Modulatory L-Alliin Effect on Acute Inflammatory Cytokines in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diets
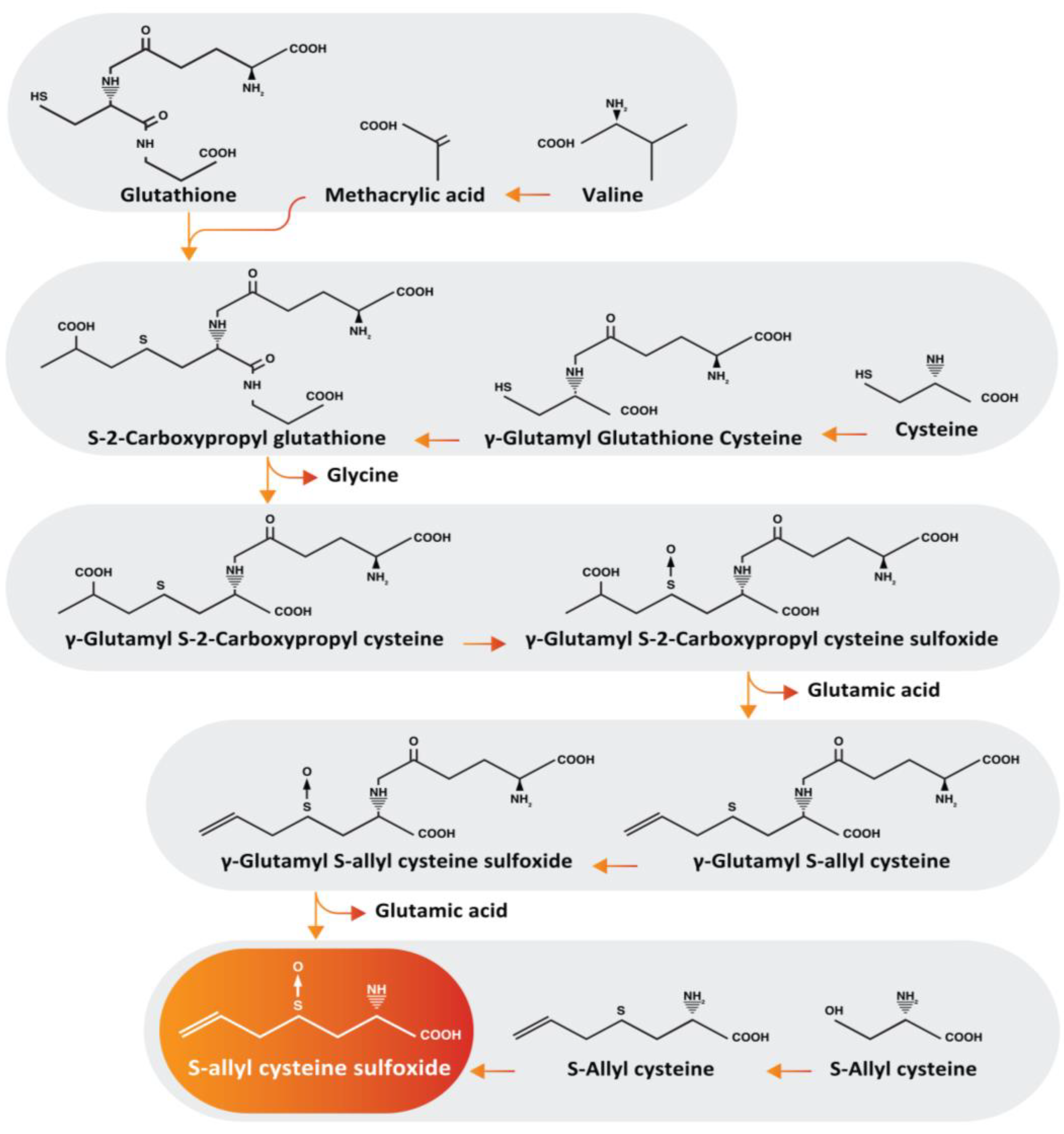
2.2. Alliin
2.3. Lipopolysaccharide
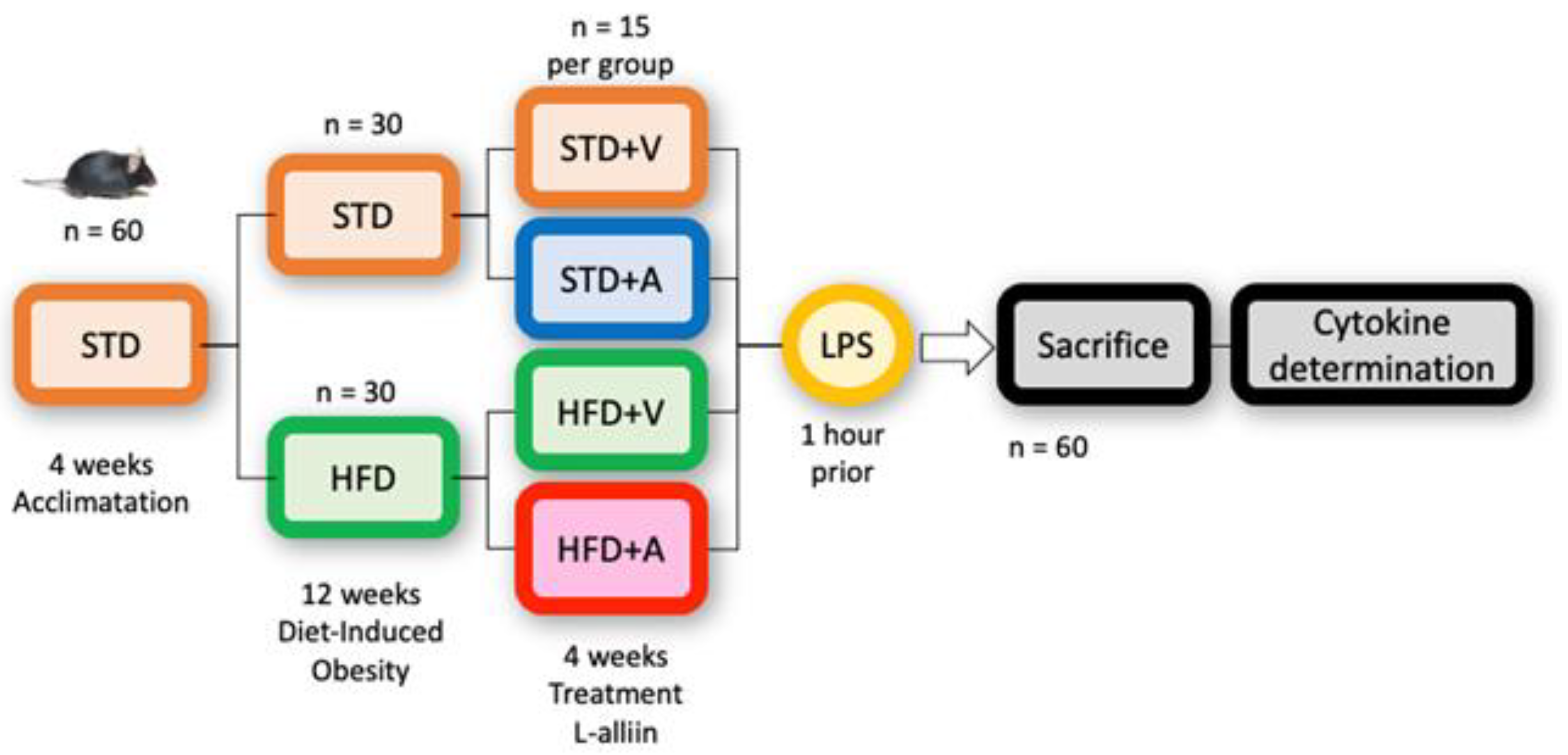
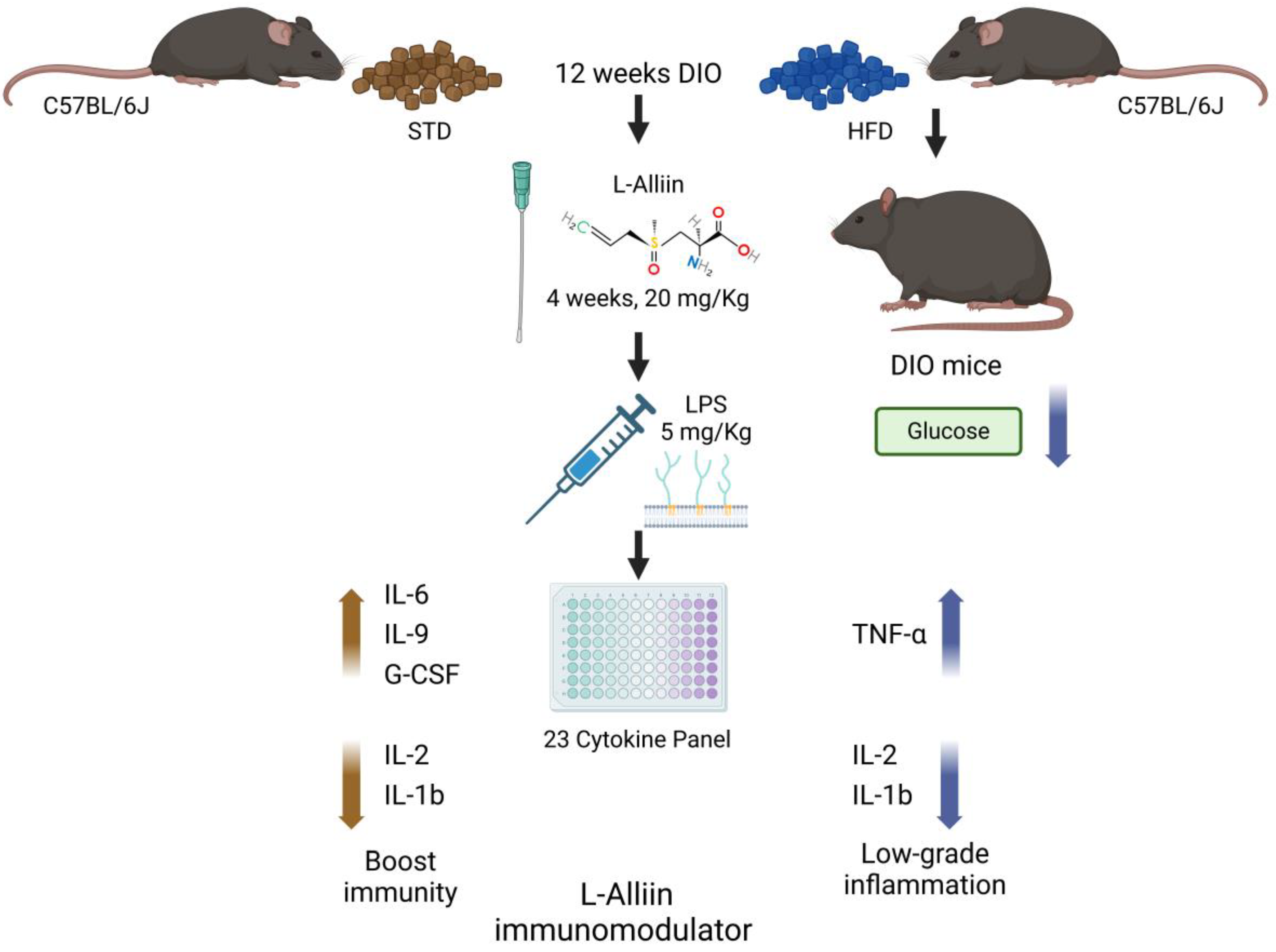
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Determination of Cytokines in Serum
2.6. Statistical Analysis
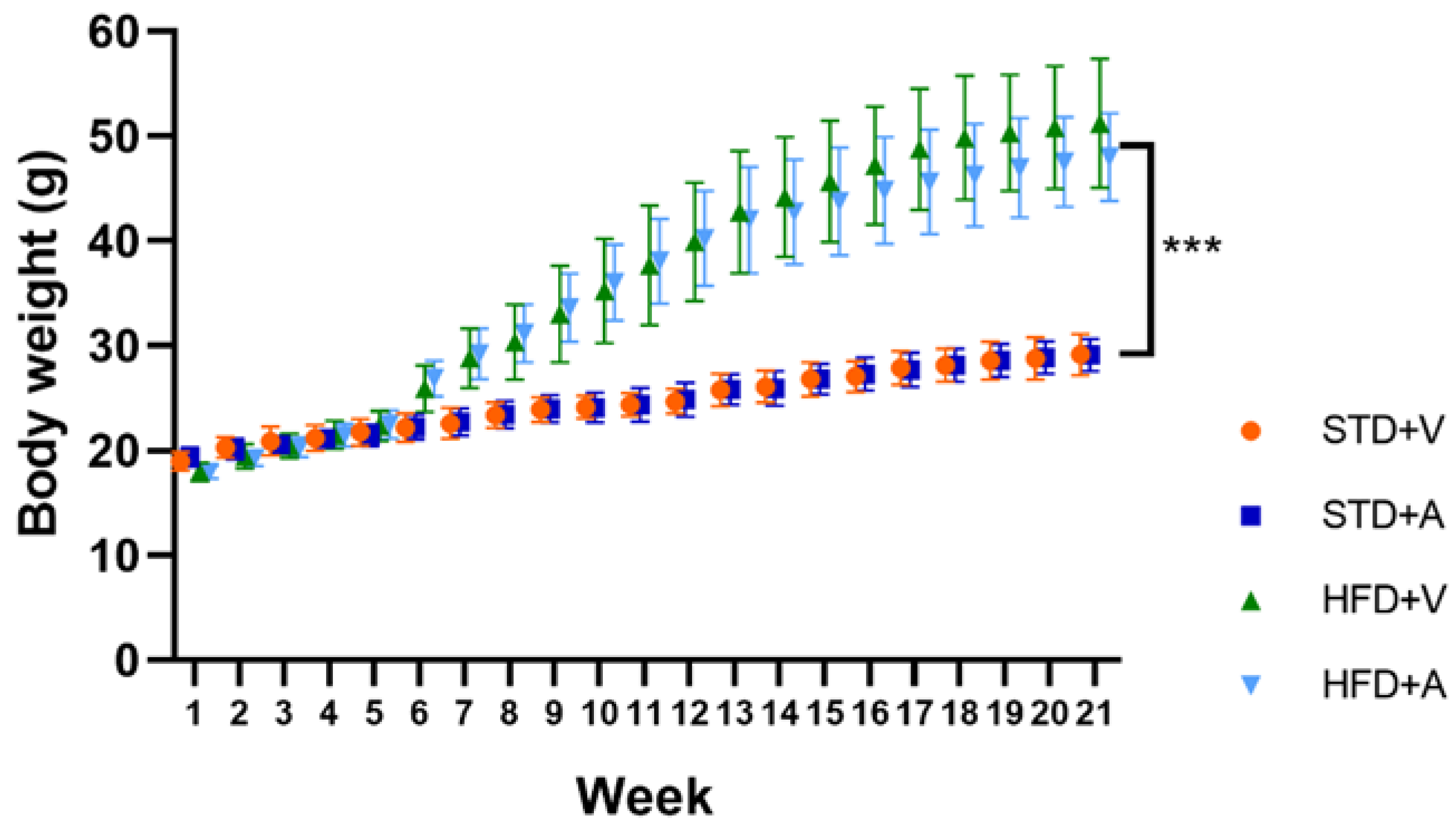
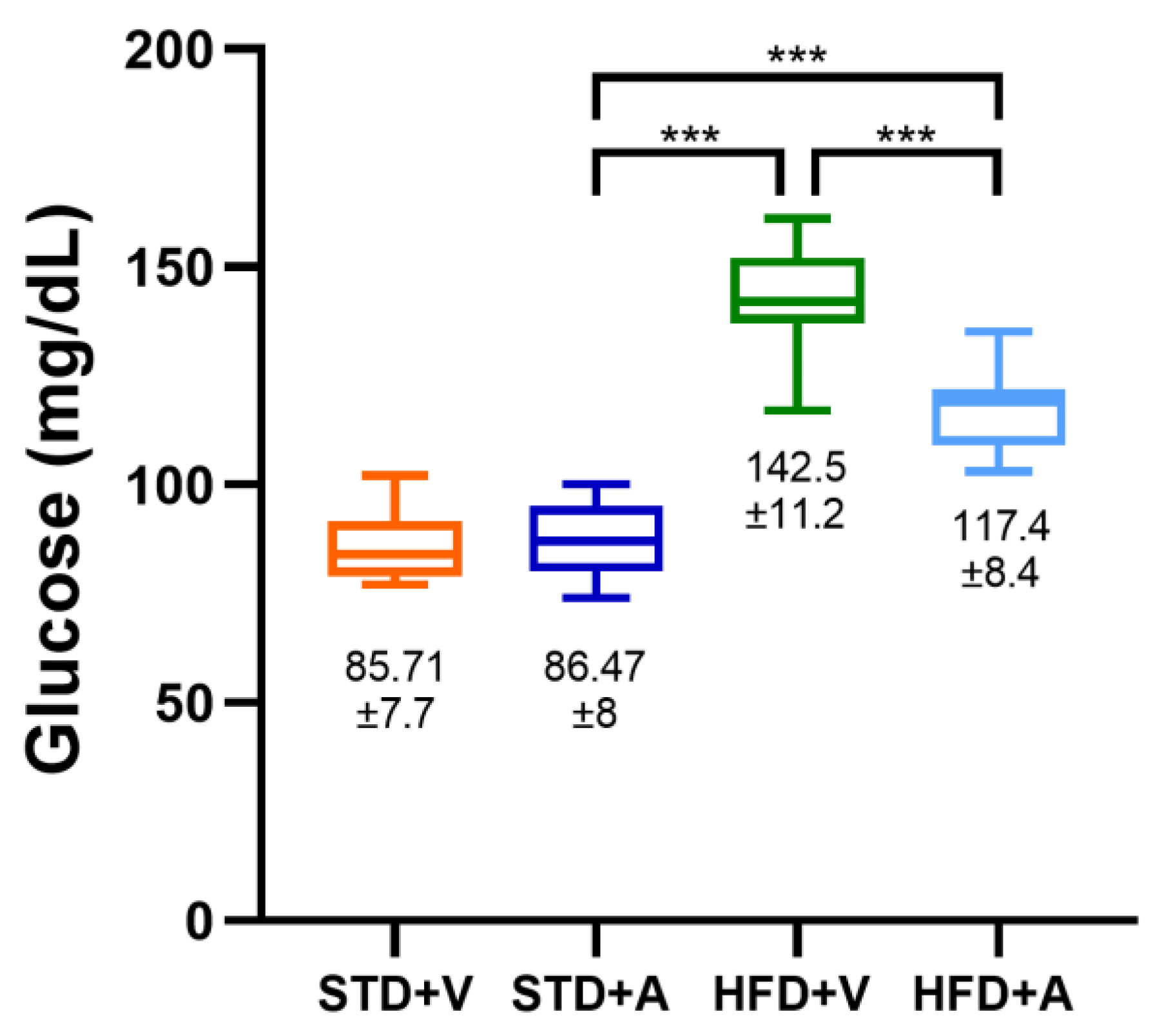
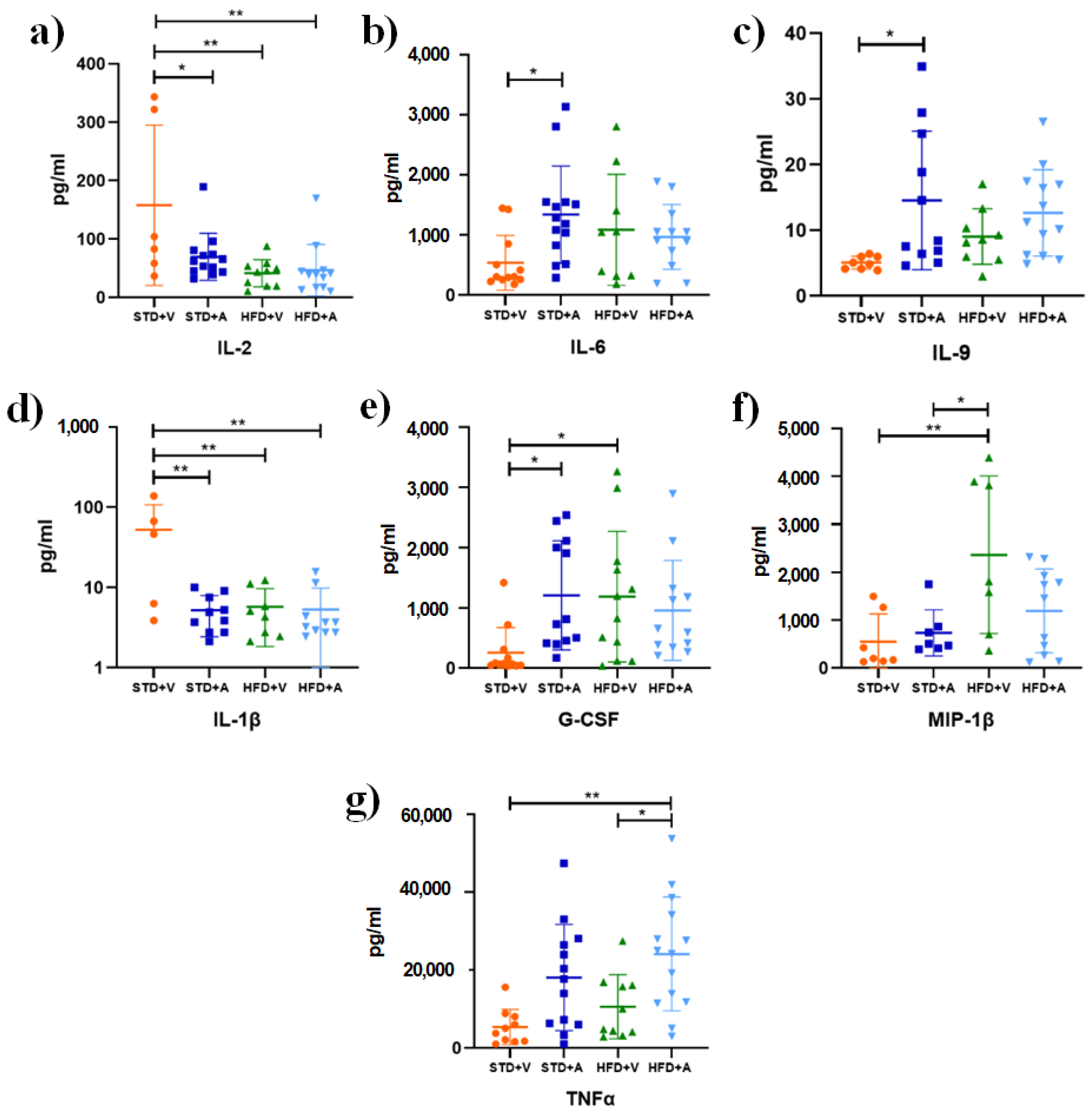
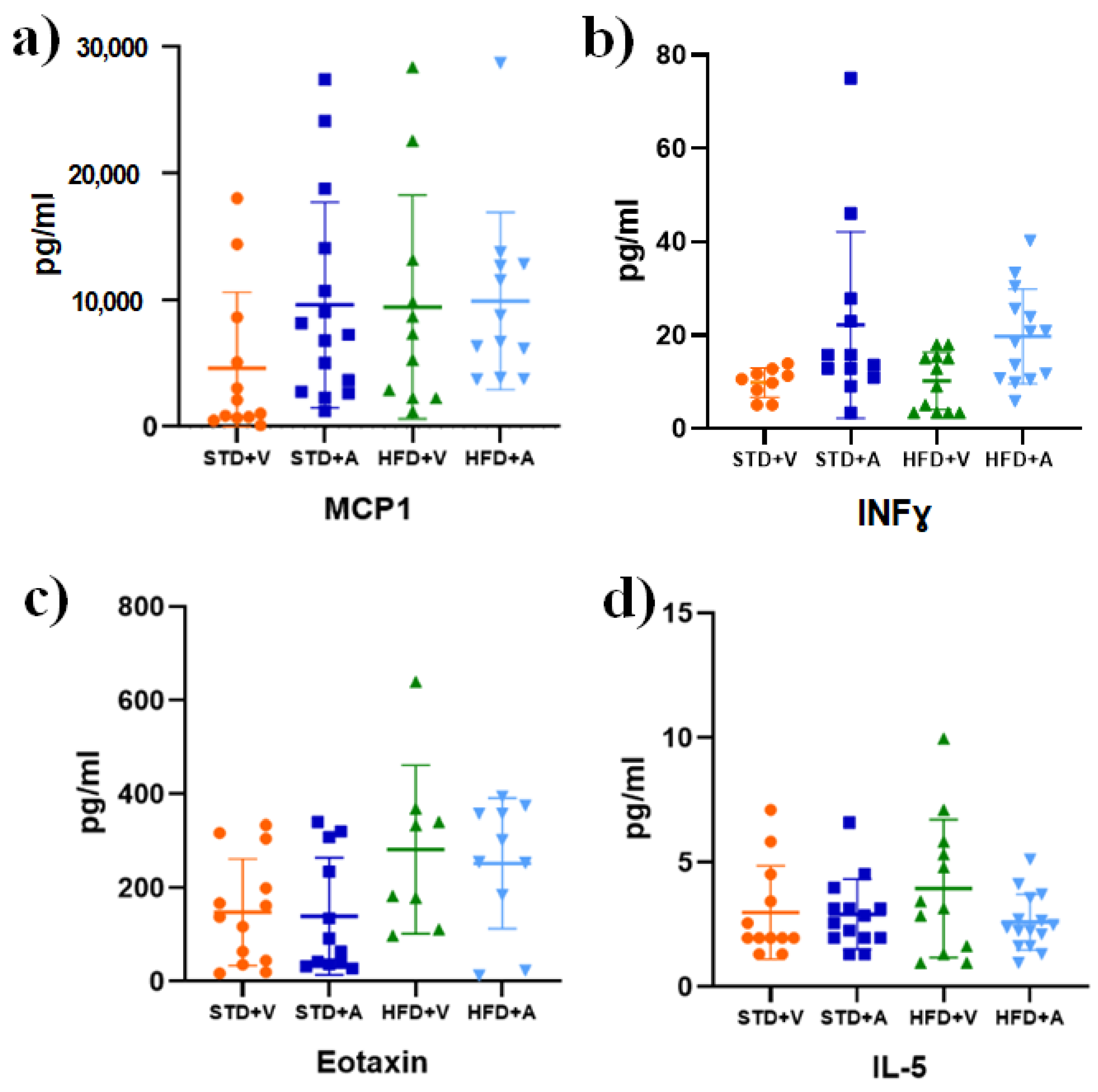
3. Results
Metabolic Effects of L-Alliin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Who. Int. Prevalence of Overweight among Adults, BMI ≥ 25 (age-standardized estimate) (%). Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/prevalence-of-overweight-among-adults-bmi--25-(age-standardized-estimate) (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Who. Int. Prevalence of Obesity among Adults, BMI ≥ 30 (crude estimate) (%). Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/prevalence-of-obesity-among-adults-bmi--30-(crude-estimate) (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Gibbs, B.B.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics: A report of US and global data from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e347–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotece, M.; Conde-Aranda, J. Inflammation in Health and Disease: New Insights and Therapeutic Avenues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ha, S.; Cheuk-Hay Lau, H.; Yu, J. Excess body weight: Novel insights into its roles in obesity comorbidities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 92, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain Khan, M.; Hegde, V. Obesity and Diabetes Mediated Chronic Inflammation: A Potential Biomarker in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. High fat diet and its effects on cognitive health: Alterations of neuronal and vascular components of brain. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 240, 113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.; Hogan, A.E.; Fallon, P.G.; Schwartz, C. Obesity-Mediated Immune Modulation: One Step Forward, (Th)2 Steps Back. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-S.; Shastri, N. The Role of T Cells in Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Metabolic Disease. Immune Netw. 2022, 22, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Dalamaga, M. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome and Microbial Metabolites in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders: Current Evidence and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 12, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Thiemermann, C. Role of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Systemic Inflammation and Potential Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 594150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera-Quintanar, L.; Lopez Roa, R.I.; Quintero-Fabián, S.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.A.; Vizmanos, B.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D. Phytochemicals that influence gut microbiota as prophylactics and for the treatment of obesity and inflammatory diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9734845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, E.K. Nutraceutical-definition and introduction. Aaps Pharm. Sci. 2003, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouf, R.; Uddin, S.J.; Sarker, D.K.; Islam, M.T.; Ali, E.S.; Shilpi, J.A.; Nahar, L.; Tiralongo, E.; Sarker, S.D. Antiviral potential of garlic (Allium sativum) and its organosulfur compounds: A systematic update of pre-clinical and clinical data. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, J.; Gracián, C.; Baños, A.; Guillamón, E.; Gálvez, J.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Fonollá, J. Beneficial effects of daily consumption of garlic and onion extract concentrate on infectious respiratory diseases in elderly resident volunteers. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola, R.; Quintero-Fabián, S.; López-Roa, R.I.; Flores-Gutiérrez, E.O.; Reyes-Grajeda, J.P.; Carrera-Quintanar, L.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D. Immunomodulation and anti-inflammatory effects of garlic compounds. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 1, 401630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, O.; Dokunmu, T.; Okafor, E.; Sokoya, I.; Israel, E.; Olusegun, D.; Bella-Omunagbe, M.; Uche, M.; Ugbogu, E.A.; Iweala, E. The ethnobotanical, bioactive compounds, pharmacological activities and toxicological evaluation of garlic (Allium sativum): A review. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2023, 8, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, M.A.; Zepeda-Morales, A.S.M.; Carrera-Quintanar, L.; Viveros-Paredes, J.M.; Franco-Arroyo, N.N.; Godínez-Rubí, M.; Ortuño-Sahagun, D.; López-Roa, R.I. Alliin, an Allium sativum Nutraceutical, Reduces Metaflammation Markers in DIO Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D.; Vázquez-Carrera, M.; López-Roa, R. Alliin, a Garlic (Allium sativum) Compound, Prevents LPS-Induced Inflammation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 1, 381815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Reyes, D.U.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.M.; Carrera-Quintanar, L.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D. Physiologically Beneficial Actions of Alliin in Health and Disease. Curr. Nutraceuticals 2022, 3, e150822207471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Zhang, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, C.; He, X.; Xu, W.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effect of S-allyl-cysteine sulfoxide (alliin) in DIO mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colín-González, A.L.; Santana, R.A.; Silva-Islas, C.A.; Chánez-Cárdenas, M.E.; Santamaría, A.; Maldonado, P.D. The antioxidant mechanisms underlying the aged garlic extract-and S-allylcysteine-induced protection. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 2012, 907162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colín-González, A.L.; Ali, S.F.; Túnez, I.; Santamaría, A. On the antioxidant, neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of S-allyl cysteine: An update. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 89, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethier, B.; Nott, K.; Fauconnier, M.L. (Bio)synthesis, extraction and purification of garlic derivatives showing therapeutic properties. Commun. Agric Appl. Biol. Sci. 2013, 78, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seemann, S.; Zohles, F.; Lupp, A. Comprehensive comparison of three different animal models for systemic inflammation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odom, M.R.; Hunt, T.C.; Pak, E.S.; Hannan, J.L. High-fat diet induces obesity in adult mice but fails to develop pre-penile and penile vascular dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2022, 34, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Phuong, T.; Seo, S.; Cho, B.K.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.; Park, C.G. Determination of progressive stages of type 2 diabetes in a 45% high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mouse model is achieved by utilizing both fasting blood glucose levels and a 2-h oral glucose tolerance test. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergadi, E.; Vaporidi, K.; Tsatsanis, C. Regulation of endotoxin tolerance and compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome by non-coding RNAs. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, H.; Xie, J.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Ou, S.; Zhang, G.; Peng, X. The alternate consumption of quercetin and alliin in the traditional Asian diet reshaped microbiota and altered gene expression of colonic epithelial cells in rats. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Pugliese, G.; Laudisio, D.; Castellucci, B.; Barrea, L.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. The impact of obesity on immune response to infection: Plausible mechanisms and outcomes. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutagy, N.E.; McMillan, R.P.; Frisard, M.I.; Hulver, M.W. Metabolic endotoxemia with obesity: Is it real and is it relevant? Biochimie 2016, 124, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.M.; Macedo-de la Concha, L.E.; Pantoja-Meléndez, C.A. Low-grade inflammation and its relation to obesity and chronic degenerative diseases. Rev. Médica Hosp. Gen. México 2017, 80, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Eeckhout, B.; Tavernier, J.; Gerlo, S. Interleukin-1 as innate mediator of T cell immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 621931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Alsayed, B.A.; Mir, R.; Amle, D. IL-2 and IL-1β patient immune responses are critical factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection outcomes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puc, I.; Ho, T.-C.; Yen, K.-L.; Vats, A.; Tsai, J.-J.; Chen, P.-L.; Chien, Y.-W.; Lo, Y.-C.; Perng, G.C. Cytokine signature of dengue patients at different severity of the disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleebrahim-Dehkordi, E.; Molavi, B.; Mokhtari, M.; Deravi, N.; Fathi, M.; Fazel, T.; Mohebalizadeh, M.; Koochaki, P.; Shobeiri, P.; Hasanpour-Dehkordi, A. T helper type (Th1/Th2) responses to SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A (H1N1) virus: From cytokines produced to immune responses. Transpl. Immunol. 2022, 70, 101495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzanelli Rocha, V.; Folco, E.J.; Sukhova, G.; Shimizu, K.; Gotsman, I.; Vernon, A.H.; Libby, P. Interferon-γ, a Th1 Cytokine, Regulates Fat Inflammation. A Role for Adaptive Immunity in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Lin, Q.; Li, X.; Nie, Y.; Sun, S.; Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Tang, Y.; Luo, F. Alliin, a garlic organosulfur compound, ameliorates gut inflammation through MAPK-NF-κB/AP-1/STAT-1 inactivation and PPARγ activation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1601013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Li, T.; Li, F. Study on the multitarget mechanism of alliin activating autophagy based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5590–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Kanoski, S.E.; Yan, J.; Grill, H.J.; Hayes, M.R. Hindbrain leptin and glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor signaling interact to suppress food intake in an additive manner. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleni, P.E.; Akieda-Asai, S.; Koda, S.; Sakurai, M.; Bae, C.R.; Senba, K.; Cha, Y.S.; Furuya, M.; Date, Y. Possible involvement of melanocortin-4-receptor and AMP-activated protein kinase in the interaction of glucagon-like peptide-1 and leptin on feeding in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmouni, K.; Sigmund, C.D.; Haynes, W.G.; Mark, A.L. Hypothalamic ERK mediates the anorectic and thermogenic sympathetic effects of leptin. Diabetes 2009, 58, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolivalt, C.G.; Calcutt, N.A.; Masliah, E. Similar pattern of peripheral neuropathy in mouse models of type 1 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namkoong, H.; Ishii, M.; Fujii, H.; Asami, T.; Yagi, K.; Suzuki, S.; Azekawa, S.; Tasaka, S.; Hasegawa, N.; Betsuyaku, T. Obesity worsens the outcome of influenza virus infection associated with impaired type I interferon induction in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirgholami, Z.; Borji, H.; Mohebalian, H.; Heidarpour, M. Effects of Allium sativum on IFN-γ and IL4 concentrations in mice with cystic echinococcosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2021, 220, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjabian, T.; Hosseinpur Yektaei, Z.; Naghizadeh, M.M.; Ghazanfari, T. Immunomodulatory Impacts of Bulbs Extracts from Five Allium Species on IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-17 Cytokines. Immunoregulation 2022, 4, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theyab, A.; Algahtani, M.; Alsharif, K.F.; Hawsawi, Y.M.; Alghamdi, A.; Alghamdi, A.; Akinwale, J. New insight into the mechanism of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) that induces the mobilization of neutrophils. Hematology 2021, 26, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.I.; Elkhalifa, A.M.E.; Nabi, S.U.; Hayyat, F.S.; Nazar, M.; Taifa, S.; Rakhshan, R.; Shah, I.H.; Shaheen, M.; Wani, I.A.; et al. Aged garlic extract preserves beta-cell functioning via modulation of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB)/Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 and sarco endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA)/Ca2+ in diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, T.; Aggarwal, A.; Dey, P.; Chauhan, A.K.; Rashid, S.; Chen, K.-T.; Sharma, R. Medicinal and therapeutic properties of garlic, garlic essential oil, and garlic-based snack food: An updated review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1120377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yue, R.; Liu, G.; Yang, M.; Long, C.; Yan, D. Evidential support for garlic supplements against diabetic kidney disease: A preclinical meta-analysis and systematic review. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 12–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Feng, J. Dietary Garlic Powder Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress through Regulating the Immunity and Intestinal Barrier Function in Broilers. Animals 2022, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Lv, J.; Gao, X.; Zheng, H.; Shi, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Song, Q. Effects of garlic supplementation on components of metabolic syndrome: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, W.; Lau, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. The association of garlic intake and cardiovascular risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8013–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Reyes, D.U.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.A.; de la Rocha, C.; Rojas-Mayorquín, A.E.; López-Roa, R.I.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D.; Carrera-Quintanar, L. Modulatory L-Alliin Effect on Acute Inflammatory Cytokines in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice. Metabolites 2024, 14, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110580
Torres-Reyes DU, Sánchez-Sánchez MA, de la Rocha C, Rojas-Mayorquín AE, López-Roa RI, Ortuño-Sahagún D, Carrera-Quintanar L. Modulatory L-Alliin Effect on Acute Inflammatory Cytokines in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice. Metabolites. 2024; 14(11):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110580
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Reyes, Daniel Ulises, Marina Alma Sánchez-Sánchez, Carmen de la Rocha, Argelia Esperanza Rojas-Mayorquín, Rocío Ivette López-Roa, Daniel Ortuño-Sahagún, and Lucrecia Carrera-Quintanar. 2024. "Modulatory L-Alliin Effect on Acute Inflammatory Cytokines in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice" Metabolites 14, no. 11: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110580
APA StyleTorres-Reyes, D. U., Sánchez-Sánchez, M. A., de la Rocha, C., Rojas-Mayorquín, A. E., López-Roa, R. I., Ortuño-Sahagún, D., & Carrera-Quintanar, L. (2024). Modulatory L-Alliin Effect on Acute Inflammatory Cytokines in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice. Metabolites, 14(11), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110580






