Targeted Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Present and Future
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. T Cell Immunotherapy in Tumors
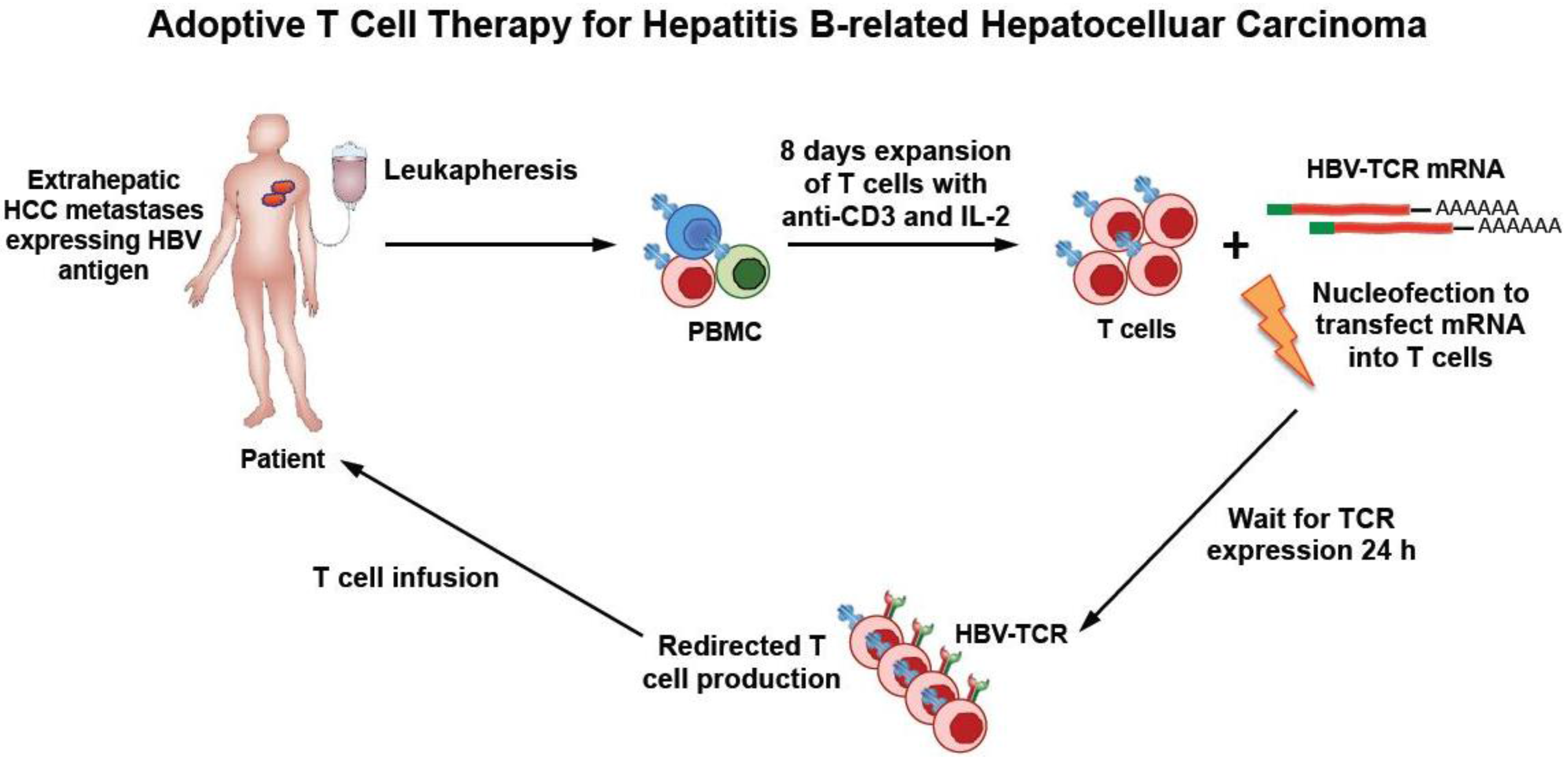
3. Rationale of HBV-Specific T Cell Therapy in HBV-Related HCC
4. HBV–TCR Therapy in Liver Transplanted Patients with HCC Relapse
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qasim, W.; Brunetto, M.; Gehring, A.J.; Xue, S.-A.; Schurich, A.; Khakpoor, A.; Zhan, H.; Ciccorossi, P.; Gilmour, K.; Cavallone, D.; et al. Immunotherapy of HCC metastases with autologous T cell receptor redirected T cells, targeting HBsAg in a liver transplant patient. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, M.-W.; Bechstein, W.-O.; Zeuzem, S.; Trojan, J. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation—An emerging clinical challenge. Transpl. Int. 2012, 26, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, M.; Bleackley, R.C. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: All roads lead to death. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Yang, J.C.; Topalian, S.L.; Chang, A.E.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Aebersold, P.; Leitman, S.; Linehan, W.M.; Seipp, C.A. Prospective randomized trial of high-dose interleukin-2 alone or in conjunction with lymphokine-activated killer cells for the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muul, L.M.; Spiess, P.J.; Director, E.P.; Rosenberg, S.A. Identification of specific cytolytic immune responses against autologous tumor in humans bearing malignant melanoma. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Packard, B.S.; Aebersold, P.M.; Topalian, S.L.; Toy, S.T.; Lotze, M.T. Use of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2 in the immunotherapy of patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June, C.H. Principles of adoptive T cell cancer therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June, C.H.; Blazar, B.R.; Riley, J.L. Engineering lymphocyte subsets: Tools, trials and tribulations. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupp, S.A.; Kalos, M.; Barrett, D.; Aplenc, R.; Porter, D.L.; Rheingold, S.R.; Teachey, D.T.; Chew, A.; Hauck, B.; Wright, J.F.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor–Modified T Cells for Acute Lymphoid Leukemia. New Engl J. Med. 2013, 368, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.A.; Chinnasamy, N.; Abate-daga, D.; Gros, A.; Robbins, P.F.; Zheng, Z.; Dudley, M.E.; Feldman, S.A.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; et al. Cancer Regression and Neurological Toxicity Following Anti-MAGE-A3 TCR Gene Therapy. J. Immunother 2013, 36, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.A.; Morgan, R.A.; Dudley, M.E.; Cassard, L.; Yang, J.C.; Hughes, M.S.; Kammula, U.S.; Royal, R.E.; Sherry, R.M.; Wunderlich, J.R.; et al. Gene therapy with human and mouse T-cell receptors mediates cancer regression and targets normal tissues expressing cognate antigen. Blood 2009, 114, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, P.F.; Morgan, R.A.; Feldman, S.A.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; Dudley, M.E.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Nahvi, A.V.; Helman, L.J.; Mackall, C.L.; et al. Tumor regression in patients with metastatic synovial cell sarcoma and melanoma using genetically engineered lymphocytes reactive with NY-ESO-1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.-K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brechot, C.; Pourcel, C.; Louise, A.; Rain, B.; Tiollais, P. Presence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in cellular DNA of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature 1980, 286, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-Z.; Jo, J.; Tan, A.T.; Sandalova, E.; Chia, A.; Tan, K.C.; Lee, K.H.; Gehring, A.J.; De Libero, G.; Bertoletti, A. IL-7 licenses activation of human liver intrasinusoidal mucosal-associated invariant T cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3142–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Stauss, H.; Brunetto, M.; Maini, M.K.; Bonino, F.; Qasim, W.; Bertoletti, A.; Brunetto, M.; Maini, M.K.; Bonino, F.; et al. T cell receptor-therapy in HBV-related hepatocellularcarcinoma. Oncolmmunology 2015, 4, e1008354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, A.J.; Ho, Z.Z.; Tan, A.T.; Aung, M.O.; Lee, K.H.; Tan, K.C.; Lim, S.G.; Bertoletti, A. Profile of tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flecken, T.; Schmidt, N.; Hild, S.; Gostick, E.; Drognitz, O.; Blum, E.; Neumann-haefelin, C.; Thimme, R. Immunodominance and functional alterations of tumor-associated antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell responses in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargel, C.; Bassani-sternberg, M.; Hasreiter, J.; Zani, F.; Bockmann, J.; Thiele, F.; Bohne, F.; Wisskirchen, K.; Wilde, S.; Sprinzl, M.F.; et al. T Cells Engineered to Express a T-Cell Receptor Specific for Glypican-3 to Recognize and Kill Hepatoma Cells in Vitro and in Mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhurst, M.R.; Yang, J.C.; Langan, R.C.; Dudley, M.E.; Nathan, D.-A.N.; Feldman, S.A.; Davis, J.L.; Morgan, R.A.; Merino, M.J.; Sherry, R.M.; et al. T cells targeting carcinoembryonic antigen can mediate regression of metastatic colorectal cancer but induce severe transient colitis. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorashian, S.; Velica, P.; Chua, I.; McNicol, A.-M.; Carpenter, B.; Holler, A.; Nicholson, E.; Ahmadi, M.; Zech, M.; Xue, S.-A.; et al. CD8 T Cell Tolerance to a Tumor-Associated Self-Antigen Is Reversed by CD4 T Cells Engineered To Express the Same T Cell Receptor. J. Immunol. 2014, 194, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, A.J.; Xue, S.-A.; Ho, Z.Z.; Teoh, D.; Ruedl, C.; Chia, A.; Koh, S.; Lim, S.G.; Maini, M.K.; Stauss, H.; et al. Engineering virus-specific T cells that target HBV infected hepatocytes and hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, S.; Shimasaki, N.; Suwanarusk, R.; Ho, Z.Z.; Chia, A.; Banu, N.; Howland, S.W.; Ong, A.S.; Gehring, A.J.; Stauss, H.; et al. A practical approach to immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma using T cells redirected against hepatitis B virus. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, K.; Böttinger, N.; Huang, L.-R.; Chmielewski, M.; Arzberger, S.; Gasteiger, G.; Jäger, C.; Schmitt, E.; Bohne, F.; Aichler, M.; et al. T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor that binds hepatitis B virus envelope proteins control virus replication in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim, W.; Brunetto, M.; Gehring, A.J.; Maini, M.K.; Bonino, F.; Stauss, H.J.; Bertoletti, A. Reply to: “To target or not to target viral antigens in HBV related HCC?”. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1438–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, K.S.R.; Too, C.T.; Kaur, K.; Gehring, A.J.; Low, L.; Javiad, A.; Pollicino, T.; Li, L.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Lopatin, U.; et al. Targeting hepatitis B virus-infected cells with a T-cell receptor-like antibody. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemberger, C.; Graef, P.; Odendahl, M.; Albrecht, J.; Georg, D.; Anderl, F.; Buchholz, V.R.; Gasteiger, G.; Schiemann, M.; Grigoleit, U.; et al. Lowest numbers of primary CD8 1 T cells can reconstitute protective immunity upon adoptive immunotherapy. Blood 2014, 124, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Avolio, A.W.; Lerut, J.; Singh, G.; Chan, S.C.; Berloco, P.B.; Tisone, G.; Agnes, S.; Chok, K.S.; Sharr, W.; et al. Recurrence of hepatocellular cancer after liver transplantation: The role of primary resection and salvage transplantation in East and West. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacein-bey-abina, S.; Garrigue, A.; Wang, G.P.; Soulier, J.; Lim, A.; Morillon, E.; Clappier, E.; Caccavelli, L.; Delabesse, E.; Beldjord, K.; et al. Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 3132–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, L.C.; Gigou, M.; Roque-Afonso, A.M.; Sebagh, M.; Roche, B.; Fallot, G.; Ferrari, T.C.A.; Guettier, C.; Dussaix, E.; Castaing, D.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with an increased risk of hepatitis B virus recurrence after liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Squadrito, G.; Cerenzia, G.; Cacciola, I.; Farinati, F.; Missale, G.; Raffa, G.; Craxi, A.; Smedile, A.; Tiribelli, C.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Maintains its Pro-oncogenic Properties in the Case of Occult HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, S.; Yeganeh, M.; Nguyen, K.; Durazo, F.; Han, S.; Yersiz, H.; Farmer, D.G.; Goldstein, L.I.; Tong, M.J.; Busuttil, R.W. Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Hepatitis B Reinfection in Hepatitis B Surface Antigen—Positive Patients After Liver Transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2009, 15, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koh, S.; Tan, A.T.; Li, L.; Bertoletti, A. Targeted Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Present and Future. Diseases 2016, 4, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4010010
Koh S, Tan AT, Li L, Bertoletti A. Targeted Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Present and Future. Diseases. 2016; 4(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoh, Sarene, Anthony Tanoto Tan, Lietao Li, and Antonio Bertoletti. 2016. "Targeted Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Present and Future" Diseases 4, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4010010
APA StyleKoh, S., Tan, A. T., Li, L., & Bertoletti, A. (2016). Targeted Therapy of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Present and Future. Diseases, 4(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases4010010




