Association Between Obesity and Serum Leptin Levels in Brazilian Female Shift Workers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Sample and Sampling
2.3. Data Collection and Instruments
2.4. Outcome: Serum Leptin
2.5. Main Exposure: General and Abdominal Obesity
2.6. Covariates
2.7. Statistical Analyses
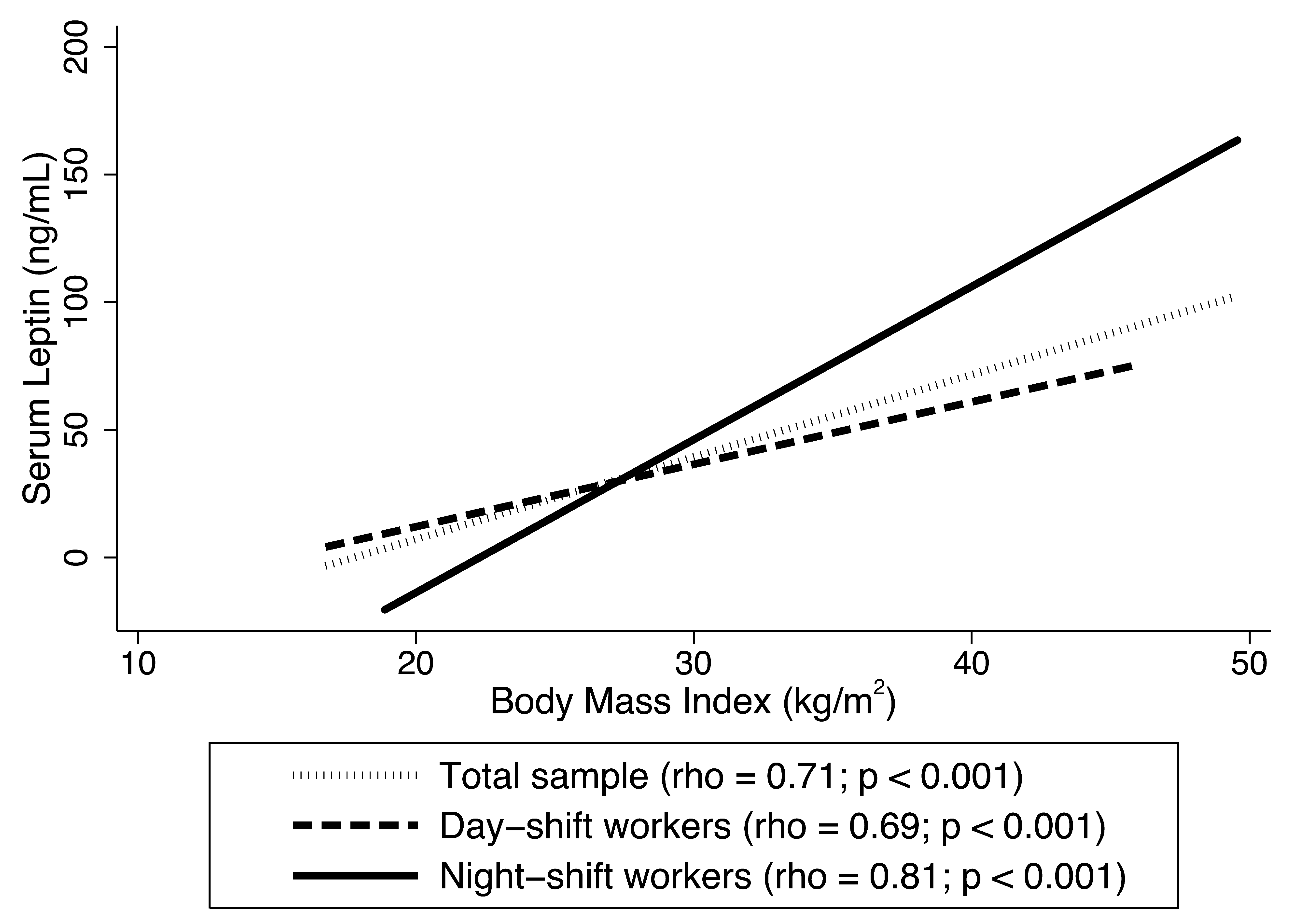
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| WC | Waist Circumference |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| PR | Prevalence Ratios |
| EIA | Enzyme Immunoassay |
References
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and obesity: Role and clinical implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakakis, N.; Farr, O.M.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in Leanness and Obesity. JACC 2021, 77, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.F.; Hassan, M.; Nazar, H.S.; Gillani, S.; Afzal, N.; Qayyum, I. Effect of body mass index on serum leptin levels. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2011, 23, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, V.A.; D’oria, R.; Palma, G.; Caccioppoli, C.; Cignarelli, A.; Natalicchio, A.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F.; Perrini, S. Impaired Leptin Signalling in Obesity: Is Leptin a New Thermolipokine? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.L.; Bluher, S.; Yiannakouris, N.; Suchard, M.A.; Kratzsch, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Regulation of circulating soluble leptin receptor levels by gender, adiposity, sex steroids, and leptin: Observational and interventional studies in humans. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.K.; Caro, J.F. Clinical aspects of leptin. Vitam. Horm. 1998, 54, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.K.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Magosin, S.; Marco, C.; Caro, J.F. Nocturnal rise of leptin in lean, obese, and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, B.O.; Suchard, M.A.; Wong, M.-L.; McCann, S.M.; Licinio, J. Alterations in the dynamics of circulating ghrelin, adiponectin, and leptin in human obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10434–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Liu, H. Leptin signaling and its central role in energy homeostasis. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1238528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodur, C.; Duensing, A.; Myers, M.G. Molecular mechanisms and neural mediators of leptin action. Genes. Dev. 2025, 39, 792–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzberg, H.; Björnholm, M.; Bates, S.H.; Myers, M.G. Leptin receptor action and mechanisms of leptin resistance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxton, R.A.; Caveney, N.A.; Moya-Garzon, M.D.; Householder, K.D.; Rodriguez, G.E.; Burdsall, K.A.; Long, J.Z.; Garcia, K.C. Structural insights into the mechanism of leptin receptor activation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flak, J.N.; Myers, M.G. Minireview: CNS Mechanisms of Leptin Action. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T.; Kelesidis, I.; Chou, S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Narrative Review: The Role of Leptin in Human Physiology: Emerging Clinical Applications. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2006, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdeva, O.; Borodkina, D.; Uchasova, E.; Dyleva, Y.; Barbarash, O. Leptin resistance: Underlying mechanisms and diagnosis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obesity Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E. Leptin’s Physiologic Role: Does the Emperor of Energy Balance Have No Clothes? Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, A.G.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Carreira, M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Foundation for Safety and Occupational Medicine. [Approximately 20 Million People Work During the Night Shift]. 2022. Available online: https://www.gov.br/fundacentro/pt-br/comunicacao/noticias/noticias/2016/10/aproximadamente-20-milhoes-de-pessoas-trabalham-no-periodo-noturno (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Boivin, D.B.; Boudreau, P.; Kosmadopoulos, A. Disturbance of the Circadian System in Shift Work and Its Health Impact. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2022, 37, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.M.; Honn, K.A.; Gaddameedhi, S.; Van Dongen, H.P. Shift Work: Disrupted Circadian Rhythms and Sleep—Implications for Health and Well-being. Curr. Sleep. Med. Rep. 2017, 3, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Langenberg, D.; Vlaanderen, J.J.; Dollé, M.E.T.; A Rookus, M.; van Kerkhof, L.W.M.; Vermeulen, R.C.H. Diet, Physical Activity, and Daylight Exposure Patterns in Night-Shift Workers and Day Workers. Ann. Work. Expo. Heal. 2018, 63, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Schoeller, D.; Cella, L.K.; Sinha, M.K.; Caro, J.F. Entrainment of the diurnal rhythm of plasma leptin to meal timing. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravibabu, K.; Jakkam, S.; Prakash, J.R.; Adepu, V.K. Association of industrial work schedules with development of metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and serum adipokine concentrations. Asian Biomed. 2021, 15, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, K.G.; Reid, K.J.; Kern, A.S.; Zee, P.C. Role of sleep timing in caloric intake and BMI. Obesity 2011, 19, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland Clinic. Leptin: What It Is, Function & Levels. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22446-leptin (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a WHO Consultation; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/42330 (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- WHO. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio. Report of a WHO Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241501491 (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Lean, M.E.J.; Han, T.S.; E Morrison, C. Waist circumference as a measure for indicating need for weight management. BMJ 1995, 311, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Huttly, S.R.; Fuchs, S.C.; Olinto, M.T. The role of conceptual frameworks in epidemiological analysis: A hierarchical approach. Leuk. Res. 1997, 26, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Kusminski, C.M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Scherer, P.E. Leptin: Less Is More. Diabetes 2020, 69, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Gabrielsen, J.S.; Simcox, J.A.; Lee, S.-H.; Jones, D.; Cooksey, B.; Stoddard, G.; Cefalu, W.T.; McClain, D.A. Adipocyte iron regulates leptin and food intake. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3681–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G., Jr.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Haft, C.; Kahn, B.B.; Laughlin, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Challenges and Opportunities of Defining Clinical Leptin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Seon, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, O.Y. Relationship between Adipose Tissue Derived Hormones and Cardiometabolic Risk according to Obesity Status. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2021, 10, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragino, Y.; Polonskaya, Y.; Spiridonov, A.; Striukova, E.; Shcherbakova, L.; Khudiakova, A.; Shramko, V.; Stakhneva, E.; Kashtanova, E. Adipokines, Metabolic Hormones and Their Associations with Abdominal Obesity against a Background of Hyper-LDL-C in Young People. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoro, H.; Bassani, D.G.; da Silva, J.C.; Mendes, K.G.; Cibeira, G.H.; Schenkel, J.C.; Olinto, M.T.A. Behavioural characteristics and abdominal obesity among Brazilian shift working women. Public. Health Nutr. 2020, 24, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, C.A.; Allison, M.A.; Cushman, M.; Jenny, N.S.; Miles, M.P.; Larsen, B.; Lakoski, S.G.; Michos, E.D.; Blaha, M.J. Physical activity and adiposity-related inflammation: The MESA. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczewski Carhuatanta, K.A.; Demuro, G.; Tschop, M.H.; Pfluger, P.T.; Benoit, S.C.; Obici, S. Voluntary exercise improves high-fat diet-induced leptin resistance independent of adiposity. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, R.A.; Maiya, G.A.; Hombali, A.; Umakanth, S.; Shivashankar, K.N. Effect of physical activity promotion on adiponectin, leptin and other inflammatory markers in prediabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 58, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessa, H.B.; Chomistek, A.K.; Hankinson, S.E.; Barnett, J.B.; Rood, J.; Matthews, C.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B.; Tobias, D.K. Objective Measures of Physical Activity and Cardiometabolic and Endocrine Biomarkers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, A.M.; Strollo, F.; Moreè, M.; Caprio, M.; Aversa, A.; Moretti, C.; Frajese, G.; Riondino, G.; Fabbri, A. Leptin and Aging: Correlation with Endocrine Changes in Male and Female Healthy Adult Populations of Different Body Weights. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.S.; Fowke, J.H.; Cai, Q.; Buchowski, M.S.; Signorello, L.B.; Hargreaves, M.K.; Zheng, W.; Blot, W.J.; Matthews, C.E. Differences in the Association between Serum Leptin Levels and Body Mass Index in Black and White Women: A Report from the Southern Community Cohort Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 60, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, B.H. Leptin levels in relation to marital status and neuroendocrine function in Iraqi females with polycystic ovary syndrome. Saudi Pharm. J. 2009, 18, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.M. Variation of Leptin During Menstrual Cycle and Its Relation to the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal (HPG) Axis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Women’s Heal. 2021, 13, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon Andreasson, A.; Jernelov, S.; Szulkin, R.; Unden, A.L.; Brismar, K.; Lekander, M. Associations between leptin and self-rated health in men and women. Gend. Med. 2010, 7, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogteloo, A.; Pijl, H.; Roelfsema, F.; Frölich, M.; Meinders, A. Impact of Meal Timing and Frequency on the Twenty-Four-Hour Leptin Rhythm. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2004, 62, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Serum Leptin (ng/mL) | Prevalence of Altered Leptin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | Mean | SD | p-Value * | % | p-Value ** | |
| Age | 0.83 | 0.67 | ||||
| 18–30 years | 106 (35.1) | 34.3 | 26.6 | 78.3 | ||
| 31–40 years | 103 (34.1) | 34.8 | 26.4 | 80.6 | ||
| ≥41 years | 93 (30.8) | 32.2 | 26.7 | 75.3 | ||
| Skin color | 0.30 | 0.74 | ||||
| White | 210 (69.5) | 34.6 | 28.3 | 77.6 | ||
| Other | 92 (30.5) | 31.2 | 21.7 | 79.3 | ||
| Marital status | 0.82 | 0.64 | ||||
| Without partner | 157 (52) | 33.9 | 26.7 | 77.1 | ||
| With partner | 145 (48) | 33.2 | 26.3 | 79.3 | ||
| Educational level | 0.15 | 0.63 | ||||
| Primary school | 21 (7.0) | 39.6 | 29.7 | 85.7 | ||
| Secondary school | 163 (54) | 31.0 | 23.4 | 76.7 | ||
| Technical/higher | 118 (39.1) | 36.1 | 29.5 | 78.8 | ||
| Menstruated in the last 12 months | 0.45 | 0.16 | ||||
| Yes | 213 (70.5) | 34.3 | 25.5 | 80.3 | ||
| No | 89 (29.5) | 31.8 | 28.7 | 73.0 | ||
| Work shift | <0.001 | 0.01 | ||||
| Day shift | 262 (86.8) | 31.2 | 20.3 | 76.7 | ||
| Night shift | 40 (13.2) | 48.8 | 48.6 | 87.5 | ||
| Physical activity | 0.006 | 0.001 | ||||
| No | 213 (70.5) | 36.3 | 28.8 | 83.1 | ||
| Yes | 89 (29.5) | 27.1 | 18.2 | 63.3 | ||
| Self-perception of health | 0.02 | 0.14 | ||||
| Excellent/Very good | 73 (24.2) | 30.2 | 19.1 | 78.1 | ||
| Good | 142 (47) | 31.2 | 23.9 | 73.4 | ||
| Fair/poor | 87 (28.8) | 40.3 | 33.8 | 85.1 | ||
| Number of meals per day | 0.02 | 0.54 | ||||
| 3 or fewer | 115 (38.1) | 39.6 | 34.5 | 80.0 | ||
| 4 or more | 187 (61.9) | 29.8 | 19.2 | 77.0 | ||
| Use of sleeping medication | 0.15 | 0.75 | ||||
| Yes | 29 (9.6) | 40.3 | 32.0 | 75.9 | ||
| No | 273 (90.4) | 32.9 | 25.7 | 78.4 | ||
| Use of medication for diabetes | 0.30 | 0.20 | ||||
| Yes | 13 (4.3) | 41.0 | 15.0 | 92.3 | ||
| No | 289 (95.7) | 33.3 | 26.8 | 77.5 | ||
| BMI classification | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Normal | 98 (32.5) | 17.6 | 10.9 | 53.1 | ||
| Overweight | 113 (37.4) | 30.1 | 13.8 | 85.0 | ||
| Obesity | 91 (30.1) | 55.1 | 34.8 | 96.7 | ||
| Abdominal obesity | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| No | 158 (53.4) | 23.8 | 17.6 | 64.6 | ||
| Yes | 138 (46.6) | 45.2 | 30.3 | 94.3 | ||
| Altered Serum Leptin (>15.2 ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | PR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Level 1—Demographic, socioeconomic, and reproductive variables | ||
| Education | 0.65 | |
| Primary school | 1.00 | |
| Secondary school | 0.89 (0.73–1.07) | |
| Technical/higher | 0.89 (0.74–1.09) | |
| Menstruated in the last 12 months | 0.18 | |
| No | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 1.10 (0.95–1.27) | |
| Level 2—Work shift | ||
| Work shift | 0.05 | |
| Day shift | 1.00 | |
| Night shift | 1.14 (1.01–1.30) | |
| Level 3—Behavioral variables | ||
| Physical activity | 0.01 | |
| No | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 0.80 (0.68–0.94) | |
| Self-perceived health | 0.67 | |
| Excellent/very good | 1.00 | |
| Good | 0.90 (0.77–1.06) | |
| Fair/poor | 1.01 (0.87–1.18) | |
| Number of meals per day | 0.99 | |
| 3 or fewer | 1.00 | |
| 4 or more | 1.01 (0.89–1.13) | |
| Level 4—Health variables | ||
| Use of sleeping medication | 0.33 | |
| Yes | 1.00 | |
| No | 0.92 (0.74–1.13) | |
| Use of medication for diabetes | 0.40 | |
| No | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 1.08 (0.93–1.26) | |
| BMI classification | <0.001 | |
| Normal | 1.00 | |
| Overweight | 1.55 (1.27–1.91) | |
| Obesity | 1.63 (1.32–2.02) | |
| Abdominal obesity | 0.14 | |
| No | 1.00 | |
| Yes | 1.10 (0.97–1.24) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andretta, R.T.; da Silva, J.C.; Garcez, A.; Kohl, I.S.; Mendes, K.G.; Basso, T.; Olinto, M.T.A.; Theodoro, H. Association Between Obesity and Serum Leptin Levels in Brazilian Female Shift Workers. Diseases 2025, 13, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120401
Andretta RT, da Silva JC, Garcez A, Kohl IS, Mendes KG, Basso T, Olinto MTA, Theodoro H. Association Between Obesity and Serum Leptin Levels in Brazilian Female Shift Workers. Diseases. 2025; 13(12):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120401
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndretta, Raquel Toresan, Janaína Cristina da Silva, Anderson Garcez, Ingrid Stähler Kohl, Karina Giane Mendes, Thais Basso, Maria Teresa Anselmo Olinto, and Heloísa Theodoro. 2025. "Association Between Obesity and Serum Leptin Levels in Brazilian Female Shift Workers" Diseases 13, no. 12: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120401
APA StyleAndretta, R. T., da Silva, J. C., Garcez, A., Kohl, I. S., Mendes, K. G., Basso, T., Olinto, M. T. A., & Theodoro, H. (2025). Association Between Obesity and Serum Leptin Levels in Brazilian Female Shift Workers. Diseases, 13(12), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13120401






