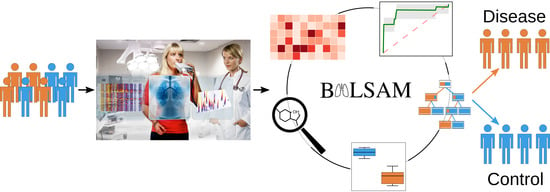
BALSAM—An Interactive Online Platform for Breath Analysis, Visualization and Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
- Automatic—Enables a fully autonomous analysis. Automatic selection of preprocessing and evaluation parameters. Selection of best-performing peak detection methods according to ROC-AUC (receiver operating characteristic area under curve) performance.
- Custom—Offers guided and step-wise tuning of analysis parameters. Users can select between prediction models according to their requirements.
- Existing Results—Allows usage of preprocessed data or previous analysis results and tuning of evaluation parameters. Feature matrices can be uploaded, skipping preprocessing and peak detection (see Supplementary Section S1.2 for file-format description).
2.1. Application Example: Candy Data-Set
2.2. Application Example 2: COPD Data-Set
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
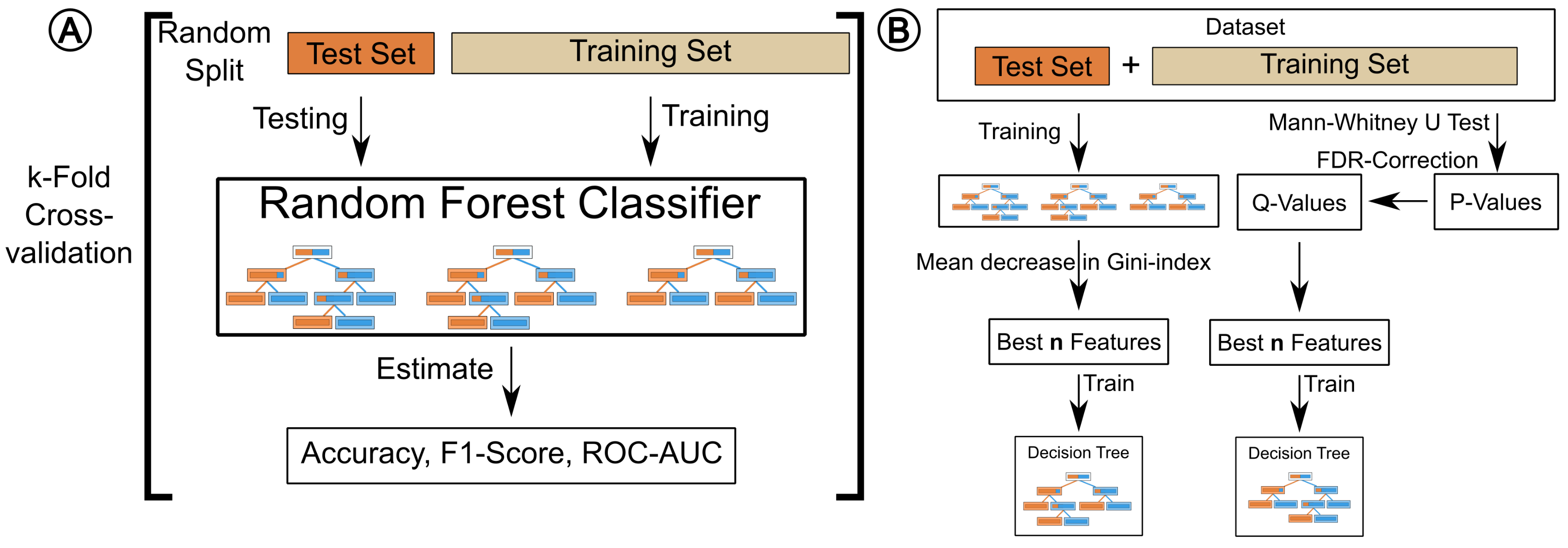
4.1. Testing and Validation
4.2. Methods Overview
4.3. Preprocessing
- Normalization and baseline correction;
- De-noising and smoothing;
- Peak detection.
4.3.1. Normalization and Baseline Correction
4.3.2. De-Noising and Smoothing
4.3.3. Peak Detection
4.4. Peak Alignment
4.5. Feature Reduction
4.6. Performance Estimation
4.7. Feature Selection
4.8. Prediction
4.9. Metabolite Discovery
4.10. Implementation
4.11. Software Availability and License
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BALSAM | Breath AnaLysis viSualizAtion Metabolite discovery |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| DBSCAN | Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| IMS | Ion-Mobility-Spectrometry |
| IRM | Inverse Reduced ion Mobility |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| MCC | Multi-Capillary-Column |
| RFC | Random Forest Classifier |
| RIP | Reactant Ion Peak |
| ROC-AUC | Receiver Operating Characteristic Area Under Curve |
| RT | Retention Time |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compound |
References
- Baumbach, J.I.; Eiceman, G.A. Ion mobility spectrometry: Arriving on site and moving beyond a low profile. Appl. Spectrosc. 1999, 53, 338A–355A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.C.C.; Kopczynski, D.; D’Addario, M.; Baumbach, J.J.I.; Rahmann, S.; Baumbach, J.J.I. Peak detection method evaluation for ion mobility spectrometry by using machine learning approaches. Metabolites 2013, 3, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, J.; Porto-Figueira, P.; Cavaco, C.; Taunk, K.; Rapole, S.; Dhakne, R.; Nagarajaram, H.; Câmara, J. Breath Analysis as a Potential and Non-Invasive Frontier in Disease Diagnosis: An Overview. Metabolites 2015, 5, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cumeras, R.; Figueras, E.; Davis, C.E.; Baumbach, J.I.; Gracia, I. Review on Ion Mobility Spectrometry. Part 1: Current Instrumentation. Analyst 2015, 140, 1376–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dweik, R.A.; Amann, A. Exhaled breath analysis: The new frontier in medical testing. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 030301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horsch, S.; Baumbach, J.I.; Rahnenführer, J. Statistical analysis of MCC-IMS data for two group comparisons-an exemplary study on two devices. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 036011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafiek, H.; Fiorentino, F.; Merino, J.L.; López, C.; Oliver, A.; Segura, J.; de Paul, I.; Sibila, O.; Agustí, A.; Cosío, B.G. Using the Electronic Nose to Identify Airway Infection during COPD Exacerbations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vries, R.; Brinkman, P.; van der Schee, M.P.; Fens, N.; Dijkers, E.; Bootsma, S.K.; de Jongh, F.H.C.; Sterk, P.J. Integration of electronic nose technology with spirometry: Validation of a new approach for exhaled breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligor, T.; Ligor, M.; Amann, A.; Ager, C.; Bachler, M.; Dzien, A.; Buszewski, B. The analysis of healthy volunteers’ exhaled breath by the use of solid-phase microextraction and GC-MS. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 046006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geer Wallace, M.A.; Pleil, J.D.; Oliver, K.D.; Whitaker, D.A.; Mentese, S.; Fent, K.W.; Horn, G.P. Non-targeted GC/MS analysis of exhaled breath samples: Exploring human biomarkers of exogenous exposure and endogenous response from professional firefighting activity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2019, 82, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.R.; Amaral, D.G.; Bais, P.; Smith, A.M.; Egnash, L.A.; Ross, M.E.; Palmer, J.A.; Fontaine, B.R.; Conard, K.R.; Corbett, B.A.; et al. Metabolomics as a Tool for Discovery of Biomarkers of Autism Spectrum Disorder in the Blood Plasma of Children. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, M.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Jia, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C. LC-MS/MS Method for Serum Creatinine: Comparison with Enzymatic Method and Jaffe Method. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furtwängler, R.; Hauschild, A.C.; Hübel, J.; Rakicioglou, H.; Bödeker, B.; Maddula, S.; Simon, A.; Baumbach, J.I. Signals of neutropenia in human breath? Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2014, 17, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, T.; Wolf, A.; Maurer, F.; Albrecht, F.W.; Heim, N.; Wolf, B.; Hauschild, A.C.; Bödeker, B.; Baumbach, J.I.; Volk, T.; et al. Volatile Organic Compounds during Inflammation and Sepsis in Rats. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, M.; Rickermann, M.; Franieck, E.; Littterst, P.; Baumbach, J.I. Time series of indoor analytes and influence of exogeneous factors on interpretation of breath analysis using ion mobility spectrometry (MCC/IMS). Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2019, 22, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, N.; Weigel, C.; Vautz, W.; Schwerdtfeger, K.; Jünger, M.; Quintel, M.; Perl, T. Multi-capillary column-ion mobility spectrometry (MCC-IMS) as a new method for the quantification of occupational exposure to sevoflurane in anaesthesia workplaces: An observational feasibility study. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2015, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurer, F.; Walter, L.; Geiger, M.; Baumbach, J.I.; Sessler, D.I.; Volk, T.; Kreuer, S. Calibration and validation of a MCC/IMS prototype for exhaled propofol online measurement. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, Y.i.; Yamada, G.; Otsuka, M.; Nishikiori, H.; Ikeda, K.; Umeda, Y.; Ohnishi, H.; Kuronuma, K.; Chiba, H.; Baumbach, J.I.; et al. Volatile Organic Compounds in Exhaled Breath of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis for Discrimination from Healthy Subjects. Lung 2017, 195, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Ke, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Luo, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Volatile organic metabolites identify patients with breast cancer, cyclomastopathy, and mammary gland fibroma. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruzsanyi, V.; Baumbach, J.I.; Sielemann, S.; Litterst, P.; Westhoff, M.; Freitag, L. Detection of human metabolites using multi-capillary columns coupled to ion mobility spectrometers. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1084, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Wilde, M.; Cordell, R.; Salman, D.; Ruszkiewicz, D.; Bryant, L.; Richardson, M.; Free, R.C.; Zhao, B.; Yousuf, A.; et al. Assessment of breath volatile organic compounds in acute cardiorespiratory breathlessness: A protocol describing a prospective real-world observational study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.C.; Frisch, T.; Baumbach, J.I.; Baumbach, J. Carotta: Revealing Hidden Confounder Markers in Metabolic Breath Profiles. Metabolites 2015, 5, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hauschild, A.C.A.; Baumbach, J.; Baumbach, J.I. Paving the Way for Automated Clinical Breath Analysis and Biomarker Detection. In Proceedings of the GCB 2013, Göttingen, Germany, 10–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Horsch, S.; Kopczynski, D.; Kuthe, E.; Baumbach, J.I.; Rahmann, S.; Rahnenführer, J. A detailed comparison of analysis processes for MCC-IMS data in disease classification—Automated methods can replace manual peak annotations. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szymańska, E.; Davies, A.; Buydens, L. Chemometrics for ion mobility spectrometry data: Recent advances and future prospects. Analyst 2016, 5689–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumbach, J.I.J.; Bunkowski, A.; Lange, S.; Oberwahrenbrock, T.; Kleinbölting, N.; Rahmann, S.; Baumbach, J.I.J. IMS2—n integrated medical software system for early lung cancer detection using ion mobility spectrometry data of human breath. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2007, 4, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Hauschild, A.C.; Baumbach, J.I.; Baumbach, J. An integrative clinical database and diagnostics platform for biomarker identification and analysis in ion mobility spectra of human exhaled air. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, I.; Ludescher, T.; King, J.; Ager, C.; Trosin, M.; Senocak, U.; Brezany, P.; Feilhauer, T.; Amann, A. ABA-Cloud: Support for collaborative breath research. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Bertsch, A.; Gröpl, C.; Hildebrandt, A.; Hussong, R.; Lange, E.; Pfeifer, N.; Schulz-Trieglaff, O.; Zerck, A.; Reinert, K.; et al. OpenMS—An open-source software framework for mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röst, H.L.; Sachsenberg, T.; Aiche, S.; Bielow, C.; Weisser, H.; Aicheler, F.; Andreotti, S.; Ehrlich, H.C.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Kenar, E.; et al. OpenMS: A flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.C. Computational Methods for Breath Metabolomics in Clinical Diagnostics. Ph.D. Thesis, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild, A.C.; Baumbach, J.; Baumbach, J. Integrated statistical learning of metabolic ion mobility spectrometry profiles for pulmonary disease identification. Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 11, 2733–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, M.; Litterst, P.; Maddula, S.; Bödeker, B.; Baumbach, J.I. Statistical and bioinformatical methods to differentiate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) including lung cancer from healthy control by breath analysis using ion mobility spectrometry. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2011, 14, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmeier, C.F.; Criner, G.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Chen, R.; Decramer, M.; Fabbri, L.M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Report. Respirology 2017, 22, 575–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Gerretzen, J.; Szymańska, E.; Jansen, J.J.; Downey, G.; Blanchet, L.; Buydens, L.M. Breaking with trends in pre-processing? TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Tinnevelt, G.H.; Brodrick, E.; Williams, M.; Davies, A.N.; van Manen, H.J.; Buydens, L.M. Increasing conclusiveness of clinical breath analysis by improved baseline correction of multi capillary column—Ion mobility spectrometry (MCC-IMS) data. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 127, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbas, A.A.; Harrington, P.B. Two-dimensional wavelet compression of ion mobility spectra. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 446, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Gommers, R.; Waselewski, F.; Wohlfahrt, K.; O’Leary, A. PyWavelets: A Python package for wavelet analysis. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addario, M.; Kopczynski, D.; Baumbach, J.; Rahmann, S. A modular computational framework for automated peak extraction from ion mobility spectra. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sternberg, S. Grayscale morphology. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1986, 35, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkowski, A. MCC-IMS Data Analysis Using Automated Spectra Processing And Explorative Visualisation Methods. Ph.D. thesis, Bielefeld University, Bielefeld, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bödeker, B.; Vautz, W.; Baumbach, J.I. Peak finding and referencing in MCC/IMS-data. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spectrom. 2008, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.; Sander, J.; Kdd, X.X.; 1996, U. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. Kdd 1996, 96, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünger, M.; Bödeker, B.; Baumbach, J.I. Peak assignment in multi-capillary column–ion mobility spectrometry using comparative studies with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for VOC analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, P. BreathPy (Version 0.8.5)· PyPI · Process Breath Samples of Multi-Capillary-Column Ion-Mobility-Spectrometry Files, 2020. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/breathpy/0.8.5/ (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python. 2019. Available online: http://www.scipy.org/ (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Röst, H.L.; Schmitt, U.; Aebersold, R.; Malmström, L. pyOpenMS: A Python-based interface to the OpenMS mass-spectrometry algorithm library. Proteomics 2014, 14, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Django Software Foundation. Django v2.2. 2019. Available online: https://www.djangoproject.com (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Group, P.G.D. PostgreSQL. 2019. Available online: http://www.postgresql.org (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- Celery: Distributed Task Queue. 2020. Available online: http://www.celeryproject.org (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- PolicyStat/Jobtastic: User-Responsive Long-Running Celery Jobs. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/PolicyStat/jobtastic (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Van der Walt, S.C.C.; Varoquaux, G. The NumPy Array: A Structure for Efficient Numerical Computation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Pandas Development Team. pandas-dev/pandas: Pandas 1.0.3. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3715232#.X3b-H-0RXIU (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and Statistical Modeling with Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28–30 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.; Botvinnik, O.; Ostblom, J.; Gelbart, M.; Lukauskas, S.; Hobson, P.; Gemperline, D.C.; Augspurger, T.; Halchenko, Y.; Cole, J.B.; et al. Mwaskom/seaborn: v0.10.1 (April 2020). 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3767070#.X3b-le0RXIU (accessed on 1 May 2020).




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, P.; Pauling, J.K.; List, M.; Baumbach, J. BALSAM—An Interactive Online Platform for Breath Analysis, Visualization and Classification. Metabolites 2020, 10, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100393
Weber P, Pauling JK, List M, Baumbach J. BALSAM—An Interactive Online Platform for Breath Analysis, Visualization and Classification. Metabolites. 2020; 10(10):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100393
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Philipp, Josch Konstantin Pauling, Markus List, and Jan Baumbach. 2020. "BALSAM—An Interactive Online Platform for Breath Analysis, Visualization and Classification" Metabolites 10, no. 10: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100393
APA StyleWeber, P., Pauling, J. K., List, M., & Baumbach, J. (2020). BALSAM—An Interactive Online Platform for Breath Analysis, Visualization and Classification. Metabolites, 10(10), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10100393