Triglycerides, Cholesterol, and Depressive Symptoms Among Undergraduate Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Sociodemographic and Academic Variables
2.2.2. Substance Use, Comorbidities, and Family History
2.2.3. Reproductive Health Variables
2.2.4. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2.5. Depressive Symptoms
2.2.6. Triglycerides and Total Cholesterol
2.2.7. Data Collection Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HDL-C | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol’ |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ENSANUT | the National Health and Nutrition Survey (Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición), |
| CESD-7 | Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale |
| IPAQ-7 | International Physical Activity Questionnaire |
| RP | Ratio prevalence |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| DAGs | Directed acyclic graphs |
References
- World Health Organization. Depression. Fact Sheets. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, D.; Yin, H.; Shi, L. Factors Associated with Academic Burnout and Its Prevalence among University Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofatteh, M. Risk Factors Associated with Stress, Anxiety, and Depression among University Undergraduate Students. AIMS Public Health 2020, 8, 36–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, D.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Z. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms among College Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2022, 63, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consuelos-Sánchez, K.S.; Cano-Estrada, A.; Castañeda-Márquez, A.C.; Hernández-Mariano, J.Á. Nursing Training and Its Association with Burnout Syndrome among Mexican Undergraduate Students. Salud Ment. 2023, 46, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosme, J.A.G. Depresión, ansiedad y conducta suicida en la formación médica en una universidad en México. Investig. Educ. Méd. 2020, 9, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthran, R.; Zhang, M.W.B.; Tam, W.W.; Ho, R.C. Prevalence of Depression amongst Medical Students: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Educ. 2016, 50, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Saragih, I.D.; Lin, C.-J.; Liu, H.-L.; Chen, C.-W.; Yeh, Y.-S. Global Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression among Medical Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Psychol. 2024, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, P.W.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Pavlatou, M.G. Clinical and Biochemical Manifestations of Depression: Relation to the Neurobiology of Stress. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 581976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Ramírez, A.A.; Peláez, J.L.; Bermúdez, I.M.; Gordon Botero, J.Y. Prevalence of Hyperlipidemia and Its Associated Factors in University Students in Colombia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Duais, M.A.; Al-Awthan, Y.S. Prevalence of Dyslipidemia among Students of a Yemeni University. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2019, 14, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizmanos, B.; Betancourt-Nuñez, A.; Márquez-Sandoval, F.; González-Zapata, L.I.; Monsalve-Álvarez, J.; Bressan, J.; de Carvalho Vidigal, F.; Figueredo, R.; López, L.B.; Babio, N.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome Among Young Health Professionals in the Multicenter Latin America Metabolic Syndrome Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2020, 18, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Role of Inflammation in Depression: From Evolutionary Imperative to Modern Treatment Target|Nature Reviews Immunology. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nri.2015.5 (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Lopresti, A.L.; Drummond, P.D. Obesity and Psychiatric Disorders: Commonalities in Dysregulated Biological Pathways and Their Implications for Treatment. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Salas, A.; Hubert, C.; Portillo-Romero, A.; Valdez-Santiago, R.; Barrientos-Gutiérrez, T.; Villalobos, A. Sintomatología depresiva en adolescentes y adultos mexicanos: Ensanut 2022. Salud Públ. Méx. 2023, 65, s117–s125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alcaraz, C.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Mendoza-Herrera, K.; Pedroza-Tobías, A.; Villalpando, S.; Shamah-Levy, T.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.; Hernández-Ávila, M.; Barquera, S. Dyslipidemia Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control in Mexico: Results of the Ensanut 2012. Salud Públ. Méx. 2020, 62, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Martínez, R.; Escamilla-Núñez, C.; Castro-Porras, L.; Basto-Abreu, A.; Barrientos-Gutiérrez, T.; Romero-Martínez, M.; Aguilar-Salinas, C. Tamizaje, prevalencia, diagnóstico previo, tratamiento y control de hipertensión, hipercolesterolemia y diabetes en adultos mexicanos. Ensanut 2022. Salud Públ. Méx. 2023, 65, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadeo-Álvarez, M.A.; Munguía-Ortíz, C.D.; Benítez-López, V.; Valles-Medina, A.M.; Delgadillo-Ramos, G.; Flores-Castillo, P.M.; Romo-Guardado, M. Presencia de síntomas depresivos en estudiantes de medicina en una universidad pública de México. Salud Ment. 2019, 42, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.Z.T.; Guevara, E.G.; Nava, M.G.; Estala, M.A.C.; García, K.Y.R.; Peña, E.G.R. Depresión, ansiedad y estrés en estudiantes de nuevo ingreso a la educación superior. RESPYN Rev. Salud Públ. Nutr. 2018, 17, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna, M.F.B.; López, F.A.R. Ansiedad y depresión en alumnos de la escuela de medicina como consecuencia del confinamiento y afección por COVID-19: Anxiety and depression in alumni at medicine school as a consequence due to COVID 19 confinement. LATAM Rev. Latinoam. Cienc. Soc. Humanid. 2024, 5, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldo, E.L.; Santiago, O.G.; Quiroga, K.A.F. Dislipidemias y riesgo cardiovascular por género relacionado con el consumo de una dieta hipercalórica e inactividad física en estudiantes del Noreste de México Agosto 2018–Febrero 2019. Rev. Cienc. Farm. Biomed. 2019, 2, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zenteno, C.A.C.; Pérez, J.D.G.; Feliciano, M.Á.R. Relación del Índice de Masa Corporal (IMC) y Circunferencia de Cintura (CC) con Glucosa, Colesterol y Triglicéridos en Estudiantes de Medicina. Espac. ID Innov. Más Desarro. 2020, 9, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuamatzin-García, F.; Baez-Duarte, B.G.; Zamora-Ginez, I.; Martínez-Montaño, M.d.L.C.; Limón-Cerón, J.F.; García-Juárez, A. Relación entre la enfermedad periodontal y el índice triglicéridos/HDL-colesterol en estudiantes universitarios. Horiz. Sanit. 2024, 23, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, C.B.; Jan, A. BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas-Rodríguez, A.; Manrique-Espinoza, B.; Acosta-Castillo, G.I.; Franco-Núñez, A.; Rosas-Carrasco, Ó.; Gutiérrez-Robledo, L.M.; Sosa-Ortiz, A.L. Validación de un punto de corte para la versión breve de la Escala de Depresión del Centro de Estudios Epidemiológicos en adultos mayores mexicanos. Salud Públ. Méx. 2014, 56, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueiro, R.d.S.; Santos, M.C.; Neto, J.d.S.L.; Queiroz, B.M.d.; Brügger, N.A.J.; Barbosa, A.R. Validity of a Portable Glucose, Total Cholesterol, and Triglycerides Multi-Analyzer in Adults. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2014, 16, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurstjens, S.; Gemen, E.; Walk, S.; Njo, T.; Krabbe, J.; Gijzen, K.; Elisen, M.G.; Kusters, R. Performance of Commercially-Available Cholesterol Self-Tests. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 58, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnardellis, C.; Notara, V.; Papadakaki, M.; Gialamas, V.; Chliaoutakis, J. Overestimation of Relative Risk and Prevalence Ratio: Misuse of Logistic Modeling. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corraini, P.; Olsen, M.; Pedersen, L.; Dekkers, O.M.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Effect Modification, Interaction and Mediation: An Overview of Theoretical Insights for Clinical Investigators. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 9, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digitale, J.C.; Martin, J.N.; Glymour, M.M. Tutorial on directed acyclic graphs. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 142, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, J.; Hardt, J.; Knüppel, S. DAGitty: A Graphical Tool for Analyzing Causal Diagrams. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.E.l.; Jesús-Pérez, R.d.; Schargrodsky, H.; Champagne, B. Prevalencia de dislipidemias en la ciudad de México y su asociación con otros factores de riesgo cardiovascular. Resultados del estudio CARMELA. Gac. Méd. Méx. 2014, 150, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, G.; Chen, G.; Luo, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Qian, J. Distribution of Lipid Levels and Prevalence of Hyperlipidemia: Data from the NHANES 2007–2018. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, K.-S.; Han, K.; Park, C.-Y. Trends in Prevalence of Hypertriglyceridemia and Related Factors in Korean Adults: A Serial Cross-Sectional Study. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2023, 12, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkhtugs, K.; Tsedev-Ochir, T.-O.; Yadamsuren, E.; Bayartsogt, B.; Dangaa, B.; Altangerel, O.; Byambasukh, O.; Enebish, O. Prevalence of Elevated Blood Triglycerides and Associated Risk Factors: Findings from a Nationwide Health Screening in Mongolia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.F.; Castro Cabezas, M. Dyslipidemia in Obesity: Mechanisms and Potential Targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.V. Insulin Resistance and Lipid Metabolism. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 84, 28J–32J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-R.; Gao, X.; Zhao, L.-B.; Liu, S.-D.; Tang, G.; Zhou, C.-J.; Chen, Y. Association between Triglyceride and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, J.; Guo, P.; Wang, C.; Tang, N.; Wu, W. Is Triglyceride Associated with Adult Depressive Symptoms? A Big Sample Cross-Sectional Study from the Rural Areas of Central China. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 273, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Ming, J.; Li, C. Association between Dyslipidemia and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of NHANES Data from 2007 to 2018. BMC Psychiatry 2024, 24, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; Fu, Q. Association between TG/HDL-C and Depression in US Adults: A Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study. Medicine 2025, 104, e42337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Bo, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Xue, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhuoma, C.; Yu, Z.; Han, Z.; et al. Association of the Triglyceride-Glucose Index with Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 391, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jung, S.J.; Jung, Y.; Ahn, S.V.; Lee, E.; Kim, H.C. Association between the Change of Total Cholesterol during Adolescence and Depressive Symptoms in Early Adulthood. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 30, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deisenhammer, E.A.; Kramer-Reinstadler, K.; Liensberger, D.; Kemmler, G.; Hinterhuber, H.; Fleischhacker, W.W. No Evidence for an Association between Serum Cholesterol and the Course of Depression and Suicidality. Psychiatry Res. 2004, 121, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergün, U.G.O.; Uguz, S.; Bozdemir, N.; Güzel, R.; Burgut, R.; Saatçi, E.; Akpinar, E. The Relationship between Cholesterol Levels and Depression in the Elderly. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2004, 19, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, X. Low Cholesterol Is Not Associated with Depression: Data from the 2005-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, M.S.; Kern, D.M.; Blacketer, C.; Drevets, W.C. Low Levels of Cholesterol and the Cholesterol Type Are Not Associated with Depression: Results of a Cross-Sectional NHANES Study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020, 14, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaster, M.P.; Gadotti, V.M.; Calixto, J.B.; Santos, A.R.S.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Depressive-like Behavior Induced by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, B.R.; de Araujo Borba, L.; Borges de Souza, P.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Role of Inflammatory Mechanisms in Major Depressive Disorder: From Etiology to Potential Pharmacological Targets. Cells 2024, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, G.; Márton, J.; Nagy, Z.; Mándi, Y.; Takács, T.; Deli, M.A.; Ábrahám, C.S. Experimental Acute Pancreatitis Results in Increased Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability in the Rat: A Potential Role for Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin 6. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 242, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.I.; Moreira, P.I.; Oliveira, C.R. Insulin in Central Nervous System: More than Just a Peripheral Hormone. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 384017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.-G.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, D.-D.; Wu, S.-X.; Huang, S.-Y.; Saimaiti, A.; Yang, Z.-J.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Anxiety, Depression, and Other Mental Disorders as Well as the Protective Effects of Dietary Components. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, M.; Bellosta, S. Cholesterol: Its Regulation and Role in Central Nervous System Disorders. Cholesterol 2012, 2012, 292598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, G.; Biasi, F.; Leonarduzzi, G. Oxysterols in the Pathogenesis of Major Chronic Diseases. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, J.; Faraci, F.M.; Lentz, S.R.; Heistad, D.D. Cerebral Vascular Dysfunction during Hypercholesterolemia. Stroke 2007, 38, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, A.A.; Phang, V.W.X.; Lee, Y.Z.; Kow, A.S.F.; Tham, C.L.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lee, M.T. Chronic Stress-Associated Depressive Disorders: The Impact of HPA Axis Dysregulation and Neuroinflammation on the Hippocampus—A Mini Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, M.; Laakasuo, M. Obesity as a Causal Risk Factor for Depression: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies and Implications for Population Mental Health. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 163, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, F.R.; Larrad-Mur, L.; Kallen, A.; Chedraui, P.; Taylor, H.S. Gender Differences in Cardiovascular Disease: Hormonal and Biochemical Influences. Reprod. Sci. Thousand Oaks Calif. 2010, 17, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendis, P.C.; Zimmerman, S.; Onisiforou, A.; Zanos, P.; Georgiou, P. The Impact of Estradiol on Serotonin, Glutamate, and Dopamine Systems. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1348551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Features | n = 219 |
| f (%) | |
| Sex | |
| Woman | 137 (62.6) |
| Man | 82 (37.4) |
| Age | |
| 18–20 years | 90 (41.1) |
| 21–23 years | 78 (35.6) |
| ≥24 years | 51 (23.3) |
| Marital status | |
| No partner | 206 (94.1) |
| With partner | 13 (5.9) |
| Family monthly income | |
| <543 American dollars | 46 (21.0) |
| ≥543 American dollars | 173 (79.0) |
| Living arrangements | |
| Living with parents | 188 (85.8) |
| Living away from the family home | 31 (14.2) |
| Remunerated employment | |
| Yes | 15 (6.8) |
| No | 204 (93.2) |
| Year in program | |
| First | 71 (32.4) |
| Second | 38 (17.4) |
| Third | 43 (19.6) |
| Fourth | 32 (14.6) |
| Fifth | 35 (16.0) |
| Scholarship | |
| Yes | 29 (13.2) |
| No | 190 (86.8) |
| Regular alcohol consumption | |
| Yes | 61 (27.8) |
| No | 158 (72.2) |
| Regular cigarette smoking | |
| Yes | 39 (17.8) |
| No | 180 (82.2) |
| Body Mass Index categories | |
| Normal weight (18.5–24.9) | 151 (68.9) |
| Overweight (25.0–29.9) | 56 (25.6) |
| Obesity (≥30.0) | 12 (5.5) |
| Chronic medical conditions | |
| Yes | 12 (5.5) |
| No | 207 (94.5) |
| Parental history of depression (any parent) | |
| Yes | 21 (9.6) |
| No | 198 (90.4) |
| Parental overweight/obesity (any parent) | |
| Yes | 52 (23.7) |
| No | 167 (76.3) |
| Hormonal contraceptive use (women only). | |
| Yes | 43 (19.6) |
| No | 176 (80.4) |
| Menstrual irregularities | |
| Yes | 63 (28.8) |
| No | 156 (71.2) |
| Variables | Total (n = 219) | Depressive Symptoms | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 134) | Yes (n = 85) | p-Value a | ||
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 138 (63) | 128.5 (73) | 163 (120) | 0.011 |
| Triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL, f (%) | ||||
| Yes | 90 (41.1) | 42 (46.7) | 48 (53.3) | 0.001 |
| No | 129 (58.9) | 92 (71.3) | 37 (28.7) | |
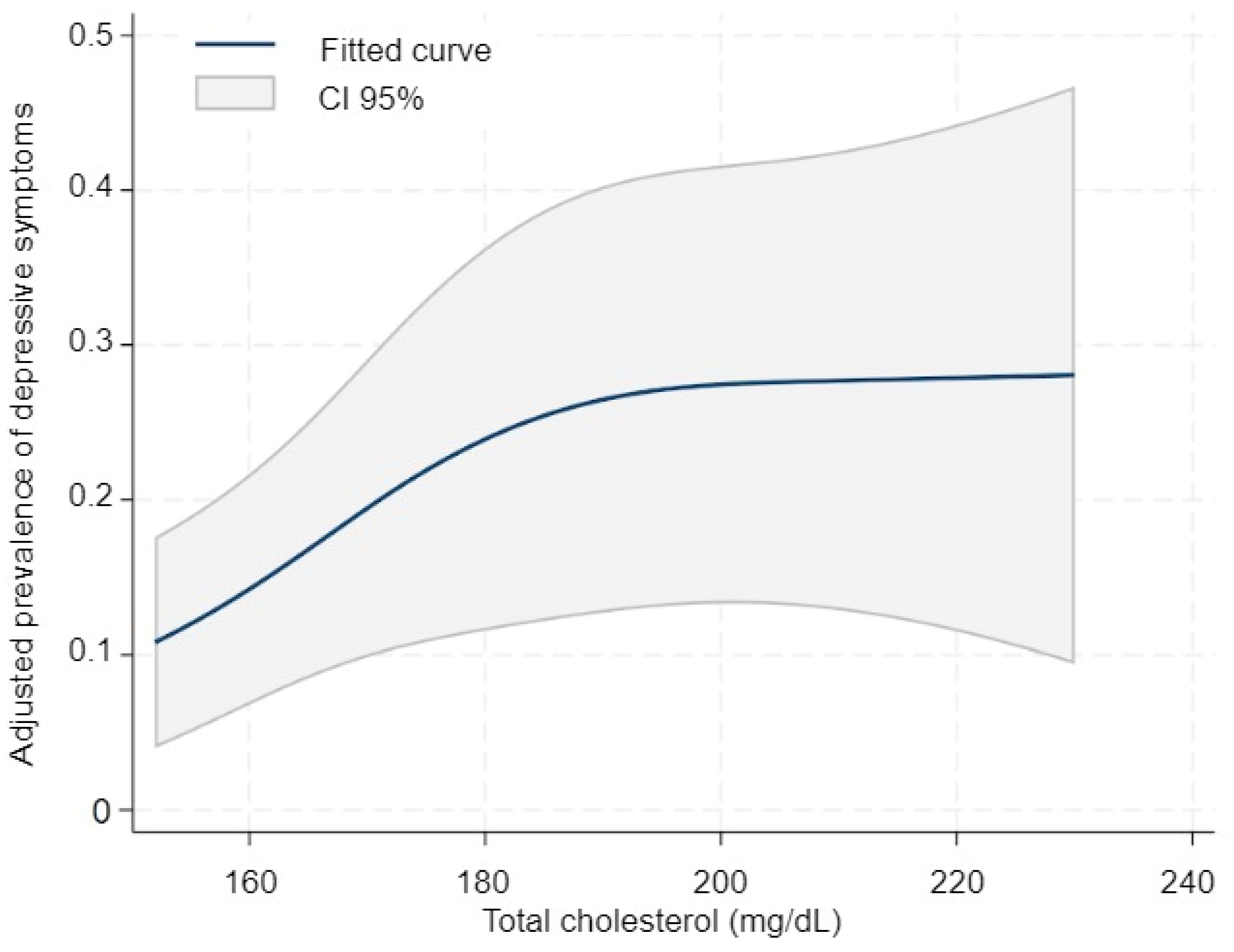
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 172 (33) | 167 (26) | 180 (40) | 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL, f (%) | ||||
| Yes | 46 (21.0) | 20 (43.5) | 26 (56.5) | 0.006 |
| No | 173 (79.0) | 114 (65.9) | 59 (34.1) | |
| Lipid Profile | Depressive Symptoms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR (95% CI) | Valor-p | PR a (95% CI) | Valor-p | |
| Triglycerides | ||||
| <150 mg/dL | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥150 mg/dL | 1.86 (1.33, 2.59) | <0.001 | 1.76 (1.24, 2.48) | 0.001 |
| Total Cholesterol | ||||
| <200 mg/dL | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥200 mg/dL | 1.66 (1.19, 2.30) | 0.003 | 1.66 (1.19, 2.31) | 0.003 |
| Panel A. Multiplicative scale | |||
| Triglycerides | BMI < 25 kg/m2 (Normal) | BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 (Overweight/Obesity) | Interaction p-Value |
| PR (95% CI) a, p-value | PR (95% CI) a, p-value | ||
| <150 mg/dL | Ref. | Ref. | — |
| ≥150 mg/dL | 1.53 (1.01–2.32), p = 0.043 | 1.90 (0.86–4.16), p = 0.109 | 0.582 |
| Panel B. Additive scale | |||
| Measure | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value |
| RERI | 0.23 | −0.67 to 1.14 | 0.611 |
| AP | 0.13 | −0.36 to 0.63 | 0.599 |
| SI | 1.45 | −0.90 to 3.80 | 0.228 |
| Panel A. Multiplicative scale | |||
| Total Cholesterol | BMI < 25 kg/m2 (Normal) | BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 (Overweight/Obesity) | Interaction p-Value |
| PR (95% CI) a, p-value | PR (95% CI) a, p-value | ||
| <200 mg/dL | Ref. | Ref. | — |
| ≥200 mg/dL | 1.69 (1.03–2.79), p = 0.038 | 1.78 (0.99–3.23), p = 0.060 | 0.287 |
| Panel B. Additive scale | |||
| Measure | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value |
| RERI | 0.04 | −0.93 to 1.01 | 0.934 |
| AP | 0.03 | −0.58 to 0.63 | 0.933 |
| SI | 1.07 | −0.79 to 2.94 | 0.258 |
| Panel A. Multiplicative scale | |||
| Triglycerides | Man | Women | Interaction p-Value |
| PR (95% CI) a, p-value | PR (95% CI) b, p-value | ||
| <150 mg/dL | Ref. | Ref. | — |
| ≥150 mg/dL | 3.01 (1.14–7.93), p = 0.026 | 1.50 (1.06–2.13), p = 0.020 | 0.019 |
| Panel B. Additive scale | |||
| Measure | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value |
| RERI | −1.71 | −4.66–1.25 | 0.258 |
| AP | −0.35 | −0.87–0.17 | 0.189 |
| SI | 0.69 | 0.38–1.01 | <0.001 |
| Panel A. Multiplicative scale | |||
| Total Cholesterol | Man | Women | Interaction p-Value |
| PR (95% CI) a, p-Value | PR (95% CI) b, p-Value | ||
| <200 mg/dL | Ref. | Ref. | — |
| ≥200 mg/dL | 2.0 (0.81–4.92), p = 0.132 | 1.59 (1.12–2.26), p = 0.009 | 0.834 |
| Panel B. Additive scale | |||
| Measure | Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value |
| RERI | −0.20 | −2.35–1.95 | 0.855 |
| AP | −0.05 | −0.61–0.50 | 0.855 |
| SI | 0.93 | 0.28–1.59 | 0.845 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olguín-Montiel, M.; Álvarez-Flores, A.; Razo-Blanco-Hernández, D.M.; Mejía-Blanquel, M.A.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; Olmos-Rivera, G.M.; Castañeda-Márquez, A.C.; Cano-Estrada, E.A.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Hernández-Mariano, J.Á. Triglycerides, Cholesterol, and Depressive Symptoms Among Undergraduate Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diseases 2025, 13, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100326
Olguín-Montiel M, Álvarez-Flores A, Razo-Blanco-Hernández DM, Mejía-Blanquel MA, Fernández-Sánchez V, Olmos-Rivera GM, Castañeda-Márquez AC, Cano-Estrada EA, Cureño-Díaz MA, Hernández-Mariano JÁ. Triglycerides, Cholesterol, and Depressive Symptoms Among Undergraduate Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diseases. 2025; 13(10):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100326
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlguín-Montiel, Maximiliano, Alejandro Álvarez-Flores, Dulce Milagros Razo-Blanco-Hernández, María Alicia Mejía-Blanquel, Verónica Fernández-Sánchez, Gledy Manuela Olmos-Rivera, Ana Cristina Castañeda-Márquez, Edith Araceli Cano-Estrada, Mónica Alethia Cureño-Díaz, and José Ángel Hernández-Mariano. 2025. "Triglycerides, Cholesterol, and Depressive Symptoms Among Undergraduate Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study" Diseases 13, no. 10: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100326
APA StyleOlguín-Montiel, M., Álvarez-Flores, A., Razo-Blanco-Hernández, D. M., Mejía-Blanquel, M. A., Fernández-Sánchez, V., Olmos-Rivera, G. M., Castañeda-Márquez, A. C., Cano-Estrada, E. A., Cureño-Díaz, M. A., & Hernández-Mariano, J. Á. (2025). Triglycerides, Cholesterol, and Depressive Symptoms Among Undergraduate Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diseases, 13(10), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13100326






