Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab Use in Japanese Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Retrospective, 104-Week, Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Patients
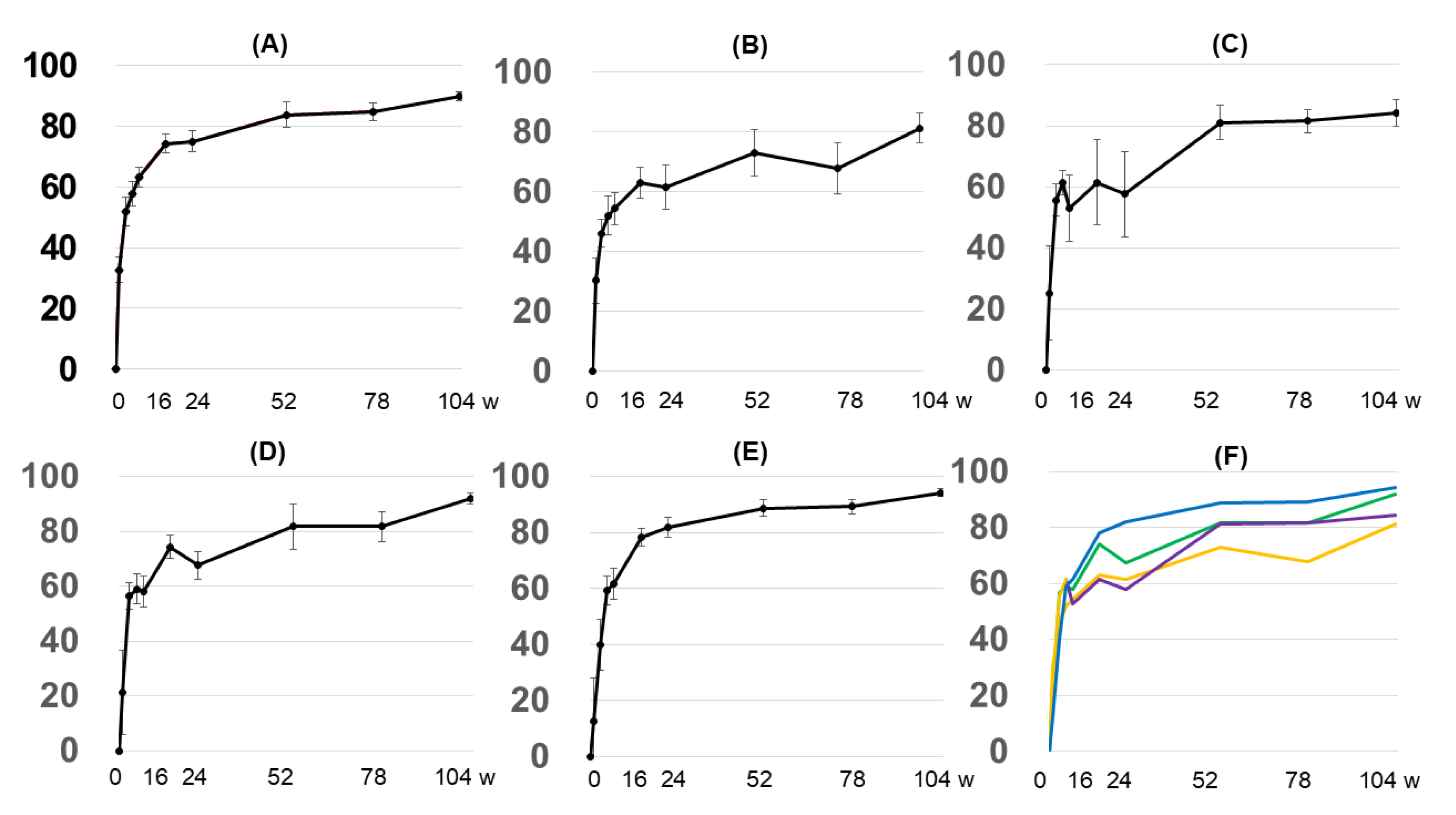
3.2. Changes over Time in Objective Indices (e.g., EASI), Subjective Indices (POEM, Itch VAS, and DLQI), and Serum Markers (IgE, TARC, and Eosinophil Count)
3.2.1. Overall EASI Score
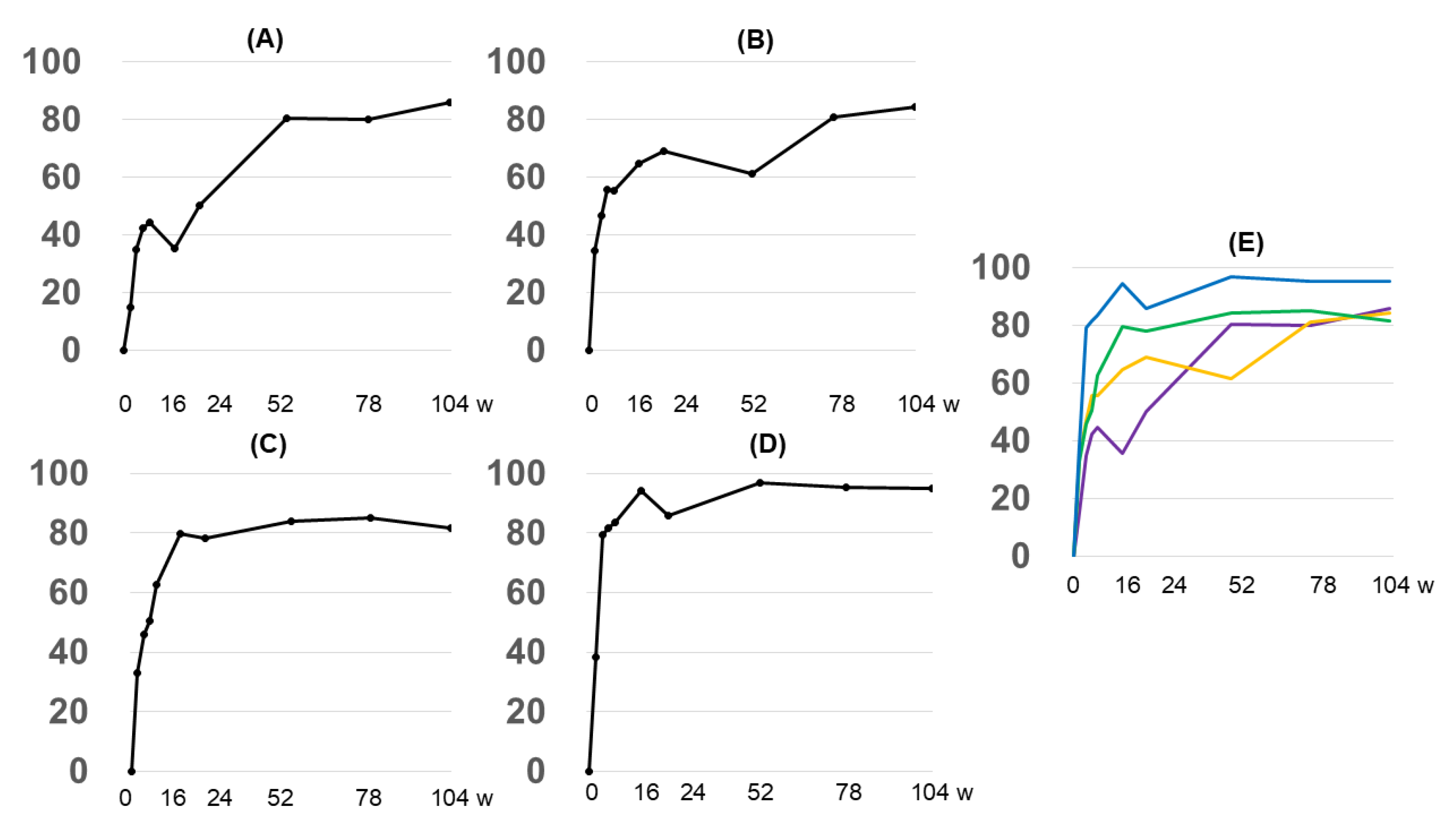
3.2.2. EASI Score by Anatomy
3.2.3. Grouping by Early Treatment Response and EASI Score
3.2.4. Subjective Indices
3.2.5. Biomarkers
3.3. Safety Issues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EASI | Eczema Area and Severity Index |
| IGA | investigator’s global assessment |
| BSA | body surface area |
| POEM | patient-oriented eczema measure |
| DLQI | Dermatology Life Quality Index |
| VAS | visual analog scale |
| TARC | thymus and activation-regulated chemokine |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
References
- Bieber, T.; Paller, A.S.; Kabashima, K.; Feely, M.; Rueda, M.J.; Ross Terres, J.A.; Wollenberg, A. Atopic dermatitis: Pathomechanisms and lessons learned from novel systemic therapeutic options. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1432–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis: An expanding therapeutic pipeline for a complex disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegräber, M.; Srour, J.; Walter, A.; Knop, M.; Wollenberg, A. Dupilumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Rosmarin, D.; Bieber, T.; Simpson, E.L.; Bagel, J.; Worm, M.; Deleuran, M.; Katoh, N.; Kawashima, M.; Shumel, B.; et al. Improvement of atopic dermatitis with dupilumab occurs equally well across different anatomical regions: Data from phase III clinical trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, A.; Du-Thanh, A.; Seneschal, J.; Jachiet, M.; Staumont-Sallé, D.; Barbarot, S. GREAT Research Group. Development or Exacerbation of Head and Neck Dermatitis in Patients Treated for Atopic Dermatitis with Dupilumab. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; Delevry, D.; Yang, M.; Chuang, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Bégo-Le-Bagousse, G.; Martins, B.; Wu, E.; Shumel, B.; Wang, J.; et al. Long-Term Effectiveness of Dupilumab in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: Results up to 3 Years from the RELIEVE-AD Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniotti, M.; Ribero, S.; Mastorino, L.; Ortoncelli, M.; Gelato, F.; Bailon, M.; Trioni, J.; Stefan, B.; Quaglino, P.; Leombruni, P. Long-term psychological outcome of patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis continuously treated with Dupilumab: Data up to 3 years. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Akiyama, M.; Abe, M.; Igarashi, A.; Imafuku, S.; Ohya, Y.; Katoh, N.; Kameda, H.; Kabashima, K.; Tsunemi, Y.; et al. English version of Japanese guidance for biologics in treating atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2023, 50, e311–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Kamata, M.; Mizukawa, I.; Watanabe, A.; Agematsu, A.; Nagata, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; Fukuyasu, A.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Real-world effectiveness and safety of dupilumab for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in Japanese patients: A single-centre retrospective study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Luo, X.; Yao, X. High loading-dose of dupilumab resulted in rapid disease control in pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1160710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzolo, E.; Rossi, M.; Caroppo, F.; Bianchelli, T.; Belloni Fortina, A.; Giacchetti, A.; Calzavara Pinton, P.; Naldi, L. Long-term drug survival of dupilumab and associated predictors in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A real-world prospective cohort study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, e757–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Gooderham, M.; Cather, J.C.; Weisman, J.; Pariser, D.; Simpson, E.L.; Papp, K.A.; Hong, H.C.; Rubel, D.; et al. Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids (LIBERTY AD CHRONOS): A 1-year, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2287–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.E.; Finstad, A.; Georgakopoulos, J.R.; Piguet, V.; Yeung, J.; Drucker, A.M. Facial and neck erythema associated with dupilumab treatment: A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Gori, N.; Di Nardo, L.; Antonelli, F.; Caruso, C.; Caldarola, G.; Calabrese, L.; Guerriero, C.; De Simone, C.; Peris, K. Therapeutic Impact and Management of Persistent Head and Neck Atopic Dermatitis in Dupilumab-Treated Patients. Dermatology 2022, 238, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittrup, I.; Krogh, N.S.; Larsen, H.H.P.; Elberling, J.; Skov, L.; Ibler, K.S.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Mortz, C.G.; Bach, R.O.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; et al. A nationwide 104 weeks real-world study of dupilumab in adults with atopic dermatitis: Ineffectiveness in head-and-neck dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Simpson, E.L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Shumel, B. Dupilumab with Topical Corticosteroids Provides Rapid and Sustained Improvement in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis Across Anatomic Regions Over 52 Weeks. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, M.; Sugiura, H.; Uehara, M. Histopathological features of recalcitrant erythema of the face in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 1994, 21, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K. Atopic eczema of adult type in Japan. Australas. J. Dermatol. 1996, 37 (Suppl. 1), S7–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, Y.; Katayama, I.; Furue, M. Suplatast/tacrolimus combination therapy for refractory facial erythema in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: A meta- analysis study. Allergol. Int. 2007, 56, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, D.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Drylewicz, J.; van Wijk, F.; Thijs, J. Biomarkers in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gu, C.; Wang, S.; Yin, H.; Qiu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Li, W. Serum biomarker-based endotypes of atopic dermatitis in China and prediction for efficacy of dupilumab. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, F.Y.; Kang, E.Y.; Hwang, Y.S. Association between Dupilumab and Conjunctivitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, C.M.; Halling, A.S. Conjunctivitis in atopic dermatitis patients treated with dupilumab-Worsening of pre-existing disease or de novo development? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 1258–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Mean |
|---|---|
| Age, y | 34.2 |
| F/M (n) | 11/19 |
| IGA * | IGA3: 17 (n) IGA4: 13 (n) |
| EASI score | 27.3 |
| Athma (n) | 20 |
| Rhinitis (n) | 15 |
| Pollinosis (n) | 23 |
| DLQI | 12.8 |
| POEM | 20.2 |
| Itch VAS | 63.5 |
| Serum TARC level (pg/mL) | 7945.9 |
| Serum IgE level (IU/mL) | 7296 |
| Eosinophil count (/µL) | 830 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikegami, T.; Igawa, K. Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab Use in Japanese Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Retrospective, 104-Week, Observational Study. Diseases 2025, 13, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13020044
Ikegami T, Igawa K. Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab Use in Japanese Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Retrospective, 104-Week, Observational Study. Diseases. 2025; 13(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkegami, Tetsuharu, and Ken Igawa. 2025. "Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab Use in Japanese Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Retrospective, 104-Week, Observational Study" Diseases 13, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13020044
APA StyleIkegami, T., & Igawa, K. (2025). Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab Use in Japanese Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-Center, Retrospective, 104-Week, Observational Study. Diseases, 13(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13020044





