Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) aggressiveness is caused by cancer angiogenesis which promotes the cancer growth and metastasis associated with poor prognosis and poor survival. The vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and its receptor (VEGFR-2) form the major signaling pathway in cancer angiogenesis. This study aimed to investigate the anti-angiogenesis activity of quercetin in both colorectal cancer cells and endothelial cells. The tube formation of human vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was determined by using conditioned media of HT-29 cells treated with quercetin co-cultured with HUVECs. The VEGF-A and NF-κB p65 protein expressions in the quercetin-treated HT-29 cells were determined by fluorescence assay and Western blot analysis. The VEGFR-2 protein expression in HUVECs was determined after they were co-cultured with the quercetin-treated HT-29 cells. Quercetin markedly decreased the HT-29 cell-induced angiogenesis in HUVECs. NF-κB p65 and VEGF-A protein expression were also inhibited by quercetin. Moreover, quercetin significantly inhibited VEGFR-2 expression and translocation in HUVECs after they were co-cultured with high dose quercetin-treated HT-29 cells. Taken together, quercetin had an anti-angiogenesis effect on VEGF-A inhibition related to the NF-κB signaling pathway in the HT-29 cells and reduced VEGFR-2 expression and translocation in HUVECs.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is currently the third most common cause of cancer mortality worldwide with more than 1.85 million cases and 850,000 deaths annually [1]. The occurrence of CRC is strongly associated with lifestyle habits, including unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and the high consumption of alcohol and tobacco [1,2]. Other risk factors related to the onset and progression of CRC are complications of inflammatory bowel disease, a chronic intestinal inflammation, which is known to encourage carcinogenesis in combination with genetic factors in the sequence of inflammation–dysplasia–carcinoma, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease [3,4].
CRC aggressiveness is caused by cancer angiogenesis, a type of neovascular formation which is essential for the normal physiological functions of tissues, such as wound healing and embryonic development, but which is also an important factor in cancer progression due to cancer cells requiring it to provide them with proper nourishment and the removal of metabolic wastes, without which, cancer cells would die [5]. However, angiogenesis not only promotes cancer proliferation but also facilitates cancer metastasis and increases chemotherapeutic drug resistance [6,7]. There are two regulations of angiogenic factors involved in cancer angiogenesis—up-regulation of angiogenic activators and down-regulation of their inhibitors—which is called an angiogenic switch [8,9]. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the important pro-angiogenic signals and is composed of five different glycoproteins of the VEGF family: VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and placental growth factor [10]. Previous studies have reported that the binding of VEGF-A to VEGFR-2 is mainly potent in the angiogenic mechanism [11]. The expression of VEGF is increased by being induced both dependently and independently from hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF) mechanisms through the activation of the NF-κB pathway in endothelial cells; when NF-κB is activated, it will translocate into the nucleus and up-regulate the angiogenic signals which are necessary for the vascularization process [12,13,14,15,16]. One recent study by Lei Yin et al. also showed the expression and significance of VEGF in CRC patients, which were analyzed by using immunohistochemistry analysis in the patients. Their study showed that HIF-1α and VEGF were overexpressed in both the primary and matched metastatic tissues of the CRC. Therefore, inhibiting VEGF-A is needed for inhibiting both primary and metastatic CRC [17].
Quercetin (3,3′,4′,5,7-pentahydroxyflavone) is a dietary flavonoid compound found in various fruits and vegetables, such as onion, buckwheat, and broccoli [18]. It has several potential benefits for human health, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer agents, which make it act as an anti-cancer agent through broad-spectrum mechanisms from anti-carcinogenesis to anti-metastasis [19,20,21]. Several studies have reported that quercetin has an anti-angiogenic effect in prostate cancer, breast cancer, retinoblastoma, and head and neck carcinoma [22,23,24,25,26,27]. However, the precise anti-angiogenic effect of quercetin remains unclear. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the angiogenic effect of quercetin in HT-29 cell-induced angiogenesis in both colorectal and endothelial cells through the VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 pathway.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Quercetin was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA), dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and stored at −20 °C. Matrigel was purchased from Corning, USA. The antibodies—anti-VEGF-A and anti-β–actin—were purchased from Merck, Germany, while anti-VEGFR-2 was purchased from GeneTex, North America (Alton Pkwy Irvine, CA, USA). Anti-NF-κB p65 antibody was purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK).
2.2. Cell Culture
HT-29 cells and human umbilical vein endothelium cells (HUVECs) was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). HT-29 cells were cultured in completed Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium-F12 supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 1% L-glutamine, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Human umbilical vein endothelium cells (HUVECs) were maintained in complete endothelial cell growth medium supplemented with 2% fetal calf serum and growth factor supplements from the endothelial cell growth medium 2 kit (PromoCell, Heidelberg, Germany). The cells were maintained at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere within an incubator that was supplied with 5% CO2.
2.3. Conditioned Media and Co-Cultured Experiment
The HT-29 cells were cultured in 6-well plates until 80% confluence was reached. Then, the media were changed to serum-free media, and the conditioned media were harvested after 24 h of incubation. After the conditioned media were centrifuged, they were filtered through a 0.02 µm filter and then stored at −20 °C for use in tubulogenesis assay. For the co-culture in the proteins expression study, HUVECs 5 × 104 cells were seeded on coverslips and placed at the bottom of 6-well plates for IFA or seeded directly on 6-well plates for western blot analysis. They were incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 48 h. Then the HUVEC cells were co-cultured with the HT-29 cells in polycarbonate Membrane Transwell® Inserts with 3 µm pore for 24 h.
2.4. MTT Assay
The cell proliferation of the HT-29 and HUVEC cells were evaluated by using a 3-(4,5-dimethythiazol-2-yl)-2,5 diphenyltetrasodium bromide (MTT) reagent. For the HT-29 cells, 1.5 × 104 cells, and for the HUVEC, 1.0 × 104 cells were seeded in a 96-well plates and incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 for 24 h. Then, the media were changed to serum-free media, which contained quercetin at various concentrations and incubated for 24 h. The old media were replaced by 100 µL of media, which contained MTT solution, and incubated for 2 hours before 100 µL of DMSO was added. The results were detected at 570 nm with a microplate reader (1420 victor2, Wallac (Boston, MA, USA)).
2.5. Tubulogenesis Assay
Matrigel solution was added into 96-well plates and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. For the HUVEC cells, 8 × 103 cells were resuspended in the HT-29 conditioned media with or without 5 and 10 µg/mL of quercetin. Then, the HUVEC cells, 8 × 103 cells, were seeded onto a layer of Matrigel and incubated for 6 h. Tubular structures on the Matrigel were photographed from 3 randomly chosen fields. The total length of each tube per area was measured and analyzed by Image J software with an angiogenic analyzer.
2.6. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay
Indirect immunofluorescence (IFA) was used to measure NF-κB p65 and VEGF-A expression in the HT-29 cells and VEGFR-2 expression in HUVECs. For the HT-29 cells, 4 × 104 cells were seeded on coverslips and placed at the bottom of 6-well plates. They were incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for 48 h, after which, serum-free media containing 5 or 10 µg/mL quercetin were added and then incubated for another 24 h. The HT-29 cells were fixed with cold methanol, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100, and then a primary antibody; including anti-NF-kB (1:1000), anti-VEGF-A (1:1000), and anti-VEGFR-2 (1:1000) was added. This was then incubated for 1.5 h before a secondary antibody was added and incubated for another 30 min. Hoechst-33342 in dilution 1:500 was used for counterstaining for 15 min. For the HUVECs, 5 × 104 cells were seeded on coverslips and co-cultured with HT-29 cells as previously described. Then, the coverslips of HUVEC cells were harvested and fixed for immunostaining as previously described as above. The cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus BX53, Japan) at the excitation and emission wavelength of 490/515 nm and the results are presented as the mean intensity of fluorescence that was analyzed by Image J program of 3 random fields in triplicate.
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
Total protein was obtained from the HT-29 cells treated with quercetin at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL by using a cold RIPA buffer and scratched the cells. Then, the protein extracts were collected and centrifuged with 4 °C and 12,000 rpm. The supernatants were collected and measured protein concentration by using the Bradford assay. Then, NF-κB p65 and VEGF-A were detected by the Jess Simple Western System, a ProteinSimple automated Western blot system, under the principle of Western blot analysis with a specific capillary vacuum system in accordance with the instructions. Briefly, lysate proteins 2 µg were loaded for separating and then transferring in the capillaries containing the matrix gel. Afterwards, the surface was blocked and then probed with primary antibodies; including anti-NF-kB (1:1000) and anti-VEGF-A (1:1000) and then detected with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. The signals were developed, and the image was acquired for the pattern of protein separation according to molecular weight. β-actin was used as a loading control.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The values were presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for statistical analysis by using GraphPad Prism version 9. p < 0.05 was considered significantly different.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Quercetin on Cell Proliferation in HT-29 and HUVEC Cells
The results demonstrated that quercetin at concentrations of 0.1, 1, and 10 μg/mL decreased HT-29 cell proliferation to 98.91 ± 3.84%, 92.50 ± 3.53%, and 93.93 ± 2.45%, respectively, while quercetin at a concentration of 100 µg/mL significantly decreased HT-29 cell proliferation to 70.90 ± 1.88% when compared with untreated cells (p < 0.001) as shown in Figure 1a. Similarly, quercetin at concentrations of 0.1, 1, and 10 μg/mL decreased HUVEC cell proliferation to 98.12 ± 0.31%, 93.73 ± 4.70%, and 85.58 ± 2.19%, respectively, while quercetin at a concentration of 100 µg/mL significantly decreased HUVEC cell proliferation to 65.83 ± 1.25% when compared with untreated cells (p < 0.001) as shown in Figure 1b. These results demonstrate that, at a high dose, quercetin inhibits cells proliferation, whereas low concentrations have no anti-proliferative effect on either cells type.
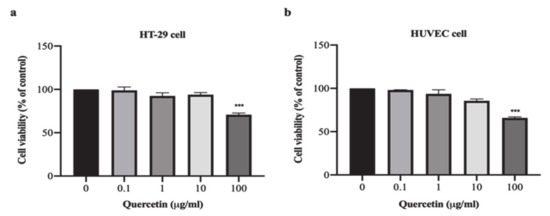
Figure 1.
Effect of quercetin on cell proliferation in HT-29 and HUVEC cells. Cell proliferation of HT-29 and HUVEC cells treated with quercetin at various concentrations for 24 h was determine using MTT assay. The cell viability of HT-29 cells (a) and HUVEC cells (b) Bar graph were represented as mean ± SD, n = 3, *** p < 0.001.
3.2. Quercetin Significantly Inhibits HT-29 Cells-Induced Tube Formation of HUVECs
The tube formation on the HT-29 cell-induced HUVECs greatly increased with more tubular branching and elongated shapes. In contrast, the HUVECs treated with quercetin at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL showed little tubular branching or elongated shapes as shown in Figure 2a. After analyzing the total tube length, quercetin at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL was found to significantly decrease tube formation to 27.60 ± 2.88 and 23.42 ± 3.68, respectively when compared with the control (84.75 ± 1.68; p < 0.001) as shown in Figure 2b. These results indicate that HT-29 cells have the capability to induce tube formation on HUVECs while quercetin dramatically inhibits HT-29 cell-induced tube formation in a dose-dependent manner.
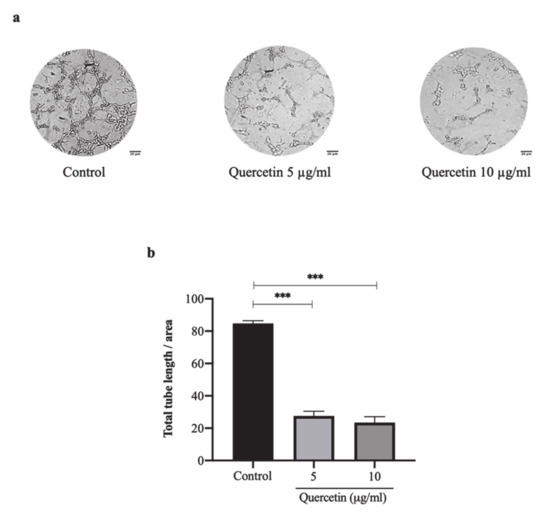
Figure 2.
Quercetin inhibits HT-29 cells-induced tube formation of HUVECs. HUVEC cells were incubated with HT-29 cells conditioned media with or without quercetin for 6 h. The pictures revealed tubular morphology of HUVECs on the Matrigel layer (a) Scale bar: 20 µm. Total tube length was measured and analyzed by ImageJ program with angiogenic analyzer which represented as bar graph (b), mean ± SD, n = 3, *** p < 0.001.
3.3. Quercetin Significantly Inhibits NF-κB p65 Expression in HT-29 Cells
NF-κB p65 protein was mainly localized at the perinuclear and intranuclear regions. After treatment with quercetin at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL, NF-κB p65 protein was observed in the cytoplasm, as shown in Figure 3a. The percentage of fluorescent intensity of NF-κB p65 expression in the quercetin-treated cells was markedly decreased to 60.77 ± 1.44% and 53.96 ± 8.80% at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL, respectively, when compared with the control (100.00 ± 2.30%, p < 0.001) as shown in Figure 3b. Correlating with and confirming the Western blot analysis, quercetin significantly decreased NF-κB p65 protein expression in a dose-dependent manner as shown in Figure 3c,d. These findings indicate that quercetin inhibited the expression of NF-κB p65 protein in HT-29 cells.
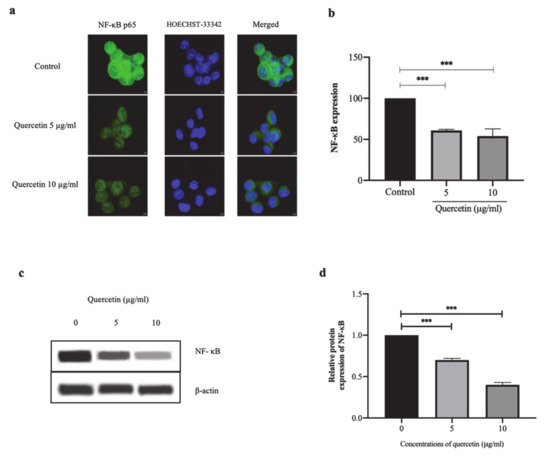
Figure 3.
Quercetin significantly inhibits NF-κB p65 expression in HT-29 cells. In HT-29 cells treated with quercetin at concentrations 5 and 10 μg/mL for 24 h, the localization and expression of NF-κB p65 by immunofluorescence assay was investigated. (a) Immunofluorescence images of NF-κB p65 as represented in green and Hoechst-33342 as represented in blue for nuclear staining. Scale bar: 5 μm. (b) The fluorescent intensity of NF-κB p65 expression was calculated and presented as % of control. (c) Western blot analysis of NF-κB p65 expression. (d) Relative protein expression of NF-κB (normalized to ß-actin). Bar graph expressed as means ± SD, n = 3, *** p < 0.001.
3.4. Quercetin Significantly Suppresses VEGF-A Protein Expression in HT-29 Cells
HT-29 cells were treated with quercetin at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL for 24 h. Then, IFA and Western blot analysis were used to investigate the VEGF-A protein expression. The IFA staining of VEGF-A protein expression was observed in the cytoplasm of HT-29 cells as shown in Figure 4a. When the HT-29 cells were treated with 5 µg/mL of quercetin, VEGF-A protein expression was significantly reduced to 80.48 ± 6.48% (p < 0.01), whereas when the HT-29 cells were treated with 10 µg/mL of quercetin, the expression of VEGF-A protein was significantly suppressed when compared with the control (100 ± 7.54%, p < 0.001) as shown in Figure 4b. Western blot analysis also showed that quercetin significantly reduced the expression of VEGF-A protein, as shown in Figure 4c,d.
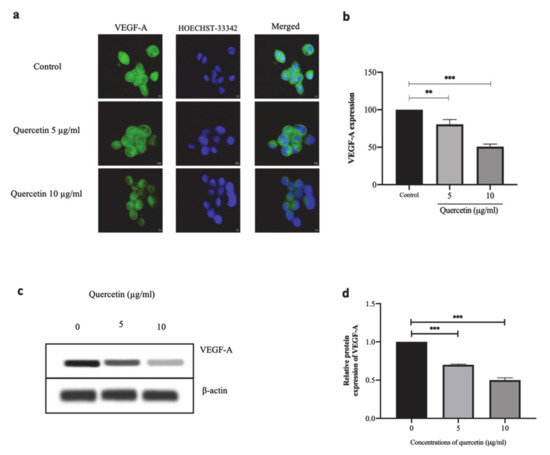
Figure 4.
Quercetin significantly suppresses VEGF-A protein expression in HT-29 cells. In HT-29 cells treated with quercetin at concentrations 5 and 10 µg/mL for 24 h, the localization and expression of VEGF-A protein by immunofluorescence assay was investigated. (a) Immunofluorescence images of VEGF-A as represented in green and Hoechst-33342 as represented in blue for nuclear staining. Scale bar: 5 µm. (b) The fluorescent intensity of VEGF-A expression was calculated and presented as % of control. (c) Western blot analysis of VEGF-A expression. (d) Relative protein expression of VEGF-A (normalized to ß-actin). Bar graph expressed as means ± SD, n = 3, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.5. Quercetin Significantly Decreased VEGFR-2 Expression in HT-29 Cells-Induced HUVECs
VEGFR-2 expression was determined in HUVEC cells co-cultured with HT-29 cells treated with or without quercetin by using IFA. The HUVEC cells co-cultured with HT-29 cells showed a presence of green spots of VEGFR-2 in the cytoplasm, while the co-cultured cells treated with quercetin VEGFR-2 were mainly located in the nucleus (Figure 5a). The fluorescent intensity was analyzed, which showed that the fluorescence intensity of VEGFR-2 was decreased to 96.01 ± 4.42% and 79.11 ± 3.89% in HUVEC cells co-cultured with quercetin at concentrations of 5 and 10 µg/mL, respectively, compared with 100 ± 4.49% in the control (Figure 5b). These findings suggest that, at a concentration of 10 µg/mL, quercetin significantly decreased VEGFR-2 expression and translocation in HT-29 cell-induced HUVECs.
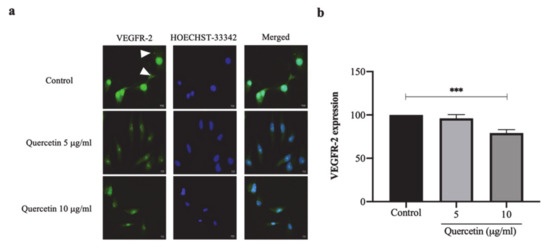
Figure 5.
Quercetin significantly decreased VEGFR-2 expression in HT-29 cells-induced HUVECs. HUVEC cells were co-cultured with HT-29 cells with or without quercetin in polycarbonate Membrane Transwell® Inserts with 3 µm pore for 24 h and observed VEGFR-2 expression by immunofluorescence assay. (a) Immunofluorescence images of VEGFR-2 as represented in green and localization as shown in white arrowhead. Hoechst-33342 as represented in blue for nuclear staining. Scale bar: 5 μm. (b) The fluorescent intensity of VEGFR-2 expression was calculated and presented as % of control. Bar graph expressed as means ± SD, n = 3, *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
Our findings showed the tube formation in HT-29 cell-induced HUVECs was markedly inhibited by quercetin in a dose-dependent manner, which indicates the anti-angiogenic activity of quercetin. The present study concurred with previous studies that quercetin is an anti-angiogenesis agent in various types of cancer, including colorectal cancer Our results showed quercetin 10 ug/mL effectively suppressed angiogenesis as similar concentration with previously observed in breast cancer, retinoblastoma, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma [23,24,25,27]. Zhao et al. also demonstrated the anti-angiogenic activity of quercetin in transgenic zebrafish embryos and in HUVECs, with their findings showing that quercetin inhibited cell viability, VEGFR-2 expression, and tube formation in a dose-dependent manner [26]. In CRC, activated NF-κB is found in increasing amounts, with previous studies revealing the greater roles of NF-κB as a main regulator of VEGF and IL-8 expression in cancer angiogenesis [28,29,30,31,32]. Our findings also showed the effect of quercetin on suppressing both NF-κB p65 and VEGF-A expression in HT-29 cells. These results suggest that the anti-angiogenic effect of quercetin is caused by inhibited VEGF-A expression, which is the main mediator of the angiogenic process. Suppressing VEGF-A expression might be caused by the inhibitory effects of the NF-κB signaling pathway because VEGF-A is known to be one of the target genes of NF-κB activation [33].
In addition, quercetin inhibited angiogenesis, not only in colorectal cancer cells but also in endothelial cells. Our findings showed that quercetin inhibits VEGFR-2, the specific receptor for VEGF-A located on endothelial cells, which is the major molecule associated with initiating the cancer angiogenesis process through proliferating, migrating, and differentiating regulation of endothelial cells [34,35]. Our findings showed that high dose quercetin significantly inhibited VEGFR-2 expression in HUVEC, which is in line with the findings of a previous study that reported the angiogenesis inhibition of quercetin through targeting VEGFR-2 expression [27]. Moreover, our study also showed HT-29 cell-induced angiogenesis via the upregulation of VEGFR-2 on the cell surface of HUVECs, which corelates with a previous study by Liu et al., who observed the role of VEGFR-2 in promoting the morphologically and functionally endothelial differentiation of CRC [34].
Interestingly, our findings showed that quercetin also inhibited the translocation of VEGFR-2 into the surface of HUVECs. This concurs with the findings of Abhinand CS et al., who noted that the angiogenesis and the function of endothelial cells are regulated by recycling VEGFR-2 from endosome to plasma membrane. The binding between VEGF-A and the surface of endothelial cells stimulates VEGFR-2 trafficking from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane [35]. Moreover, from previous research, the increased expression of VEGFR-2 correlated with differentiation, metastasis/recurrence, and poor prognosis in human colon cancer samples [17]. These findings suggest that VEGFR-2 is functional at the surface of the endothelial cell and VEGFR-2 has the potential as a molecule to be used for anti-angiogenesis cancer therapy. Taken together, the anti-angiogenic activity of quercetin could be an angiogenesis inhibitor that directly inhibits the translocation and expression of VEGFR-2 in endothelial cells in colorectal cancer cell-induced angiogenesis. The particular localization of colorectal cancer in the digestive tract enables the achievement of significantly higher doses of quercetin at the cancer site, which is an advantage considering the low bioavailability of this compound.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings demonstrated that quercetin inhibited HT-29 colorectal cancer cell-induced angiogenesis through the suppression of VEGF-A related with NF-κB p65 expression in HT-29 cells. Moreover, quercetin inhibited both the translocation and the expression of VEGFR-2 in HUVECs, although clarification is still needed to determine the certain mechanisms of the inhibitory effect of quercetin, which could then be used in targeted therapy for the treatment of colorectal cancer with less adverse effects.
Author Contributions
Investigation and writing draft manuscript, C.K. and T.U.; visualization, T.U.; investigation and resources, T.I.; supervision, P.S. and N.S.; conceptualization, writing review and editing, W.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Faculty of Science, Mahidol University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data presented or analyzed during this study are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
This study would not be accomplished without grants from the Faculty of Science, Mahidol University. In western blot analysis, JESS model of ProteinSimple automated western blot system and the test kit were kindly supported by N.Y.R. Limited Partnership, Thailand.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hazafa, A.; Rehman, K.U.; Jahan, N.; Jabeen, Z. The Role of Polyphenol (Flavonoids) Compounds in the Treatment of Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 72, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner, E.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Rzeski, W. Lycopene, sulforaphane, quercetin, and curcumin applied together show improved antiproliferative potential in colon cancer cells in vitro. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carchman, E. Crohn’s Disease and the Risk of Cancer. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2019, 32, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, C.; Ou, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Peng, X. Alternating consumption of β-glucan and quercetin reduces mortality in mice with colorectal cancer. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3273–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvelo, F.; Sojo, F.; Cotte, C. Tumour progression and metastasis. Ecancermedicalscience 2016, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J.; Watson, K.; Ingber, D.; Hanahan, D. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 1989, 339, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Mousa, S.A. The role of angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameron, K.M.; Volpert, O.V.; Tainsky, M.A.; Bouck, N. Control of angiogenesis in fibroblasts by p53 regulation of thrombospondin-1. Science 1994, 265, 1582–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology 2005, 69, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, M.E.; Kleespies, A.; Angele, M.K.; Jauch, K.-W.; Bruns, C.J. Angiogenesis in cancer: Molecular mechanisms, clinical impact. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2007, 392, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, Y.; Kohgo, Y.; Chung, DC. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 independent pathways in tumor angiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5670–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S.; Trzyna, W.C.; McClintock, D.S.; Schumacker, PT. Role of oxidants in NF-kappa B activation and TNF-alpha gene transcription induced by hypoxia and endotoxin. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozes, O.N.; Mayo, L.D.; Gustin, J.A.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Donner, DB. NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 1999, 401, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, B. In vitro angiogenesis and expression of nuclear factor kappaB and VEGF in high and low metastasis cell lines of salivary gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, J.; Ma, D.; Li, D.; Sun, Y. Angiogenesis in primary colorectal cancer and matched metastatic tissues: Biological and clinical implications for anti-angiogenic therapies. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-M.; Deng, X.-T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.-P.; Ge, X.-X.; Miao, L. Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, S.J.; Dobson, VL. Dietary flavonoids protect human colonocyte DNA from oxidative attack in vitro. Eur. J. Nutr. 1999, 38, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.A.; Takaishi, Y.; Shirotori, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T.; Tadokoto, T.; Takeuchi, M. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of quercetin oxidation products from yellow onion (Allium cepa) skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Kang, T.; Deng, W. Quercetin Suppresses Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression and Angiogenesis through Inactivation of P300 Signaling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zou, Z.; Cai, D. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis by targeting calcineurin in the xenograft model of human breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 781, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis–mediated human retinoblastoma growth by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3343–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.-Y.; Dai, Z.-R.; Li, W.-M.; Wang, R.-G.; Yang, S.-M. Inhibition of EGF expression and NF-κB activity by treatment with quercetin leads to suppression of angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Qin, C.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, B. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on angiogenesis in larval zebrafish and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Budhraja, A.; Son, Y.-O.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, S.; Wang, L.; Hitron, A.; Lee, J.-C.; Xu, M.; et al. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGFR- 2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Maeda, S.; Hikiba, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Hayakawa, Y.; Shibata, W.; Yanai, A.; Ogura, K.; Omata, M. Constitutive NF-kappaB activation in colorectal carcinoma plays a key role in angiogenesis, promoting tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voboril, R.; Weberova-Voborilova, J. Constitutive NF-kappaB activity in colorectal cancer cells: Impact on radiation-induced NF-kappaB activity, radiosensitivity, and apoptosis. Neoplasma 2006, 53, 518–523. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, A. Nf-kappa B, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; DeGuzman, A.; Bucana, C.D.; Fidler, IJ. Nuclear factor-kappaB activity correlates with growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis of human melanoma cells in nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.-C.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Zhao, J.-K.; Ou, B.-C.; Sun, J.; Zheng, M.; Zong, Y.; Lu, A. CCR6 promotes tumor angiogenesis via the AKT/NF-κB/VEGF pathway in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kenawi, A.E.; El-Remessy, AB. Angiogenesis inhibitors in cancer therapy: Mechanistic perspective on classification and treatment rationales. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 712–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, B. VEGFR2 regulates endothelial differentiation of colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Soumya, S.J.; Arya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, PR. VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J. Cell. Commun. Signal. 2016, 10, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).