Research Progress on the Efficacy and Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Chronic Gastritis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification and Pathogenesis of CG
2.1. Classification of CG
2.2. Pathogenesis of CG
3. Mechanism of Action of Acupuncture in Treating CG
3.1. Regulate Stomach and Gastric Mucosal Function
| Objective | Disease | Animals | Intervention | Acupoint | Course of Treatment | Molecular Mechanism | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improve gastric motility | CAG | SD rats | Moxibustion | Moxa stick 0.8 cm × 12 cm | CV12 | 40 min QD d1–28 | ↑: Ghrelin, GHSR | [30] | |
| Smokeless moxa stick 0.4 cm × 12 cm | ST36 | 30 min QD d1–6,7d cycle, repeat × 4 | ↑: Gastric antral motility index, gastric emptying rate, MUC1, MUC5AC, MUC6 | [29] | |||||
| Regulate the state of the gastric mucosa | Moxa stick 0.8 cm × 12 cm | CV12 | 40 min QD d1–28 | ↑: GH, PGⅠ, PGⅡ, PGR | [35] | ||||
| Regulate gastric electrical rhythms | EA and TENS | Continuous wave, frequency 50 Hz, intensity 2–5 V | ST36,CV12,ST25,BL20 | 20 min QD × 2 months | ↑: PGE2, PGF2a | [31] | |||
| Promote mucosal regeneration and repair | Wistar rats | LA | Output power: 30 mW Wavelength: 632.8 nm Spot diameter: 2 cm Spot center aligned with acupoint Fiber tip distance from skin: 10 cm | ST36 | 5 min QD d1–14 | ↓:TFF3 | ↑: TFF1 | [33] | |
| Promote mucosal regeneration and repair | SD rats | ACE | Size 6 disposable syringe needle,0000 chromium-plated catgut suture | ST36,CV12 | Q10D × 6 | ↓:HIF-α,VEGF | [39] | ||
| SD rats | BL17,BL18,BL20,BL21,BL23 | 15 min QD d1–30 | ↑: PGI, PGⅡ | [44] | |||||
| Increase gastric mucosal blood flow | PLGC | AA | ST36,ST21 | 1 h QD | ↑: Gastric mucosal blood flow | [38] | |||
3.2. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Hormones
- (1)
- GAS: Acupuncture intervention primarily upregulates GAS expression. G cells in the gastric antrum synthesize and secrete this hormone. Gastrin’s key physiological functions include directly and indirectly stimulating the secretion of gastric acid and pepsin, as well as promoting the proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenesis of gastric mucosal epithelial cells. Additionally, gastrin enhances gastrointestinal motility and accelerates gastric emptying [45].
- (2)
- MOT: Acupuncture produces effects opposite to its action on GAS, downregulating both MOT levels. These peptides stimulate gastrointestinal motility and accelerate the process of emptying. Elevated MOT enhances gastric contractions, but sustained intense smooth muscle compression may compromise gastric wall vasculature, reducing mucosal blood flow and causing ischemic injury. Similarly, increased MOT contributes to pyloric dysfunction and gastroduodenal discoordination, delaying gastric emptying and prolonging mucosal exposure to inflammatory stimuli [46].
- (3)
- SS: This hormone is mainly secreted by D cells in the gastric antrum. SS preserves gastric mucosal protection by maintaining non-protein-bound sulfhydryl groups through glutathione reductase activity [47]. Additionally, it inhibits both gastric acid secretion and GAS release, establishing a coordinated axis between GAS, SS, and gastric acid that helps maintain normal gastrointestinal function. Studies demonstrate that in rats with CAG, glandular atrophy and a reduction in the gastric antrum lead to decreased levels of GAS and SS. However, heat-sensitive moxibustion can enhance SS expression to support mucosal repair [48].
- (4)
- CCK: This gastrointestinal hormone and neuropeptide plays a crucial role in regulating digestive and nervous system functions. CCK significantly inhibits both solid and liquid gastric emptying [49]. It acts through peripheral and central pathways to delay gastric emptying. Both physiological and pharmacological CCK concentrations inhibit postprandial gastric emptying, with higher CCK levels correlating with slower rates of emptying [50]. Experimental evidence suggests that acupoint application therapy downregulates CCK expression, modulates gastrointestinal motility, and enhances gastric mucosal protection, thereby facilitating the repair of injury [51].
- (5)
- PGI, PGR, and G-17: Studies demonstrate that reduced PGI, PGR, and G-17 levels serve as biomarkers for gastric corpus and antrum atrophy. G-17, secreted by G cells, enhances gastric mucosal blood flow. PG, comprising PGI and PGII, reflects the quantity of gastric glands and pepsin secretion, indicating the mucosal status and function. Studies confirm that reduced PGR elevates gastric cancer risk, even in patients without mucosal atrophy [52]. Research shows that acupuncture significantly improves the general condition and mucosal tissue in rats with CAG by regulating PGI, PGR, and G-17 levels. Furthermore, multi-acupoint combinations prove more effective than single-point therapy for CAG [53].
- (6)
- Others: SP, a neuropeptide widely distributed in the enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal tract, serves as the primary excitatory neurotransmitter regulating gastrointestinal motility. It strongly stimulates gastrointestinal smooth muscle contraction, accelerating motility and gastric emptying [54]. Ghrelin, initially identified from human and rat stomachs, represents a brain–gut peptide primarily produced in the stomach [55]. This hormone promotes food absorption and gastric emptying while regulating energy expenditure and providing gastrointestinal protection and healing. Research demonstrates that acupoint application significantly upregulates both SP and Ghrelin levels in the gastric mucosa of rats with CAG [51]. Meanwhile, EGF counteracts pepsin-induced damage, suppresses excessive acid secretion, and exhibits anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, thereby protecting the gastric mucosa. Mechanistic studies suggest that acupressure at Back-shu points may function through regulating EGF expression [43].
| Disease | Animals | Intervention | Acupoint | Course of Treatment | Molecular Mechanism | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | Wistar rats | EA | Sawtooth wave, frequency 2 Hz, voltage 2 V, current 1 mA | ST36 | 20 min QD d1–7 | ↑:GAS | [57] | |
| CAG | SD rats | AC | BL20,BL21,BL23,BL18,BL17 | 15 min QD d1–30 | ↓:MOT | ↑:GAS, EGF | [43] | |
| acupuncture needle 0.30 mm × 25 mm | BL17,BL18,BL20,BL21,BL23 | 15 min QD d1–30 | ↓:MOT | ↑:GAS | [58] | |||
| Wistar rats | acupuncture needle 0.25 mm × 25 mm | ST36,CV12 | 30 min QD d1–6, 7 d cycle, repeat × 8 | ↑:PGI, PGR, G-17 | [53] | |||
| SD rats | AA | ST36,ST21 | 1 h QD × 8 weeks | ↓:CCK | ↑:SP, ghrelin | [51] | ||
| Wistar rats | Moxibustion and Chinese herb | ST36 | 20 min QD d1–30 | ↑:Gas | [59] | |||
| SD rats | ST36,CV12 | QD d1–30 | ↓:MOT | [60] | ||||
| CNAG | Moxibustion | CV12 | 40 min QD d1–28 | ↓:MOT, IL—6 | ↑:GAS, SS | [48] | ||
3.3. Regulation of Metabolism and Gut Microbiota
| Objective | Disease | Animals | Intervention | Acupoint | Course of Treatment | Molecular Mechanism | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regulating glucose metabolism | CAG | Wistar rats | Moxibustion | CV12, CV6 | 2 moxa cones/point, QD, 6 times/week × 4 weeks | ↓: STAT3, HIF-1α, PKM2, LDH | [65] | ||
| Regulating tissue metabolism in acupoint areas | SD rats | ST36, CV12 | 15 min QD d1–14 | ↓: Ala, Glu, Gln, NAA, Asn, DM), Thr, Suc, PC, GPC, UDG, AMP, ADP, ATP, HX, Ino | ↑: Ace, Ade, ADP | [66] | |||
| WA | CV12, ST36 | 20 min QD d1–14 | ↓: Betaine, Threonine, Phosphocholine, Glycerophosphocholine, Adenosine Diphosphate, Inosine | ↑: Lactic acid, N,N-dimethylglycine, inositol, adenosine monophosphate, adenosine, hypoxanthine | [67] | ||||
| Regulating gastric tissue metabolism | Moxibustion | ST36, CV12 | 15 min QD × 2 weeks | ↓: Leucine, Valine, N-Acetylaspartic Acid, Glutathione, Serine | ↑: Glutamine, Inositol, Adenosine Ribonucleotide, Phosphocholine, Uracil | [64] | |||
| Moxibustion/AC | Moxa sticks (l.8 cm diameter), 0.2 mm × 0.25 mm stainless steel acupuncture needles | ST36, CV12 | 15 min QD × 2 weeks | ↑: Moxibustion: Adenosine, lactic acid, glycerol, alanine, and NADP+ levels; EGF, EGFR, and ERK Acupuncture: Adenosine monophosphate and glycerol levels; ERK | [63] | ||||
| Regulating liver and kidney metabolism | Moxibustion/EA | two-channel electrical stimulations at irregular waves (intermittent wave: 4 Hz; irregular wave: 50 Hz) with voltage (2~4 V) was used. | ST36, ST21 | 30 min QD × 2 weeks | ↑: SP, auxin-releasing peptide | [68] | |||
| Regulate fluid balance (urine and serum) and tissue metabolism (stomach, cortex, and medulla) | two-channel electrical stimulations at irregular waves (intermittent wave: 4 Hz; irregular wave: 50 Hz) with voltage (2~4 V) | ST36, ST21 | 30 min QD × 2 weeks | ↓: glycogen, glucose and acetoacetate, glutathione and glutamine, inosine, methylmalonate and malonic acid, hypoxanthine, nicotinamide and glycerol occurred | ↑: P and ghrelin, methionine, lactate and betaine, ethanolamine, phenylalanine and inositol | [62] | |||
| Regulating the Gut Microbiome | EA | were sparse and dense waves (sparse wave 4 Hz, dense wave 50 Hz) and voltage (2–4 V) | ST36 | 30 min QD × 4 weeks | ↓: p53, c-myc, Desulfobacterota, Helicobacter | ↑: Bcl-2,Oscillospirales, Romboutsia, Christensenellaceae | [70] | ||
3.4. Regulation of Apoptosis and Proliferation
| Disease | Animals | Intervention | Acupoint | Course of Treatment | Molecular Mechanism | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAG | Wistar rats | Moxibustion | CV12,CV6 | 2 moxa cones/acupoint, QD, 6 times/week × 4 weeks | ↓:P-AKT,PIP2,MDM2 | ↑:PTEN/Caspase-9, PI3KCA | [82] | |
| CV12,CV6 | 1 moxa cones/acupoint, QD × 4 weeks | ↑:Foxo3,Uba52,S100a1,Nod2 | [83] | |||||
| SD rats | CV12,CV6 | 2 moxa cones/acupoint, QD, 6 times/week × 4 weeks | ↓:STAT3,HIF-1α,PKM2,LDH | [65] | ||||
| CV12 | 40 min QD d1–28 | ↓:cmyc, survivin, cyclin D1 | [71] | |||||
| PLGC | ST36,ST21 | 30 min QD × 20 weeks | ↓:EGF, TGF-a, PCNA, VEGF, Ag-NORs | [72] | ||||
| Wistar rats | CV12,ST36 | 40 min QD × 4 weeks | ↓:EGF, TGF-β, P53, Bcl-2, Ag-NORs, PCNA | ↑: Smad3 | [78] | |||
| Moxibustion and Chinese herb | BL18,BL20,BL21,ST36,PC6,CV12 | 1 moxa cone/acupoint,QD × 10 d,then rest 2–3 d. repeat × 3. | ↓:Survivin, p53 | ¬:Syk | [84] | |||
| CAG | SD rats | Moxibustion/AC | Moxibustion stick 1.8 × 12 cm, Ac needles SS 0.25 × 25 mm | ST36,CV12 | 15 min QD × 2 weeks | ↓:NF-KB, Bcl-2 | [85] | |
| AC | DS Ac needles 0.3 × 40 mm | CV12,PC6,ST36 | 3 times/week, 10 sessions/course, ×6 courses | ↑: Notch2, Notch3 | [86] | |||
| ACE | 4-0 Catgut Suture, 0.5 cm Needle, 6-Gauge Injection Needle | BL20,ST36 | Q10D × 6 | ↓:JAK2, STAT3, Bcl-2, CyclinD1 | ↑:SOCS3 | [80] | ||
| EA | Disperse-Dense wave (4/20 Hz, 60 V) | ST36,ST21 | 30 min QD × 4 weeks | ↓:P53 | [87] | |||
| Electro-acupuncture: Intermittent–Irregular wave (4/50 Hz, 2–4 V) | ST2,ST36,ST21 | 30 min QD × 2 weeks | ↓: PCNA, Ag-NORs, EGF, VEGF, c-myc, NF-κB | [60] | ||||
3.5. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Stress
| Objective | Disease | Animals | Intervention | Acupoint | Course of Treatment | Molecular Mechanism | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | CAG | SD rats | Moxibustion | Moxa stick 8 mm × 9 mm | ST36,ST25 | 20 min QD × 2 weeks | ↓: COX-2,NF-κBp65 | ↑: miR-146a | [110] |
| Moxa stick, 1.8 cm diameter | ST36 | 15 min QD d1–14 | ↑: IL-1β,IL-10,TNF-α | [36] | |||||
| Moxibustion and AC | Moxa stick 0.8 cm × 12 cm | ST36,CV12 | 15 min QD d1–14 | ↓: CK18,CK19 | ↑: CGRP, NPY | [101] | |||
| Wistar rats | AC | ST36,SP6,BL25,CV6,CV12,CV10,ST25,LI10, BL26,BL20,SP10 | 15 min QOD × 4 weeks | ↓: GLi1,GLi2,GLi3,COX-2,TNF-α,G-17,IL-1β,IL-4 | : | [77] | |||
| SD rats | 0.25 mm × 25 mm stainless steel acupuncture needles | ST36 | 20 min QD d1–14 | ↓: IL-6,IL-1β,TNF-α | ↑: SP, HRH2 | [103] | |||
| ST36,CV12 | 15 min QD d1–60 | ↓:miR-155, miR-21,NF-κB p65 | ↑: miR-146a | [111] | |||||
| ACE | 0.5 cm 0000 catgut suture 6-gauge injection needle | BL20,ST36,CV12 | q10d × 6 | ↓: IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α | [112] | ||||
| AA | ST36,ST21 | 1 h QD × 8 weeks | ↓: TNF-α, PCNA | [81] | |||||
| EA | intermittent and irregular waves (intermittent wave: 4 Hz; irregular wave: 50 Hz) with voltage ranging from 2 to 4 V. | ST2,ST36,ST21 | 30 min QD × 2 weeks | ↓: PCNA, Ag-NORs, EGF, VEGF, c-myc, NF-κB | [61] | ||||
| C57BL/6 mouse | ST36,CV12 | 30 min QD d1–14 | ↓: IL-6, IL-1β, Fas, FasL | [79] | |||||
| CG | Wistar rats | EA and Chinese herb | EA 2 Hz, 3 V, 0.3 mA | BL20,BL21 | 15 min QOD × 6 weeks | ↓: IL-10,TNF-α | [113] | ||
| CAG | LA | ST36 | 6 min QD d1–14 | ↓: IL-2,IL-6,TGF-β1 | [114] | ||||
| ear acupoint bean pressing and Chinese herb | CO13,CO4,AH6a,CO18,AT4 | 10 min TID, alternate ears, change q3d × 6 months | ↓: NF-κB, Ubiquitin | [115] | |||||
| Antioxidant Stress | SD rats | ACE | 4-0 chromic catgut suture, 0.5 cm in length, Size 6 disposable injection needle | BL20,CV12,ST36 | q10d × 6 | ↓: MDA | ↑: SOD | [106] | |
| AC | BL17,BL18,BL20,BL21,BL23 | 15 min QD d1–30 | ↓:MDA | ↑:SOD | [107] | ||||
4. Current Status of Clinical Research on Acupuncture Treatment for CG
4.1. Acupuncture and EA
4.2. Moxibustion
4.3. Warm Needle Acupuncture (WA)
4.4. Other Therapies
| Disease | Location | Center | Age (Mean ± SD), y | Intervention | Acupoint | Time of Intervention | Duration | N | Control | Measurement Time Points | Validated Scale Used | Objective Evaluation Criteria | Post-Acupuncture Changes Compared to Baseline | Adverse Events | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± SD), y | Treatment | N | References | ||||||||||||||
| CNAG | CN | SC | 39 ± 11 | EA | ST2,ST21,ST36 | 30 min QD | 4 weeks | 33 | 38 ± 11 | Conv acup | 33 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCM Consensus on Chronic Superficial Gastritis Dx & Tx, Chinese Consensus on Chronic Gastritis Symptom Score | S-GAS levels, gastrogram parameters | Total effective rate 90.9%; total scores decreased, S-GAS decreased; gastric electrical activity amplitude and frequency increased, rhythm disorders decreased (p < 0.05) | [119] | |
| CNAG | CN | SC | 42 ± 5 | AC | ST36, RN12,SP3, ST40 | AC: QD, 5 times/week, needles retained 30 min, manipulation every 10 min | 4 weeks | 37 | 41 ± 5 | Conv acup | 37 | Before treatment, after treatment | Primary symptom score, Secondary symptom score | Inflammatory factors, gastric mucosal repair indicators | Total effective rate 83.8% (p < 0.05); primary and secondary symptom scores decreased, serum inflammatory factors decreased, gastric mucosal repair indicators improved (p < 0.05) | [121] | |
| CNAG | CN | SC | 41.5 ± 9.4 | AC | ST36,RN12,RN4,ST25,DU24,EX-HN1,PC6,SP6 | QOD, TIW, needles retained 30 min | 8 weeks | 30 | 42.3 ± 8.7 | Oral omeprazole + sucralfate susp + mosapride citrate PRN, per Rx for 8 weeks | 30 | Before treatment, after treatment | Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research, GI Diseases TCMSS, SAS, SDS, etc. | Gastroscopy score | Total effective rate 86.67%; GS, symptom scores, SAS, SDS decreased (p < 0.05) | [147] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 51 ± 7 | AC | RN12,ST36,PC6,SP4,RN4,BL20,BL21 | QD, needles retained 30 min, manipulation every 15 min | 2.14 weeks | 31 | 51 ± 6 | Conv acup | 31 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCM Consensus on Chronic Atrophic Gastritis (2009), Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research-TCMSS | Total effective rate 93.5% (p < 0.05); TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | [148] | ||
| CAG | CN | SC | 46.28 ± 1.31 | Ten Old Needles | ST25,PC6,BL21,RN13,RN12,RN10,RN6 | QD, 5 times/week, needles retained 20 min | 8 weeks | 25 | 45.96 ± 1.54 | Oral vit tabs + metoclopramide tabs + rabeprazole EC caps, per Rx for 8 weeks | 25 | Before treatment, after treatment | Chinese Consensus on Chronic Gastritis, Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research—TCMSS | Gastric mucosal gland atrophy degree, intestinal metaplasia degree | Total effective rate 92% (p < 0.05); gastric mucosal gland atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | [124] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 55.36 ± 5.35 | AC + FSN | ST40,SP3,SP4,ST42 | Tech1: QD, 5 times/week; Tech2: QOD, TIW | 4 weeks | 50 | 55.26 ± 5.29 | FSN ther | 56 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCMSSS, GSRS, SF-36 PCS | Gastric mucosal score, S-GAS, S-MOT, S-SS levels | Total effective rate 96.00% (p < 0.05); TCM syndrome scores decreased, PCS increased, S-GAS, S-MOT, S-SS decreased, gastric mucosal scores decreased (p < 0.05) | [123] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 56.43 ± 5.80 | AC + Fire needle | RN12,BL21,SP4,ST42 | Needle1: QOD, TIW; Tech: QD, 5 times/week | 4 weeks | 49 | 56.55 ± 5.88 | Filiform Fire Needle | 49 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCMSSS, SF-36 PCS | Gastric mucosal score, PCS score, S-GAS/MOT/SS | Total effective rate 95.92% (p < 0.05); TCM syndrome scores decreased, PCS increased, gastric mucosal scores decreased, S-GAS and S-MOT decreased, S-SS increased (p < 0.05) | [124] | |
| CAG | Chinese | SC | 52.32 ± 1.75 | AC | ST36,RN12,BL20,LI4,KI3 | needles retained 30 min, manipulation every 10 min, 5 times/week | 12 weeks | 53 | 54.26 ± 1.65 | Oral omeprazole + amoxicillin + metronidazole × 2 wks + celecoxib until 12 wks | 53 | Before treatment, 2 weeks after treatment, 12 weeks after treatment | No specific scale | Gastroscopy findings, H. pylori eradication rate | Total effective rate 92.5%; endoscopic efficacy 88.7% (p < 0.05); H. pylori eradication rate 84.9% | [149] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 58 ± 8 | AC | RN13, RN12 | 2 times/week, needles retained 30 min with techniques | 24 weeks | 36 | 59 ± 8 | Conv acup | 35 | Before treatment, after treatment, 6-month follow-up | TCMSS | Gastroscopic mucosal scoring | Total effective rate 86.1% (p < 0.05); TCMSS and gastroscopic mucosal scores decreased | [150] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 62.63 ± 3.66 | AC | RN12, PC6,ST36 | TIW, needles retained 20 min, 10 sessions/course | 15–16 weeks | 8 | Untreated | Each group consists of 8 people. | Before treatment, after treatment | TCMSSS | Serum protein testing | Protein levels: thymosin β-4, Profilin-1, myosin-4, transglutaminase-2 decreased; Notch2, Notch3 increased (p < 0.05) | [86] | ||
| CG | CN | SC | 54.4 ± 8.5 | AC | DU24,DU22,DU21,PC6,ST36,RN12 | 30 min QD, manipulation every 10 min | 4.57 weeks | 46 | 54.8 ± 8.4 | Conv acup | 46 | Before treatment, after treatment | Chinese Consensus on Chronic Gastritis, ICD-10, SAS, SDS, etc. | Clinical symptom score, gastroscopic morphology, SAS/SDS score, clinical efficacy | Clinical symptom scores decreased, gastroscopic improvements, SAS and SDS decreased (p < 0.05) | [151] | |
| CG | CN | SC | 43.2 | AC | LI4,LR3,RN12 | 10 min/session | Single treatment | 40 | Oral scopolamine tabs 20 mg/dose | 40 | Before treatment, 30 min after treatment, 60 min after treatment | Gastroscopy/barium meal follow-up results | Total effective rate 95% (p < 0.05); faster and more pronounced pain relief | [152] | |||
| CG | CN | SC | 47.89 ± 7.03 | AC | Primary Point: Taiyin of the Head. Additional Points Based on Pattern Differentiation: For Liver and Stomach Qi Stagnation, add Taiyang / Jueyin; For Liver and Stomach Heat Stagnation, add Yangming / Jueyin. | 30 min QD, 7-day course | 1 week | 35 | 48.96 ± 7.14 | Oral omeprazole 10 mg QD + mosapride citrate 5 mg TID | 35 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCMSS System, TCM Expert Consensus on Functional Dyspepsia (2017)—upper abdominal pain syndrome score | GI hormones, pepsin, gastroscopy/pathology score | Total effective rate 94.29%; TCMSS, upper abdominal pain, upper abdominal burning, gastroscopy, pathology decreased (p < 0.05); S-G-17, S-MOT, S-PGI, S-PGII increased (p < 0.05); recurrence rate 8.57% | Adverse reactions occurred in 6 individuals. | [120] |
| CG | CN | SC | 46.83 ± 10.75 | AC | EX-B3, BL20, BL21, BL18, BL19 | QD, 5 times/week, needles retained after deqi | 4 weeks | 30 | 46.83 ± 11.03 | Conv western meds for triple therapy for gastritis | 30 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCMSS | S-CD4+, S-CD8+, S-CD4+/CD8+ ratio | Improvement rate 70% (p < 0.05); TCMSS decreased, S-CD4+ and S-CD4+/CD8+ ratios increased (p < 0.05) | [122] | |
| CNAG | CN | SC | 52.22 + 9.70 | Mox | CV12, PC, ST36 | QD, 30 min per session | 8 weeks | 29 | 63.54 + 8.97 | Mox at non-sensitive points | 20 | Before treatment, After treatment, Follow-up | TCMSSS, SF-36 | Total effective rate 100%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05), SF-36 scores increased (p < 0.05) | [129] | ||
| CNAG | SC | 46.02 ± 10.12 | Mox | From the xiphoid process to the umbilicus, with lateral margins extending to the midclavicular line. | Each session: wait until moxa wool self-ignites before replacing, repeat for 3 consecutive times, total about 60 min, once every 3 days | 3 weeks | 25 | 44.83 ± 9.54 | Oral lansoprazole EC tabs 30 mg QD | 25 | Before treatment, After treatment | “GI Diseases TCM Syndrome Rating Scale” | Total effective rate 92%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | [132] | |||
| CAG | CN | SC | 57.63 ± 9.17 | Electronic Mox | ST36,CV12,ST25,CV8 | QD, 30 min per session | 2 weeks | 30 | 52.06 ± 12.61 | Conv treat | 30 | Before treatment, Day 7 of treatment, Day 14 of treatment | TCMSSS, VAS | Total effective rate 93%; TCMSS and pain scores decreased (p < 0.05) | [127] | ||
| CAG | CN | SC | 61.55 | Mox | CV12,CV6,ST36,PC6 | 1 unit per point per session, TIW | 24 weeks | 33 | 59.36 | Mox | 33 | Before treatment, After treatment | “GI Diseases TCM Symptom Rating Scale” | Gastroscopy: gastric mucosa histopathology; peripheral blood DNA methylation sequencing | Total effective rate 87.88%; gastric mucosa pathological efficacy 82.14%; TCMSSS, individual TCMSS, gastric mucosa tissue lesion scores decreased (p < 0.05); post-treatment DMR genes involved cAMP, AMPK, NF-κB pathways | [133] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 59.90 ± 10.5 | Mox | CV12,CV4,PC6,ST36 | 30 min per session, QOD, TIW | 4 weeks | 40 | 60.60 ± 9.56 | Smokeless mox | 40 | Before treatment, After treatment | “GI Diseases TCM Syndrome Rating Scale” | Acupoint temperature, S-GAS, S-PGI, S-PGR | Total effective rate 75%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05); S-GAS, S-PGI, S-PGR increased (p < 0.05) | [153] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | Mox | CV12,CV4,PC6,ST36 | 1 unit per point per session | 4.57 weeks | 47 | Western med conv treat | 48 | Before treatment, After treatment | TCMSSS | Gastroscopy: gastric mucosa histomorphology; S-G-17, S-PGR | Total effective rate 89.4%; TCMSS, gastroscopy, pathological gastric mucosa histomorphology scores decreased (p < 0.05); S-G-17, S-PGR increased (p < 0.05) | Five cases developed small blisters at the ginger-isolated Mox site, which healed completely after management with no complications such as infection. | [126] | ||
| CAG | SC | 57 + 11 | Mox | CV12,ST36 | 20–25 min per session, QD | 12 weeks | 32 | 55 ± 9 | Oral Weifuchun tabs 1.44 g TID | 31 | Before treatment, After treatment, Follow-up | TCMSSS | S-PGI, S-PGII, S-G-17 | Total effective rate 93.8%; TCMSS and gastroscopic gastric mucosa scores decreased (p < 0.05); S-PGI, S-PGR, S-G-17 increased (p < 0.01) | [131] | ||
| CAG | CN | SC | 51.82 + 11.45 | Mox | From GV14 to GV1 | QW, for 3 consecutive sessions | 12 weeks | 32 | 52.56 + 9.62 | Oral Huangqi Jianzhong decoc | 32 | Before treatment, Week 4, Week 8, Week 12 | TCMSSS | Gastroscopy: gastric mucosa score | Total effective rate 96.67%; TCMSS and gastroscopic gastric mucosa scores decreased (p < 0.05) | [130] | |
| CG | CN | SC | 59.5 | Mox | CV12,CV6,ST25 | 25 min per point, QOD, TIW | 4 weeks | 30 | 56.5 | Mox | 30 | Before treatment, After treatment | TCMSS for Digestive Diseases, VAS | S-Ghrelin, S-SS, S-MOT | Gastrointestinal disease-related TCMSS and VAS scores decreased (p < 0.05); S-SS decreased (p < 0.05), S-Ghrelin, S-MOT increased (p < 0.05) | One adverse event occurred during the treatment period. This event was a mild burn during the Mox procedure, which healed before the next treatment session. No serious adverse events occurred. | [134] |
| CG | CN | SC | 60.45 ± 10.37 | Mox | CV12,CV6,PC6,ST36 | 1 unit per point per session, TIW | 4 weeks | 31 | 60.71 ± 10.22 | Mox placebo | 31 | Before treatment, After treatment | TCMSSS | S-PGI, S-PGII, S-PGR, S-GAS | Total effective rate 83.9%; TCMSS and S-GAS decreased (p < 0.05); S-PGI, S-PGR increased (p < 0.05) | [128] | |
| CNAG | CN | SC | 39.6 ± 3.3 | WA | SP4,PC6,SP9,RN12,ST36,RN4 | 2 cones/point, QOD | 1.71 weeks | 50 | 39.2 ± 3.7 | Conv acup | 50 | before treatment, after treatment | TCM syndrome rating scale, TCMSSS, SF-36 | Total effective rate 90%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05), SF-36 scores increased (p < 0.05) | [137] | ||
| CNAG | CN | SC | 42.88 ± 3.82 | WA | ST36,RN4,RN12 | 2 cones/point, QD | 5.71 weeks | 37 | 42.56 ± 3.75 | Conv acup | 35 | before treatment, after treatment | TCM syndrome rating scale, TCMSSS, SF-36 | Total effective rate 96.83%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05), SF-36 scores increased (p < 0.05) | [135] | ||
| CNAG | CN | SC | 47.56 ± 2.82 | WA | ST36,SP4,SP9,PC6,RN12 | 2 cones/point, QOD | 1.71 weeks | 40 | 46.83 ± 3.62 | Conv acup | 39 | before treatment, after treatment | TCM syndrome rating scale, TCMSSS, SF-36 | Total effective rate 62.5%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05), SF-36 scores increased (p < 0.05) | [136] | ||
| CNAG | CN | SC | 48.08 ± 11.32 | WA | DU20,EX-HN1,MS3,RN12,SP15,RN4,RN6,PC6,ST36,SP6,SP4,ST44 | 30 min, QD | 8 weeks | 43 | 47.99 ± 11.19 | Conv Western med treat | 43 | before treatment, 2 weeks after treatment, 4 weeks after treatment, 6 weeks after treatment | TCM syndrome rating scale, TCMSSS, SF-36 | Gastroscopy, gastric mucosal biopsy | Total effective rate 90.7%; GS decreased (p < 0.05); H. pylori eradication rate 93.02%; recurrence rate 9.3% at 1-year follow-up | [138] | |
| CG | CN | SC | 48 ± 9 | WA | RN12,RN4,ST36,BL17,SP10,BL20,BL21 | 30 min, QD | 8 weeks | 30 | 48 ± 9 | Oral omeprazole caps 20 mg QAM; amoxicillin caps 0.5 g BID; metronidazole tabs 0.4 g BID | 30 | before treatment, after treatment | Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research—efficacy standards | Gastroscopy | Total effective rate 93.3%; GS decreased (p < 0.05) | [154] | |
| CAG | CN | SC | 52 ± 6 | WA | RN4,ST36,RN17,RN8,RN12 | QOD | 4 weeks | 63 | 53 ± 6 | Oral rabeprazole EC tabs 10 mg BID | 63 | before treatment, 1 week after treatment, 2 weeks after treatment, 1 month after treatment | TCM syndrome rating scale, TCMSS | TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | Four patients were dissatisfied with the treatment. | [155] | |
| CG | CN | SC | 47.61 ± 7.65 | WA Combined AC Method (AC + WA) | WA: EX-HN1, DU20, RN12, RN4, SP15, RN6, ST36, ST44, PC6, SP4, SP6;AC: ST36, Left SP3, Left LR3 | WA: QOD, needles retained 30 min; Rotation: QOD, needles retained 30 min | 8 weeks | 60 | 47.69 ± 7.71 | Pure WA ther (Western med) | 60 | Before treatment, 2 months after treatment | GSRS | Total effective rate 93.33%; GS decreased (p < 0.05); S-MOT and S-GAS increased, S-VIP decreased (p < 0.05); H. pylori conversion rate 79.24% | [156] | ||
| CAG | CN | SC | 52.44 ± 3.2 | AA | RN12,BL20,BL21 | 24 h, QOD | 24 weeks | 80 | 51.95 ± 3.6 | Weifuchun tabs 4 tabs TID | 80 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCM Symptom Score | Gastroscopy: mucosal score, pathological score; 13C-UBT | Total effective rate 77.92%; H. pylori conversion rate 65.63%, pathological efficacy 71.43%, gastroscopic efficacy 76.63%, syndrome efficacy 89.61%; symptom scores, syndrome scores, mucosal image scores, pathological scores decreased (p < 0.05) | One case of localized allergy | [141] |
| CG | CN | SC | 37.47 + 8.81 | AA | RN12,RN8,ST36,BL20 | 6–8 h, TIW | 4 weeks | 30 | 34.53 ± 9.60 | Oral omeprazole EC caps 20 mg/dose | 30 | Before treatment, after treatment | VAS | Total effective rate 86.7%; VAS for stomach pain decreased (p < 0.05) | [142] | ||
| CG | CN | SC | 54.27 + 10.92 | AA | RN8,RN12,BL18,BL20,BL21,ST36 | 4 h, QD | 1 week | 44 | 54.76 + 11.28 | Placebo AA | 42 | Before treatment, 3 days after treatment, 7 days after treatment | TCMSS per Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research | TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | [140] | ||
| CG | CN | SC | 51.25 ± 12.59 | AA | ST36,BL20,RN12,RN13,RN4,RN6 | 4 h, QD, d1–5 | 1.43 weeks | 40 | 55.28 ± 10.56 | Treat and nursing per TCM clinical pathway | 40 | Before treatment, 3 days after treatment, 10 days after treatment | VAS, TCMSS per Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research | Total effective rate 97.5%; gastric pain VAS and TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | Five patients experienced itching at the AA sites, which resolved spontaneously after discontinuing the medication. One patient developed an allergic reaction at the AA site. | [143] | |
| CG | CN | SC | AA | RN13,RN12,RN11,ST25 | QD | 1.43 weeks | 30 | Pantoprazole sodium 40 mg IV BID; oral herbal decoc 100 mL TID | 30 | Before treatment, after treatment | GI Diseases TCMSS | Total effective rate 96.7%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | [144] | ||||
| CAG | CN | SC | ACE | ST36,BL20,BL21,ST37,ST39, RN12 | QW | 24 weeks | 65 | 45 | After treatment | GI Diseases TCMSS | Gastroscopy: gastric mucosal lesion degree, gastric mucosa histopathology | [145] | |||||
| CG | CN | SC | 48.72 ± 9.13 | ACE | RN12,ST21,ST36,SP | QD | 1 week | 45 | 46.31 ± 8.64 | Omeprazole IV 40 mg | 45 | Before treatment, after treatment | TCMSS per Guidelines for New TCM Drugs Clinical Research | Total effective rate 95.55%; TCMSS decreased (p < 0.05) | [146] | ||
4.5. Combined Therapy
5. Discussion
6. Outlook and Future Direction
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CG | Chronic gastritis |
| CNAG | Chronic non-atrophic gastritis |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| ST36 | Zusanli |
| CV12 | Zhongwan |
| ST21 | Liangmen |
| BL20 | Pishu |
| H. pylori | Helicobacter pylori |
| EA | Electroacupuncture |
| RCTs | randomized controlled trials |
| CSG | Chronic superficial gastritis |
| CAG | Chronic atrophic gastritis |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-kappa B |
| JAK2 | Janus Kinase 2 |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| GAS-CCK | gastrin-cholecystokinin |
| SS | somatostatin |
| SP | substance P |
| Ala | Alanine |
| Asn | Asparagine |
| Ace | Acetate |
| AMP | Adenosine Monophosphate |
| ADP | Adenosine Diphosphate |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| Ins | Inositol |
| Ino | Inosine |
| DMG | N,N-Dimethylglycine |
| GPC | Glycerophosphocholine |
| Glu | Glutamate |
| Gly | Glycine |
| Gro | Glycerol |
| Gln | Glutamine |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HX | Hypoxanthine |
| Leu | Leucine |
| Met | Methionine |
| NAM | Nicotinamide |
| NAA | N-Acetylaspartate |
| PC | Phosphocholine |
| Phe | Phenylalanine |
| Suc | Succinate |
| Ser | Serine |
| Thr | Threonine |
| Val | Valine |
| AC | Acupuncture |
| LA | Laser Acupuncture |
| ACE | Acupoint catgut embedding |
| TENS | Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation |
| AA | Acupoint Application |
| MI | gastric antrum motility index |
| TFF | trefoil factor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| PG | Pepsinogen |
| GAS | gastrin |
| MOT | motilin |
| GH | Growth Hormone |
| MTL | Motilin |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| VLDL | very-low-density lipoprotein |
| NMDA | N-Methyl aspartic acid |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase M2 |
| UDG | Uracil-DNA Glycosylase |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| PCNA | Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| MUC | Mucin |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| CK | Cytokeratin |
| HRH2 | histamine receptor H2 |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| WA | Warm Needle Acupuncture |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| MA | moxibustion acupuncture |
| TCMSSS | Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Score Scale |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| hs-CRP | high-sensitivity C-reactive protei |
References
- Chinese Society of Gastroenterology; Cancer Collaboration Group of Chinese Society of Gastroenterology; Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of chronic gastritis in China (2022, Shanghai). J. Dig. Dis. 2023, 24, 150–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Gu, X.; Ruan, G.; Chen, S. Probiotics for the Treatment of Gastric Diseases. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobert, A.P.; Wilson, K.T. Induction and Regulation of the Innate Immune Response in Helicobacter pylori Infection. Cell Mol. Gastroenter. 2022, 13, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.M. Helicobacter pylori: Epidemiology and routes of transmission. Epidemiol. Rev. 2000, 22, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.L.; Chan, W.K.; Shiota, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection and public health implications. Helicobacter 2011, 16 (Suppl 1), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Lyu, N.H.; Zhu, H.Y.; Cai, Q.C.; Kong, X.Y.; Xie, P.; Zhou, L.Y.; Ding, S.Z.; Li, Z.S.; Du, Y.Q. Large-scale, national, family-based epidemiological study on Helicobacter pylori infection in China: The time to change practice for related disease prevention. Gut 2023, 72, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; de Martel, C.; Charvat, H.; Clifford, G.M.; Vaccarella, S.; Wang, L. Time trends and other sources of variation in Helicobacter pylori infection in mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Liu, Q.; Mao, X.Y.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, G.X.; Xu, S.F. Downward trend in the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infections and corresponding frequent upper gastrointestinal diseases profile changes in Southeastern China between 2003 and 2012. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Zhuang, L.X. Effect of acupuncture and moxibustion of Shu- and Mu-acupoints on the quality of life in patients chronic superficial gastritis. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2009, 34, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, H.; Ren, S. Clinical research on acupuncture and moxibustion treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2007, 27, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, H. Progress in traditional Chinese medicine against chronic gastritis: From chronic non-atrophic gastritis to gastric precancerous lesions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Lai, J.; et al. Identification of chronic non-atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia stages in the Correa’s cascade through machine learning analyses of SERS spectral signature of non-invasively-collected human gastric fluid samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 262, 116530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Valko, R.; Liska, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Flavonoids and their role in oxidative stress, inflammation, and human diseases. Chem-Biol. Interact. 2025, 413, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, H. Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Astaxanthin on Gastrointestinal Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukanov, V.V.; Smirnova, O.V.; Kasparov, E.V.; Sinyakov, A.A.; Vasyutin, A.V.; Tonkikh, J.L.; Cherepnin, M.A. Dynamics of Oxidative Stress in Helicobacter pylori-Positive Patients with Atrophic Body Gastritis and Various Stages of Gastric Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zhao, S.; Fang, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, M.; et al. Vitamin E Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Stress-Induced Gastritis via Modulating Nrf2 and NF-kappaB Signalling Pathways. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbarigia, C.; Carabotti, M.; Corsetti, M.; Annibale, B. Chronic atrophic gastritis and dyspepsia: A forgotten link? Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Huang, K.; Xu, M.; Hua, H.; Ye, F.; Yan, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y. Deoxycholic acid induces gastric intestinal metaplasia by activating STAT3 signaling and disturbing gastric bile acids metabolism and microbiota. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2120744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kuang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, F.; Ge, K.; Li, M.; Zhao, M.; et al. Bile Acid-Microbiome Interaction Promotes Gastric Carcinogenesis. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2200263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Yin, Z.; Chen, X.; Mao, R.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, M.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Gut microbiota-driven metabolic alterations reveal the distinct pathogenicity of chemotherapy-induced cachexia in gastric cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 209, 107476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Wei, S.; Zou, W.; Zhao, Y. Elucidation of the mechanism of berberine against gastric mucosa injury in a rat model with chronic atrophic gastritis based on a combined strategy of multi-omics and molecular biology. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1499753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Guo, S.; Chai, S.; Yang, J.; Yue, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, P.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Zhou, J.; et al. Autophagy in Gastric Mucosa: The Dual Role and Potential Therapeutic Target. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 2648065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, H.; Han, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Jia, X.; Jia, Q.; Yang, Q. High Hepcidin Levels Promote Abnormal Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis in Chronic Atrophic Gastritis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wan, S.Y.; Deng, F.C.; Dang, W.C.; Zhang, Y.C. Relationship between vagal nerve circuits and gastrointestinal motility. J. Neuroanat. 2020, 36, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziolek, M.; Garbacz, G.; Neumann, M.; Weitschies, W. Simulating the postprandial stomach: Physiological considerations for dissolution and release testing. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futagami, S.; Wakabayashi, M. Pancreatic Dysfunction and Duodenal Inflammatory Responses Coordinate with Refractory Epigastric Pain Including Functional Dyspepsia: A Narrative Review. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2022, 89, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.K.; Guo, Y.; Mashimo, H. Advances in the physiology of gastric emptying. Neurogastroent Motil. 2019, 31, e13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Wang, X.J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.L.; Mi, D.H. Effect of moxibustion at Zusanli (ST36) on gastric motility and gastric mucosal mucin expression in a rat model of chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Clin. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2024, 40, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Fu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Luo, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Ge, L.A.; Zhang, H.F. Effect of heat-sensitive moxibustion on Ghrelin and GHSR in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2020, 35, 5480–5485. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, C.; Yi, H.J. Combined effect of acupuncture and intelligent collaterals-activating therapy apparatus on gastric electrical rhythm and gastric mucosal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Acupunct. Res. 2014, 39, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Shen, Y.; Shao, X.H.; Zhang, X.L. Experimental study on laser acupuncture in the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis in rats. J. Hebei North. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 33, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.H.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Gao, J.W. Effect of laser acupuncture on trefoil factor expression in gastric mucosa of rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossinger, V.; Kayademir, T.; Blin, N.; Gott, P. Down-regulation of TFF expression in gastrointestinal cell lines by cytokines and nuclear factors. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 12, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F.; Luo, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, B.; Ge, L.A.; Kang, M.F.; Fu, Y.; Xiong, J. Effect of heat-sensitive moxibustion at Zhongwan (CV12) on serum GH and PG in chronic atrophic gastritis model rats. Chin. J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2020, 40, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.T.; Zhong, H.; Xu, X.; Liang, Z.Y.; Chang, X.R.; Liu, M. Effect of moxibustion on inflammatory factors in the skin of Zusanli (ST36) area in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 50, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. On acupoints and acupoint specificity. Chin. J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2021, 41, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, Z.B.; Wang, C.G.; Liu, Q.; Luo, J.L.; Wang, S.H.; Yang, L.X. Effect of Yuhan Nuanguan Gao on gastric mucosa in rats with precancerous gastric lesions. Henan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 37, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, C.Z.; Huang, D.Y. Mechanism of acupoint catgut embedding in improving gastric mucosal congestion in chronic atrophic gastritis based on hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor. Acupunct. Res. 2020, 45, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, N.; Chang, X.; Zha, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Gui, S. Platycodonis radix polysaccharides suppress progression of high-fat-induced obesity through modulation of intestinal microbiota and metabolites. Phytomedicine 2025, 142, 156653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, H. Effect of Gastrin G-17 Combined with Pepsinogen PGI and PGII on the Early Screening of Gastric Cancer in the Department of Gastroenterology. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2024, 30, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.H.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Gao, J.W.; Zhu, X.B.; Yang, Y.P. Effect of laser irradiation at Zusanli (ST36) on gastric acid secretion and nitric oxide content in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 38, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Yang, G.Q.; Qin, C.J.; Bi, Y.F. Effect of acupuncture at back-shu points on gastrin, motilin, and epidermal growth factor in CAG model rats. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 38, 1613–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.Q.; Jia, C.W.; Zuo, J.; Jia, S.S. Effect of acupuncture at back-shu points on serum PGI and PGII in CAG model rats. Chin. J. Basic. Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 20, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furgala, A.; Ciesielczyk, K.; Przybylska-Felus, M.; Jablonski, K.; Gil, K.; Zwolinska-Wcislo, M. Postprandial effect of gastrointestinal hormones and gastric activity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Sci. Rep-Uk 2023, 13, 9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yan, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Su, K.; Liu, W. Effects of Zuojin pill on depressive behavior and gastrointestinal function in rats with chronic unpredictable mild stress: Role of the brain-gut axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Deng, H.; Zhou, W.; Liang, Z. Effects of electroacupuncture combined with acupoint catgut embedding on gastrointestinal motility and gastrointestinal hormones in rats with functional dyspepsia. Chin. J. Physiol. 2023, 66, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Fu, Y.; Hong, E.S.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.F. Effect of heat-sensitive moxibustion on gastrointestinal hormones in chronic atrophic gastritis model rats. J. Jiangxi Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 31, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Jensen, R.T. P21-activated kinase 4 in pancreatic acinar cells is activated by numerous gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth factors by novel signaling, and its activation stimulates secretory/growth cascades. Am. J. Physiol-Gastr Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G302–G317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T. Anatomical basis of gastrin- and CCK-secreting cells and their functions. A review. Biomed. Res-Tokyo 2023, 44, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, Z.B.; Wang, S.H.; Peng, Z.H. Effect of acupoint application of Yuhan Nuanguan Gao on gastrointestinal hormones in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. New Chin. Med. 2016, 48, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagari, R.M.; Rabitti, S.; Greenwood, D.C.; Eusebi, L.H.; Vestito, A.; Bazzoli, F. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Diagnostic performance of the combination of pepsinogen, gastrin-17 and anti-Helicobacter pylori antibodies serum assays for the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 46, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.X.; Wang, B.Y.; Liu, C.F.; Yang, L.; Li, D.D.; Zhang, Y.L. Effect of combination of He-Mu acupoints on PGI, PGII, PGR, and G-17 in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2016, 27, 496–498. [Google Scholar]
- Lecci, A.; Capriati, A.; Altamura, M.; Maggi, C.A. Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors in the gut, with special reference to NK2 receptors in human. Auton. Neurosci-Basic. 2006, 126, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, T.D.; Nogueiras, R.; Andermann, M.L.; Andrews, Z.B.; Anker, S.D.; Argente, J.; Batterham, R.L.; Benoit, S.C.; Bowers, C.Y.; Broglio, F.; et al. Ghrelin. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 437–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Shen, G.; Zhang, M.; Huang, S.; He, Y. Neural mechanism of gastric motility regulation by electroacupuncture at RN12 and BL21: A paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus-dorsal vagal complex-vagus nerve-gastric channel pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 13480–13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.R.; Wang, P.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Gu, X.; Xie, T.Y.; Fu, P. Effect of acupuncture at different depths at Zusanli (ST36) on digestive and immune indices in rats with chronic gastritis. World J. Chin. Med. 2017, 12, 2147–2150. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.Q.; Zhang, B.Q.; Jia, C.W.; Zuo, J.; Jia, S.S. Effect of acupuncture at back-shu points on gastrin and motilin in chronic atrophic gastritis model rats. Int. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 36, 819–820. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.H.; Luo, S.J.; Li, Y.L. Efficacy of moxibustion combined with spleen-invigorating method in treating spleen deficiency-type chronic atrophic gastritis model rats. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2014, 34, 5498–5499. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.L.; Wu, Q.H.; Huang, S.P. Experimental study on the effect of Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction combined with moxibustion box on motilin in spleen deficiency-type chronic atrophic gastritis rats. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 35, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, K.K.; Chang, X.; Shen, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; et al. NMR-based metabolomics Reveals Alterations of Electro-acupuncture Stimulations on Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Rats. Sci. Rep-Uk 2017, 7, 45580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Chen, J.L.; Chang, X.R.; He, Q.D.; Shen, J.C.; Lian, L.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, F.Q.; Huang, H.Y.; et al. Comparative metabolomics study on therapeutic mechanism of electro-acupuncture and moxibustion on rats with chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG). Sci. Rep-Uk 2017, 7, 14362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Shen, J.; Liu, C.; Zhong, H.; Yang, Q.; Shu, W.; Ma, M.; Dong, J.; Yang, Z.; Chang, X.; et al. Effects of moxibustion and acupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36) and Zhongwan (CV 12) on chronic atrophic gastritis in rats. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; She, C.; Zhong, H.; Liu, T.; Cao, J.N.; Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Chang, X.R. Effects of moxibustion at Zusanli (ST36) on gastric tissue metabolites in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis based on metabolomics technology. Acupunct. Res. 2019, 44, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, M.D.; Liu, S.M.; Xiao, Y.Z.; Wang, W.J.; Ma, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.R. Mechanism of indirect moxibustion in regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression to inhibit glycolysis in chronic atrophic gastritis rats. World J. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yin, H.Z.; Jin, J.Y.; Zhong, H.; Shi, J.; Chang, X.R.; Liu, M. Effect of moxibustion on local acupoint tissue metabolism in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Hunan Univ. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.N.; Zhong, H.; Liu, M.; Luo, X.T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chang, X.R.; Feng, F. Effect of warm acupuncture on local acupoint tissue metabolism in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Hunan Univ. Chin. Med. 2020, 40, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Qi-da, H.; Yuan-Peng, H.; Li-Bing, Z.; Jia-Cheng, S.; Lin-Yu, L.; Yuan, Z.; Long-Bin, Z.; Lin-Chao, Q.; Xian-Jun, M.; Mi, L.; et al. Difference of Liver and Kidney Metabolic Profiling in Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Rats between Acupuncture and Moxibustion Treatment. Evid-Based Compl Alt. Med. 2018, 2018, 6030929. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, E.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. Feeding gut microbes to nourish the brain: Unravelling the diet-microbiota-gut-brain axis. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1454–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yau, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Gan, H.; Qian, L.; Yang, Z. Effect of Electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) on Intestinal Microbiota in Rats with Chronic Atrophic Gastritis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 824739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Luo, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, B.; Ge, L.A.; Xiong, J.; Fu, Y. Effect of heat-sensitive moxibustion on c-Myc, Survivin, and Cyclin D1 in chronic atrophic gastritis model rats. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2020, 31, 746–749. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.B.; Wang, C.G.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.D.; Ma, F.Q. Effect of moxibustion on gastric mucosal cell proliferation factors in rats with precancerous lesions of chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2015, 35, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, Z.E.; Walton, Z.E.; Altman, B.J.; Hsieh, A.L.; Dang, C.V. MYC, Metabolism, and Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1024–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, J. Research Progress of PCNA in Reproductive System Diseases. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2021, 2021, 2391917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Cardoso Rodriguez, F.; Sufi, J.; Vlckova, P.; Claus, J.; Tape, C.J. An oncogenic phenoscape of colonic stem cell polarization. Cell 2023, 186, 5554–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, W.; Kong, Y.; Liu, B.; Zeng, M.; Wang, W. Restoration of microRNA-130b expression suppresses osteosarcoma cell malignant behavior in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, S.P.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Gong, A.; Le, Y.M.; Yi, X.Q. Effect of Yiqi Shengyang acupuncture on GLi and COX-2 protein expression in gastric mucosa of rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 41, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Gong, A. Effect of moxibustion therapy on TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in reversing precancerous lesions of chronic atrophic gastritis. Contemp. Med. Forum 2021, 19, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.G.; Xue, X.J.; Zhang, C.L. Mechanism of electroacupuncture on chronic atrophic gastritis mice via Fas/FasL signaling pathway. Chin. Health Preserv. 2024, 42, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, C.Z.; Huang, D.Y. Effect of acupoint catgut embedding on JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway-related factors in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Acupunct. Res. 2018, 43, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, Z.B.; Wu, Y.T.; Wang, S.H. Effect of Yuhan Nuanguan Gao on repair mechanisms in chronic atrophic gastritis. Guangming J. Chin. Med. 2016, 31, 2034–2038. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Xiao, Y.Z.; Wu, M.D.; Wu, H.G.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Mechanism of herbal cake-separated moxibustion on the PTEN-AKT tumor-suppressing pathway in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2021, 40, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, L.X.; Ma, Z.; Gu, M.E.; Huang, R.D.; Li, J.; Wu, L.Y.; Liu, H.R.; Ma, X.P.; Zhang, J.F.; et al. Effect of moxibustion on peripheral blood gene expression profiles in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 21, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.L.; Fan, J.W.; Jiang, W. Modified Chaihu Shao Liu Junzi Formula combined with Zhuang medicine thread moxibustion for gastric precancerous lesions. Acta Chin. Med. 2018, 33, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, Q.; Shu, W.N.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, L.; Chang, X.R.; Zhong, H.; Liu, M. Effects of moxibustion and acupuncture on apoptosis and NF-κB, Bcl-2 gene expression in gastric mucosa of rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Acupunct. Res. 2021, 46, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Lv, S.; Qi, Q.; Liu, H.; Shi, Z.; et al. Acupuncture Regulates Serum Differentially Expressed Proteins in Patients with Chronic Atrophic Gastritis: A Quantitative iTRAQ Proteomics Study. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2021, 2021, 9962224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Wang, Y.D.; Chang, X.R.; Wang, C.G.; Liu, M. Mechanism of electroacupuncture in inhibiting gastric mucosal cell apoptosis in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2016, 31, 3005–3008. [Google Scholar]
- Jaroenlapnopparat, A.; Bhatia, K.; Coban, S. Inflammation and Gastric Cancer. Diseases 2022, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ye, Y.; Guan, Q.; Zhou, Y. A comprehensive evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of celecoxib in combination with chemotherapy in metastatic or postoperative recurrent gastric cancer patients: A preliminary, three-center, clinical trial study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Acupuncture at ST36 Point: A Literature Review in Animal Studies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 813748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, M.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jin, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.; Sun, M.; Li, T. Assessment of anti-inflammatory efficacy of acupuncture in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2023, 74, 102946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Tu, J.; Bao, X.; Yang, J.; Lee, M.S.; Wang, L. Clinical effect and contributing factors of acupuncture for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and pairwise and exploratory network meta-analysis. Bmj Evid-Based Med. 2024, 29, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Jin, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Acupuncture improves the symptoms, intestinal microbiota, and inflammation of patients with mild to moderate Crohn’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Eclinicalmedicine 2022, 45, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Shaik, A.S.; Shaik, A.P.; Alyousef, A.A.; Bardia, A.; Habeeb, M.A.; Khan, A.A. Gene expression patterns of COX-1, COX-2 and iNOS in H. Pylori infected histopathological conditions. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Sakata, D.; Esaki, Y.; Li, Y.; Matsuoka, T.; Kuroiwa, K.; Sugimoto, Y.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin E2-EP4 signaling promotes immune inflammation through Th1 cell differentiation and Th17 cell expansion. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Carmona, M.; Lesage, J.; Cataldo, D.; Gilles, C. EMT and inflammation: Inseparable actors of cancer progression. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 805–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, M.; Spyratos, F.; Le Doussal, V.; Desplaces, A.; Rouesse, J. Flow cytometric analysis of DNA content and keratins by using CK7, CK8, CK18, CK19, and KL1 monoclonal antibodies in benign and malignant human breast tumors. Cytometry 1990, 11, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Lai, J.; Luo, L.; Zhou, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, B. Cytokeratin 18 fragment in liver inflammation and fibrosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 569, 120147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, T.O.; Steininger, R.; Agrawal, D.K. NPY and NPY receptors in airway structural and inflammatory cells in allergic asthma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassett, M.S.; Braz, J.M.; Castellanos, C.A.; Salvatierra, J.J.; Sadeghi, M.; Yu, X.; Schroeder, A.W.; Caston, J.; Munoz-Sandoval, P.; Roy, S.; et al. IL-31-dependent neurogenic inflammation restrains cutaneous type 2 immune response in allergic dermatitis. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eabi6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.Y.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Q.; Yin, H.Z.; Liu, M.; Chang, X.R.; Wang, C. Effects of different acupuncture methods on Merkel cell markers and neuropeptide expression in the Zusanli (ST36) area of rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Acupunct. Res. 2022, 47, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. Acupoint sensitization phenomenon and its biological significance. Chin. J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2019, 39, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Jin, J.Y.; Chang, X.R.; Zhong, H.; Liu, M. Effect of acupuncture on HRH2, SP, and inflammatory factor expression in the Zusanli (ST36) area of rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Hunan Univ. Chin. Med. 2021, 41, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Zhong, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Qu, S.; Zhang, J. Acupuncture Decreases NF-kappaB p65, miR-155, and miR-21 and Increases miR-146a Expression in Chronic Atrophic Gastritis Rats. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2016, 2016, 9404629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, E.C.; Sahingur, S.E. The Ubiquitin System and A20: Implications in Health and Disease. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.R.; Fehlings, M.G. Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis and inflammation are key features of acute human spinal cord injury: Implications for translational, clinical application. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, D.Y. Effect of acupoint catgut embedding on gastric mucosal morphology and serum SOD, MDA levels in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Guangzhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 37, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Q.; Jia, C.W.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zuo, J.; Jia, S.S. Effect of acupuncture at back-shu points on serum SOD and MDA in CAG model rats. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 35, 621–623. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiecien, S.; Jasnos, K.; Magierowski, M.; Sliwowski, Z.; Pajdo, R.; Brzozowski, B.; Mach, T.; Wojcik, D.; Brzozowski, T. Lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species and antioxidative factors in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions and mechanism of protection against oxidative stress-induced gastric injury. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 65, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, W.J.; Li, P.; Liu, S.Y.; Huang, W.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, Y.P.; Meng, X.J. Effect of moxibustion at stomach meridian points on miR-146a, NF-κBp65, and COX-2 expression in gastric mucosa of rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2022, 37, 3480–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Li, M.Y.; Shu, W.N.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, M.; Chang, X.R. Comparative study on the effects of acupuncture and moxibustion on cyclooxygenase-2 and inflammatory factors in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2022, 37, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, C.Z.; Huang, D.Y. Effect of acupoint catgut embedding on gastric mucosal and serum inflammatory factors in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Shandong J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 38, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Yang, L.J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.G. Effect of combined acupuncture and herbal medicine on IL-10 and TNF-α levels in gastric tissue of rats with chronic gastritis. Hunan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 33, 168–169, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Wang, J.G.; Ma, Y.F.; Li, D.D.; Gao, J.W.; Yang, Y.P. Effect of laser acupuncture on serum inflammatory factors in rats with chronic atrophic gastritis. Laser J. 2016, 37, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.L.; Xie, W.C.; Xie, Y.F.; Huang, B. Effect of Weiwei Granules combined with auricular plaster therapy on the NF-κB pathway in gastric mucosa of patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. Acta Chin. Med. 2018, 33, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Kuang, D.; Li, D.; Yan, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mediating effect of gastrointestinal symptoms on dietary behavior and quality of life in Chinese adults with chronic gastritis-a cross-sectional study. Front. Med-Lausanne 2023, 10, 1178897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, S.; Larsson, S.C. Depression and 24 gastrointestinal diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Transl. Psychiatr. 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Jing, J.; Wang, Z.; He, T.; Tian, M.; Yuan, Z.; Cui, Y.; Rong, W.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Zuojin Pill for the Treatment of Chronic Nonatrophic Gastritis: A Randomized Active-Controlled Clinical Trial. Evid-Based Compl. Alt. Med. 2022, 2022, 2266023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Li, J.X.; Fan, L.Y.; Zhao, B.F.; Hu, S.; Lou, B.D.; Yan, J. Clinical observation of electroacupuncture at “three-segment stomach meridian points” for chronic superficial gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2017, 36, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.P.; Wu, Z.Q.; Huang, S.R. Clinical study on reconstructing gastric mucosal functional homeostasis in chronic gastritis patients using Five Circuits-Six Qi Kaihe acupuncture. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 42, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.W.; Chang, X.H.; Wang, Z.F.; Du, C.H. Clinical observation on acupuncture with Host-Guest Yuan-Luo point combination for chronic superficial gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2021, 40, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Yang, G.Q.; Huang, L.P.; Qin, C.J.; Zhang, X.X. Effect of acupuncture at back-shu points on serum CD4+ and CD8+ in chronic gastritis patients. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 38, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.H.; Shi, W.Y.; Shi, B. Clinical study on Yuan-Luo Tongjing acupuncture combined with floating acupuncture for spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Clin. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2024, 40, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ye, H.; Chen, X.Q.; He, C.B. Efficacy of Yuan-Luo Tongjing acupuncture combined with filiform-fire needling on serum MTL, SS, and GAS levels in spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic atrophic gastritis. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 39, 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Q.; Xu, K.K.; Dai, M. Clinical efficacy of “Spleen-Stomach Old Ten Needles” in chronic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia. China Med. Her. 2018, 15, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, J.J.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, Y. Clinical study on ginger-partitioned moxibustion for chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2021, 40, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tao, T. Effect observation of electronic moxibustion in spleen-stomach qi deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Nurs. Sci. 2017, 24, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.S.; He, J.; Zhu, H.W.; Gu, M.E.; Gu, J.W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.G. Clinical effects of indirect moxibustion on gastric mucosal protection in chronic gastritis patients. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Feng, F.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Liu, M.; Chang, X.R.; Xie, H. Effect of moxibustion at sensitized acupoints on quality of life in chronic superficial gastritis patients. J. Acupunct. Tuina Sci. 2020, 18, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Luo, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.J. Effect observation of Panlong moxibustion on spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic atrophic gastritis. Guid. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2020, 26, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yuan, X.X.; Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Clinical observation on He-Mu point combination moxibustion for chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2017, 36, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.M.; Li, Y.M. Clinical observation of spreading moxibustion in 25 cases of chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Jiangsu J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 49, 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, M.E.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, H.R.; Huang, R.D.; Wu, L.Y.; Peng, G.B.; Li, G.N.; Li, J.; Wu, H.G. Clinical observation of moxibustion on chronic atrophic gastritis and its effect on peripheral blood DNA methylation. World J. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Wang, S.S.; Wu, H.G.; Zhao, J.M.; Ma, X.P.; Huang, R.J.; Liu, H.R.; Tian, T.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, J.; et al. Clinical study on the efficacy of moxibustion for chronic gastritis and its effect on serum brain-gut peptides (in Chinese). J Acupunct. Tuina Sci. 2016, 14, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Z.; Zhou, S.J.; Gui, S.H.; Cai, Y. Effect of warm acupuncture on symptom improvement and quality of life in patients with spleen-stomach deficiency (cold) syndrome of chronic superficial gastritis. World J. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.; Yang, G.Q.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, L.J.; Guo, Z. Warm acupuncture for spleen-stomach deficiency (cold) type chronic superficial gastritis. Jilin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 38, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.R.; Sun, M.Q. Clinical efficacy of warm acupuncture in treating spleen-stomach deficiency (cold) type chronic superficial gastritis. Mod. Dig. Interv. 2019, 24, 2563–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.C. Endoscopic efficacy of warm acupuncture for chronic superficial gastritis and its effect on gastric Hp levels. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 35, 190–192. [Google Scholar]
- Situ, Y.X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, M.Y. Effect of moxa stick moxibustion combined with TCM nursing on spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanxi Med. J. 2020, 49, 3030–3032. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.S.; Dai, X.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, C. Effect of Xiangshu Fang acupoint application on TCM symptom scores in chronic gastritis patients with qi stagnation syndrome. J. Nurs. Sci. 2018, 25, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.S.; Cao, Z.Q.; Zhou, X.F.; Chen, T. Clinical observation of Qilian Shupi Gao acupoint application for precancerous lesions of chronic atrophic gastritis. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2018, 29, 2953–2955. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.J.; Chen, D.F.; Chen, Z.L.; Xie, H.M.; Dai, L.; Chu, X. Efficacy observation of Wenpi Plaster for spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type epigastric pain. J. Chengdu Med. Coll. 2021, 16, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.Y.; Kuang, Y.X.; Li, Z.X. Efficacy observation of Wentong Plaster for spleen-stomach qi deficiency type chronic gastritis. Chin. Nurs. Res. 2017, 31, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.F.; Jiang, W.; Wang, C.J. Clinical observation of Weining Fang acupoint application for chronic gastritis. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Dig. 2014, 22, 158–159. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.H.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Song, X.J.; Ke, S.H. Acupoint catgut embedding for 65 cases of chronic atrophic gastritis. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 35, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Zhang, J. Clinical observation on acupoint injection for acute exacerbation of chronic gastritis. World J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2020, 15, 1898–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yang, W.L. Clinical observation of “Mind-Regulating Acupuncture” for chronic superficial gastritis. Acta Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 2017, 45, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Li, G.Q. Clinical observation of “Warm-Unblocking Acupuncture” for spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2017, 37, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, Z.X.; Hu, W. Efficacy observation of acupuncture for chronic atrophic gastritis with Helicobacter pylori infection. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 37, 1078–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, R.D.; Liu, Y.P.; Wei, J.W.; Wang, J.N.; He, X.; Zhou, W. Efficacy observation of “Left Yin-Right Yang Meridian Regulation” for chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2021, 40, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ben, D.Y.; Xiang, J.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Chen, H.J.; Xue, Y.T.; Chen, J.J.; Li, T.L.; Han, C.P. Clinical study on Congnao Tongluo acupuncture for alcohol-related chronic gastritis with depression (in Chinese). J. Acupunct. Tuina Sci. 2016, 14, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H. Efficacy of soothing liver and harmonizing stomach acupuncture for acute qi-stagnation type gastralgia. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2014, 34, 1059–1060. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Li, J.; Gu, M.E.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.J. Study on the efficacy of ginger-partitioned moxibustion with different moxa materials for chronic atrophic gastritis. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 43, 797–800. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.M.; Li, G.M.; He, W.J.; Xie, H. Clinical observation of warm acupuncture for chronic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2015, 34, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M. Effect of moxa stick moxibustion combined with TCM nursing on spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic atrophic gastritis. Today’s Health 2021, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Qu, B.; Tan, Y.Z. Efficacy of Harmonizing Acupuncture combined with warm acupuncture on GAS, MTL, and VIP levels in spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic gastritis. J. Clin. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2020, 36, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Gu, Y.J.; Fei, J.L. Clinical observation of Wu Zhu Yu Bing Lang Tang acupoint application for chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2019, 25, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.F.; Wang, F.L. Clinical observation of Li medicine Binglang acupoint application combined with Western medicine for chronic superficial gastritis. Guid. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2019, 25, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, H.F.; Wang, F.L. Efficacy of Huangqi Jianzhong Decoction combined with Binglang acupoint application for cold-coagulation qi-stagnation type chronic superficial gastritis. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 39, 752–754. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, D.X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Yang, X.R. Efficacy and safety of Chailong Niwei Decoction combined with acupoint catgut embedding for non-HP-infected liver-stomach qi-stagnation type chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 38, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, G.T.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.X. Efficacy observation of acupoint catgut embedding combined with proton pump inhibitors for chronic non-atrophic gastritis. World J. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 1884–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Feng, S.B.; Liu, H.W.; Jin, Y.; Lei, F. Efficacy of warm acupuncture combined with Huanglian Wendan Decoction for chronic superficial gastritis. World J. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Guo, Q.; Hu, J.; Wei, B.L.; Xie, Y.Y. Clinical efficacy of Fuling Sini Decoction combined with back-shu Thunder-Fire moxibustion for yang-deficiency constitution chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2021, 32, 677–679. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.J.; Cao, C.D.; Tang, L.H.; Huang, B. Efficacy and safety of back-shu acupuncture combined with acupoint catgut embedding for spleen-stomach qi deficiency type chronic superficial gastritis. J. Clin. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2021, 37, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiao, Y. Efficacy of Banxia Xiexin Decoction combined with acupuncture for cold-heat complex type chronic atrophic gastritis. China Med. Her. 2021, 18, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Han, J.; Yin, S.; Luo, H.H.; Xie, A.W. Efficacy observation of acupuncture combined with Danggui Sini Decoction for chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2020, 39, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.T.; Shi, Z.H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Shi, T.; Yang, L.; Cao, D. Clinical efficacy of Jianpi Huoxue Formula combined with acupuncture on gastric collateral blood stasis type chronic atrophic gastritis and its effects on inflammatory markers and gastric mucosal function. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2024, 30, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, O.N.; He, X.Y.; Xiang, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, J. Clinical study on combined acupuncture and herbal medicine for qi-stagnation blood-stasis type chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Basic. Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 21, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.H.; Huang, Z.B.; Zhou, H. Clinical observation of Tiaozhong Yiwei Decoction combined with Mu-He acupoint moxibustion for spleen-stomach deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 39, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.R.; Ye, Y.; Pei, B.; Song, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.T.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.J. Clinical study of Piwei Peiyuan Pill combined with moxibustion for spleen-stomach deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2025, 48, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.J.; Wu, Y.Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.Y. Clinical efficacy of Wenpi San acupoint application combined with Lizhong Fuyuan Formula for spleen-deficiency phlegm-stasis type chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 2902–2907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.R. Efficacy observation of acupuncture combined with acupoint application on chronic atrophic gastritis and its effects on serum inflammatory factors and gastrointestinal hormones. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2023, 42, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Lu, Y.T.; Huo, Y.L.; Yang, Q.; Li, D.G. Clinical study of Huazhuo Jiedu Formula combined with acupoint application for chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Dig. 2021, 29, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.J.; Liang, J.W.; Miao, X.M.; Yan, H.; Chi, L.L. Efficacy observation of acupoint catgut embedding combined with quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori (+)-spleen-stomach deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis. Acupunct. Res. 2022, 47, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Li, M.; Wang, K. Clinical study of acupoint catgut embedding combined with moxibustion for chronic atrophic gastritis. Shandong J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 38, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, C.L.; Shi, Y. Efficacy of Shenhu Ezhu Granules combined with acupoint application for elderly chronic gastritis. Northwest Pharm. J. 2022, 37, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Z.Q.; Gong, X.Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Lü, L.; Liu, X.Y. Effect of acupotomy release combined with acupoint catgut embedding on electrogastrogram in chronic gastritis patients. Hubei J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 37, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, F.; Yan, B.; Zhang, A.; Li, C. Effect of auricular plaster therapy combined with acupoint massage on pain and anxiety in chronic gastritis. Chin. Nurs. Res. 2015, 29, 2419–2421. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Jiao, L.; Gong, Y.; Shi, J. Research on Electroacupuncture Parameters for Cancer Pain Based on Data Mining. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2023, 22, 15347354231192017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Chang, X.; Zhan, D.; Diao, D.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, D.; Hu, M.; et al. Acupuncture for Quality of Life in Gastric Cancer Patients Undergoing Adjuvant Chemotherapy. J. Pain. Symptom Manag. 2022, 63, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Lim, X.Y.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T. Mechanisms of acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) and its combinational acupoints for stress gastric ulcer based on the correlation between Zang-fu and acupoints. J. Integr. Med-Jim 2025, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondrup, R.; Tidwell, T.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Lobsang, D.; Hua, Q.; Geri, D.; Suonan, D.C.; Fan, G.; Samdrup, G. Tibetan medicine Liuwei Muxiang pills (LWMX pills) effectively protects mice from chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Phytomedicine 2023, 115, 154826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, J.; Xiao, D.; Shen, N.; Wang, R.; Miao, H.; Pu, P.; Zhang, H.; Yv, X.; Xing, L. Chronic atrophic gastritis and risk of incident upper gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, J.L.; Jiao, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.H. Application of acupoint application combined with Huangqi Jianzhong Decoction for spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic superficial gastritis. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Dig. 2017, 25, 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.H.; Dai, E.Q.; Bai, Y.R.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.B. Clinical study on herbal medicine combined with acupuncture and acupoint catgut embedding under the guidance of “Yiqi Shengyang Huoxue method” for chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. Gen. Pr. Pract. 2017, 20, 492–496. [Google Scholar]
- Shui, D.K.; Qin, L.N.; Wang, L. Clinical efficacy of Lizhong Tongluo Huazhuo Decoction combined with acupoint catgut embedding for spleen-deficiency dampness accumulation type chronic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia based on “Yiqi Zhouliu” theory. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2021, 32, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Lu, Y.X.; Han, F. Efficacy of Yiqi Shugan Formula combined with acupoint catgut embedding for liver-qi stagnation type Helicobacter pylori-positive chronic atrophic gastritis and its effect on laboratory indicators. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2019, 39, 2912–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Hu, Z.J. Efficacy and safety evaluation of self-designed Tiaowei Shengtang Decoction and acupoint catgut embedding for chronic atrophic gastritis. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 37, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, F. Efficacy observation of self-designed Yangwei Decoction combined with acupoint catgut embedding for chronic atrophic gastritis. Mod. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2018, 27, 2893–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lai, J.S.; Peng, W.J.; Ge, Y. Clinical study of syndrome-differentiated herbal medicine combined with bee venom therapy in reversing gastric precancerous lesions. Acta Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 2014, 42, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, H.; Fu, Y.M.; Du, X. Danshi Jianpi Decoction combined with acupuncture for 43 cases of precancerous lesions in chronic atrophic gastritis. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 16, 765–768. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; An, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.B.; Xu, J.Z. Clinical observation of modified Thunder-Fire moxibustion combined with herbal decoction for chronic atrophic gastritis. J. Clin. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2015, 31, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.J.; Zheng, X.M.; Liang, J.H. Effect of Jianwei Xiaopi Decoction combined with acupuncture on serum epidermal growth factor and nitric oxide in chronic atrophic gastritis. Hebei J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 39, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.R.; Ye, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Pei, B.; Li, X.J.; Cheng, H.L. Multicenter randomized controlled trial on the efficacy of modified Piwei Peiyuan Formula combined with acupuncture for chronic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia. Chin. Gen. Pr. Pract. 2024, 27, 2466–2475. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.J.; Du, J.H.; Bi, L.B.; Sha, R.G.W.; Hu, G.J.L. Efficacy observation of “Three Gastric Needles” combined with PPI triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori-positive chronic atrophic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2020, 39, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y. Clinical observation of Weishu Mixture combined with acupuncture for spleen-stomach dampness-heat type chronic atrophic gastritis. West. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 35, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.L.; Hu, Z.J.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.H.; Hong, X.F. Efficacy and safety of Yangyin Hewei Huayu Decoction combined with acupuncture for chronic atrophic gastritis. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 37, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wen, A.Y. Efficacy evaluation of Weipi Formula combined with Huangqi injection at acupoints for spleen-stomach deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis using targeted biopsy technology. J. Guangzhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 33, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Wu, D. Efficacy of Yuan-Luo Tongjing acupuncture combined with medication for chronic atrophic gastritis (spleen-stomach deficiency type). Chin. J. Gerontol. 2016, 36, 3751–3752. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Y.K. Treatment of 35 cases of chronic atrophic gastritis with acupuncture at Liangqiu (ST34) combined with modified Lizhong Decoction. Shaanxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 35, 740–741. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Deng, X.X.; Luo, Y.W.; Li, Z.S.; Chen, C.L. Effects of acupuncture combined with modified Xiangsha Liujunzi Decoction on TCM symptoms, histology, and efficacy in spleen-stomach deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2022, 40, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Zhang, X.M.; Guo, T.T.; Yan, X.H.; Li, X.H. Clinical observation of Hu’s Yiwei Decoction combined with acupuncture for chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2025, 43, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.A.; Liu, Y. Clinical efficacy of combined acupuncture and herbal medicine for chronic atrophic gastritis and its effect on the NF-κB/COX-2 signaling pathway. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2023, 34, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Li, W.D.; Chen, G.H.; Wei, Y.; Liu, F. Clinical efficacy of Niwei Cuyu Decoction combined with warm acupuncture on chronic atrophic gastritis and its effect on vascular endothelial factors. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 37, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.Z.; Liao, A.; Liao, J.P.; Zhong, Y. Efficacy of Shengwei San combined with warm acupuncture on chronic atrophic gastritis and its effect on serum pepsinogen levels. J. Chengdu Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 41, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.J.; Liu, L.D. Clinical efficacy of Lizhong Fuyuan Formula combined with Wenpi San acupoint application for spleen-stomach deficiency type chronic atrophic gastritis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2020, 42, 2537–2541. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, J.S.; Ye, G.W.; Xu, X.Z. Effect of Zhizhu Lianxia Decoction combined with acupuncture on prognosis of chronic gastritis patients. Sichuan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 37, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.C.; Chen, H.M.; Zhang, B. Efficacy observation of “Old Ten Moxibustion” combined with herbal medicine for spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic gastritis. Shanghai J. Acupunct. Moxibust. 2017, 36, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Kang, L.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Lu, D.; Bai, Y.S.; Li, F.P. Effect of moxibustion box combined with warmed herbal external application on spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic gastritis. Hebei J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 2023, 38, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.M.; Li, X.J. Long-term efficacy observation of combined acupuncture and herbal medicine for liver-stomach heat stagnation type chronic gastritis. World J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2015, 10, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lü, Y.; Liang, R.; Shi, D.M.; Cao, Y.Y.; Chen, R.H.; Li, X. Efficacy observation of acupoint application combined with warm meridian ginger therapy in 100 cases of spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type epigastric pain. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2015, 26, 2196–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhou, X.L.; Shui, D.K. Efficacy observation of Huangqi Jianzhong Decoction combined with herbal acupoint application for 120 cases of spleen-stomach deficiency-cold type chronic gastritis. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Dig. 2014, 22, 471–472. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.M.; Gong, X.Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Lü, L.; Liu, X.Y. Effect of acupotomy release combined with acupoint catgut embedding on serum EGF and PGE2 in chronic gastritis patients. China Med. Her. 2017, 14, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
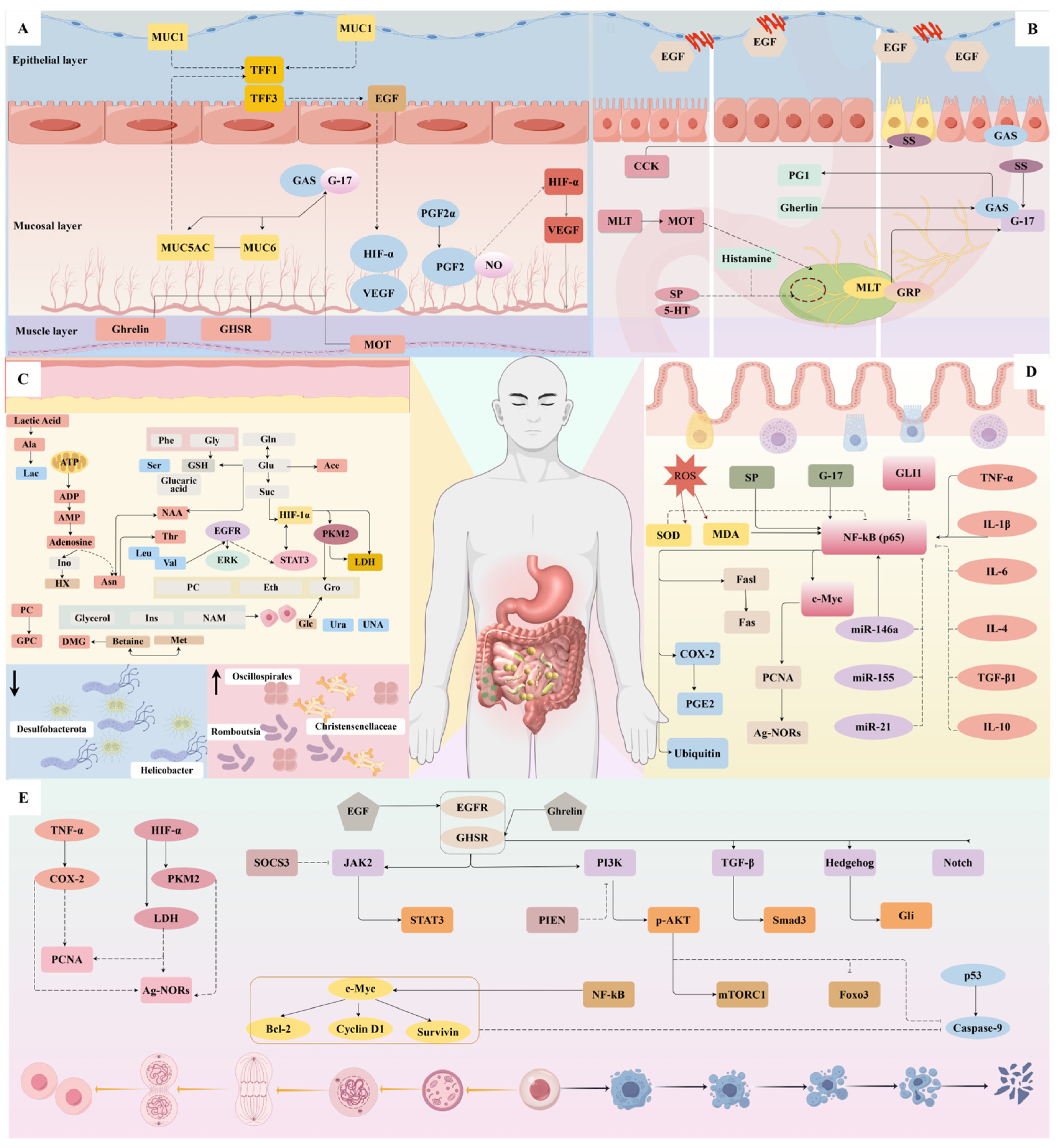
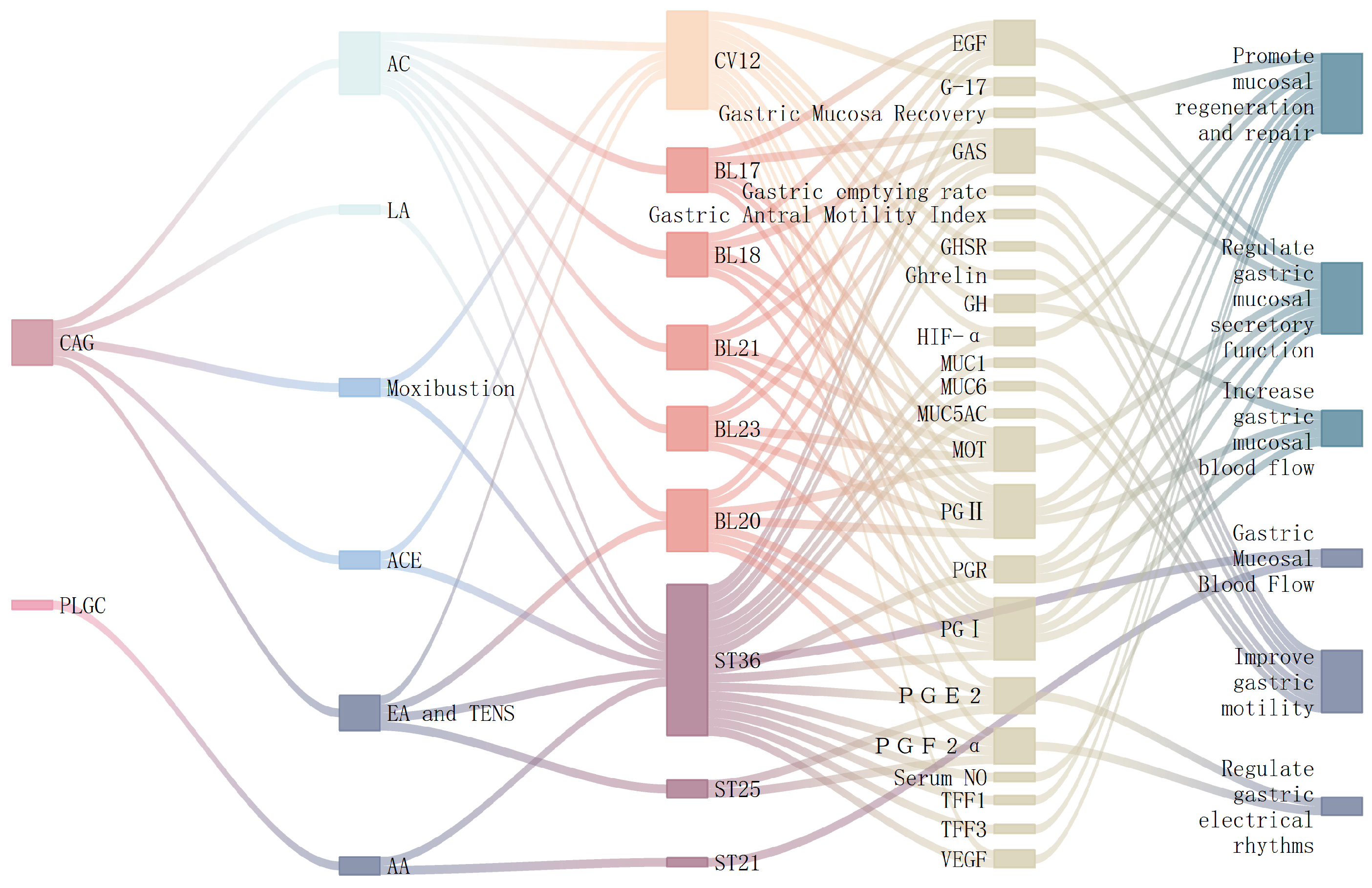
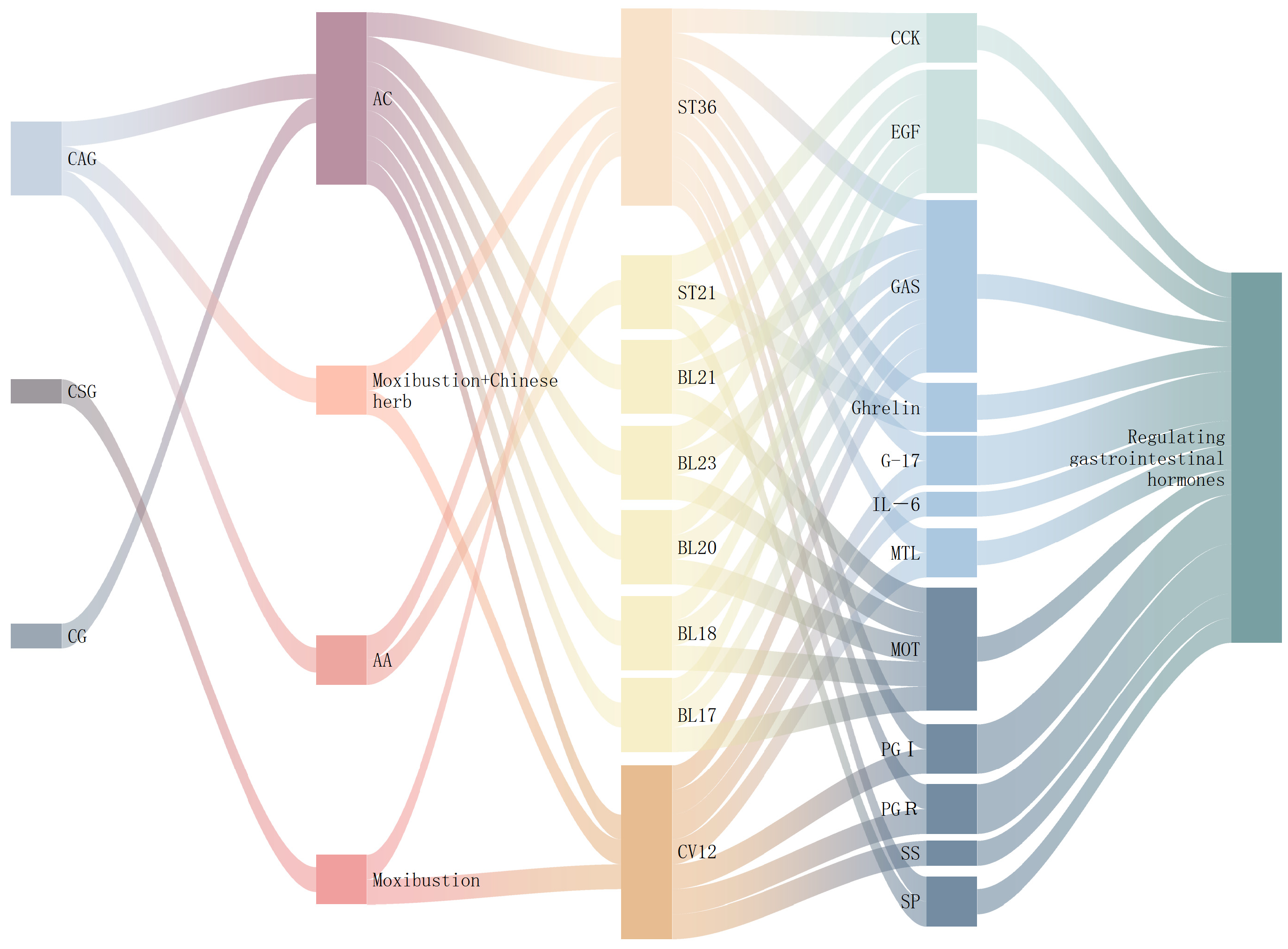
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Wang, H.; Che, C.; Wang, A.; Nie, R.; Tan, J.; Jia, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Dong, G. Research Progress on the Efficacy and Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Chronic Gastritis. Diseases 2025, 13, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13110363
He J, Wang H, Che C, Wang A, Nie R, Tan J, Jia J, Liu Z, Li T, Dong G. Research Progress on the Efficacy and Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Chronic Gastritis. Diseases. 2025; 13(11):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13110363
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jing, Hongye Wang, Cong Che, Anjie Wang, Ru Nie, Jinghong Tan, Jialin Jia, Zijian Liu, Tie Li, and Guojuan Dong. 2025. "Research Progress on the Efficacy and Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Chronic Gastritis" Diseases 13, no. 11: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13110363
APA StyleHe, J., Wang, H., Che, C., Wang, A., Nie, R., Tan, J., Jia, J., Liu, Z., Li, T., & Dong, G. (2025). Research Progress on the Efficacy and Mechanism of Acupuncture in Treating Chronic Gastritis. Diseases, 13(11), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13110363






