Abstract
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Metabolic reprogramming is a fundamental trait associated with lung cancer development that fuels tumor proliferation and survival. Monitoring such metabolic pathways and their intermediate metabolites can provide new avenues concerning treatment strategies, and the identification of prognostic biomarkers that could be utilized to monitor drug responses in clinical practice. In this review, recent trends in the analytical techniques used for metabolome mapping of lung cancer are capitalized. These techniques include nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and imaging mass spectrometry (MSI). The advantages and limitations of the application of each technique for monitoring the metabolite class or type are also highlighted. Moreover, their potential applications in the analysis of many biological samples will be evaluated.
1. Introduction
Metabolomics is a comprehensive measurement of the repertoire of small molecules, i.e., metabolites, in a biological system [1]. It can be subdivided into two main complementary categories: untargeted metabolomics, which allows a more comprehensive evaluation of as many metabolites as possible in biological systems, and targeted metabolomics, where the research focuses on a set of predefined metabolites for quantitation [2]. Among the different analytical technologies used in metabolomics studies, the utilization of high-throughput instruments, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS), is imperative for their universal detection and excellent identification capacities. Furthermore, the hyphenation of chromatographic methods, such as gas chromatography (GC) or liquid chromatography (LC) with MS detection, offers a significant advantage, allowing the separation of different types of metabolites with reduced matrix effects [3]. However, the performance of GC/LC-MS and NMR for absolute metabolites quantification remain challenging. NMR can quantify metabolites with high reproducibility but relatively low sensitivity, which required concentrations in the micromolar levels. In contrast, MS permits sensitive detection of metabolites up to pico- and nanomolar concentrations suffer from the need for large-scale external calibration or isotopically labeled internal standards, in addition to the confounding matrix effects [4]. Hence, a combination of NMR and MS can provide complementary information to broaden the level of metabolite coverage with adequate sensitivity [5,6].
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide with 1.79 million deaths, amounting to 18% of total deaths due to cancer in 2020 [7]. On a molecular level, metabolic reprogramming is a fundamental trait associated with cancer development to fuel the proliferation and survival of the tumor [8]. The Warburg effect, an increase in Krebs cycle intermediates, and glutamine exploitation are common metabolic traits observed in the lung for its survival [9,10,11]. Monitoring of such metabolic pathways and their intermediate metabolites during treatment courses can provide new avenues concerning the mechanisms of drug actions and treatment strategies, in addition to the identification of prognostic biomarkers that could be utilized in monitoring drug responses in clinical practice [12,13]. Hence, metabolomics has been applied extensively in cancer biology to unveil biomarkers for diagnosis, classifications, and monitoring therapy, as they can provide useful insight into what is currently taking place inside the cells [14]. In lung cancer, metabolomics experiments have unraveled different biomarkers that discriminate lung cancer patients from healthy controls [15], predict lung cancer risk in smokers [16] and discriminate lung cancer from chronic respiratory disease [17]. Moreover, metabolomics studies have been employed to determine the rewired metabolic pathways in lung cancer disease viz. up-regulation and reprogramming of glycolysis and TCA [9], up-regulation of phospholipid metabolic pathways and fatty synthesis [18], and suppression of the oxidative pentose pathway [19]. However, few metabolomics studies have been applied to monitor lung cancer therapy and discover novel prognostic biomarkers during the treatment course [20].
In this review, we do not aim to completely cover every single aspect of metabolomics analysis, such as sample pretreatment methods and data analysis strategies, as these items have been recently covered [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Instead, the recent trends in measuring the lung cancer metabolome will be highlighted concerning their metabolic pathways and potential applications. Moreover, the advantages and limitations concerning the application of each technique towards monitoring which metabolite class or type will also be emphasized.
2. NMR Metabolomics in Lung Cancer Research
NMR spectroscopy provides rapid, unbiased metabolite detection capabilities in addition to high-throughput and quantitative properties. Although NMR is a less sensitive technique, and requires more expensive instrumentation compared to MS, its major advantages lie in its high repeatability, noninvasiveness, and minimum sample preparation procedures [27]. Such advantages allow visualization of the actual metabolic state of the studied living organism at a particular point in time [28]. Hence, NMR metabolomics has been reported extensively in analyzing many biological specimens, including serum [29], plasma [30], tissues [31], cerebrospinal fluid [32], amniotic fluid [33], seminal fluid [34], and fecal extracts [35], as well as cell lysates and cell growth media [36]. The most common pulse sequences used in 1D NMR-based metabolomics studies include the 1D NOESY, 1H CPMG (Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill), and 1H diffusion-edited [28,37]. Employing these sequences allows the detection of low and high molecular weight metabolites, which are particularly useful in biofluids such as serum/plasma. However, the analysis of NMR spectra can be challenging due to signal overlap, which limits the number of compounds that can be unambiguously identified and quantified [38]. To overcome these challenges, advanced NMR techniques like two-dimensional (2D) NMR spectroscopy have been developed to enable the separation of the congested signals in a secondary frequency domain by transferring magnetization between nuclei of the same type, as seen in correlated spectroscopy (COSY) and total correlated spectroscopy (TOCSY), or between different types of nuclei, such as multiple bond correlation experiments using heteronuclear nuclei (HMBC) and single quantum coherence spectroscopy (HSQC) [39]. Such acquisitions of more detailed and resolved spectra enable the identification and quantification of a larger number of metabolites. A detailed workflow of NMR-based metabolomics experiments is presented in Figure 1.
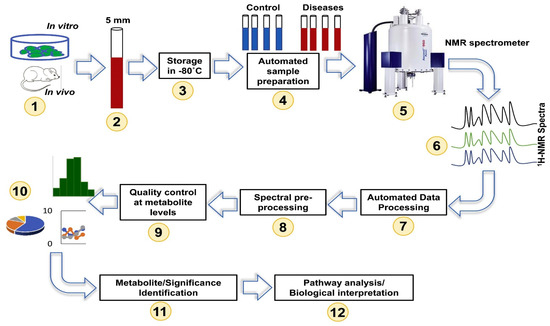
Figure 1.
Overview of NMR-based metabolomics workflow. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [40].
Hence, NMR-based metabolomics has become a powerful clinical tool in precision oncology, particularly lung cancer research (Table 1) [40]. For example, a study by Fan et al. utilized stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM) to investigate metabolic changes in human lung cancer patients [9]. They infused uniformly labeled 13C-glucose into patients and analyzed the metabolic profiles of lung cancer tissues and paired non-cancerous lung tissues using NMR and GC-MS. This study highlighted the altered regulation of metabolic pathways in lung cancer, such as anaplerotic pyruvate carboxylation, more active glycolysis, and Krebs cycle via tracing the carbon flux through these metabolic pathways [9]. In addition, NMR-based metabolomics has shown promise in the identification of diagnostic biomarkers. For example, a study by Chung et al. used 1H-NMR-based serum metabolomics in combination with 18F-FDG PET/CT to diagnose metastatic lung cancers [41]. They identified potentially increased pyruvate carboxylase and high proliferation rates of metastatic tumors that could be associated with high utilization of pyruvate, leading to a decrease in the serum pyruvate level. This is in line with another study by Sarlinova et al., which demonstrated significant increases in glucose, citrate, acetate, 3-hydroxybutyrate, and creatinine, and decreases in pyruvate, lactate, alanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan in cancer patients compared with healthy control subjects, posing the potential of NMR plasma metabolomics as a screening tool for lung cancer and showing promising statistical discrimination against healthy controls [42]. The use of 1H-NMR spectroscopy aids in the identification of serum biomarkers for detecting NSLC at an early stage, distinguishing it from healthy individuals. A group of 18 metabolites, including organic acids, amino acids, alcohols, lipids, and molecules involved in lipid metabolism, were observed to have significant differences between the two groups [43]. 1H-NMR-based metabolomics shows promising capabilities in distinguishing lung cancer from those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), even in the early stages of lung cancer [17].
NMR-based metabolomics approaches show excellent potential in identifying prognostic metabolites during the course of treatment. For example, 1H-NMR identified the changes in pre-and postoperative plasma metabolites of 74 patients diagnosed with resectable stage I-IIIA NSCLC, revealing a significant increase in lactate, cysteine, and asparagine levels and decreased acetate levels in the postoperative plasma patients [44]. In addition, 1H-NMR-based metabolomics has been employed to assess the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with NSCLC, revealing high levels of critical metabolites such as pyruvate and alanine in non-responder subjects [37]. Another study by Hao et al. analyzes 1H-NMR and GC-MS serum metabolomic profiles of 25 lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation to evaluate the feasibility of metabolites as temporal biomarkers of clinical outcomes [45].
High-resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectroscopy has emerged as a powerful tool for investigating tissue metabolism, including in the context of lung cancer metabolomics [46]. This technique has been used to study the metabolomic characteristics of lung tissues from patients with lung cancer, revealing important metabolic alterations associated with the disease such as high levels of aspartate, phosphocholine, glycerophosphocholine, and lactate, and significantly low levels of glucose and valine in cancer tissues compared to non-cancerous counterparts [46]. Another investigation utilized HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy to compare the metabolite composition between NSCLC cell lines that were induced with cisplatin resistance and their subsequently de-induced counterparts [47]. The metabolites primarily altered in both the cisplatin-resistant cells and their de-induced counterparts include glutathione and taurine, suggesting these metabolites could serve as significant biomarkers for identifying cisplatin resistance. These identified metabolites, such as those involved in glutathione synthesis, indicate potential mechanisms of resistance that may be targeted by modified drugs or novel combinations to combat this form of resistance [47]. Additionally, HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy was utilized to investigate the metabolic changes in A549 human lung cells in response to cisplatin exposure, both in vitro and ex vivo. The results revealed an increase in unsaturated triglycerides and nucleotide sugars in the cisplatin-treated cells, indicating their potential as biomarkers for treatment response. [20].

Table 1.
Summary of the NMR metabolomics studies investigating lung cancer.
Table 1.
Summary of the NMR metabolomics studies investigating lung cancer.
| No. | Aim of the Study | Sample | Participants | Altered Metabolites Associated with Lung Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Investigating the altered metabolic pathways in lung cancer | Tissues | 12 | ↑ Alanine ↑ Lactate ↑ Glutamic acid | [9] |
| 2 | Investigating the metabolomic changes in primary and secondary lung cancer patients vs. control | Plasma | 256 | ↑ Glucose, ↑ Citrate, ↑ Acetate, ↑ Hydroxybutyrate, and↑ Creatinine, ↓ Pyruvate, ↓ Tyrosine, ↓ Tryptophan | [42] |
| 3 | Biomarker discovery to support the early diagnosis and prognosis of NSCLC | Serum | 269 | ↑ Leucine, ↑ Acetate, ↑ Glutamate, ↑ Creatine, ↑ Lactate, ↓ Adipic acid, | [43] |
| 4 | Investigating the metabolomic changes after complete NSCLC removal | Plasma | 74 | ↑ Lactate, ↑ Cysteine, ↑ Asparagine, ↓ Acetate | [44] |
| 5 | Investigating the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with NSCLC | Serum | 50 | ↑Pyruvate, ↑ Alanine | [37] |
| 6 | Investigating the metabolic disturbances and metabolites of diagnostic potential in lung cancer | Serum | 81 | ↓ Histidine, ↓ Glutamine, ↓ Glycine, ↓ Threonine, ↓ Alanine, ↓ Valine | [48] |
| 7 | Investigating lung cancer metabolic signatures in urine and assessing the diagnostic potential of this approach | Urine | 125 | ↑ N-Acetylglutamine, ↑ Hydroxyisobutyrate, ↑ Creatinine, ↓ Trigonelline, ↓ Hippurate | [49] |
| 8 | Investigating the variations in the metabolicprofile of lung cancer patients and healthy control | Plasma | 163 | ↑ Pyruvate, ↑ Lactate, ↓ Glucose, ↓ Citrate, ↓ Acetate, ↓ Formate, ↓ Methanol, ↓ Histidine, ↓ Glutamine, ↓ Tyrosine, ↓ Alanine | [50] |
| 9 | Investigating metabolomic characteristics and identifying possible biomarkers in lung tissue | Tissues | 17 | ↑ aspartate, ↑ phosphocholine, ↑ glycerophosphocholine, ↑ lactate, ↓glucose, ↓ valine | [46] |
| 10 | Investigate the metabolic changes in A549 human lung cells in response to cisplatin exposure | A549 Cell line | -- | ↓ unsaturated triglycerides, ↓ nucleotide sugars | [20] |
3. GC-MS Metabolomics in Lung Cancer Research
The use of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) in the realm of lung cancer metabolomics has emerged as a crucial methodology for identifying biomarkers and altered metabolic pathways in patients with lung cancer (Table 2). GC-MS has proven to be highly effective at providing both quantitative and qualitative analysis, particularly for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) with high sensitivity and specificity, posing these compounds as reliable indicators for diagnosing and predicting lung cancer [51,52]. Hence, several studies have used GC-MS to analyze VOCs present in the exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer and healthy controls [53,54]. For example, GC-MS was applied to analyze the breath exhaled by 107 patients with lung cancer and 29 healthy controls, and identified concentrations of 56 VOCs [54]. Four target VOCs were selected for further analysis, including nonanal, acetoin, acetic acid, and propanoic acid. The concentrations of these VOCs were significantly different between patients with lung cancer and healthy controls. In addition, GC-MS analysis from 65 individuals with lung cancer to those of 31 healthy participants showed variations in the levels of over 50 substances. Utilizing a combination of these different VOCs, achievable sensitivity rates ranging from 52% to 80% were obtained, while maintaining a specificity rate of 100% for detecting lung cancer patients [53]. Interestingly, GC-MS has also been employed in detecting VOCs released from lung cancer cells (A549) and non-cancerous lung cells (WI38VA13), identifying decane and heneicosane as noticeable VOCs produced from the cancerous cell line (A549), whereas non-cancerous WI38VA13 cells emitted 1-Heptanol and heptadecane, suggesting the potential employment of these metabolites as a non-invasive screening methodology for lung cancer [55].
Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC × GC-MS) has played a significant role in the analysis of complex mixtures of VOCs [56]. This technique uses a dual-column system, with one column being nonpolar to separate analytes based on their volatilities and the other column being polar to increase peak capacities. The columns are interconnected through a modulator that selectively traps and releases analytes from the primary column onto the secondary column, thus enhancing separation capabilities using a 2D approach [57]. Hence, two-dimensional gas chromatography has proven to be a valuable technique for the identification and quantification of VOCs in patients with lung cancer [58,59]. For example, this approach was employed to reveal the metabolic abnormalities in the volatile content of human breath of lung cancer patients and healthy volunteers. Interestingly, overexpression of fatty acid methyl ester and ketone compounds was observed in cancer patients which could be attributed to the inflammation processes inside the lungs [58].
The identification and quantification of VOCs using GC-MS or GC × GC-MS can be challenging because of the low concentrations of these compounds in patients’ samples [60]. However, advancements in extraction and preconcentration techniques, such as needle trap and solid phase microextraction (SPME) devices, have enabled the detection and analysis of low-level VOCs in breath samples from patients with lung cancer [61,62]. Furthermore, the on-fiber-derivatization SPME-GC/MS method has been used to assess straight aldehydes C3–C9 in exhaled breath samples from patients with NSCLC. The SPME fiber was loaded with pentafluorobenzyl hydroxylamine as a derivatization reagent for the aldehydes, and various extraction times were examined. This technique demonstrated favorable accuracy, precision, and sensitivity in detecting aldehydes in exhaled breath specimens. In addition, advancements in nanoparticle technology have contributed to the progress in this area. Specifically, the use of single-walled carbon nanotubes coated with non-polymeric organic materials as preconcentration kits has enabled the detection of lung cancer biomarkers in breath samples through GC-MS analysis [63].
On the other hand, GC-MS has also been applied to analyze primary metabolites in the serum of patients with lung cancer, providing valuable insights into the metabolic changes associated with this disease [45]. The identified metabolites, including hydroxylamine, tridecan-1-ol, and octadecan-1-ol, were associated with survival in lung cancer patients. In contrast, other primary metabolites such as tagatose, hydroxylamine, glucopyranose, and threonine have shown potential as biomarkers for disease progression [45]. Another study examined the plasma metabolome of individuals with lung cancer by GC-MS, identifying notable changes in the levels of organic acids such as pipecolic acid, 3-hydroxybutyric acid, and uric acid, in addition to amino acids such as alanine, glycine, glutamine, threonine, and 5-hydroxytryptophan, and fatty acids such as palmitic acid [64]. Furthermore, GC-MS metabolomic analysis of primary metabolites in blood samples has also been employed for the detection of lung cancer. This approach successfully identified specific metabolites that demonstrated significant differences between patients with lung cancer and controls. For instance, elevated levels of maltose, glycerol, palmitic acid, glutamic acid, lactic acid, and ethanolamine were observed in lung cancer samples compared with controls. Conversely, decreased levels of amino acids such as lysine, tryptophan, and histidine were found in patients with lung cancer. These findings highlight the potential value of metabolomics in diagnosing lung cancer and monitoring treatment progress [65]. Nevertheless, a significant limitation in the analysis of these metabolites using GC-MS is the requirement for robust derivatization techniques that enhance the volatility and stability of these compounds [66]. Such derivatization techniques include silylation and methylation to convert non-volatile or polar compounds into more volatile and stable derivatives, making them suitable for GC-MS analysis [67]. Such pre-sample treatment steps could aid with discrepancies in the analysis results, such as glutamate, which was found elevated in the blood of lung cancer patients by Fahrmann et al. [68], whereas Hori et al. [69] reported a decreased level of glutamate, posing the need for a robust metabolomics approach when analyzing this class of metabolites.

Table 2.
Summary of the GC-MS metabolomics studies investigating lung cancer.
Table 2.
Summary of the GC-MS metabolomics studies investigating lung cancer.
| No. | Aim of the Study | Sample | Participants | Altered Metabolites Associated with Lung Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Developing a non-invasive lung diagnostic method for detection of lung cancer | Breath | 96 | ↓ Isoprene, ↓ Acetone, ↓ Methanol | [53] |
| 2 | Investigating the difference of VOCs in breath exhaled by patients with lung cancer from healthy control and after resection surgery | Breath | 136 | ↑ Nonanal, ↑ Acetoin, ↑ Acetic acid, ↑ Propanoic acid | [54] |
| 3 | Identifying VOC biomarkers in patients with NSCLC vs. healthy smokers, non-smokers, and patients with COPD | Breath | 136 | ↑ 2-Methylpentane, ↑ Isoprene, ↓ Ethylbenzene, ↓ Styrene | [70] |
| 4 | Investigating the potential of GC × GC-MS for lung cancer screening | Breath | 29 | ↑ Fatty acid methyl esters, ↑ Ketones | [58] |
| 5 | Investigating the use of needle trap device with GC-MS for assessment of asthma, COPD and lung cancer patients VOCs | Breath | 56 | ↑ 2-Propanol, ↑ Undecane, ↑ 4-Methyl Octane, ↑ Dodecanone, ↑ 3-Amino butanoic Acid, ↑ Nonanal | [61] |
| 6 | Investigating the difference of VOCs in breath exhaled by patients with lung cancer from healthy control | Breath | 53 | ↑ Propane, ↑ Carbon disulfide, ↓ 2-Propenal, ↓ Ethylbenzene, ↑ Isopropyl alcohol | [62] |
| 7 | Studying VOCs emitted by the in vitro cultured human lung cancer cells and non-cancerous lung cells | (A549), (WI38VA13) Cell lines | -- | ↑ Decane, ↑ Heneicosane, ↓ 1-Heptanol, ↓ Heptadecane | [55] |
| 8 | Evaluating prognostic markers of clinical outcomes for lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation treatment | Serum | 25 | ↓ Hydroxylamine, ↓ Tridecan-1-ol, ↓ Octadecan-1-ol, ↑ Tagatose, ↑ Hydroxylamine, ↑ Glucopyranose, ↑ Threonine | [45] |
| 9 | Investigating the pathophysiological changes during early lung adenocarcinoma development | Plasma | 59 | ↓ Alanine, ↓ Glutamine, ↓ Glycine, ↓ 5-Hydroxytryptophan, ↓ 3-Hydroxy butyric acid, ↓ Pipecolic acid, ↓ Uric acid, ↑ Palmitic acid | [64] |
| 10 | Investigating the difference of primary metabolites in blood of patients with lung cancer from healthy control | Plasma | 62 | ↑ Maltose, ↑ Glycerol, ↑ Palmitic acid, ↑ Glutamic acid, ↑ Lactic acid, ↑ Ethanolamine, ↓ Lysine, ↓ Tryptophan, ↓ Histidine | [65] |
4. LC-MS Metabolomics in Lung Cancer Research
The combining of LC and MS has become a cornerstone in the field of metabolomics research due to its ability to provide high resolution and sensitivity [71]. Such combinations offer significant advantages viz. low ion suppression effects and highly effective chromatographic separation. Recently, the adoption of ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography techniques (UHPLC) has further enhanced column efficiency, peak resolution, and sensitivity compared to traditional LC-MS methods [72]. Unlike NMR spectroscopy and GC-MS, which have limitations in terms of metabolite coverage, LC-MS allows for broader analysis thanks to the availability of diverse chromatographic columns with varied characteristics like different polarities and different MS ionization modes. RP columns such as C8 and C18 are often utilized when measuring weakly polar or non-polar metabolites, whereas HILIC columns are preferred for analyzing polar metabolites [73]. Currently, LC-MS is widely embraced within the cancer metabolomics field due to its desirable attributes including excellent reproducibility and stability during various metabolic studies.
There are currently two primary approaches in lung cancer metabolomics research that utilize LC-MS: untargeted and targeted. The untargeted approach involves the comprehensive, unsupervised analysis of all metabolites in a sample (Figure 2) [74]. It is inevitable to use high-resolution MS detectors like time-of-flight or orbitraps for this type of analysis to ensure the identity of the detected metabolites [75]. This approach has been applied extensively in lung cancer research to identify potential biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and treatment response, as well as the altered metabolic pathways (Table 3). For example, LC-MS orbitrap-based global metabolomic approach has been adopted to examine the serum of early-stage NSCLC patients [11]. The analysis revealed several significant metabolites belonging to various classes such as acylcarnitines, organic acids, and amino acids. Remarkably, these metabolites demonstrated a strong discrimination ability when evaluated using a multivariate ROC curve with an AUC value of 0.836 between the patient group and their corresponding control group [11]. The same technology has been also utilized to characterize KRAS mutants in NSCLC cells [76], and also to compare two metabolomes (plasma and serum) of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients undergoing treatment with standard chemotherapy [77], as well as to detect the metabolic alteration in the serum of NSCLS patients identifying several perturbed pathways such phenylalanine metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, and biosynthesis of bile acids [78]. Quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (QTOF-MS) analyzer is another advanced and cost-effective technology that has been combined with LC in numerous untargeted metabolomics studies, particularly in the field of lung cancer research. For example, LC-QTOF-MS was utilized to analyze the metabolic profiles of different histological subtypes of NSCLS, using both RP and HILIC columns [79]. The analysis of surgically resected lung cancer tissues from NSCLC patients using this developed methodology revealed increased levels of acylcarnitines, fatty acids, phospholipids, and amino acids compared to control tissues [79]. UHPLC-QTOF-MS also has been applied for untargeted analysis of lung cancer serum samples compared to healthy control groups identifying differential metabolites related to lipid metabolism such as choline, free fatty acids, and lysophosphatidylcholines [80].
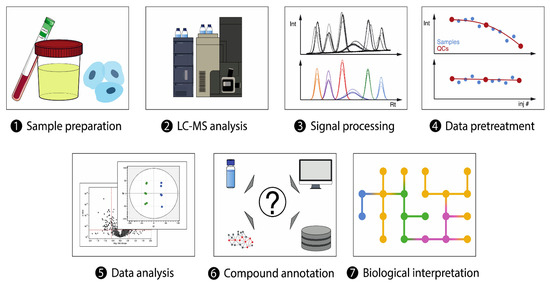
Figure 2.
Overview of LC−MS-based untargeted metabolomics workflow. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [74].
Lung cancer research has also utilized targeted metabolomics approaches that involve the measurement and quantification of specific metabolites or classes of metabolites related to the altered metabolic pathways (Table 3). To this end, mass spectrometry-based approaches, particularly triple quadrupole mass spectrometry coupled to LC (LC-QqQ-MS) with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions have been commonly used for a focused analysis of these metabolites. LC-QqQ-MS was employed to investigate the changes in free amino acid profiles in patients with NSCLS as a targeted approach. These studies identified abnormalities in the blood profiles of certain free amino acids that have potential diagnostic value for NSCLC [81,82,83]. It is important to mention that when analyzing amino acids using LC-MS, a precolumn derivatization step is typically necessary for increased sensitivity [84]. One method to accomplish this is by using the iTRAQ®-LC-MS/MS with 42 internal standards of physiological amino acids and amines as an isobaric tagging reagent, allowing for absolute quantification of these amino acids through isotope ratio analysis [85]. Organic acids are another class of metabolites that have been targeted in lung cancer research using LC-MS. For example, a study utilized LC-QqQ-MS to analyze six low-molecular-weight organic acids, including fumaric glutaric acid, pyroglutamic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, and succinic acid in lung cancer patients [86]. Among the studied acids, pyroglutamic showed the most promising discriminatory potential and accurately distinguished between NSCLC patients and control subjects. LC-QqQ-MS analysis was also used to identify elevated differential metabolites levels related to fatty acid metabolism, such as arachidonic acid, linoleic acid, and their intermediate hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, in lung cancer serum samples compared to healthy control groups [87].

Table 3.
Summary of the LC-MS metabolomics studies investigating lung cancer.
Table 3.
Summary of the LC-MS metabolomics studies investigating lung cancer.
| No. | Aim of the Study | Sample | Participants | Altered Metabolites Associated with Lung Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Applying LC-MS orbitrap-based global metabolomic approach for studying NSCLC potential markers | Serum | 75 | ↓ Histidine, ↑ Carnitine, ↓ Malic acid, ↓ Methionine, ↓ pyroglutamic acid, ↓ Leucine, ↓ Tyrosine | [11] |
| 2 | Comparing plasma and serum metabolomes of SCLC patients undergoing treatment with standard chemotherapy | Serum Plasma | 29 | No significant difference between the two biofluids | [77] |
| 3 | Characterize the metabolic alteration of NSCLC and biomarkers discovery | Serum | 436 | ↑ Hypoxanthine, ↑Glycoursodeoxycholic acid, ↓ Linoleic acid, ↓ 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, ↓ Testosterone sulfate, ↓ Choline, ↓ Piperine | [78] |
| 4 | Development of an LC-QTOF-MS method that could discriminate NSCLC histological subtypes | Tissue | 15 | ↑ Acylcarnitines, ↑ Fatty acids, ↑ Phospholipids, ↑ Amino acids | [79] |
| 5 | Identifying metabolites differentially regulated in lung cancer from healthy controls | Serum | 46 | ↓ Choline, ↓ Linoleic Acid, ↑ Lysophosphatidylcholines | [80] |
| 6 | Investigating plasma free amino acids for detecting lung cancer | Plasma | 4020 | ↑ Proline, ↑ Isoleucine, ↑ Ornithine, ↓ Glutamine, ↓ Histidine, ↓ Tryptophan | [81] |
| 7 | Investigating serum organic acids for detecting lung cancer | Serum | 152 | ↑ 2-Hydroxybutyric acid, ↓ Fumaric acid, ↓ Lactic acid, ↓ Pyroglutamic acid | [86] |
| 8 | Investigating the role of free fatty acids in lung cancer development | Serum | 220 | ↑ Arachidonic acid, ↑ linoleic acid, ↑ Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids | [87] |
| 9 | Identifying potential plasma biomarkers for NSCL | Plasma | 211 | ↑ Cortisol, ↑ Cortisone, ↓ 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid | [88] |
| 10 | Identifying potential biomarker for lung cancer early detection | Urine | 1005 | ↑ Creatine riboside, ↑N-Acetylneuraminic acid | [89] |
5. Mass Spectrometry Imaging in Lung Cancer Research
MS imaging (MSI) is a valuable technology for the spatial characterization of biological molecules in tissue sections through direct ionization and detection [90]. This technique often incorporates matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI), which gently ionizes various biological molecules. A typical MALDI-MSI analysis achieves spatial resolutions ranging from 10 to 200 μm, with resolution primarily determined by the size of the laser-treated region, typically exceeding 5 µm. However, the application of MALDI-MSI can be challenging due to many factors such as diffusion of metabolites during matrix application and variations in crystal formation, which may limit the spatial resolution. Additionally, analysis of low-molecular-weight metabolites using MALDI-MS has been limited because various matrix compounds and their ion peaks interfere with detection. As a result, lipid molecules have emerged as preferable targets for MSI studies since they have higher m/z ranges compared to other metabolites [91]. Furthermore, lipids are abundant in tissues and readily ionized due to their polar head group composition. Hence, MALDI-MSI lipidomics approaches have been utilized to investigate and characterize the lipid profiles of lung cancer tissues. For example, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI-MSI) has been used to identify and localize specific phospholipids within lung cancer tissue, revealing significant differences between tumor and adjacent healthy tissue with a substantial increase in the selected phospholipids species in cancer regions [92]. Similarly, numerous studies used MALDI-MSI-based metabolomics to identify variances between NSCLC tumors and normal lung regions through lipidomic analysis [93,94,95]. MALDI-MSI was also utilized to validate lipidomic variations among different subtypes of NSCLC [96,97]. Additionally, MALDI-MSI was utilized to elucidate therapeutic effects of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with NSLC, identifying alterations in lipid metabolism as a potential indicator of treatment response [98]. Among all the analyzed lipids, sphingomyelin-specifically SM d18:1/15:0 or d16:1/17:0-was exemplified as a prognostic marker in individuals with NSCLC. It was found that high mass intensity for SM correlated significantly with favorable prognosis [98]. These findings demonstrate the utility of MALDI-MSI in investigating the changed metabolic processes observed in lung cancer, particularly through the examination of the differential lipids.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Lung cancer-based metabolomics studies have utilized various analytical techniques, including NMR, GC-MS, LC-MS, and MSI. Each of these techniques offers unique advantages and limitations in terms of sensitivity, selectivity, and spatial resolution. NMR is a powerful technique for non-targeted metabolite profiling and allows for the identification and quantification of many metabolites with excellent reproducibility and high-throughput analysis. However, its limited sensitivity and inability to detect low-abundance metabolites restrict its application in certain metabolomics studies. In addition, signal overlapping and spectral complexity can pose challenges in identifying significant metabolites. Hence, emphasis should be placed on multidimensional techniques such 2D and even 3D NMR experiments in metabolomics lung cancer research. Additionally, employing complementary techniques such as GC-MS seems inevitable, particularly for analyzing another class of metabolites, i.e., VOCs. The peak capacities and resolution of GC-MS analysis can be also enhanced using two-dimensional chromatography setups such as GC × GC-MS providing higher separation capabilities and improved metabolite coverage posing them as powerful techniques in next-generation metabolomics lung cancer research. LC-MS, on the other hand, offers excellent sensitivity and the ability to analyze a wide range of metabolites, thus it has been employed extensively in many untargeted and targeted metabolomics studies. Furthermore, recent advancements in LC-MS technologies, such as the use of high-resolution mass spectrometers, have significantly improved the resolution and coverage of metabolite analysis in lung cancer metabolomics. Another area of emerging technology is the spatial metabolomics approach, which involves the use of MALDI-MSI to visualize the spatial distribution of metabolites in lung cancer tissues. However, such an approach is restricted to analyzing relatively high molecular metabolites, such as lipids, due to a matrix effect. Hence, other ionization techniques, such as secondary ion mass spectrometry and desorption electrospray ionization, should be explored to expand the scope of metabolite analysis in lung cancer tissues. Overall, in metabolomics research, it is important to carefully select the appropriate analytical technique based on the specific goals and requirements of the study.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Goodacre, R.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Dunn, W.B.; Harrigan, G.G.; Kell, D.B. Metabolomics by numbers: Acquiring and understanding global metabolite data. TRENDS Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebani, A.; Afonso, C.; Bekri, S. Advances in metabolome information retrieval: Turning chemistry into biology. Part I: Analytical chemistry of the metabolome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begou, O.; Gika, H.; Wilson, I.; Theodoridis, G. Hyphenated MS-based targeted approaches in metabolomics. Analyst 2017, 142, 3079–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, A.; Shakkour, Z.; Halboup, A.M.; Kobeissy, F.; Farag, M.A. Sweat metabolome and proteome: Recent trends in analytical advances and potential biological functions. J. Proteom. 2021, 246, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Q.; Wang, D.; Jasbi, P.; Zhang, P.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D.; Gu, H. Combining NMR and MS with Chemical Derivatization for Absolute Quantification with Reduced Matrix Effects. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4055–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Raftery, D. Comparing and combining NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry in metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, B.S.; Parang, K. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: The trends projection analysis. Chem. Biol. Lett. 2022, 10, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.P.; Sabatini, D.M. Cancer Cell Metabolism: Warburg and Beyond. Cell 2008, 134, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.W.M.; Lane, A.N.; Higashi, R.M.; Farag, M.A.; Gao, H.; Bousamra, M.; Miller, D.M. Altered regulation of metabolic pathways in human lung cancer discerned by 13C stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM). Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhove, K.; Derveaux, E.; Graulus, G.-J.; Mesotten, L.; Thomeer, M.; Noben, J.-P.; Guedens, W.; Adriaensens, P. Glutamine Addiction and Therapeutic Strategies in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klupczynska, A.; Dereziński, P.; Garrett, T.J.; Rubio, V.Y.; Dyszkiewicz, W.; Kasprzyk, M.; Kokot, Z.J. Study of early stage non-small-cell lung cancer using Orbitrap-based global serum metabolomics. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayet-Robert, M.; Morvan, D.; Chollet, P.; Barthomeuf, C. Pharmacometabolomics of docetaxel-treated human MCF7 breast cancer cells provides evidence of varying cellular responses at high and low doses. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 120, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Wu, J.; Kim, S.; LoRusso, P.; Li, J. Pharmacometabolomics Reveals Irinotecan Mechanism of Action in Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 59, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Emerging applications of metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.J.S.; Lewis, K.E.; Beckmann, M.; Allison, G.G.; Ghosal, R.; Lewis, P.D.; Mur, L.A.J. The metabolomic detection of lung cancer biomarkers in sputum. Lung Cancer 2016, 94, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.-P.; Zhang, F.; Liang, D.; Wen, C.; Gu, J.; Skinner, H.; Chow, W.-H.; Ye, Y.; Pu, X.; Hildebrandt, M.A.T.; et al. The Ability of Bilirubin in Identifying Smokers with Higher Risk of Lung Cancer: A Large Cohort Study in Conjunction with Global Metabolomic Profiling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deja, S.; Porebska, I.; Kowal, A.; Zabek, A.; Barg, W.; Pawelczyk, K.; Stanimirova, I.; Daszykowski, M.; Korzeniewska, A.; Jankowska, R.; et al. Metabolomics provide new insights on lung cancer staging and discrimination from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, C.M.; Barros, A.S.; Gil, A.M.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M.; Carreira, I.M.; Melo, J.B.; Bernardo, J.; Gomes, A.; et al. Metabolic Profiling of Human Lung Cancer Tissue by 1H High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HRMAS) NMR Spectroscopy. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes de Araújo, R.; Bertoni, N.; Seneda, A.L.; Felix, T.F.; Carvalho, M.; Lewis, K.E.; Hasimoto, É.N.; Beckmann, M.; Drigo, S.A.; Reis, P.P.; et al. Defining Metabolic Rewiring in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Metabolites 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.F.; Ladeirinha, A.F.; Lamego, I.; Gil, A.M.; Carvalho, L.; Carreira, I.M.; Melo, J.B. Potential Markers of Cisplatin Treatment Response Unveiled by NMR Metabolomics of Human Lung Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4242–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.-G.; Hu, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.-J. The Recent Developments in Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Want, E.J. From Samples to Insights into Metabolism: Uncovering Biologically Relevant Information in LC-HRMS Metabolomics Data. Metabolites 2019, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Song, Y.P.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Recent developments in sample preparation and data pre-treatment in metabonomics research. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 589, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xia, Y. Pretreating and normalizing metabolomics data for statistical analysis. Genes Dis. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbels, T.M.D.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Chatelaine, H.; Broeckling, C.; Zamboni, N.; Hassoun, S.; Mathé, E.A. Recent advances in mass spectrometry-based computational metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2023, 74, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Low, B.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Huan, T. Quantitative challenges and their bioinformatic solutions in mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 161, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; Perez de Souza, L.; Serag, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Farag, M.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Alseekh, S. Metabolomics in the Context of Plant Natural Products Research: From Sample Preparation to Metabolite Analysis. Metabolites 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, A.; Risi, E.; McCartney, A.; Migliaccio, I.; Moretti, E.; Malorni, L.; Luchinat, C.; Biganzoli, L.; Tenori, L. Precision Oncology via NMR-Based Metabolomics: A Review on Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei-Gardini, A.; Del Coco, L.; Marisi, G.; Conti, F.; Rovesti, G.; Ulivi, P.; Canale, M.; Frassineti, G.L.; Foschi, F.G.; Longo, S.; et al. (1)H-NMR Based Serum Metabolomics Highlights Different Specific Biomarkers between Early and Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stages. Cancers 2020, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliziotis, N.G.; Engelke, U.F.H.; Aspers, R.; Engel, J.; Deinum, J.; Timmers, H.; Wevers, R.A.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J. A comparison of high-throughput plasma NMR protocols for comparative untargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkova, N.J.; Davis, D.M.; Steiner, J.; Agarwal, R. Quantitative NMR-Based Metabolomics on Tissue Biomarkers and Its Translation into In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1978, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, A.; Paciotti, S.; Tenori, L.; Eusebi, P.; Biscetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Scheltens, P.; Turano, P.; Teunissen, C.; Luchinat, C.; et al. Fingerprinting Alzheimer’s disease by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cerebrospinal fluid. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graca, G.; Duarte, I.F.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Carreira, I.M.; Couceiro, A.B.; Domingues, M.d.R.; Spraul, M.; Tseng, L.-H.; Gil, A.M. Metabolite profiling of human amniotic fluid by hyphenated nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6085–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, A.D.; Cloarec, O.; Patki, P.; Craggs, M.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Dynamic biochemical information recovery in spontaneous human seminal fluid reactions via 1H NMR kinetic statistical total correlation spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, G.; Noor, S.O.; Ridgway, K.; Scovell, L.; Jamieson, C.; Johnson, I.T.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Kemsley, E.K.; Narbad, A. Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4208–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiziani, S.; Kang, Y.; Choi, J.S.; Roberts, W.; Paternostro, G. Metabolomic high-content nuclear magnetic resonance-based drug screening of a kinase inhibitor library. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghini, V.; Laera, L.; Fantechi, B.; Monte, F.D.; Benelli, M.; McCartney, A.; Leonardo, T.; Luchinat, C.; Pozzessere, D. Metabolomics to Assess Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, C.; Ward, D.R.; Martin, A.J.; Viant, M.R.; Ismail, T.; Johnson, P.J.; Wakelam, M.J.; Günther, U.L. Fast Targeted Multidimensional NMR Metabolomics of Colorectal Cancer. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, S68–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, A.; Salem, M.A.; Gong, S.; Wu, J.-L.; Farag, M.A. Decoding Metabolic Reprogramming in Plants under Pathogen Attacks, a Comprehensive Review of Emerging Metabolomics Technologies to Maximize Their Applications. Metabolites 2023, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, G.; Jung, Y.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, T.-J. 1H-NMR-based metabolomics for cancer targeting and metabolic engineering—A review. Process. Biochem. 2020, 99, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-H.; Hung, T.-H.; Yu, C.-F.; Tsai, C.-K.; Weng, C.-C.; Jhang, F.; Chen, F.-H.; Lin, G. Glycolytic Plasticity of Metastatic Lung Cancer Captured by Noninvasive 18F-FDG PET/CT and Serum 1H-NMR Analysis: An Orthotopic Murine Model Study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlinova, M.; Baranovicova, E.; Skaličanová, M.; Dzian, A.; Petras, M.; Lehotský, J.; Kalenska, D.; Racay, P.; Matáková, T.; Halasova, E. Metabolomic Profiling of Blood Plasma of Patients with Lung Cancer and Malignant Tumors with Metastasis in the Lungs Showed Similar Features and Promising Statistical Discrimination Against Controls. Neoplasma 2021, 68, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchades-Carrasco, L.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Pérez-Rambla, C.; García-García, F.; Lucas, R.; Calabuig, S.; Blasco, A.; Dopazo, J.; Camps, C.; Pineda-Lucena, A. Serum metabolomic profiling facilitates the non-invasive identification of metabolic biomarkers associated with the onset and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12904–12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derveaux, E.; Geubbelmans, M.; Criel, M.; Demedts, I.; Himpe, U.; Tournoy, K.; Vercauter, P.; Johansson, E.; Valkenborg, D.; Vanhove, K.; et al. NMR-Metabolomics Reveals a Metabolic Shift after Surgical Resection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Sarfaraz, M.O.; Farshidfar, F.; Bebb, D.G.; Lee, C.Y.; Card, C.M.; David, M.; Weljie, A.M. Temporal characterization of serum metabolite signatures in lung cancer patients undergoing treatment. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, F.; Wang, G.; Lan, W.; Bai, C.; Lu, S.; Yue, Y.; Deng, F. Study on metabonomic characteristics of human lung cancer using high resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermathen, M.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Hungerbühler, M.N.; Vermathen, P.; Ruprecht, N. 1H HR-MAS NMR Based Metabolic Profiling of Lung Cancer Cells with Induced and De-Induced Cisplatin Resistance to Reveal Metabolic Resistance Adaptations. Molecules 2021, 26, 6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Prakash, V.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Kant, R.; Kumar, D. Serum Metabolic Disturbances in Lung Cancer Investigated through an Elaborative NMR-Based Serum Metabolomics Approach. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 5510–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrola, J.; Rocha, C.M.; Barros, A.S.; Gil, A.M.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Carreira, I.M.; Bernardo, J.; Gomes, A.; Sousa, V.; Carvalho, L.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Lung Cancer in Biofluids: NMR-Based Metabonomics of Urine. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.M.; Carrola, J.; Barros, A.S.; Gil, A.M.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Carreira, I.M.; Bernardo, J.; Gomes, A.; Sousa, V.; Carvalho, L.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Lung Cancer in Biofluids: NMR-Based Metabonomics of Blood Plasma. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4314–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.-A.; Kumar, U.; Chen, D.D. Review of recent developments in determining volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath as biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 996, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashimova, E.; Osipova, A.; Temerdashev, A.; Porkhanov, V.; Polyakov, I.; Perunov, D.; Dmitrieva, E. Exhaled breath analysis using GC-MS and an electronic nose for lung cancer diagnostics. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4793–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajtarevic, A.; Ager, C.; Pienz, M.; Klieber, M.; Schwarz, K.; Ligor, M.; Ligor, T.; Filipiak, W.; Denz, H.; Fiegl, M.; et al. Noninvasive Detection of Lung Cancer by Analysis of Exhaled Breath. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Miwa, T.; Tsuruta, A.; Akamatsu, T.; Izu, N.; Shin, W.; Park, J.; Hida, T.; Eda, T.; Setoguchi, Y. Development of an Exhaled Breath Monitoring System with Semiconductive Gas Sensors, a Gas Condenser Unit, and Gas Chromatograph Columns. Sensors 2016, 16, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thriumani, R.; Zakaria, A.; Jeffree, A.I.; Hasyim, Y.Z.H.-Y.; Helmy, K.M.; Omar, M.I.; Shakaff, A.Y.; Kamarudin, L.M. A Study on VOCs Released by Lung Cancer Cell Line Using GCMS-SPME. Procedia Chem. 2016, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, D.M.; Serag, A.; Abdel Shakour, Z.T.; Farag, M. Novel trends and applications of multidimensional chromatography in the analysis of food, cosmetics and medicine bearing essential oils. Talanta 2021, 223, 121710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.S.S.; Nolvachai, Y.; Marriott, P.J. Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography Advances in Technology and Applications: Biennial Update. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesesse, R.; Stefanuto, P.H.; Schleich, F.; Louis, R.; Focant, J.F. Multimodal chemometric approach for the analysis of human exhaled breath in lung cancer patients by TD-GC × GC-TOFMS. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1114–1115, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, T.; Chen, K.; Xu, S. Analysis of human breath samples of lung cancer patients and healthy controls with solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and flow-modulated comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC × GC). Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 6841–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Passos, M.; Câmara, J.S. Solid Phase Microextraction, Mass Spectrometry and Metabolomic Approaches for Detection of Potential Urinary Cancer Biomarkers—A Powerful Strategy for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Talanta 2012, 89, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedeiro, F.; Monedeiro-Milanowski, M.; Ratiu, I.-A.; Brożek, B.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B. Needle Trap Device-GC-MS for Characterization of Lung Diseases Based on Breath VOC Profiles. Molecules 2021, 26, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicka, J.; Kowalkowski, T.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B. Determination of volatile organic compounds as biomarkers of lung cancer by SPME–GC–TOF/MS and chemometrics. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3360–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Trock, E.; Haick, H. Detecting Simulated Patterns of Lung Cancer Biomarkers by Random Network of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Coated with Nonpolymeric Organic Materials. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3631–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Gao, L.; Wen, Z.; Wu, C.; Tan, C.S.; Toh, W.Z.; Ong, C.N. Exploratory investigation of plasma metabolomics in human lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. BioSyst. 2013, 9, 2370–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Barupal, D.K.; Taguchi, A.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Wikoff, W.R.; Yoneda, K.Y.; Gandara, D.R.; Hanash, S.M.; Kim, K.; et al. Systemic Metabolomic Changes in Blood Samples of Lung Cancer Patients Identified by Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2015, 5, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X. Next-Generation Metabolomics in Lung Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Precision Medicine: Mini Review. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115774–115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.4.1–30.4.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrmann, J.F.; Kim, K.; DeFelice, B.C.; Taylor, S.L.; Gandara, D.R.; Yoneda, K.Y.; Cooke, D.T.; Fiehn, O.; Kelly, K.; Miyamoto, S. Investigation of Metabolomic Blood Biomarkers for Detection of Adenocarcinoma Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, S.; Nishiumi, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Shinohara, M.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Kotani, Y.; Hatano, N.; Maniwa, Y.; Nishio, W.; Bamba, T.; et al. A metabolomic approach to lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Carbognani, P.; Corradi, M.; Goldoni, M.; Acampa, O.; Balbi, B.; Bianchi, L.; Rusca, M.; Mutti, A. Exhaled volatile organic compounds in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Cross sectional and nested short-term follow-up study. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhong, L. Applications of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Based Metabolomics in Predictive and Personalized Medicine. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1049016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.; Haywood, A.; Khan, S.; Radovanovic, M.; Simmonds, J.; Norris, R. Enhancement and Suppression of Ionization in Drug Analysis Using HPLC-MS/MS in Support of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: A Review of Current Knowledge of Its Minimization and Assessment. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreldeen, H.A.A.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Metabolomics of lung cancer: Analytical platforms and their applications. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzatti, J.; Boccard, J.; Codesido, S.; Gagnebin, Y.; Joshi, A.; Picard, D.; González-Ruiz, V.; Rudaz, S. Implementation of liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry methods for untargeted metabolomic analyses of biological samples: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1105, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, X.; Wang, H. Untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics identified four subtypes of small cell lung cancer. Metabolomics 2022, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, L.; Caiola, E.; Marabese, M.; Broggini, M.; Pastorelli, R. Capturing the metabolomic diversity of KRAS mutants in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4722–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedge, D.C.; Allwood, J.W.; Dunn, W.; Vaughan, A.A.; Simpson, K.; Brown, M.; Priest, L.; Blackhall, F.H.; Whetton, A.D.; Dive, C.; et al. Is Serum or Plasma More Appropriate for Intersubject Comparisons in Metabolomic Studies? An Assessment in Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6689–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, K.; Ji, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Long, T.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, L. Serum untargeted metabolomics reveal metabolic alteration of non-small cell lung cancer and refine disease detection. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciborowski, M.; Kisluk, J.; Pietrowska, K.; Samczuk, P.; Parfieniuk, E.; Kowalczyk, T.; Kozlowski, M.; Kretowski, A.; Niklinski, J. Development of LC-QTOF-MS method for human lung tissue fingerprinting. A preliminary application to nonsmall cell lung cancer. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, X.; Zou, L.; Xu, G. Serum metabolic profiling study of lung cancer using ultra high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 966, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingyoji, M.; Iizasa, T.; Higashiyama, M.; Imamura, F.; Saruki, N.; Imaizumi, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Daimon, T.; Tochikubo, O.; Mitsushima, T.; et al. The significance and robustness of a plasma free amino acid (PFAA) profile-based multiplex function for detecting lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, J.; Long, T.; Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Long, J.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, L. Changes in serum amino acid levels in non-small cell lung cancer: A case-control study in Chinese population. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, S.H.; Ryu, J.-S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, M.K.; Jang, T.W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Nakamura, H.; Nishikata, N.; et al. The performance of a novel amino acid multivariate index for detecting lung cancer: A case control study in Korea. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Imaizumi, A.; Yoshida, H. Methods for Absolute Quantification of Human Plasma Free Amino Acids by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using Precolumn Derivatization. In Amino Acid Analysis; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Hu, T.; Lv, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, L. Targeted amino acid and related amines analysis based on iTRAQ®-LC-MS/MS for discovering potential hepatotoxicity biomarkers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupczynska, A.; Plewa, S.; Dyszkiewicz, W.; Kasprzyk, M.; Sytek, N.; Kokot, Z.J. Determination of low-molecular-weight organic acids in non-small cell lung cancer with a new liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mazzone, P.J.; Cata, J.P.; Kurz, A.; Bauer, M.; Mascha, E.J.; Sessler, D.I. Serum Free Fatty Acid Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. Chest 2014, 146, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.; Shu, Y.; Guo, R. Cortisol, cortisone, and 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid as potential plasma biomarkers for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2018, 33, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathé, E.A.; Patterson, A.D.; Haznadar, M.; Manna, S.K.; Krausz, K.W.; Bowman, E.D.; Shields, P.G.; Idle, J.R.; Smith, P.B.; Anami, K.; et al. Noninvasive urinary metabolomic profiling identifies diagnostic and prognostic markers in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3259–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, Y.; Miura, D. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Visualizing In Situ Metabolism of Endogenous Metabolites and Dietary Phytochemicals. Metabolites 2014, 4, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto-Inoue, N.; Hayasaka, T.; Zaima, N.; Setou, M. Imaging mass spectrometry for lipidomics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1811, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marien, E.; Meister, M.; Muley, T.; Gomez Del Pulgar, T.; Derua, R.; Spraggins, J.M.; Van de Plas, R.; Vanderhoydonc, F.; Machiels, J.; Binda, M.M.; et al. Phospholipid profiling identifies acyl chain elongation as a ubiquitous trait and potential target for the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12582–12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, Z. Significantly increased monounsaturated lipids relative to polyunsaturated lipids in six types of cancer microenvironment are observed by mass spectrometry imaging. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muranishi, Y.; Sato, T.; Ito, S.; Satoh, J.; Yoshizawa, A.; Tamari, S.; Ueda, Y.; Yutaka, Y.; Menju, T.; Nakamura, T.; et al. The Ratios of monounsaturated to saturated phosphatidylcholines in lung adenocarcinoma microenvironment analyzed by Liquid Chromatography-Mass spectrometry and imaging Mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.E.; Dworski, S.; Canals, D.; Casas, J.; Fabrias, G.; Schoenling, D.; Levade, T.; Denlinger, C.; Hannun, Y.A.; Medin, J.A.; et al. On-tissue localization of ceramides and other sphingolipids by MALDI mass spectrometry imaging. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8303–8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, J.M.; Freitag, H.; Hartmann, J.S.; Niehaus, K.; Galanis, M.; Griesshammer, M.; Kellner, U.; Bednarz, H. Subtyping non-small cell lung cancer by histology-guided spatial metabolomics. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.K.; Lee, H.S.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Shanta, S.R.; Park, H.M.; Kim, H.R.; et al. Lipid MALDI profile classifies non-small cell lung cancers according to the histologic type. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Sun, N.; Zens, P.; Kunzke, T.; Buck, A.; Prade, V.M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, R.; Feuchtinger, A.; et al. Spatial metabolomics for evaluating response to neoadjuvant therapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).