Insights on the Organ-Dependent, Molecular Sexual Dimorphism in the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, Revealed by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Model of D. polymorpha
2.2. Extract Preparation from Mussel Tissues and Metabolome Analysis by Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Data Treatment, Statistical Analyses, and Annotation by Molecular Network
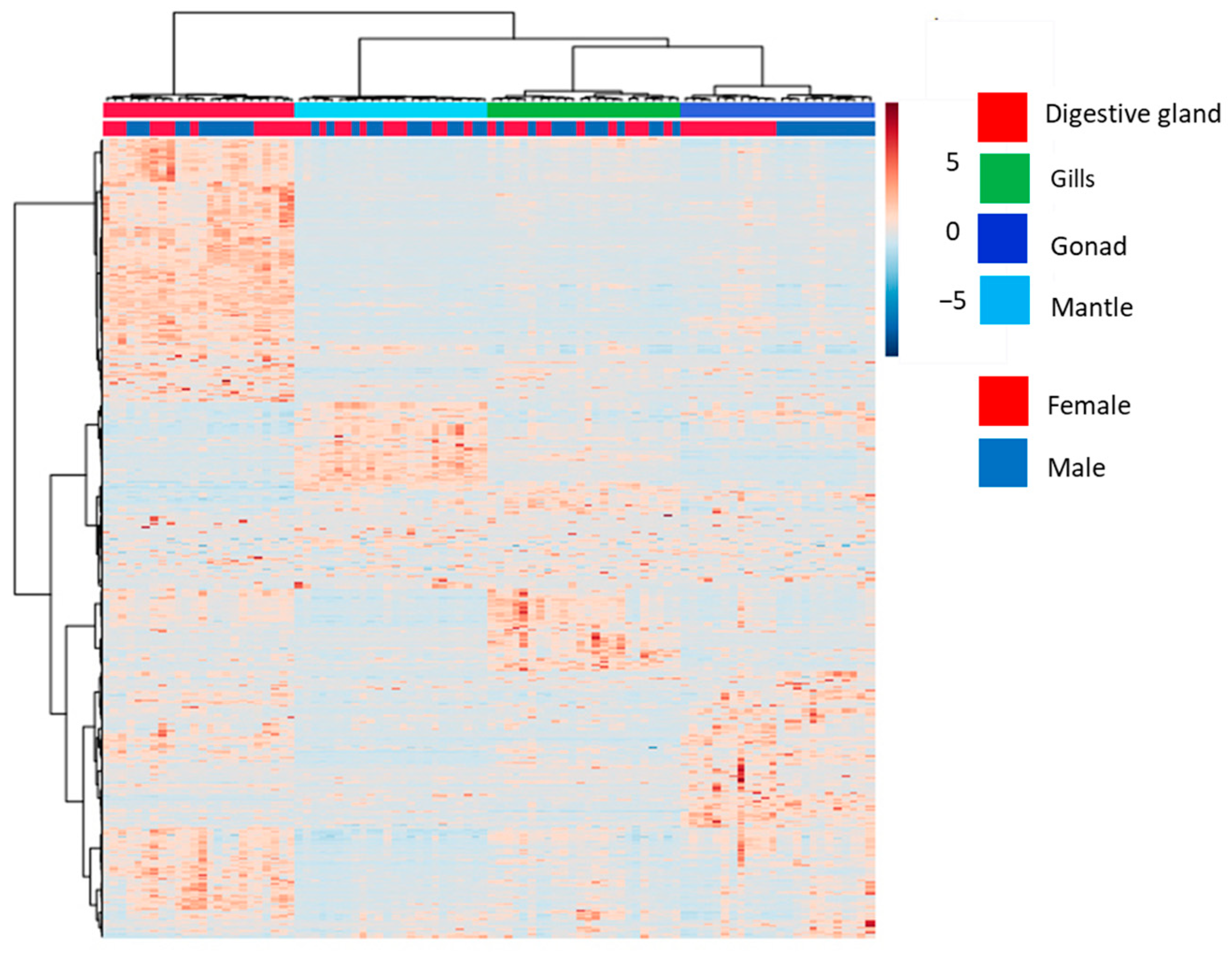
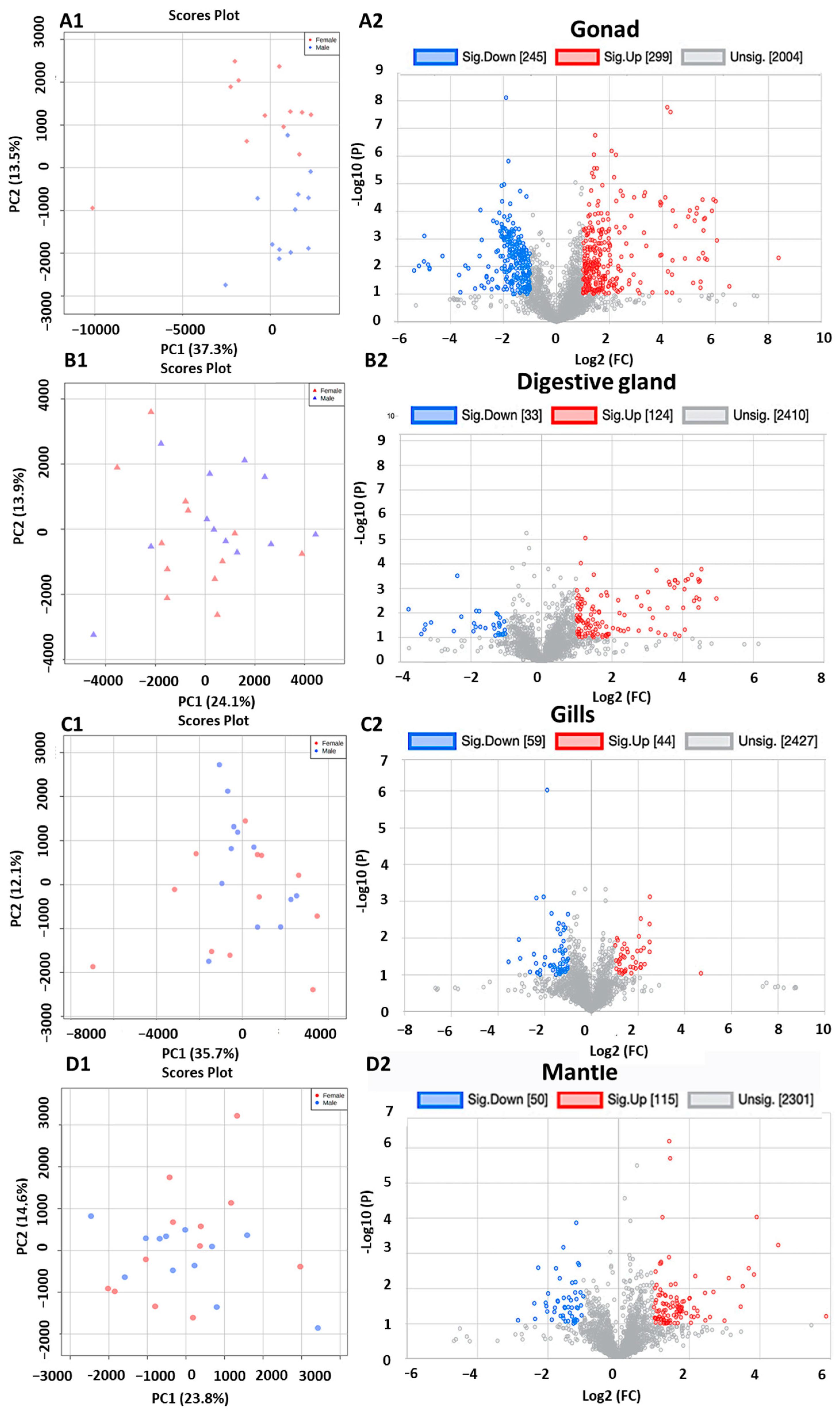
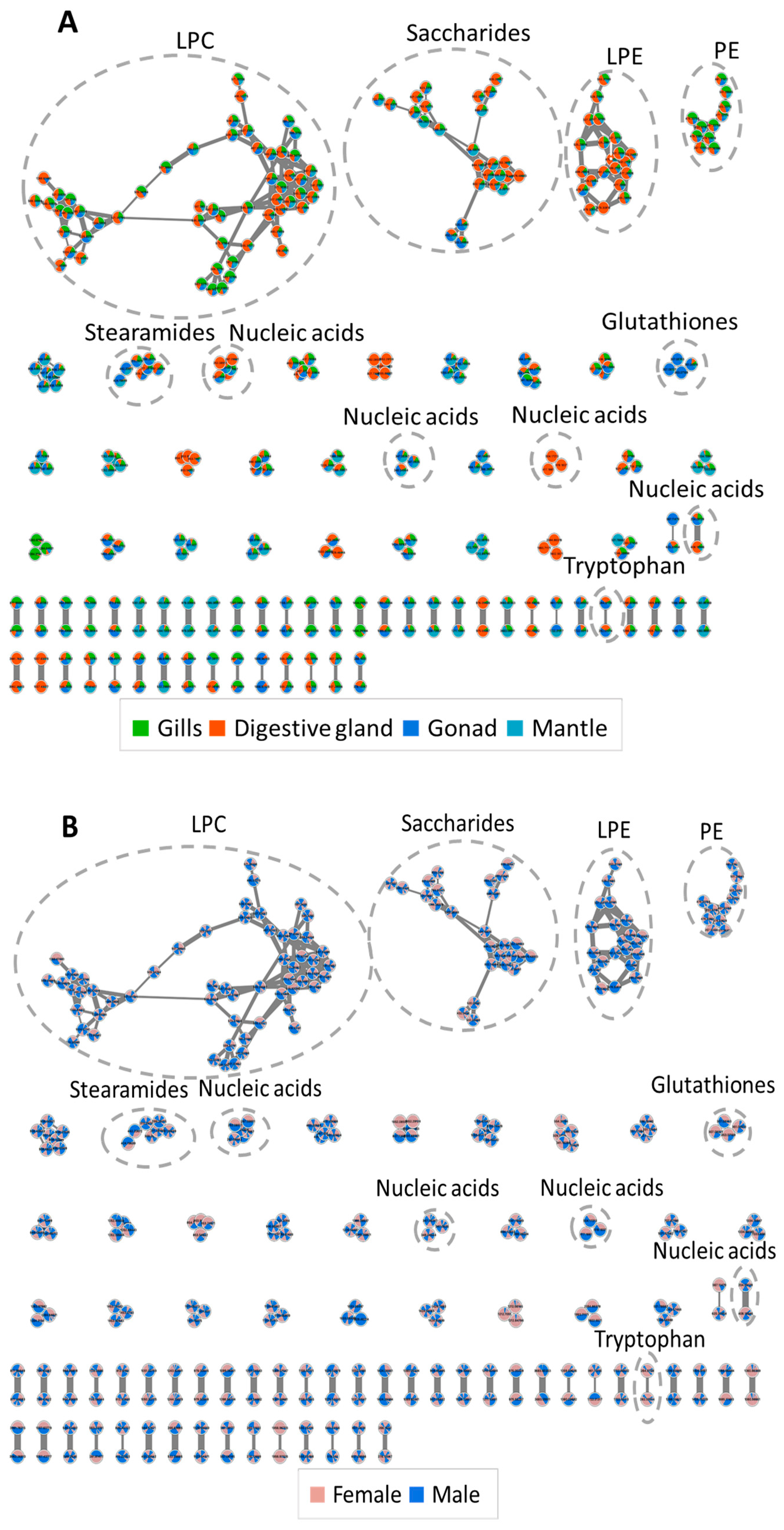
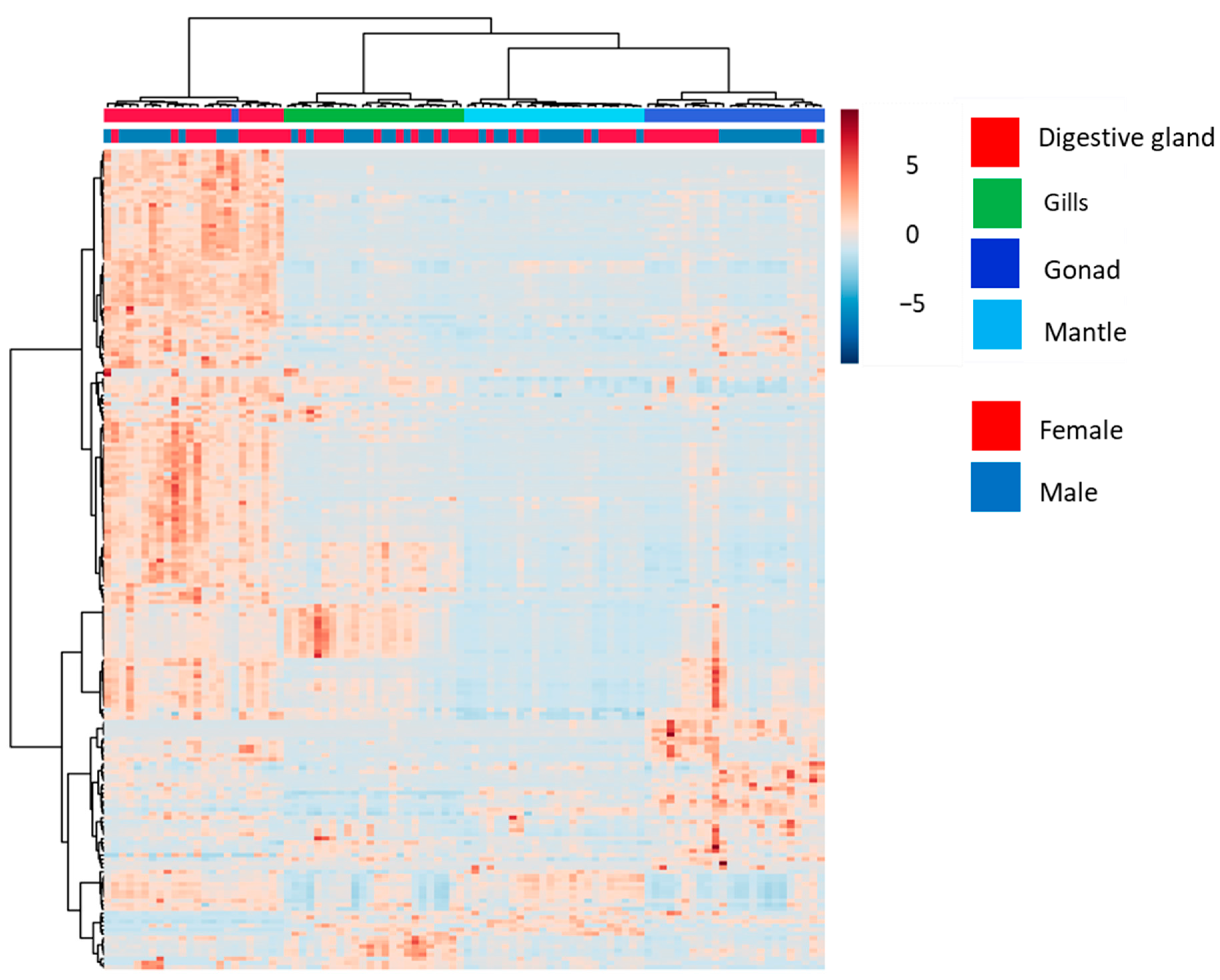
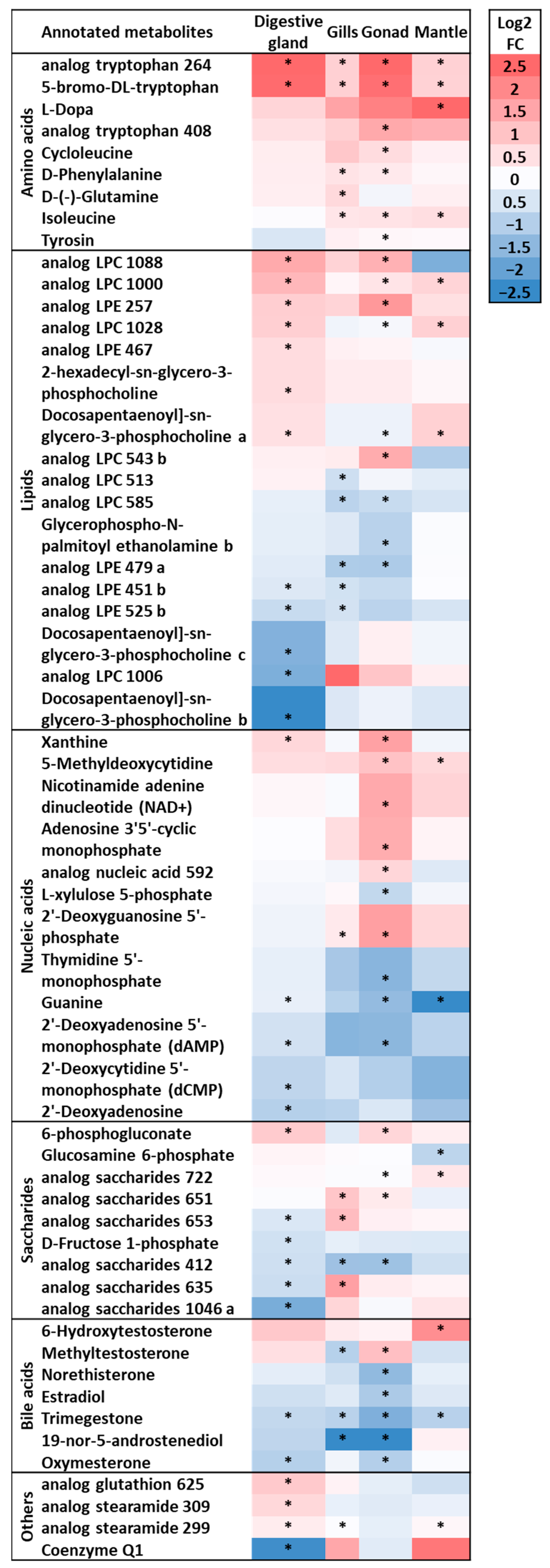
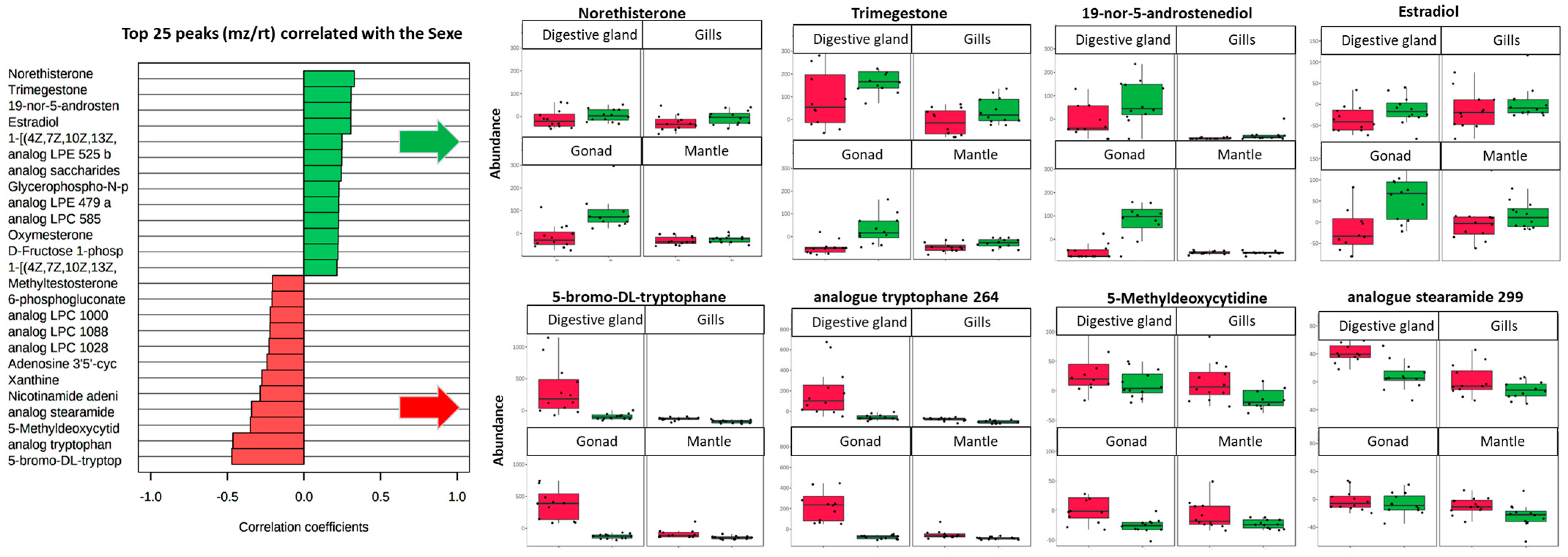
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of the Global Metabolome of Tissues from D. polymorpha Males and Females
3.2. Analysis of Annotated Analytes from Male and Female D. polymorpha Tissues
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goode, K.L.; Dunphy, B.J.; Parsons, D.M. Environmental Metabolomics as an Ecological Indicator: Metabolite Profiles in Juvenile Fish Discriminate Sites with Different Nursery Habitat Qualities. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, B.; Gallet, A. Fish Metabolome from Sub-Urban Lakes of the Paris Area (France) and Potential Influence of Noxious Metabolites Produced by Cyanobacteria. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, T.; Courant, F.; Fenet, H.; Gomez, E. Environmental Metabolomics Promises and Achievements in the Field of Aquatic Ecotoxicology: Viewed through the Pharmaceutical Lens. Metabolites 2022, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefille, B.; Gomez, E.; Alali, M.; Rosain, D.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Metabolomics Assessment of the Effects of Diclofenac Exposure on Mytilus galloprovincialis: Potential Effects on Osmoregulation and Reproduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 613–614, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, J.A.; Sevilla, A.; González-Fernández, C.; Bellas, J.; Bernal, C.; Cánovas, M.; Albentosa, M. Metabolomic Responses of Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis to Fluoranthene Exposure under Different Nutritive Conditions. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 144, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Mauceri, A.; Corsaro, C.; Maisano, M.; Parrino, V.; Lo Paro, G.; Messina, G.; Fasulo, S. Impact of Environmental Pollution on Caged Mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis Using NMR-Based Metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Giannetto, A.; Parrino, V.; Maisano, M.; Oliva, S.; De Marco, G.; Guerriero, G.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S. Baseline Levels of Metabolites in Different Tissues of Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2018, 26, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, D. Dreissena polymorpha. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Son, M.O. Native Range of the Zebra Mussel and Quagga Mussel and New Data on Their Invasions within the Ponto-Caspian Region. Aquat. Invasions 2007, 2, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L. Twenty Years of Zebra Mussels: Lessons from the Mollusk That Made Headlines. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergs, R.; Rinke, K.; Rothhaupt, K.O. Zebra Mussels Mediate Benthic–Pelagic Coupling by Biodeposition and Changing Detrital Stoichiometry. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuhel, R.L.; Aguilar, C. Ecosystem Transformations of the Laurentian Great Lake Michigan by Nonindigenous Biological Invaders. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 289–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strayer, D.L.; Cid, N.; Malcom, H.M. Long-Term Changes in a Population of an Invasive Bivalve and Its Effects. Oecologia 2011, 165, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlakova, L.E.; Karatayev, A.Y.; Boltovskoy, D.; Correa, N.M. Ecosystem Services Provided by the Exotic Bivalves Dreissena polymorpha, D. rostriformis bugensis, and Limnoperna fortunei. Hydrobiologia 2022, 850, 2811–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlmann, J.; Schulte-Oehlmann, U. Chapter 17 Molluscs as Bioindicators. In Trace Metals and Other Contaminants in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 6, pp. 577–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Ochoa, V.; Blázquez, M.; Juan, M.F.S.; Lazzara, R.; Lacorte, S.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Barata, C. Separating Natural from Anthropogenic Causes of Impairment in Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) Populations Living across a Pollution Gradient. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pain-Devin, S.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Geffard, A.; Giambérini, L.; Jouenne, T.; Minguez, L.; Naudin, B.; Parant, M.; Rodius, F.; Rousselle, P.; et al. Towards a Better Understanding of Biomarker Response in Field Survey: A Case Study in Eight Populations of Zebra Mussels. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolini, M.; Magni, S.; Castiglioni, S.; Zuccato, E.; Binelli, A. Realistic Mixture of Illicit Drugs Impaired the Oxidative Status of the Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Chemosphere 2015, 128, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, G.; Binelli, A.; Volta, P.; Roscioli, C.; Guzzella, L. Evaluation of Spatial Distribution and Accumulation of Novel Brominated Flame Retardants, HBCD and PBDEs in an Italian Subalpine Lake Using Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9655–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Châtel, A.; Faucet-Marquis, V.; Gourlay-Francé, C.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Vincent-Hubert, F. Genotoxicity and Activation of Cellular Defenses in Transplanted Zebra Mussels Dreissena polymorpha along the Seine River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerambrun, E.; Rioult, D.; Delahaut, L.; Evariste, L.; Pain-Devin, S.; Auffret, M.; Geffard, A.; David, E. Variations in Gene Expression Levels in Four European Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, Populations in Relation to Metal Bioaccumulation: A Field Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, E.H.T.; Davids, C. Food Selection by Dreissena polymorpha Pallas (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Freshw. Biol. 1982, 12, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, S.B.; Fisher, N.S.; Cole, J.J. Uptake of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) and Its Importance to Metabolic Requirements of the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Della Torre, C.; Magni, S.; Parolini, M. Does Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) Represent the Freshwater Counterpart of Mytilus in Ecotoxicological Studies? A Critical Review. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palos Ladeiro, M.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Geffard, A.; Bigot, A. Bioaccumulation of Human Waterborne Protozoa by Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): Interest for Water Biomonitoring. Water Res. 2014, 48, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Géba, E.; Aubert, D.; Durand, L.; Escotte, S.; La Carbona, S.; Cazeaux, C.; Bonnard, I.; Bastien, F.; Palos Ladeiro, M.; Dubey, J.P.; et al. Use of the Bivalve Dreissena polymorpha as a Biomonitoring Tool to Reflect the Protozoan Load in Freshwater Bodies. Water Res. 2020, 170, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capizzi-Banas, S.; Ladeiro, M.P.; Bastien, F.; Bonnard, I.; Boudaud, N.; Gantzer, C.; Geffard, A. The Utility of Dreissena polymorpha for Assessing the Viral Contamination of Rivers by Measuring the Accumulation of F-Specific RNA Bacteriophages. Water 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, G.; Fieu, M.; Joachim, S.; James-Casas, A.; Andres, S.; Baudoin, P.; Bonnard, M.; Bonnard, I.; Geffard, A.; Vulliet, E. Development of a Multi-Residue Analysis of Diclofenac and Some Transformation Products in Bivalves Using QuEChERS Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Application to Samples from Mesocosm Studies. Talanta 2016, 155, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evariste, L.; David, E.; Cloutier, P.L.; Brousseau, P.; Auffret, M.; Desrosiers, M.; Groleau, P.E.; Fournier, M.; Betoulle, S. Field Biomonitoring Using the Zebra Mussel Dreissena polymorpha and the Quagga Mussel Dreissena bugensis Following Immunotoxic Reponses. Is There a Need to Separate the Two Species? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camusso, M.; Balestrini, R.; Muriano, F.; Mariani, M. Use of Freshwater Mussel Dreissena polymorpha to Assess Trace Metal Pollution in the Lower River Po (Italy). Chemosphere 1994, 29, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuykov, M.; Pelletier, E.; Harper, D.A.T. Bivalve Mollusks in Metal Pollution Studies: From Bioaccumulation to Biomonitoring. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeault, A.; Gourlay-Francé, C.; Vincent-Hubert, F.; Palais, F.; Geffard, A.; Biagianti-Risbourg, S.; Pain-Devin, S.; Tusseau-Vuillemin, M.-H. Lessons from a Transplantation of Zebra Mussels into a Small Urban River: An Integrated Ecotoxicological Assessment. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoutre, A.; Grilot, T.; Jean, S.; Geffard, A.; Lance, E. Free or Protein-Bound Microcystin Accumulation by Freshwater Bivalves as a Tool to Evaluate Water Contamination by Microcystin-Producing Cyanobacteria? Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoutre, A.; Hervieux, J.; Faassen, E.J.; Zweers, A.J.; Lurling, M.; Geffard, A.; Lance, E. Usability of the Bivalves Dreissena polymorpha and Anodonta anatina for a Biosurvey of the Neurotoxin BMAA in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepoutre, A.; Faassen, E.J.; Zweers, A.J.; Lürling, M.; Geffard, A.; Lance, E. How the Neurotoxin β-N-Methylamino-l-Alanine Accumulates in Bivalves: Distribution of the Different Accumulation Fractions among Organs. Toxins 2020, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrough, K.L.; Johnson, W.E.; Lauenstein, G.G.; Christensen, J.D.; Apeti, D.A. Mussel Watch Program: An Assessment of Two Decades of Contaminant Monitoring in the Nation’s Coastal Zone; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008. Available online: https://archive.org/details/TwoDecadesofMusselWatchProgram (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Schöne, B.R.; Krause, R.A. Retrospective Environmental Biomonitoring—Mussel Watch Expanded. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 144, 228–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, Y.M.I.; Prud’Homme, S.M.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Bonnard, I.; Robert, C.; Nott, K.; Ronkart, S.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Geffard, A. 1H-NMR Metabolomics Profiling of Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): A Field-Scale Monitoring Tool in Ecotoxicological Studies. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catteau, A.; Porcher, J.M.; Bado-Nilles, A.; Bonnard, I.; Bonnard, M.; Chaumot, A.; David, E.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Delahaut, L.; Delorme, N.; et al. Interest of a Multispecies Approach in Active Biomonitoring: Application in the Meuse Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, S.M.; Hani, Y.M.I.; Cox, N.; Lippens, G.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Geffard, A. The Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Model Organism for Ecotoxicological Studies: A Prior 1H NMR Spectrum Interpretation of a Whole Body Extract for Metabolism Monitoring. Metabolites 2020, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.B.D.; Benskin, J.P.; Cosgrove, J.R.; Duncker, B.P.; Ekman, D.R.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Sherry, J.P. Omics for Aquatic Ecotoxicology: Control of Extraneous Variability to Enhance the Analysis of Environmental Effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jia, X.; Cai, W. Gender-Specific Metabolic Responses in Gonad of Mussel Perna viridis to Triazophos. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, H. Metabolomic Analysis Revealed That Female Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Was Sensitive to Bisphenol A Exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.A.; Cope, W.G.; Barnhart, M.C.; Bringolf, R.B. Metabolomic, Behavioral, and Reproductive Effects of the Aromatase Inhibitor Fadrozole Hydrochloride on the Unionid Mussel Lampsilis fasciola. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 206, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y. Gender-Specific Metabolic Responses in Hepatopancreas of Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Challenged by Vibrio Harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy, N.J.; Dodson, J.; Tassone, S.J.; Bukaveckas, P.A.; Bulluck, L.P. Biotransport of Algal Toxins to Riparian Food Webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10007–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, L.; Gomez, E.; Ramirez, G.; Dumas, T.; Courant, F. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics Investigation of Different Tissues of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 45, 101051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Feswick, A.; Simmons, D.; Martyniuk, C.J. Environmental Toxicology and Omics: A Question of Sex. J. Proteom. 2018, 172, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Santen, J.A.; Poynton, E.F.; Iskakova, D.; Mcmann, E.; Alsup, T.A.; Clark, T.N.; Fergusson, C.H.; Fewer, D.P.; Hughes, A.H.; Mccadden, C.A.; et al. The Natural Products Atlas 2.0: A Database of Microbially-Derived Natural Products. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1317–D1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivon, F.; Elie, N.; Grelier, G.; Roussi, F.; Litaudon, M.; Touboul, D. MetGem Software for the Generation of Molecular Networks Based on the T-SNE Algorithm. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13900–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Kashin, A.G.; Stefanov, K. Comparative Investigation of Phospholipids and Fatty Acids of Freshwater Molluscs from the Volga River Basin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1992, 102, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Rezanka, T.; Kashin, A.G. Comparative Study of the Endemic Freshwater Fauna of Lake Baikal—I. Phospholipid and Fatty Acid Composition of Two Mollusc Species, Baicalia oviformus and Benedictia baicalensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1993, 106, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Di, L.; Wu, H. Abundance of Saccharides and Scarcity of Glycosaminoglycans in the Soft Tissue of Clam, Meretrix meretrix (Linnaeus). Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, R.R.; Saleh, N.S.M.; Shokeer, A.; Guneidy, R.A.; Abdel-Ghany, S.S. Glutathione and Its Related Enzymes in the Gonad of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringwood, A.H.; Conners, D.E. The Effects of Glutathione Depletion on Reproductive Success in Oysters, Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 50, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Kong, H.; Chang, X.; Dupont, S.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Gonadal Antioxidant Responses to Seawater Acidification and Hypoxia in the Marine Mussel Mytilus coruscus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53847–53856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magniez, G.; Franco, A.; Geffard, A.; Rioult, D.; Bonnard, I.; Delahaut, L.; Joachim, S.; Daniele, G.; Vulliet, E.; Porcher, J.M.; et al. Determination of a New Index of Sexual Maturity (ISM) in Zebra Mussel Using Flow Cytometry: Interest in Ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11252–11263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.G.; Šrut, M.; Štambuk, A.; Klobučar, G.I.V.; Seitz, A.; Griebeler, E.M. Effects of Freshwater Pollution on the Genetics of Zebra Mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) at the Molecular and Population Level. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 795481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, T.; Boccard, J.; Gomez, E.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Multifactorial Analysis of Environmental Metabolomic Data in Ecotoxicology: Wild Marine Mussel Exposed to WWTP Effluent as a Case Study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P. Do Mollusks Use Vertebrate Sex Steroids as Reproductive Hormones? Part I: Critical Appraisal of the Evidence for the Presence, Biosynthesis and Uptake of Steroids. Steroids 2012, 77, 1450–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janer, G.; Porte, C. Sex Steroids and Potential Mechanisms of Non-Genomic Endocrine Disruption in Invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado, R.; Janer, G.; Porte, C. Steroid Levels and Steroid Metabolism in the Mussel Mytilus edulis: The Modulating Effect of Dispersed Crude Oil and Alkylphenols. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, S65–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafont, R.; Mathieu, M. Steroids in Aquatic Invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.; Loi, B.; Porte, C. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Steroids in Molluscs. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong Sánchez, F.; Enriquez Díaz, M.; Murillo Rodríguez, E.; Aranda, D.A.; Aldana, D.; Mx, A.D. First Use of a Non-Invasive Technique for Determination of Sex Hormones in the Queen Conch Lobatus gigas, Mollusca Gastropoda. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier-Clerc, S.; Pellerin, J.; Amiard, J.C. Estradiol-17β and Testosterone Concentrations in Male and Female Mya arenaria (Mollusca Bivalvia) during the Reproductive Cycle. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 145, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knigge, T.; Dahboul, F.; Alain, D.; Monsinjon, T. The Gametogenic Cycle and Oestradiol Levels in the Zebra Mussel Dreissena polymorpha: A 1-Year Study. J. Molluscan Stud. 2015, 81, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, R.; Blázquez, M.; Porte, C.; Barata, C. Low Environmental Levels of Fluoxetine Induce Spawning and Changes in Endogenous Estradiol Levels in the Zebra Mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 106–107, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palais, F.; Dedourge-Geffard, O.; Beaudon, A.; Pain-Devin, S.; Trapp, J.; Geffard, O.; Noury, P.; Gourlay-Francé, C.; Uher, E.; Mouneyrac, C.; et al. One-Year Monitoring of Core Biomarker and Digestive Enzyme Responses in Transplanted Zebra Mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 888–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketata, I.; Guermazi, F.; Rebai, T.; Hamza-Chaffai, A. Variation of Steroid Concentrations during the Reproductive Cycle of the Clam Ruditapes decussatus: A One Year Study in the Gulf of Gabès Area. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (A) | |||
| Tissues | PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| 28.634 | 0.48286 | 0.001 | |
| Pairwise Tissues | Pairwise PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| Digestive gland vs. mantle | 60.33 | 0.57 | 0.001 |
| Gills vs. digestive gland | 28.22 | 0.38 | 0.001 |
| Gills vs. mantle | 26.99 | 0.37 | 0.001 |
| Digestive gland vs. gonads | 26.81 | 0.37 | 0.001 |
| Gonads vs. mantle | 19.85 | 0.3 | 0.001 |
| Gills vs. gonads | 14.11 | 0.23 | 0.001 |
| (B) | |||
| Sex | PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| 13.989 | 0.52669 | 0.001 | |
| Pairwise Female vs. Male | Pairwise.PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| Gonads | 3.59 | 0.14 | 0.001 |
| Digestive gland | 1.61 | 0.07 | 0.042 |
| Mantle | 1.14 | 0.05 | 0.272 |
| Gills | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.317 |
| (A) | |||
| Tissues | PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| 33.193 | 0.51978 | 0.001 | |
| Pairwise Tissues | Pairwise.PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| Digestive gland vs. mantle | 71.45 | 0.61 | 0.001 |
| Gills vs. mantle | 38.68 | 0.46 | 0.001 |
| Digestive gland vs. gonads | 32.07 | 0.41 | 0.001 |
| Gills vs. digestive gland | 28.14 | 0.38 | 0.001 |
| Gonads vs. mantle | 18.14 | 0.28 | 0.001 |
| Gills vs. gonads | 17.47 | 0.28 | 0.001 |
| (B) | |||
| Sex | PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| 15.433 | 0.55109 | 0.001 | |
| Pairwise Female vs. Male | Pairwise.PERMANOVA | ||
| F.Model | R2 | p-Value | |
| Gonads | 2.65 | 0.11 | 0.048 |
| Digestive gland | 1.38 | 0.06 | 0.207 |
| Gills | 0.63 | 0.03 | 0.587 |
| Mantle | 0.47 | 0.02 | 0.930 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lance, E.; Sartor, L.; Foucault, P.; Geffard, A.; Marie, B. Insights on the Organ-Dependent, Molecular Sexual Dimorphism in the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, Revealed by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101046
Lance E, Sartor L, Foucault P, Geffard A, Marie B. Insights on the Organ-Dependent, Molecular Sexual Dimorphism in the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, Revealed by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2023; 13(10):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101046
Chicago/Turabian StyleLance, Emilie, Lucas Sartor, Pierre Foucault, Alain Geffard, and Benjamin Marie. 2023. "Insights on the Organ-Dependent, Molecular Sexual Dimorphism in the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, Revealed by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics" Metabolites 13, no. 10: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101046
APA StyleLance, E., Sartor, L., Foucault, P., Geffard, A., & Marie, B. (2023). Insights on the Organ-Dependent, Molecular Sexual Dimorphism in the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, Revealed by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics. Metabolites, 13(10), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13101046









