Factors Influencing Green Innovation Adoption and Its Impact on the Sustainability Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Hypothesis Development
3.1. Impact of GS on the GIA
3.2. Impact of EPC on the GIA
3.3. Impact of RR on the GIA
3.4. Impact of MC on the GIA
3.5. Impact of OH on the GIA
3.6. Impact of GIS on the GIA
3.7. Impact of TF on the GIA
3.8. Impact of GIA on the EP
3.9. Impact of GIA on the SP
3.10. Impact of GIA on the ENP
4. Enterprise Profile
5. Methods of Data Collection, Instruments, Sampling Procedures, and Statistical Techniques
Research Design
6. Data Collection
Research Instrument, Reliability, and Convergent Validity
7. Data Analysis
8. Results and Discussion
8.1. Data Analysis, Results, and Hypothesis Testing
8.2. Measurement Model Assessment
8.3. Measurement Model
8.4. Structural Model Assessment
8.5. Hypotheses Testing
9. Conclusions and Policy Implications
10. Limitations and Future Scope of Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leonidou, L.C.; Christodoulides, P.; Kyrgidou, L.P.; Palihawadana, D. Internal drivers and performance consequences of small firm green business strategy: The moderating role of external forces. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 140, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soewarno, N.; Tjahjadi, B.; Fithrianti, F. Green innovation strategy and green innovation: The roles of green organizational identity and environmental organizational legitimacy. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 3061–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Wang, R.; Chiu, A.S.F.; Geng, Y.; Lin, Y.H. Improving performance of green innovation practices in uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 40, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y. Impacts of green finance on green innovation: A spatial and nonlinear perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 32548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangmee, C.; Dacko-Pikiewicz, Z.; Meekaewkunchorn, N.; Kassakorn, N.; Khalid, B. Green entrepreneurial orientation and green innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Soc. Sci. 2021, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Khan, A.; Yahya, S.; Zafar, A.U.; Shahzad, M. Green core competencies to prompt green absorptive capacity and bolster green innovation: The moderating role of organization’s green culture. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 65, 536–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Arif, H.; Sahar, N.E.; Ali, A.; Abbasi, M.A. The role of financial resources in SMEs’ financial and environmental performance; the mediating role of green innovation. Green Financ. 2022, 4, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albort-Morant, G.; Henseler, J.; Leal-Millán, A.; Cepeda-Carrión, G. Mapping the field: A bibliometric analysis of green innovation. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albort-Morant, G.; Leal-Millán, A.; Cepeda-Carrión, G. The antecedents of green innovation performance: A model of learning and capabilities. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 4912–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, C.; Gavilan, D.; García-Madariaga, J.; Gonçalves, H.M. Green Consumer Segmentation: Managerial and Environmental Implications from the Perspective of Business Strategies and Practices. In Sustainability in Innovation and Entrepreneurship; Leal-Millan, A., Peris-Ortiz, M., Leal-Rodríguez, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 137–151. [Google Scholar]
- Anazonwu, H.O.; Egbunike, F.C.; Gunardi, A. Corporate board diversity and sustainability reporting: A study of selected listed manufacturing firms in Nigeria. Indones. J. Sustain. Account. Manag. 2018, 2, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bø, E.; Hammervoll, T.; Tvedt, K. Environmental impact of refillable vs. non-refillable plastic beverage bottles in Norway. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 12, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Yi, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. Does institutional pressure foster corporate green innovation? Evidence from China’s top 100 companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1st Voluntary National Review “Transformation Towards Sustainable and Resilient Societies”, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia UN High-Level Political Forum 2018, 9–18 July 2018, New York. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/20230SDGs_English_Report972018_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Song, W.; Yu, H. Green innovation strategy and green innovation: The roles of green creativity and green organizational identity. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2018, 25, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alraja, M.N.; Imran, R.; Khashab, B.M.; Shah, M. Technological Innovation, Sustainable Green Practices and SMEs Sustainable Performance in Times of Crisis (COVID-19 pandemic). Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 24, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Khan, M.A.S.; Anwar, F.; Shahzad, F.; Adu, D.; Murad, M. Green innovation practices and its impacts on environmental and organizational performance. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Jiang, D.; Wang, T. The impact of green innovation on manufacturing small and medium enterprises corporate social responsibility fulfilment: The moderating role of regional environmental regulation. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 712–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zou, F.; Zhang, P. The role of innovation for performance improvement through corporate social responsibility practices among small and medium-sized suppliers in China. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Nilashi, M.; Safaei, M.; Abdullah, R.; Saeed, F.; Yadegaridehkordi, E.; Samad, S. Investigating factors influencing decision-makers’ intention to adopt Green IT in Malaysia manufacturing industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 148, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W.; Ali, W.; Bhutto, M.Y.; Hussain, H.; Khan, N.A. Examining the determinants of green innovation adoption in SMEs: A PLS-SEM approach. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Scandurra, G.; Carfora, A. Adoption of green innovations by SMEs: An investigation about the influence of stakeholders. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 25, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Ahmad, H.; Rehman, F.U.; Fawad, A. Green innovation and Sustainable Development Goals in SMEs: The moderating role of government incentives. J. Econ. Adm. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zeng, S.; Sheng, S.; Gong, S. Green innovation and brand equity: Moderating effects of industrial institutions. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2021, 38, 573–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Pourhashemi, S.O.; Nilashi, M.; Abdullah, R.; Samad, S.; Yadegaridehkordi, E.; Razali, N.S. Investigating influence of green innovation on sustainability performance: A case on Malaysian hotel industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Spalanzani, A. Sustainability of manufacturing and services: Investigations for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, C. Towards green trust: The influences of green perceived quality, green perceived risk, and green satisfaction. Manag. Decis. 2013, 51, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Nowakowska-Grunt, J.; Gorbanyov, V.; Egorova, M. Green Technology and Sustainable Development: Assessment and Green Growth Frameworks. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y. Critical success factors of green innovation: Technology, organization and environment readiness. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, A.; Moreno-Mondéjar, L.; Davia, M.A. Drivers of different types of eco-innovation in European SMEs. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 92, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeshen, Y.; Soomro, Y.A.; Bhutto, M.Y. Determinants of Green Innovation to Achieve Sustainable Business Performance: Evidence from SMEs. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 767968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, S.; Nawaz, M.S.; Naz, S. Effects of innovation types on firm performance: An empirical study on Pakistan’s manufacturing sector. Pak. J. Commer. Soc. Sci. PJCSS 2013, 7, 243–262. [Google Scholar]
- Keremidchiev, S. Theoretical Foundations of Stakeholder Theory. Econ. Stud. J. 2021, 30, 70–88. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.W.; Xie, Y.; Shahab, S.; Faisal, C.; Nadeem, M.; Hafeez, M.; Qamri, G.M. Towards achieving sustainable development: Role of technology innovation, technology adoption and CO2 emission for BRICS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Badir, Y.; Chonglerttham, S. Green innovation and performance: Moderation analyses from Thailand. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 22, 446–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiganjo, M.; Godinic, D.; Obrenovic, B. Strategic Planning and Sustainable Innovation during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Literature Review. Int. J. Innov. Econ. Dev. 2021, 7, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.L.; Cullen, R.; Grout, R. Adoption of environmental innovations: Analysis from the Waipara wine industry. Wine Econ. Policy 2013, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Liu, L. Customer participation, and green product innovation in SMEs: The mediating role of opportunity recognition and exploitation. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 119, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S. The driver of green innovation and green image–green core competence. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 81, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lai, S.B.; Wen, C.T. The influence of green innovation performance on corporate advantage in Taiwan. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrini, F. SMEs and CSR theory: Evidence and implications from an Italian perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, L.J. CSR and small business in a European policy context: The five “C” s of CSR and small business research agenda 2007. Bus. Soc. Rev. 2007, 112, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffen, C.A.; Rothenberg, S. Suppliers and environmental innovation: The automotive paint process. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2000, 20, 166–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepoutre, J.; Heene, A. Investigating the impact of firm size on small business social responsibility: A critical review. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.K.; Smith, H.L. Social responsibility and small business: Suggestions for research. J. Small Bus. Manag. 1991, 29, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Chandrashekar, D.; Hillemane, B.S.M.; Sukumar, A.; Jafari-Sadeghi, V. Network cooperation and economic performance of SMEs: Direct and mediating impacts of innovation and internationalisation. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 148, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, M.; Della Peruta, M.R. The impact of IT-based knowledge management systems on internal venturing and innovation: A structural equation modeling approach to corporate performance. J. Knowl. Manag. 2016, 20, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, M.; Soto-Acosta, P.; Carayannis, E.; Scuotto, V. Emerging perspectives on business process management (BPM): IT-based processes and ambidextrous organizations, theory and practice. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2018, 24, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, R. Eco-Innovation: Definition, measurement and open research issues. Econ. Politica 2010, 27, 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- Aboelmaged, M.; Hashem, G. Absorptive capacity and green innovation adoption in SMEs: The mediating effects of sustainable organisational capabilities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afum, E.; Osei-Ahenkan, V.Y.; Agyabeng-Mensah, Y.; Owusu, J.A.; Kusi, L.Y.; Ankomah, J. Green manufacturing practices and sustainable performance among Ghanaian manufacturing SMEs: The explanatory link of green supply chain integration. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 1457–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderman, C.J.; van Hal, L.; Lambrechts, W.; Schijns, J. The impact of buying power on corporate sustainability-The mediating role of suppliers’ traceability data. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2021, 3, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, W.B.; Hikkerova, L.; Sahut, J.M. External knowledge sources, green innovation and performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 129, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.; Hou, P. Impacts of government subsidies for environmental-friendly products in a dual-channel supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1558–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Ho, Y.H. Determinants of Green Practice Adoption for Logistics Companies in China. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 98, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, G. The Impact of Government Subsidies on Private R&D Investment in Different Markets. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Del Giudice, M.; Chierici, R.; Graziano, D. Green innovation and environmental performance: The role of green transformational leadership and green human resource management. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 150, 119762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamvada, M. Corporate social responsibility and accountability: A new theoretical foundation for regulating CSR. Int. J. Corp. Soc. Responsib. 2020, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, S.; Khan, F.U.; Ahmad, N. Promoting sustainability through green innovation adoption: A case of manufacturing industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 21119–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cainelli, G.; Mazzanti, M.; Montresor, S. Environmental innovations, local networks an internationalization. Ind. Innov. 2012, 19, 697–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J.; Lai, K.H. Confirmation of a measurement model for green supply chain management practices implementation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggoner, D.B.; Neely, A.D.; Kennerley, M.P. The forces that shape organisational performance measurement systems: An interdisciplinary review. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1999, 60, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Dou, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, N. The effects of firm capabilities on external collaboration and performance: The moderating role of market turbulence. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsawan, I.W.E.; Koval, V.; Duginets, G.; Kalinin, O.; Korostova, I. The impact of green innovation on environmental performance of SMEs in an emerging economy. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2021; Volume 255, p. 01012. [Google Scholar]
- Dyllick, T.; Hockerts, K. Beyond the business case for corporate sustainability. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 11, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Salmador, M.P.; Li, D.; Lloria, M.B. Green entrepreneurship and SME performance: The moderating effect of firm age. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2021, 18, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisetti, C.; Mancinelli, S.; Mazzanti, M.; Zoli, M. Financial barriers and environmental innovations: Evidence from EU manufacturing firms. Clim. Policy 2017, 17, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Q.; Liu, J.; Herndon, N.C. SHRM and product innovation: Testing the moderating effects of organizational culture and structure in Chinese firms. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2011, 22, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeck, H.; Diehl, M.R. A literature review on HRM and innovation–taking stock and future directions. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2017, 28, 913–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, Z. The driving effect of internal and external environment on green innovation strategy-The moderating role of top management’s environmental awareness. Nankai Bus. Rev. Int. 2019, 10, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiadat, Y.; Kelly, A.; Roche, F.; Eyadat, H. Green and competitive? An empirical test of the mediating role of environmental innovation strategy. J. World Bus. 2008, 43, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Shabbir, M.S.; Haseeb, M.; Kamal, M.; Anwar, A.; Khan, M.F.; Malik, S. The dynamic effect of information and communication technology and renewable energy on CO2 emission: Fresh evidence from panel quantile regression. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shen, N.; Ying, H.; Wang, Q. Can environmental regulation directly promote green innovation behavior? based on situation of industrial agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Research on the impact mechanism of green finance on the green innovation performance of China’s manufacturing industry. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2022, 43, 2678–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaohong, X.; Qinghong, T.; Zhanjie, W. Can stakeholder′ environmental orientation promote green innovation? A moderated mediation models. Sci. Res. Manag. 2021, 42, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, Y.X.; Yen, S.Y. Top-management’s role in adopting green purchasing standards in high-tech industrial firms. J. Bus. Res. 2012, 65, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; Yan, W. Impact of green finance and environmental regulations on the green innovation efficiency in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.Q.; Phuong, N.V. The Impact of External Environment, Technology and Innovation Capacities, and Leadership Development on Organizational Performance in Food Industry: A Qualitative Study of Food Enterprises in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Int. J. Bus. Humanit. Technol. 2021, 3, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Voulvoulis, N.; Burgman, M.A. The contrasting roles of science and technology in environmental challenges. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Itoo, H.H.; Dar, J.A. On the environmental effects of development and non-development expenditure in India: Evidence from an asymmetric ARDL model. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2022, 31, 835–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.; Ajaz, T.; Andlib, Z.; Chau, K.Y.; Ahmad, P.; Sharif, A. The role of technology innovation, renewable energy and globalization in reducing environmental degradation in Pakistan: A step towards sustainable environment. Renew. Energy 2021, 177, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoo, H.H.; Ali, N. Analyzing the causal nexus between CO2 emissions and its determinants in India: Evidences from ARDL and EKC approach. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2022, 34, 192–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Obrenovic, B.; Du, J.; Godinic, D.; Khudaykulov, A. COVID-19 Pandemic Implications for Corporate Sustainability and Society: A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttol, P.; Buonamici, R.; Naldesi, L.; Rinaldi, C.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P. Integrating services and tools in an ICT platform to support eco-innovation in SMEs. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2012, 14, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilar, P.G.; Marta, A.P.; Antonio, A. Profit efficiency and its determinants in small and medium-sized enterprises in Spain. BRQ Bus. Res. Q. 2018, 21, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J. Relationships between operational practices and performance among early adopters of green supply chain management practices in Chinese manufacturing enterprises. J. Oper. Manag. 2004, 22, 265–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, J.; Panwar, R.; Jorge, R. Toward a place-based understanding of business sustainability: The role of green competitors and green locales in firms’ voluntary environmental engagement. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 940–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.; Inman, R. Using a just-in-time selling strategy to strengthen supply chain linkages. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2005, 43, 3437–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; He, B. Measuring incoordination-adjusted sustainability performance during the urbanization process: Spatial-dimensional perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Byl, C.A.; Slawinski, N. Embracing tensions in corporate sustainability: A review of research from win-wins and trade-offs to paradoxes and beyond. Organ. Environ. 2015, 28, 54–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, J.-F.; Journeault, M. Eco-efficiency and organizational practices: An exploratory study of manufacturing firms. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2009, 27, 894–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; Cagno, E.; Di Sebastiano, G.; Trianni, A. Industrial sustainability: Modelling drivers and mechanisms with barriers. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 452–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Usman, M.; Jahanger, A.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Revisiting the role of fiscal policy, financial development, and foreign direct investment in reducing environmental pollution during globalization mode: Evidence from linear and nonlinear panel data approaches. Energies 2021, 14, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, P.; Pérez, A.; Rodríguez del Bosque, I. Measuring corporate social responsibility in tourism: Development and validation of an efficient measurement scale in the hospitality industry. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2013, 30, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, L.C.; Searcy, C. An analysis of indicators disclosed in corporate sustainability reports. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 20, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, D.K.; Li, X.L.; Huang, S. Financial deregulation and operational risks of energy enterprise: The shock of liberalization of bank lending rate in China. Energy Econ. 2021, 93, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L.; Milstein, M.B. Creating sustainable value. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2003, 17, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H. The influence of corporate environmental ethics on competitive advantage: The mediation role of green innovation. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 104, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, B.; Cankaya, S.Y. Effects of green manufacturing and eco-innovation on sustainability performance. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 99, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M. ‘Green’ human resource benefits: Do they matter as determinants of environmental management system implementation? J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 114, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.; Chugan, P.K. Green HRM in pursuit of environmentally sustainable business. Pursuit of Environmentally Sustainable Business. Univers. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2015, 3, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Antón, J.M.; del Mar Alonso-Almeida, M.; Celemín, M.S.; Rubio, L. Use of different sustainability management systems in the hospitality industry. The case of Spanish hotels. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 22, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, B.F.; Bishop, J.W.; Massoud, J.A. The role of training and empowerment in environmental performance: A study of the Mexican maquiladora industry. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2012, 32, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montabon, F.; Sroufe, R.; Narasimhan, R. An examination of corporate reporting, environmental management practices and firm performance. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 998–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. How to write up and report PLS analyses. In Handbook of Partial Least Squares; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010; pp. 655–690. [Google Scholar]
- Fahad, S.; Alnori, F.; Su, F.; Deng, J. Adoption of green innovation practices in SMEs sector: Evidence from an emerging economy. Econ. Res. Ekon. Istraživanja 2022, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, A.; Nordin, N.; Khan, R.U. Does government support enhance the relation between networking structure and sustainable competitive performance among SMEs? J. Innov. Entrep. 2020, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Shin, K.; Kim, S.; Kim, E. What Types of Government Support on Food SMEs Improve Innovation Performance? Sustainability 2021, 13, 9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Asheq, A.; Hossain, M.U. SME performance: Impact of market, customer and brand orientation. Acad. Mark. Stud. J. 2019, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chege, S.M.; Wang, D.; Suntu, S.L. Impact of information technology innovation on firm performance in Kenya. Inf. Technol. Dev. 2020, 26, 316–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P.; Fischer, A.; Nitzl, C.; Menictas, C. Partial least squares structural equation modeling-based discrete choice modeling: An illustration in modeling retailer choice. Bus. Res. 2019, 12, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geisser, S. The predictive sample reuse method with applications. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1975, 70, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.C.; Ding, J.H.; Chen, P.S. The effects of GSCM drivers and institutional pressures on GSCM practices in Taiwan’s textile and apparel industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 135, 618–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercantan, O.; Eyupoglu, S. How Do Green Human Resource Management Practices Encourage Employees to Engage in Green Behavior? Perceptions of University Students as Prospective Employees. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Zailani, S.; Iranmanesh, M.; Jayaraman, K. Barriers to green innovation initiatives among manufacturers: The Malaysian case. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2016, 10, 683–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.; Tilt, C.; Qian, W. Factors influencing sustainability reporting by Sri Lankan companies. Pac. Account. Rev. 2019, 31, 84–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.K.; Yee, R.W.; Dai, J.; Lim, M.K. The moderating effect of environmental dynamism on green product innovation and performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 181, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



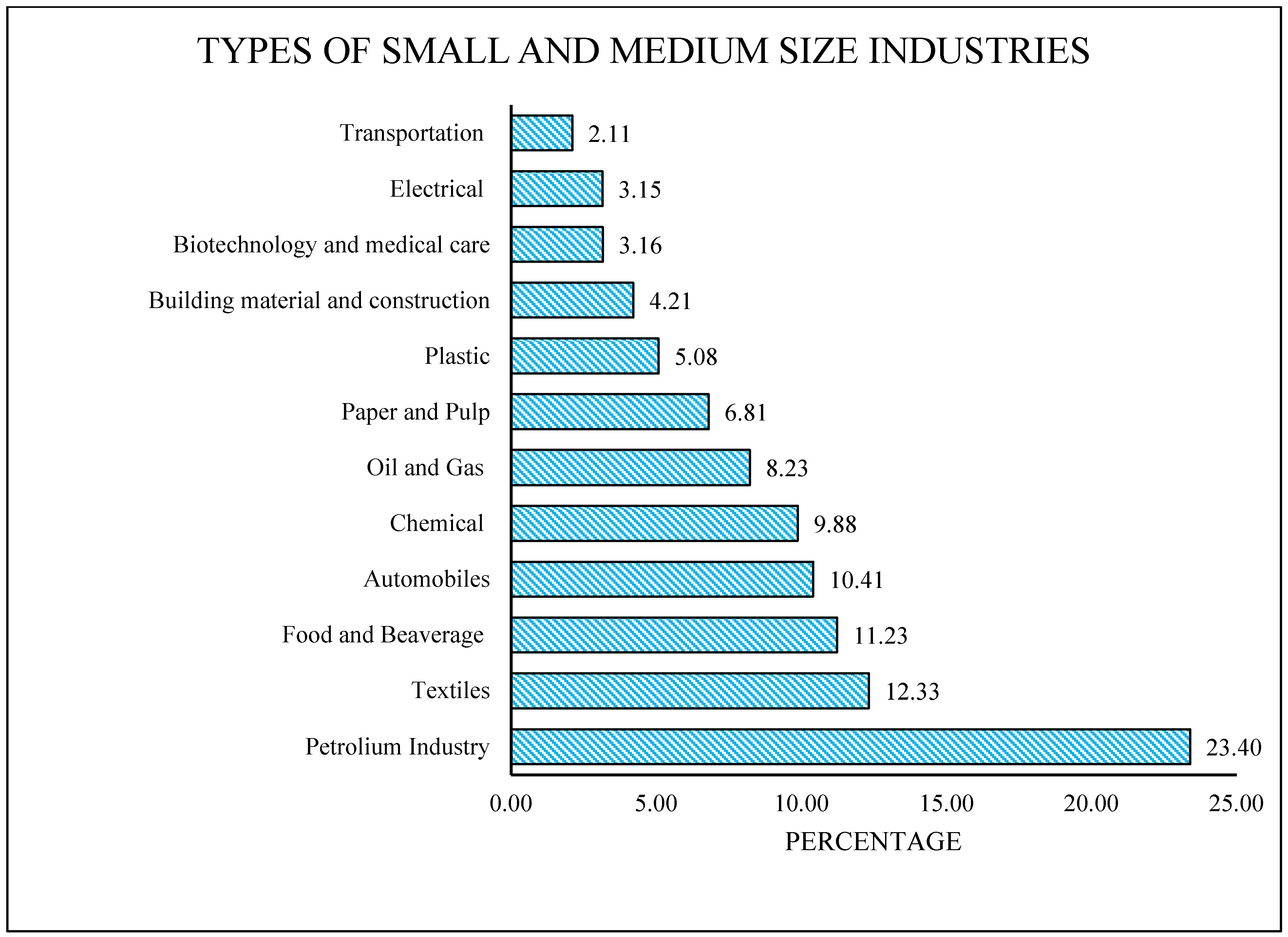

| Variable | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 55.33 |
| Female | 44.67 |
| Age | |
| Less than 30 | 23.71 |
| 30–40 | 29.18 |
| 40–50 | 31.22 |
| Above 50 | 15.89 |
| Positions | |
| CEO | 26.63 |
| Director | 25.86 |
| Manager | 15.77 |
| Executive | 16.23 |
| Supervisor | 12.69 |
| Other | 2.82 |
| Ownership Structure of Enterprise | Percentage |
|---|---|
| State-owned or state holding enterprise | 11.54 |
| Private/own enterprise | 51.79 |
| Joint venture | 36.67 |
| Number of years operating | - |
| Less than 5 | 32.47 |
| 5–10 | 30.98 |
| 11–15 | 16.51 |
| 16–20 | 14.69 |
| Above 20 | 5.34 |
| Number of employees | - |
| 1–5 | 6.33 |
| 6–10 | 9.11 |
| 11–30 | 24.32 |
| 31–50 | 25.15 |
| 51–100 | 22.14 |
| More than 100 but fewer than 300 | 12.17 |
| More than 300 | 0.77 |
| Constructs | Items | Mean | SD | LF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Innovation Adoption (GIA) | GIA-1: Materials that consume less energy and emit the least amount of pollutants are used in the production process. | 3.542 | 0.934 | 0.792 |
| GIA-2: The item is simple to disassemble, recycle, and reuse. | 3.522 | 0.992 | 0.701 | |
| GIA-3: The manufacturing process lowers hazardous substances and recycles trash. | 3.389 | 0.981 | 0.707 | |
| GIA-4: The least quantity of materials are used. | 3.552 | 0.970 | 0.737 | |
| Government Support (GS) | GS-1: The government assists the practice with financial/technical assistance and logistical skills. | 3.517 | 0.997 | 0.751 |
| GS-2: Government authorities provide assistance to the organisation for GI information. | 3.744 | 0.852 | 0.763 | |
| GS-3: For SMEs, credit approval for green practises is simple. | 3.759 | 0.854 | 0.781 | |
| External Partnership and Cooperation (EPC) | EPC-1: Suppliers promote the development of environmentally friendly products. | 3.621 | 0.985 | 0.753 |
| EPC-2: The business cooperates with other businesses to share knowledge about GI, and it has environmental partnerships or certifications with suppliers. | 3.591 | 0.799 | 0.797 | |
| EPC-3: Universities and other research institutions provide our organisation with information on environmentally friendly procedures. | 3.626 | 0.837 | 0.719 | |
| Rules and Regulatory Factors (RR) | RR-1: For logistical operations, the government establishes environmental laws, and industrial associations demand that we abide by those regulations. | 3.532 | 0.858 | 0.746 |
| RR-2: High demands are made of the company by worldwide environmental rules. | 3.645 | 0.935 | 0.764 | |
| RR-3: There are numerous calls for regional and municipal environmental restrictions for the business. | 3.773 | 0.776 | 0.782 | |
| Market and Customer Factors (MC) | MC-1: For our clients, protecting the environment is a top priority. | 3.704 | 0.759 | 0.631 |
| MC-2: An incentive for a company of gaining a sizable market share can be seen in green products. | 3.724 | 0.759 | 0.667 | |
| MC-3: Publicity and advertising for green products have greater potential for success. | 3.611 | 0.804 | 0.664 | |
| Organization and Human Resource Factors (OH) | OH-1: Company is committed to increasing green behavior within the firm. | 3.613 | 0.763 | 0.667 |
| OH-2: Company offers rewards to employees for obtaining green knowledge and behavior. | 3.621 | 0.731 | 0.689 | |
| OH-3: Employees can quickly pick up new technology and exchange expertise with one another. | 3.622 | 0.732 | 0.811 | |
| Green Innovation Strategy (GIS) | GIS-1: ISO 14000 | 3.524 | 0.761 | 0.669 |
| GIS-2: Capital and technology investment | 3.613 | 0.811 | 0.699 | |
| GIS-3: Waste destruction or containment, as well as modifications aimed at preventing contamination | 3.601 | 0.801 | 0.679 | |
| Technological Factors (TF) | TF-1: Green technology potentially brings greater economic benefits with improved environmental performance. | 3.627 | 0.739 | 0.701 |
| TF-2: Green technology potentially improves company credibility. | 3.672 | 0.782 | 0.841 | |
| TF-3: Green practices can be easily implemented into any organisational framework. | 3.661 | 0.764 | 0.839 | |
| Economic Performance(EP) | EP-1: Costs of energy consumption are falling. | 3.609 | 0.809 | 0.699 |
| EP-2: Garbage treatment has been made cost-effective with improved capacity utilization. | 3.631 | 0.787 | 0.697 | |
| EP-3: Penalty fines for environmental accidents are reduced. | 3.449 | 0.791 | 0.712 | |
| Environmental Performance (ENP) | ENP-1: Company has received environmental certifications for increment in performance over the last five years. | 3.697 | 0.809 | 0.824 |
| ENP-2: During the last three years, resource use, such as water, energy, and gas, has declined. | 3.617 | 0.907 | 0.757 | |
| ENP-3: Environmental compliance and standards are being improved and followed (i.e., emissions, waste disposal). | 3.521 | 0.905 | 0.754 | |
| Social Performance (SCP) | SCP-1: In the last three years, client satisfaction and motivation have improved. | 3.849 | 0.847 | 0.789 |
| SCP-2: More beneficiaries (disadvantaged persons) and environmental issues are addressed by our business. | 3.618 | 0.893 | 0.739 | |
| SCP-3: Our industry delivers social/environmentally responsible services. | 3.749 | 0.802 | 0.767 |
| Constructs | Cronbach’s Alpha | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Support (GS) | 0.818 | 0.917 | 0.603 |
| External Partnership and Cooperation (EPC) | 0.856 | 0.909 | 0.747 |
| Rules and Regulatory Factors (RR) | 0.843 | 0.901 | 0.728 |
| Market and Customer Factors (MC) | 0.846 | 0.883 | 0.712 |
| Organization and Human Resource Factors (OH) | 0.820 | 0.919 | 0.605 |
| Green Innovation Strategy (GIS) | 0.842 | 0.879 | 0.708 |
| Technology Factors (TF) | 0.786 | 0.852 | 0.663 |
| Economic Performance (EP) | 0.736 | 0.881 | 0.594 |
| Social Performance (SP) | 0.841 | 0.899 | 0.726 |
| Environmental Performance (ENP) | 0.855 | 0.906 | 0.746 |
| Green Innovation Adoption (GIA) | 0.913 | 0.937 | 0.786 |
| GS | EPC | RR | MC | OH | GIS | TF | GIA | EP | SP | ENP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | 0.863 | ||||||||||
| ECP | 0.629 ** | 0.767 | |||||||||
| RR | 0.566 ** | 0.616 ** | 0.857 | ||||||||
| MC | 0.416 ** | 0.517 ** | 0.467 ** | 0.811 | |||||||
| OH | 0.654 ** | 0.554 ** | 0.594 ** | 0.589 ** | 0.816 | ||||||
| GIS | 0.633 ** | 0.535 ** | 0.613 ** | 0.633 ** | 0.611 ** | 0.771 | |||||
| TF | 0.613 ** | 0.633 ** | 0.595 ** | 0.613 ** | 0.589 ** | 0.673 ** | 0.853 | ||||
| GIA | 0.626 ** | 0.526 ** | 0.617 ** | 0.526 ** | 0.602 ** | 0.681 ** | 0.526 ** | 0.763 | |||
| EP | 0.563 ** | 0.663 ** | 0.671 ** | 0.663 ** | 0.563 ** | 0.431 ** | 0.463 ** | 0.663 ** | 0.777 | ||
| SP | 0.413 ** | 0.513 ** | 0.423 ** | 0.431 ** | 0.435 ** | 0.513 ** | 0.613 ** | 0.513 ** | 0.682 ** | 0.813 | |
| ENP | 0.651 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.621 ** | 0.611 ** | 0.643 ** | 0.659 ** | 0.631 ** | 0.539 ** | 0.599 ** | 0.586 ** | 0.852 |
| Variable | R2 | R2 Adjusted |
|---|---|---|
| EP | 0.392 | 0.391 |
| ENP | 0.664 | 0.663 |
| SP | 0.651 | 0.650 |
| GIA | 0.913 | 0.911 |
| Variable | SSO | SSE | Q² (=1 − SSE/SSO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GS | 1182 | 1182 | |
| EPC | 1182 | 1182 | |
| RR | 1182 | 1182 | |
| MC | 1182 | 1182 | |
| OH | 1182 | 1182 | |
| GIS | 1182 | 1182 | |
| TF | 1182 | 1182 | |
| EP | 788 | 614.119 | 0.221 |
| SP | 788 | 402.561 | 0.489 |
| ENP | 788 | 423.499 | 0.463 |
| GIA | 1576 | 467.533 | 0.703 |
| PTH | β = Value | CIL | CIU | t-Statistics | p-Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1: GS → GIA | 0.795 | 0.491 | 0.682 | 29.849 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H2: EPC → GIA | 0.815 | 0.277 | 0.878 | 41.543 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H3: RR → GIA | 0.731 | 0.435 | 0.748 | 21.567 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H4: MC → GIA | 0.788 | 0.559 | 0.734 | 23.853 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H5: OH → GIA | 0.811 | 0.291 | 0.782 | 34.372 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H6: GIS → GIA | 0.043 | -0.089 | 0.159 | 0.076 | 0.000 *** | Rejected |
| H7: TF→ GIA | 0.781 | 0.467 | 0.821 | 22.831 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H8: GIA → EP | 0.745 | 0.590 | 0.795 | 20.667 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H9: GIA → SP | 0.831 | 0.521 | 0.895 | 49.997 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
| H10: GIA → ENP | 0.801 | 0.511 | 0.811 | 32.490 | 0.000 *** | Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wasiq, M.; Kamal, M.; Ali, N. Factors Influencing Green Innovation Adoption and Its Impact on the Sustainability Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032447
Wasiq M, Kamal M, Ali N. Factors Influencing Green Innovation Adoption and Its Impact on the Sustainability Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032447
Chicago/Turabian StyleWasiq, Mohammad, Mustafa Kamal, and Nazim Ali. 2023. "Factors Influencing Green Innovation Adoption and Its Impact on the Sustainability Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Saudi Arabia" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032447
APA StyleWasiq, M., Kamal, M., & Ali, N. (2023). Factors Influencing Green Innovation Adoption and Its Impact on the Sustainability Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 15(3), 2447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032447







