Investigation of the Bioequivalence of Rosuvastatin 20 mg Tablets after a Single Oral Administration in Mediterranean Arabs Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Volunteers and Clinical Protocol
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Tested Brand and Formulated Tablets
2.4. Instruments and Chromatographic Separations
2.5. Preparation of Standard and Working Solutions
2.6. Validation Procedures
2.7. In Vitro Release of RC from Tablets
2.8. Pharmacokinetic and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Validation Procedures
3.2. Results of Dissolution Testing
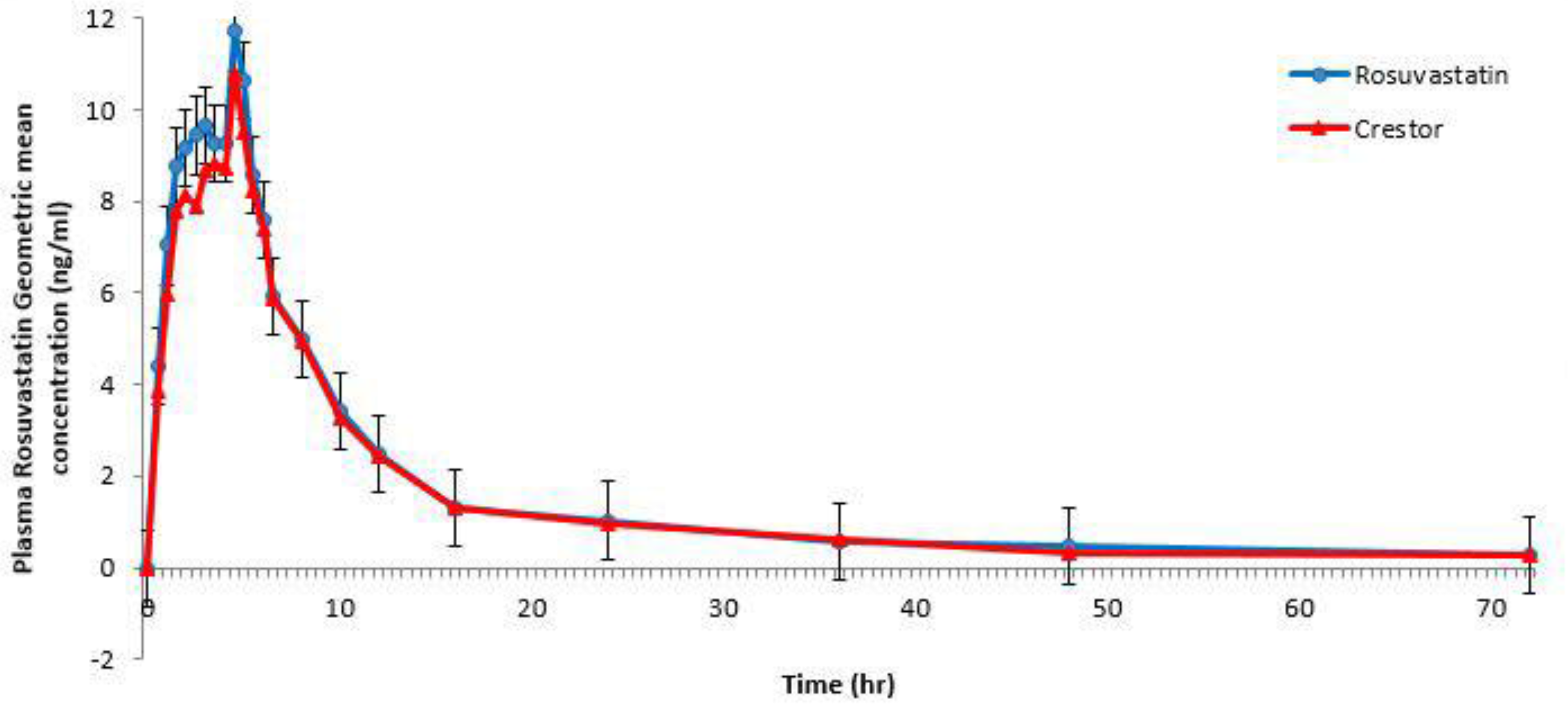
3.3. Results of the Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Food and, Drug Administration. Crestor (rosuvastatin calcium) Tablets. Prescribing Information Label. 2012. Available online: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/021366s026lbl.pdf (accessed on 22 Feburary 2015). [Google Scholar]
- RXList. Crestor. 2013. Available online: http://www.rxlist.com/crestor-drug.htm (accessed on 20 March 2015).
- White, C.M. A review of the pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic aspects of rosuvastatin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.H. Rosuvastatin: A highly efficacious statin for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2002, 11, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.D.; Mitchell, P.D.; Schneck, D.W. Pharmacodynamic effects and pharmacokinetics of a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, rosuvastatin, after morning or evening administration in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.K.; Shah, V.D. Simultaneous uvspectrophotometric estimation of rosuvastatin and ezetimibe in their combined dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 2, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Devika, G.S.; Sudhakar, M.; Venkateshwara, R.J. A new improved RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of rosuvastatin calcium and fenofibrate in tablets. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, F.; Bartunek, A.; Vlavonou, R.; Navratilova, L.; Dube, C.; Tanguay Mm Hauser, T. Single-dose, 2-way crossover, bioequivalence study of two rosuvastatin formulations in normal healthy subjects under fasting conditions. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 50, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliepaard, M.; Nofziger, C.; Papaluca, M.; Zineh, I.; Uyama, Y.; Prasad, K.; Grimstein, C.; Pacanowski, M.; Ehmann, F.; Dossena, S.; et al. Pharmacogenetics in the evaluation of new drugs: A multiregional regulatory perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesko, L.J.; Woodcock, J. Translation of pharmacogenomics and pharmacogenetics: A regulatory perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varenhorst, C.; Eriksson, N.; Johansson, Å.; Barratt, B.J.; Hagström, E.; Åkerblom, A.; Syvänen, A.C.; Becker, R.C.; James, S.K.; Katus, H.A.; et al. Effect of genetic variations on ticagrelor plasma levels and clinical outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 6, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krintel, S.B.; Dehlendorff, C.; Hetland, M.L.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Andersen, K.K.; Junker, P.; Pødenphant, J.; Ellingsen, T.; Ahlquist, P.; Lindegaard, H.M.; et al. Prediction of treatment response to adalimumab: A double-blind placebo-controlled study of circulating microRNA in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. J. 2016, 16, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De VriesSchultink, A.H.; Zwart, W.; Linn, S.C.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D. Effects of Pharmacogenetics on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Tamoxifen. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajinami, K.; Akao, H.; Polisecki, E.; Schaefer, E.J. Pharmacogenomics of statin responsiveness. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Lui, S.S.; Mak, V.W.; Chu, T.T.; Lee, V.W.; Poon, E.W.; Tsui, T.K.; Ko, G.T.; Baum, L.; Tam, L.S.; et al. Pharmacogenetic analysis of lipid responses to rosuvastatin in Chinese patients. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2010, 20, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Ryan, S.; Birmingham, B.; Zalikowski, J.; March, R.; Ambrose, H. Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in white and Asian subjects residing in the same environment. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 78, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birmingham, B.K.; Bujac, S.R.; Elsby, R.; Azumaya, C.T.; Zalikowski, J.; Chen, Y.; Kim, K.; Ambrose, H.J. Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in Caucasian and Asian subjects residing in the United States. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AstraZeneca Canada Inc. Product Monograph; Crestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) Tablets 5, 10, 20 and 40 mg. 2012. Available online: http://hcp.crestor.ca/crestorhcp/documents/Crestor_PM_en.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2015).
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsiniki as Amended by the 59th World Medical Assembly; WMA: Seoul, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Note for Guidance on Good Clinical Practice; CPMP/ICH/135/95; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ICH harmonization tripartite guideline. Guidelines for good clinical practice. J. Postgrad. Med. 2001, 47, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Statistical Approaches to Establishing Bioequivalence; Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- European Medical Agency. Guideline on the Investigation of Bioequivalence; CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98; Rev. 1/Corr; European Medical Agency: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/dissolution/dsp_getallData.cfm (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Emami, J. In vitro—In vivo correlation: From theory to applications. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 9, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, D. Dissolution method development for immediate release solid oral dosage forms. Dissolution Technol. 2005, 12, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R.; Shah, D.R. Personalized medicine: Is it a pharmacogenetic mirage? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 698–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.; Roh, H.; Lee, D.; Chang, H.; Kim, J.; Yun, C.; Park, K. Pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin/olmesartan fixed-dose combination: A single-dose, randomized, open-label, 2-period crossover study in healthy Korean subjects. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, B.N.; He, Y.J.; Fan, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.L.; Tan, Z.R.; Jiang, F.; et al. Role of BCRP 421C>A polymorphism on rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese males. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2006, 373, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mobile Phase | Buffer Solution Preparation: Transfer 10 mL of Glacial Acetic Acid by Using a Volumetric Pipette in 5000 mL of Water. Mobile Phase Preparation: Mix 4500 mL of Buffer with 2500 mL of Methanol and 3000 mL of Acetonitrile. |
| Diluent | Dissolution media: 0.05 M of sodium citrate pH 6.6 (dissolve 74.9 g of sodium citrate and 45.9 g sodium chloride in 7000 mL of purified water, add 28 g sodium hydroxide and stir until dissolved and check pH). Adjust pH to 6.6 with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid. |
| HPLC | Shimadzu system (Shimadzu corporation, Kyoto, Japan) |
| Column | Inertsil ODS-2 (25 cm × 4.6 mm) 5 μm. |
| Detector | UV detector @ 248 nm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 mL/min |
| Injection Volume | 20 μL |
| Column Oven Temperature | 25 °C |
| Standard Solution Preparation | Standard solution contains: 0.0222 mg/mL of rosuvastatin. |
| Sample Solution Preparation | After the end of the run or at a certain sampling time point, withdraw 10 mL from each vessel and filter through a 0.45 μm filter. |
| Run Time | 15 min |
| Filter | a. 0.45 μm PTFE (saturate the filter, discard the first 3 mL from the standard solution). b. 0.45 μm nylon (saturate the filter, discard the first 3 mL from the standard solution). |
| Short-Term Stability (Plasma) | Up to 24 h at RT. | |
| Short-Term Stability (Stock Solution) | Up to 20 h at RT (for RC and rosuvastatin-d6). | |
| FTC Stability | Up to 4 cycles at −70 °C. Up to 4 cycles at −20 °C. | |
| Long-Term Stability (Stock Solution) | Up to 30 days for RC and rosuvastatin-d6 at −20°C. | |
| Long-Term Stability (Plasma) | Up to 60 days at −70 °C. Up to 60 days at −20 °C. | |
| Post-Preparative | Injection Phase | Up to 44 h at 5 °C. Up to 44 h at −20 °C. |
| Dry Phase | ||
| Whole Blood Stability | % of change between QCL and QCH = −0.48 | |
| Matrix-Dilution Integrity | Samples above ULOQ (46.840 ng/mL) and up to 140.520 ng/mL can be diluted with a dilution factor of 3. | |
| Matrix Effect | CV% of rosuvastatin-d6 normalized was 8.75% and 1.93%. | |
| Efficacy Results Summary | Parameters (unit) | Test Rosuvastatin | Reference Crestor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As Geometric Means (Ranges) for Cmax and AUC Ratios | Cmax (ng/mL) | 12.059 | 11.194 | ||
| 5.973 | 37.323 | 3.495 | 35.545 | ||
| AUC0→last (ng·h/mL) | 104.263 | 100.635 | |||
| 40.335 | 254.681 | 30.152 | 263.448 | ||
| AUC0→∞ (ng·h/mL) | 110.786 | 106.294 | |||
| 42.642 | 267.086 | 33.354 | 271.362 | ||
| As Medians (Ranges) for tmax and t1/2 | tmax (h) | 4.50 | 4.50 | ||
| 0.50 | 5.50 | 0.50 | 5.0 | ||
| t1/2 (h) | 6.80 | 7.73 | |||
| 4.87 | 21.07 | 3.34 | 22.26 | ||
| Bioequivalence Results Summary | Parameter | Point estimate (ratio of geometric mean %) | Lower limit % | Upper limit % | CV% |
| Cmax | 107.73 | 96.57 | 120.17 | 23.34 | |
| AUC0→last | 103.61 | 94.03 | 114.16 | 20.66 | |
| AUC0→∞ | 104.23 | 94.84 | 114.54 | 20.09 | |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | J | K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0→t (ng·h/mL) Gmean Ratio * | 202 1.74 | 207 1.79 | 213 1.84 | 146 1.26 | 191 1.64 | 205 1.76 | 193 1.66 | 116 1.00 | 104 0.90 | 101 0.87 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) Gmean Ratio* | 22.0 1.85 | 22.4 1.89 | 23.3 1.97 | 15.3 1.29 | 20.5 1.72 | 20.2 1.7 | 23.6 1.98 | 11.9 1.00 | 12.1 1.02 | 11.2 0.94 |
| tmax (h) Median | 4.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.54 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 4.50 | 4.50 | 4.50 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaid, A.N.; Al Ramahi, R.; Cortesi, R.; Mousa, A.; Jaradat, N.; Ghazal, N.; Bustami, R. Investigation of the Bioequivalence of Rosuvastatin 20 mg Tablets after a Single Oral Administration in Mediterranean Arabs Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Sci. Pharm. 2016, 84, 536-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm84030536
Zaid AN, Al Ramahi R, Cortesi R, Mousa A, Jaradat N, Ghazal N, Bustami R. Investigation of the Bioequivalence of Rosuvastatin 20 mg Tablets after a Single Oral Administration in Mediterranean Arabs Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2016; 84(3):536-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm84030536
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaid, Abdel Naser, Rowa Al Ramahi, Rita Cortesi, Ayman Mousa, Nidal Jaradat, Nadia Ghazal, and Rana Bustami. 2016. "Investigation of the Bioequivalence of Rosuvastatin 20 mg Tablets after a Single Oral Administration in Mediterranean Arabs Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method" Scientia Pharmaceutica 84, no. 3: 536-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm84030536
APA StyleZaid, A. N., Al Ramahi, R., Cortesi, R., Mousa, A., Jaradat, N., Ghazal, N., & Bustami, R. (2016). Investigation of the Bioequivalence of Rosuvastatin 20 mg Tablets after a Single Oral Administration in Mediterranean Arabs Using a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 84(3), 536-546. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm84030536







