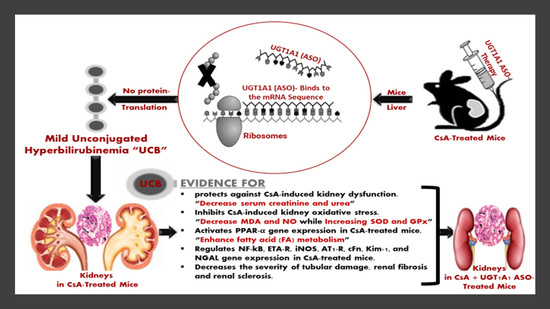
The Potential Protective Effect and Underlying Mechanisms of Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mediated by UGT1A1 Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in a Mouse Model of Cyclosporine A-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Design and Treatment
2.4. Blood and Tissue Harvesting
2.5. Tissue Processing
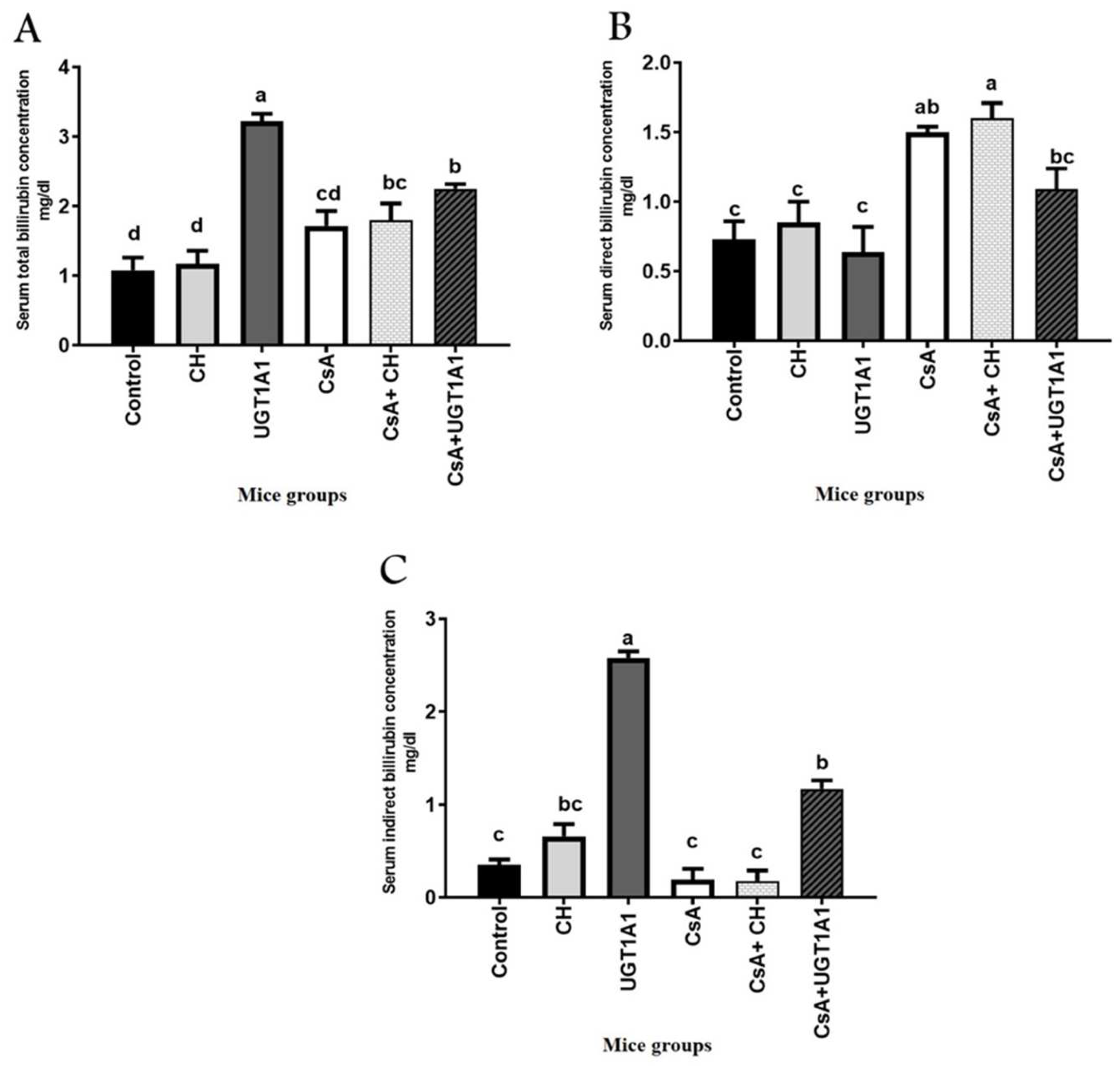
2.6. Serum Bilirubin Analysis
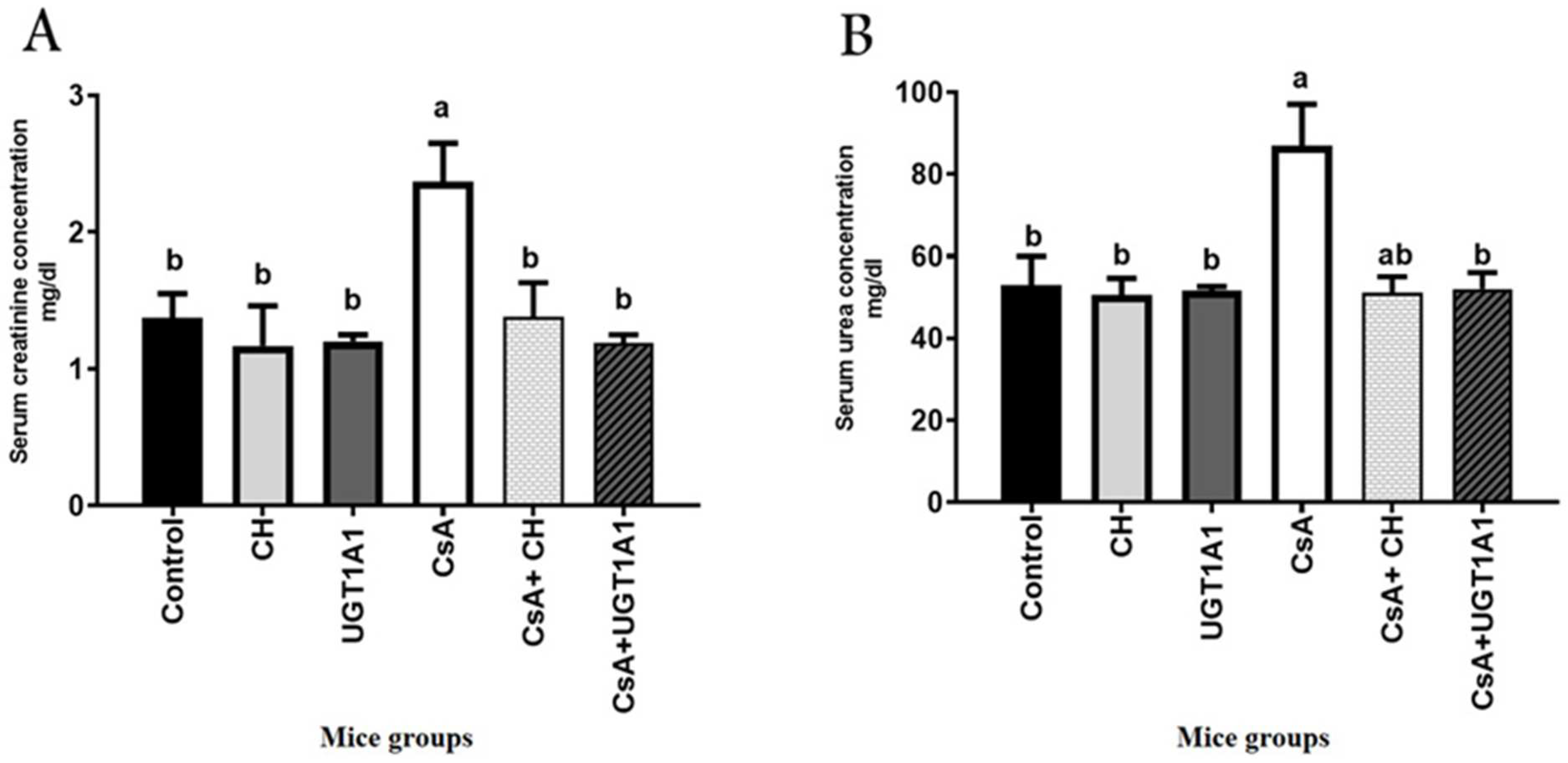
2.7. Serum Creatinine and Urea Analysis
2.8. Tissue Oxidative Stress Markers and Enzymatic Antioxidant Analysis
2.9. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.10. Quantitative Real-Rime PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.11. Histological Examination and Quantitative Analysis of Renal Tissue Lesions
Quantitative Analysis of Renal Tissue Lesions
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. UGT1A1 Antisense Oligonucleotide Mediates Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in CsA-Treated Mice
3.2. Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Protects against CsA-Induced Kidney Dysfunction
3.3. Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Inhibits CsA-Induced Kidney Oxidative Stress
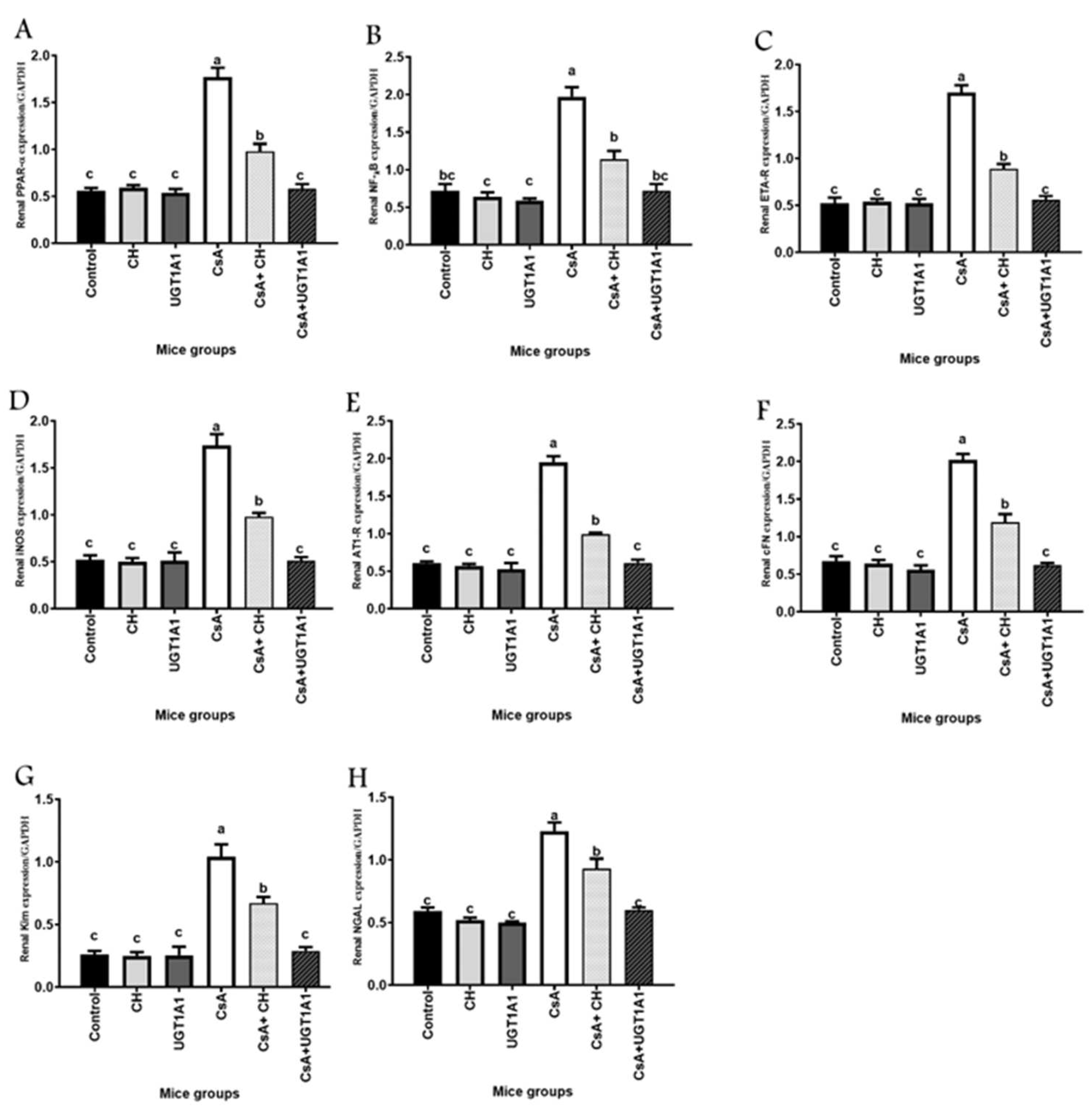
3.4. Unconjugated Bilirubin, a Signaling Molecule, Activates PPAR-α Gene Expression in CsA-Treated Mice
3.5. Unconjugated Bilirubin, a Signaling Molecule, Regulates NF-kB, ETA-R, iNOS, AT1-R, cFn, Kim-1, and NGAL Gene Expression in CsA-Treated Mice
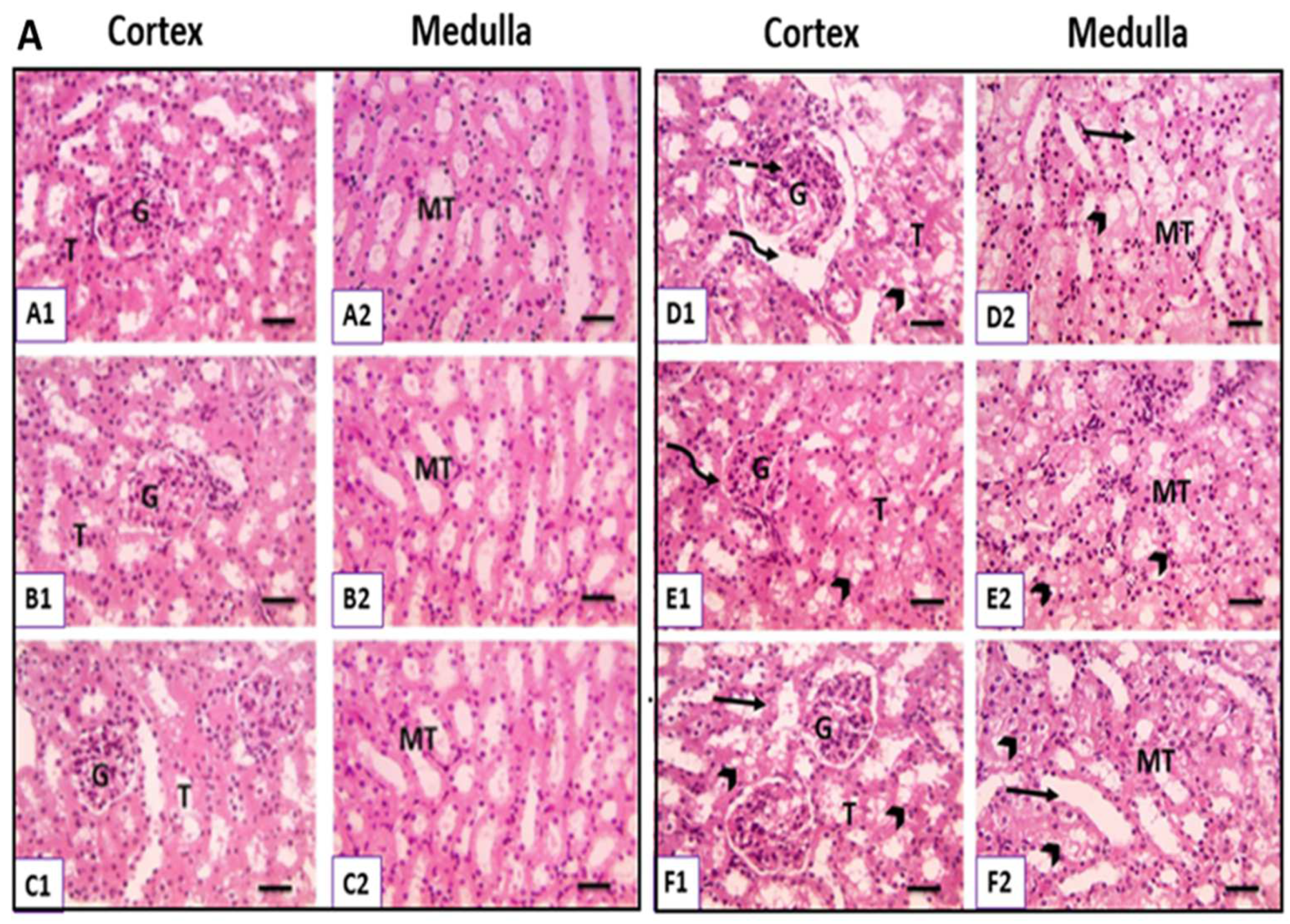
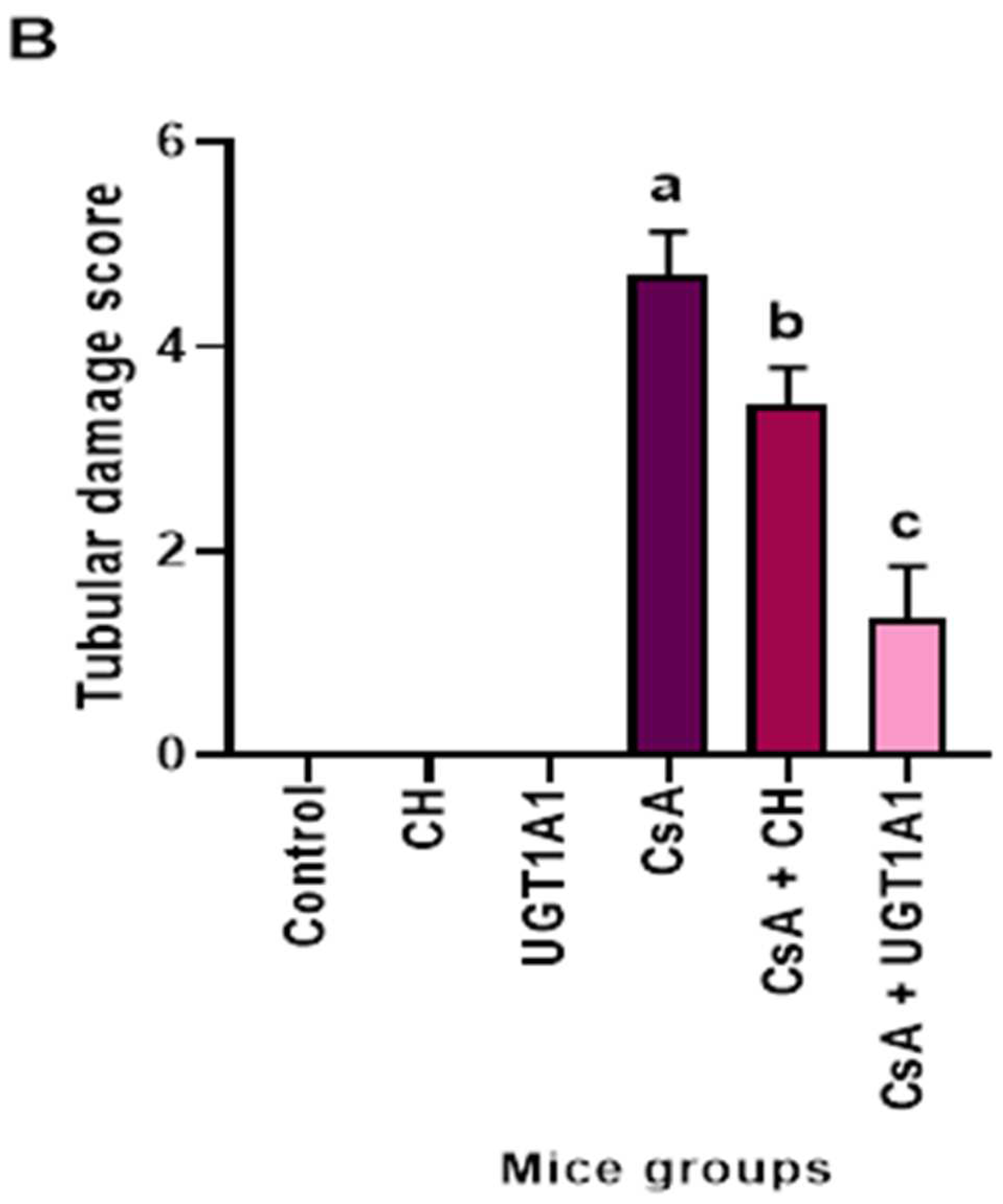
3.6. Physiological UC Hyperbilirubinemia Alleviates CsA-Induced Histological Changes in the Kidney
3.6.1. Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Kidney Sections
3.6.2. Masson Trichrome-Stained Kidney Sections
3.6.3. PAS-Stained Kidney Sections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| AF | Atherosclerotic factor |
| ARF | Acute renal failure |
| AT1-R | Angiotensinogen type-1 receptor |
| BVs | Blood vessels |
| bp | Base pair |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CB | Conjugated bilirubin |
| cFn | Cellular fibronectin |
| CHD | Coronary heart disease |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| CNIs | Calcineurin inhibitors |
| CsA | Cyclosporine A |
| CH | Chitosan |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| ET-1 | Endothelin-1 |
| ETA-R | Endothelin type A-receptor |
| FAS | Fatty acid synthase |
| G | Glomeruli: |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| H&E | Hematoxylin & Eosin |
| IFKB | Inhibitory factor kB |
| INOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| Kim1 | Kidney injury molecule 1 |
| LSD | Least significant difference |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MERC | Medical experimental research center |
| MT | Medullary tubules |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NGAL | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PRAR-α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| PAS | Periodic acid–Schiff |
| RCT | Reverse cholesterol transfer |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT | Reverse transcription |
| RT-PCR | Real-time-polymerase chain reaction |
| SE | Standard error |
| SiRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SOD | Super oxide dismutase |
| SPPARM | Selective PPAR modulator |
| T | Tubules |
| TB | Total bilirubin |
| U | Urea: |
| UCB | Unconjugated bilirubin |
| UGT1A1 | Uridine diphosphate-glucuronyl transferase1A1 |
References
- Tsai, M.; Tarng, D. Beyond a measure of liver function—Bilirubin acts as a potential cardiovascular protector in chronic kidney disease patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifert, W.R.; Abeywardena, M.Y. Grape seed and red wine polyphenol extracts inhibit cellular cholesterol uptake, cell proliferation, and 5-lipoxygenase activity. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Painer, J.; Kuro-o, M.; Lanaspa, M.; Arnold, W.; Ruf, T.; Johnson, R.J. Novel treatment strategies for chronic kidney disease: Insights from the animal kingdom. Nat. Rev. Neephrol. 2018, 14, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaghavan, V.L.; Binepal, S.; Stec, D.E.; Sindhwani, P.; Hinds, T.D. Bilirubin, a new therapeutic for kidney transplant? Transpl. Rev.-Orlan. 2018, 32, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purnell, T.S.; Auguste, P.; Crews, D.C.; Lamprea-Montealegre, J.; Olufade, T.; Greer, R.; Boulware, L.E. Comparison of life participation activities among adults treated by hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and kidney transplantation: A systematic review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 953–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, M.; Álvarez, M.; Marco, J.; Mahíllo, B.; Domínguez-Gil, B.; Núñez, J.R.; Matesanz, R. Global organ transplant activities in 2015. Data from the global observatory on donation and transplantation (GODT). Transplantion 2017, 101, S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chighizola, C.B.; Ong, V.H.; Meroni, P.L. The use of Cyclosporine a in rheumatology: A 2016 comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allerg. Immu. 2016, 52, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebru, U.; Burak, U.; Yusuf, S.; Reyhan, B.; Arif, K.; Faruk, T.H.; Kemal, E. Cardioprotective effects of Nigella sativa Oil on Cyclosporine A-induced Cardiotoxicity in rats. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 103, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.; Bayomy, M.; Azab, A. Effect of acute and chronic treatment of cyclosporin a on liver and kidney functions in rats. J. App. Pharma. Sci. 2016, 6, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yousef, O.M.; ALRajhi, W.I. The probable protective role of vitamin C against Cyclosporine an induced pulmonary change in mice. J. Life Sci. Echnol. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yao, X.; Weng, G.; Qi, H.; Ye, X. Protective effect of curcumin against cyclosporine A-induced rat nephrotoxicity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6038–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.R. Chronic Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity-lest we forget. Am. J. Transpl. 2011, 11, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilmore, H.L.; Dittmer, I.D. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity: Reduction in dose results in marked improvement in renal function in patients with coexisting chronic allograft nephropathy. Clin. Transpl. 2002, 16, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, A.C.; Bakrania, B.; Du Toit, E.F.; Boon, A.; Clark, P.J.; Powell, L.W.; Headrick, J.P. Bilirubin acts as a multipotent guardian of cardiovascular integrity: More than just a radical idea. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H429–H447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Redox functions of heme oxygenase-1 and biliverdin reductase in diabetes. Trends Endocrin. Met. 2018, 29, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, L.; Hosick, P.A.; John, K.; Stec, D.E.; Hinds, T.D. Biliverdin reductase isozymes in metabolism. Trends Endocrin. Met. 2015, 26, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, D. The roles of mrp2, mrp3, oatp1b1, and OATP1B3 in conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chan, W.; Leu, H.; Huang, P.; Lin, S.; Chen, J. Serum bilirubin levels predict future development of metabolic syndrome in healthy middle-aged Nonsmoking men. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 1138.e35–1138.e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, A.; Hawkins, C.; Coombes, J.; Wagner, K.; Bulmer, A. Bilirubin scavenges chloramines and inhibits myeloperoxidase-induced protein/lipid oxidation in physiologically relevant hyperbilirubinemic serum. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 2015, 86, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neužil, J.; Stocker, R. Bilirubin attenuates radical-mediated damage to serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 1993, 331, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neužil, J.; Gebicki, J.M.; Stocker, R. Radical-induced chain oxidation of proteins and its inhibition by chain-breaking antioxidants. Biochem. J. 1993, 293, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuzil, J.; Stocker, R. Free and albumin-bound bilirubin are efficient Co-antioxidants for Alpha-tocopherol, inhibiting plasma and low-density lipoprotein lipid peroxidation. Int. J. Biol. Chem.-Kaz. 1994, 29, 16712–16719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Fung, K.; Yang, C. Unconjugated bilirubin inhibits the oxidation of human low-density lipoprotein better than Trolox. Life Sci. 1994, 54, PL477–PL481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, T.; Stec, D.E. Moderate hyperbilirubinemia improves renal hemodynamics in ANG II-dependent hypertension. Am. J. Physiol.-Reg. I 2010, 299, R1044–R1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugbaja, R.N.; Ogungbemi, K.; James, A.S.; Ayodele, P.F.; Abolade, O.S.; Ajamikoko, S.; Adedeji, O.V. Chitosan from crabs (Scylla Serrata) represses hepato-renal dysfunctions in rats via modulation of CD43 and p53 expression in high fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbaja, R.N.; Akinloye, D.I.; James, A.S.; Ugwor, E.I.; Kareem, S.E.; David, G.; Oyebade, O.E. Crab derived dietary chitosan mollifies hyperlipidemia-induced oxidative stress and histopathological derangements in male albino rats. Obes. Med. 2020, 20, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Song, B.C.; Yeum, K.-J. Impact of volatile anesthetics on oxidative stress and inflammation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 242709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasson, V.L.; Bounds, K.R.; Chatterjee, P.; Manandhar, L.; Pakanati, A.R.; Hernandez, M.; Aziz, B.; Mitchell, B.M. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells ameliorate cyclosporine A–induced hypertension in mice. Hypertension 2018, 71, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, I.; Greco, D.; Lusardi, G.; Zimetti, F.; Potì, F.; Arnaboldi, L.; Corsini, A.; Bernini, F. Cyclosporine A impairs the macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in mice by reducing sterol fecal excretion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds Jr, T.D.; Hosick, P.A.; Chen, S.; Tukey, R.H.; Hankins, M.W.; Nestor-Kalinoski, A.; Stec, D.E. Mice with hyperbilirubinemia due to Gilbert’s syndrome polymorphism are resistant to hepatic steatosis by decreased serine 73 phosphorylation of PPARα. Am. J. Physiol. -Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 312, E244–E252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, T.S.; Carpenter, C.B.; McGirr, R. Animal research biosafety. Appl. Biosaf. 2018, 23, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, D.C.; Hartnett, M.; Campbell-Boswell, M.; Porter, G.; Bennett, W. A light and electron microscopic analysis of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am. J. Pathol. 1976, 82, 589. [Google Scholar]
- Oruc, O.; Inci, K.; Aki, F.T.; Zeybek, D.; Muftuoglu, S.F.; Kilinc, K.; Ergen, A. Sildenafil attenuates renal ischemia reperfusion injury by decreasing leukocyte infiltration. Acta Histochem. 2010, 112, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yan, F. Diffusion-weighted imaging in assessing renal pathology of chronic kidney disease: A preliminary clinical study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, A. Cyclosporine a: Clinical experience and therapeutic drug monitoring. Therap. Drug Monit. 1995, 17, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, D.; Perico, N.; Gaspari, F.; Remuzzi, G. Nephrotoxic aspects of cyclosporine. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, S234–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.T.; Mcmurray, J.J.; Rodger, R.S.C.; Farmer, R.; Jardine, A.G. Endothelial dysfunction in renal transplant recipients maintained on cyclosporine. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancia, P.; Aurich, B.; Ha, P.; Maisin, A.; Baudouin, V.; Jacqz-Aigrain, E. Adverse events under Tacrolimus and Cyclosporine in the first 3 years post-renal transplantation in children. Clin. Drug Invest. 2017, 138, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.P.; Kim, H.; Yang, S.H.; Hwang, J.H.; An, J.N.; Min, S.I.; Lim, C.S. Serum bilirubin affects Graft outcomes through UDP-glucuronosyltransferase sequence variation in kidney transplantation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J. LiverTox: An online information resource and a site for case report submission on drug-induced liver injury. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 4, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahorski, S. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th edition. Trends Pharm. Sci. 1990, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.; Mittal, A.; Yadav, B.K.; Sharma, P.; Jha, B.; Raut, K.B. Estimation and comparison of serum levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphorus in different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 1, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemionow, M.; Ozer, K.; Izycki, D.; Unsal, M.; Klimczak, A. A new method of bone marrow transplantation leads to Extention of skin allograft survival. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereno, J.; Rodrigues-Santos, P.; Vala, H.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Alves, R.; Fernandes, J.; Reis, F. Transition from cyclosporine-induced renal dysfunction to Nephrotoxicity in an in vivo rat model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8979–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deger, M.; Kaya, B.; Akdogan, N.; Kaplan, H.; Bağır, E.; Izol, V.; Arıdogan, I. Protective effect of dapagliflozin against cyclosporine a-induced nephrotoxicity. Eur. Urol. 2021, 7, S477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryniak, R.K.; Roy First, M.; Weiss, M.A. Transplant glomerulopathy: Evolution of morphologically distinct changes. Kidney Int. 1985, 27, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasaki, S.; Sakaida, I.; Uchida, K.; Kimura, T.; Kayano, K.; Okita, K. Preventive effect of cyclosporin a on experimentally induced acute liver injury in rats. Liver 2008, 17, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Li, L.; Ji, D.; Takiguchi, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Effect of Chitosan on renal function in patients with chronic renal failure. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 721–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Sun, M.; Su, Z.; Xie, Y.; Chen, M.; Zong, L.; Ping, Q. Kidney-specific drug delivery system for renal fibrosis based on coordination-driven assembly of catechol-derived chitosan. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7157–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu-ke, C. Study on chitosan-modified tripterygium glycoside nanoparticles and its renal targeting property. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, S.; Na, K.Y.; Chae, D.W.; Kim, S.; Chin, H.J. Bilirubin attenuates the renal tubular injury by inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, H.J.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, T.W.; Na, K.Y.; Oh, K.H.; Joo, K.W. The mildly elevated serum bilirubin level is negatively associated with the incidence of end stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2009, 24, S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riphagen, I.J.; Deetman, P.E.; Bakker, S.J.; Navis, G.; Cooper, M.E.; Lewis, J.B.; Lambers Heerspink, H.J. Bilirubin, and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: A post hoc analysis of RENAAL with independent replication in IDNT. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, E.; Aoyagi, R.; Aizawa, Y. Hypobilirubinemia might be a possible risk factor of end-stage kidney disease independently of estimated glomerular filtration rate. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2012, 36, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameiro-Faria, M.D.; Kohlova, M.; Ribeiro, S.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Teixeira, L.; Nascimento, H.; Santos-Silva, A. Potential cardiovascular risk protection of bilirubin in end-stage renal disease patients under hemodialysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duni, A.; Liakopoulos, V.; Rapsomanikis, K.; Dounousi, E. Chronic kidney disease and disproportionally increased cardiovascular damage: Does oxidative stress explain the burden? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Watanabe, M.; Qureshi, A.R.; Heimbürger, O.; Bárány, P.; Anderstam, B.; Lindholm, B. Oxidative DNA damage and mortality in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Periton. Dial. Int. 2015, 35, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezejiofor, A.N.; Udowelle, N.A.; Orisakwe, O.E. Nephroprotective and antioxidant effect of aqueous leaf extract of costus Afer Ker gawl on cyclosporin-a (CSA) induced nephrotoxicity. Clin. Phytosci. 2016, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arriba, G.; De Hornedo, J.P.; Rubio, S.R.; Fernández, M.C.; Martínez, S.B.; Camarero, M.M.; Cid, T.P. Vitamin E protects against the mitochondrial damage caused by cyclosporin a in LLC-PK1 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2009, 239, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amudha, G.; Josephine, A.; Sudhahar, V.; Varalakshmi, P. Protective effect of lipoic acid on oxidative and peroxidative damage in cyclosporine A-induced renal toxicity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghani, B.H.; Fehaid, A.; Ateya, A.I.; Ezz, M.A.; Saleh, R.M. Photothermal therapeutic potency of plasmonic silver nanoparticles for apoptosis and anti-angiogenesis in testosterone induced benign prostate hyperplasia in rats. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinds, T.D.; Sodhi, K.; Meadows, C.; Fedorova, L.; Puri, N.; Kim, D.H.; Kappas, A. Increased HO-1 levels ameliorate fatty liver development through a reduction of heme and recruitment of FGF21. Obesity 2013, 22, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; McDonagh, A.F.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 1987, 235, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, A.; Hawkins, C.L.; Bisht, K.; Coombes, J.S.; Bakrania, B.; Wagner, K.; Bulmer, A.C. Reduced circulating oxidized LDL is associated with hypocholesterolemia and enhanced thiol status in Gilbert syndrome. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 2012, 52, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corredor, Z.; Filho, M.I.; Rodríguez-Ribera, L.; Velázquez, A.; Hernández, A.; Catalano, C.; Pastor, S. Genetic variants associated with chronic kidney disease in a Spanish population. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Martin, N.; Slattery, C.; McMorrow, T.; Ryan, M.P. TGF-β mediates sirolimus and cyclosporine A-induced alteration of barrier function in renal epithelial cells via a noncanonical ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. 2011, 301, F1281–F1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipphardt, M.; Song, J.W.; Matsumoto, K.; Dadafarin, S.; Dihazi, H.; Müller, G.; Goligorsky, M.S. The third path of tubulointerstitial fibrosis: Aberrant endothelial secretome. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, T.; Rodriguez-Calvo, R.; Barroso, E.; Serrano, L.; Eyre, E.; Palomer, X.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)β /δ: A new potential therapeutic target for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 2, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, F.; Wu, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Che, C. PPARα targeting GDF11 inhibits vascular endothelial cell senescence in an atherosclerosis model. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gokden, N.; Okusa, M.D.; Bhatt, R.; Portilla, D. Anti-inflammatory effect of fibrate protects from cisplatin induced ARF. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. 2005, 289, F469–F480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassossy, H.M.; Banjar, Z.M.; El-Mas, M.M. The inflammatory state provokes sexual dimorphism in left ventricular and electrocardiographic effects of chronic cyclosporine in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Walsh, S.B.; Verney, Z.M.; Kopelovich, L.; Elmets, C.A.; Athar, M. Procarcinogenic effects of cyclosporine a are mediated through the activation of TAK1/TAB1 signaling pathway. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Salahudeen, A.K. Cyclosporine nephrotoxicity: Attenuation by an antioxidant-inhibitor of lipid peroxidation in vitro and in vivo. Transplantation 1994, 58, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffitz, J.E. Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2017, 28, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedapo, A.; Oyekan, A. Effects of fenofibrate, a PPAR-α ligand, on the hemodynamics of glycerol-induced renal failure in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariee, A.D.; Abd-Ellah, M.F. Protective effect of Docosahexaenoic acid against Cyclosporine A-induced Nephrotoxicity in rats: A possible mechanism of action. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stec, D.E.; John, K.; Trabbic, C.J.; Luniwal, A.; Hankins, M.W.; Baum, J.; Hinds, T.D. Bilirubin binding to PPARα inhibits lipid accumulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, P.G.; Feehally, J. Pathophysiology of cyclosporin a nephrotoxicity: Experimental and clinical observations. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1992, 7, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaun, N.; Goddard, J.; Webb, D. The Endothelin system and its antagonism in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffrin, E. Role of endothelin-1 in hypertension and vascular disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, S83–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopoulos, A.; Goumenos, D.S.; Vlachojannis, J.G.; Tsakas, S. Endothelin receptors in the kidney of patients with Proteinuric and non-proteinuric Nephropathies. Ren. Fail. 2006, 28, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomeusz, B.; Hardy, K.J.; Nelson, A.S.; Phillips, P.A. Bosentan ameliorates cyclosporin A–induced hypertension in rats and primates. Hypertension 1996, 27, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amore, A.; Emancipator, S.N.; Cirina, P.; Conti, G.; Ricotti, E.; Bagheri, N.; Coppo, R. Nitric oxide mediates cyclosporine-induced apoptosis in cultured renal cells. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, W.S.; Shin, J.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, K.T. Xanthotoxin suppresses LPS-induced expression of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6 via AP-1, NF-κb, and JAK-STAT inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, R.; Peterhans, E. Antioxidant properties of conjugated bilirubin and biliverdin: Biologically relevant scavenging of hypochlorous acid. Free Radic. Res. 1989, 6, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.D.; Chalmers, R.J.; Testa, H.J.; Lawson, R.S.; Ballardie, F.W. Angiotensin II rises during cyclosporin nephrotoxicity in patients with psoriasis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 1993, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junko, I.; Yoshiharu, K.; Nobuo, N.; Takatoshi, I.; Mikio, O.; Tadanao, T. Increased endothelial gene expression of angiotensin AT1A receptor in cyclosporine induced hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 248, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, J.; Farge, D.; Kreft-Jais, C.; Guyene, T.; Plouin, P.; Houssin, D.; Corvol, P. Cyclosporine-induced stimulation of the renin-angiotensin system after liver and heart transplantation. Transplantation 1993, 56, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassila, M. Interaction of Cyclosporine A and the renin-angiotensin system new perspectives. Curr. Drug Metab. 2002, 3, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erman, A.; Chen-Gal, B.; Zabludowski, J.; Rosenfeld, J.B. Cyclosporin a treatment enhances angiotensin converting enzyme activity in lung and serum of rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990, 42, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufro-McReddie, A.; Gomez, R.A.; Norling, L.L.; Omar, A.A.; Moore, L.C.; Kaskel, F.J. Effect of CSA on the expression of renin and angiotensin type 1 receptor genes in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1993, 43, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Auch-Schwelk, W.; Bossaller, C.; Götze, S.; Thelen, J.; Fleck, E. Endothelial and vascular smooth muscle function after chronic treatment with cyclosporin a. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 1993, 21, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, T.; Granger, J.P.; Stec, D.E. Inhibition of bilirubin metabolism induces moderate hyperbilirubinemia and attenuates ANG II-dependent hypertension in mice. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R738–R743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, D.; Storm, M.; Gousette, M. Antihypertensive actions of moderate Hyperbilirubinemia: Role of superoxide inhibition. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflueger, A.; Croatt, A.J.; Peterson, T.E.; Smith, L.A.; D’Uscio, L.V.; Katusic, Z.S.; Nath, K.A. The hyperbilirubinemic Gunn rat is resistant to the pressor effects of angiotensin II. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. 2005, 288, F552–F558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekley, C.C.; Peralta, C.A. Advances in the use of multimarker panels for renal risk stratification. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twigg, S. Fibrosis in diabetes complications: Pathogenic mechanisms and circulating and urinary markers. Vasc. Health Risk Man. 2008, 4, 575–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ozer, J.S.; Dieterle, F.; Collings, F.B.; Ramirez, V.; Troth, S.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1 outperforms traditional biomarkers of kidney injury in preclinical biomarker qualification studies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, A.; Zoch-Zwierz, W.; Taranta-Janusz, K.; Michaluk-Skutnik, J. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): A new marker of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hielscher, A.; Ellis, K.; Qiu, C.; Porterfield, J.; Gerecht, S. Fibronectin deposition participates in Extracellular matrix assembly and vascular morphogenesis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, C.P.; Sonehara, N.M.; Oliani, S.M.; Burdmann, E.A. Predictive usefulness of urinary biomarkers for the identification of Cyclosporine A-induced Nephrotoxicity in a rat model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Park, C.; Centrella, M.; McCarthy, T.; Chen, L.; Moeckel, G.W. Aldosterone stimulates fibronectin synthesis in renal fibroblasts through mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms. Gene 2013, 531, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ford, G.M.; Waikar, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Clement, M.B.; Ramirez, V.; Bonventre, J.V. A rapid urine test for early detection of kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, D.; Shi, W.; Zheng, A. Evaluation of novel biomarkers for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in asphyxiated full-term newborns: A case-control study. Med. Prin. Pract. 2019, 29, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.I.; Tang, S.C.; Lai, K.N.; Leung, J.C. Kidney injury molecule 1: More than just an injury marker of tubular epithelial cells? J. Cell Physiol. 2013, 228, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamianowska, M.; Wasilewska, A.; Szczepański, M.; Kulikowska, E.; Bebko, B.; Koput, A. Health term-born girls had higher levels of urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin than boys during the first postnatal days. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Pozos, K.; Lee-Montiel, F.; Perez-Villalva, R.; Uribe, N.; Gamba, G.; Bazan-Perkins, B.; Bobadilla, N.A. Polymerized type I collagen reduces chronic cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2010, 25, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, A.S.; Belcher, J.M. Bile acids are important contributors to AKI associated with liver disease: CON. Kidney360 2022, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetouh, F.A.; Hegazy, A.A. Effect of cyclosporine a on the kidney of rabbit: A light and ultrastructural study. Int. J. Anat. Res. 2014, 2, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rezzani, R. Cyclosporine A and adverse effects on organs: Histochemical studies. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 39, 85–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marghani, B.H.; El-Adl, M.; Ateya, A.I.; Othman, B.H.; Ghamry, H.I.; Shukry, M.; Soliman, M.M.; Rizk, M.A. The Potential Protective Effect and Underlying Mechanisms of Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mediated by UGT1A1 Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in a Mouse Model of Cyclosporine A-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Metabolites 2022, 12, 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100999
Marghani BH, El-Adl M, Ateya AI, Othman BH, Ghamry HI, Shukry M, Soliman MM, Rizk MA. The Potential Protective Effect and Underlying Mechanisms of Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mediated by UGT1A1 Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in a Mouse Model of Cyclosporine A-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):999. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100999
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarghani, Basma H., Mohamed El-Adl, Ahmed I. Ateya, Basma H. Othman, Heba I. Ghamry, Mustafa Shukry, Mohamed Mohamed Soliman, and Mohamed Abdo Rizk. 2022. "The Potential Protective Effect and Underlying Mechanisms of Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mediated by UGT1A1 Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in a Mouse Model of Cyclosporine A-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease" Metabolites 12, no. 10: 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100999
APA StyleMarghani, B. H., El-Adl, M., Ateya, A. I., Othman, B. H., Ghamry, H. I., Shukry, M., Soliman, M. M., & Rizk, M. A. (2022). The Potential Protective Effect and Underlying Mechanisms of Physiological Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Mediated by UGT1A1 Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in a Mouse Model of Cyclosporine A-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Metabolites, 12(10), 999. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100999