Reversed-Phase UHPLC Enantiomeric Separation of Rasagiline Salts Using a Chiralpak® AGP Column
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
2.4. Preparation of the Standard and Sample Solutions
2.5. Preparation of the Stress Study Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development
3.2. Analytical Method Validation
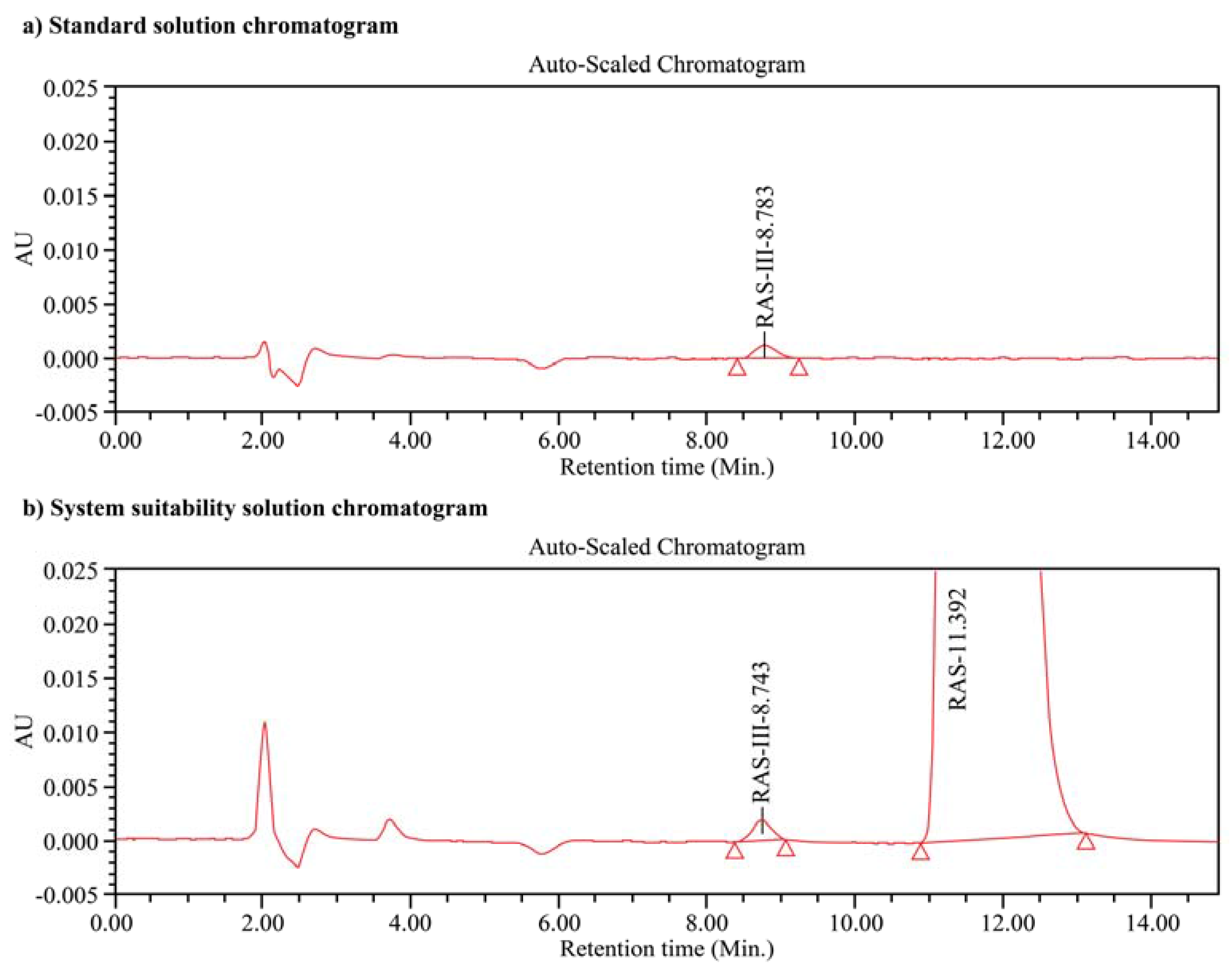
3.3. System Suitability and Precision
3.4. Method Precision
3.5. Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantification
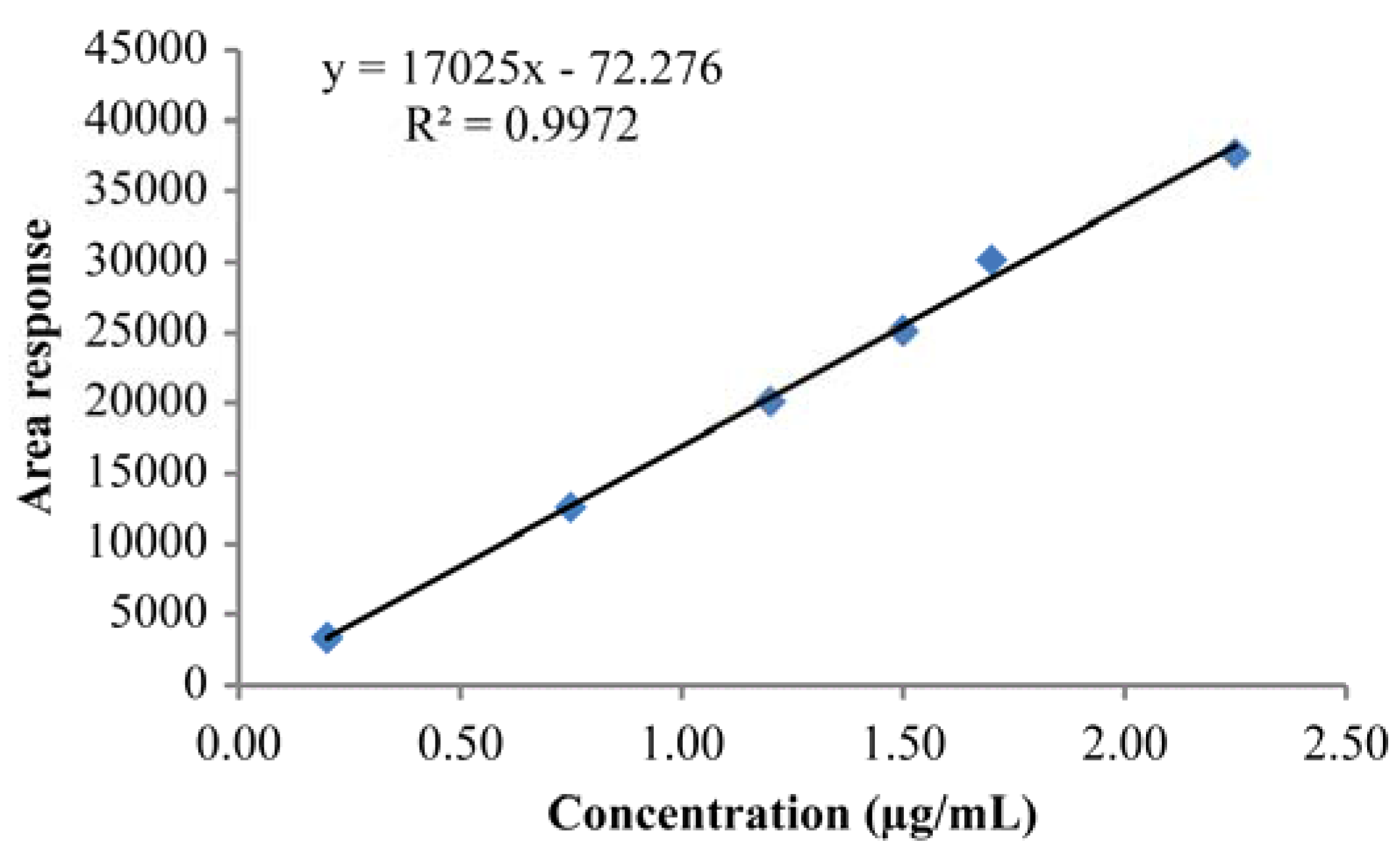
3.6. Linearity and Range
3.7. Accuracy
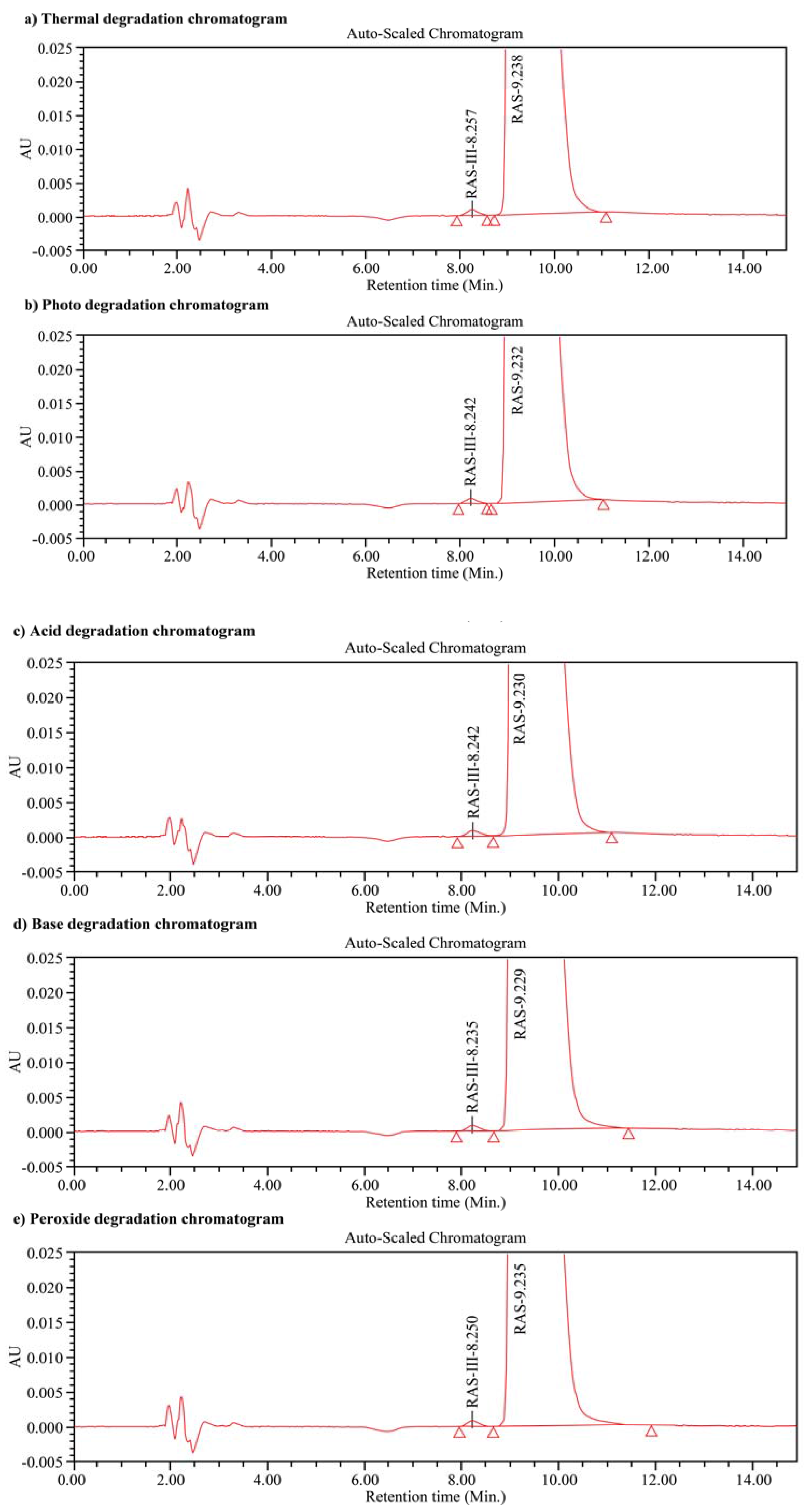
3.8. Specificity and Stability Studies
3.9. Robustness
3.10. Solution Stability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akao, Y.; Maruyama, W.; Yi, H.; Shamoto-Nagai, M.; Youdim, M.B.; Naoi, M. An anti-Parkinson’s disease drug, N-propargyl-1(R)-aminoindan (rasagiline), enhances expression of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 326, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for drug evaluation and research. Chemistry review. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_dcos/nda/2006/021641s000_Azilect_ChemR.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2016).
- Oldfield, V.; Keating, G.M.; Perry, C.M. Rasagiline: A review of its use in the management of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs 2007, 67, 1725–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.A.; Schrag, A. Impact of newer pharmacological treatments on quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 563–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, S.E. From a Parkinson’s disease expert: Rasagiline and the future of therapy. Mol. Neurodegener. 2007, 2, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medicines & Healthcare Products, Regulatory Agency. Public Assessment Report, Decentralised Procedure for Rasagiline Tartrate. Available online: http://www.mhra.gov.uk/home/groups/par/documents/websiteresources/con592269.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2016).
- Peskin, T.B.; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (Jerusalem). Rasagiline Formulations of Improved Content Uniformity. U.S. Patent 20,060,188,581, 24 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kathirvel, S.; Satyanarayana, S.V.; Devala Rao, G. Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPTLC method for analysis of rasagiline mesylate in the bulk drug and tablet dosage form. Chromatogr. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devala Rao, G.; Kathirvel, S.; Satyanarayana, S.V. Simple spectrophotometric methods for the determination of rasagiline mesylate in pharmaceutical dosage form. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 4, 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bukka, R.; Prakasam, K. UV spectrophotometric method for the determination of rasagiline mesylate in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chennaiah, M.; Veeraiah, T.; Charan Singh, T.; Venkateshwarlu, G. Extractive spectrophotometry methods for determination of rasagiline mesylate in pharmaceutical formulations using acidic triphenylmethane dyes. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2011, 56, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayavarapu, K.R.; Murugeasn, J.; Mantada, P.K. Validated RP-HPLC method for the estimation of rasagiline in pure and tablet dosage form. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 4, 1376–1377. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.N.; Rao, G.N.; Naidu, P.Y. Stability indicating RP-LC method for determination of rasagiline mesylate in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Int. J. Appl. Biol. Pharm. Technol. 2010, 1, 247–259. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaramurthy, P.; Balaji, V.; Rajasekhara, R.; Raju, I. Validated and stability indicating dissolution test with RP-HPLC analysis for rasagiline mesylate in tablet dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2011, 10, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, M.V.; Rao, J.V.L.N.S.; Rao, A.L. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for the estimation of rasagiline tablet dosage forms. Rasayan J. Chem. 2010, 3, 621–624. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, M.; Barcia, E.; Negro, S. Development and validation of a reverse phase liquid chromatography method for the quantification of rasagiline mesylate in biodegradable PLGA microspheres. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.U.; Sriramulu, J.; Reddy, U.M.; Reddy, Y.P. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for the determination of rasagiline in pharmaceutical products. Int. J. Sci. Innov. Discov. 2011, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Hang, T.; Wen, A.; Yang, L.; Jia, L. Rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Assay development, validation and application to a human pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 875, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Duan, X.; Deng, P.; Wang, H.; Zhong, D. Validated LC-MS/MS method for quantitative determination of rasagiline in human plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 873, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.S.; Babu, K.S.; Kumar, N. A validated normal phase LC method for enantiomeric separation of rasagiline mesylate and its (S) enantiomer on cellulose derivative based chiral stationary phase. Chirality 2013, 25, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirogi, R.; Doguparthi, M.R.; Lingavarapu, B.; Thota, K.R.; Sivasekhar Yarra, N.K. Reverse phase high performance liquid chromatographic method for separation of R-rasagiline mesylate from S-isomer. Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, K.M.; Park, E.J.; Hyun, M.H. Liquid chromatographic resolution of racemic rasagiline and its analogues on a chiral stationary phase based on (+)-(18-crown-6)-2,3,11,12-tetracarboxylic acid. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3682–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacel Corporation. Available online: https://www.daicelchiral.com/en/chiral-columns/protein.html (accessed on 12 February 2017).
- Sigma Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/docs/Supelco/Product_Information_Sheet/t709074.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2017).
- European Pharmacopoeia. Available online: http://library.njucm.edu.cn/yaodian/ep/EP5.0/02_methods_of_analysis/2.2.__physical_and_physicochemical_methods/2.2.46.%20Chromatographic%20separation%20techniques.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2017).
- ICH Guidelines. Available online: http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2017).
- Snyder, L.R.; Kirkland, J.J. Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Column | Resolution | LOD; LOQ * | Run Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC | Chiralcel OJ-H 250 × 4.6 mm; | 5.4 | 0.35 μg/mL; 1.05 μg/mL | Requires more time to stabilize the LC system. | [20] |
| Normal phase (n-hexane/isopropyl alcohol/ethanol/diethyl amine) (96:2:2:0.01, v/v/v/v) | Run time: 20 min. | ||||
| HPLC | Chiralpak AD-RH 150 × 4.6 mm; | 3.5 | 0.16 μg/mL; 0.49 μg/mL | Requires less time to stabilize the LC system compared to method [21]. | [21] |
| Reversed-phase (20 mmol/L potassium dihydrogen phosphate in water/acetonitrile (65:35, v/v) adjusted to pH 6.9 using 10 wt % potassium hydroxide) | Run time: 25 min. | ||||
| HPLC | Chirosil RCA(+) 250 × 4.6 mm; | >2.0 | Not available | ~20 min. | [22] |
| Polar organic phase (ethanol/acetonitrile/acetic acid/triethylamine (80:20:0.2:0.3, v/v/v/v)) | |||||
| UHPLC | Chiralpak® AGP 50 × 2.0 mm | 2.9 | 0.06 μg/mL; 0.20 μg/mL | MS-compatible, rapid analysis, easy to stabilize the LC system compared to other normal phase [20] and reversed-phase [21] methods. | Present work |
| Reversed phase (ammonium acetate/isopropyl alcohol (90:10, v/v)) | Run time: 15 min. |
| % RSD of Peak Area | ||
| Inj. No. | S-Rasagiline (RAS-III) (1.5 μg/mL) | Criteria |
| 1 | 24,865 | ≤5% |
| 2 | 24,510 | |
| 3 | 24,279 | |
| 4 | 23,787 | |
| 5 | 22,957 | |
| 6 | 24,881 | |
| Mean | 24,213 | |
| SD | 738 | |
| % RSD | 3.0 | |
| Resolution between RAS-III and R-Rasagiline (RAS) | ||
| Inj. No. | Resolution | Criteria |
| 1 | 2.9 | ≥1.5 |
| K Prime (Retention Factor) | ||
| Inj. No. | S-Rasagiline (RAS-III) | S-Rasagiline (RAS-III) Repeatability of K |
| 1 | 8.9 | 8.8 |
| Peak Symmetry Factor | ||
| Inj. No. | S-Rasagiline (RAS-III) | R-Rasagiline (RAS) |
| 1 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| Inj. No. | Selectivity | |
| 1 | 2.9 | |
| Preparation No. | RAS-III Content (1.5 μg/mL) | RAS-III Content (1.5 μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Method Precision | Intermediate Precision | |
| 1 | 0.145 | 0.151 |
| 2 | 0.147 | 0.152 |
| 3 | 0.149 | 0.150 |
| 4 | 0.150 | 0.153 |
| 5 | 0.150 | 0.149 |
| 6 | 0.151 | 0.148 |
| Mean | 0.148 | 0.150 |
| % RSD | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| Sample No. | % Level | Concentration (μg/mL) | Peak Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LOQ | 0.20 | 3349.00 |
| 2 | 50 | 0.75 | 12,560.50 |
| 3 | 80 | 1.20 | 20,096.80 |
| 4 | 100 | 1.50 | 25,121.00 |
| 5 | 120 | 1.70 | 30,145.20 |
| 6 | 150 | 2.25 | 37,681.50 |
| Accuracy Level | Spiked Amount (wt %) | Mean Content (wt %) | Content in Spiked Sample (wt %) | Recovered Content (wt) | % Recovery | Mean % Recovery | % RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOQ-1 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 100.000 | 100.00 | 0.00 |
| LOQ-2 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 100.000 | |||
| LOQ-3 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 100.000 | |||
| 50%-1 | 0.074 | 0.004 | 0.075 | 0.071 | 95.945 | 95.93 | 0.03 |
| 50%-2 | 0.073 | 0.074 | 0.070 | 95.890 | |||
| 50%-3 | 0.074 | 0.075 | 0.071 | 95.945 | |||
| 100%-1 | 0.147 | 0.004 | 0.144 | 0.140 | 95.238 | 95.48 | 0.40 |
| 100%-2 | 0.147 | 0.145 | 0.141 | 95.918 | |||
| 100%-3 | 0.148 | 0.145 | 0.141 | 95.270 | |||
| 150%-1 | 0.222 | 0.004 | 0.215 | 0.211 | 95.045 | 95.19 | 1.18 |
| 150%-2 | 0.221 | 0.217 | 0.213 | 96.380 | |||
| 150%-3 | 0.222 | 0.213 | 0.209 | 94.144 |
| Accuracy Level | Spiked Amount (wt %) | Mean Content (wt %) | Content in Spiked Sample (wt %) | Recovered Content (wt) | % Recovery | Mean % Recovery | % RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOQ-1 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 100.000 | 100.0 | 0.00 |
| LOQ-2 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 100.000 | |||
| LOQ-3 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 100.000 | |||
| 50%-1 | 0.072 | 0.001 | 0.067 | 0.066 | 91.666 | 91.59 | 0.07 |
| 50%-2 | 0.071 | 0.066 | 0.065 | 91.549 | |||
| 50%-3 | 0.071 | 0.066 | 0.065 | 91.549 | |||
| 100%-1 | 0.143 | 0.001 | 0.135 | 0.134 | 93.706 | 93.47 | 0.43 |
| 100%-2 | 0.143 | 0.134 | 0.133 | 93.006 | |||
| 100%-3 | 0.143 | 0.135 | 0.134 | 93.706 | |||
| 150%-1 | 0.215 | 0.001 | 0.198 | 0.197 | 91.627 | 92.24 | 1.60 |
| 150%-2 | 0.214 | 0.202 | 0.201 | 93.925 | |||
| 150%-3 | 0.215 | 0.197 | 0.196 | 91.162 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balaji, N.; Sultana, S. Reversed-Phase UHPLC Enantiomeric Separation of Rasagiline Salts Using a Chiralpak® AGP Column. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 85, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85030026
Balaji N, Sultana S. Reversed-Phase UHPLC Enantiomeric Separation of Rasagiline Salts Using a Chiralpak® AGP Column. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2017; 85(3):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85030026
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalaji, Nagarajan, and Sayeeda Sultana. 2017. "Reversed-Phase UHPLC Enantiomeric Separation of Rasagiline Salts Using a Chiralpak® AGP Column" Scientia Pharmaceutica 85, no. 3: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85030026
APA StyleBalaji, N., & Sultana, S. (2017). Reversed-Phase UHPLC Enantiomeric Separation of Rasagiline Salts Using a Chiralpak® AGP Column. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 85(3), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm85030026






