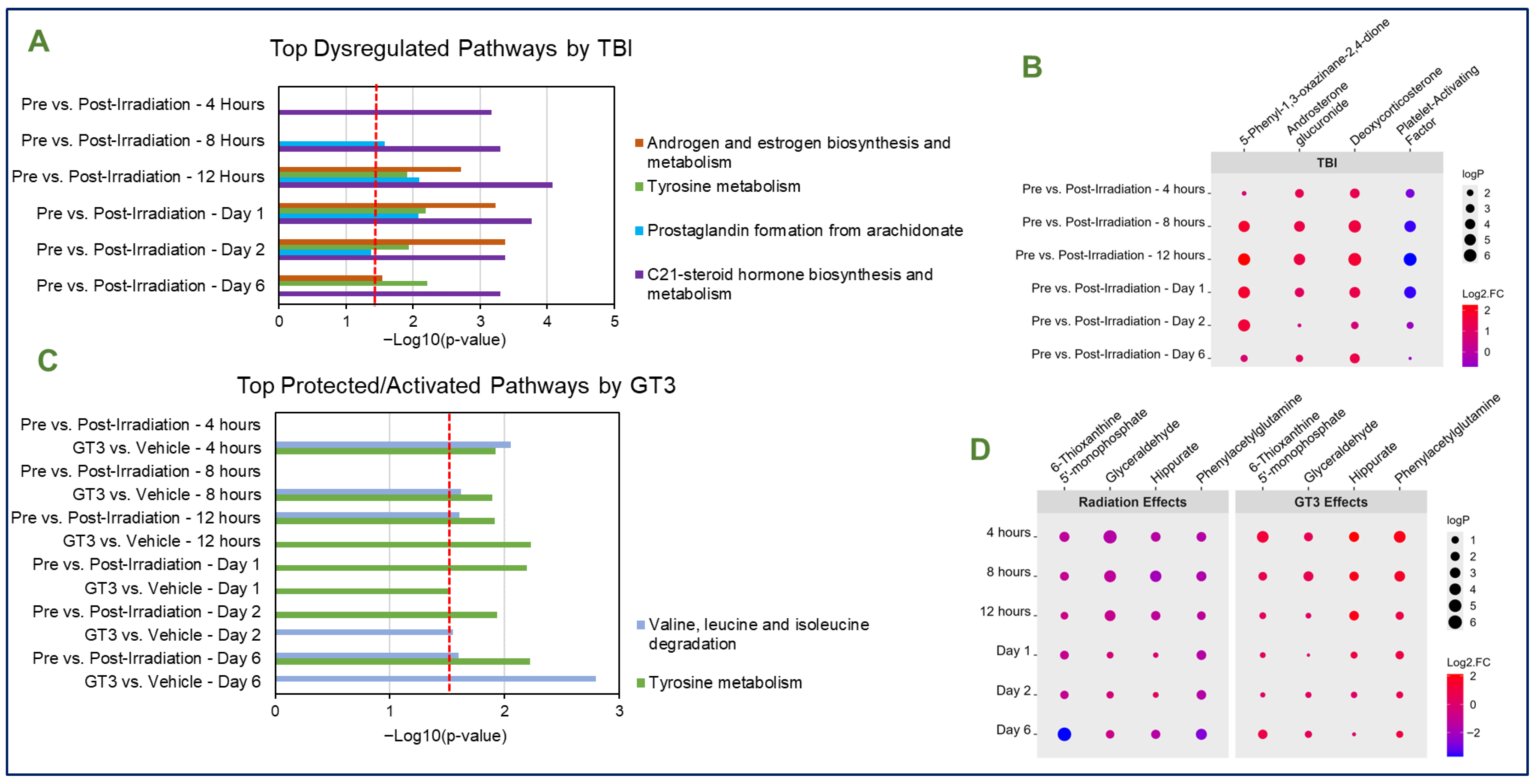
3.2. Effects of Total-Body Radiation on Metabolomic Profiles
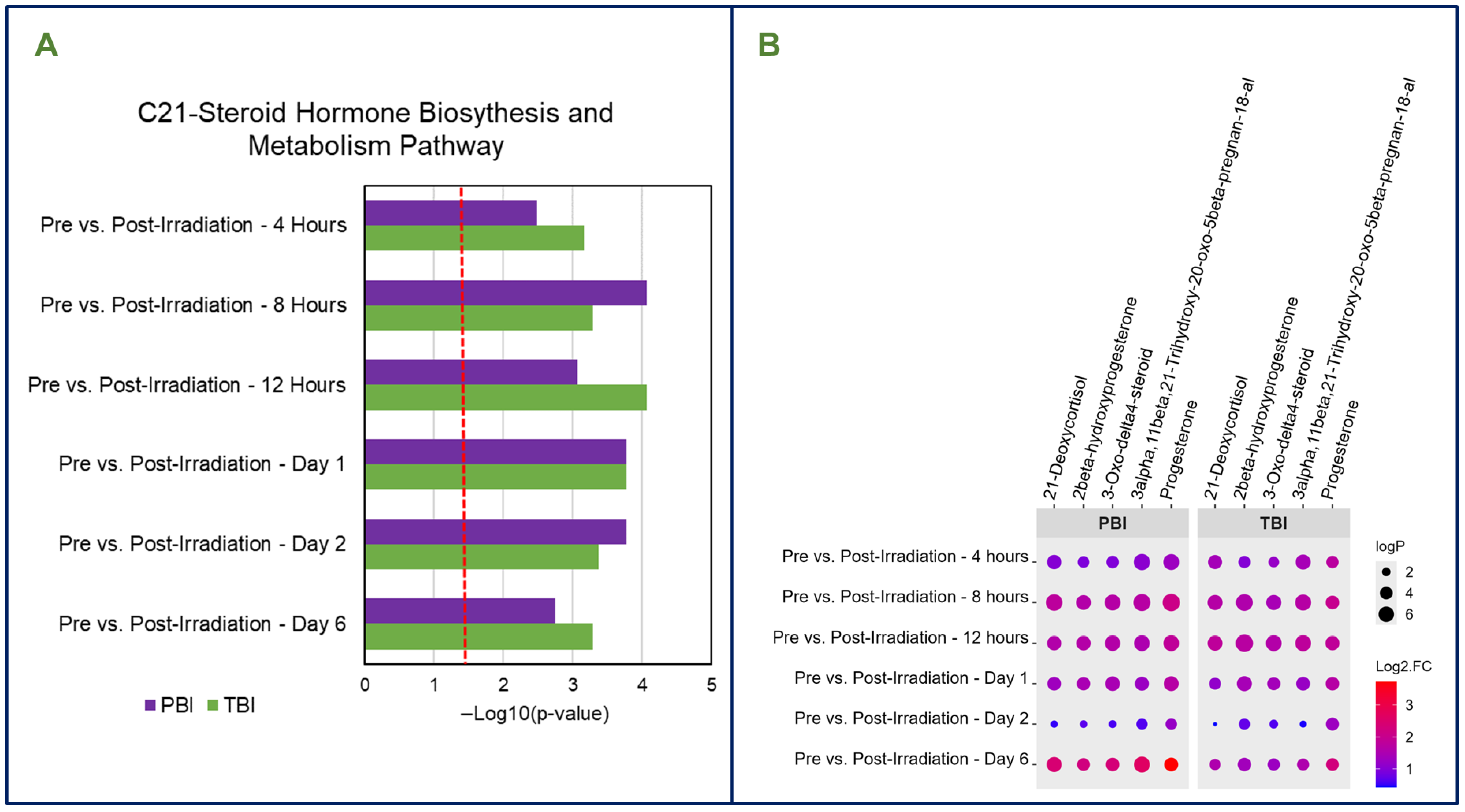
3.3. Metabolic Patterns Are Consistent Across Radiation Types
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, J.P.; Brown, S.L.; Georges, G.E.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Hill, R.P.; Huser, A.K.; Kirsch, D.G.; MacVittie, T.J.; Mason, K.A.; Medhora, M.M.; et al. Animal models for medical countermeasures to radiation exposure. Radiat. Res. 2010, 173, 557–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerveny, T.J.; MacVittie, T.M.; Young, R.W. Acute radiation syndrome in humans. In Medical Consequences of Nuclear Warfare, Textbook of Military Medicine; Walker, R.I., Jan Cerveny, T., Eds.; TMM Publications, Office of the Surgeon General: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dorr, H.; Meineke, V. Acute radiation syndrome caused by accidental radiation exposure-therapeutic principles. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, D.G.C. Radiation poisoning: Current concepts in the acute radiation syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Med. 2006, 3, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.J.; Giaccia, A.J. Radiobiology for the Radiobiologist, 7th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Farese, A.M.; MacVittie, T.J. Filgrastim for the treatment of hematopoietic acute radiation syndrome. Drugs Today 2015, 51, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, K.G.; Farese, A.M.; Blaauw, E.C.; Gibbs, A.M.; Smith, C.P.; Katz, B.P.; Tong, Y.; Prado, K.L.; MacVittie, T.J. Pegfilgrastim improves survival of lethally irradiated nonhuman primates. Radiat. Res. 2015, 183, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Pouliot, M.; Downey, A.M.; Mockbee, C.; Roychowdhury, D.; Wierzbicki, W.; Authier, S. Efficacy of delayed administration of sargramostim up to 120 hours post exposure in a nonhuman primate total body radiation model. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2021, 97, S100–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, N.P.; Khan-Malek, R.C.; Dangler, C.A.; Zhang, D.; Ascah, A.; Gains, M.; Gardner, B.; Mockbee, C.; Keutzer, J.M.; McManus, J.; et al. Sargramostim (rhu gm-csf) improves survival of non-human primates with severe bone marrow suppression after acute, high-dose, whole-body irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2021, 195, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Animal Rule Approvals. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/nda-and-bla-approvals/animal-rule-approvals (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Wong, K.; Chang, P.Y.; Fielden, M.; Downey, A.M.; Bunin, D.; Bakke, J.; Gahagen, J.; Iyer, L.; Doshi, S.; Wierzbicki, W.; et al. Pharmacodynamics of romiplostim alone and in combination with pegfilgrastim on acute radiation-induced thrombocytopenia and neutropenia in non-human primates. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, R.P.; Armitage, J.O. Use of molecularly-cloned haematopoietic growth factors in persons exposed to acute high-dose, high-dose rate whole-body ionizing radiations. Blood Rev. 2020, 45, 100690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farese, A.M.; Cohen, M.V.; Katz, B.P.; Smith, C.P.; Gibbs, A.; Cohen, D.M.; MacVittie, T.J. Filgrastim improves survival in lethally irradiated nonhuman primates. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunin, D.I.; Bakke, J.; Green, C.E.; Javitz, H.S.; Fielden, M.; Chang, P.Y. Romiplostim (nplate) as an effective radiation countermeasure to improve survival and platelet recovery in mice. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunin, D.I.; Javitz, H.S.; Gahagen, J.; Bakke, J.; Lane, J.H.; Andrews, D.A.; Chang, P.Y. Survival and hematologic benefits of romiplostim after acute radiation exposure supported fda approval under the animal rule. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 17, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, M.A. Biomarkers for human radiation exposure. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 15, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcomb, R.C., Jr.; Ansari, A.J.; Buzzell, J.J.; McCurley, M.C.; Miller, C.W.; Smith, J.M.; Evans, D.L. A public health perspective on the u.S. Response to the fukushima radiological emergency. Health Phys. 2015, 108, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.L.; Dawsey, S.M.; Kamangar, F.; Fan, J.H.; Abnet, C.C.; Sun, X.D.; Johnson, L.L.; Gail, M.H.; Dong, Z.W.; Yu, B.; et al. Total and cancer mortality after supplementation with vitamins and minerals: Follow-up of the linxian general population nutrition intervention trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompier, F.; Burbidge, C.; Bassinet, C.; Baumann, M.; Bortolin, E.; De Angelis, C.; Eakins, J.; Della Monaca, S.; Fattibene, P.; Quattrini, M.C.; et al. Overview of physical dosimetry methods for triage application integrated in the new european network reneb. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch-Lefevre, S.; Mandina, T.; Voisin, P.; Gaetan, G.; Mesa, J.E.; Valente, M.; Bonnesoeur, P.; Garcia, O.; Voisin, P.; Roy, L. Quantification of gamma-h2ax foci in human lymphocytes: A method for biological dosimetry after ionizing radiation exposure. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.M.; Prasanna, P.G.; Grace, M.B.; Wathen, L.K.; Wallace, R.L.; Koerner, J.F.; Coleman, C.N. Assessment of biodosimetry methods for a mass-casualty radiological incident: Medical response and management considerations. Health Phys. 2013, 105, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Seed, T.M.; Cheema, A.K. Metabolomics-based predictive biomarkers of radiation injury and countermeasure efficacy: Current status and future perspectives. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannkuk, E.L.; Fornace, A.J., Jr.; Laiakis, E.C. Metabolomic applications in radiation biodosimetry: Exploring radiation effects through small molecules. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 1151–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R. Improved methods for the acquisition and interpretation of nmr metabolomic data. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kell, D.B. Metabolomics and systems biology: Making sense of the soup. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Animal Rule Information. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/EmergencyPreparedness/Counterterrorism/MedicalCountermeasures/MCMRegulatoryScience/ucm391604.htm (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration. Guidance Document: Product Development Under the Animal Rule. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm399217.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Ghosh, S.P.; Kulkarni, S.; Hieber, K.; Toles, R.; Romanyukha, L.; Kao, T.C.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Kumar, K.S. Gamma-tocotrienol, a tocol antioxidant as a potent radioprotector. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Singh, P.K.; Ghosh, S.P.; Posarac, A.; Singh, V.K. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor antibody abrogates radioprotective efficacy of gamma-tocotrienol, a promising radiation countermeasure. Cytokine 2013, 62, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Kulkarni, S.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Wise, S.Y.; Newman, V.L.; Romaine, P.L.; Hendrickson, H.; Gulani, J.; Ghosh, S.P.; Kumar, K.S.; et al. Radioprotective efficacy of gamma-tocotrienol in nonhuman primates. Radiat. Res. 2016, 185, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Seed, T.M. Development of gamma-tocotrienol as a radiation medical countermeasure for the acute radiation syndrome: Current status and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaladi, M.R.; Poldy, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Carpenter, A.D.; Singh, V.K. Multi-faceted approach for identifying biomarkers for radiation injury and regulatory approval of radiation medical countermeasures. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2025, 233, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, E.A.; Badie, C. Radiation biomarkers: Silver bullet, or wild goose chase? J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Garg, T.K.; Miousse, I.R.; Wise, S.Y.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Savenka, A.V.; Basnakian, A.G.; Singh, V.K.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Effects of gamma-tocotrienol on partial-body irradiation-induced intestinal injury in a nonhuman primate model. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Garg, T.K.; Wise, S.Y.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Miousse, I.R.; Savenka, A.V.; Basnakian, A.G.; Singh, V.K.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Effects of gamma-tocotrienol on intestinal injury in a gi-specific acute radiation syndrome model in nonhuman primate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vellichirammal, N.N.; Sethi, S.; Avuthu, N.; Wise, S.Y.; Carpenter, A.D.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Guda, C.; Singh, V.K. Transcriptome profile changes in the jejunum of nonhuman primates exposed to supralethal dose of total- or partial-body radiation. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellichirammal, N.N.; Sethi, S.; Pandey, S.; Singh, J.; Wise, S.Y.; Carpenter, A.D.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Guda, C.; Singh, V.K. Lung transcriptome of nonhuman primates exposed to total- and partial-body irradiation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, A.; Li, Y.; Wise, S.Y.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Petrus, S.A.; Fam, C.M.; Carlson, S.J.; Cox, G.N.; Cheema, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Pharmacokinetic and metabolomic studies with a promising radiation countermeasure, bbt-059 (pegylated interleukin-11), in rhesus nonhuman primates. Radiat. Res. 2024, 202, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custodio, D.E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. Metlin: A metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-de-la-Fuente, A.; Godzien, J.; Saugar, S.; Garcia-Carmona, R.; Badran, H.; Wishart, D.S.; Barbas, C.; Otero, A. Ceu mass mediator 3.0: A metabolite annotation tool. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. Hmdb 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Girgis, M.; Wise, S.Y.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Seed, T.M.; Maniar, M.; Cheema, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Analysis of the metabolomic profile in serum of irradiated nonhuman primates treated with ex-rad, a radiation countermeasure. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, K.; Li, Y.; Yeh, C.; Barac, A.; Srichai, M.B.; Ballew, E.A.; Girgis, M.; Jayatilake, M.; Sridharan, V.; Boerma, M.; et al. Plasma metabolite biomarkers predictive of radiation induced cardiotoxicity. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 152, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, A.K.; Li, Y.; Girgis, M.; Jayatilake, M.; Simas, M.; Wise, S.Y.; Olabisi, A.O.; Seed, T.M.; Singh, V.K. Metabolomic studies in tissues of mice treated with amifostine and exposed to gamma-radiation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.D.; Li, Y.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Wise, S.Y.; Petrus, S.A.; Janocha, B.L.; Cheema, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Metabolomic profiles in tissues of nonhuman primates exposed to total- or partial-body radiation. Radiat. Res. 2024, 201, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichy, A.; Carpenter, A.D.; Li, Y.; Rydlova, G.; Rehulka, P.; Markova, M.; Milanova, M.; Chmil, V.; Cheema, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Radiation signature in plasma metabolome of total-body irradiated nonhuman primates and clinical patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Ghosh, S.P.; Satyamitra, M.; Mog, S.; Hieber, K.; Romanyukha, L.; Gambles, K.; Toles, R.; Kao, T.C.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; et al. Gamma-tocotrienol protects hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in mice after total-body irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2010, 173, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperetti, T.; Miller, T.; Gao, F.; Narayanan, J.; Jacobs, E.R.; Szabo, A.; Cox, G.N.; Orschell, C.M.; Fish, B.L.; Medhora, M. Polypharmacy to mitigate acute and delayed radiation syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 634477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Radiation Group | Time Point | Total Significant Metabolites (p-Value) | Metabolites (↑ | ↓) | Total Significant Metabolites (FDR) | Metabolites (↑ | ↓) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBI | Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—4 h | 134 | (105 | 29) | 122 | (99 | 23) |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—8 h | 102 | (88 | 14) | 58 | (55 | 3) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—12 h | 91 | (55 | 36) | 58 | (35 | 23) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—Day 1 | 72 | (38 | 34) | 40 | (25 | 15) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—Day 2 | 45 | (24 | 21) | 11 | (6 | 5) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—Day 6 | 73 | (53 | 20) | 53 | (39 | 14) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—4 h | 91 | (17 | 74) | 4 | (1 | 3) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—8 h | 67 | (10 | 57) | 3 | (1 | 2) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—12 h | 51 | (14 | 37) | 3 | (3 | 0) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—Day 1 | 36 | (15 | 21) | 0 | (0 | 0) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—Day 2 | 34 | (7 | 27) | 0 | (0 | 0) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—Day 6 | 21 | (2 | 19) | 0 | (0 | 0) |
| Radiation Group | Time Point | Total Significant Metabolites (p-Value) | Metabolites (↑ | ↓) | Total Significant Metabolites (FDR) | Metabolites (↑ | ↓) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBI | Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—4 h | 115 | (88 | 27) | 70 | (57 | 13) |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—8 h | 86 | (41 | 45) | 53 | (25 | 28) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—12 h | 66 | (32 | 34) | 52 | (28 | 24) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—Day 1 | 57 | (37 | 20) | 37 | (27 | 10) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—Day 2 | 63 | (53 | 10) | 5 | (4 | 1) | |
| Pre vs. Post-Irradiation (Vehicle-Treated)—Day 6 | 60 | (36 | 24) | 27 | (17 | 10) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—4 h | 74 | (34 | 40) | 5 | (5 | 0) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—8 h | 54 | (52 | 2) | 2 | (2 | 0) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—12 h | 39 | (14 | 25) | 1 | (0 | 1) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—Day 1 | 23 | (4 | 19) | 0 | (0 | 0) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—Day 2 | 72 | (8 | 64) | 19 | (0 | 19) | |
| GT3-Treated vs. Vehicle-Treated—Day 6 | 13 | (10 | 3) | 0 | (0 | 0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpenter, A.D.; Li, Y.; Packer, B.E.; Fatanmi, O.O.; Wise, S.Y.; Petrus, S.A.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Cheema, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Serum Metabolomic Signatures in Nonhuman Primates Treated with a Countermeasure and Exposed to Partial- or Total-Body Radiation. Metabolites 2025, 15, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080546
Carpenter AD, Li Y, Packer BE, Fatanmi OO, Wise SY, Petrus SA, Hauer-Jensen M, Cheema AK, Singh VK. Serum Metabolomic Signatures in Nonhuman Primates Treated with a Countermeasure and Exposed to Partial- or Total-Body Radiation. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080546
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpenter, Alana D., Yaoxiang Li, Benjamin E. Packer, Oluseyi O. Fatanmi, Stephen Y. Wise, Sarah A. Petrus, Martin Hauer-Jensen, Amrita K. Cheema, and Vijay K. Singh. 2025. "Serum Metabolomic Signatures in Nonhuman Primates Treated with a Countermeasure and Exposed to Partial- or Total-Body Radiation" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080546
APA StyleCarpenter, A. D., Li, Y., Packer, B. E., Fatanmi, O. O., Wise, S. Y., Petrus, S. A., Hauer-Jensen, M., Cheema, A. K., & Singh, V. K. (2025). Serum Metabolomic Signatures in Nonhuman Primates Treated with a Countermeasure and Exposed to Partial- or Total-Body Radiation. Metabolites, 15(8), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080546







