Elucidation of Mechanisms by Which Microplastics (PET) Facilitates the Rapid Growth of Benthic Cyanobacteria and Toxin Production in Aquatic Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) in Aquatic Environments
2.1. Sources and Distribution of PET Microplastics
2.2. Environmental Aging and Surface Modification of PET
2.3. PET Leachates: Composition and Environmental Relevance
3. Production of Cyanotoxins and Taste and Odor Compounds
3.1. Cyanotoxins
3.2. Anatoxin-a
3.3. Microcystins (MCs) and Nodularins (NODs)
3.4. Saxitoxins (STXs)
3.5. Cylindrospermopsins (CYNs)
3.6. Factors Affecting Toxin Production
3.7. Taste and Odor (T&O) Compounds
3.8. Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol (MIB)
| Compound | Type | Effects | Environmental Influences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anatoxin-a | Neurotoxin | Disrupts nervous system, causing muscle paralysis and respiratory failure. | Produced during early stages of mat formation, influenced by nutrient fluctuations and competition [127]. |
| Microcystins (MCs) | Hepatotoxins | Inhibit protein phosphatases, leading to liver cell damage and potential tumor formation. | Increased production under nutrient stress, particularly in oligotrophic conditions [128]. |
| Nodularins (NODs) | Hepatotoxins | Similarly to microcystins, targeting liver cells and promoting cellular damage. | Less common, but produced under environmental stress, including nutrient limitation [129]. |
| Saxitoxins (STXs) | Neurotoxin | Block sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse conduction. | Geographic variability, with higher production in certain species under environmental stress [130]. |
| Cylindrospermopsins (CYNs) | Cytotoxins | Inhibit protein synthesis, causing damage to multiple organs. | Found primarily in Australian systems; influenced by nutrient availability and temperature [131]. |
| Geosmin | Taste and Odor (T&O) | Imparts an earthy or musty odor to water, even at very low concentrations. | Strongly correlated with warm temperatures, elevated in floating mats [16]. |
| 2-Methylisoborneol (MIB) | Taste and Odor (T&O) | Causes musty or earthy odors in water. | Elevated in warmer temperatures, with higher concentrations in floating mats [132]. |
3.9. Dominance in Benthic Mats
3.10. Environmental Influences
3.11. Impact on Water Quality and Public Perception
3.12. Monitoring and Early Detection
4. Interactions Between PET Microplastics and Benthic Cyanobacteria
4.1. Colonization of PET Microplastics by Benthic Biofilms
- ➢
- PET microplastics have surface characteristics that enable bacteria to adhere to them because they are rough and hydrophobic [146].
- ➢
- PET particles experience surface roughness increases because of UV radiation and mechanical abrasion which leads to enhanced microbial attachment [147].
- ➢
- The EPS production of benthic cyanobacteria functions as biological adhesive material which captures PET microplastics into forming mats [148].
4.2. Retention, Stabilization, and Transport Dynamics
- Biofilms modify hydrodynamic conditions by modifying boundary layer characteristics which promotes suspended particles including PET fragments to settle down [149].
- PET microplastics become physically trapped inside the mat structure through physical entrapment [150].
- The aged PET particles develop negative surface charges which create electrostatic bonds with EPS components [146].
4.3. Ecotoxicological Implications for Benthic Cyanobacteria
- 1.
- Physical Disruption:
- 2.
- Chemical Stress:
- 3.
- Selective Pressure and Community Shifts:
- 4.
- Alterations in EPS Composition:
5. Impacts on Nutrient Cycling and Contaminant Dynamics
6. Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities
7. Molecular Responses of Benthic Cyanobacteria to PET and PET Leachates
7.1. Gene Expression Related to Growth and Metabolism
7.2. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense Pathways
7.3. Regulation of Toxin and Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis
7.4. Signal Transduction Pathways and Quorum Sensing
8. Implications for Ecosystem Health and Water Quality
Bioaccumulation and Trophic Transfer Risks
9. Challenges for Drinking Water Treatment
10. Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, S.S.; Elsamahy, T.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Sun, J. A critical review of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems: Degradation mechanisms and removing strategies. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 21, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafy, A.; Liza, A.A.; Islam, M.N.; Billah, M.M.; Arafat, S.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, S.M. Microplastics Pollution: A Brief Review of Its Source and Abundance in Different Aquatic Ecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, C.; Li, F. Research progress on the origin, fate, impacts and harm of microplastics and antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; van Alst, N.; Vollertsen, J. Quantification of microplastic mass and removal rates at wastewater treatment plants applying Focal Plane Array (FPA)-based Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) imaging. Water Res. 2018, 142, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setala, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution—Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.S.; Tahir, I.; Ali, A.; Ayub, I.; Nasir, A.; Abbas, N.; Sajjad, U.; Hamid, K. Innovative technologies for removal of micro plastic: A review of recent advances. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M.; Pohl, A.; Rosik-Dulewska, C. Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Characteristics, Occurrence and Removal Technologies. Water 2024, 16, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.-J.; Sun, X.-D.; Zhu, F.-P.; Feng, Y.; Duan, J.-L.; Xiao, F.; Li, X.-Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.-W.; et al. Nanoplastics Promote Microcystin Synthesis and Release from Cyanobacterial Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3386–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, S.; Duan, X.; Zhang, N.; Ren, Y.; Liang, L.; Ye, X. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on growth, physiological traits of Microcystis aeruginosa and microcystin production and release. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind kumar, J.; Krithiga, T.; Sathish, S.; Renita, A.A.; Prabu, D.; Lokesh, S.; Geetha, R.; Namasivayam, S.K.R.; Sillanpaa, M. Persistent organic pollutants in water resources: Fate, occurrence, characterization and risk analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, V.; Singh, S.; Anil, A.G.; Sunil Kumar Naik, T.S.; Garg, S.; Samuel, J.; Kumar, M.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Singh, J. Occurrence, toxicity and remediation of polyethylene terephthalate plastics. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1777–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, Z.; Xiang, S.; Yan, H.; Tian, H. Degradation of Polymer Materials in the Environment and Its Impact on the Health of Experimental Animals: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadeh Allaf, M.; Peerhossaini, H. Cyanobacteria: Model Microorganisms and Beyond. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part I-chemical control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, M.R.; Oh, S.E.; Lee, K.H.; Park, H.D. 2-Methylisoborneol (2-MIB) Excretion by Pseudanabaena yagii under Low Temperature. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, M.; Testai, E.; Tazart, Z.; Scardala, S.; Codd, G.A. Co-Occurrence of Taste and Odor Compounds and Cyanotoxins in Cyanobacterial Blooms: Emerging Risks to Human Health? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Hsueh, H.-T.; Lin, T.-F. Quantitative PCR based detection system for cyanobacterial geosmin/2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB) events in drinking water sources: Current status and challenges. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshni, K.; Renjithkumar, C.R.; Amal, R.; Devipriya, S.P. Characterization and risk assessment of microplastics accumulated in sediments and benthic molluscs in the mangrove wetlands along the south-west coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 216, 117955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Grossart, H.P.; Gadd, G.M. Microplastics provide new microbial niches in aquatic environments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6501–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Pei, H.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Y.; Xu, H. Molecular mechanisms by which polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastic and PET leachate promote the growth of benthic cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2025, 280, 123476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Liu, G.; Qi, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Oduro, C.; Khan, S.; Zhou, S.; Chu, T. Different facets of alpha and beta diversity of benthic diatoms along stream watercourse in a large near-natural catchment. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matavos-Aramyan, S. Addressing the microplastic crisis: A multifaceted approach to removal and regulation. Environ. Adv. 2024, 17, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkar, P.R.; Gadewar, R.D.; Dhulap, V.P. Recent trends in degradation of microplastics in the environment: A state-of-the-art review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcharla, E.; Vinayagam, S.; Gnanasekaran, L.; Soto-Moscoso, M.; Chen, W.-H.; Thanigaivel, S.; Ganesan, S. Microplastics in marine ecosystems: A comprehensive review of biological and ecological implications and its mitigation approach using nanotechnology for the sustainable environment. Environ. Res. 2024, 256, 119181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahmatkesh, S.; Klemes, J.J.; Bokhari, A.; Wang, C.; Sillanpaa, M.; Amesho, K.T.T.; Vithanage, M. Various advanced wastewater treatment methods to remove microplastics and prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2 to airborne microplastics. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2229–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, M.E.; Song, B.; Passie, R.; Hale, R.C. Microplastics affect sedimentary microbial communities and nitrogen cycling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimassi, S.N.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Yahia, M.N.D.; Ahmad, M.I.; Sayadi, S.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Degradation-fragmentation of marine plastic waste and their environmental implications: A critical review. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, Z.; Aqeel, M.; Sarfraz, W.; Fatima Rizvi, Z.; Noman, A.; Naeem, S.; Khalid, N. Microplastics in wastewaters and their potential effects on aquatic and terrestrial biota. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popall, R.M.; Bolhuis, H.; Muyzer, G.; Sanchez-Roman, M. Stromatolites as Biosignatures of Atmospheric Oxygenation: Carbonate Biomineralization and UV-C Resilience in a Geitlerinema sp.—Dominated Culture. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Wolfschlaeger, I.; Geist, J.; Fastner, J.; Schmalz, C.W.; Raeder, U. Occurrence, Distribution and Toxins of Benthic Cyanobacteria in German Lakes. Toxics 2023, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, E.; Evans, C.; Dunstan, R.H.; Geary, P.; Cole, B. Distribution, abundance and activity of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol-producing Streptomyces in drinking water reservoirs. Water Res. 2018, 145, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, J. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Sources, Fates, Impacts and Microbial Degradation. Toxics 2021, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosbois, G.; Anjum Mou, T.; Girona, M.M. Cyanobacteria in winter: Seasonal dynamics of harmful algal blooms and their driving factors in boreal lakes. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.; Kutz, M.C.S.; Mendes, A.B.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Mafra, L.L., Jr. Toxic plastisphere: How the characteristics of plastic particles can affect colonization of harmful microalgae and adsorption of phycotoxins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 137019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.S.; Wang, H.; Luster-Teasley, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, R. Microplastics in landfill leachate: Sources, detection, occurrence, and removal. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 16, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J. 11—Material Modeling Case Studies. In Mechanics of Solid Polymers; Bergström, J., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 455–497. [Google Scholar]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kye, H.; Kim, J.; Ju, S.; Lee, J.; Lim, C.; Yoon, Y. Microplastics in water systems: A review of their impacts on the environment and their potential hazards. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossatto, A.; Arlindo, M.Z.F.; de Morais, M.S.; de Souza, T.D.; Ogrodowski, C.S. Microplastics in aquatic systems: A review of occurrence, monitoring and potential environmental risks. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.K.; Uddin, M.E.; Jamal, M. Detection and removal of microplastics in wastewater: Evolution and impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Human health concerns regarding microplastics in the aquatic environment—From marine to food systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Yousif Abdellah, Y.A.; Wang, L.; Elsheikh, E.A.E.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, G. NaCl as an excellent trigger-induced biodiesel production and phenol-containing wastewater treatment in a novel salt-tolerant microalgae Ankistrodesmus sp. ACC. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 429, 132515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bexeitova, K.; Baimenov, A.; Varol, E.A.; Kudaibergenov, K.; Zhantikeyev, U.; Sailaukhanuly, Y.; Toshtay, K.; Tauanov, Z.; Azat, S.; Berndtsson, R. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of classification, sources, and environmental impacts. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2024, 20, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, S.; Abolfathi, S.; Bending, G.D.; Pearson, J. Quantifying microplastic dispersion due to density effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Sharma, P.; Bano, A.; Nadda, A.K.; Varjani, S. Microbial communities in plastisphere and free-living microbes for microplastic degradation: A comprehensive review. Green Anal. Chem. 2022, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Lee, J.-Y.; Redwan, M. Animal exposure to microplastics and health effects: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Liang, Y.; Kim, M.; Byun, J.; Choi, H. Microplastics with adsorbed contaminants: Mechanisms and Treatment. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhu, R.; Cai, Y.; Xu, N.; Yap, P.S.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. Environmental fate and impacts of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15762–15784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, C.; He, D.; Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Pan, X. Environmental behaviors of microplastics in aquatic systems: A systematic review on degradation, adsorption, toxicity and biofilm under aging conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostampour, S.; Cook, R.; Jhang, S.S.; Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Sung, L.P. Changes in the Chemical Composition of Polyethylene Terephthalate Under UV Radiation in Various Environmental Conditions. Res. Sq. 2024, 16, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Gedik, K.; Gaga, E.O. A preliminary study on the natural aging behavior of microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 1923–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatge, S.; Yang, Y.; Ahn, J.-H.; Hur, H.-G. Biodegradation of polyethylene: A brief review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, S.; Roychand, R.; Hai, F.I.; Bhuiyan, M.; Dhar, B.R.; Pramanik, B.K. Nano and microplastics occurrence in wastewater treatment plants: A comprehensive understanding of microplastics fragmentation and their removal. Chemosphere 2023, 334, 139011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairul Anuar, N.F.S.; Huyop, F.; Ur-Rehman, G.; Abdullah, F.; Normi, Y.M.; Sabullah, M.K.; Abdul Wahab, R. An Overview into Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Hydrolases and Efforts in Tailoring Enzymes for Improved Plastic Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelic, B.; Araujo, J.A.; Jeremic, S.; Azeem, M.; Attallah, O.A.; Siaperas, R.; Mojicevic, M.; Chen, Y.; Fournet, M.B.; Topakas, E.; et al. A novel Bacillus subtilis BPM12 with high bis(2 hydroxyethyl)terephthalate hydrolytic activity efficiently interacts with virgin and mechanically recycled polyethylene terephthalate. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Q. Determination of key factors affecting biofilm formation on the aged Poly(ethylene terephthalate) during anaerobic digestion. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, B.; Al-Ansari, M.; Al-Humaid, L.; Sebastin Raj, J.; Kim, W.; Karmegam, N.; Mohamed Rafi, K. In vivo degradation of polyethylene terephthalate using microbial isolates from plastic polluted environment. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Hong, Z.; Ma, L.; He, M.; Ma, H.; Cui, F. Plastic leachates lead to long-term toxicity in fungi and promote biodegradation of heterocyclic dye. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, O.A.; Rahman, M.S. An ecotoxicological approach to microplastics on terrestrial and aquatic organisms: A systematic review in assessment, monitoring and biological impact. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 84, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalrinfela, P.; Vanlalsangi, R.; Lalrinzuali, K.; Babu, P.J. Microplastics: Their effects on the environment, human health, and plant ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. Manag. 2024, 1, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Valsami-Jones, E. Nanoplastics in aquatic environments: The hidden impact of aging on fate and toxicity. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Chen, L.; Wang, N.; Cui, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhao, S.; He, H.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, W.; Duan, C.; et al. Unveiling the impacts of microplastic pollution on soil health: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G.; Chang, R.; Du, L. A systematic review of PET circularity technologies and management strategies: Challenges and future directions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 219, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muringayil Joseph, T.; Azat, S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Moini Jazani, O.; Esmaeili, A.; Kianfar, E.; Haponiuk, J.; Thomas, S. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) recycling: A review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Roy, A.; Popek, R.; Sarkar, A. Micro- and nano- plastic degradation by bacterial enzymes: A solution to ‘White Pollution’. Microbe 2024, 3, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiochetta, C.G.; Goetten, L.C.; Almeida, S.M.; Quaranta, G.; Cotelle, S.; Radetski, C.M. Leachates from solid wastes: Chemical and eco(geno)toxicological differences between leachates obtained from fresh and stabilized industrial organic sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Dey, T.K.; Jamal, M. Microplastic/nanoplastic toxicity in plants: An imminent concern. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridson, J.H.; Masterton, H.; Theobald, B.; Risani, R.; Doake, F.; Wallbank, J.A.; Maday, S.D.M.; Lear, G.; Abbel, R.; Smith, D.A.; et al. Leaching and transformation of chemical additives from weathered plastic deployed in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samak, N.A.; Jia, Y.; Sharshar, M.M.; Mu, T.; Yang, M.; Peh, S.; Xing, J. Recent advances in biocatalysts engineering for polyethylene terephthalate plastic waste green recycling. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, L. Polyethylene terephthalate may yield endocrine disruptors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keresztes, S.; Tatár, E.; Czégény, Z.; Záray, G.; Mihucz, V.G. Study on the leaching of phthalates from polyethylene terephthalate bottles into mineral water. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Sühring, R. The unusual suspects: Screening for persistent, mobile, and toxic plastic additives in plastic leachates. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotowska, U.; Kapelewska, J.; Sawczuk, R. Occurrence, removal, and environmental risk of phthalates in wastewaters, landfill leachates, and groundwater in Poland. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauser, P.; Vorkamp, K.; Strand, J. Residual additives in marine microplastics and their risk assessment—A critical review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Mayes, W.M.; Rogerson, M.; Stewart, D.I.; Burke, I.T. Alkaline residues and the environment: A review of impacts, management practices and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3571–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Tan, W.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Y. Influence of landfill leachate microenvironment on the occurrence of microplastics: TOC changes are the main driving factor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 492, 138080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Jin, J.L.; Sun, H.T.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.F.; Yu, X.H.; Cao, Q.Z.; Song, Y.X.; Li, N.; Lu, Z.H.; et al. Perspectives on the microorganisms with the potentials of PET-degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1541913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, M.; Sørensen, L.; Jayasena, K.D.R.; Booth, A.M.; Fabbri, E. Chemical composition and ecotoxicity of plastic and car tire rubber leachates to aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Pu, H.-F.; He, X.; Deng, S.-Y. Anti-seepage performance and oxygen barrier performance of the three-layered landfill cover system comprising neutralized slag under extreme climate conditions. Eng. Geol. 2024, 342, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganos, P.; Ullmann, C.V.; Gaglio, D.; Bonanomi, M.; Salmistraro, N.; Arnone, M.I.; Jimenez-Guri, E. Plastic leachate-induced toxicity during sea urchin embryonic development: Insights into the molecular pathways affected by PVC. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 160901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Fan, Z.; Xie, Y.; Fang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, R. Transcriptome analysis of the effect of bisphenol A exposure on the growth, photosynthetic activity and risk of microcystin-LR release by Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, M.-C.; Juneau, P. Effect of endocrine disrupters on photosystem II energy fluxes of green algae and cyanobacteria. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; He, Y.; Xiao, H.; Fang, D.; Chen, C. Toxic Effects of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol S on Chlorella Pyrenoidosa under Single and Combined Action. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didaran, F.; Kordrostami, M.; Ghasemi-Soloklui, A.A.; Pashkovskiy, P.; Kreslavski, V.; Kuznetsov, V.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. The mechanisms of photoinhibition and repair in plants under high light conditions and interplay with abiotic stressors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2024, 259, 113004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.N.; Che, X.K.; Zhao, S.J.; Zhang, Z.S.; Gao, H.Y. Mechanisms by which Bisphenol A affect the photosynthetic apparatus in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) leaves. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.S.; Hong, Y.H.; Nishikawa, Y.; Kage-Nakadai, E.; Chiou, T.Y.; Wu, C.C. Impacts of Endocrine Disruptor di-n-Butyl Phthalate Ester on Microalga Chlorella vulgaris Verified by Approaches of Proteomics and Gene Ontology. Molecules 2020, 25, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, T.; He, C.; Xu, J.; Lin, D.; Zhang, L. Nanoplastics inhibit carbon fixation in algae: The effect of aging. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wowkonowicz, P.; Kijenska, M.; Koda, E. Potential environmental risk assessment of di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate emissions from a municipal solid waste landfill leachate. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, E.A.; Paley, A.S.; Gulizia, A.M.; Motti, C.A.; Vamvounis, G.; Hoogenboom, M.O. Bisphenol A leachate from polystyrene microplastics has species-specific impacts on scleractinian corals. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Getzinger, G.J.; Ferguson, P.L.; Orihuela, B.; Zhu, M.; Rittschof, D. Effects of Toxic Leachate from Commercial Plastics on Larval Survival and Settlement of the Barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlatt, V.L.; Bayen, S.; Castaneda-Cortès, D.; Delbès, G.; Grigorova, P.; Langlois, V.S.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Parent, L.; Rwigemera, A.; et al. Impacts of endocrine disrupting chemicals on reproduction in wildlife and humans. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidoyin, K.C.; Jho, E.H. Environmental occurrence and ecotoxicological risks of plastic leachates in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuijt, L.M.; Peng, F.J.; van den Berg, S.J.P.; Dingemans, M.M.L.; Van den Brink, P.J. (Eco)toxicological tests for assessing impacts of chemical stress to aquatic ecosystems: Facts, challenges, and future. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiß, F.; Kiefer, N.; Noll, M.; Kalkhof, S. Application, release, ecotoxicological assessment of biocide in building materials and its soil microbial response. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagwar, P.P.; Dutta, D. Landfill leachate a potential challenge towards sustainable environmental management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, W.; Xi, Y.; Li, S. Comprehensive review of emerging contaminants: Detection technologies, environmental impact, and management strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, S.R.; Liu, R.; George, S.; Sinilal, B. Polyethylene terephthalate nanoparticles induce oxidative damage in Chlorella vulgaris. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 215, 108987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gao, P.; Ye, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhu, L. Micro/nano-plastics and microalgae in aquatic environment: Influence factor, interaction, and molecular mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; He, X.; Kong, D.; Hu, X.; Wang, F. Characterization and biotoxicity of landfill leachate and concentrates from controlled municipal solid waste landfills. Water Sci. Technol. 2025, 91, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelangeli, M.E.; Brandsma, S.H.; Margalef, M.; Forsman, E.; Kuehr, S.; Spanu, D.; Gomes, T. Chemical leachates from car tyre granulates and PET bottles induce toxic effects on Mytilus edulis haemocytes. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, X. Interactions between Microcystis aeruginosa and coexisting bisphenol A at different phosphorus levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Miroglio, R.; Costa, E.; Cachot, J.; Morin, B.; Clérandeau, C.; Rotander, A.; Rocco, K.; d’Errico, G.; Almeda, R.; et al. New insights into the impact of leachates from in-field collected plastics on aquatic invertebrates and vertebrates. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 355, 124233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhetaer, G.; Jayasanka, S.M.D.H.; Fujino, T. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Responses of Phormidium ambiguum and Microcystis aeruginosa Under Diurnally Varying Light Conditions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, D.; Pardal, M.Â. Ecological and Economic Importance of Benthic Communities. In Life Below Water; Leal Filho, W., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Lange Salvia, A., Wall, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.C.; Dezotti, M.; Sant’Anna, G.L. Treatment and detoxification of a sanitary landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, C.S.; Takada, H. Release of Additives and Monomers from Plastic Wastes. In Hazardous Chemicals Associated with Plastics in the Marine Environment; Takada, H., Karapanagioti, H.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, E.; Kim, S.-H.; Yun, M.; Choi, W.-G. Recapitulation of the Function and Role of ROS Generated in Response to Heat Stress in Plants. Plants 2021, 10, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.P. Climate Change and Aquatic Phytoremediation of Contaminants: Exploring the Future of Contaminant Removal. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 93, 2127–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozan, M.; Berreth, H.; Lindberg, P.; Bühler, K. Cyanobacterial biofilms: From natural systems to applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2025, 43, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaget, V.; Hobson, P.; Keulen, A.; Newton, K.; Monis, P.; Humpage, A.R.; Weyrich, L.S.; Brookes, J.D. Toolbox for the sampling and monitoring of benthic cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavčar Verdev, P.; Dolinar, M. A Pipeline for the Isolation and Cultivation of Microalgae and Cyanobacteria from Hypersaline Environments. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaget, V.; Almuhtaram, H.; Kibuye, F.; Hobson, P.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.; Brookes, J.D. Benthic cyanobacteria: A utility-centred field study. Harmful Algae 2022, 113, 102185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, P.P.; Tripathi, V.; Verma, H.; Singh, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Kumar, A. Distribution of cyanobacteria and their interactions with pesticides in paddy field: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, L.; Gan, N.; Song, L. Optimization of an effective extraction procedure for the analysis of microcystins in soils and lake sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, M.J.; Cresswell, S.L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Combining non-targeted high resolution mass spectrometry with effect-directed analysis to identify contaminants of emerging concern in the field of ecotoxicology: A systematic quantitative literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 972, 179122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bher, A.; Mayekar, P.C.; Auras, R.M.; Schvezov, C.E. Biodegradation of Biodegradable Polymers in Mesophilic Aerobic Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, N.; Junaid, M.; Pei, D.-S. Combined toxicity of endocrine-disrupting chemicals: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, S.; Walker, D.; Chicana, R.; Snyder, S.; Baurès, E.; Thomas, O. State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchett, G.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: From impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects. Toxins 2013, 5, 1896–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, S.; Marie, B.; Lance, E.; Quiblier, C.; Tricoire-Leignel, H.; Mattei, C. Anatoxin-a: Overview on a harmful cyanobacterial neurotoxin from the environmental scale to the molecular target. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaram, R.; Newton, A.R.; Lee, A.; Herber, S.; El-Khouri, A.; Chafin, J. A review of microcystin and nodularin toxins derived from freshwater cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms and their impact on human health. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2024, 16, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S.E. Saxitoxin. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd, ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 218–220. [Google Scholar]
- Shishido, T.K.; Delbaje, E.; Wahlsten, M.; Vuori, I.; Jokela, J.; Gugger, M.; Fiore, M.F.; Fewer, D.P. A cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacterium isolated from a microbial mat in the Baltic Sea. Toxicon 2023, 232, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, B.J.; Jankowiak, J.G.; Nanjappa, D.; Harke, M.J.; Gobler, C.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus significantly alter growth, nitrogen fixation, anatoxin-a content, and the transcriptome of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium, Dolichospermum. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 955032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.M.; Blaszczak, J.R.; Shriver, R.K.; Jones, R.C.; Sohrab, A.; Goel, R.; Boyer, G.L.; Wei, B.; Manoylov, K.M.; Nelson, T.R.; et al. Growth and anatoxin-a production of Microcoleus (Cyanobacteria) strains from streams in California, USA. Harmful Algae 2025, 144, 102834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathi, T.; Ki, J.S. Impact of environmental factors on the regulation of cyanotoxin production. Toxins 2014, 6, 1951–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Merwe, D. Chapter 31—Cyanobacterial (Blue-Green Algae) Toxins. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents, 2nd ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Molecular mechanisms of microcystin toxicity in animal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, J.F. CHAPTER 27—Toxins of Cyanobacteria. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.P.; Longley-Wood, K.; Reenstra, W.R. Chapter 156—Marine Toxin Attack. In Ciottone’s Disaster Medicine, 2nd ed.; Ciottone, G.R., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 798–800. [Google Scholar]
- Méjean, A.; Ploux, O. Chapter Six—A Genomic View of Secondary Metabolite Production in Cyanobacteria. In Advances in Botanical Research; Chauvat, F., Cassier-Chauvat, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 65, pp. 189–234. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; O’Shea, K.E. Ultrasonically induced degradation of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2672–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, T.G.; Graham, J.L.; Harris, T.D.; Dreher, T.W. Elucidation of Taste- and Odor-Producing Bacteria and Toxigenic Cyanobacteria in a Midwestern Drinking Water Supply Reservoir by Shotgun Metagenomic Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5410–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Song, K.; Yan, Z.; Liu, G. Monitoring phycocyanin in global inland waters by remote sensing: Progress and future developments. Water Res. 2025, 275, 123176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Zamyadi, A.; Wert, E.C. A critical review on operation and performance of source water control strategies for cyanobacterial blooms: Part II-mechanical and biological control methods. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Park, R.; Yu, M.; Byeon, M.; Kang, T. qPCR-Based Monitoring of 2-Methylisoborneol/Geosmin-Producing Cyanobacteria in Drinking Water Reservoirs in South Korea. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varg, J.E.; Svanbäck, R. Multi stress system: Microplastics in freshwater and their effects on host microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cheng, Q.; Kumar, A.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Z.; Hui, D.; Zhang, C.; Shan, S. Effect of degradable microplastics, biochar and their coexistence on soil organic matter decomposition: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 183, 118082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, B.A.; Potts, M. Introduction to the Cyanobacteria. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria: Their Diversity in Time and Space; Whitton, B.A., Potts, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Labrenz, M. Marine Microbial Assemblages on Microplastics: Diversity, Adaptation, and Role in Degradation. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessi, I.S.; Lara, Y.; Durieu, B.; Maalouf, P.d.C.; Verleyen, E.; Wilmotte, A. Community structure and distribution of benthic cyanobacteria in Antarctic lacustrine microbial mats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Lee, J. Toxin-producing cyanobacteria in freshwater: A review of the problems, impact on drinking water safety, and efforts for protecting public health. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Carey, C.C.; Hamilton, D.P.; Huisman, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Wood, S.A.; Wulff, A. Perspective: Advancing the research agenda for improving understanding of cyanobacteria in a future of global change. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Rout, A.K.; Behera, B.K.; Ghosh, K. Plastisphere community assemblage of aquatic environment: Plastic-microbe interaction, role in degradation and characterization technologies. Environ. Microbiome 2022, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Jiang, L.; He, R. Uncovering anaerobic oxidation of methane and active microorganisms in landfills by using stable isotope probing. Environ. Res. 2025, 271, 121139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chio, C.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Qin, W. Colonization characteristics and surface effects of microplastic biofilms: Implications for environmental behavior of typical pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 937, 173141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-L.; Xiang, H.; Xiong, H.-Q.; Fang, Y.-C.; Wang, Y. Bioremediation of microplastics in freshwater environments: A systematic review of biofilm culture, degradation mechanisms, and analytical methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, C. Exopolysaccharides from Microalgae and Cyanobacteria: Diversity of Strains, Production Strategies, and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krsmanovic, M.; Biswas, D.; Ali, H.; Kumar, A.; Ghosh, R.; Dickerson, A.K. Hydrodynamics and surface properties influence biofilm proliferation. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmandrad, Z.; Kaykhaii, M.; Gębicki, J. Microplastics removal from aqueous environment by metal organic frameworks. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- En-Nejmy, K.; El Hayany, B.; Al-Alawi, M.; Jemo, M.; Hafidi, M.; El Fels, L. Microplastics in soil: A comprehensive review of occurrence, sources, fate, analytical techniques and potential impacts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 288, 117332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alijagic, A.; Suljević, D.; Fočak, M.; Sulejmanović, J.; Šehović, E.; Särndahl, E.; Engwall, M. The triple exposure nexus of microplastic particles, plastic-associated chemicals, and environmental pollutants from a human health perspective. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, X.H.; Yu, M. Microbial colonization and degradation of marine microplastics in the plastisphere: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1127308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, B.; Si, M.; Chen, Z.; Geng, J.; Liang, F.; Xi, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, R. Roles of extracellular polymeric substances on Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to different sizes of polystyrene microplastics. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J.; Sieber, V.; Rehm, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides: Biosynthesis pathways and engineering strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Dey, P. Bacterial exopolysaccharides as emerging bioactive macromolecules: From fundamentals to applications. Res. Microbiol. 2023, 174, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, P.; Schwarz, C.; Zhang, B.-W.; Huo, L.; Shi, B.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Phthalate Esters Released from Plastics Promote Biofilm Formation and Chlorine Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; De Philippis, R. Role of Cyanobacterial Exopolysaccharides in Phototrophic Biofilms and in Complex Microbial Mats. Life 2015, 5, 1218–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomiak, K.M.; Owens-Rios, W.A.; Bangkong, C.M.; Day, S.W.; Eddingsaas, N.C.; Hoffman, M.J.; Hudson, A.O.; Tyler, A.C. Impact of Microplastic on Freshwater Sediment Biogeochemistry and Microbial Communities Is Polymer Specific. Water 2024, 16, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging contaminants: A One Health perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, N.K.; Kundu, S.; Debnath, P.; Mondal, A.; Sen, K. Effects of polyethylene terephthalate microplastic on germination, biochemistry and phytotoxicity of Cicer arietinum L. and cytotoxicity study on Allium cepa L. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 94, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachedi, R.; Foglino, M.; Latifi, A. Stress Signaling in Cyanobacteria: A Mechanistic Overview. Life 2020, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucius, S.; Hagemann, M. The primary carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria and its regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1417680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma-Gregson, K.; Olm, M.R.; Probst, A.J.; Anantharaman, K.; Power, M.E.; Banfield, J.F. Impacts of microbial assemblage and environmental conditions on the distribution of anatoxin-a producing cyanobacteria within a river network. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1618–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, R. Combined toxicity of micro/nanoplastics loaded with environmental pollutants to organisms and cells: Role, effects, and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P.; Moh, S.H.; Lee, T.K.; Kottuparambil, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Rhee, J.-S.; Choi, E.-M.; Brown, M.T.; Häder, D.-P.; et al. Ultraviolet radiation and cyanobacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 141, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, P.; Schnug, E. Reactive Oxygen Species, Antioxidant Responses and Implications from a Microbial Modulation Perspective. Biology 2022, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, A.B.; Samal, R.R.; Bhol, N.K.; Duttaroy, A.K. Cellular Red-Ox system in health and disease: The latest update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Singh, A.K.; McIntyre, L.M.; Sherman, L.A. Differential gene expression in response to hydrogen peroxide and the putative PerR regulon of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3331–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillett, D.; Dittmann, E.; Erhard, M.; von Döhren, H.; Börner, T.; Neilan, B.A. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: An integrated peptide–polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhiainen, L.; Vakkilainen, T.; Siemer, B.L.; Buikema, W.; Haselkorn, R.; Sivonen, K. Genes coding for hepatotoxic heptapeptides (microcystins) in the cyanobacterium Anabaena strain 90. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomutovska, N.; Sandzewicz, M.; Lach, L.; Suska-Malawska, M.; Chmielewska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Ceglowska, M.; Niyatbekov, T.; Wood, S.A.; Puddick, J.; et al. Limited Microcystin, Anatoxin and Cylindrospermopsin Production by Cyanobacteria from Microbial Mats in Cold Deserts. Toxins 2020, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, J.S.; Giani, A. Microcystin production and regulation under nutrient stress conditions in toxic microcystis strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Ruiz, M.; Zhang, C.C. Oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, D.A.; Zorina, A.; Sinetova, M.; Kryazhov, S.; Mironov, K.; Zinchenko, V.V. Stress Sensors and Signal Transducers in Cyanobacteria. Sensors 2010, 10, 2386–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Steffen, M.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Otten, T.G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wood, S.A.; Paerl, H.W. A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 4–20. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Gobler, C.J. Global transcriptional responses of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to nitrogen stress, phosphorus stress, and growth on organic matter. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, A.; Hess, W.R. How Small Proteins Adjust the Metabolism of Cyanobacteria Under Stress: The Role of Small Proteins in Cyanobacterial Stress Responses. Bioessays 2025, 47, e202400245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, V.; Arockiaraj, J. Unveiling the trifecta of cyanobacterial quorum sensing: LuxI, LuxR and LuxS as the intricate machinery for harmful algal bloom formation in freshwater ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdura, J.; Jankiewicz, U.; Galazka, A.; Orzechowski, S. The Role of Quorum Sensing Molecules in Bacterial-Plant Interactions. Metabolites 2023, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangwani, N.; Supriya, K.; Das, S. Bacterial biofilms and quorum sensing: Fidelity in bioremediation technology. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2016, 32, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, C.R.; Searle, C.L.; Schaber, J.; Höök, T.O. Microplastics impact simple aquatic food web dynamics through reduced zooplankton feeding and potentially releasing algae from consumer control. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, M.; Provenza, F.; Grazioli, E.; Cavallo, A.; Terlizzi, A.; Renzi, M. PET microplastics toxicity on marine key species is influenced by pH, particle size and food variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeogun, A.O.; Adeogun, A.O.; Ibor, O.R.; Ibor, O.R.; Khan, E.A.; Chukwuka, A.V.; Omogbemi, E.D.; Arukwe, A. Detection and occurrence of microplastics in the stomach of commercial fish species from a municipal water supply lake in southwestern Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31035–31045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristanti, R.M.; Wong, W.L.; Darmayati, Y.; Hatmanti, A.; Wulandari, N.F.; Sibero, M.T.; Afianti, N.F.; Hernandes, E.; Lopez-Martinez, F. Characteristics of Microplastic in Commercial Aquatic Organisms. Trop. Aquat. Soil Pollut. 2022, 2, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Wang, Z.-M.; Ghosal, S.; Murphy, M.; Wall, S.; Cook, A.-M.; Robberson, W.; Allen, H.L. Nondestructive Extraction and Identification of Microplastics from Freshwater Sport Fish Stomachs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14496–14506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Addey, C.I.; Oderinde, O.; Okoro, J.O.; Uwamungu, J.Y.; Ikechukwu, C.K.; Okeke, E.S.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; Odii, E.C. Toxic Chemicals and Persistent Organic Pollutants Associated with Micro-and Nanoplastics Pollution. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Nath, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mukherjee, S. Unveiling the effects of microplastics pollution on marine fauna. Blue Biotechnol. 2024, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocar, P.; Grieco, V.; Aidos, L.; Borromeo, V. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Their Effects in Pet Dogs and Cats: An Overview. Animals 2023, 13, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.-D.-T.; Vo, D.-H.T.; Pham, M.-D.-T.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, T.-B.; Le, L.-T.; Mukhtar, H.; Nguyen, H.-V.; Visvanathan, C.; Bui, X.-T. Microplastics contamination in water supply system and treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puteri, M.N.; Gew, L.T.; Ong, H.C.; Ming, L.C. Technologies to eliminate microplastic from water: Current approaches and future prospects. Environ. Int. 2025, 199, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Sun, C.; He, C.; Li, J.; Ju, P.; Li, F. Microplastics in four bivalve species and basis for using bivalves as bioindicators of microplastic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanigaivel, S.; Kamalesh, R.; Ragini, Y.P.; Saravanan, A.; Vickram, A.S.; Abirami, M.; Thiruvengadam, S. Microplastic pollution in marine environments: An in-depth analysis of advanced monitoring techniques, removal technologies, and future challenges. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 205, 106993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ren, R.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y. Effects of microplastics on dissipation of oxytetracycline and its relevant resistance genes in soil without and with Serratia marcescens: Comparison between biodegradable and conventional microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 287, 117235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhali, S.L.; Parida, D.; Kumar, B.; Bala, K. Recent trends in microbial and enzymatic plastic degradation: A solution for plastic pollution predicaments. Biotechnol. Sustain. Mater. 2024, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.N.; Kallem, P.; Mounika, K.V.S.S.N.; Muqeet, A.; Raj, J.C.J.; Aishwarya, C.V.S.; Gupta, R.K.; Polisetti, V.; Mishra, B.; Yadavalli, R.; et al. Review of microplastic degradation: Understanding metagenomic approaches for microplastic degrading organisms. Polym. Test. 2023, 128, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Gong, H.; Yan, M. Biological Degradation of Plastics and Microplastics: A Recent Perspective on Associated Mechanisms and Influencing Factors. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, P.; Shobika, R.; Omer, S.; Reddy, M.; Saravanan, P.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Saravanan, V.; Venkatkumar, S. Bioremediation of plastics by the help of microbial tool: A way for control of plastic pollution. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2023, 3, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

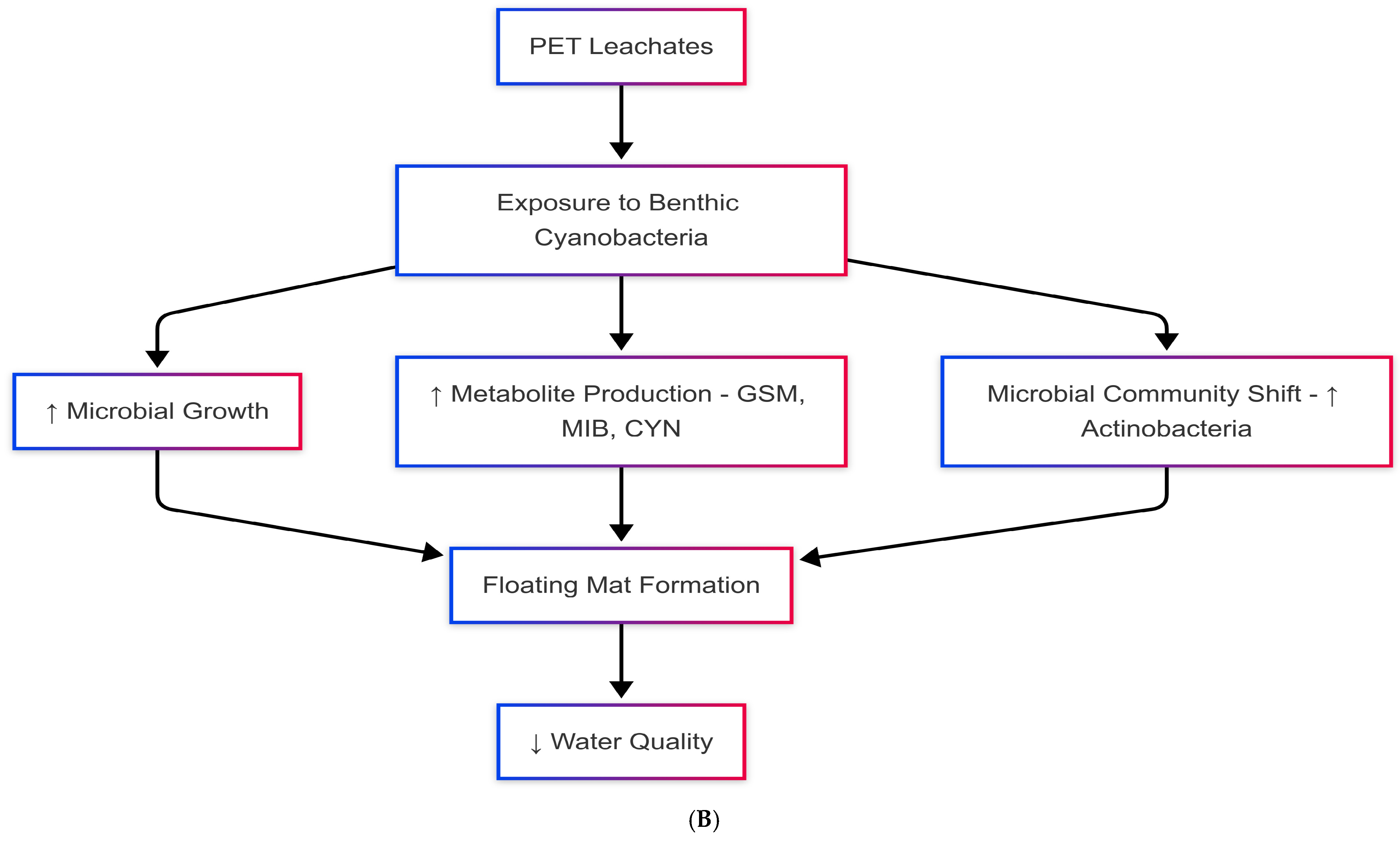
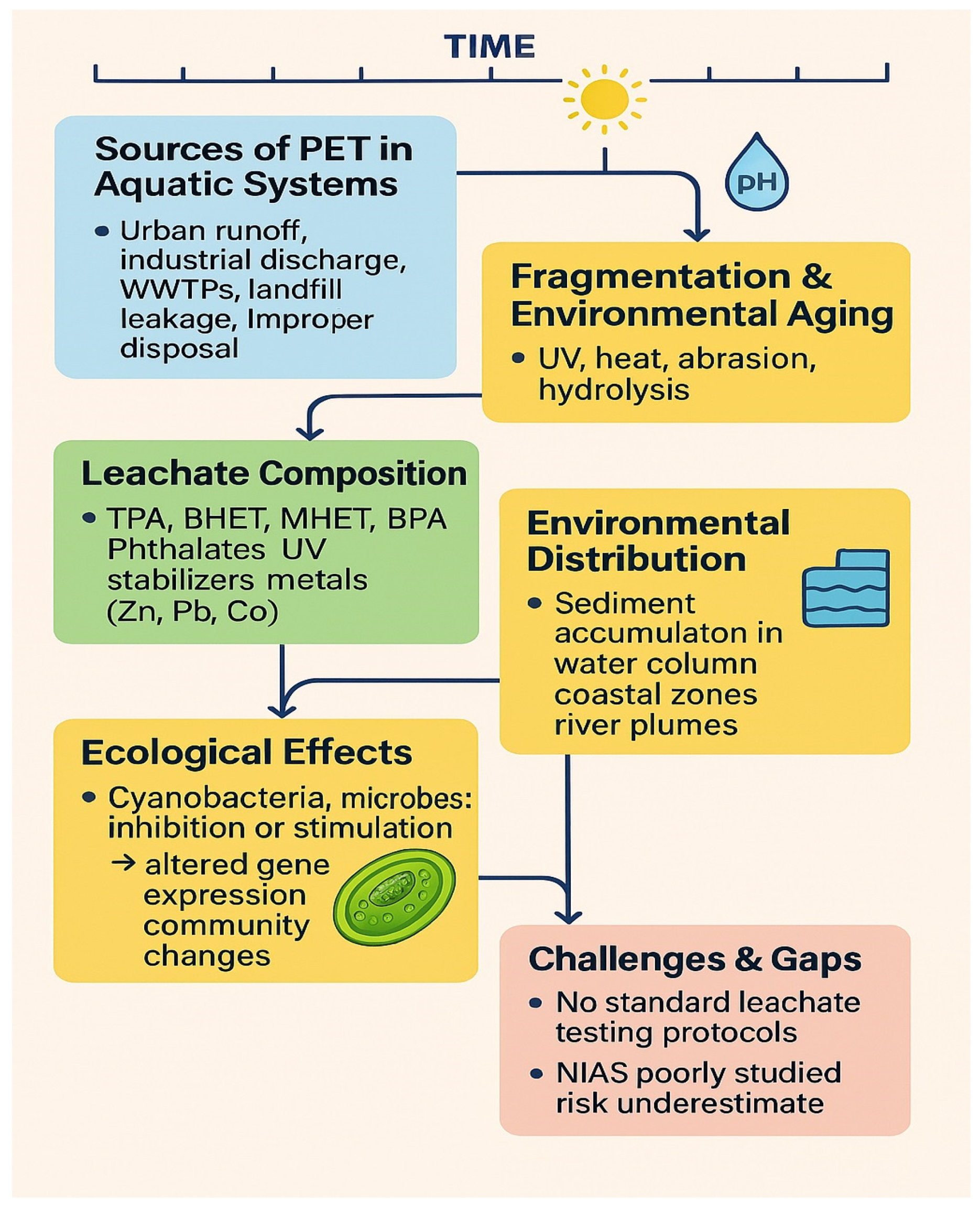
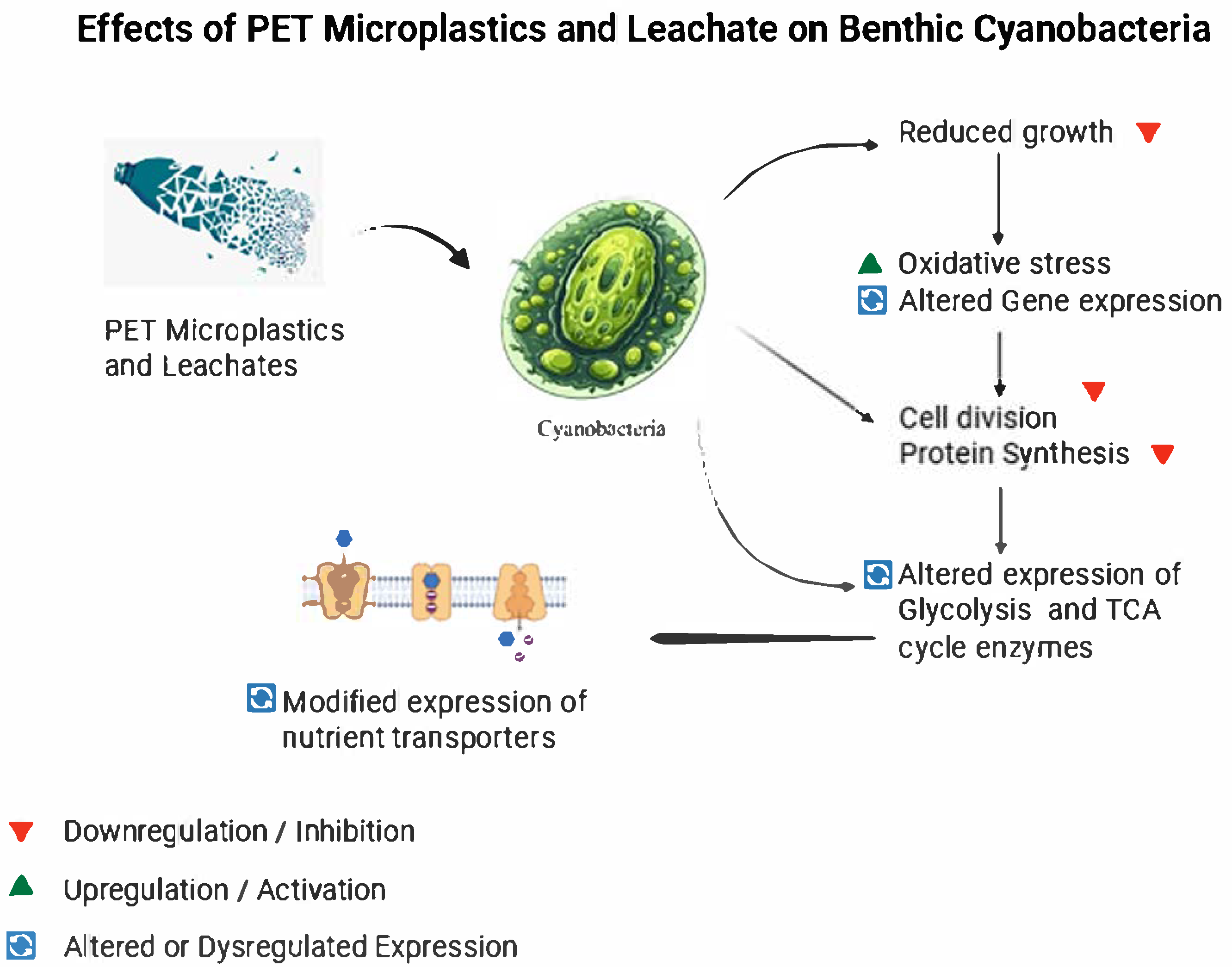
| Aspect | Key Points | Details/Examples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sources and Distribution of PET Microplastics | Origin and environmental dispersion of PET microplastics | Primary sources: microbeads, pellets; Secondary: fragmentation of larger debris; Pathways: improper disposal, runoff, industrial discharge, WWTPs; Found in water, sediments globally | [38] |
| Environmental Aging and Surface Modification of PET | Degradation processes and enhanced ecological risks | Factors: UV radiation, mechanical abrasion, hydrolysis, bioactivity; Effects: increased roughness, biofilm formation, chemical release | [116] |
| PET Leachates: Composition and Environmental Relevance | Chemical makeup and toxicological impact | Components: TPA, BHET, phthalates, metals; Effects: photosynthesis inhibition, oxidative stress, endocrine disruption; Risk from complex chemical mixtures | [117] |
| Aspect | Planktonic Cyanobacteria | Benthic Cyanobacteria | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology | Unicellular or small colonies (e.g., Microcystis, ~3.6 μm) | Filamentous, mat-forming (e.g., Oscillatoria, >180 μm) | [139] |
| PET Adhesion | Limited due to small size and lack of EPS matrix | Enhanced by EPS and filamentous structure, promoting plastisphere formation | [140] |
| Photosynthetic Impact | High sensitivity to shading by microplastics | Moderate sensitivity; adapted to low-light benthic environments | [141] |
| Toxin Production Response | Variable; often inhibited by high leachate concentrations (e.g., mcyD downregulation) | Upregulation of toxin genes (e.g., mcyD 1.8-fold increase) at low concentrations | [142] |
| Ecological Role | Primary producers in water column; bloom formation | Nutrient cycling in sediments; mat stabilization | [143] |
| Leachate Metabolism | Limited assimilation of PET monomers due to short exposure times | Potential use of monomers as carbon sources in stable benthic mats | [19] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mir, R.; Albarqi, S.; Albalawi, W.; Alanazi, G.; Alsubaie, S.S.; Alghaban, R.I.; Alanazi, H.S.; Alsharif, N.T.; Aljammaz, M.M.; Alghabban, N.F.; et al. Elucidation of Mechanisms by Which Microplastics (PET) Facilitates the Rapid Growth of Benthic Cyanobacteria and Toxin Production in Aquatic Ecosystems. Metabolites 2025, 15, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060383
Mir R, Albarqi S, Albalawi W, Alanazi G, Alsubaie SS, Alghaban RI, Alanazi HS, Alsharif NT, Aljammaz MM, Alghabban NF, et al. Elucidation of Mechanisms by Which Microplastics (PET) Facilitates the Rapid Growth of Benthic Cyanobacteria and Toxin Production in Aquatic Ecosystems. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060383
Chicago/Turabian StyleMir, Rashid, Shrooq Albarqi, Wed Albalawi, Ghaida Alanazi, Shouq S. Alsubaie, Razan I. Alghaban, Hanadi Saud Alanazi, Nora Taleb Alsharif, Manal M. Aljammaz, Nouf Faisal Alghabban, and et al. 2025. "Elucidation of Mechanisms by Which Microplastics (PET) Facilitates the Rapid Growth of Benthic Cyanobacteria and Toxin Production in Aquatic Ecosystems" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060383
APA StyleMir, R., Albarqi, S., Albalawi, W., Alanazi, G., Alsubaie, S. S., Alghaban, R. I., Alanazi, H. S., Alsharif, N. T., Aljammaz, M. M., Alghabban, N. F., Alhwiti, W. S., Albogmi, A., & Alblwi, F. F. (2025). Elucidation of Mechanisms by Which Microplastics (PET) Facilitates the Rapid Growth of Benthic Cyanobacteria and Toxin Production in Aquatic Ecosystems. Metabolites, 15(6), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060383







