Fufang Muji Granules Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Inhibiting Apoptosis, and Modulating Overall Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Compounds and Reagents
2.2. Determination of Chemical Composition and Content
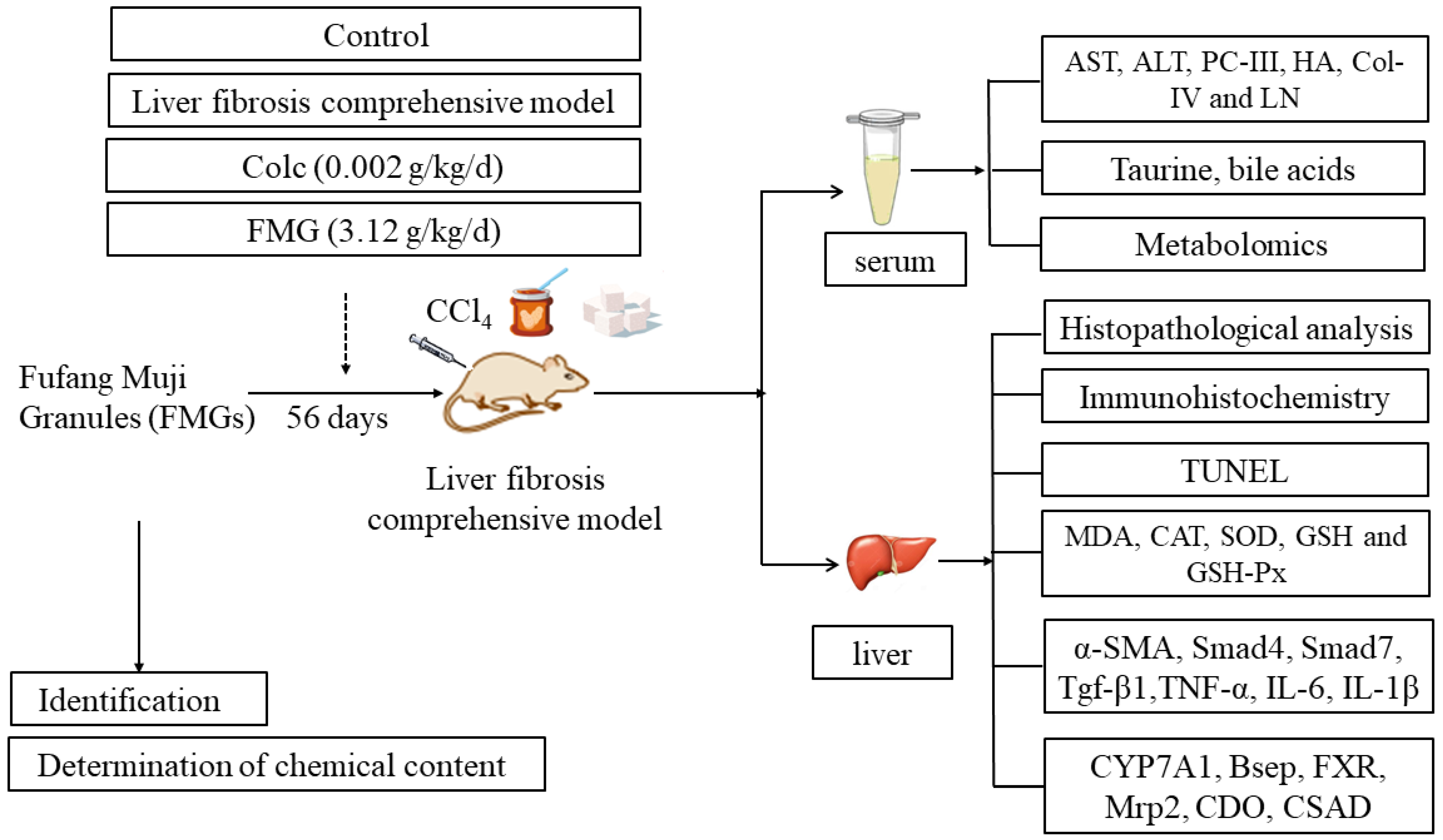
2.3. Animal Study
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Serum and Liver Biochemistry Analysis
2.6. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
2.7. TUNEL Analysis
2.8. HPLC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics
2.8.1. Sample Preparation
2.8.2. HPLC-MS/MS Method
2.8.3. Data Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.10. Determination of Bile Acid Levels in Serum
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ingredient Identification and Quality Control Results of FMGs
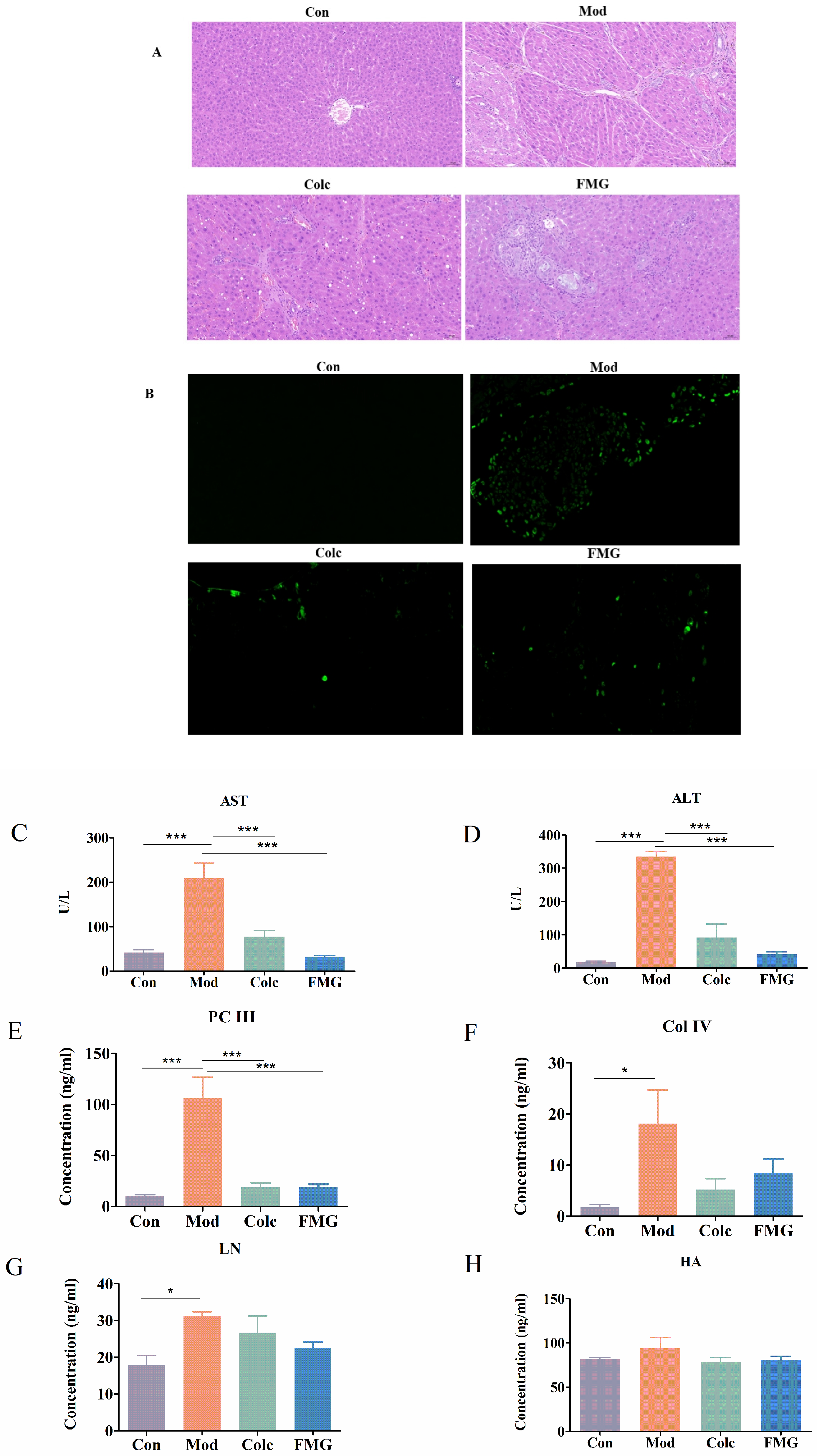
3.2. FMGs Alleviate Hepatic Pathological and Functional Changes in Liver Fibrosis
3.3. FMGs Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis in Rats
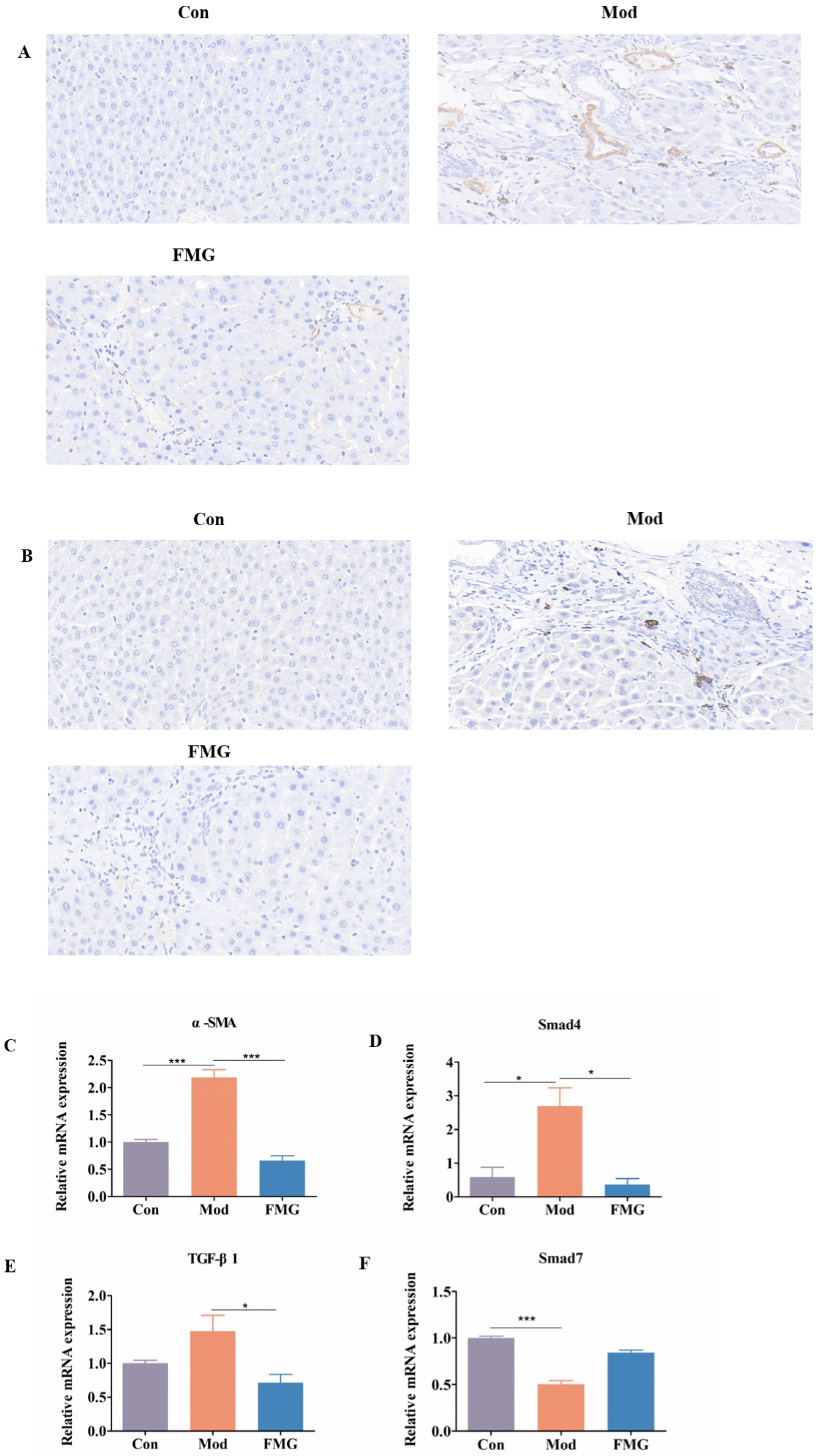
3.4. FMGs Ameliorate Myofibroblast Activation in Liver Fibrotic Rats
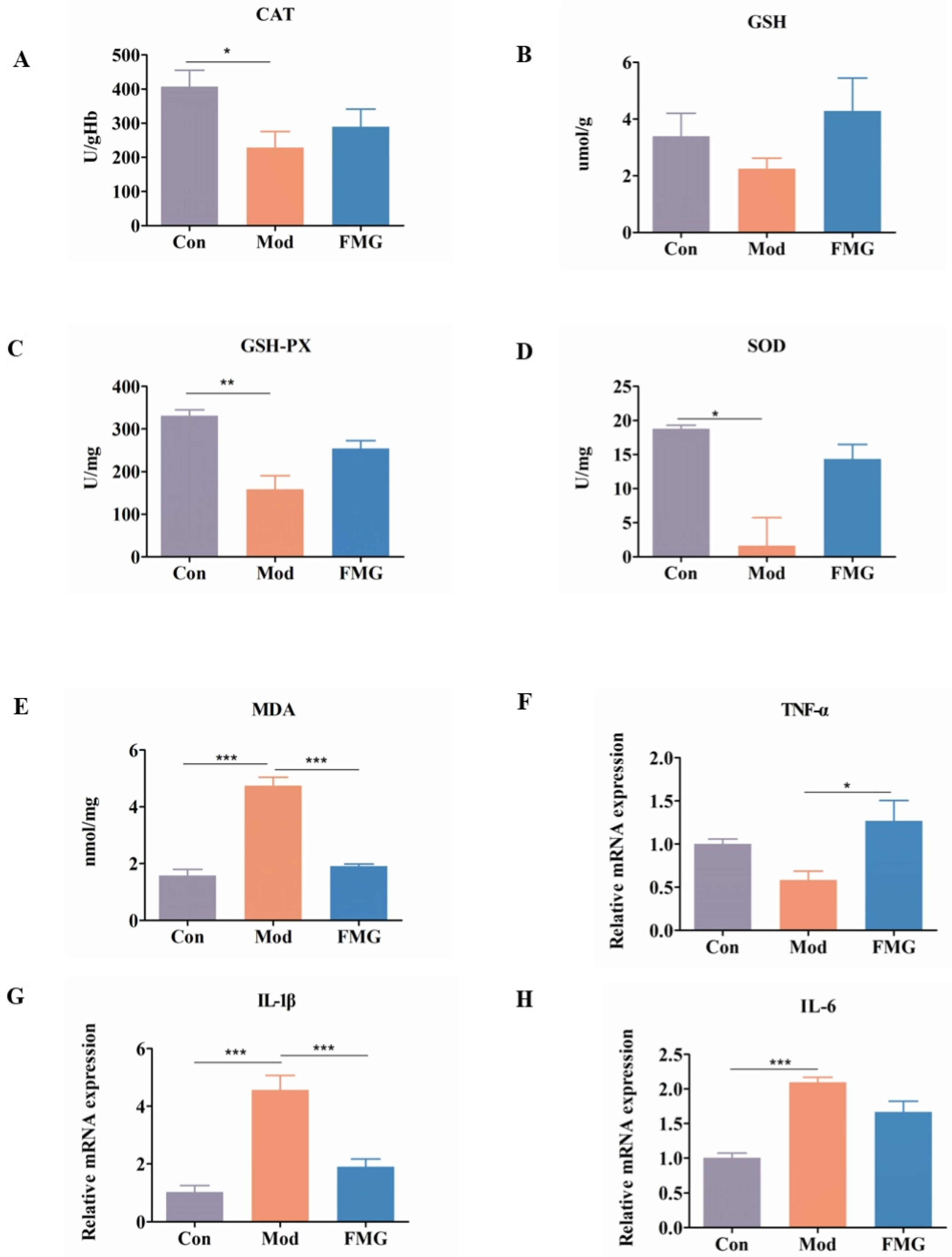
3.5. FMGs Ameliorate Oxidative Stress Caused by Liver Fibrosis in Rats
3.6. FMGs Reduce Inflammatory Factors in Hepatic Fibrotic Rats
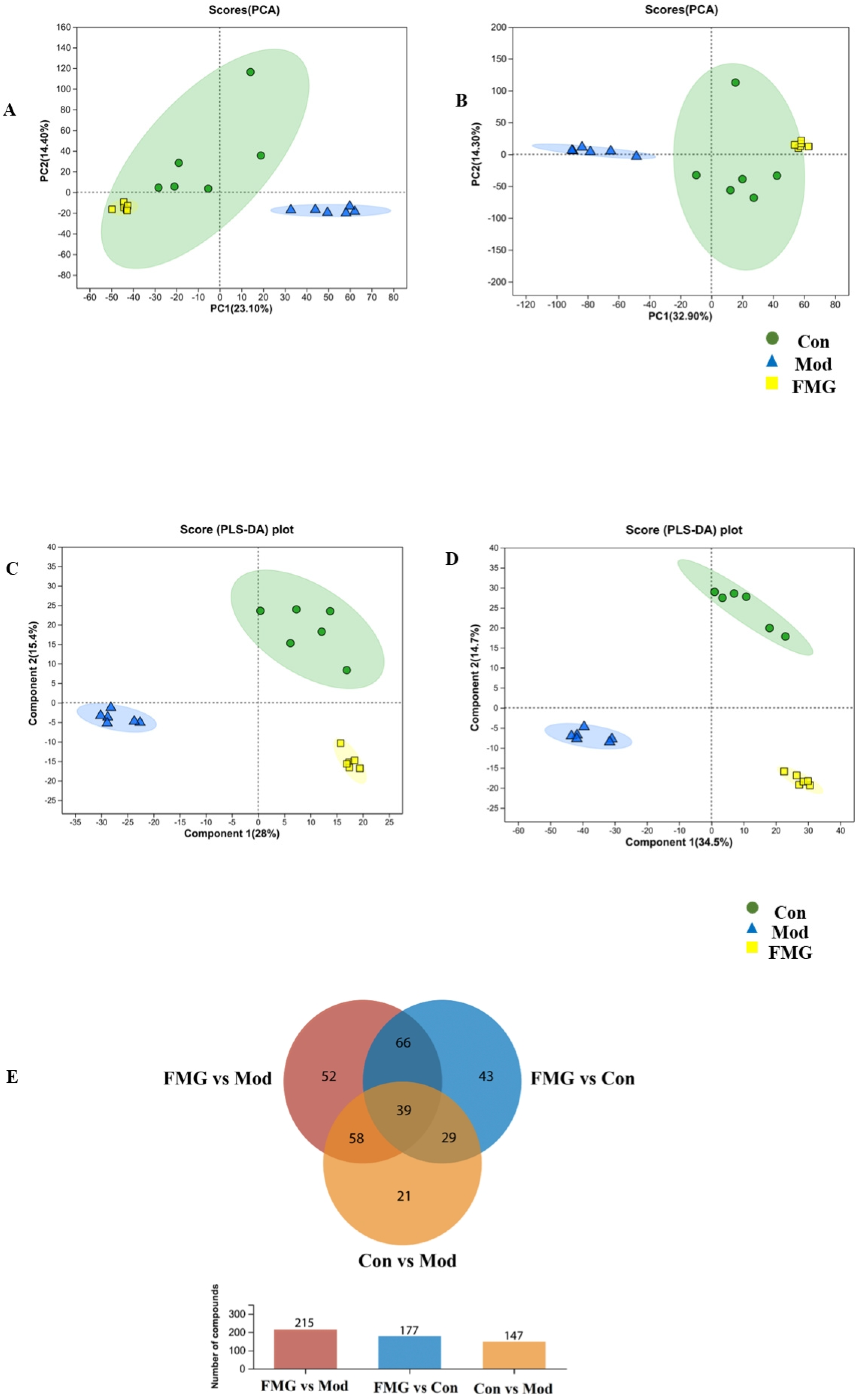
3.7. FMGs Reverse the Metabolic Profiles of Hepatic Fibrotic Rats
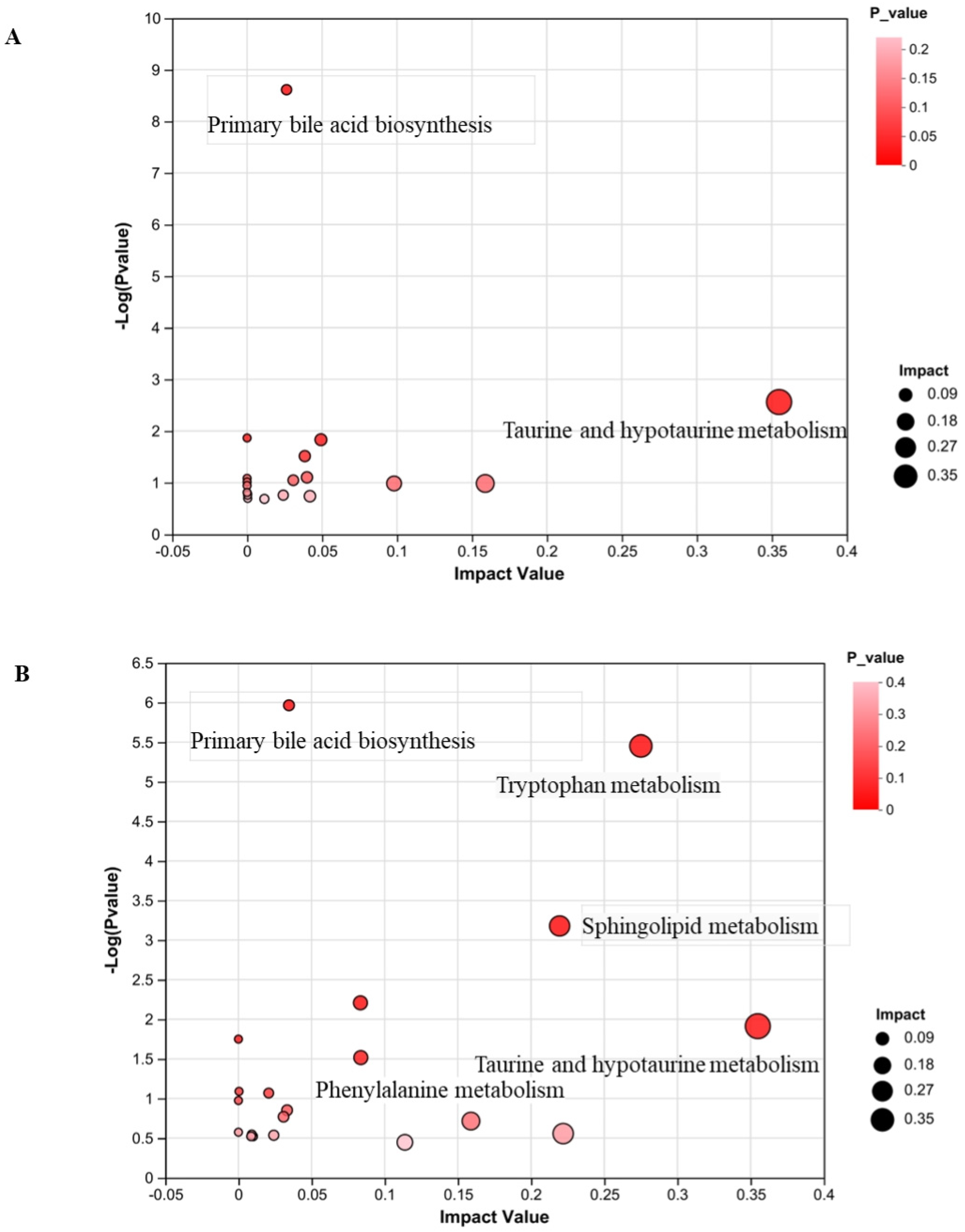
3.8. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
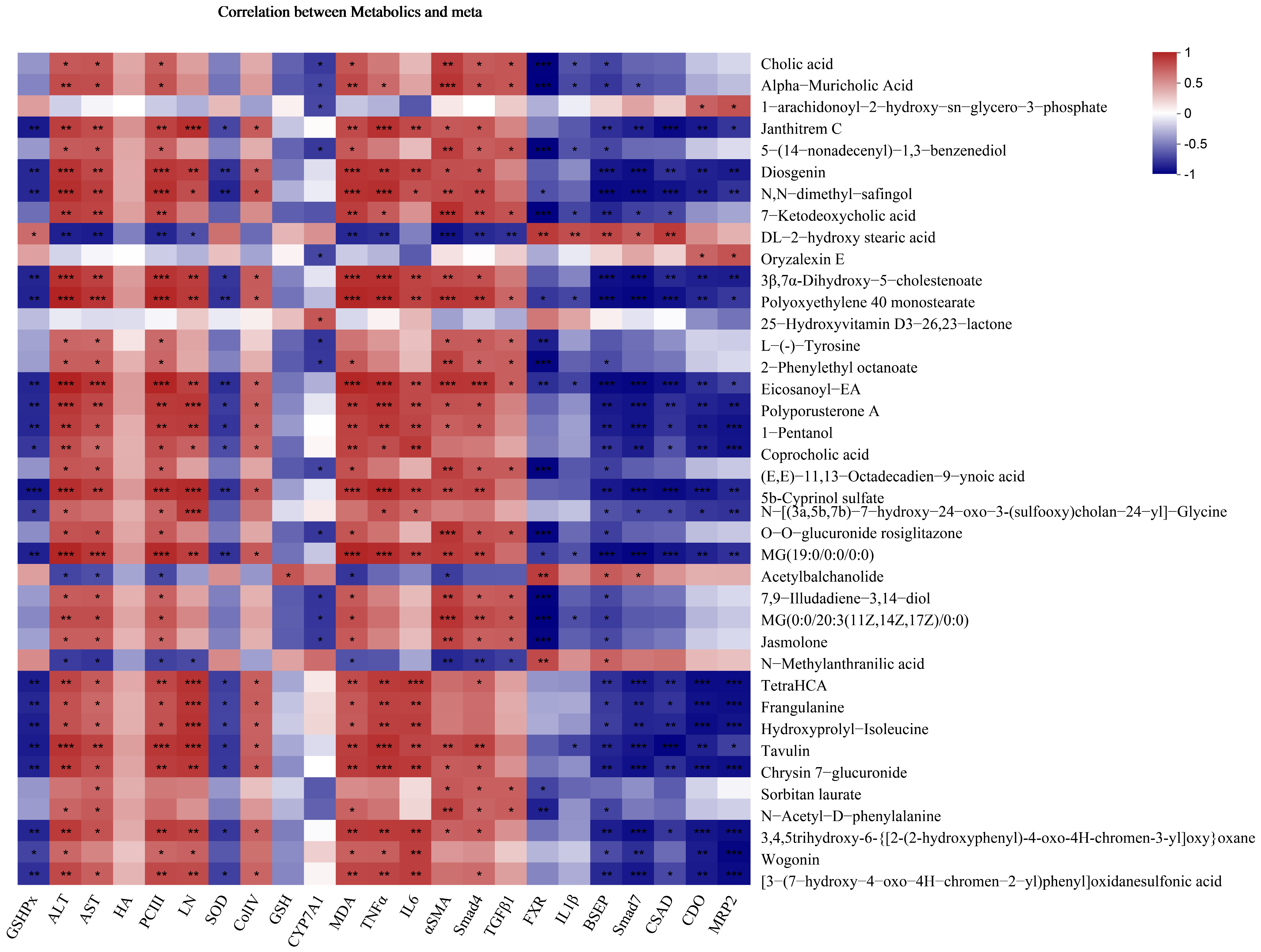
3.9. FMGs Regulate Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism in Liver Fibrotic Rats
3.10. FMGs Regulate Bile Metabolism in Liver Fibrotic Rats
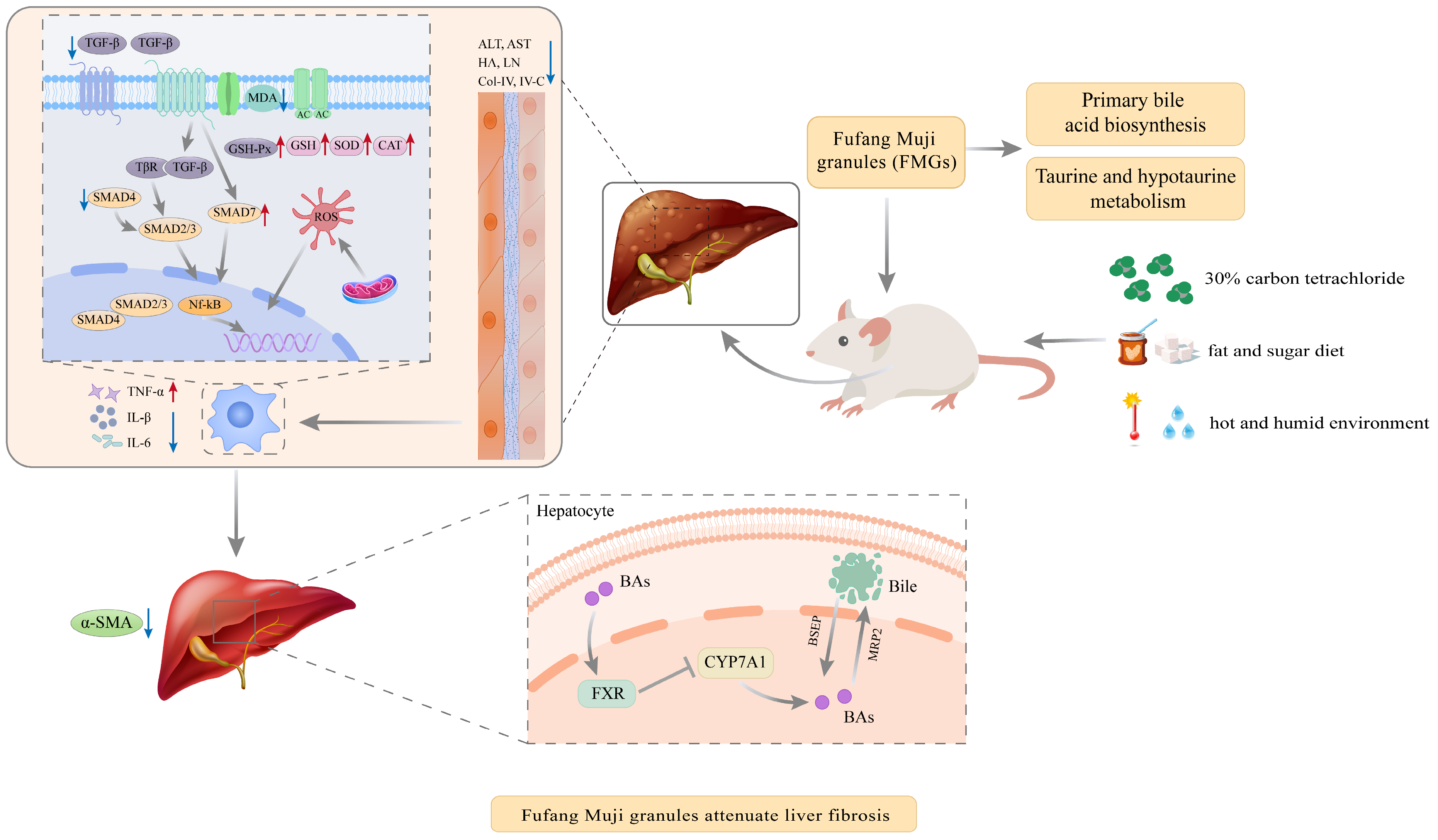
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moon, A.M.; Singal, A.G.; Tapper, E.B. Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2650–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Hu, N.; Yu, C.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Baihe Wuyao decoction ameliorates CCl4-induced chronic liver injury and liver fibrosis in mice through blocking TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling, anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Zhong, G.Y.; Zhu, J.X. Molecular mechanism and research progress on pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine in liver injury. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qinna, N.A.; Ghanim, B.Y. Chemical induction of hepatic apoptosis in rodents. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, D.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, M.M.; Akcali, K.C. Liver fibrosis. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 29, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-B.; Bao, Y.-R.; Wang, S.; Li, T.-J.; Tai, H.; Leng, J.-P.; Yang, X.-X.; Wang, B.-C.; Meng, X.-S. Possible mechanisms associated with immune escape and apoptosis on anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effect of Mu Ji Fang granules. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 15, 504–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, L.; Hou, M.; Hu, W. Identification and characterization of chemical constituents in compound Muji granules based on LC-LTQ-Orbitrap/MS. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 39, 1048. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z.-P.; Zhu, X.-J.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Zhang, X.-D.; Tian, J.-L.; Li, W.; Zhao, P. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and clinical applications of Cortex Juglandis Mandshuricae: A comprehensive review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Trametes versicolor (Synn. Coriolus versicolor) Polysaccharides in Cancer Therapy: Targets and Efficacy. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winder, M.; Bulska-Będkowska, W.; Chudek, J. The use of Hericium erinaceus and Trametes versicolor extracts in supportive treatment in oncology. Acta Pharm. 2021, 71, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Qi, C.; Wang, G.; Dai, X.; Hou, X. Enrichment and purification of total flavonoids from Cortex Juglandis Mandshuricae extracts and their suppressive effect on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury in Mice. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1007, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, N.; Hong, M.; Tan, H.-Y.; Pan, G.; Feng, Y. Hepatoprotective Effects of a Functional Formula of Three Chinese Medicinal Herbs: Experimental Evidence and Network Pharmacology-Based Identification of Mechanism of Action and Potential Bioactive Components. Molecules 2018, 23, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, Z.; Gong, X.; Ou, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yao, C.; Qin, S.; Yan, B.; Li, Q.; et al. Chloroform extract from Sophora Tonkinensis Gagnep. inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion and promote apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by silencing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jiang, C. New study progress of Compound Muji Granule of Manchu medicine. China Med. Her. 2013, 10, 2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ding, X.; Ma, J.; Tan, G. Chemical profile of Swertia mussotii Franch and its potential targets against liver fibrosis revealed by cross-platform metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics for Investigating Physiological and Pathophysiological Processes. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1819–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.-J.; Zhang, P.-P.; Zhang, W.; Song, D.; Wei, X.; Yin, X.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Pu, X.; Zhou, Y. Biological Activities and Secondary Metabolites from Sophora tonkinensis and Its Endophytic Fungi. Molecules 2022, 27, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Shi, W. Cuscuta chinensis flavonoids reducing oxidative stress of the improve sperm damage in bisphenol A exposed mice offspring. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, F.-L.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, L.-T.; Lin, C.-C. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Cuscuta chinensis against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, L. Research Progress on the Extraction, Structure, and Bioactivities of Polysaccharides from Coriolus versicolor. Foods 2022, 11, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, M.; Lau-Cam, C.A. Comparison of the protective actions of N-acetylcysteine, hypotaurine and taurine against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.K.; Do, Y.K.; Choi, K.H.; Dal, W.C.; Young, C.K. lmpaired metabolomics of sulfur-containing substances in rats acutely treated with carbon tetrachloride. Off. J. Korean Soc. Toxicol. 2008, 24, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Cao, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, H.; Kuang, H. Determination of metabolic phenotype and potential biomarkers in the liver of heroin addicted mice with hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 2021, 287, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Huo, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K. Protective effects of alisol B 23-acetate from edible botanical Rhizoma alismatis against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, W. Simultaneous determination of cytosine, matrine, sophocarpine and quercitrin in Fufang Muji Granules. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2020, 37, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, M. Simultaneous determination of six phenolic acid constituents in Compound Muji granules by HPLC. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharmacy 2019, 28, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Men, L.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Z.; Kou, J.; Wei, X. Determination of polysaccharides content in seven batches of compound muji granules based on anthrone-sulfuric acid method. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 1685–1687. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zheng, H.; Yang, Z.-T.; Cheng, B.; Wu, J.-X.; Liu, X.-W.; Tang, C.-L.; Lu, S.-Y.; Chen, Z.-N.; Song, F.-M.; et al. Urinary metabonomics study of the hepatoprotective effects of total alkaloids from Corydalis saxicola Bunting on carbon tetrachloride-induced chronic hepatotoxicity in rats using 1 H NMR analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 140, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Bao, Y.; Meng, X. The influence of Compound Muji Granules on chronic liver injury in mice. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2016, 12, 13–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Bao, Y.; Li, T.; Meng, X. Preventive effect of Fufang muji granules on CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis in rats. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2017, 39, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, V.; Cicek, M.; Sabancilar, I. Toxicity of carbon tetrachloride, free radicals and role of antioxidants. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 36, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangmonkong, T.; Suriguga, S.; Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Olinga, P.; Boersema, M. Targeting Oxidative Stress for the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Liao, S.-L.; Chen, Y.-F.; Huang, W.-C.; Chen, C.-J.; Chen, W.-Y. Plumbagin ameliorates bile duct ligation-induced cholestatic liver injury in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, I.; Moreno-Càceres, J.; Sánchez, A.; Dooley, S.; Dewidar, B.; Giannelli, G.; ten Dijke, P.; IT-LIVER Consortium. TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Jiang, J.; Jing, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Hou, X.; Gao, L.; Wei, L. The concentration of tumor necrosis factor-α determines its protective or damaging effect on liver injury by regulating Yap activity. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kou, X.; Jing, Y.; Sun, K.; Sheng, D.; Yu, G.; Yu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, X.; et al. The protective or damaging effect of Tumor necrosis factor-α in acute liver injury is concentration-dependent. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Wu, J.; Ding, M.; Gao, F.; Zhou, F.; Xu, B.; Lu, M.; Li, J.; Li, X. Si-Wu-Tang ameliorates fibrotic liver injury via modulating intestinal microbiota and bile acid homeostasis. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Fu, K.; Liu, Y.; Gong, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Hepatoprotective effect of phillygenin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and its effects on short chain fatty acid and bile acid metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.; Ma, C.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Forsythiaside A alleviated carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by modulating gut microbiota composition to increase short-chain fatty acids and restoring bile acids metabolism disorder. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Pang, L.; Dai, W.; Wu, S.; Kong, J. Regulatory mechanisms of the bile salt export pump (BSEP/ABCB11) and its role in related diseases. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2021, 45, 101641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | AAGGACACCATGAGCACTGAAAGC | AGGAAGGAGAAGAGGCTGAGGAAC |
| TGF-β1 | TATTGAGCACCTTGGGCACTGTTG | CCTTAACCTCTCTGGGCTTGTTTCC |
| IL-1β | GGACAGGATATGGAGCAACAAGTGG | TCATCTTTCAACACGCAGGACAGG |
| IL-6 | GAAACCGCTATGAAGTTCCTCTCTG | GTATCCTCTGTGAAGTCTCCTCTCC |
| α-SMA | CAGGGAGTAATGGTTGGAATGGG | AGTTGGTGATGATGCCGTGTTC |
| Smad4 | CTGTTGTGACTGTGGATGGCTATG | CTCTCAATCGCTTCTGTCCTGTG |
| Smad7 | AAGAGGCTGTGTTGCTGTGAATC | ATTGGGTATCTGGAGTAAGGAGGAG |
| FXR | ACCTCGGCTCCTTCTCAGTTG | GGTGGCTGTGGTGAAGACTAATC |
| CYP7A1 | ACAGAGGCCCATAGCATCCC | ACAAGGCAAAGCAGGAAGCA |
| CSAD | TCATCACGGAGAGCCTCAACAC | GGAGCCACCAGGACAGAAGAC |
| Mrp2 | TAGCCTCATTCAGACGACCATCC | TTCAGGACTGCCGTATTCAACAATC |
| Bsep | GAAGCCATTGCCGACCAGATG | TGAGAGGACTGACAGCGAGAATC |
| CDO | GATTCCATTGGCTTACACCGAGTAG | TTTATGCCCTGTTCTCTGGTCAAAG |
| Bile Acids | Abbreviation | Parent Ion (m/z) | Daughter Ion (m/z) | DP (Volts) | CE (Volts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Muricholic Acid | α-MAC | 407.4 | 371.2 | −50 | −46 |
| Cholic acid | CA | 407.4 | 343.1 | −60 | −47 |
| Chenodeoxycholic acid | CDCA | 391.3 | 391.3 | −160 | −60 |
| Deoxycholic acid | DCA | 391.4 | 345.1 | −60 | −44 |
| Glycocholic acid | GCA | 464.4 | 464.4 | −50 | −8 |
| Glydeoxycholic acid | GDCA | 448.4 | 448.4 | −150 | −8 |
| Taurocholic acid | TCA | 514.4 | 79.9 | −270 | −120 |
| Taurochenodeoxycholic acid | TCDCA | 498.4 | 123.9 | −43 | −66 |
| Tauroursodeoxycholic acid | TUDCA | 498.4 | 79.8 | −80 | −120 |
| Tauro-α-muricholic acid | T-α-MAC | 514.4 | 514.4 | −41 | −15 |
| Bile Acids | Retention Time (min) | Calibration Curves | Correlation Coefficient (r2) | Linear Range (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-MAC | 3.25 | y = 6.090 × 10−3x + 6.530 × 10−3 | 0.9925 | 1–1000 |
| CA | 4.09 | y = 2.123 × 10−2x + 4.413 × 10−2 | 0.9946 | 1–1000 |
| CDCA | 5.57 | y = 0.2421x + 2.572 | 0.9945 | 1–1000 |
| DCA | 5.78 | y = 3.328 × 10−2x + 3.209 × 10−2 | 0.9926 | 1–1000 |
| GCA | 3.13 | y = 0.1203x + 0.1686 | 0.9951 | 1–1000 |
| GDCA | 4.22 | y = 0.1828x + 0.3437 | 0.9907 | 1–1000 |
| TCA | 2.57 | y = 2.894 × 10−2x + 3.643 × 10−2 | 0.9910 | 1–1000 |
| TCDCA | 3.36 | y = 1.461 × 10−2x + 1.598 × 10−2 | 0.9905 | 1–1000 |
| TUDCA | 2.51 | y = 9.325 × 10−2x + 1.062 × 10−2 | 0.9922 | 1–1000 |
| T-α-MAC | 1.95 | y = 0.1631x + 0.1663 | 0.9908 | 1–1000 |
| Bile Acids | Control (ng/mL) | Model (ng/mL) | FMG (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-MAC | 836.4 ± 398.7 | 3686 ± 306.3 ### | 33.19 ± 22.42 *** |
| CA | 3700 ± 1877 | 22,973 ± 2894 ### | 368.1 ± 138.3 *** |
| CDCA | 1110 ± 636.3 | 2365 ± 34.49 | 33.20 ± 14.90 |
| DCA | 389.6 ± 187.5 | 229.9 ± 57.5 | 54.02 ± 20.2 |
| GCA | 1411 ± 659.6 | 6669 ± 1532 ## | 983.3 ± 446.4 ** |
| GDCA | 250.2 ± 125.1 | 908.3 ± 350.1 ## | 223.5 ± 24.2 * |
| TCA | 3155 ± 841.2 | 26,283 ± 1365 ### | 1397 ± 561.5 *** |
| TCDCA | 330.2 ± 159.8 | 1499 ± 272.6 ### | 131.4 ± 159.8 ** |
| TUDCA | 174.8 ± 79.0 | 200.9 ± 57.1 | 131.4 ± 18.0 |
| T-α-MAC | 806.4 ± 386.4 | 3696 ± 1216 ## | 643.0 ± 198.9 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Men, L.; Gu, Z.; Wang, E.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Gong, X. Fufang Muji Granules Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Inhibiting Apoptosis, and Modulating Overall Metabolism. Metabolites 2024, 14, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080446
Men L, Gu Z, Wang E, Li J, Li Z, Li K, Li C, Gong X. Fufang Muji Granules Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Inhibiting Apoptosis, and Modulating Overall Metabolism. Metabolites. 2024; 14(8):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080446
Chicago/Turabian StyleMen, Lei, Zhihong Gu, Enhua Wang, Jiwen Li, Zhongyu Li, Keke Li, Chunbin Li, and Xiaojie Gong. 2024. "Fufang Muji Granules Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Inhibiting Apoptosis, and Modulating Overall Metabolism" Metabolites 14, no. 8: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080446
APA StyleMen, L., Gu, Z., Wang, E., Li, J., Li, Z., Li, K., Li, C., & Gong, X. (2024). Fufang Muji Granules Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Inhibiting Apoptosis, and Modulating Overall Metabolism. Metabolites, 14(8), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080446






