LC-QToF-MS Analysis of Stimulant Drugs and Their Metabolites in Wastewater During Football Games
Abstract
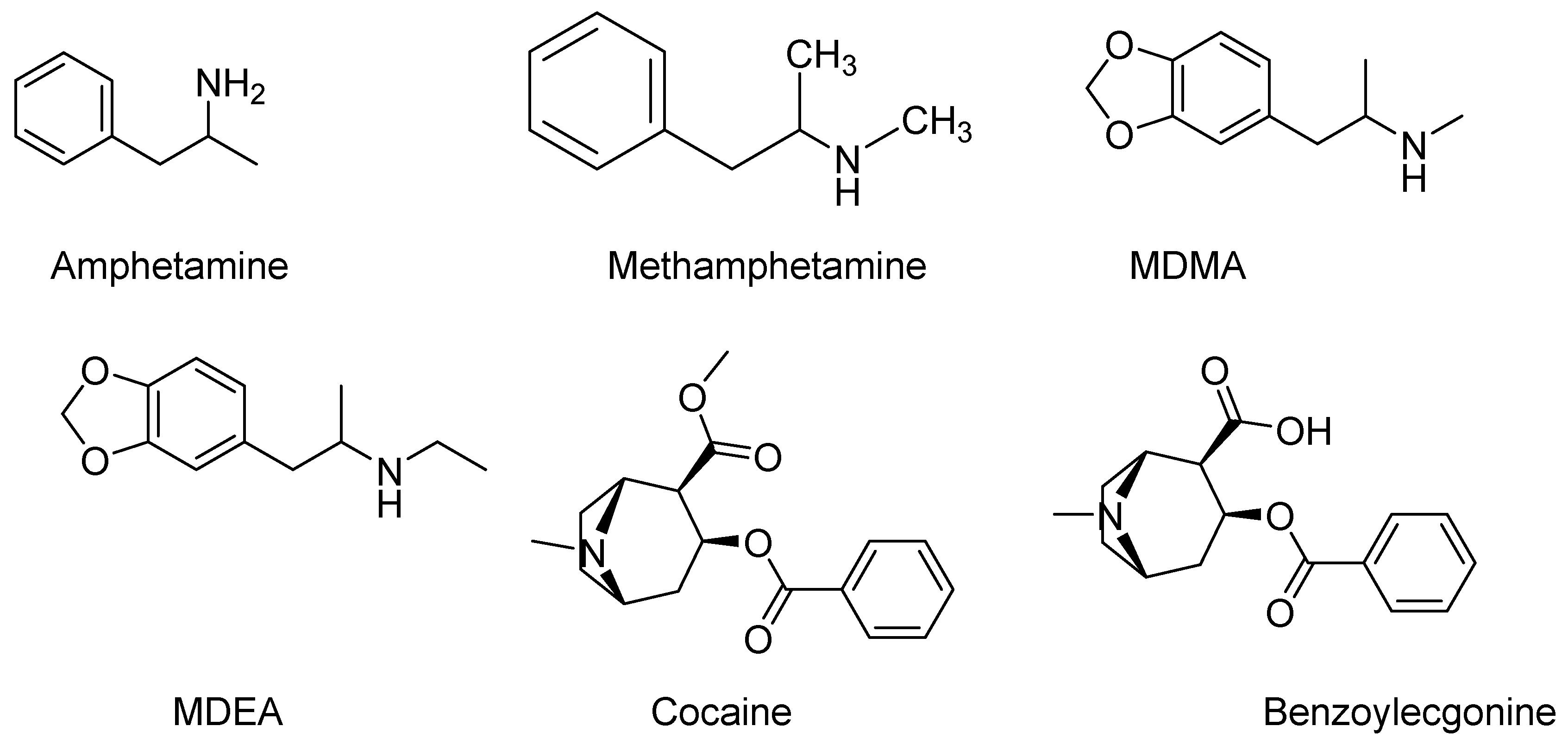
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Extraction Procedure
2.3. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Conditions
Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (LC-QToF-MS)
2.4. Chemicals
2.5. Validation of the Analytical Procedure
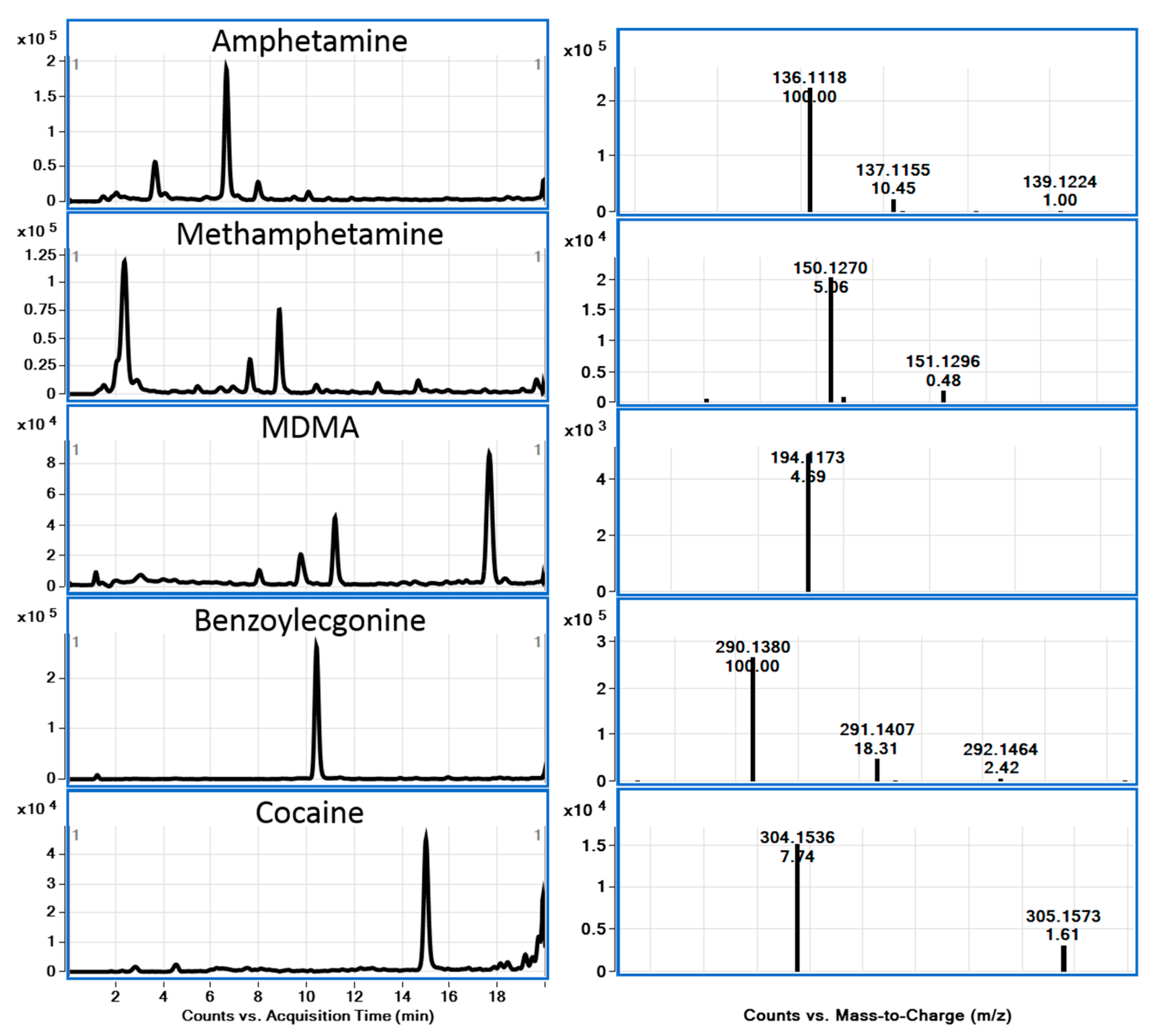
2.6. Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Nuijs, A.L.N.; Pecceu, B.; Theunis, L.; Dubois, N.; Charlier, C.; Jorens, P.G.; Bervoets, L.; Blust, R.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Occurrence of Cocaine and Benzoylecgonine in Waste- and Surface Water from Belgium and Removal during Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2021 National Survey on Drug Use and Health; HHS Publication No. PEP22-07-01-005, NSDUH Series H-57; Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health, Department of Health and Human: Rockville, MD, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt39443/2021NSDUHFFRRev010323.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Farrell, M.; Martin, N.K.; Stockings, E.; Bórquez, A.; Cepeda, J.A.; Degenhardt, L.; Ali, R.; Tran, L.T.; Rehm, J.; Torrens, M.; et al. Responding to Global Stimulant Use: Challenges and Opportunities. Lancet 2019, 394, 1652–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Megharaj, M.; Kirkbride, K.P.; Naidu, R. Illicit Drugs and the Environment—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G. Illicit drugs in municipal sewage. Proposed new nonintrusive tool to heighten public awareness of societal use of illicit-abused drugs and their potential for ecological consequences. Pharm. Care Prod. Environ. 2001, 791, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Chiabrando, C.; Castiglioni, S.; Calamari, D.; Bagnati, R.; Schiarea, S.; Fanelli, R. Cocaine in Surface Waters: A New Evidence-Based Tool to Monitor Community Drug Abuse. Environ. Health 2005, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zergui, A.; Nkontcheu Kenko, D.B. Drugs of Abuse and Psychoactive Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater as Worldwide Contaminants of Emerging Concern: A Systematic Review. J. Environ. Pollut. Manag. 2024, 1, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuori, E.; Happonen, M.; Gergov, M.; Nenonen, T.; Järvinen, A.; Ketola, R.A.; Vahala, R. Wastewater Analysis Reveals Regional Variability in Exposure to Abused Drugs and Opioids in Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefau, T.; Karolak, S.; Castillo, L.; Boireau, V.; Levi, Y. Presence of Illicit Drugs and Metabolites in Influents and Effluents of 25 Sewage Water Treatment Plants and Map of Drug Consumption in France. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, W.; Stamper, B.J.; Godfrey, M.; ElSohly, M.A. LC–MS-MS Method for Stimulants in Wastewater During Football Games. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, W.; Stamper, B.; Godfrey, M.; Gul, S.W.; ElSohly, M.A. LC–MS-MS Method for Analysis of Opiates in Wastewater During Football Games II. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarone, D. Stimulant Abuse: Pharmacology, Cocaine, Methamphetamine, Treatment, Attempts at Pharmacotherapy. Prim. Care 2011, 38, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudenmann, R.W.; Spitzer, M. The Neuropsychopharmacology and Toxicology of 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethyl-amphetamine (MDEA). CNS Drug Rev. 2004, 10, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, C.W.; Goldberg, S.R. Accelerating Cocaine Metabolism as an Approach to the Treatment of Cocaine Abuse and Toxicity. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH Q2(R1). Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines, International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals For Human Use Nov. 2005. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Stamper, B.; Gul, W.; Godfrey, M.; Gul, S.W.; ElSohly, M.A. LC–MS-MS Method for the Analysis of Miscellaneous Drugs in Wastewater During Football Games III. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamper, B.; Gul, W.; Godfrey, M.; Gul, S.W.; ElSohly, M.A. LC–MS-MS Method for Analysis of Benzodiazepines in Wastewater During Football Games IV. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, C.; De Alda, M.L.; Barceló, D. Evaluation of Drugs of Abuse Use and Trends in a Prison through Wastewater Analysis. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.; Tindale, K.; Li, H.; Rodayan, A.; Yargeau, V. Illicit Drugs in Canadian Municipal Wastewater and Estimates of Community Drug Use. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Fontela, M.; Galceran, M.T.; Ventura, F. Stimulatory Drugs of Abuse in Surface Waters and Their Removal in a Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6809–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Ibáñez, M.; Botero-Coy, A.-M.; Bade, R.; Bustos-López, M.C.; Rincón, J.; Moncayo, A.; Bijlsma, L. LC-QTOF MS Screening of More than 1000 Licit and Illicit Drugs and Their Metabolites in Wastewater and Surface Waters from the Area of Bogotá, Colombia. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6405–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geue, N.; Bennett, T.S.; Ramakers, L.A.I.; Timco, G.A.; McInnes, E.J.L.; Burton, N.A.; Armentrout, P.B.; Winpenny, R.E.P.; Barran, P.E. Adduct Ions as Diagnostic Probes of Metallosupramolecular Complexes Using Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Paul, R.; Osselton, D.; Woolley, T. Analysis of Crude Wastewater from Two Treatment Plants in South Wales for 35 New Psychoactive Substances and Cocaine, and Cannabis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roveri, V.; Guimarães, L.L.; Kiyotani, R.B.; Assis Junior, W.R.A.D.; Metropolo, A.P.; Santos, G.A.D.; Rodrigues, A.Z.; Pereira, C.D.S.; Correia, A.T. Temporal Variability and Ecological Risks of Pharmaceuticals and Cocaine during the Christmas and New Year Holidays in a Beach Area of North Coast of São Paulo, Brazil. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, S.; Daiwile, A.P.; Cadet, J.L. Neurotoxicity of Methamphetamine: Main Effects and Mechanisms. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 344, 113795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucoloto, A.D.; Eller, S.; De Oliveira, T.F.; Wagner, G.A.; Fruchtengarten, L.V.G.; De Oliveira, C.D.R.; Yonamine, M. Relationship between Cocaine and Cocaethylene Blood Concentration with the Severity of Clinical Manifestations. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 50, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, A.; Zieske, L.; Jacobs, A. Analysis of the Cocaine Metabolite in the Urine of Patients and Physicians during Clinical Use. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1994, 111, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quireyns, M.; Boogaerts, T.; Van Wichelen, N.; Covaci, A.; Van Nuijs, A.L.N. State-of-the-art Analytical Approaches and Strategies to Assess Disposal of Drugs for Wastewater-based Epidemiology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Forensic Sci. 2022, 5, e1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
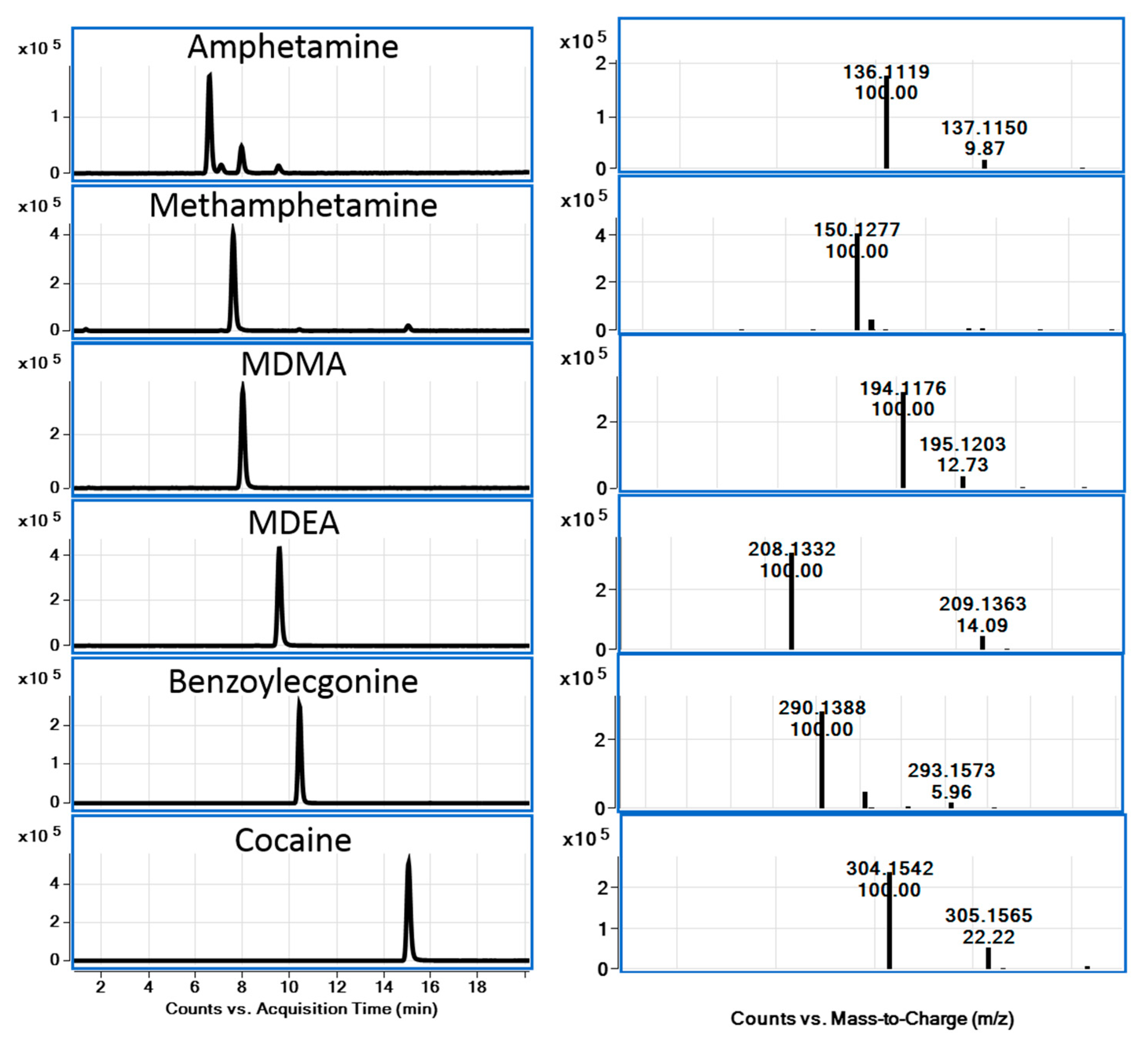
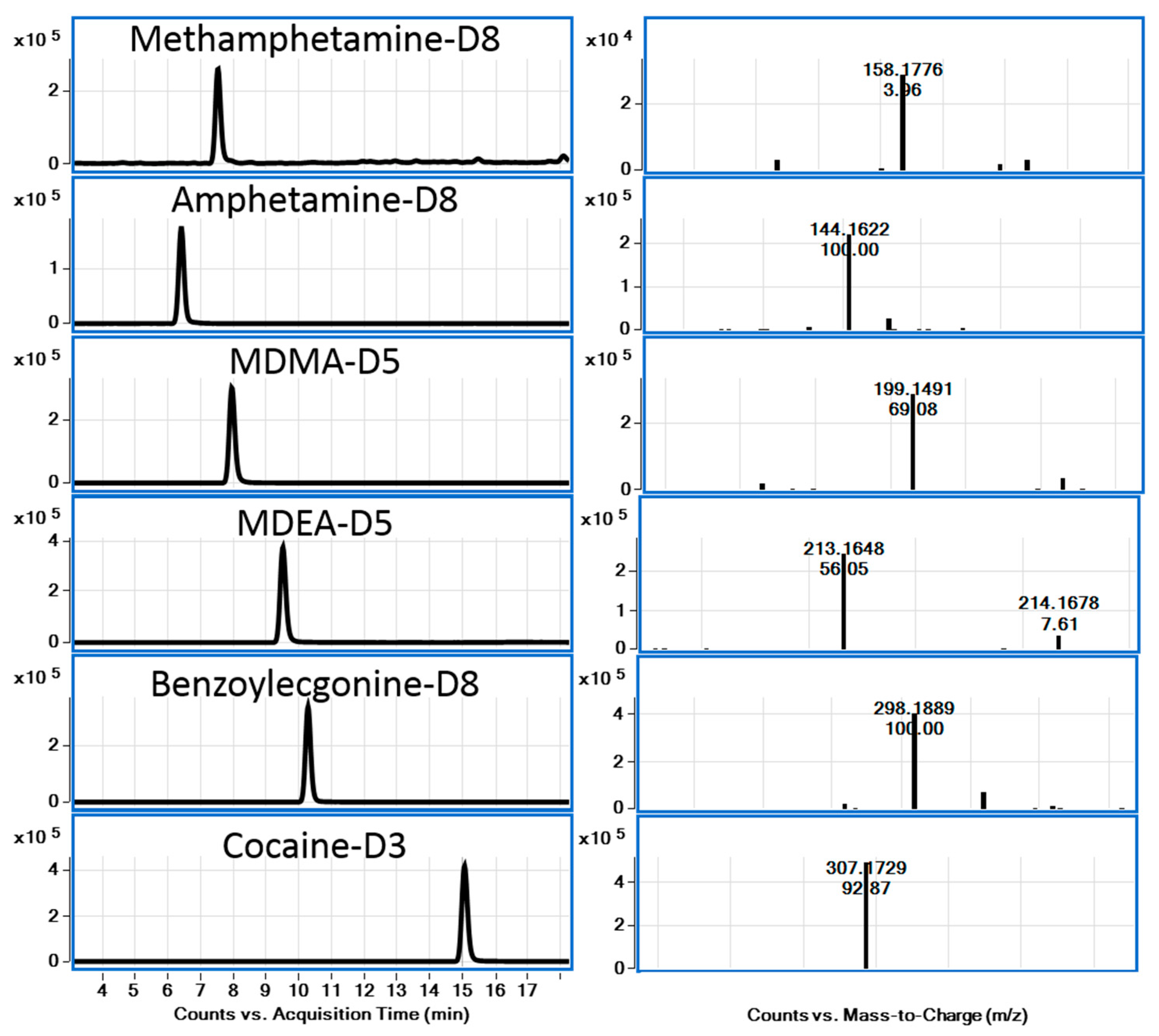
| Analyte | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | ULOL (ng/mL) | Correlation Coefficient (r2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | 1 | 2.5 | 500 | 0.9996 |
| Methamphetamine | 1 | 2.5 | 100 | 0.9996 |
| MDMA | 1 | 5 | 500 | 0.9999 |
| MDEA | 1 | 2.5 | 500 | 1.0000 |
| Cocaine | 1 | 2.5 | 100 | 0.9999 |
| Benzoylecgonine | 1 | 5 | 100 | 0.9996 |
| Analyte (10 ng/mL) | Within-Batch Accuracy | Within-Batch %CV | Batch-to-Batch Accuracy | Batch-to-Batch %CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | 95–104% | 2.7–9.0% | 99% | 6.2% |
| Methamphetamine | 98–101% | 1.1–4.4% | 99% | 2.7% |
| MDMA | 95–104% | 1.9–6.6% | 99% | 4.5% |
| MDEA | 91–100% | 1.6–5.5% | 96% | 3.7% |
| Cocaine | 95–100% | 2.2–8.4% | 98% | 4.4% |
| Benzoylecgonine | 95–109% | 0.9–6.5% | 102% | 4.1% |
| Date/Day of Week (Year 2017) | Amphetamine | Meth | MDMA | MDEA | Cocaine | BE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20-October | Fri | 1.0 * | 0.1 | - | - | 0.2 | 1.8 * |
| 21-October | Sat | 0.9 | 0.3 | <LOQ | - | 0.3 | 3.7 * |
| 22-October | Sun | 0.8 | 0.1 | - | - | 0.2 | 3.8 * |
| 25-October | Wed | 0.7 | 0.2 | - | - | 0.1 | 1.2 |
| 28-October | Sat | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | - | 0.3 | 1.4 |
| 29-October | Sun | 0.6 | 0.3 | - | - | 0.2 | 3.3 * |
| Date/Day of Week (Year 2017) | Amphetamine | Meth | MDMA | MDEA | Cocaine | BE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13-October | Fri | 1.2 | 0.1 | - | - | 0.1 | 0.6 |
| 14-October | Sat | 2.1 * | 0.2 | <LOQ | - | 0.2 | 1.8 * |
| 20-October | Fri | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | - | 0.1 | 0.6 |
| 21-October | Sat | 2.9 * | 0.2 | 0.1 | - | 0.2 | 3.2 * |
| 22-October | Sun | 0.1 | - | <LOQ | - | - | 0.8 |
| 25-October | Wed | 2.1 * | - | - | - | - | 0.4 |
| 28-October | Sat | 2.1 * | 0.3 | <LOQ | - | 0.1 | 1.4 * |
| 29-October | Sun | 0.4 | 0.4 | - | - | - | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stamper, B.J.; Chaturvedi, K.; Avula, B.; Bae, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Bledsoe, K.S.; Khan, I.A.; Godfrey, M. LC-QToF-MS Analysis of Stimulant Drugs and Their Metabolites in Wastewater During Football Games. Metabolites 2025, 15, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020069
Stamper BJ, Chaturvedi K, Avula B, Bae J-Y, Wang Y-H, Bledsoe KS, Khan IA, Godfrey M. LC-QToF-MS Analysis of Stimulant Drugs and Their Metabolites in Wastewater During Football Games. Metabolites. 2025; 15(2):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020069
Chicago/Turabian StyleStamper, Brandon J., Krishna Chaturvedi, Bharathi Avula, Ji-Yeong Bae, Yan-Hong Wang, Kyle S. Bledsoe, Ikhlas A. Khan, and Murrell Godfrey. 2025. "LC-QToF-MS Analysis of Stimulant Drugs and Their Metabolites in Wastewater During Football Games" Metabolites 15, no. 2: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020069
APA StyleStamper, B. J., Chaturvedi, K., Avula, B., Bae, J.-Y., Wang, Y.-H., Bledsoe, K. S., Khan, I. A., & Godfrey, M. (2025). LC-QToF-MS Analysis of Stimulant Drugs and Their Metabolites in Wastewater During Football Games. Metabolites, 15(2), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020069






